Chapter 4 Control Structures
|
|
|
- Philomena Lee
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 4 Control Structures Foundational Java Key Elements and Practical Programming 1
2 if - else switch Control Structures break and continue Ternary operator while and do-while loops for loops 2
3 Two forms if if-else Making Selections The if is always followed by parentheses the expression in the parentheses must evaluate to a boolean (true or false) if (booleanexpression) 3
4 Using Braces If only one line of code is conditional, braces are not required if (booleanexpression) statement; For more than one line, braces are essential if (booleanexpression) statement(s); Safer to always use braces 4
5 if else Statements if(condition) // do this else // do this instead The else part is optional If the condition is false and there is no else part then no code in the conditional statement will be executed 5
6 Nested Statements Use braces for each block if(condition) // statements else if(condition) // statements else // statements 6
7 Comparison Operators Used to create Boolean expressions (return true or false) The relational operators: < less than > greater than <= less than or equal to >= greater than or equal to Can only be used with numeric primitives The equality operators: == equal!= not equal can be used with all data types a common error in Java is to confuse the = and == operators 7
8 Examples Condition Operator Example equal to == if(temperature == 100) not equal to!= if(grade!= 'F') less than < if(sales < target) less than or equal to <= if(enginesize <= 2000) greater than > if(hoursworked > 40) greater than or equal to >= if(age >= 18) 8
9 Boolean Operators Boolean Operator Java Operator Meaning AND && Return true if both sides of the expression are true OR Return true if at least one side of the expression is true NOT! Return true if the expression is false Example if(age > 4 && age < 16) if(timeelapsed > 60 stopped == true) if(!drawingchanged) // assumes drawingchanged // is a boolean variable & AND operator (full evaluation) OR operator (full evaluation) 9
10 Using Selection: the CoinExample Class if statement based on using a randomly generated number to represent a coin being flipped The Java Math class random operation Returns a random double >= 0.0 and < 1.0 double randomnumber = Math.random(); Using a random number in an if statement if (randomnumber < 0.5) System.out.println("The coin shows heads"); else System.out.println("The coin shows tails"); 10
11 Exercise 4.1 Create a class with a main method In main, generate a random integer between 1 and 10 (inclusive) Using an if statement, work out if the random number is odd or even Write a message to the console that displays both the random integer and whether it is an odd or an even number 11
12 Selection and Test Code A test compares the result you expect with the result you actually get if(dievalue >= 1 && dievalue <= 6) System.out.println("Valid die value: " + dievalue); else System.out.println("Error. Expected value between 1 and 6 but was " + dievalue); Tests written in code can be run repeatedly as regression tests 12
13 switch Statement When multiple selections are based on a single (whole number) variable Switch variable and case literals must be byte, char, short or int (can also be Strings since Java 7) switch(variable) case literalvalue1 : // some code here break; case literalvalue2 : // some code here break; // etc. for as many cases as need to be handled default: // default code to handle cases not already dealt with 13
14 Using break (or not) break sends control to the end of the switch statement without evaluating any other cases Often (but not always) what you need Don t use break if you want logic shared by multiple cases switch (achar) case a : case A : // my code here break; case b // etc 14
15 Dice Man Example Switches on the state of a die No default needed in this example switch (dievalue) case 1: System.out.println("forget the whole affair"); break; case 2: System.out.println("wait until the party on Saturday"); break; case 3: System.out.println("do what Arlene says"); break; case 4: System.out.println("have a platonic relationship"); break; case 5: System.out.println("follow your emotions"); break; case 6: System.out.println("go to Arlene s apartment tonight"); break; 15
16 break and continue The use of break in a switch statement is not the only context in which this keyword can be used moves execution to the end of the current block (i.e. the next closing brace) continue has a similar function takes control back to the beginning of the current code block rather than the end Useful for searching and sorting large arrays act rather like structured goto statements 16
17 Exercise 4.2 In a main method, generate a random integer between 1 and 13 to represent the possible values in a suit of playing cards Use a switch statement that applies cases to your random integer if the random number is 1, print out Ace to the console if the random number is 11, print out Jack to the console if the random number is 12, print out Queen to the console if the random number is 13, print out King to the console The default case should simply print the random integer to the console 17
18 Ternary Operator Shorthand if - else statement expression? op1 : op2 If expression is true, return op1, otherwise return op2 String result = x % 2 == 0? "even" : "odd"; Used when intent is to focus on returned result, rather than a branch in program flow 18
19 Iteration Iteration can be achieved in three slightly different ways: while loops do...while loops for loops In each case, there will be a condition that allows the loop to terminate Which one to use depends on a number of factors and we often find that more than one will meet our requirements we have to be aware of their differences in order to use them correctly 19
20 while and do while These loops continue while the condition is true while tests a precondition (zero or more iterations) do while tests a post condition (one or more iterations) do // statements while(condition); while(condition) // statements Note the semicolon! 20
21 do while example This do while loop simulates the throwing of a die until it shows a six int dievalue = 0; // loop until throwing the Die gets a six do // generate a random number in the range 0.0 to 1.0 double randomnumber = Math.random(); // to get a number in the range 1 to 6, we need to multiply the // random number by 6 and add 1 randomnumber *= 6; randomnumber++; // to convert this value into an integer we cast it dievalue = (int)randomnumber; System.out.println("You have thrown a " + dievalue); while (dievalue!= 6); 21
22 for Loops Statement has three sections initialise - executed once before loop begins condition - executed before each loop If true then loop body executes update - executed at the end of each loop for(initialisation; 'while' condition; action) // some code here 22
