LAB 4 Extending Signed and Unsigned Numbers
|
|
|
- Daniel Ball
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 LAB 4 Extending Signed and Unsigned Numbers Objective: Explain unsigned and signed numbers, zero extension and sign extension, and variable declarations. The 80x86 provides several instructions that will let you sign or zero extend a number, for instance, an 8-bit binary number extending to a 16-bit binary number, a 16-bit binary number extending to a 32-bit binary number, or a 8-bit binary number extending to a 32-bit binary number. 80x86 instructions for sign extension and zero extension: MOVSX - move with sign extension for a signed number MOVSXD move with sign extension for a double word signed number MOVZX - move with zero extension for a unsigned number Another group of instructions will sign extend the AL, AX, or EAX registers. These instructions are: CBW - convert the byte in the AL register to a word in the AX register. CWD - convert the word in the AX register to a double word in DX:AX registers CDQ - convert the double word in the EAX register to the quad word in EDX:EAX registers CWDE - convert the word in the AX register to a double word in EAX register CDQE - convert the double word in the EAX register to a quad word in RAX register Include in your lab experiment the following: 1) Type and explain Example 1 (extendingnum.cpp). Compile, Build, and Run the program. Example 1 illustrates to use of a. unsigned numbers: an 8-bit unsigned char, a 16-bit unsigned short, a 32-bit unsigned int b. signed numbers: an 8-bit signed char, a 16-bit signed short, a 32-bit signed int c. printf() formatting %x (or %X) in C programming to display an 8-bit hexadecimal number d. printf() formatting %u in C programming to display a unsigned number e. printf() formatting %d (or %i) in C programming to display a signed number f. std::hex in C++ programming to display a 16-bit hexadecimal number or a 32-bit hexadecimal number g. std::dec to display a 16 bit decimal number or a 32 bit decimal number 2) Explain each line of Example 1 (extendingnum.cpp) and describe the output of each in your lab report 3) Initializing hexadecimal value in extendingnumtemp.cpp. Convert the hexadecimal number to decimal number. Show both hexadecimal number and decimal number of the output by using printf or cout functions: 1
2 Initialize hexadecimal value to an 8 bit unsigned memory variable, display the value in hexadecimal format and decimal format. Initialize hexadecimal value to an 8 bit signed memory variable, display the value in hexadecimal format and decimal format. Initialize hexadecimal value to a 16 bit unsigned memory variable, display the value in hexadecimal format and decimal format. Initialize hexadecimal value to a 16 bit signed memory variable, display the value in hexadecimal format and decimal format. 4) Modify the Example 2 provided in extendingnumtemp.cpp, and write an in-line assembly program that performs zero extension for an unsigned number and sign extension for a signed number. a. An 8-bit unsigned number to a 16-bit unsigned number conversion Input an 8-bit unsigned number (for example, hexadecimal of FD), and convert this value to the identical value with 16-bit unsigned number. Show before and after values of the b. An 8-bit signed number to a 16-bit signed number conversion Input an 8-bit signed number (for example, hexadecimal of FD), and convert this value to the identical value with 16-bit signed number. Show before and after values of the converted hexadecimal information and decimal information c. An 8-bit unsigned number to a 32-bit unsigned number conversion Input an 8-bit unsigned number (for example, hexadecimal of FD), and convert this value to the identical value with 32-bit unsigned number. Show before and after values of the d. An 8-bit signed number to a 32-bit signed number conversion Input an 8-bit signed number (for example, hexadecimal of FD), and convert this value to the identical value with 32-bit signed number. Show before and after values of the converted hexadecimal information and decimal information e. A 16-bit unsigned number to a 32-bit unsigned number conversion Input a 16-bit unsigned number (for example, hexadecimal of FFFD), and convert this value to the identical value with 32-bit unsigned number. Show before and after values of the f. A 16-bit signed number to a 32-bit signed number conversion 2
3 Input a 16-bit signed number (for example, hexadecimal of FFFD), and convert this value to the identical value with 32-bit signed number. Show before and after values of the Example 1 /*********************************************************** File name: extendingnum.cpp Extending Signed and Unsigned Numbers Method: Embedding an in-line assembly language module in a C/C++ program A. Extending 16-bit unsigned number to a 32-bit unsigned number B. Extending 16-bit signed number to a 32-bit signed number conversion printf() is used to display information on the console std::cout is used to display the output on the console std::cin is used to input the information from the keyboard std::hex is used to display hexadecimal value std::dec is used todisplay decimal value system ("pause") is used to hold console *************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() //more variables should be declared //unsigned char us8 = 0xfd; //signed char s8 = 0xfd; unsigned short int us16 = 0xfffd; signed short int s16 = 0xffffd; unsigned int us32; signed int s32 ; //A 16-bit unsigned number extending to a 32-bit unsigned number printf("a 16-bit unsigned number extending to a 32-bit unsigned number\n"); printf("unsigned hexadecimal value is 0x%x\n", us16); printf("its associated unsigned decimal value is %u\n", us16); MOV AX, us16; //unsigned number move to AX MOVZX EAX, AX; //zero extension MOV us32, EAX; //move to 32-bit unsigned number cout << "After zero extension,\n" <<"the identical hex value with 32-bit unsigned number is " <<hex << us32 <<'\n' <<"and its associated decimal is "<< dec<< us32 <<'\n'; //A 16-bit signed number extending to a 32-bit signed number printf("a 16-bit signed number extending to a 32-bit signed number\n"); 3
4 cout << "signed hexadecimal value is " << hex<< s16 <<endl; cout << "its associated signed decimal value is "<<dec << s16<<endl; MOV BX, s16; //unsigned number move to BX MOVSX EBX, BX; //sign extension MOV s32, EBX; //move to 32-bit signed number cout << "After sign extension,\n" <<"the identical hex value with 32-bit signed number is " <<hex << s32 <<'\n' <<"and its associated decimal is "<< dec<< s32 <<'\n'; system ("pause"); return 0; The output from extendingnum.cpp Example 2 (Template) /*********************************************************** File name: extendingnumtemp.cpp Extending Signed and Unsigned Numbers Method: Embedding an in-line assembly language module in a C/C++ program A. Extending 16-bit unsigned number to a 32-bit unsigned number B. Extending 16-bit signed number to a 32-bit signed number conversion printf() is used to display information on the console std::cout is used to display the output on the console std::cin is used to input the information from the keyboard std::hex is used to display hexadecimal value std::dec is used todisplay decimal value system ("pause") is used to hold console *************************************************************/ #include <stdio.h> #include <iostream> 4
