Filtering and Enhancing Images
|
|
|
- Rosemary Cole
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 KECE471 Computer Vision Filtering and Enhancing Images Chang-Su Kim Chapter 5, Computer Vision by Shapiro and Stockman Note: Some figures and contents in the lecture notes of Dr. Stockman are used partly.
2 Make it better for human or (a) original machine vision (b) Laplacian of (a) (e) smoothed (a) (f) = (c)x(e) (c) = (a)+(b) (d) gradient of (a) (g) = (a)+(f) (h) power-law transform of (g)
3 Make it better for human or machine vision
4 Make it better for human or machine vision Strong noise Medium noise Weak noise
5 Image Enhancement and Enhancement Restoration Subjective improvement of image quality to increase the detectability of important image details or objects by human or machine Restoration Object recovery of original image from degraded image Knowledge on the image degradation process is required
6 Point Operator Input Image f(x,y) T Output Image g(x,y) Point processing g(x,y) = T[ f(x,y) ] Output pixel value depends only on the input pixel value at the same location The enhancement system is fully described by s = T(r) where s = g(x,y) and r = f(x,y)
7 Point Operator Contrast stretching for medium gray levels Gray-to-binary image converter
8 Point Operator s = c r g c =255 1-g : [0,255] [0,255] Gamma Correction g<1: expand dark levels and compress bright levels g>1 : expand bright levels and compress dark levels Varying g controls the amount of expansion and compression
9 Point Operator Histogram Equalization Histograms are the basis for numerous spatial domain image processing techniques Rough estimate of probability distribution of gray levels Simple to compute Histogram h(r k ) = n k r k : k-th gray level n k : the number of pixels in the image having gray level r k Normalized histogram p(r k ) = n k /n n: the total number of pixels pr ( k ) 1 k
10 Point Operator Histogram Equalization In general, the uniform distribution of gray levels is desirable high contrast a great deal of details high dynamic range
11 Point Operator Histogram Equalization Example: An image of 128 pixels. There are 8 gray levels only. Note that each gray level should have 16 pixels in the output histogram r k n k n k T(r k ) Ideally, starting from the smallest gray level, the first 16 pixels should be assigned gray level 0 (0, 1 => 0) 32 pixels => gray level 0 or 1 (0, 1, 2 => 0, 1) 48 pixels => gray level 0, 1, or 2 Skip 64 pixels => gray level 0, 1, 2, 3 (0, 1, 2, 3 => 0, 1, 2, 3) 80 pixels => gray level 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 Skip 96 pixels => gray level 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Skip 112 pixels => gray level 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 (0, 1, 2, 3, 4 => 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6) 128 pixels => gray level 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 => 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)
12 Point Operator Histogram Equalization Example: An image of 128 pixels. There are 8 gray levels only. Note that each gray level should have 16 pixels in the output histogram More sophisticated equalization r k n k n k T(r k ) 0 0 0: 8 pixels 1: 13 pixels 1: 3 pixels 2: 16 pixels 3: 16 pixels
13 Removal of Small Image Regions Removal of Salt-and-Pepper Noise Input 8-neighbor decision 4-neighbor decision
14 Removal of Small Image Regions Removal of Small Components Count the number of pixels in a component. If it is less than a threshold, remove the component. ex) Threshold 12
15 Masking (Linear Filtering) Mask is moved from pixel to pixel At each location, the mask coefficients are multiplied by the corresponding pixel values, and then summed up g(x,y) = w(-1,-1)f(x-1,y-1) + w(-1,0)f(x-1,y) w(1,1)f(x+1,y+1) Masking with Convolving with a b c i h g d e f = f e d g h i c b a
16 Masking (Linear Filtering)
17 Masking (Linear Filtering) Boundary problem 1. Limit the excursion of the center of the mask, so that the mask is fully contained within the image Output image is smaller than input image 2. Extrapolate the input image sufficiently, so that the mask can be applied near the boundaries also. Zero padding Repetition Mirroring etc a a a d g a b c 0 d e f 0 g h i a a b c a a b c a a b c d d e f g g h i a a b e h a d e f a a b c a a b c d d e f g g h i
18 Smoothing Filters Averaging filter (box filter) and weighted averaging filter Blends with adjacent pixel values Blurring Removal of small details before large object extraction Bridging of small gaps in lines or curves Reduction of sharp transitions in gray levels Advantage: noise reduction Disadvantage: edge blurring
19 Smoothing Filters Gaussian filter g( x, y) c w( s, t) f ( x s, y t) where 2 2 ( s t ) 2 2 w( s, t) e s t
20 Smoothing Filters Losing edges Reducing noises Removing small objects
21 Finding objects of interest Smoothing Filters
22
23
24 Order-Statistics Filter Sort the gray levels of the neighborhood (0, 1, 2, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 6) min median max Min filter Replace the center pixel with the minimum gray level (0) Max filter Replace the center pixel with the maximum gray level (6) Median filter Replace the center pixel with the median (3) Excellent suppression of salt-and-pepper noises without blurring x3 averaging filter 3x3 median filter
25 Edge Detection Using Difference Masks Finding the image points of high contrast
26 Edge Detection Using Difference Masks Difference masks cf. Sum masks for smoothing Derivative in digital domain 1 st -order derivative (1D case) 2 nd -order derivative f f ( x) f ( x 1) x 2 f f ( x 1) f ( x) [ f ( x) f ( x 1)] f ( x 1) 2 f ( x) f ( x 1) 2 x