23 Initialisation and Update Any or all of the three sections can be left empty This is an endless loop for(;;)... Only use a for loop when you need initialisation and update actions Otherwise code is more complex that it needs to be e.g. endless while loop is simpler while(true) 23
24 Iteration with a for Loop This example uses a for loop to display the printable ASCII characters of the Unicode table // the 'for' loop counts from 33 to 126, the range of the printable ASCII characters for (int i = 33; i < 127; i++) // convert the integer to a 'char' using a cast char character = (char)i; // display the ASCII number along with its character then add a tab System.out.print(i + ": " + character + '\t'); // if there are 9 characters on a row, add a line feed if ((i - 32) % 9 == 0) System.out.println('\n'); 24
25 for Loops and Arrays for loops are frequently used to loop through arrays Use the array s length field to control the loop String[] monthnames = "January","February","March","April","May","June","July","August", "September","October","November","December"; int[] monthlyrainfall = 74,81,86,93,100,116,126,111,93,80,84,91; System.out.println("Average monthly rainfall"); for(int i = 0; i < monthlyrainfall.length; i++) System.out.println(monthNames[i] + ": " + monthlyrainfall[i] + "mm."); Note the use of two arrays one of int and the other of String 25
26 The Array Passed to main The parameter we always use with main is an array of Strings, which may or may not be empty The size of this array depends entirely on how many Strings are passed to it at run time public static void main(string[] args) for (int i = 0; i < args.length; i++) System.out.println(args[i]); 26
27 Passing Strings to main From the command line java com.introjava.chapter4.mainarrayloopexample hello I am some strings In Eclipse Run -> Run Configuration 27
28 Multiple Initialisations and Actions The initialisation and action sections of the for statement can contain lists of values, separated by commas public class MultiValueForLoopExample public static void main(string[] args) for (int lettercount = 1, uppercount = 65, lowercount = 97; lettercount <= 26; lettercount++, uppercount++, lowercount++) System.out.println("Lower case: " + (char)lowercount + " Upper case: " + (char)uppercount); 28
29 Exercise 4.3 Create a new class with a main method In main, take the following steps: Create and initialise an array containing the integers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 Use a for loop to print out the contents of the array Add a while loop that prints out the contents of the array in reverse order Add a do..while loop that iterates forward through the array. Inside the loop, add an if statement so that only even numbered values from the array are printed 29
30 Summary Control structures for selection and iteration Selection syntax if and switch statements Relational and Boolean operators Different kinds of loop while, do while, for Iterating through arrays Math class for random number generation Passing an array of Strings to the main method of a class at run time 30
Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups:
 JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
Review for Test 1 (Chapter 1-5)
 Review for Test 1 (Chapter 1-5) 1. Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java a) What is a computer? b) What is a computer program? c) A bit is a binary digit 0 or 1. A byte is a sequence of 8 bits.
Review for Test 1 (Chapter 1-5) 1. Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java a) What is a computer? b) What is a computer program? c) A bit is a binary digit 0 or 1. A byte is a sequence of 8 bits.
Java Loop Control. Programming languages provide various control structures that allow for more complicated execution paths.
 Loop Control There may be a situation when you need to execute a block of code several number of times. In general, statements are executed sequentially: The first statement in a function is executed first,
Loop Control There may be a situation when you need to execute a block of code several number of times. In general, statements are executed sequentially: The first statement in a function is executed first,
PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS
 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS Q1. Name any two Object Oriented Programming languages? Q2. Why is java called a platform independent language? Q3. Elaborate the java Compilation process. Q4. Why do we write
PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS Q1. Name any two Object Oriented Programming languages? Q2. Why is java called a platform independent language? Q3. Elaborate the java Compilation process. Q4. Why do we write
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Fall 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements
 Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
Lesson 3: Introduction to the Java Basics: Control Flow Statements Repetition Structures THEORY Variable Assignment You can only assign a value to a variable that is consistent with the variable s declared
Sequence structure. The computer executes java statements one after the other in the order in which they are written. Total = total +grade;
 Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Control Statements Control Statements All programs could be written in terms of only one of three control structures: Sequence Structure Selection Structure Repetition Structure Sequence structure The
Following is the general form of a typical decision making structure found in most of the programming languages:
 Decision Making Decision making structures have one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements that are to be executed if the condition is determined
Decision Making Decision making structures have one or more conditions to be evaluated or tested by the program, along with a statement or statements that are to be executed if the condition is determined
An overview of Java, Data types and variables
 An overview of Java, Data types and variables Lecture 2 from (UNIT IV) Prepared by Mrs. K.M. Sanghavi 1 2 Hello World // HelloWorld.java: Hello World program import java.lang.*; class HelloWorld { public
An overview of Java, Data types and variables Lecture 2 from (UNIT IV) Prepared by Mrs. K.M. Sanghavi 1 2 Hello World // HelloWorld.java: Hello World program import java.lang.*; class HelloWorld { public
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Loops (Part II)
 CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Loops (Part II) Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Review Is this an infinite loop? Why (not)?
CS1150 Principles of Computer Science Loops (Part II) Yanyan Zhuang Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.uccs.edu/~yzhuang CS1150 UC. Colorado Springs Review Is this an infinite loop? Why (not)?