5 using namespace std; int main() //more variables should be declared unsigned char us8 = 0xfd; signed char s8 = 0xfd; unsigned short int us16; signed short int s16; unsigned int us32; signed int s32 ; //A 8-bit unsigned number extending to a 16-bit unsigned number printf("an 8-bit unsigned number extending to a 16-bit unsigned number\n"); printf("unsigned hexadecimal value is 0x%x\n", us8); printf("its associated unsigned decimal value is %u\n", us8); //After zero extension, the identical unsigned 16-bit hexadecimal value //After zero extension, the identical unsigned 16-bit decimal value //A 8-bit signed number extending to a 16-bit signed number printf("an 8-bit signed number extending to a 16-bit signed number\n"); printf("signed hexadecimal value is 0x%x\n", s8); printf("its associated signed decimal value is %d\n", s8); //After sign extension, the identical signed 16-bit hexadecimal value //After sign extension, the identical signed 16-bit decimal value r //A 8-bit unsigned number extending to a 32-bit unsigned number printf("an 8-bit unsigned number extending to a 32-bit unsigned number\n"); printf("unsigned hexadecimal value is 0x%x\n", us8); printf("its associated unsigned decimal value is %u\n", us8); 5
6 //After zero extension, the identical unsigned 32-bit hexadecimal value //After zero extension, the identical unsigned 32-bit decimal value //A 8-bit signed number extending to a 32-bit signed number printf("an 8-bit signed number extending to a 32-bit signed number\n"); printf("signed hexadecimal value is 0x%x\n", s8); printf("its associated signed decimal value is %d\n", s8); //After sign extension, the identical signed 32-bit hexadecimal value //After sign extension, the identical signed 32-bit decimal value r system ("pause"); return 0; 6
LAB 5 Arithmetic Operations Simple Calculator
 LAB 5 Arithmetic Operations Simple Calculator Objective: Practice arithmetic operation for the 80x86, such as add, subtract, multiple, divide, and mod. When dealing with the multiply, divide, and mod instructions
LAB 5 Arithmetic Operations Simple Calculator Objective: Practice arithmetic operation for the 80x86, such as add, subtract, multiple, divide, and mod. When dealing with the multiply, divide, and mod instructions
Lab 8 The Stack (LIFO) Structure
 Lab 8 The Stack (LIFO) Structure Objective: The stack segment in memory is where the 80x86 maintains the stack. The stack stores important information about program including local variables, subroutine
Lab 8 The Stack (LIFO) Structure Objective: The stack segment in memory is where the 80x86 maintains the stack. The stack stores important information about program including local variables, subroutine
Introduction to 8086 Assembly
 Introduction to 8086 Assembly Lecture 7 Multiplication and Division Multiplication commands: mul and imul mul source (source: register/memory) Unsigned Integer Multiplication (mul) mul src (src: register/memory)
Introduction to 8086 Assembly Lecture 7 Multiplication and Division Multiplication commands: mul and imul mul source (source: register/memory) Unsigned Integer Multiplication (mul) mul src (src: register/memory)
INFO-I308 Laboratory Session #2
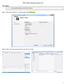 INFO-I308 Laboratory Session #2 LAB GOALS Understanding datatypes and bitwise operators Step 1: Start with a simple C++ console project called I308_Lab2. Step 2: Add a new (main.cpp) item (file) under
INFO-I308 Laboratory Session #2 LAB GOALS Understanding datatypes and bitwise operators Step 1: Start with a simple C++ console project called I308_Lab2. Step 2: Add a new (main.cpp) item (file) under
LAB 3 Memory Addresses
 LAB 3 Memory Addresses Objective: To access and explain the computer memory and memory addresses. To develop a program for moving data between CPU and RAM, and find the contents and addresses for each
LAB 3 Memory Addresses Objective: To access and explain the computer memory and memory addresses. To develop a program for moving data between CPU and RAM, and find the contents and addresses for each
Defining and Using Simple Data Types
 85 CHAPTER 4 Defining and Using Simple Data Types This chapter covers the concepts essential for working with simple data types in assembly-language programs The first section shows how to declare integer
85 CHAPTER 4 Defining and Using Simple Data Types This chapter covers the concepts essential for working with simple data types in assembly-language programs The first section shows how to declare integer
Islamic University Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering ECOM 2125: Assembly Language LAB
 Islamic University Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering ECOM 2125: Assembly Language LAB Lab # 9 Integer Arithmetic and Bit Manipulation April, 2014 1 Assembly Language LAB Bitwise
Islamic University Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering ECOM 2125: Assembly Language LAB Lab # 9 Integer Arithmetic and Bit Manipulation April, 2014 1 Assembly Language LAB Bitwise
Instructions moving data
 do not affect flags. Instructions moving data mov register/mem, register/mem/number (move data) The difference between the value and the address of a variable mov al,sum; value 56h al mov ebx,offset Sum;
do not affect flags. Instructions moving data mov register/mem, register/mem/number (move data) The difference between the value and the address of a variable mov al,sum; value 56h al mov ebx,offset Sum;
We will first study the basic instructions for doing multiplications and divisions
 MULTIPLICATION, DIVISION AND NUMERICAL CONVERSIONS We will first study the basic instructions for doing multiplications and divisions We then use these instructions to 1. Convert a string of ASCII digits
MULTIPLICATION, DIVISION AND NUMERICAL CONVERSIONS We will first study the basic instructions for doing multiplications and divisions We then use these instructions to 1. Convert a string of ASCII digits
Standard I/O in C and C++
 Introduction to Computer and Program Design Lesson 7 Standard I/O in C and C++ James C.C. Cheng Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Standard I/O in C There three I/O memory buffers
Introduction to Computer and Program Design Lesson 7 Standard I/O in C and C++ James C.C. Cheng Department of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University Standard I/O in C There three I/O memory buffers
ECOM Computer Organization and Assembly Language. Computer Engineering Department CHAPTER 7. Integer Arithmetic
 ECOM 2325 Computer Organization and Assembly Language Computer Engineering Department CHAPTER 7 Integer Arithmetic Presentation Outline Shift and Rotate Instructions Shift and Rotate Applications Multiplication
ECOM 2325 Computer Organization and Assembly Language Computer Engineering Department CHAPTER 7 Integer Arithmetic Presentation Outline Shift and Rotate Instructions Shift and Rotate Applications Multiplication
X86 Assembly Language and C Fundamentals. Chapter 5. Data Transfer Instructions. X86 Code Figures
 1 X86 Assembly Language and C Fundamentals Chapter 5 Data Transfer Instructions X86 Code Figures 2 Page 200, Figure 5.4 ;swap_bytes.asm ;-----------------------------------------------------------.STACK
1 X86 Assembly Language and C Fundamentals Chapter 5 Data Transfer Instructions X86 Code Figures 2 Page 200, Figure 5.4 ;swap_bytes.asm ;-----------------------------------------------------------.STACK
mith College Computer Science CSC231 Assembly Week #5 Fall 2017 Dominique Thiébaut
 mith College Computer Science CSC231 Assembly Week #5 Fall 2017 Dominique Thiébaut dthiebaut@smith.edu 0000 0 0 0001 1 1 0010 2 2 0011 3 3 0100 4 4 0101 5 5 0110 6 6 0111 7 7 1000 8 8 1001 9 9 1010 A 10
mith College Computer Science CSC231 Assembly Week #5 Fall 2017 Dominique Thiébaut dthiebaut@smith.edu 0000 0 0 0001 1 1 0010 2 2 0011 3 3 0100 4 4 0101 5 5 0110 6 6 0111 7 7 1000 8 8 1001 9 9 1010 A 10
C++ Basics. Data Processing Course, I. Hrivnacova, IPN Orsay
 C++ Basics Data Processing Course, I. Hrivnacova, IPN Orsay The First Program Comments Function main() Input and Output Namespaces Variables Fundamental Types Operators Control constructs 1 C++ Programming
C++ Basics Data Processing Course, I. Hrivnacova, IPN Orsay The First Program Comments Function main() Input and Output Namespaces Variables Fundamental Types Operators Control constructs 1 C++ Programming
Computer Programming. Dr. Fahad Computer Science Deptt.