27 Edge Detection Using Difference Masks First derivative Masks Second derivative
28 Mask [-1, 0, 1] for 1 st Derivative Double responses at the transition
29 Mask [-1, 0, 1] for 1 st Derivative An impulse signal generates an up-and-down response
30 Mask [-1, 2, -1] for 2 nd Derivative Up-and-down responses at edges
31 Mask [-1, 2, -1] for 2 nd Derivative A ramp edge generates zero responses except at the starting and ending points.
32 Difference Masks for 2D Images Gradient f f f ( x, y), x y The maximum change occurs along the direction of gradient
33 Difference Masks for 2D Images Prewitt Masks f x f y In this example, f f x y f x f y Magitude of gradient f o Angle of gradient tan (100 /107) 43.1
34 Difference Masks for 2D Images Sobel Masks f x f y For computational efficiency, the magnitude of gradient is sometimes approximated by 2 f f f x y f x f y 2
35 Examples of Gradient Images Gradient image = f x + f y
36 Examples of Gradient Images Input image Gradient image
CHAPTER 3 IMAGE ENHANCEMENT IN THE SPATIAL DOMAIN
 CHAPTER 3 IMAGE ENHANCEMENT IN THE SPATIAL DOMAIN CHAPTER 3: IMAGE ENHANCEMENT IN THE SPATIAL DOMAIN Principal objective: to process an image so that the result is more suitable than the original image
CHAPTER 3 IMAGE ENHANCEMENT IN THE SPATIAL DOMAIN CHAPTER 3: IMAGE ENHANCEMENT IN THE SPATIAL DOMAIN Principal objective: to process an image so that the result is more suitable than the original image
Chapter 3: Intensity Transformations and Spatial Filtering
 Chapter 3: Intensity Transformations and Spatial Filtering 3.1 Background 3.2 Some basic intensity transformation functions 3.3 Histogram processing 3.4 Fundamentals of spatial filtering 3.5 Smoothing
Chapter 3: Intensity Transformations and Spatial Filtering 3.1 Background 3.2 Some basic intensity transformation functions 3.3 Histogram processing 3.4 Fundamentals of spatial filtering 3.5 Smoothing
Image Processing. Traitement d images. Yuliya Tarabalka Tel.
 Traitement d images Yuliya Tarabalka yuliya.tarabalka@hyperinet.eu yuliya.tarabalka@gipsa-lab.grenoble-inp.fr Tel. 04 76 82 62 68 Noise reduction Image restoration Restoration attempts to reconstruct an
Traitement d images Yuliya Tarabalka yuliya.tarabalka@hyperinet.eu yuliya.tarabalka@gipsa-lab.grenoble-inp.fr Tel. 04 76 82 62 68 Noise reduction Image restoration Restoration attempts to reconstruct an
Linear Operations Using Masks
 Linear Operations Using Masks Masks are patterns used to define the weights used in averaging the neighbors of a pixel to compute some result at that pixel Expressing linear operations on neighborhoods
Linear Operations Using Masks Masks are patterns used to define the weights used in averaging the neighbors of a pixel to compute some result at that pixel Expressing linear operations on neighborhoods
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Jen-Hui Chuang Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University 2 3 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain 3.1 Background 3.4 Enhancement Using Arithmetic/Logic Operations
Digital Image Processing Jen-Hui Chuang Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University 2 3 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain 3.1 Background 3.4 Enhancement Using Arithmetic/Logic Operations
Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain (Chapter 3)
 Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain (Chapter 3) Yun Q. Shi shi@njit.edu Fall 11 Mask/Neighborhood Processing ECE643 2 1 Point Processing ECE643 3 Image Negatives S = (L 1) - r (3.2-1) Point processing
Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain (Chapter 3) Yun Q. Shi shi@njit.edu Fall 11 Mask/Neighborhood Processing ECE643 2 1 Point Processing ECE643 3 Image Negatives S = (L 1) - r (3.2-1) Point processing
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems
 EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 WRI C225 Lecture 04 130131 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Histogram Equalization Image Filtering Linear
EE795: Computer Vision and Intelligent Systems Spring 2012 TTh 17:30-18:45 WRI C225 Lecture 04 130131 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg795/ 2 Outline Review Histogram Equalization Image Filtering Linear
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Lecture # 6 Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain- II ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Local/
Digital Image Processing Lecture # 6 Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain- II ALI JAVED Lecturer SOFTWARE ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT U.E.T TAXILA Email:: ali.javed@uettaxila.edu.pk Office Room #:: 7 Local/
Vivekananda. Collegee of Engineering & Technology. Question and Answers on 10CS762 /10IS762 UNIT- 5 : IMAGE ENHANCEMENT.
 Vivekananda Collegee of Engineering & Technology Question and Answers on 10CS762 /10IS762 UNIT- 5 : IMAGE ENHANCEMENT Dept. Prepared by Harivinod N Assistant Professor, of Computer Science and Engineering,
Vivekananda Collegee of Engineering & Technology Question and Answers on 10CS762 /10IS762 UNIT- 5 : IMAGE ENHANCEMENT Dept. Prepared by Harivinod N Assistant Professor, of Computer Science and Engineering,
EELE 5310: Digital Image Processing. Lecture 2 Ch. 3. Eng. Ruba A. Salamah. iugaza.edu
 EELE 5310: Digital Image Processing Lecture 2 Ch. 3 Eng. Ruba A. Salamah Rsalamah @ iugaza.edu 1 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain 2 Lecture Reading 3.1 Background 3.2 Some Basic Gray Level Transformations
EELE 5310: Digital Image Processing Lecture 2 Ch. 3 Eng. Ruba A. Salamah Rsalamah @ iugaza.edu 1 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain 2 Lecture Reading 3.1 Background 3.2 Some Basic Gray Level Transformations
EEM 463 Introduction to Image Processing. Week 3: Intensity Transformations
 EEM 463 Introduction to Image Processing Week 3: Intensity Transformations Fall 2013 Instructor: Hatice Çınar Akakın, Ph.D. haticecinarakakin@anadolu.edu.tr Anadolu University Enhancement Domains Spatial
EEM 463 Introduction to Image Processing Week 3: Intensity Transformations Fall 2013 Instructor: Hatice Çınar Akakın, Ph.D. haticecinarakakin@anadolu.edu.tr Anadolu University Enhancement Domains Spatial
EELE 5310: Digital Image Processing. Ch. 3. Eng. Ruba A. Salamah. iugaza.edu
 EELE 531: Digital Image Processing Ch. 3 Eng. Ruba A. Salamah Rsalamah @ iugaza.edu 1 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain 2 Lecture Reading 3.1 Background 3.2 Some Basic Gray Level Transformations
EELE 531: Digital Image Processing Ch. 3 Eng. Ruba A. Salamah Rsalamah @ iugaza.edu 1 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain 2 Lecture Reading 3.1 Background 3.2 Some Basic Gray Level Transformations
Point and Spatial Processing
 Filtering 1 Point and Spatial Processing Spatial Domain g(x,y) = T[ f(x,y) ] f(x,y) input image g(x,y) output image T is an operator on f Defined over some neighborhood of (x,y) can operate on a set of