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
In this chapter, you will:
 Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 4 Control Structures I: Selection In this chapter, you will: Make decisions with the if and if else structures Use compound statements in an
Java Programming: Guided Learning with Early Objects Chapter 4 Control Structures I: Selection In this chapter, you will: Make decisions with the if and if else structures Use compound statements in an
Programming Basics. Digital Urban Visualization. People as Flows. ia
 Programming Basics Digital Urban Visualization. People as Flows. 28.09.2015 ia zuend@arch.ethz.ch treyer@arch.ethz.ch Programming? Programming is the interaction between the programmer and the computer.
Programming Basics Digital Urban Visualization. People as Flows. 28.09.2015 ia zuend@arch.ethz.ch treyer@arch.ethz.ch Programming? Programming is the interaction between the programmer and the computer.
x = 3 * y + 1; // x becomes 3 * y + 1 a = b = 0; // multiple assignment: a and b both get the value 0
 6 Statements 43 6 Statements The statements of C# do not differ very much from those of other programming languages. In addition to assignments and method calls there are various sorts of selections and
6 Statements 43 6 Statements The statements of C# do not differ very much from those of other programming languages. In addition to assignments and method calls there are various sorts of selections and
Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word. Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java
 Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations Chapter 3 Selection
Basic computer skills such as using Windows, Internet Explorer, and Microsoft Word Chapter 1 Introduction to Computers, Programs, and Java Chapter 2 Primitive Data Types and Operations Chapter 3 Selection
Pace University. Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1
 Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
CS313D: ADVANCED PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE
 CS313D: ADVANCED PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE Computer Science department Lecture 2 : C# Language Basics Lecture Contents 2 The C# language First program Variables and constants Input/output Expressions and casting
CS313D: ADVANCED PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE Computer Science department Lecture 2 : C# Language Basics Lecture Contents 2 The C# language First program Variables and constants Input/output Expressions and casting
For that purpose, java provides control structures that serve to specify what has to be done by our program, when and under which circumstances.
 Control Structures A program is usually not limited to a linear sequence of instructions. During its process it may bifurcate, repeat code or take decisions. For that purpose, java provides control structures
Control Structures A program is usually not limited to a linear sequence of instructions. During its process it may bifurcate, repeat code or take decisions. For that purpose, java provides control structures
School of Computer Science CPS109 Course Notes 5 Alexander Ferworn Updated Fall 15
 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388)
 Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types
 Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types LECTURER: ATHENA TOUMBOURI How to Create a New Java Project in Eclipse Eclipse is one of the most popular development environments for Java, as it contains
Introduction to Java & Fundamental Data Types LECTURER: ATHENA TOUMBOURI How to Create a New Java Project in Eclipse Eclipse is one of the most popular development environments for Java, as it contains
Object-Oriented Programming
 Object-Oriented Programming Java Syntax Program Structure Variables and basic data types. Industry standard naming conventions. Java syntax and coding conventions If Then Else Case statements Looping (for,
Object-Oriented Programming Java Syntax Program Structure Variables and basic data types. Industry standard naming conventions. Java syntax and coding conventions If Then Else Case statements Looping (for,
Flow Control. CSC215 Lecture
 Flow Control CSC215 Lecture Outline Blocks and compound statements Conditional statements if - statement if-else - statement switch - statement? : opertator Nested conditional statements Repetitive statements
Flow Control CSC215 Lecture Outline Blocks and compound statements Conditional statements if - statement if-else - statement switch - statement? : opertator Nested conditional statements Repetitive statements
Getting started with Java
 Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
Chapter 4: Control Structures I
 Chapter 4: Control Structures I Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Second Edition Chapter Objectives Learn about control structures. Examine relational and logical operators. Explore
Chapter 4: Control Structures I Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Second Edition Chapter Objectives Learn about control structures. Examine relational and logical operators. Explore
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Recap: Exceptions. Summary: for loop. Recap: CaesarFile using Loop. Summary: Flow Control Statements
 Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Puzzle Day from Friday to Monday Arrays; Loop Patterns (break) Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email:
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Puzzle Day from Friday to Monday Arrays; Loop Patterns (break) Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email:
CS313D: ADVANCED PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE
 CS313D: ADVANCED PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE Computer Science Department Lecture 3: C# language basics Lecture Contents 2 C# basics Conditions Loops Methods Arrays Dr. Amal Khalifa, Spr 2015 3 Conditions and
CS313D: ADVANCED PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE Computer Science Department Lecture 3: C# language basics Lecture Contents 2 C# basics Conditions Loops Methods Arrays Dr. Amal Khalifa, Spr 2015 3 Conditions and
Chapter 3 Selection Statements
 Chapter 3 Selection Statements 3.1 Introduction Java provides selection statements that let you choose actions with two or more alternative courses. Selection statements use conditions. Conditions are