 Computer Programming Dr. Fahad Computer Science Deptt. Course Description This course provides the fundamental programming concepts. The emphasis will be on problem solving rather than just learning the
Computer Programming Dr. Fahad Computer Science Deptt. Course Description This course provides the fundamental programming concepts. The emphasis will be on problem solving rather than just learning the
CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ C++ Basics
 CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ C++ Basics Integers Basic Types Can be short, long, or just plain int C++ does not define the size of them other than short
CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ C++ Basics Integers Basic Types Can be short, long, or just plain int C++ does not define the size of them other than short
Lab # 02. Basic Elements of C++ _ Part1
 Lab # 02 Basic Elements of C++ _ Part1 Lab Objectives: After performing this lab, the students should be able to: Become familiar with the basic components of a C++ program, including functions, special
Lab # 02 Basic Elements of C++ _ Part1 Lab Objectives: After performing this lab, the students should be able to: Become familiar with the basic components of a C++ program, including functions, special
PROGRAMMING IN C++ KAUSIK DATTA 18-Oct-2017
 PROGRAMMING IN C++ KAUSIK DATTA 18-Oct-2017 Objectives Recap C Differences between C and C++ IO Variable Declaration Standard Library Introduction of C++ Feature : Class Programming in C++ 2 Recap C Built
PROGRAMMING IN C++ KAUSIK DATTA 18-Oct-2017 Objectives Recap C Differences between C and C++ IO Variable Declaration Standard Library Introduction of C++ Feature : Class Programming in C++ 2 Recap C Built
Variables Data types Variable I/O. C introduction. Variables. Variables 1 / 14
 C introduction Variables Variables 1 / 14 Contents Variables Data types Variable I/O Variables 2 / 14 Usage Declaration: t y p e i d e n t i f i e r ; Assignment: i d e n t i f i e r = v a l u e ; Definition
C introduction Variables Variables 1 / 14 Contents Variables Data types Variable I/O Variables 2 / 14 Usage Declaration: t y p e i d e n t i f i e r ; Assignment: i d e n t i f i e r = v a l u e ; Definition
Computer Architecture and System Programming Laboratory. TA Session 3
 Computer Architecture and System Programming Laboratory TA Session 3 Stack - LIFO word-size data structure STACK is temporary storage memory area register points on top of stack (by default, it is highest
Computer Architecture and System Programming Laboratory TA Session 3 Stack - LIFO word-size data structure STACK is temporary storage memory area register points on top of stack (by default, it is highest
Integer Arithmetic Part2
 Islamic University Of Gaza Assembly Language Faculty of Engineering Discussion Computer Department Chapter 7 Eng. Ahmed M. Ayash Date: 21/04/2013 Chapter 7 Integer Arithmetic Part2 7.4: Multiplication
Islamic University Of Gaza Assembly Language Faculty of Engineering Discussion Computer Department Chapter 7 Eng. Ahmed M. Ayash Date: 21/04/2013 Chapter 7 Integer Arithmetic Part2 7.4: Multiplication
Assembler Programming. Lecture 10
 Assembler Programming Lecture 10 Lecture 10 Mixed language programming. C and Basic to MASM Interface. Mixed language programming Combine Basic, C, Pascal with assembler. Call MASM routines from HLL program.
Assembler Programming Lecture 10 Lecture 10 Mixed language programming. C and Basic to MASM Interface. Mixed language programming Combine Basic, C, Pascal with assembler. Call MASM routines from HLL program.
Structured Programming Using C++ Lecture 2 : Introduction to the C++ Language. Dr. Amal Khalifa. Lecture Contents:
 Structured Programming Using C++ Lecture 2 : Introduction to the C++ Language Dr. Amal Khalifa Lecture Contents: Introduction to C++ Origins Object-Oriented Programming, Terms Libraries and Namespaces
Structured Programming Using C++ Lecture 2 : Introduction to the C++ Language Dr. Amal Khalifa Lecture Contents: Introduction to C++ Origins Object-Oriented Programming, Terms Libraries and Namespaces
Assembler lecture 4 S.Šimoňák, DCI FEEI TU of Košice
 Assembler lecture 4 S.Šimoňák, DCI FEEI TU of Košice Addressing data access specification arrays - specification and manipulation impacts of addressing to performance Processor architecture CISC (more
Assembler lecture 4 S.Šimoňák, DCI FEEI TU of Košice Addressing data access specification arrays - specification and manipulation impacts of addressing to performance Processor architecture CISC (more
Basic program The following is a basic program in C++; Basic C++ Source Code Compiler Object Code Linker (with libraries) Executable
 Basic C++ Overview C++ is a version of the older C programming language. This is a language that is used for a wide variety of applications and which has a mature base of compilers and libraries. C++ is
Basic C++ Overview C++ is a version of the older C programming language. This is a language that is used for a wide variety of applications and which has a mature base of compilers and libraries. C++ is
3.1 DATA MOVEMENT INSTRUCTIONS 45
 3.1.1 General-Purpose Data Movement s 45 3.1.2 Stack Manipulation... 46 3.1.3 Type Conversion... 48 3.2.1 Addition and Subtraction... 51 3.1 DATA MOVEMENT INSTRUCTIONS 45 MOV (Move) transfers a byte, word,