Filtering 1 Point and Spatial Processing Spatial Domain g(x,y) = T[ f(x,y) ] f(x,y) input image g(x,y) output image T is an operator on f Defined over some neighborhood of (x,y) can operate on a set of
Lecture 4 Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain
 Digital Image Processing Lecture 4 Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain Fall 2010 2 domains Spatial Domain : (image plane) Techniques are based on direct manipulation of pixels in an image Frequency Domain
Digital Image Processing Lecture 4 Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain Fall 2010 2 domains Spatial Domain : (image plane) Techniques are based on direct manipulation of pixels in an image Frequency Domain
Digital Image Processing, 2nd ed. Digital Image Processing, 2nd ed. The principal objective of enhancement
 Chapter 3 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain The principal objective of enhancement to process an image so that the result is more suitable than the original image for a specific application. Enhancement
Chapter 3 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain The principal objective of enhancement to process an image so that the result is more suitable than the original image for a specific application. Enhancement
Digital Image Processing. Image Enhancement - Filtering
 Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement - Filtering Derivative Derivative is defined as a rate of change. Discrete Derivative Finite Distance Example Derivatives in 2-dimension Derivatives of Images
Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement - Filtering Derivative Derivative is defined as a rate of change. Discrete Derivative Finite Distance Example Derivatives in 2-dimension Derivatives of Images
Digital Image Processing. Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain (Chapter 4)
 Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain (Chapter 4) Objective The principal objective o enhancement is to process an images so that the result is more suitable than the original
Digital Image Processing Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain (Chapter 4) Objective The principal objective o enhancement is to process an images so that the result is more suitable than the original
ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Spatial Domain Filtering http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/ 2 Outline Background Intensity
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Spatial Domain Filtering http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/ 2 Outline Background Intensity
Topic 4 Image Segmentation
 Topic 4 Image Segmentation What is Segmentation? Why? Segmentation important contributing factor to the success of an automated image analysis process What is Image Analysis: Processing images to derive
Topic 4 Image Segmentation What is Segmentation? Why? Segmentation important contributing factor to the success of an automated image analysis process What is Image Analysis: Processing images to derive
Image Processing Lecture 10
 Image Restoration Image restoration attempts to reconstruct or recover an image that has been degraded by a degradation phenomenon. Thus, restoration techniques are oriented toward modeling the degradation
Image Restoration Image restoration attempts to reconstruct or recover an image that has been degraded by a degradation phenomenon. Thus, restoration techniques are oriented toward modeling the degradation
Digital Image Procesing
 Digital Image Procesing Spatial Filters in Image Processing DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Spatial filters for image enhancement Spatial filters
Digital Image Procesing Spatial Filters in Image Processing DR TANIA STATHAKI READER (ASSOCIATE PROFFESOR) IN SIGNAL PROCESSING IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON Spatial filters for image enhancement Spatial filters
Babu Madhav Institute of Information Technology Years Integrated M.Sc.(IT)(Semester - 7)
 5 Years Integrated M.Sc.(IT)(Semester - 7) 060010707 Digital Image Processing UNIT 1 Introduction to Image Processing Q: 1 Answer in short. 1. What is digital image? 1. Define pixel or picture element?
5 Years Integrated M.Sc.(IT)(Semester - 7) 060010707 Digital Image Processing UNIT 1 Introduction to Image Processing Q: 1 Answer in short. 1. What is digital image? 1. Define pixel or picture element?
Line, edge, blob and corner detection
 Line, edge, blob and corner detection Dmitri Melnikov MTAT.03.260 Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis April 5, 2011 1 / 33 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Line detection 3 Edge detection 4 Blob detection 5
Line, edge, blob and corner detection Dmitri Melnikov MTAT.03.260 Pattern Recognition and Image Analysis April 5, 2011 1 / 33 Outline 1 Introduction 2 Line detection 3 Edge detection 4 Blob detection 5
Filtering Images. Contents
 Image Processing and Data Visualization with MATLAB Filtering Images Hansrudi Noser June 8-9, 010 UZH, Multimedia and Robotics Summer School Noise Smoothing Filters Sigmoid Filters Gradient Filters Contents
Image Processing and Data Visualization with MATLAB Filtering Images Hansrudi Noser June 8-9, 010 UZH, Multimedia and Robotics Summer School Noise Smoothing Filters Sigmoid Filters Gradient Filters Contents
Lecture 4: Image Processing
 Lecture 4: Image Processing Definitions Many graphics techniques that operate only on images Image processing: operations that take images as input, produce images as output In its most general form, an
Lecture 4: Image Processing Definitions Many graphics techniques that operate only on images Image processing: operations that take images as input, produce images as output In its most general form, an
EECS490: Digital Image Processing. Lecture #19
 Lecture #19 Shading and texture analysis using morphology Gray scale reconstruction Basic image segmentation: edges v. regions Point and line locators, edge types and noise Edge operators: LoG, DoG, Canny
Lecture #19 Shading and texture analysis using morphology Gray scale reconstruction Basic image segmentation: edges v. regions Point and line locators, edge types and noise Edge operators: LoG, DoG, Canny
ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing
 Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Spring 2014 TTh 14:30-15:45 CBC C313 Lecture 03 Image Processing Basics 13/01/28 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/
Professor Brendan Morris, SEB 3216, brendan.morris@unlv.edu ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Spring 2014 TTh 14:30-15:45 CBC C313 Lecture 03 Image Processing Basics 13/01/28 http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/
Classification of image operations. Image enhancement (GW-Ch. 3) Point operations. Neighbourhood operation
 Image enhancement (GW-Ch. 3) Classification of image operations Process of improving image quality so that the result is more suitable for a specific application. contrast stretching histogram processing