Chapter 3 Selection Statements 3.1 Introduction Java provides selection statements that let you choose actions with two or more alternative courses. Selection statements use conditions. Conditions are
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Arrays; Loop Patterns (break) Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin. q Puzzle Day
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Arrays; Loop Patterns (break) Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu Admin. q Puzzle Day
10/30/2010. Introduction to Control Statements. The if and if-else Statements (cont.) Principal forms: JAVA CONTROL STATEMENTS SELECTION STATEMENTS
 JAVA CONTROL STATEMENTS Introduction to Control statements are used in programming languages to cause the flow of control to advance and branch based on changes to the state of a program. In Java, control
JAVA CONTROL STATEMENTS Introduction to Control statements are used in programming languages to cause the flow of control to advance and branch based on changes to the state of a program. In Java, control
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming. Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015
 COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Slides will be posted before the class. There might be few
COMP-202: Foundations of Programming Lecture 3: Boolean, Mathematical Expressions, and Flow Control Sandeep Manjanna, Summer 2015 Announcements Slides will be posted before the class. There might be few
Programming: Java. Chapter Objectives. Control Structures. Chapter 4: Control Structures I. Program Design Including Data Structures
 Chapter 4: Control Structures I Java Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures Chapter Objectives Learn about control structures Examine relational and logical operators Explore how to form
Chapter 4: Control Structures I Java Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures Chapter Objectives Learn about control structures Examine relational and logical operators Explore how to form
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Spring 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types
BIT Java Programming. Sem 1 Session 2011/12. Chapter 2 JAVA. basic
 BIT 3383 Java Programming Sem 1 Session 2011/12 Chapter 2 JAVA basic Objective: After this lesson, you should be able to: declare, initialize and use variables according to Java programming language guidelines
BIT 3383 Java Programming Sem 1 Session 2011/12 Chapter 2 JAVA basic Objective: After this lesson, you should be able to: declare, initialize and use variables according to Java programming language guidelines
Flow of Control. Chapter 3 Part 3 The Switch Statement
 Flow of Control Chapter 3 Part 3 The Switch Statement Agenda Hw 03 comments Review of Ch03 - Parts 1 & 2 Conditional operator I/O of boolean values The switch statement Random numbers Methods with arguments
Flow of Control Chapter 3 Part 3 The Switch Statement Agenda Hw 03 comments Review of Ch03 - Parts 1 & 2 Conditional operator I/O of boolean values The switch statement Random numbers Methods with arguments
Lecture 6: While Loops and the Math Class
 Lecture 6: While Loops and the Math Class Building Java Programs: A Back to Basic Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. while loops 2 Categories of loops
Lecture 6: While Loops and the Math Class Building Java Programs: A Back to Basic Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. while loops 2 Categories of loops
Java Control Statements
 Java Control Statements An introduction to the Java Programming Language Produced by: Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Dr. Siobhan Drohan (sdrohan@wit.ie) Department of Computing and Mathematics http://www.wit.ie/
Java Control Statements An introduction to the Java Programming Language Produced by: Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Dr. Siobhan Drohan (sdrohan@wit.ie) Department of Computing and Mathematics http://www.wit.ie/
The Java language has a wide variety of modifiers, including the following:
 PART 5 5. Modifier Types The Java language has a wide variety of modifiers, including the following: Java Access Modifiers Non Access Modifiers 5.1 Access Control Modifiers Java provides a number of access
PART 5 5. Modifier Types The Java language has a wide variety of modifiers, including the following: Java Access Modifiers Non Access Modifiers 5.1 Access Control Modifiers Java provides a number of access
QUIZ: What value is stored in a after this
 QUIZ: What value is stored in a after this statement is executed? Why? a = 23/7; QUIZ evaluates to 16. Lesson 4 Statements, Expressions, Operators Statement = complete instruction that directs the computer
QUIZ: What value is stored in a after this statement is executed? Why? a = 23/7; QUIZ evaluates to 16. Lesson 4 Statements, Expressions, Operators Statement = complete instruction that directs the computer
Java Basic Programming Constructs
 Java Basic Programming Constructs /* * This is your first java program. */ class HelloWorld{ public static void main(string[] args){ System.out.println( Hello World! ); A Closer Look at HelloWorld 2 This
Java Basic Programming Constructs /* * This is your first java program. */ class HelloWorld{ public static void main(string[] args){ System.out.println( Hello World! ); A Closer Look at HelloWorld 2 This
Object oriented programming. Instructor: Masoud Asghari Web page: Ch: 3
 Object oriented programming Instructor: Masoud Asghari Web page: http://www.masses.ir/lectures/oops2017sut Ch: 3 1 In this slide We follow: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/index.html Trail: Learning
Object oriented programming Instructor: Masoud Asghari Web page: http://www.masses.ir/lectures/oops2017sut Ch: 3 1 In this slide We follow: https://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/index.html Trail: Learning
Eng. Mohammed S. Abdualal
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 3 Selections
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Dept. Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 3 Selections
ARG! Language Reference Manual
 ARG! Language Reference Manual Ryan Eagan, Mike Goldin, River Keefer, Shivangi Saxena 1. Introduction ARG is a language to be used to make programming a less frustrating experience. It is similar to C