3.1.1 General-Purpose Data Movement s 45 3.1.2 Stack Manipulation... 46 3.1.3 Type Conversion... 48 3.2.1 Addition and Subtraction... 51 3.1 DATA MOVEMENT INSTRUCTIONS 45 MOV (Move) transfers a byte, word,
Overview. - General Data Types - Categories of Words. - Define Before Use. - The Three S s. - End of Statement - My First Program
 Overview - General Data Types - Categories of Words - The Three S s - Define Before Use - End of Statement - My First Program a description of data, defining a set of valid values and operations List of
Overview - General Data Types - Categories of Words - The Three S s - Define Before Use - End of Statement - My First Program a description of data, defining a set of valid values and operations List of
C C C C++ 2 ( ) C C++ 4 C C
 # 7 11 13 C 4 8 11 20 C 9 11 27 C++ 1 10 12 4 C++ 2 11 12 11 C++ 3 12 12 18 C++ 4 C++ 5 13 1 8 ( ) 14 1 15 C++ 15 1 22 2 (D) ( ) C++ 3 6 Hello C++ 4 5 1. make Makefile.c (arithmetic.c) main main arithmetic
# 7 11 13 C 4 8 11 20 C 9 11 27 C++ 1 10 12 4 C++ 2 11 12 11 C++ 3 12 12 18 C++ 4 C++ 5 13 1 8 ( ) 14 1 15 C++ 15 1 22 2 (D) ( ) C++ 3 6 Hello C++ 4 5 1. make Makefile.c (arithmetic.c) main main arithmetic
Computer Architecture and Assembly Language. Practical Session 3
 Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Practical Session 3 Advanced Instructions division DIV r/m - unsigned integer division IDIV r/m - signed integer division Dividend Divisor Quotient Remainder
Computer Architecture and Assembly Language Practical Session 3 Advanced Instructions division DIV r/m - unsigned integer division IDIV r/m - signed integer division Dividend Divisor Quotient Remainder
Lab 4: Basic Instructions and Addressing Modes
 COE 205 Lab Manual Lab 4: Basic Instructions and Addressing Modes - page 36 Lab 4: Basic Instructions and Addressing Modes Contents 4.1. Data Transfer Instructions 4.2. Addition and Subtraction 4.3. Data
COE 205 Lab Manual Lab 4: Basic Instructions and Addressing Modes - page 36 Lab 4: Basic Instructions and Addressing Modes Contents 4.1. Data Transfer Instructions 4.2. Addition and Subtraction 4.3. Data
Review: Exam 1. Your First C++ Program. Declaration Statements. Tells the compiler. Examples of declaration statements
 Review: Exam 1 9/20/06 CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 1 Your First C++ Program 1 //*********************************************************** 2 // File name: hello.cpp 3 // Author: Shereen Khoja
Review: Exam 1 9/20/06 CS150 Introduction to Computer Science 1 1 Your First C++ Program 1 //*********************************************************** 2 // File name: hello.cpp 3 // Author: Shereen Khoja
CS242 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING
 CS242 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING I.Safa a Alawneh Variables Outline 2 Data Type C++ Built-in Data Types o o o o bool Data Type char Data Type int Data Type Floating-Point Data Types Variable Declaration Initializing
CS242 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING I.Safa a Alawneh Variables Outline 2 Data Type C++ Built-in Data Types o o o o bool Data Type char Data Type int Data Type Floating-Point Data Types Variable Declaration Initializing
Computer Systems Programming. Practice Midterm. Name:
 Computer Systems Programming Practice Midterm Name: 1. (4 pts) (K&R Ch 1-4) What is the output of the following C code? main() { int i = 6; int j = -35; printf( %d %d\n,i++, ++j); i = i >
Computer Systems Programming Practice Midterm Name: 1. (4 pts) (K&R Ch 1-4) What is the output of the following C code? main() { int i = 6; int j = -35; printf( %d %d\n,i++, ++j); i = i >
Computer Systems Lecture 9
 Computer Systems Lecture 9 CPU Registers in x86 CPU status flags EFLAG: The Flag register holds the CPU status flags The status flags are separate bits in EFLAG where information on important conditions
Computer Systems Lecture 9 CPU Registers in x86 CPU status flags EFLAG: The Flag register holds the CPU status flags The status flags are separate bits in EFLAG where information on important conditions
2.2: Bitwise Logical Operations
 2.2: Bitwise Logical Operations Topics: Introduction: logical operations in C/C++ logical operations in MIPS In 256 lecture, we looked at bitwise operations in C/C++ and MIPS. We ll look at some simple
2.2: Bitwise Logical Operations Topics: Introduction: logical operations in C/C++ logical operations in MIPS In 256 lecture, we looked at bitwise operations in C/C++ and MIPS. We ll look at some simple
OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING
 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING LAB 1 REVIEW THE STRUCTURE OF A C/C++ PROGRAM. TESTING PROGRAMMING SKILLS. COMPARISON BETWEEN PROCEDURAL PROGRAMMING AND OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING Course basics The Object
OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING LAB 1 REVIEW THE STRUCTURE OF A C/C++ PROGRAM. TESTING PROGRAMMING SKILLS. COMPARISON BETWEEN PROCEDURAL PROGRAMMING AND OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING Course basics The Object
Outline. Introduction. Arrays declarations and initialization. Const variables. Character arrays. Static arrays. Examples.