Image enhancement (GW-Ch. 3) Classification of image operations Process of improving image quality so that the result is more suitable for a specific application. contrast stretching histogram processing
Lecture: Edge Detection
 CMPUT 299 Winter 2007 Lecture: Edge Detection Irene Cheng Overview. What is a pixel in an image? 2. How does Photoshop, + human assistance, detect an edge in a picture/photograph? 3. Behind Photoshop -
CMPUT 299 Winter 2007 Lecture: Edge Detection Irene Cheng Overview. What is a pixel in an image? 2. How does Photoshop, + human assistance, detect an edge in a picture/photograph? 3. Behind Photoshop -
Ulrik Söderström 16 Feb Image Processing. Segmentation
 Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 16 Feb 2011 Image Processing Segmentation What is Image Segmentation? To be able to extract information from an image it is common to subdivide it into background
Ulrik Söderström ulrik.soderstrom@tfe.umu.se 16 Feb 2011 Image Processing Segmentation What is Image Segmentation? To be able to extract information from an image it is common to subdivide it into background
Lecture 4: Spatial Domain Transformations
 # Lecture 4: Spatial Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Reminder 2 nd Quiz on the manipulator Part is this Fri, April 7 205, :5 AM to :0 PM Open Book, Open Notes, Focus on the material
# Lecture 4: Spatial Domain Transformations Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Reminder 2 nd Quiz on the manipulator Part is this Fri, April 7 205, :5 AM to :0 PM Open Book, Open Notes, Focus on the material
Chapter 10: Image Segmentation. Office room : 841
 Chapter 10: Image Segmentation Lecturer: Jianbing Shen Email : shenjianbing@bit.edu.cn Office room : 841 http://cs.bit.edu.cn/shenjianbing cn/shenjianbing Contents Definition and methods classification
Chapter 10: Image Segmentation Lecturer: Jianbing Shen Email : shenjianbing@bit.edu.cn Office room : 841 http://cs.bit.edu.cn/shenjianbing cn/shenjianbing Contents Definition and methods classification
Part 3: Image Processing
 Part 3: Image Processing Moving Window Transform Georgy Gimel farb COMPSCI 373 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 1 / 62 1 Examples of linear / non-linear filtering 2 Moving window transform 3 Gaussian
Part 3: Image Processing Moving Window Transform Georgy Gimel farb COMPSCI 373 Computer Graphics and Image Processing 1 / 62 1 Examples of linear / non-linear filtering 2 Moving window transform 3 Gaussian
Image Processing. Daniel Danilov July 13, 2015
 Image Processing Daniel Danilov July 13, 2015 Overview 1. Principle of digital images and filters 2. Basic examples of filters 3. Edge detection and segmentation 1 / 25 Motivation For what image processing
Image Processing Daniel Danilov July 13, 2015 Overview 1. Principle of digital images and filters 2. Basic examples of filters 3. Edge detection and segmentation 1 / 25 Motivation For what image processing
Edge Detection Lecture 03 Computer Vision
 Edge Detection Lecture 3 Computer Vision Suggested readings Chapter 5 Linda G. Shapiro and George Stockman, Computer Vision, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall,. Chapter David A. Forsyth and Jean Ponce,
Edge Detection Lecture 3 Computer Vision Suggested readings Chapter 5 Linda G. Shapiro and George Stockman, Computer Vision, Upper Saddle River, NJ, Prentice Hall,. Chapter David A. Forsyth and Jean Ponce,
Image Enhancement: To improve the quality of images
 Image Enhancement: To improve the quality of images Examples: Noise reduction (to improve SNR or subjective quality) Change contrast, brightness, color etc. Image smoothing Image sharpening Modify image
Image Enhancement: To improve the quality of images Examples: Noise reduction (to improve SNR or subjective quality) Change contrast, brightness, color etc. Image smoothing Image sharpening Modify image
PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CANNY AND OTHER COMMONLY USED EDGE DETECTORS Sandeep Dhawan Director of Technology, OTTE, NEW YORK
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 3, No 5, 2014, 1759 1766 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CANNY AND OTHER COMMONLY USED EDGE DETECTORS Sandeep Dhawan Director
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 3, No 5, 2014, 1759 1766 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) PERFORMANCE ANALYSIS OF CANNY AND OTHER COMMONLY USED EDGE DETECTORS Sandeep Dhawan Director
Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain. By Dr. Rajeev Srivastava
 Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain By Dr. Rajeev Srivastava CONTENTS Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain Spatial Domain Methods 1. Point Processing Functions A. Gray Level Transformation functions for
Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain By Dr. Rajeev Srivastava CONTENTS Image Enhancement in Spatial Domain Spatial Domain Methods 1. Point Processing Functions A. Gray Level Transformation functions for
Chapter - 2 : IMAGE ENHANCEMENT
 Chapter - : IMAGE ENHANCEMENT The principal objective of enhancement technique is to process a given image so that the result is more suitable than the original image for a specific application Image Enhancement
Chapter - : IMAGE ENHANCEMENT The principal objective of enhancement technique is to process a given image so that the result is more suitable than the original image for a specific application Image Enhancement
Segmentation and Grouping
 Segmentation and Grouping How and what do we see? Fundamental Problems ' Focus of attention, or grouping ' What subsets of pixels do we consider as possible objects? ' All connected subsets? ' Representation
Segmentation and Grouping How and what do we see? Fundamental Problems ' Focus of attention, or grouping ' What subsets of pixels do we consider as possible objects? ' All connected subsets? ' Representation
EECS 556 Image Processing W 09. Image enhancement. Smoothing and noise removal Sharpening filters
 EECS 556 Image Processing W 09 Image enhancement Smoothing and noise removal Sharpening filters What is image processing? Image processing is the application of 2D signal processing methods to images Image
EECS 556 Image Processing W 09 Image enhancement Smoothing and noise removal Sharpening filters What is image processing? Image processing is the application of 2D signal processing methods to images Image
Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong)
 Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong) References: [1] http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/hipr2/index.htm [2] http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~dyer/cs540/notes/vision.html
Biometrics Technology: Image Processing & Pattern Recognition (by Dr. Dickson Tong) References: [1] http://homepages.inf.ed.ac.uk/rbf/hipr2/index.htm [2] http://www.cs.wisc.edu/~dyer/cs540/notes/vision.html
Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors
 #1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