ARG! Language Reference Manual Ryan Eagan, Mike Goldin, River Keefer, Shivangi Saxena 1. Introduction ARG is a language to be used to make programming a less frustrating experience. It is similar to C
( &% class MyClass { }
 Recall! $! "" # ' ' )' %&! ( &% class MyClass { $ Individual things that differentiate one object from another Determine the appearance, state or qualities of objects Represents any variables needed for
Recall! $! "" # ' ' )' %&! ( &% class MyClass { $ Individual things that differentiate one object from another Determine the appearance, state or qualities of objects Represents any variables needed for
Glossary. (Very) Simple Java Reference (draft, v0.2)
 (Very) Simple Java Reference (draft, v0.2) (Very) Simple Java Reference (draft, v0.2) Explanations and examples for if and for (other things to-be-done). This is supposed to be a reference manual, so we
(Very) Simple Java Reference (draft, v0.2) (Very) Simple Java Reference (draft, v0.2) Explanations and examples for if and for (other things to-be-done). This is supposed to be a reference manual, so we
CCHAPTER SELECTION STATEMENTS HAPTER 3. Objectives
 LIANMC03v3_0132221586.QXD 5/15/06 7:41 PM Page 67 CCHAPTER HAPTER 3 1 SELECTION STATEMENTS Objectives To declare boolean type and write Boolean expressions ( 3.2). To distinguish between conditional and
LIANMC03v3_0132221586.QXD 5/15/06 7:41 PM Page 67 CCHAPTER HAPTER 3 1 SELECTION STATEMENTS Objectives To declare boolean type and write Boolean expressions ( 3.2). To distinguish between conditional and
Review Chapter 6 in Bravaco. Short Answers 1. This type of method does not return a value. a. null b. void c. empty d. anonymous
 Assignment 3 Methods Review CSC 123 Fall 2018 Notes: All homework must be submitted via e-mail. All parts of assignment must be submitted in a single e-mail with multiple attachments when required. Notes:
Assignment 3 Methods Review CSC 123 Fall 2018 Notes: All homework must be submitted via e-mail. All parts of assignment must be submitted in a single e-mail with multiple attachments when required. Notes:
Object Oriented Software Design
 Object Oriented Software Design Introduction to Java - II Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa September 30, 2010 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna) Introduction
Object Oriented Software Design Introduction to Java - II Giuseppe Lipari http://retis.sssup.it/~lipari Scuola Superiore Sant Anna Pisa September 30, 2010 G. Lipari (Scuola Superiore Sant Anna) Introduction
Flow of Control. Chapter 3
 Flow of Control Chapter 3 Outline The if-else Stetement The Type boolean The switch statement Flow of Control Flow of control is the order in which a program performs actions. Up to this point, the order
Flow of Control Chapter 3 Outline The if-else Stetement The Type boolean The switch statement Flow of Control Flow of control is the order in which a program performs actions. Up to this point, the order
Tools : The Java Compiler. The Java Interpreter. The Java Debugger
 Tools : The Java Compiler javac [ options ] filename.java... -depend: Causes recompilation of class files on which the source files given as command line arguments recursively depend. -O: Optimizes code,
Tools : The Java Compiler javac [ options ] filename.java... -depend: Causes recompilation of class files on which the source files given as command line arguments recursively depend. -O: Optimizes code,
Java Programming. Atul Prakash
 Java Programming Atul Prakash Java Language Fundamentals The language syntax is similar to C/ C++ If you know C/C++, you will have no trouble understanding Java s syntax If you don't, it will be easier
Java Programming Atul Prakash Java Language Fundamentals The language syntax is similar to C/ C++ If you know C/C++, you will have no trouble understanding Java s syntax If you don't, it will be easier
Java is an objet-oriented programming language providing features that support
 Java Essentials CSCI 136: Spring 2018 Handout 2 February 2 Language Basics Java is an objet-oriented programming language providing features that support Data abstraction Code reuse Modular development
Java Essentials CSCI 136: Spring 2018 Handout 2 February 2 Language Basics Java is an objet-oriented programming language providing features that support Data abstraction Code reuse Modular development
Review. Primitive Data Types & Variables. String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > <= >= == int, long float, double boolean char
 Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
Review Primitive Data Types & Variables int, long float, double boolean char String Mathematical operators: + - * / % Comparison: < > = == 1 1.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in
Computer Programming, I. Laboratory Manual. Experiment #6. Loops
 Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #6
Think Twice Code Once The Islamic University of Gaza Engineering Faculty Department of Computer Engineering Fall 2017 ECOM 2005 Khaleel I. Shaheen Computer Programming, I Laboratory Manual Experiment #6
Week 6: Review. Java is Case Sensitive
 Week 6: Review Java Language Elements: special characters, reserved keywords, variables, operators & expressions, syntax, objects, scoping, Robot world 7 will be used on the midterm. Java is Case Sensitive
Week 6: Review Java Language Elements: special characters, reserved keywords, variables, operators & expressions, syntax, objects, scoping, Robot world 7 will be used on the midterm. Java is Case Sensitive
Output :: /* display results */ System.out.print( Call Duration: );
 Introduction 7 : JAVA BASICS Java is object oriented programming language developed by Sun Microsystems in 1991. A company best known for its high-end UNIX workstations. Modelled after C++ Java language
Introduction 7 : JAVA BASICS Java is object oriented programming language developed by Sun Microsystems in 1991. A company best known for its high-end UNIX workstations. Modelled after C++ Java language
Language Reference Manual
 ALACS Language Reference Manual Manager: Gabriel Lopez (gal2129) Language Guru: Gabriel Kramer-Garcia (glk2110) System Architect: Candace Johnson (crj2121) Tester: Terence Jacobs (tj2316) Table of Contents