 Outline Introduction. Arrays declarations and initialization. Const variables. Character arrays. Static arrays. Examples. 1 Arrays I Array One type of data structures. Consecutive group of memory locations
Outline Introduction. Arrays declarations and initialization. Const variables. Character arrays. Static arrays. Examples. 1 Arrays I Array One type of data structures. Consecutive group of memory locations
Adding Binary Integers. Part 5. Adding Base 10 Numbers. Adding 2's Complement. Adding Binary Example = 10. Arithmetic Logic Unit
 Part 5 Adding Binary Integers Arithmetic Logic Unit = Adding Binary Integers Adding Base Numbers Computer's add binary numbers the same way that we do with decimal Columns are aligned, added, and "'s"
Part 5 Adding Binary Integers Arithmetic Logic Unit = Adding Binary Integers Adding Base Numbers Computer's add binary numbers the same way that we do with decimal Columns are aligned, added, and "'s"
ECE2049: Embedded Computing in Engineering Design C Term Spring Lecture #3: Of Integers and Endians (pt. 2)
 ECE2049: Embedded Computing in Engineering Design C Term Spring 2018 Lecture #3: Of Integers and Endians (pt. 2) Reading for Today: Davies Ch 2, MSP430 User's Guide Ch 6.1, 6.3 Reading for Next Class:
ECE2049: Embedded Computing in Engineering Design C Term Spring 2018 Lecture #3: Of Integers and Endians (pt. 2) Reading for Today: Davies Ch 2, MSP430 User's Guide Ch 6.1, 6.3 Reading for Next Class:
Microprocessors & Assembly Language Lab 1 (Introduction to 8086 Programming)
 Microprocessors & Assembly Language Lab 1 (Introduction to 8086 Programming) Learning any imperative programming language involves mastering a number of common concepts: Variables: declaration/definition
Microprocessors & Assembly Language Lab 1 (Introduction to 8086 Programming) Learning any imperative programming language involves mastering a number of common concepts: Variables: declaration/definition
CS , Spring 2004 Exam 1
 Andrew login ID: Full Name: CS 15-213, Spring 2004 Exam 1 February 26, 2004 Instructions: Make sure that your exam is not missing any sheets (there should be 15), then write your full name and Andrew login
Andrew login ID: Full Name: CS 15-213, Spring 2004 Exam 1 February 26, 2004 Instructions: Make sure that your exam is not missing any sheets (there should be 15), then write your full name and Andrew login
Chapter 1. C++ Basics. Copyright 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved
 Chapter 1 C++ Basics Copyright 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Learning Objectives Introduction to C++ Origins, Object-Oriented Programming, Terms Variables, Expressions, and Assignment
Chapter 1 C++ Basics Copyright 2010 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved Learning Objectives Introduction to C++ Origins, Object-Oriented Programming, Terms Variables, Expressions, and Assignment
WARM UP LESSONS BARE BASICS
 WARM UP LESSONS BARE BASICS CONTENTS Common primitive data types for variables... 2 About standard input / output... 2 More on standard output in C standard... 3 Practice Exercise... 6 About Math Expressions
WARM UP LESSONS BARE BASICS CONTENTS Common primitive data types for variables... 2 About standard input / output... 2 More on standard output in C standard... 3 Practice Exercise... 6 About Math Expressions
This watermark does not appear in the registered version - Slide 1
 Slide 1 Chapter 1 C++ Basics Slide 2 Learning Objectives Introduction to C++ Origins, Object-Oriented Programming, Terms Variables, Expressions, and Assignment Statements Console Input/Output Program Style
Slide 1 Chapter 1 C++ Basics Slide 2 Learning Objectives Introduction to C++ Origins, Object-Oriented Programming, Terms Variables, Expressions, and Assignment Statements Console Input/Output Program Style
Semantics of C++ Hauptseminar im Wintersemester 2009/10 Templates
 Semantics of C++ Hauptseminar im Wintersemester 2009/10 Templates Sebastian Wild Technische Universität München 11.01.2010 Abstract In this work we will discuss about templates in C++, especially their
Semantics of C++ Hauptseminar im Wintersemester 2009/10 Templates Sebastian Wild Technische Universität München 11.01.2010 Abstract In this work we will discuss about templates in C++, especially their
6.096 Introduction to C++ January (IAP) 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.096 Introduction to C++ January (IAP) 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Welcome to 6.096 Lecture
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.096 Introduction to C++ January (IAP) 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Welcome to 6.096 Lecture
Input and Output. Data Processing Course, I. Hrivnacova, IPN Orsay
 Input and Output Data Processing Course, I. Hrivnacova, IPN Orsay Output to the Screen Input from the Keyboard IO Headers Output to a File Input from a File Formatting I. Hrivnacova @ Data Processing Course
Input and Output Data Processing Course, I. Hrivnacova, IPN Orsay Output to the Screen Input from the Keyboard IO Headers Output to a File Input from a File Formatting I. Hrivnacova @ Data Processing Course
Outline. Review of Last Week II. Review of Last Week. Computer Memory. Review Variables and Memory. February 7, Data Types
 Data Types Declarations and Initializations Larry Caretto Computer Science 16 Computing in Engineering and Science February 7, 25 Outline Review last week Meaning of data types Integer data types have
Data Types Declarations and Initializations Larry Caretto Computer Science 16 Computing in Engineering and Science February 7, 25 Outline Review last week Meaning of data types Integer data types have
By the end of this section you should: Understand what the variables are and why they are used. Use C++ built in data types to create program
 1 By the end of this section you should: Understand what the variables are and why they are used. Use C++ built in data types to create program variables. Apply C++ syntax rules to declare variables, initialize
1 By the end of this section you should: Understand what the variables are and why they are used. Use C++ built in data types to create program variables. Apply C++ syntax rules to declare variables, initialize
Introduction to Programming
 Introduction to Programming session 5 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Fall 2010 These slides are created using Deitel s slides Sahrif University of Technology Outlines
Introduction to Programming session 5 Instructor: Reza Entezari-Maleki Email: entezari@ce.sharif.edu 1 Fall 2010 These slides are created using Deitel s slides Sahrif University of Technology Outlines
EE 109 Lab 8a Conversion Experience
 EE 109 Lab 8a Conversion Experience 1 Introduction In this lab you will write a small program to convert a string of digits representing a number in some other base (between 2 and 10) to decimal. The user
EE 109 Lab 8a Conversion Experience 1 Introduction In this lab you will write a small program to convert a string of digits representing a number in some other base (between 2 and 10) to decimal. The user
Dr. Md. Humayun Kabir CSE Department, BUET
 C++ Dr. Md. Humayun Kabir CSE Department, BUET History of C++ Invented by Bjarne Stroustrup at Bell Lab in 1979 Initially known as C with Classes Classes and Basic Inheritance The name was changed to C++
C++ Dr. Md. Humayun Kabir CSE Department, BUET History of C++ Invented by Bjarne Stroustrup at Bell Lab in 1979 Initially known as C with Classes Classes and Basic Inheritance The name was changed to C++
Introduction to 8086 Assembly
 Introduction to 8086 Assembly Lecture 6 Working with memory Why using memory? Registers are limited in number and size Program data Program code etc. The data segment dd 1234 dw 13 db -123 The data segment
Introduction to 8086 Assembly Lecture 6 Working with memory Why using memory? Registers are limited in number and size Program data Program code etc. The data segment dd 1234 dw 13 db -123 The data segment
Data Structures and Programming with C++