#1 Lecture 7: Most Common Edge Detectors Saad Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Edge Detection Goal: Identify sudden changes (discontinuities) in an image Intuitively, most semantic and shape information from the
Outlines. Medical Image Processing Using Transforms. 4. Transform in image space
 Medical Image Processing Using Transforms Hongmei Zhu, Ph.D Department of Mathematics & Statistics York University hmzhu@yorku.ca Outlines Image Quality Gray value transforms Histogram processing Transforms
Medical Image Processing Using Transforms Hongmei Zhu, Ph.D Department of Mathematics & Statistics York University hmzhu@yorku.ca Outlines Image Quality Gray value transforms Histogram processing Transforms
CS534: Introduction to Computer Vision Edges and Contours. Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University
 CS534: Introduction to Computer Vision Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators Laplacian
CS534: Introduction to Computer Vision Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators Laplacian
Lecture 6: Edge Detection
 #1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
#1 Lecture 6: Edge Detection Saad J Bedros sbedros@umn.edu Review From Last Lecture Options for Image Representation Introduced the concept of different representation or transformation Fourier Transform
Edge and local feature detection - 2. Importance of edge detection in computer vision
 Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
Edge and local feature detection Gradient based edge detection Edge detection by function fitting Second derivative edge detectors Edge linking and the construction of the chain graph Edge and local feature
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393
 Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
Digital Image Processing COSC 6380/4393 Lecture 21 Nov 16 th, 2017 Pranav Mantini Ack: Shah. M Image Processing Geometric Transformation Point Operations Filtering (spatial, Frequency) Input Restoration/
Point operation Spatial operation Transform operation Pseudocoloring
 Image Enhancement Introduction Enhancement by point processing Simple intensity transformation Histogram processing Spatial filtering Smoothing filters Sharpening filters Enhancement in the frequency domain
Image Enhancement Introduction Enhancement by point processing Simple intensity transformation Histogram processing Spatial filtering Smoothing filters Sharpening filters Enhancement in the frequency domain
Image processing. Reading. What is an image? Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2017
 Reading Jain, Kasturi, Schunck, Machine Vision. McGraw-Hill, 1995. Sections 4.2-4.4, 4.5(intro), 4.5.5, 4.5.6, 5.1-5.4. [online handout] Image processing Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2017 1 2 What is an
Reading Jain, Kasturi, Schunck, Machine Vision. McGraw-Hill, 1995. Sections 4.2-4.4, 4.5(intro), 4.5.5, 4.5.6, 5.1-5.4. [online handout] Image processing Brian Curless CSE 457 Spring 2017 1 2 What is an
Neighborhood operations
 Neighborhood operations Generate an output pixel on the basis of the pixel and its neighbors Often involve the convolution of an image with a filter kernel or mask g ( i, j) = f h = f ( i m, j n) h( m,
Neighborhood operations Generate an output pixel on the basis of the pixel and its neighbors Often involve the convolution of an image with a filter kernel or mask g ( i, j) = f h = f ( i m, j n) h( m,
What will we learn? Neighborhood processing. Convolution and correlation. Neighborhood processing. Chapter 10 Neighborhood Processing
 What will we learn? Lecture Slides ME 4060 Machine Vision and Vision-based Control Chapter 10 Neighborhood Processing By Dr. Debao Zhou 1 What is neighborhood processing and how does it differ from point
What will we learn? Lecture Slides ME 4060 Machine Vision and Vision-based Control Chapter 10 Neighborhood Processing By Dr. Debao Zhou 1 What is neighborhood processing and how does it differ from point
Biomedical Image Analysis. Spatial Filtering
 Biomedical Image Analysis Contents: Spatial Filtering The mechanics of Spatial Filtering Smoothing and sharpening filters BMIA 15 V. Roth & P. Cattin 1 The Mechanics of Spatial Filtering Spatial filter:
Biomedical Image Analysis Contents: Spatial Filtering The mechanics of Spatial Filtering Smoothing and sharpening filters BMIA 15 V. Roth & P. Cattin 1 The Mechanics of Spatial Filtering Spatial filter:
Texture. Frequency Descriptors. Frequency Descriptors. Frequency Descriptors. Frequency Descriptors. Frequency Descriptors
 Texture The most fundamental question is: How can we measure texture, i.e., how can we quantitatively distinguish between different textures? Of course it is not enough to look at the intensity of individual
Texture The most fundamental question is: How can we measure texture, i.e., how can we quantitatively distinguish between different textures? Of course it is not enough to look at the intensity of individual
Image Processing. BITS Pilani. Dr Jagadish Nayak. Dubai Campus
 Image Processing BITS Pilani Dubai Campus Dr Jagadish Nayak Image Segmentation BITS Pilani Dubai Campus Fundamentals Let R be the entire spatial region occupied by an image Process that partitions R into
Image Processing BITS Pilani Dubai Campus Dr Jagadish Nayak Image Segmentation BITS Pilani Dubai Campus Fundamentals Let R be the entire spatial region occupied by an image Process that partitions R into
In this lecture. Background. Background. Background. PAM3012 Digital Image Processing for Radiographers
 PAM3012 Digital Image Processing for Radiographers Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain (Part I) In this lecture Image Enhancement Introduction to spatial domain Information Greyscale transformations
PAM3012 Digital Image Processing for Radiographers Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain (Part I) In this lecture Image Enhancement Introduction to spatial domain Information Greyscale transformations
Digital Image Processing. Prof. P. K. Biswas. Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering
 Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Image Enhancement Frequency Domain Processing
Digital Image Processing Prof. P. K. Biswas Department of Electronic & Electrical Communication Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture - 21 Image Enhancement Frequency Domain Processing
CS334: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Edges and Contours. Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University
 CS334: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators From Edges
CS334: Digital Imaging and Multimedia Edges and Contours Ahmed Elgammal Dept. of Computer Science Rutgers University Outlines What makes an edge? Gradient-based edge detection Edge Operators From Edges
CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler
 CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 2 Computer Vision Introduction, Filtering Some slides from: D. Jacobs, D. Lowe, S. Seitz, A.Efros, X. Li, R. Fergus, J. Hayes, S. Lazebnik,
CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 2 Computer Vision Introduction, Filtering Some slides from: D. Jacobs, D. Lowe, S. Seitz, A.Efros, X. Li, R. Fergus, J. Hayes, S. Lazebnik,
Sampling and Reconstruction
 Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Spatial Resolution Spatial Aliasing Problem: Spatial aliasing is insufficient sampling of data along the space axis, which occurs because
Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Reconstruction Sampling and Spatial Resolution Spatial Aliasing Problem: Spatial aliasing is insufficient sampling of data along the space axis, which occurs because
CS4733 Class Notes, Computer Vision
 CS4733 Class Notes, Computer Vision Sources for online computer vision tutorials and demos - http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/hipr and Computer Vision resources online - http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/cvonline Vision
CS4733 Class Notes, Computer Vision Sources for online computer vision tutorials and demos - http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/hipr and Computer Vision resources online - http://www.dai.ed.ac.uk/cvonline Vision
Image restoration. Restoration: Enhancement:
 Image restoration Most images obtained by optical, electronic, or electro-optic means is likely to be degraded. The degradation can be due to camera misfocus, relative motion between camera and object,
Image restoration Most images obtained by optical, electronic, or electro-optic means is likely to be degraded. The degradation can be due to camera misfocus, relative motion between camera and object,
Introduction to Digital Image Processing
 Fall 2005 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain: Histograms, Arithmetic/Logic Operators, Basics of Spatial Filtering, Smoothing Spatial Filters Tuesday, February 7 2006, Overview (1): Before We Begin
Fall 2005 Image Enhancement in the Spatial Domain: Histograms, Arithmetic/Logic Operators, Basics of Spatial Filtering, Smoothing Spatial Filters Tuesday, February 7 2006, Overview (1): Before We Begin
Lecture 4. Digital Image Enhancement. 1. Principle of image enhancement 2. Spatial domain transformation. Histogram processing
 Lecture 4 Digital Image Enhancement 1. Principle of image enhancement 2. Spatial domain transformation Basic intensity it tranfomation ti Histogram processing Principle Objective of Enhancement Image enhancement
Lecture 4 Digital Image Enhancement 1. Principle of image enhancement 2. Spatial domain transformation Basic intensity it tranfomation ti Histogram processing Principle Objective of Enhancement Image enhancement
Basic relations between pixels (Chapter 2)
 Basic relations between pixels (Chapter 2) Lecture 3 Basic Relationships Between Pixels Definitions: f(x,y): digital image Pixels: q, p (p,q f) A subset of pixels of f(x,y): S A typology of relations:
Basic relations between pixels (Chapter 2) Lecture 3 Basic Relationships Between Pixels Definitions: f(x,y): digital image Pixels: q, p (p,q f) A subset of pixels of f(x,y): S A typology of relations:
CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler
 CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 8 Computer Vision Introduction, Filtering Some slides from: D. Jacobs, D. Lowe, S. Seitz, A.Efros, X. Li, R. Fergus, J. Hayes, S. Lazebnik,
CS4442/9542b Artificial Intelligence II prof. Olga Veksler Lecture 8 Computer Vision Introduction, Filtering Some slides from: D. Jacobs, D. Lowe, S. Seitz, A.Efros, X. Li, R. Fergus, J. Hayes, S. Lazebnik,
Noise Model. Important Noise Probability Density Functions (Cont.) Important Noise Probability Density Functions
 Others -- Noise Removal Techniques -- Edge Detection Techniques -- Geometric Operations -- Color Image Processing -- Color Spaces Xiaojun Qi Noise Model The principal sources of noise in digital images
Others -- Noise Removal Techniques -- Edge Detection Techniques -- Geometric Operations -- Color Image Processing -- Color Spaces Xiaojun Qi Noise Model The principal sources of noise in digital images
Anno accademico 2006/2007. Davide Migliore
 Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Robotica Anno accademico 6/7 Davide Migliore migliore@elet.polimi.it Today What is a feature? Some useful information The world of features: Detectors Edges detection Corners/Points detection Descriptors?!?!?
Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing. Image segmentation: thresholding
 Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing Image Segmentation: Thresholding Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 18-1 Image segmentation: thresholding Suppose an image f(y) is composed of several light objects on
Computer Vision & Digital Image Processing Image Segmentation: Thresholding Dr. D. J. Jackson Lecture 18-1 Image segmentation: thresholding Suppose an image f(y) is composed of several light objects on
Broad field that includes low-level operations as well as complex high-level algorithms
 Image processing About Broad field that includes low-level operations as well as complex high-level algorithms Low-level image processing Computer vision Computational photography Several procedures and
Image processing About Broad field that includes low-level operations as well as complex high-level algorithms Low-level image processing Computer vision Computational photography Several procedures and
Computer Vision. Image Segmentation. 10. Segmentation. Computer Engineering, Sejong University. Dongil Han
 Computer Vision 10. Segmentation Computer Engineering, Sejong University Dongil Han Image Segmentation Image segmentation Subdivides an image into its constituent regions or objects - After an image has
Computer Vision 10. Segmentation Computer Engineering, Sejong University Dongil Han Image Segmentation Image segmentation Subdivides an image into its constituent regions or objects - After an image has
Image Segmentation Image Thresholds Edge-detection Edge-detection, the 1 st derivative Edge-detection, the 2 nd derivative Horizontal Edges Vertical
 Image Segmentation Image Thresholds Edge-detection Edge-detection, the 1 st derivative Edge-detection, the 2 nd derivative Horizontal Edges Vertical Edges Diagonal Edges Hough Transform 6.1 Image segmentation
Image Segmentation Image Thresholds Edge-detection Edge-detection, the 1 st derivative Edge-detection, the 2 nd derivative Horizontal Edges Vertical Edges Diagonal Edges Hough Transform 6.1 Image segmentation
Edge detection. Stefano Ferrari. Università degli Studi di Milano Elaborazione delle immagini (Image processing I)
 Edge detection Stefano Ferrari Università degli Studi di Milano stefano.ferrari@unimi.it Elaborazione delle immagini (Image processing I) academic year 2011 2012 Image segmentation Several image processing
Edge detection Stefano Ferrari Università degli Studi di Milano stefano.ferrari@unimi.it Elaborazione delle immagini (Image processing I) academic year 2011 2012 Image segmentation Several image processing
Perception. Autonomous Mobile Robots. Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction from laser scans. Autonomous Systems Lab. Zürich.