ALACS Language Reference Manual Manager: Gabriel Lopez (gal2129) Language Guru: Gabriel Kramer-Garcia (glk2110) System Architect: Candace Johnson (crj2121) Tester: Terence Jacobs (tj2316) Table of Contents
CS5000: Foundations of Programming. Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University
 CS5000: Foundations of Programming Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Overview of Source Code Components Comments Library declaration Classes Functions Variables Comments Can
CS5000: Foundations of Programming Mingon Kang, PhD Computer Science, Kennesaw State University Overview of Source Code Components Comments Library declaration Classes Functions Variables Comments Can
CS 139 Practice Midterm Questions #2
 CS 139 Practice Midterm Questions #2 Spring 2016 Name: 1. Write Java statements to accomplish each of the following. (a) Declares numbers to be an array of int s. (b) Initializes numbers to contain a reference
CS 139 Practice Midterm Questions #2 Spring 2016 Name: 1. Write Java statements to accomplish each of the following. (a) Declares numbers to be an array of int s. (b) Initializes numbers to contain a reference
Loops. Eng. Mohammed Abdualal. Islamic University of Gaza. Faculty of Engineering. Computer Engineering Department
 Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 6 Loops
Islamic University of Gaza Faculty of Engineering Computer Engineering Department Computer Programming Lab (ECOM 2114) Created by Eng: Mohammed Alokshiya Modified by Eng: Mohammed Abdualal Lab 6 Loops
Variables and data types
 Survivor: CSCI 135 Variables Variables and data types Stores information your program needs Each has a unique name Each has a specific type Java built-in type what it stores example values operations String
Survivor: CSCI 135 Variables Variables and data types Stores information your program needs Each has a unique name Each has a specific type Java built-in type what it stores example values operations String
Programming with Java
 Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
AP COMPUTER SCIENCE A
 AP COMPUTER SCIENCE A CONTROL FLOW Aug 28 2017 Week 2 http://apcs.cold.rocks 1 More operators! not!= not equals to % remainder! Goes ahead of boolean!= is used just like == % is used just like / http://apcs.cold.rocks
AP COMPUTER SCIENCE A CONTROL FLOW Aug 28 2017 Week 2 http://apcs.cold.rocks 1 More operators! not!= not equals to % remainder! Goes ahead of boolean!= is used just like == % is used just like / http://apcs.cold.rocks
Basics of Java Programming
 Basics of Java Programming Lecture 2 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 16, 2017 Components of a Java Program statements - A statement is some action or sequence of actions, given as a command in code. A statement
Basics of Java Programming Lecture 2 COP 3252 Summer 2017 May 16, 2017 Components of a Java Program statements - A statement is some action or sequence of actions, given as a command in code. A statement
Accelerating Information Technology Innovation
 Accelerating Information Technology Innovation http://aiti.mit.edu Cali, Colombia Summer 2012 Lección 03 Control Structures Agenda 1. Block Statements 2. Decision Statements 3. Loops 2 What are Control
Accelerating Information Technology Innovation http://aiti.mit.edu Cali, Colombia Summer 2012 Lección 03 Control Structures Agenda 1. Block Statements 2. Decision Statements 3. Loops 2 What are Control
Fall 2017 CISC124 9/16/2017
 CISC124 Labs start this week in JEFF 155: Meet your TA. Check out the course web site, if you have not already done so. Watch lecture videos if you need to review anything we have already done. Problems
CISC124 Labs start this week in JEFF 155: Meet your TA. Check out the course web site, if you have not already done so. Watch lecture videos if you need to review anything we have already done. Problems
Java Programming Fundamentals - Day Instructor: Jason Yoon Website:
 Java Programming Fundamentals - Day 1 07.09.2016 Instructor: Jason Yoon Website: http://mryoon.weebly.com Quick Advice Before We Get Started Java is not the same as javascript! Don t get them confused
Java Programming Fundamentals - Day 1 07.09.2016 Instructor: Jason Yoon Website: http://mryoon.weebly.com Quick Advice Before We Get Started Java is not the same as javascript! Don t get them confused
Java Programming Basics. COMP 401, Spring 2017 Lecture 2
 Java Programming Basics COMP 401, Spring 2017 Lecture 2 AverageHeightApp take 2 Same as before, but with Eclipse. Eclipse Workspace CreaJng new project CreaJng a new package CreaJng new class Running a
Java Programming Basics COMP 401, Spring 2017 Lecture 2 AverageHeightApp take 2 Same as before, but with Eclipse. Eclipse Workspace CreaJng new project CreaJng a new package CreaJng new class Running a
Objectives. Introduce the core C# language features class Main types variables basic input and output operators arrays control constructs comments
 Basics Objectives Introduce the core C# language features class Main types variables basic input and output operators arrays control constructs comments 2 Class Keyword class used to define new type specify
Basics Objectives Introduce the core C# language features class Main types variables basic input and output operators arrays control constructs comments 2 Class Keyword class used to define new type specify
13 th Windsor Regional Secondary School Computer Programming Competition
 SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE 13 th Windsor Regional Secondary School Computer Programming Competition Hosted by The School of Computer Science, University of Windsor WORKSHOP I [ Overview of the Java/Eclipse
SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE 13 th Windsor Regional Secondary School Computer Programming Competition Hosted by The School of Computer Science, University of Windsor WORKSHOP I [ Overview of the Java/Eclipse
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal
 Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types and
Expressions and Data Types CSC 121 Fall 2015 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand the basic constructs of a Java Program Understand how to use basic identifiers Understand simple Java data types and
Discover how to get up and running with the Java Development Environment and with the Eclipse IDE to create Java programs.