 Data Structures and Programming with C++ By Dr. Atul Dwivedi ETC, BIT, Durg UNIT-I B. E., V Semester Outline Objectives of the Course Syllabus Reference Books Introduction to programming languages Basic
Data Structures and Programming with C++ By Dr. Atul Dwivedi ETC, BIT, Durg UNIT-I B. E., V Semester Outline Objectives of the Course Syllabus Reference Books Introduction to programming languages Basic
Lab 3: Defining Data and Symbolic Constants
 COE 205 Lab Manual Lab 3: Defining Data and Symbolic Constants - page 25 Lab 3: Defining Data and Symbolic Constants Contents 3.1. MASM Data Types 3.2. Defining Integer Data 3.3. Watching Variables using
COE 205 Lab Manual Lab 3: Defining Data and Symbolic Constants - page 25 Lab 3: Defining Data and Symbolic Constants Contents 3.1. MASM Data Types 3.2. Defining Integer Data 3.3. Watching Variables using
THE INTEGER DATA TYPES. Laura Marik Spring 2012 C++ Course Notes (Provided by Jason Minski)
 THE INTEGER DATA TYPES STORAGE OF INTEGER TYPES IN MEMORY All data types are stored in binary in memory. The type that you give a value indicates to the machine what encoding to use to store the data in
THE INTEGER DATA TYPES STORAGE OF INTEGER TYPES IN MEMORY All data types are stored in binary in memory. The type that you give a value indicates to the machine what encoding to use to store the data in
1/25/2018. ECE 220: Computer Systems & Programming. Write Output Using printf. Use Backslash to Include Special ASCII Characters
 University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 220: Computer Systems & Programming Review: Basic I/O in C Allowing Input from the Keyboard, Output to the Monitor
University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Dept. of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 220: Computer Systems & Programming Review: Basic I/O in C Allowing Input from the Keyboard, Output to the Monitor
C++ Code Structure. Cooperating with the Compiler
 C++ Code Structure Cooperating with the Compiler C / C++ Compilation In Java (and many other modern languages), the compiler is designed to make multiple passes over code files during compilation. In doing
C++ Code Structure Cooperating with the Compiler C / C++ Compilation In Java (and many other modern languages), the compiler is designed to make multiple passes over code files during compilation. In doing
C and C++ I. Spring 2014 Carola Wenk
 C and C++ I Spring 2014 Carola Wenk Different Languages Python sum = 0 i = 1 while (i
C and C++ I Spring 2014 Carola Wenk Different Languages Python sum = 0 i = 1 while (i
15213 Recitation Section C
 15213 Recitation Section C Outline Sept. 9, 2002 Introduction Unix and C Playing with Bits Practice Problems Introducing Myself Try to pronounce my name: My office hour: Wed 2-3pm, WeH 8019 Contact: Email:
15213 Recitation Section C Outline Sept. 9, 2002 Introduction Unix and C Playing with Bits Practice Problems Introducing Myself Try to pronounce my name: My office hour: Wed 2-3pm, WeH 8019 Contact: Email:
In order to run the program, go to the folder Release and run project.exe.
 Assembly Language and System Software Lab exercise You need to implement seven programs. In this lab exercise, you are going to get familiar with assembly programming. You should follow the guideline to
Assembly Language and System Software Lab exercise You need to implement seven programs. In this lab exercise, you are going to get familiar with assembly programming. You should follow the guideline to
C and Programming Basics
 Announcements Assignment 1 Will be posted on Wednesday, Jan. 9 Due Wednesday, Jan. 16 Piazza Please sign up if you haven t already https://piazza.com/sfu.ca/spring2019/cmpt125 Lecture notes Posted just
Announcements Assignment 1 Will be posted on Wednesday, Jan. 9 Due Wednesday, Jan. 16 Piazza Please sign up if you haven t already https://piazza.com/sfu.ca/spring2019/cmpt125 Lecture notes Posted just
Gabriel Hugh Elkaim Spring CMPE 013/L: C Programming. CMPE 013/L: C Programming
 1 Literal Constants Definition A literal or a literal constant is a value, such as a number, character or string, which may be assigned to a variable or a constant. It may also be used directly as a function
1 Literal Constants Definition A literal or a literal constant is a value, such as a number, character or string, which may be assigned to a variable or a constant. It may also be used directly as a function
Understanding main() function Input/Output Streams
 Understanding main() function Input/Output Streams Structure of a program // my first program in C++ #include int main () { cout
Understanding main() function Input/Output Streams Structure of a program // my first program in C++ #include int main () { cout
Integer Data Types. Data Type. Data Types. int, short int, long int
 Data Types Variables are classified according to their data type. The data type determines the kind of information that may be stored in the variable. A data type is a set of values. Generally two main
Data Types Variables are classified according to their data type. The data type determines the kind of information that may be stored in the variable. A data type is a set of values. Generally two main
Computer Programming : C++
 The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2003 Muath i.alnabris Computer Programming : C++ Experiment #1 Basics Contents Structure of a program
The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2003 Muath i.alnabris Computer Programming : C++ Experiment #1 Basics Contents Structure of a program
Streams. Ali Malik
 Streams Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Purpose of Streams Output Streams Input Streams Stringstream (maybe) Announcements Recap Recap - Hello, world! #include int main() { std::cout
Streams Ali Malik malikali@stanford.edu Game Plan Recap Purpose of Streams Output Streams Input Streams Stringstream (maybe) Announcements Recap Recap - Hello, world! #include int main() { std::cout
Another Simple Program: Adding Two Integers
 Another Simple Program: Adding Two Integers Another Simple Program: Adding Two Integers This program uses the input stream object std::cin and the stream extrac>, to obtain two integers
Another Simple Program: Adding Two Integers Another Simple Program: Adding Two Integers This program uses the input stream object std::cin and the stream extrac>, to obtain two integers
Tutorial 1: C-Language
 Tutorial 1: C-Language Problem 1: Data Type What are the ranges of the following data types? int 32 bits 2 31..2 31-1 OR -2147483648..2147483647 (0..4294967295 if unsiged) in some machines int is same
Tutorial 1: C-Language Problem 1: Data Type What are the ranges of the following data types? int 32 bits 2 31..2 31-1 OR -2147483648..2147483647 (0..4294967295 if unsiged) in some machines int is same
Introduction to C++ Systems Programming
 Introduction to C++ Systems Programming Introduction to C++ Syntax differences between C and C++ A Simple C++ Example C++ Input/Output C++ Libraries C++ Header Files Another Simple C++ Example Inline Functions
Introduction to C++ Systems Programming Introduction to C++ Syntax differences between C and C++ A Simple C++ Example C++ Input/Output C++ Libraries C++ Header Files Another Simple C++ Example Inline Functions
Cours de C++ Introduction
 Cours de C++ Introduction Cécile Braunstein cecile.braunstein@lip6.fr Cours de C++ 1 / 20 Généralité Notes Interros cours 1/3 Contrôle TP 1/3 Mini-projet 1/3 Bonus (Note de Participation) jusqu à 2 points
Cours de C++ Introduction Cécile Braunstein cecile.braunstein@lip6.fr Cours de C++ 1 / 20 Généralité Notes Interros cours 1/3 Contrôle TP 1/3 Mini-projet 1/3 Bonus (Note de Participation) jusqu à 2 points
Lecture 3. Input and Output. Review from last week. Variable - place to store data in memory. identified by a name should be meaningful Has a type-
 Lecture 3 Input and Output Review from last week Variable - place to store data in memory identified by a name should be meaningful Has a type- int double char bool Has a value may be garbage change value