 Autonomous Mobile Robots Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Path Perception Real World Environment Motion Control Perception Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction
Autonomous Mobile Robots Localization "Position" Global Map Cognition Environment Model Local Map Path Perception Real World Environment Motion Control Perception Sensors Vision Uncertainties, Line extraction
Comparison between Various Edge Detection Methods on Satellite Image
 Comparison between Various Edge Detection Methods on Satellite Image H.S. Bhadauria 1, Annapurna Singh 2, Anuj Kumar 3 Govind Ballabh Pant Engineering College ( Pauri garhwal),computer Science and Engineering
Comparison between Various Edge Detection Methods on Satellite Image H.S. Bhadauria 1, Annapurna Singh 2, Anuj Kumar 3 Govind Ballabh Pant Engineering College ( Pauri garhwal),computer Science and Engineering
Edge detection. Gradient-based edge operators
 Edge detection Gradient-based edge operators Prewitt Sobel Roberts Laplacian zero-crossings Canny edge detector Hough transform for detection of straight lines Circle Hough Transform Digital Image Processing:
Edge detection Gradient-based edge operators Prewitt Sobel Roberts Laplacian zero-crossings Canny edge detector Hough transform for detection of straight lines Circle Hough Transform Digital Image Processing:
CS 490: Computer Vision Image Segmentation: Thresholding. Fall 2015 Dr. Michael J. Reale
 CS 490: Computer Vision Image Segmentation: Thresholding Fall 205 Dr. Michael J. Reale FUNDAMENTALS Introduction Before we talked about edge-based segmentation Now, we will discuss a form of regionbased
CS 490: Computer Vision Image Segmentation: Thresholding Fall 205 Dr. Michael J. Reale FUNDAMENTALS Introduction Before we talked about edge-based segmentation Now, we will discuss a form of regionbased
JNTUWORLD. 4. Prove that the average value of laplacian of the equation 2 h = ((r2 σ 2 )/σ 4 ))exp( r 2 /2σ 2 ) is zero. [16]
![JNTUWORLD. 4. Prove that the average value of laplacian of the equation 2 h = ((r2 σ 2 )/σ 4 ))exp( r 2 /2σ 2 ) is zero. [16] JNTUWORLD. 4. Prove that the average value of laplacian of the equation 2 h = ((r2 σ 2 )/σ 4 ))exp( r 2 /2σ 2 ) is zero. [16]](/thumbs/78/78591353.jpg) Code No: 07A70401 R07 Set No. 2 1. (a) What are the basic properties of frequency domain with respect to the image processing. (b) Define the terms: i. Impulse function of strength a ii. Impulse function
Code No: 07A70401 R07 Set No. 2 1. (a) What are the basic properties of frequency domain with respect to the image processing. (b) Define the terms: i. Impulse function of strength a ii. Impulse function
Image Processing. Bilkent University. CS554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu
 Image Processing CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Today Image Formation Point and Blob Processing Binary Image Processing Readings: Gonzalez & Woods, Ch. 3 Slides are adapted from
Image Processing CS 554 Computer Vision Pinar Duygulu Bilkent University Today Image Formation Point and Blob Processing Binary Image Processing Readings: Gonzalez & Woods, Ch. 3 Slides are adapted from
2D Image Processing INFORMATIK. Kaiserlautern University. DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz
 2D Image Processing - Filtering Prof. Didier Stricker Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de 1 What is image filtering?
2D Image Processing - Filtering Prof. Didier Stricker Kaiserlautern University http://ags.cs.uni-kl.de/ DFKI Deutsches Forschungszentrum für Künstliche Intelligenz http://av.dfki.de 1 What is image filtering?
Biomedical Image Analysis. Point, Edge and Line Detection
 Biomedical Image Analysis Point, Edge and Line Detection Contents: Point and line detection Advanced edge detection: Canny Local/regional edge processing Global processing: Hough transform BMIA 15 V. Roth
Biomedical Image Analysis Point, Edge and Line Detection Contents: Point and line detection Advanced edge detection: Canny Local/regional edge processing Global processing: Hough transform BMIA 15 V. Roth
Announcements. Edge Detection. An Isotropic Gaussian. Filters are templates. Assignment 2 on tracking due this Friday Midterm: Tuesday, May 3.
 Announcements Edge Detection Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 9 Assignment 2 on tracking due this Friday Midterm: Tuesday, May 3. Reading from textbook An Isotropic Gaussian The picture
Announcements Edge Detection Introduction to Computer Vision CSE 152 Lecture 9 Assignment 2 on tracking due this Friday Midterm: Tuesday, May 3. Reading from textbook An Isotropic Gaussian The picture
Computer Vision 2. SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung. Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier
 Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Computer Vision 2 SS 18 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Professur für Bildverarbeitung Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier 1. IMAGE PROCESSING Computer Vision 2 Dr. Benjamin Guthier Content of this Chapter Non-linear
Computer Vision I - Filtering and Feature detection
 Computer Vision I - Filtering and Feature detection Carsten Rother 30/10/2015 Computer Vision I: Basics of Image Processing Roadmap: Basics of Digital Image Processing Computer Vision I: Basics of Image
Computer Vision I - Filtering and Feature detection Carsten Rother 30/10/2015 Computer Vision I: Basics of Image Processing Roadmap: Basics of Digital Image Processing Computer Vision I: Basics of Image
3.4& Fundamentals& mechanics of spatial filtering(page 166) Spatial filter(mask) Filter coefficients Filter response
 Image enhancement in the spatial domain(3.4-3.7) SLIDE 1/21 3.4& 3.4.1 Fundamentals& mechanics of spatial filtering(page 166) Spatial filter(mask) Filter coefficients Filter response Example: 3 3mask Linear
Image enhancement in the spatial domain(3.4-3.7) SLIDE 1/21 3.4& 3.4.1 Fundamentals& mechanics of spatial filtering(page 166) Spatial filter(mask) Filter coefficients Filter response Example: 3 3mask Linear
INTENSITY TRANSFORMATION AND SPATIAL FILTERING
 1 INTENSITY TRANSFORMATION AND SPATIAL FILTERING Lecture 3 Image Domains 2 Spatial domain Refers to the image plane itself Image processing methods are based and directly applied to image pixels Transform