 Java SE11 Development Java is the most widely-used development language in the world today. It allows programmers to create objects that can interact with other objects to solve a problem. Explore Java
Java SE11 Development Java is the most widely-used development language in the world today. It allows programmers to create objects that can interact with other objects to solve a problem. Explore Java
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming. Fall 2018 Instructors Bill Lenhart & Bill Jannen
 CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Fall 2018 Instructors Bill Lenhart & Bill Jannen Administrative Details Lab 1 handout is online Prelab (should be completed before lab): Lab 1 design doc
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Fall 2018 Instructors Bill Lenhart & Bill Jannen Administrative Details Lab 1 handout is online Prelab (should be completed before lab): Lab 1 design doc
Lesson 06 Arrays. MIT 11053, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Senior Lecturer in MIT Department of MIT FMC, SEUSL
 Lesson 06 Arrays MIT 11053, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Senior Lecturer in MIT Department of MIT FMC, SEUSL Array An array is a group of variables (called elements or components) containing
Lesson 06 Arrays MIT 11053, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Senior Lecturer in MIT Department of MIT FMC, SEUSL Array An array is a group of variables (called elements or components) containing
Introduction to Java https://tinyurl.com/y7bvpa9z
 Introduction to Java https://tinyurl.com/y7bvpa9z Eric Newhall - Laurence Meyers Team 2849 Alumni Java Object-Oriented Compiled Garbage-Collected WORA - Write Once, Run Anywhere IDE Integrated Development
Introduction to Java https://tinyurl.com/y7bvpa9z Eric Newhall - Laurence Meyers Team 2849 Alumni Java Object-Oriented Compiled Garbage-Collected WORA - Write Once, Run Anywhere IDE Integrated Development
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION
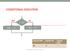 CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
CONDITIONAL EXECUTION yes x > y? no max = x; max = y; logical AND logical OR logical NOT &&! Fundamentals of Computer Science I Outline Conditional Execution if then if then Nested if then statements Comparisons
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes
 AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
1.3 Conditionals and Loops
 .3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2008 February 04, 2008 0:00 AM A Foundation for Programming A Foundation
.3 Conditionals and Loops Introduction to Programming in Java: An Interdisciplinary Approach Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne Copyright 2008 February 04, 2008 0:00 AM A Foundation for Programming A Foundation
1 Epic Test Review 2 Epic Test Review 3 Epic Test Review 4. Epic Test Review 5 Epic Test Review 6 Epic Test Review 7 Epic Test Review 8
 Epic Test Review 1 Epic Test Review 2 Epic Test Review 3 Epic Test Review 4 Write a line of code that outputs the phase Hello World to the console without creating a new line character. System.out.print(
Epic Test Review 1 Epic Test Review 2 Epic Test Review 3 Epic Test Review 4 Write a line of code that outputs the phase Hello World to the console without creating a new line character. System.out.print(
CSEN 202 Introduction to Computer Programming
 CSEN 202 Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 4: Iterations Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher and Dr Mohammed Abdel Megeed Salem, slim.abdennadher@guc.edu.eg German University Cairo, Department of Media
CSEN 202 Introduction to Computer Programming Lecture 4: Iterations Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher and Dr Mohammed Abdel Megeed Salem, slim.abdennadher@guc.edu.eg German University Cairo, Department of Media
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming
 Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Conditional Execution Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Conditional Execution 1 / 14 Structured Programming In reasoning
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming Conditional Execution Christopher Simpkins chris.simpkins@gatech.edu CS 1331 (Georgia Tech) Conditional Execution 1 / 14 Structured Programming In reasoning
Java Programming Basics. COMP 401, Fall 2017 Lecture 2
 Java Programming Basics COMP 401, Fall 2017 Lecture 2 A Java Program Line number where first loop starts * line number where an array is indexed + number of Jmes line 6 will execute total number of local
Java Programming Basics COMP 401, Fall 2017 Lecture 2 A Java Program Line number where first loop starts * line number where an array is indexed + number of Jmes line 6 will execute total number of local
Values and Variables 1 / 30
 Values and Variables 1 / 30 Values 2 / 30 Computing Computing is any purposeful activity that marries the representation of some dynamic domain with the representation of some dynamic machine that provides
Values and Variables 1 / 30 Values 2 / 30 Computing Computing is any purposeful activity that marries the representation of some dynamic domain with the representation of some dynamic machine that provides
CS251L REVIEW Derek Trumbo UNM
 CS251L REVIEW 2010.8.25 Derek Trumbo UNM Java Applications Java application defined by a Java class with a main method public static void main(string[] args) args is an array of strings represented the
CS251L REVIEW 2010.8.25 Derek Trumbo UNM Java Applications Java application defined by a Java class with a main method public static void main(string[] args) args is an array of strings represented the
CT 229 Java Syntax Continued
 CT 229 Java Syntax Continued 29/09/2006 CT229 Lab Assignments One Week Extension for Lab Assignment 1. Due Date: Oct 8 th Before submission make sure that the name of each.java file matches the name given
CT 229 Java Syntax Continued 29/09/2006 CT229 Lab Assignments One Week Extension for Lab Assignment 1. Due Date: Oct 8 th Before submission make sure that the name of each.java file matches the name given
Introduction to OOP with Java. Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017
 Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 03: Control Flow Statements: Selection Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor
Introduction to OOP with Java Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Lecture 03: Control Flow Statements: Selection Instructor: AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor Sep 2017 Instructor AbuKhleif, Mohammad Noor
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL
 JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
JAVA OPERATORS GENERAL Java provides a rich set of operators to manipulate variables. We can divide all the Java operators into the following groups: Arithmetic Operators Relational Operators Bitwise Operators
3. Java - Language Constructs I
 Educational Objectives 3. Java - Language Constructs I Names and Identifiers, Variables, Assignments, Constants, Datatypes, Operations, Evaluation of Expressions, Type Conversions You know the basic blocks
Educational Objectives 3. Java - Language Constructs I Names and Identifiers, Variables, Assignments, Constants, Datatypes, Operations, Evaluation of Expressions, Type Conversions You know the basic blocks
Basic Java Syntax. COMP 401, Fall 2015 Lecture 2 1/13/2014
 Basic Java Syntax COMP 401, Fall 2015 Lecture 2 1/13/2014 Program OrganizaDon and ExecuDon All code in Java is organized into classes and interfaces One public class or interface per file. Not strictly
Basic Java Syntax COMP 401, Fall 2015 Lecture 2 1/13/2014 Program OrganizaDon and ExecuDon All code in Java is organized into classes and interfaces One public class or interface per file. Not strictly
5/3/2006. Today! HelloWorld in BlueJ. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont.