Lecture 3 Input and Output Review from last week Variable - place to store data in memory identified by a name should be meaningful Has a type- int double char bool Has a value may be garbage change value
공학프로그래밍언어 (PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE FOR ENGINEERS) -VARIABLE AND DATA TYPES- SPRING 2015, SEON-JU AHN, CNU EE
 공학프로그래밍언어 (PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE FOR ENGINEERS) -VARIABLE AND DATA TYPES- SPRING 2015, SEON-JU AHN, CNU EE COMMENT Comment Comments are usually added with the purpose of making the source code easier to
공학프로그래밍언어 (PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE FOR ENGINEERS) -VARIABLE AND DATA TYPES- SPRING 2015, SEON-JU AHN, CNU EE COMMENT Comment Comments are usually added with the purpose of making the source code easier to
CSE 12 Spring 2018 Week One, Lecture Two
 CSE 12 Spring 2018 Week One, Lecture Two Homework One and Two: - Introduction to C - Review of basic programming principles - Building from fgetc and fputc - Input and output strings and numbers - Introduction
CSE 12 Spring 2018 Week One, Lecture Two Homework One and Two: - Introduction to C - Review of basic programming principles - Building from fgetc and fputc - Input and output strings and numbers - Introduction
Inline Assembler. Willi-Hans Steeb and Yorick Hardy. International School for Scientific Computing
 Inline Assembler Willi-Hans Steeb and Yorick Hardy International School for Scientific Computing e-mail: steebwilli@gmail.com Abstract We provide a collection of inline assembler programs. 1 Using the
Inline Assembler Willi-Hans Steeb and Yorick Hardy International School for Scientific Computing e-mail: steebwilli@gmail.com Abstract We provide a collection of inline assembler programs. 1 Using the
Distributed Real-Time Control Systems. Lecture 17 C++ Programming Intro to C++ Objects and Classes
 Distributed Real-Time Control Systems Lecture 17 C++ Programming Intro to C++ Objects and Classes 1 Bibliography Classical References Covers C++ 11 2 What is C++? A computer language with object oriented
Distributed Real-Time Control Systems Lecture 17 C++ Programming Intro to C++ Objects and Classes 1 Bibliography Classical References Covers C++ 11 2 What is C++? A computer language with object oriented
1- Write a single C++ statement that: A. Calculates the sum of the two integrates 11 and 12 and outputs the sum to the consol.
 1- Write a single C++ statement that: A. Calculates the sum of the two integrates 11 and 12 and outputs the sum to the consol. B. Outputs to the console a floating point number f1 in scientific format
1- Write a single C++ statement that: A. Calculates the sum of the two integrates 11 and 12 and outputs the sum to the consol. B. Outputs to the console a floating point number f1 in scientific format
CS , Fall 2001 Exam 1
 Andrew login ID: Full Name: CS 15-213, Fall 2001 Exam 1 October 9, 2001 Instructions: Make sure that your exam is not missing any sheets, then write your full name and Andrew login ID on the front. Write
Andrew login ID: Full Name: CS 15-213, Fall 2001 Exam 1 October 9, 2001 Instructions: Make sure that your exam is not missing any sheets, then write your full name and Andrew login ID on the front. Write
C++ Structures Programming Workshop 2 (CSCI 1061U)
 C++ Structures Programming Workshop 2 (CSCI 1061U) Faisal Qureshi http://faculty.uoit.ca/qureshi University of Ontario Institute of Technology C++ struct struct keyword can be used to define new data types
C++ Structures Programming Workshop 2 (CSCI 1061U) Faisal Qureshi http://faculty.uoit.ca/qureshi University of Ontario Institute of Technology C++ struct struct keyword can be used to define new data types
CSE 333 Lecture 9 - intro to C++
 CSE 333 Lecture 9 - intro to C++ Hal Perkins Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia & Agenda Main topic: Intro to C++ But first: Some hints on HW2 Labs: The
CSE 333 Lecture 9 - intro to C++ Hal Perkins Department of Computer Science & Engineering University of Washington Administrivia & Agenda Main topic: Intro to C++ But first: Some hints on HW2 Labs: The
Full Name: CISC 360, Fall 2008 Example of Exam
 Full Name: CISC 360, Fall 2008 Example of Exam Page 1 of 0 Problem 1. (12 points): Consider the following 8-bit floating point representation based on the IEEE floating point format: There is a sign bit
Full Name: CISC 360, Fall 2008 Example of Exam Page 1 of 0 Problem 1. (12 points): Consider the following 8-bit floating point representation based on the IEEE floating point format: There is a sign bit
#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int shownum(int digits[], int digitcount);
![#include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int shownum(int digits[], int digitcount); #include <stdio.h> #include <math.h> int shownum(int digits[], int digitcount);](/thumbs/85/92571512.jpg) Problem 1: Programming in C [20 Points] Write a C program that takes as input a positive integer number and converts it to base 4. Some examples of input and output of this program are as follow: Example
Problem 1: Programming in C [20 Points] Write a C program that takes as input a positive integer number and converts it to base 4. Some examples of input and output of this program are as follow: Example
UNIVERSITY OF LIMERICK OLLSCOIL LUIMNIGH COLLEGE OF INFORMATICS & ELECTRONICS DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONIC & COMPUTER ENGINEERING
 UNIVERSITY OF LIMERICK OLLSCOIL LUIMNIGH COLLEGE OF INFORMATICS & ELECTRONICS DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONIC & COMPUTER ENGINEERING MODULE CODE: MODULE TITLE: ET4131 Introduction to Computer Programming SEMESTER:
UNIVERSITY OF LIMERICK OLLSCOIL LUIMNIGH COLLEGE OF INFORMATICS & ELECTRONICS DEPARTMENT OF ELECTRONIC & COMPUTER ENGINEERING MODULE CODE: MODULE TITLE: ET4131 Introduction to Computer Programming SEMESTER:
! A program is a set of instructions that the. ! It must be translated. ! Variable: portion of memory that stores a value. char
 Week 1 Operators, Data Types & I/O Gaddis: Chapters 1, 2, 3 CS 5301 Fall 2016 Jill Seaman Programming A program is a set of instructions that the computer follows to perform a task It must be translated
Week 1 Operators, Data Types & I/O Gaddis: Chapters 1, 2, 3 CS 5301 Fall 2016 Jill Seaman Programming A program is a set of instructions that the computer follows to perform a task It must be translated
2.1. Unit 2. Integer Operations (Arithmetic, Overflow, Bitwise Logic, Shifting)
 2.1 Unit 2 Integer Operations (Arithmetic, Overflow, Bitwise Logic, Shifting) 2.2 Skills & Outcomes You should know and be able to apply the following skills with confidence Perform addition & subtraction
2.1 Unit 2 Integer Operations (Arithmetic, Overflow, Bitwise Logic, Shifting) 2.2 Skills & Outcomes You should know and be able to apply the following skills with confidence Perform addition & subtraction
Chapter 11 Introduction to Programming in C
 C: A High-Level Language Chapter 11 Introduction to Programming in C Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University! Gives
C: A High-Level Language Chapter 11 Introduction to Programming in C Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University! Gives
(5-1) Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) and C++ Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 4, 2019) Washington State University
 (5-1) Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) and C++ Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 4, 2019) Washington State University Key Concepts 2 Object-Oriented Design Object-Oriented Programming
(5-1) Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) and C++ Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 4, 2019) Washington State University Key Concepts 2 Object-Oriented Design Object-Oriented Programming
IBM PC Hardware CPU 8088, Pentium... ALU (Arithmetic and Logic Unit) Registers. CU (Control Unit) IP.