1 INTENSITY TRANSFORMATION AND SPATIAL FILTERING Lecture 3 Image Domains 2 Spatial domain Refers to the image plane itself Image processing methods are based and directly applied to image pixels Transform
EECS490: Digital Image Processing. Lecture #20
 Lecture #20 Edge operators: LoG, DoG, Canny Edge linking Polygonal line fitting, polygon boundaries Edge relaxation Hough transform Image Segmentation Thresholded gradient image w/o smoothing Thresholded
Lecture #20 Edge operators: LoG, DoG, Canny Edge linking Polygonal line fitting, polygon boundaries Edge relaxation Hough transform Image Segmentation Thresholded gradient image w/o smoothing Thresholded
Filtering in frequency domain
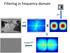 Filtering in frequency domain FFT FFT = Inverse FFT Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert
Filtering in frequency domain FFT FFT = Inverse FFT Filtering in frequency domain Can be faster than filtering in spatial domain (for large filters) Can help understand effect of filter Algorithm: 1. Convert
Intensity Transformation and Spatial Filtering
 Intensity Transformation and Spatial Filtering Outline of the Lecture Introduction. Intensity Transformation Functions. Piecewise-Linear Transformation Functions. Introduction Definition: Image enhancement
Intensity Transformation and Spatial Filtering Outline of the Lecture Introduction. Intensity Transformation Functions. Piecewise-Linear Transformation Functions. Introduction Definition: Image enhancement
SYDE 575: Introduction to Image Processing
 SYDE 575: Introduction to Image Processing Image Enhancement and Restoration in Spatial Domain Chapter 3 Spatial Filtering Recall 2D discrete convolution g[m, n] = f [ m, n] h[ m, n] = f [i, j ] h[ m i,
SYDE 575: Introduction to Image Processing Image Enhancement and Restoration in Spatial Domain Chapter 3 Spatial Filtering Recall 2D discrete convolution g[m, n] = f [ m, n] h[ m, n] = f [i, j ] h[ m i,
CMPUT 206. Introduction to Digital Image Processing
 CMPUT 206 Introduction to Digital Image Processing Overview. What is a pixel in an image? 2. How does Photoshop, + human assistance, detect an edge in a picture/photograph? 3. Behind Photoshop - How does
CMPUT 206 Introduction to Digital Image Processing Overview. What is a pixel in an image? 2. How does Photoshop, + human assistance, detect an edge in a picture/photograph? 3. Behind Photoshop - How does
SECTION 5 IMAGE PROCESSING 2
 SECTION 5 IMAGE PROCESSING 2 5.1 Resampling 3 5.1.1 Image Interpolation Comparison 3 5.2 Convolution 3 5.3 Smoothing Filters 3 5.3.1 Mean Filter 3 5.3.2 Median Filter 4 5.3.3 Pseudomedian Filter 6 5.3.4
SECTION 5 IMAGE PROCESSING 2 5.1 Resampling 3 5.1.1 Image Interpolation Comparison 3 5.2 Convolution 3 5.3 Smoothing Filters 3 5.3.1 Mean Filter 3 5.3.2 Median Filter 4 5.3.3 Pseudomedian Filter 6 5.3.4
Lecture 6 Linear Processing. ch. 5 of Machine Vision by Wesley E. Snyder & Hairong Qi. Spring (CMU RI) : BioE 2630 (Pitt)
 Lecture 6 Linear Processing ch. 5 of Machine Vision by Wesley E. Snyder Hairong Qi Spring 217 16-725 (CMU RI) : BioE 263 (Pitt) Dr. John Galeotti he content of these slides by John Galeotti, 212-217 Carnegie
Lecture 6 Linear Processing ch. 5 of Machine Vision by Wesley E. Snyder Hairong Qi Spring 217 16-725 (CMU RI) : BioE 263 (Pitt) Dr. John Galeotti he content of these slides by John Galeotti, 212-217 Carnegie
Digital Image Processing
 Digital Image Processing Image Restoration and Reconstruction (Noise Removal) Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr University of Ioannina - Department of Computer Science and Engineering 2 Image Restoration
Digital Image Processing Image Restoration and Reconstruction (Noise Removal) Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr University of Ioannina - Department of Computer Science and Engineering 2 Image Restoration
C2: Medical Image Processing Linwei Wang
 C2: Medical Image Processing 4005-759 Linwei Wang Content Enhancement Improve visual quality of the image When the image is too dark, too light, or has low contrast Highlight certain features of the image
C2: Medical Image Processing 4005-759 Linwei Wang Content Enhancement Improve visual quality of the image When the image is too dark, too light, or has low contrast Highlight certain features of the image
Other Linear Filters CS 211A
 Other Linear Filters CS 211A Slides from Cornelia Fermüller and Marc Pollefeys Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin
Other Linear Filters CS 211A Slides from Cornelia Fermüller and Marc Pollefeys Edge detection Convert a 2D image into a set of curves Extracts salient features of the scene More compact than pixels Origin
Filtering and Edge Detection. Computer Vision I. CSE252A Lecture 10. Announcement
 Filtering and Edge Detection CSE252A Lecture 10 Announcement HW1graded, will be released later today HW2 assigned, due Wed. Nov. 7 1 Image formation: Color Channel k " $ $ # $ I r I g I b % " ' $ ' = (
Filtering and Edge Detection CSE252A Lecture 10 Announcement HW1graded, will be released later today HW2 assigned, due Wed. Nov. 7 1 Image formation: Color Channel k " $ $ # $ I r I g I b % " ' $ ' = (
Point Operations and Spatial Filtering
 Point Operations and Spatial Filtering Ranga Rodrigo November 3, 20 /02 Point Operations Histogram Processing 2 Spatial Filtering Smoothing Spatial Filters Sharpening Spatial Filters 3 Edge Detection Line
Point Operations and Spatial Filtering Ranga Rodrigo November 3, 20 /02 Point Operations Histogram Processing 2 Spatial Filtering Smoothing Spatial Filters Sharpening Spatial Filters 3 Edge Detection Line
Edge Detection. CS664 Computer Vision. 3. Edges. Several Causes of Edges. Detecting Edges. Finite Differences. The Gradient
 Edge Detection CS664 Computer Vision. Edges Convert a gray or color image into set of curves Represented as binary image Capture properties of shapes Dan Huttenlocher Several Causes of Edges Sudden changes
Edge Detection CS664 Computer Vision. Edges Convert a gray or color image into set of curves Represented as binary image Capture properties of shapes Dan Huttenlocher Several Causes of Edges Sudden changes
Image Analysis. Edge Detection
 Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
Image Analysis Edge Detection Christophoros Nikou cnikou@cs.uoi.gr Images taken from: Computer Vision course by Kristen Grauman, University of Texas at Austin (http://www.cs.utexas.edu/~grauman/courses/spring2011/index.html).