 Today! Build HelloWorld yourself in BlueJ and Eclipse. Look at all the Java keywords. Primitive Types. HelloWorld in BlueJ 1. Find BlueJ in the start menu, but start the Select VM program instead (you
Today! Build HelloWorld yourself in BlueJ and Eclipse. Look at all the Java keywords. Primitive Types. HelloWorld in BlueJ 1. Find BlueJ in the start menu, but start the Select VM program instead (you
Combined Assignment Operators. Flow of Control. Increment Decrement Operators. Operators Precedence (Highest to Lowest) Slide Set 05: Java Loops
 Flow of control Flow of Control Program instruction execution sequence Sequential Control Structure Selection (Branching) Control Structure Repetition (Loop) Control Structure Operator Usage Relational
Flow of control Flow of Control Program instruction execution sequence Sequential Control Structure Selection (Branching) Control Structure Repetition (Loop) Control Structure Operator Usage Relational
In this lab, you will learn more about selection statements. You will get familiar to
 Objective: In this lab, you will learn more about selection statements. You will get familiar to nested if and switch statements. Nested if Statements: When you use if or if...else statement, you can write
Objective: In this lab, you will learn more about selection statements. You will get familiar to nested if and switch statements. Nested if Statements: When you use if or if...else statement, you can write
CS 112 Introduction to Programming
 CS 112 Introduction to Programming Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
CS 112 Introduction to Programming Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University 308A Watson, Phone: 432-6400 Email: yry@cs.yale.edu
Admin. CS 112 Introduction to Programming. Recap: Java Static Methods. Recap: Decomposition Example. Recap: Static Method Example
 Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Programming assignment 2 to be posted tonight Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University
Admin CS 112 Introduction to Programming q Programming assignment 2 to be posted tonight Java Primitive Data Types; Arithmetic Expressions Yang (Richard) Yang Computer Science Department Yale University
Flow of Control. Chapter 3. Chapter 3 1
 Flow of Control Chapter 3 Chapter 3 1 Flow of Control Flow of control is the order in which a program performs actions. Up to this point, the order has been sequential. A branching statement chooses between
Flow of Control Chapter 3 Chapter 3 1 Flow of Control Flow of control is the order in which a program performs actions. Up to this point, the order has been sequential. A branching statement chooses between
Instructor: SIR MUHAMMAD NAVEED Created by: ARSLAN AHMED SHAAD ( ) MUHAMMAD BILAL ( ) ISIT:
 Instructor: SIR MUHAMMAD NAVEED Created by: ARSLAN AHMED SHAAD ( 1163135 ) MUHAMMAD BILAL (1163122 ) ISIT:www.techo786.wordpress.com CHAPTER: 3 NOTE: CONTROL STATEMENTS Question s Given below are Long
Instructor: SIR MUHAMMAD NAVEED Created by: ARSLAN AHMED SHAAD ( 1163135 ) MUHAMMAD BILAL (1163122 ) ISIT:www.techo786.wordpress.com CHAPTER: 3 NOTE: CONTROL STATEMENTS Question s Given below are Long
Expressions & Flow Control
 Objectives Distinguish between instance and local variables 4 Expressions & Flow Control Describe how instance variables are initialized Identify and correct a Possible reference before assignment compiler
Objectives Distinguish between instance and local variables 4 Expressions & Flow Control Describe how instance variables are initialized Identify and correct a Possible reference before assignment compiler
Important Java terminology
 1 Important Java terminology The information we manage in a Java program is either represented as primitive data or as objects. Primitive data פרימיטיביים) (נתונים include common, fundamental values as
1 Important Java terminology The information we manage in a Java program is either represented as primitive data or as objects. Primitive data פרימיטיביים) (נתונים include common, fundamental values as
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I
 CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 05 / 31 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions / Comments? recap and some more details about variables, and if / else statements do lab work
CS 106 Introduction to Computer Science I 05 / 31 / 2017 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions / Comments? recap and some more details about variables, and if / else statements do lab work
Course Outline. Introduction to java
 Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
Course Outline 1. Introduction to OO programming 2. Language Basics Syntax and Semantics 3. Algorithms, stepwise refinements. 4. Quiz/Assignment ( 5. Repetitions (for loops) 6. Writing simple classes 7.