 IBM PC Hardware CPU 8088, 8086 80286 80386 80486 Pentium... ALU (Arithmetic and Logic Unit) Registers CU (Control Unit) IP Memory ROM BIOS I/O RAM OS Programs Video memory BIOS data Interrupt Vectors Memory
IBM PC Hardware CPU 8088, 8086 80286 80386 80486 Pentium... ALU (Arithmetic and Logic Unit) Registers CU (Control Unit) IP Memory ROM BIOS I/O RAM OS Programs Video memory BIOS data Interrupt Vectors Memory
Fundamentals of Programming CS-110. Lecture 2
 Fundamentals of Programming CS-110 Lecture 2 Last Lab // Example program #include using namespace std; int main() { cout
Fundamentals of Programming CS-110 Lecture 2 Last Lab // Example program #include using namespace std; int main() { cout
! A literal represents a constant value used in a. ! Numbers: 0, 34, , -1.8e12, etc. ! Characters: 'A', 'z', '!', '5', etc.
 Week 1: Introduction to C++ Gaddis: Chapter 2 (excluding 2.1, 2.11, 2.14) CS 1428 Fall 2014 Jill Seaman Literals A literal represents a constant value used in a program statement. Numbers: 0, 34, 3.14159,
Week 1: Introduction to C++ Gaddis: Chapter 2 (excluding 2.1, 2.11, 2.14) CS 1428 Fall 2014 Jill Seaman Literals A literal represents a constant value used in a program statement. Numbers: 0, 34, 3.14159,
Tutorial-2a: First steps with C++ programming
 Programming for Scientists Tutorial 2a 1 / 18 HTTP://WWW.HEP.LU.SE/COURSES/MNXB01 Introduction to Programming and Computing for Scientists Tutorial-2a: First steps with C++ programming Programming for
Programming for Scientists Tutorial 2a 1 / 18 HTTP://WWW.HEP.LU.SE/COURSES/MNXB01 Introduction to Programming and Computing for Scientists Tutorial-2a: First steps with C++ programming Programming for
Homework Assignment #2 (revised)
 CISC 2000 Computer Science II Fall, 2018 1 Recall the following functions and operators: Homework Assignment #2 (revised) sizeof function: returns the size of a variable (i.e., the number of bytes used
CISC 2000 Computer Science II Fall, 2018 1 Recall the following functions and operators: Homework Assignment #2 (revised) sizeof function: returns the size of a variable (i.e., the number of bytes used
Lab 1: First Steps in C++ - Eclipse
 Lab 1: First Steps in C++ - Eclipse Step Zero: Select workspace 1. Upon launching eclipse, we are ask to chose a workspace: 2. We select a new workspace directory (e.g., C:\Courses ): 3. We accept the
Lab 1: First Steps in C++ - Eclipse Step Zero: Select workspace 1. Upon launching eclipse, we are ask to chose a workspace: 2. We select a new workspace directory (e.g., C:\Courses ): 3. We accept the
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Chapter 18 I/O in C Standard C Library I/O commands are not included as part of the C language. Instead, they are part of the Standard C Library. A collection of functions and macros that must be implemented
Chapter 18 I/O in C Standard C Library I/O commands are not included as part of the C language. Instead, they are part of the Standard C Library. A collection of functions and macros that must be implemented
This chapter introduces the notion of namespace. We also describe how to manage input and output with C++ commands via the terminal or files.
 C++ PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE: NAMESPACE AND MANGEMENT OF INPUT/OUTPUT WITH C++. CAAM 519, CHAPTER 15 This chapter introduces the notion of namespace. We also describe how to manage input and output with C++
C++ PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE: NAMESPACE AND MANGEMENT OF INPUT/OUTPUT WITH C++. CAAM 519, CHAPTER 15 This chapter introduces the notion of namespace. We also describe how to manage input and output with C++
Chapter 2: Introduction to C++
 Chapter 2: Introduction to C++ Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright Publishing as 2010 Pearson Pearson Addison-Wesley Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley 2.1 Parts of a C++
Chapter 2: Introduction to C++ Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright Publishing as 2010 Pearson Pearson Addison-Wesley Education, Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley 2.1 Parts of a C++
CS , Fall 2007 Exam 1
 Andrew login ID: Full Name: CS 15-213, Fall 2007 Exam 1 Wednesday October 17, 2007 Instructions: Make sure that your exam is not missing any sheets, then write your full name and Andrew login ID on the
Andrew login ID: Full Name: CS 15-213, Fall 2007 Exam 1 Wednesday October 17, 2007 Instructions: Make sure that your exam is not missing any sheets, then write your full name and Andrew login ID on the
Chapter 2: Special Characters. Parts of a C++ Program. Introduction to C++ Displays output on the computer screen
 Chapter 2: Introduction to C++ 2.1 Parts of a C++ Program Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Publishing Pearson as Pearson Education, Addison-Wesley Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
Chapter 2: Introduction to C++ 2.1 Parts of a C++ Program Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Publishing Pearson as Pearson Education, Addison-Wesley Inc. Publishing as Pearson Addison-Wesley
Chapter 11 Introduction to Programming in C
 Chapter 11 Introduction to Programming in C Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University C: A High-Level Language! Gives
Chapter 11 Introduction to Programming in C Original slides from Gregory Byrd, North Carolina State University Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Colorado State University C: A High-Level Language! Gives
A Quick Look at C for C++ Programmers
 COMP 40: Machine Structure and Assembly Language Programming (Fall 2017) A Quick Look at C for C++ Programmers Noah Mendelsohn (with updates by Mark Sheldon) Tufts University Email: noah@cs.tufts.edu Web:
COMP 40: Machine Structure and Assembly Language Programming (Fall 2017) A Quick Look at C for C++ Programmers Noah Mendelsohn (with updates by Mark Sheldon) Tufts University Email: noah@cs.tufts.edu Web:
