CSc 110, Spring Lecture 28: Sets and Dictionaries. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
|
|
|
- Bartholomew Bond
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 28: Sets and Dictionaries Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1
2 Mountain peak Write a program that reads elevation data from a file, draws it on a DrawingPanel and finds the path from the highest elevation to the edge of the region. Data:
3 Mountain peak data = [ [34, 76, 87, 9, 34, 8, 22, 33, 33, 33, 45, 65, 43, 22] [5, 7, 88, 0, 56, 76, 76, 77, 4, 45, 55, 55, 4, 5]... ] Next steps: 4) Find the peak 5) Find the steepest path down 6) Draw the path in yellow 3
4 4) Find the peak data = [ [34, 76, 87, 9, 34, 8, 22, 33, 33, 33, 45, 65, 43, 22] [5, 7, 88, 0, 56, 76, 76, 77, 4, 45, 55, 55, 4, 5]... ] Find the largest elevation in the list of lists. Write find_peak(data) Return a tuple of the location in the 2d list 4
5 5) Find the steepest path data = [['2537', '2483', '2475', '2480', '2518', '2532', '2480', '2478', '2431'] ['2541', '2549', '2614', '2700', '2647', '2746', '2690', '2621', '2550'] ['2525', '2525', '2640', '2769', '2802', '2883', '2856', '2694', '2631'] ['2514', '2505', '2526', '2614', '2717', '2715', '2867', '2836', '2771'] ['2506', '2482', '2480', '2528', '2518', '2561', '2586', '2662', '2654'] ['2527', '2477', '2464', '2459', '2452', '2475', '2480', '2500', '2518'] ['2544', '2505', '2488', '2454', '2442', '2445', '2446', '2467', '2470'] ['2528', '2486', '2464', '2446', '2434', '2436', '2442', '2444', '2450'] ['2464', '2505', '2482', '2456', '2433', '2463', '2462', '2489', '2467'] ['2532', '2541', '2519', '2515', '2496', '2502', '2529', '2519', '2553']] How do we determine the steepest path? We would need to compare the peak to each neighbor. 5
6 5) Find the steepest path down data = [['2537', '2483', '2475', '2480', '2518', '2532', '2480', '2478', '2431'] ['2541', '2549', '2614', '2700', '2647', '2746', '2690', '2621', '2550'] ['2525', '2525', '2640', '2769', '2802', '2883', '2856', '2694', '2631'] ['2514', '2505', '2526', '2614', '2717', '2715', '2867', '2836', '2771'] ['2506', '2482', '2480', '2528', '2518', '2561', '2586', '2662', '2654']]... ] We will simplify this problem. Look at only three neighbors: up down front If peak is at location data[r][c], define each above. 6
7 5) Find the steepest path down data = [['2537', '2483', '2475', '2480', '2518', '2532', '2480', '2478', '2431'] ['2541', '2549', '2614', '2700', '2647', '2746', '2690', '2621', '2550'] ['2525', '2525', '2640', '2769', '2802', '2883', '2856', '2694', '2631'] ['2514', '2505', '2526', '2614', '2717', '2715', '2867', '2836', '2771']...] Compare and find the smallest of the three to create the next path element. What happens if there are ties? 7
8 5) Find the steepest path down Rules for ties. If up == down but < front, choose randomly between them. up = 2550 down = 2550 front = 2690 If front ties with up or down, choose front. up = 2690 up = 2550 down = 2550 down = 2690 front = 2550 front =
9 5) Pseudocode for find_path initialize current location (this is both a row and column) make an empty list for path while location is still within the list bounds assign up, front and down if (up < down and up < front) append up location to path else if (down < up and down < front) append down location to path else if (down == up and up < front) chose randomly between down and up append one of them to path else append front location to path update current location based on the chosen next location for path return path 9
10 6) Pseudocode for draw_path For each tuple in the path Using the column and row given in the tuple, draw a rectangle that is one pixel wide and filled in with yellow 10
11 lwrite a function print_rlist(rlist)that takes a rectangular list as a parameter and prints it out as a grid. For example, given the list defined below: grid = [[8,2,7,8,2,1], [1,5,1,7,4,7], [5,9,6,7,3,2], [7,8,7,7,7,9], [4,2,6,9,2,3], [2,2,8,1,1,3]] The call print_rlist(grid) prints the following output:
12 Exercise Write a program that counts the number of unique words in a large text file (say, Moby Dick or the King James Bible). Store the words in a structure and report the # of unique words. Once you've created this structure, allow the user to search it to see whether various words appear in the text file. What structure is appropriate for this problem? List? Tuple? 12
13 Sets set: A collection of unique values (no duplicates allowed) Sets are not indexed. They do not have an order. The following operations can be performed efficiently on sets: add, remove, search (contains) "to" in set "be" in set "if" "the" "to" "of" "down" "by" "in" "from" "she" "you" "why" "him" true false set 13
14 Creating a set Use the function set: a = set() Use {value,, valuen}: b = {"the", "hello", "happy"} a.add(val) a.discard(val) a.pop() a - b a b a & b a ^ b adds element val to a removes val from a if present removes and returns a random element from a returns a new set containing values in a but not in b returns a new set containing values in either a or b returns a new set containing values in both a and b returns a new set containing values in a or b but not both You can also use in, len(), etc. 14
15 Looping over a set? You must use a for element in structure loop needed because sets have no indexes; can't get element i Example: for item in a: print(item) Outputs: the happy hello 15
16 Exercise Write a program to count the number of occurrences of each unique word in a large text file (e.g. Moby Dick ). Allow the user to type a word and report how many times that word appeared in the book. Report all words that appeared in the book at least 500 times. What structure is appropriate for this problem? 16
17 Dictionaries dictionary: Holds a set of unique keys and a collection of values, where each key is associated with one value. a.k.a. "map", "associative array", "hash" basic dictionary operations: Add a mapping from a key to a value. Retrieve a value mapped to a key. Remove a given key and its mapped value. 17
18 Creating dictionaries Creating a dictionary {key : value,, keyn : valuen} my_dict = {"Romeo": "Montague", "Tyler" :"Durden", "Tybalt" : "Capulet", "Juliet" :"Capulet" } my_dict[key] = value adds a mapping from the given key to the given value; if the key already exists, replaces its value with the given one Accessing values: my_dict[key] returns the value mapped to the given key (error if key not found) my_dict["juliet"] produces "Capulet" 18
19 Using dictionaries A dictionary allows you to get from one half of a pair to the other. Remembers one piece of information about every index (key). # key value my_dict["suzy"] = " " Dictionary Later, we can supply only the key and get back the related value: Allows us to ask: What is Suzy's phone number? my_dict["suzy"] " " Dictionary 19
20 Maps and tallying a map can be thought of as generalization of a tallying list the "index" (key) doesn't have to be an int count digits: index value # (Roosevelt), (L)andon, (I)ndependent count votes:"rllllllrrrrrllllllrlrrirlrrirllrir" key "R" "L" "I" value "L" "R" 15 3 "I" 15 keys values 20
21 Dictionary methods items() pop(key) popitem() keys() values() return a new view of the dictionary s items ((key, value) pairs) removes any existing mapping for the given key and returns it (error if key not found) removes and returns an arbitrary (key, value) pair (error if empty) returns the dictionary's keys returns the dictionary's values You can also use in, len(), etc. 21
22 items, keys and values items function returns tuples of each key-value pair can loop over the keys in a for loop ages = {} ages["merlin"] = 4 ages["chester"] = 2 ages["percival"] = 12 for cat, age in ages.items(): print(cat + " -> " + str(age)) values function returns all values in the dictionary no easy way to get from a value to its associated key(s) keys function returns all keys in the dictionary 22
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 11 Lecture 11-1: Sets and Maps reading: 11.2-11.3 2 Exercise Write a program that counts the number of unique words in a large text file (say, Moby Dick or the King James
Building Java Programs Chapter 11 Lecture 11-1: Sets and Maps reading: 11.2-11.3 2 Exercise Write a program that counts the number of unique words in a large text file (say, Moby Dick or the King James
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 11 Sets and Maps reading: 11.2-11.3 2 Languages and Grammars 4 Languages and grammars (formal) language: A set of words or symbols. grammar: A description of a language that
Building Java Programs Chapter 11 Sets and Maps reading: 11.2-11.3 2 Languages and Grammars 4 Languages and grammars (formal) language: A set of words or symbols. grammar: A description of a language that
CSc 110, Spring 2018 Lecture 9: Parameters, Graphics and Random. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Spring 2018 Lecture 9: Parameters, Graphics and Random Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Exercise: multiple parameters def main(): print_number(4, 9) print_number(17, 6) print_number(8,
CSc 110, Spring 2018 Lecture 9: Parameters, Graphics and Random Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Exercise: multiple parameters def main(): print_number(4, 9) print_number(17, 6) print_number(8,
CS 106A, Lecture 20 ArrayLists and HashMaps
 CS 106A, Lecture 20 ArrayLists and HashMaps suggested reading: Java Ch. 13.2 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Marty Stepp, licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 License.
CS 106A, Lecture 20 ArrayLists and HashMaps suggested reading: Java Ch. 13.2 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Marty Stepp, licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 License.
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 7: Graphics. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 7: Graphics Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Graphical objects We will draw graphics in Python using a new kind of object: DrawingPanel: A window on the
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 7: Graphics Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Graphical objects We will draw graphics in Python using a new kind of object: DrawingPanel: A window on the
Topics Applications Most Common Methods Serial Search Binary Search Search by Hashing (next lecture) Run-Time Analysis Average-time analysis Time anal
 CSC212 Data Structure t Lecture 18 Searching Instructor: George Wolberg Department of Computer Science City College of New York @ George Wolberg, 2016 1 Topics Applications Most Common Methods Serial Search
CSC212 Data Structure t Lecture 18 Searching Instructor: George Wolberg Department of Computer Science City College of New York @ George Wolberg, 2016 1 Topics Applications Most Common Methods Serial Search
Module 9: Binary trees
 Module 9: Binary trees Readings: HtDP, Section 14 We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Module 9: Binary trees Readings: HtDP, Section 14 We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Lecture 19: Recursion
 Lecture 19: Recursion Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Recursion recursion: The definition of an operation
Lecture 19: Recursion Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Recursion recursion: The definition of an operation
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 38: Critters. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 38: Critters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Calling overridden methods Subclasses can call overridden methods with super super(classname, self).method(parameters)
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 38: Critters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Calling overridden methods Subclasses can call overridden methods with super super(classname, self).method(parameters)
Topic 9 More Graphics. Based on slides bu Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from
 Topic 9 More Graphics Based on slides bu Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ Clicker Question What happens if a graphics object is used to draw a shape that exceeds the
Topic 9 More Graphics Based on slides bu Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges from http://www.buildingjavaprograms.com/ Clicker Question What happens if a graphics object is used to draw a shape that exceeds the
CS 106A, Lecture 27 Final Exam Review 1
 CS 106A, Lecture 27 Final Exam Review 1 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Marty Stepp, licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 License. All rights reserved. Based on
CS 106A, Lecture 27 Final Exam Review 1 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Marty Stepp, licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 License. All rights reserved. Based on
Data Structures. Lists, Tuples, Sets, Dictionaries
 Data Structures Lists, Tuples, Sets, Dictionaries Collections Programs work with simple values: integers, floats, booleans, strings Often, however, we need to work with collections of values (customers,
Data Structures Lists, Tuples, Sets, Dictionaries Collections Programs work with simple values: integers, floats, booleans, strings Often, however, we need to work with collections of values (customers,
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 37: Critters. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 37: Critters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Calling overridden methods Subclasses can call overridden methods with super super(classname, self).method(parameters)
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 37: Critters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Calling overridden methods Subclasses can call overridden methods with super super(classname, self).method(parameters)
Recursion. Garfield AP Computer Science. As usual, significant borrowings from Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp at UW -- thanks!!
 Recursion Garfield AP Computer Science As usual, significant borrowings from Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp at UW -- thanks!! Definitions recursion: The definition of an operation in terms of itself. Solving
Recursion Garfield AP Computer Science As usual, significant borrowings from Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp at UW -- thanks!! Definitions recursion: The definition of an operation in terms of itself. Solving
CS 261 Spring 2013 Midterm
 CS 261 Spring 2013 Midterm Name: Student ID: 1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: Total: 1. (20 points) Suppose that we implement a simplified version of the dynamic array data structure in which the amount of memory allocated
CS 261 Spring 2013 Midterm Name: Student ID: 1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: Total: 1. (20 points) Suppose that we implement a simplified version of the dynamic array data structure in which the amount of memory allocated
Lesson 13: Exploring Factored Form
 Opening Activity Below is a graph of the equation y = 6(x 3)(x + 2). It is also the graph of: y = 3(2x 6)(x + 2) y = 2(3x 9)(x + 2) y = 2(x 3)(3x + 6) y = 3(x 3)(2x + 4) y = (3x 9)(2x + 4) y = (2x 6)(3x
Opening Activity Below is a graph of the equation y = 6(x 3)(x + 2). It is also the graph of: y = 3(2x 6)(x + 2) y = 2(3x 9)(x + 2) y = 2(x 3)(3x + 6) y = 3(x 3)(2x + 4) y = (3x 9)(2x + 4) y = (2x 6)(3x
CSE 332 Autumn 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators)
 Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Autumn 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Autumn 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Lecture 13: Two- Dimensional Arrays
 Lecture 13: Two- Dimensional Arrays Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Nested Loops Nested loops nested loop:
Lecture 13: Two- Dimensional Arrays Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Nested Loops Nested loops nested loop:
CSc 110, Autumn Lecture 26: Assertions. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Autumn 2017 Lecture 26: Assertions Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Section attendance question Read a file of section attendance (see next slide): yynyyynayayynyyyayanyyyaynayyayyanayyyanyayna
CSc 110, Autumn 2017 Lecture 26: Assertions Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Section attendance question Read a file of section attendance (see next slide): yynyyynayayynyyyayanyyyaynayyayyanayyyanyayna
CSc 110, Spring Lecture 11: if / else. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Spring 2018 Lecture 11: if / else Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Exercise: what is wrong with this code? # prints the location of a ball with an initial velocity of 25 accelerating
CSc 110, Spring 2018 Lecture 11: if / else Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Exercise: what is wrong with this code? # prints the location of a ball with an initial velocity of 25 accelerating
Topic 6 loops, figures, constants
 Topic 6 loops, figures, constants "Complexity has and will maintain a strong fascination for many people. It is true that we live in a complex world and strive to solve inherently complex problems, which
Topic 6 loops, figures, constants "Complexity has and will maintain a strong fascination for many people. It is true that we live in a complex world and strive to solve inherently complex problems, which
CSE 332 Spring 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators)
 Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Spring 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Spring 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
CSE 143 Lecture 10. Recursion
 CSE 143 Lecture 10 Recursion slides created by Marty Stepp and Alyssa Harding http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Recursion Iteration: a programming technique in which you describe actions to be repeated
CSE 143 Lecture 10 Recursion slides created by Marty Stepp and Alyssa Harding http://www.cs.washington.edu/143/ Recursion Iteration: a programming technique in which you describe actions to be repeated
CSc 110, Autumn Lecture 30: Methods. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 30: Methods Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Why objects? Primitive types don't model complex concepts well Cost is a float. What's a person? Classes are
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 30: Methods Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Why objects? Primitive types don't model complex concepts well Cost is a float. What's a person? Classes are
CSc 110, Spring Lecture 14: Booleans and Strings. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Spring 2018 Lecture 14: Booleans and Strings Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Exercise: Logical questions What is the result of each of the following expressions? x = 42 y =
CSc 110, Spring 2018 Lecture 14: Booleans and Strings Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Exercise: Logical questions What is the result of each of the following expressions? x = 42 y =
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 2: Static Methods reading: 1.4-1.5 (Slides adapted from Stuart Reges, Hélène Martin, and Marty Stepp) 2 Recall: structure, syntax class: a program public class
Building Java Programs Chapter 1 Lecture 2: Static Methods reading: 1.4-1.5 (Slides adapted from Stuart Reges, Hélène Martin, and Marty Stepp) 2 Recall: structure, syntax class: a program public class
Collections. Lists, Tuples, Sets, Dictionaries
 Collections Lists, Tuples, Sets, Dictionaries Homework notes Homework 1 grades on canvas People mostly lost points for not reading the document carefully Didn t play again Didn t use Y/N for playing again
Collections Lists, Tuples, Sets, Dictionaries Homework notes Homework 1 grades on canvas People mostly lost points for not reading the document carefully Didn t play again Didn t use Y/N for playing again
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 15: lists. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 15: lists Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program (input underlined): How many days' temperatures? 7 Day
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 15: lists Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Can we solve this problem? Consider the following program (input underlined): How many days' temperatures? 7 Day
CSc 110 Sample Final Exam #1
 CSc 110 Sample Final Exam #1 1. Collections Mystery Consider the following function: def mystery(list1, list2): result = {} for i in range(0, len(list1)): result[list1[i]] = list2[i] result[list2[i]] =
CSc 110 Sample Final Exam #1 1. Collections Mystery Consider the following function: def mystery(list1, list2): result = {} for i in range(0, len(list1)): result[list1[i]] = list2[i] result[list2[i]] =
CS 372: Computational Geometry Lecture 3 Line Segment Intersection
 CS 372: Computational Geometry Lecture 3 Line Segment Intersection Antoine Vigneron King Abdullah University of Science and Technology September 9, 2012 Antoine Vigneron (KAUST) CS 372 Lecture 3 September
CS 372: Computational Geometry Lecture 3 Line Segment Intersection Antoine Vigneron King Abdullah University of Science and Technology September 9, 2012 Antoine Vigneron (KAUST) CS 372 Lecture 3 September
Midterm I Practice Problems
 15-112 Midterm I Practice Problems Name: Section: andrewid: This PRACTICE midterm is not meant to be a perfect representation of the upcoming midterm! You are responsible for knowing all material covered
15-112 Midterm I Practice Problems Name: Section: andrewid: This PRACTICE midterm is not meant to be a perfect representation of the upcoming midterm! You are responsible for knowing all material covered
CSE 332 Spring 2014: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators)
 Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Spring 2014: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Spring 2014: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Binary Search and Worst-Case Analysis
 Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong A significant part of computer science is devoted to understanding the power of the RAM model in solving specific problems.
Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong A significant part of computer science is devoted to understanding the power of the RAM model in solving specific problems.
Collections. Michael Ernst CSE 190p University of Washington
 Collections Michael Ernst CSE 190p University of Washington Needed for Homework 4 (social networking assignment) Collections: lists, sets, dictionaries Sorting Graphs Outline for today Collections (built-in
Collections Michael Ernst CSE 190p University of Washington Needed for Homework 4 (social networking assignment) Collections: lists, sets, dictionaries Sorting Graphs Outline for today Collections (built-in
Topic 8 Graphics. Margaret Hamilton
 Topic 8 Graphics When the computer crashed during the execution of your program, there was no hiding. Lights would be flashing, bells would be ringing and everyone would come running to find out whose
Topic 8 Graphics When the computer crashed during the execution of your program, there was no hiding. Lights would be flashing, bells would be ringing and everyone would come running to find out whose
Hash Tables. Nate Foster Spring 2018
 Hash Tables Nate Foster Spring 2018 A3 Index and search books Extensive use of data structures and OCaml module system Competition for most scalable implementation Staff solution: ~500 LoC Review Previously
Hash Tables Nate Foster Spring 2018 A3 Index and search books Extensive use of data structures and OCaml module system Competition for most scalable implementation Staff solution: ~500 LoC Review Previously
TUPLES AND RECURSIVE LISTS 5
 TUPLES AND RECURSIVE LISTS 5 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A July 3, 2012 1 Sequences From the Pig project, we discovered the utility of having structures that contain multiple values. Today, we are going to cover
TUPLES AND RECURSIVE LISTS 5 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A July 3, 2012 1 Sequences From the Pig project, we discovered the utility of having structures that contain multiple values. Today, we are going to cover
CS 106A, Lecture 27 Final Exam Review 1
 CS 106A, Lecture 27 Final Exam Review 1 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Marty Stepp, licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 License. All rights reserved. Based on
CS 106A, Lecture 27 Final Exam Review 1 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Marty Stepp, licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 License. All rights reserved. Based on
Basic Python Revision Notes With help from Nitish Mittal
 Basic Python Revision Notes With help from Nitish Mittal HELP from Documentation dir(module) help() Important Characters and Sets of Characters tab \t new line \n backslash \\ string " " or ' ' docstring
Basic Python Revision Notes With help from Nitish Mittal HELP from Documentation dir(module) help() Important Characters and Sets of Characters tab \t new line \n backslash \\ string " " or ' ' docstring
Topic 4 Expressions and variables
 Topic 4 Expressions and variables "Once a person has understood the way variables are used in programming, he has understood the quintessence of programming." -Professor Edsger W. Dijkstra Based on slides
Topic 4 Expressions and variables "Once a person has understood the way variables are used in programming, he has understood the quintessence of programming." -Professor Edsger W. Dijkstra Based on slides
UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH. Wnter 2016 EXAMINATIONS. CSC A20H Duration 2 hours 45 mins. No Aids Allowed
 Student Number: Last Name: First Name: UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Wnter 2016 EXAMINATIONS CSC A20H Duration 2 hours 45 mins No Aids Allowed Do not turn this page until you have received the signal
Student Number: Last Name: First Name: UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO SCARBOROUGH Wnter 2016 EXAMINATIONS CSC A20H Duration 2 hours 45 mins No Aids Allowed Do not turn this page until you have received the signal
Homework Assignment #3. 1 (5 pts) Demonstrate how mergesort works when sorting the following list of numbers:
 CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 1 (5 pts) Demonstrate how mergesort works when sorting the following list of numbers: 6 1 4 2 3 8 7 5 2 Given the following array (list),
CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 1 (5 pts) Demonstrate how mergesort works when sorting the following list of numbers: 6 1 4 2 3 8 7 5 2 Given the following array (list),
Topic 8 graphics. -mgrimes, Graphics problem report 134
 Topic 8 graphics "What makes the situation worse is that the highest level CS course I've ever taken is cs4, and quotes from the graphics group startup readme like 'these paths are abstracted as being
Topic 8 graphics "What makes the situation worse is that the highest level CS course I've ever taken is cs4, and quotes from the graphics group startup readme like 'these paths are abstracted as being
Topic 7: Lists, Dictionaries and Strings
 Topic 7: Lists, Dictionaries and Strings The human animal differs from the lesser primates in his passion for lists of Ten Best H. Allen Smith 1 Textbook Strongly Recommended Exercises The Python Workbook:
Topic 7: Lists, Dictionaries and Strings The human animal differs from the lesser primates in his passion for lists of Ten Best H. Allen Smith 1 Textbook Strongly Recommended Exercises The Python Workbook:
More Examples Using Lists Tuples and Dictionaries in Python CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science, Winter 2018 Lecture #11
 More Examples Using Lists Tuples and Dictionaries in Python CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science, Winter 2018 Lecture #11 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Administrative Homework #6 is DUE
More Examples Using Lists Tuples and Dictionaries in Python CS 8: Introduction to Computer Science, Winter 2018 Lecture #11 Ziad Matni Dept. of Computer Science, UCSB Administrative Homework #6 is DUE
Lesson 06 Arrays. MIT 11053, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Senior Lecturer in MIT Department of MIT FMC, SEUSL
 Lesson 06 Arrays MIT 11053, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Senior Lecturer in MIT Department of MIT FMC, SEUSL Array An array is a group of variables (called elements or components) containing
Lesson 06 Arrays MIT 11053, Fundamentals of Programming By: S. Sabraz Nawaz Senior Lecturer in MIT Department of MIT FMC, SEUSL Array An array is a group of variables (called elements or components) containing
Python. Karin Lagesen.
 Python Karin Lagesen karin.lagesen@bio.uio.no Plan for the day Basic data types data manipulation Flow control and file handling Functions Biopython package What is programming? Programming: ordered set
Python Karin Lagesen karin.lagesen@bio.uio.no Plan for the day Basic data types data manipulation Flow control and file handling Functions Biopython package What is programming? Programming: ordered set
Practice Midterm #2. Midterm Time: Monday, July 18 th, 7pm 9pm Midterm Location: Hewlett 200
 Alisha Adam & Rohit Talreja CS 106A Summer 2016 Practice Midterm #2. Midterm Time: Monday, July 18 th, 7pm 9pm Midterm Location: Hewlett 200. Based on previous handouts by Keith Schwarz, Eric Roberts,
Alisha Adam & Rohit Talreja CS 106A Summer 2016 Practice Midterm #2. Midterm Time: Monday, July 18 th, 7pm 9pm Midterm Location: Hewlett 200. Based on previous handouts by Keith Schwarz, Eric Roberts,
PLEASE HAND IN UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science
 PLEASE HAND IN UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science APRIL 2012 EXAMINATIONS CSC 108 H1S Instructors: Campbell Duration 3 hours PLEASE HAND IN Examination Aids: None Student Number: Family
PLEASE HAND IN UNIVERSITY OF TORONTO Faculty of Arts and Science APRIL 2012 EXAMINATIONS CSC 108 H1S Instructors: Campbell Duration 3 hours PLEASE HAND IN Examination Aids: None Student Number: Family
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 3: Expressions, Variables and Loops. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 3: Expressions, Variables and Loops Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Data and expressions 2 Data types Internally, computers store everything as 1s and
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 3: Expressions, Variables and Loops Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Data and expressions 2 Data types Internally, computers store everything as 1s and
MC 302 GRAPH THEORY 10/1/13 Solutions to HW #2 50 points + 6 XC points
 MC 0 GRAPH THEORY 0// Solutions to HW # 0 points + XC points ) [CH] p.,..7. This problem introduces an important class of graphs called the hypercubes or k-cubes, Q, Q, Q, etc. I suggest that before you
MC 0 GRAPH THEORY 0// Solutions to HW # 0 points + XC points ) [CH] p.,..7. This problem introduces an important class of graphs called the hypercubes or k-cubes, Q, Q, Q, etc. I suggest that before you
clicker question Comments Using comments Topic 3 static Methods and Structured Programming
 Topic 3 static Methods and Structured Programming "The cleaner and nicer the program, the faster it's going to run. And if it doesn't, it'll be easy to make it fast." -Joshua Bloch clicker question What
Topic 3 static Methods and Structured Programming "The cleaner and nicer the program, the faster it's going to run. And if it doesn't, it'll be easy to make it fast." -Joshua Bloch clicker question What
CSc 110 Sample Midterm Exam #2
 1. Collections Mystery Consider the following function: CSc 110 Sample Midterm Exam #2 def mystery(m): s = set() for key in m.keys(): if (m[key]!= key): s.add(m[key]) else: s.add(m[key][0]) print(s) Write
1. Collections Mystery Consider the following function: CSc 110 Sample Midterm Exam #2 def mystery(m): s = set() for key in m.keys(): if (m[key]!= key): s.add(m[key]) else: s.add(m[key][0]) print(s) Write
CSE 143. Computer Programming II
 Adam Blank Lecture 11 Spring 2015 CSE 143 Computer Programming II CSE 143: Computer Programming II Recursive Programming public static void solveproblem() { solveproblem(); } Outline 1 Writing Recursive
Adam Blank Lecture 11 Spring 2015 CSE 143 Computer Programming II CSE 143: Computer Programming II Recursive Programming public static void solveproblem() { solveproblem(); } Outline 1 Writing Recursive
Organizing and Summarizing Data
 1 Organizing and Summarizing Data Key Definitions Frequency Distribution: This lists each category of data and how often they occur. : The percent of observations within the one of the categories. This
1 Organizing and Summarizing Data Key Definitions Frequency Distribution: This lists each category of data and how often they occur. : The percent of observations within the one of the categories. This
Chapter 14 Tuples, Sets, and Dictionaries. Copyright 2012 by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 14 Tuples, Sets, and Dictionaries 1 Motivations The No Fly List is a list, created and maintained by the United States government's Terrorist Screening Center, of people who are not permitted to
Chapter 14 Tuples, Sets, and Dictionaries 1 Motivations The No Fly List is a list, created and maintained by the United States government's Terrorist Screening Center, of people who are not permitted to
A Third Look At ML. Chapter Nine Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1
 A Third Look At ML Chapter Nine Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1 Outline More pattern matching Function values and anonymous functions Higher-order functions and currying Predefined higher-order
A Third Look At ML Chapter Nine Modern Programming Languages, 2nd ed. 1 Outline More pattern matching Function values and anonymous functions Higher-order functions and currying Predefined higher-order
Math 1113 Notes - Functions Revisited
 Math 1113 Notes - Functions Revisited Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University February 14, 2005 Abstract This handout contains more material on functions. It continues the material which was presented
Math 1113 Notes - Functions Revisited Philippe B. Laval Kennesaw State University February 14, 2005 Abstract This handout contains more material on functions. It continues the material which was presented
St. Benedict s High School. Computing Science. Software Design & Development. (Part 1 Computer Programming) National 5
 Computing Science Software Design & Development (Part 1 Computer Programming) National 5 VARIABLES & DATA TYPES Variables provide temporary storage for information that will be needed while a program is
Computing Science Software Design & Development (Part 1 Computer Programming) National 5 VARIABLES & DATA TYPES Variables provide temporary storage for information that will be needed while a program is
Do not turn this page until you have received the signal to start.
 CSCA08 Fall 2014 Final Exam Duration 160 minutes Aids allowed: none Student Number: A Instructor: Brian Harrington Last Name: First Name: UtorID (Markus Login): Do not turn this page until you have received
CSCA08 Fall 2014 Final Exam Duration 160 minutes Aids allowed: none Student Number: A Instructor: Brian Harrington Last Name: First Name: UtorID (Markus Login): Do not turn this page until you have received
CSc 110, Spring Lecture 2: Functions. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 2: Functions Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Review From last lecture: print, strings, escape sequences. What is the output of the following statement?
CSc 110, Spring 2017 Lecture 2: Functions Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges 1 Review From last lecture: print, strings, escape sequences. What is the output of the following statement?
Lecture 3: Working with Data Structures
 Lecture 3: Working with Data Structures Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 1 Warm Up From last lecture: - What is an example of constant time complexity - What is an example
Lecture 3: Working with Data Structures Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 SP 18 - KASEY CHAMPION 1 Warm Up From last lecture: - What is an example of constant time complexity - What is an example
Lecture 2: Operations and Data Types
 Lecture 2: Operations and Data Types Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Data types type: A category or set
Lecture 2: Operations and Data Types Building Java Programs: A Back to Basics Approach by Stuart Reges and Marty Stepp Copyright (c) Pearson 2013. All rights reserved. Data types type: A category or set
Building Java Programs
 Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops These lecture notes are copyright (C) Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges, 2007. They may not be rehosted, sold, or modified without expressed
Building Java Programs Chapter 2: Primitive Data and Definite Loops These lecture notes are copyright (C) Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges, 2007. They may not be rehosted, sold, or modified without expressed
Module 8: Binary trees
 Module 8: Binary trees Readings: HtDP, Section 14 We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Module 8: Binary trees Readings: HtDP, Section 14 We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Trees. Readings: HtDP, sections 14, 15, 16.
 Trees Readings: HtDP, sections 14, 15, 16. We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Trees Readings: HtDP, sections 14, 15, 16. We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Trees. Binary arithmetic expressions. Visualizing binary arithmetic expressions. ((2 6) + (5 2))/(5 3) can be defined in terms of two smaller
 Trees Readings: HtDP, sections 14, 15, 16. We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Trees Readings: HtDP, sections 14, 15, 16. We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Software Testing Prof. Rajib Mall Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. Lecture 13 Path Testing
 Software Testing Prof. Rajib Mall Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 13 Path Testing Welcome to this session and we will discuss about path
Software Testing Prof. Rajib Mall Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 13 Path Testing Welcome to this session and we will discuss about path
YOUR NAME PLEASE: *** SOLUTIONS ***
 YOUR NAME PLEASE: *** SOLUTIONS *** Computer Science 201b SAMPLE Exam 1 SOLUTIONS February 15, 2015 Closed book and closed notes. No electronic devices. Show ALL work you want graded on the test itself.
YOUR NAME PLEASE: *** SOLUTIONS *** Computer Science 201b SAMPLE Exam 1 SOLUTIONS February 15, 2015 Closed book and closed notes. No electronic devices. Show ALL work you want graded on the test itself.
CSCI 195 Intro to Programming w/python Parsing the Bible Text into a Python data structure
 We have been given a version of the King James Bible whose contents have been encoded using a simple text format. The following is a sample of the file s contents. Ge@1:1@In the beginning God created the
We have been given a version of the King James Bible whose contents have been encoded using a simple text format. The following is a sample of the file s contents. Ge@1:1@In the beginning God created the
CSE 332 Winter 2015: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators)
 _ UWNetID: Lecture Section: A CSE 332 Winter 2015: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will give
_ UWNetID: Lecture Section: A CSE 332 Winter 2015: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will give
Class 8 ALGORITHMS AND FLOWCHARTS. The City School
 Class 8 ALGORITHMS AND FLOWCHARTS ALGORITHMS AND FLOWCHARTS A typical programming task can be divided into two phases: Problem solving phase produce an ordered sequence of steps that describe solution
Class 8 ALGORITHMS AND FLOWCHARTS ALGORITHMS AND FLOWCHARTS A typical programming task can be divided into two phases: Problem solving phase produce an ordered sequence of steps that describe solution
Algorithms for Euclidean TSP
 This week, paper [2] by Arora. See the slides for figures. See also http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~arora/pubs/arorageo.ps Algorithms for Introduction This lecture is about the polynomial time approximation
This week, paper [2] by Arora. See the slides for figures. See also http://www.cs.princeton.edu/~arora/pubs/arorageo.ps Algorithms for Introduction This lecture is about the polynomial time approximation
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution
 https://www.dignitymemorial.com/obituaries/brookline-ma/adele-koss-5237804 Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution Logical thinking and experience was as important as theory in using the computer
https://www.dignitymemorial.com/obituaries/brookline-ma/adele-koss-5237804 Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution Logical thinking and experience was as important as theory in using the computer
CSE 341 Lecture 5. efficiency issues; tail recursion; print Ullman ; 4.1. slides created by Marty Stepp
 CSE 341 Lecture 5 efficiency issues; tail recursion; print Ullman 3.3-3.4; 4.1 slides created by Marty Stepp http://www.cs.washington.edu/341/ Efficiency exercise Write a function called reverse that accepts
CSE 341 Lecture 5 efficiency issues; tail recursion; print Ullman 3.3-3.4; 4.1 slides created by Marty Stepp http://www.cs.washington.edu/341/ Efficiency exercise Write a function called reverse that accepts
CPS 216, Problem Solving and Programming Techniques in C++ Saleh M. Alnaeli, Ph.D. Spring, Lab_Week2
 CPS 216, Problem Solving and Programming Techniques in C++ Saleh M. Alnaeli, Ph.D. Spring, 2016 Lab_Week2 1 My goals Goals for this problem set: write and evaluate expressions to compute numeric values
CPS 216, Problem Solving and Programming Techniques in C++ Saleh M. Alnaeli, Ph.D. Spring, 2016 Lab_Week2 1 My goals Goals for this problem set: write and evaluate expressions to compute numeric values
CSc 110, Autumn Lecture 14: Strings. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Autumn 2017 Lecture 14: Strings Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges "Boolean Zen", part 1 Students new to boolean often test if a result is True: if is_prime(57) == True: # bad...
CSc 110, Autumn 2017 Lecture 14: Strings Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges "Boolean Zen", part 1 Students new to boolean often test if a result is True: if is_prime(57) == True: # bad...
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 6: Parameters. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 6: Parameters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Promoting reuse Programmers build increasingly complex applications Enabled by existing building blocks, e.g.
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 6: Parameters Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Promoting reuse Programmers build increasingly complex applications Enabled by existing building blocks, e.g.
Slide 1 CS 170 Java Programming 1 The Switch Duration: 00:00:46 Advance mode: Auto
 CS 170 Java Programming 1 The Switch Slide 1 CS 170 Java Programming 1 The Switch Duration: 00:00:46 Menu-Style Code With ladder-style if-else else-if, you might sometimes find yourself writing menu-style
CS 170 Java Programming 1 The Switch Slide 1 CS 170 Java Programming 1 The Switch Duration: 00:00:46 Menu-Style Code With ladder-style if-else else-if, you might sometimes find yourself writing menu-style
Python: common syntax
 Lab 09 Python! Python Intro Main Differences from C++: True and False are capitals Python floors (always down) with int division (matters with negatives): -3 / 2 = -2 No variable data types or variable
Lab 09 Python! Python Intro Main Differences from C++: True and False are capitals Python floors (always down) with int division (matters with negatives): -3 / 2 = -2 No variable data types or variable
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution
 Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution "There are only two kinds of programming languages: those people always [complain] about and those nobody uses." Bjarne Stroustroup, creator of C++ Copyright
Topic 11 Scanner object, conditional execution "There are only two kinds of programming languages: those people always [complain] about and those nobody uses." Bjarne Stroustroup, creator of C++ Copyright
Working with recursion. From definition to template. Readings: HtDP, sections 11, 12, 13 (Intermezzo 2).
 Working with recursion Readings: HtDP, sections 11, 12, 13 (Intermezzo 2). We can extend the idea of a self-referential definition to defining the natural numbers, which leads to the use of recursion in
Working with recursion Readings: HtDP, sections 11, 12, 13 (Intermezzo 2). We can extend the idea of a self-referential definition to defining the natural numbers, which leads to the use of recursion in
2IS45 Programming
 Course Website Assignment Goals 2IS45 Programming http://www.win.tue.nl/~wsinswan/programmeren_2is45/ Rectangles Learn to use existing Abstract Data Types based on their contract (class Rectangle in Rectangle.
Course Website Assignment Goals 2IS45 Programming http://www.win.tue.nl/~wsinswan/programmeren_2is45/ Rectangles Learn to use existing Abstract Data Types based on their contract (class Rectangle in Rectangle.
Working with recursion
 Working with recursion Readings: HtDP, sections 11, 12, 13 (Intermezzo 2). We can extend the idea of a self-referential definition to defining the natural numbers, which leads to the use of recursion in
Working with recursion Readings: HtDP, sections 11, 12, 13 (Intermezzo 2). We can extend the idea of a self-referential definition to defining the natural numbers, which leads to the use of recursion in
Distributions of random variables
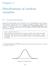 Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Chapter 3 Distributions of random variables 31 Normal distribution Among all the distributions we see in practice, one is overwhelmingly the most common The symmetric, unimodal, bell curve is ubiquitous
Lecture Notes on Tries
 Lecture Notes on Tries 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Thomas Cortina Notes by Frank Pfenning Lecture 24 April 19, 2011 1 Introduction In the data structures implementing associative arrays
Lecture Notes on Tries 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Thomas Cortina Notes by Frank Pfenning Lecture 24 April 19, 2011 1 Introduction In the data structures implementing associative arrays
CSE 373 Autumn 2010: Midterm #2 (closed book, closed notes, NO calculators allowed)
 Name: Email address: CSE 373 Autumn 2010: Midterm #2 (closed book, closed notes, NO calculators allowed) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We may give partial
Name: Email address: CSE 373 Autumn 2010: Midterm #2 (closed book, closed notes, NO calculators allowed) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We may give partial
Tree Data Structures CSC 221
 Tree Data Structures CSC 221 BSTree Deletion - Merging template // LOOK AT THIS PARAMETER!!! void BST::deleteByMerging(BSTNode* & nodepointer) { BSTNode* temp= nodepointer;
Tree Data Structures CSC 221 BSTree Deletion - Merging template // LOOK AT THIS PARAMETER!!! void BST::deleteByMerging(BSTNode* & nodepointer) { BSTNode* temp= nodepointer;
Lists, loops and decisions
 Caltech/LEAD Summer 2012 Computer Science Lecture 4: July 11, 2012 Lists, loops and decisions Lists Today Looping with the for statement Making decisions with the if statement Lists A list is a sequence
Caltech/LEAD Summer 2012 Computer Science Lecture 4: July 11, 2012 Lists, loops and decisions Lists Today Looping with the for statement Making decisions with the if statement Lists A list is a sequence
a b c d a b c d e 5 e 7
 COMPSCI 230 Homework 9 Due on April 5, 2016 Work on this assignment either alone or in pairs. You may work with different partners on different assignments, but you can only have up to one partner for
COMPSCI 230 Homework 9 Due on April 5, 2016 Work on this assignment either alone or in pairs. You may work with different partners on different assignments, but you can only have up to one partner for
Quadratic: the time that it takes to sort an array is proportional to the. square of the number of elements.
 ITEC 136 Business Programming Concepts Week 12, Part 01 Overview 1 Week 12 Overview Week 11 review Associative Arrays Common Array Operations Inserting shifting elements right Removing shifting elements
ITEC 136 Business Programming Concepts Week 12, Part 01 Overview 1 Week 12 Overview Week 11 review Associative Arrays Common Array Operations Inserting shifting elements right Removing shifting elements
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 10: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum. Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges
 CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 10: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Factoring if/else code factoring: Extracting common/redundant code. Can reduce or eliminate
CSc 110, Autumn 2016 Lecture 10: Advanced if/else; Cumulative sum Adapted from slides by Marty Stepp and Stuart Reges Factoring if/else code factoring: Extracting common/redundant code. Can reduce or eliminate
Lecture 3: Maps and Iterators
 Lecture 3: Maps and Iterators CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 19 WI - KASEY CHAMPION 1 5 Minutes Warm Up Design Decisions Discuss with your neighbors: Which implementation of which ADT
Lecture 3: Maps and Iterators CSE 373: Data Structures and Algorithms CSE 373 19 WI - KASEY CHAMPION 1 5 Minutes Warm Up Design Decisions Discuss with your neighbors: Which implementation of which ADT
CS61B Lecture #21: Tree Searching. Last modified: Wed Oct 12 19:23: CS61B: Lecture #21 1
 CS61B Lecture #21: Tree Searching Last modified: Wed Oct 12 19:23:14 2016 CS61B: Lecture #21 1 Divide and Conquer Much (most?) computation is devoted to finding things in response to various forms of query.
CS61B Lecture #21: Tree Searching Last modified: Wed Oct 12 19:23:14 2016 CS61B: Lecture #21 1 Divide and Conquer Much (most?) computation is devoted to finding things in response to various forms of query.
CSc 372, Spring 1996 Mid-term Examination Solution Key
 CSc 372, Spring 1996 Mid-term Examination Solution Key Problem 1 (6 points): State a definition for the term "programming language". In the slides, a programming language is said to be "a notation for
CSc 372, Spring 1996 Mid-term Examination Solution Key Problem 1 (6 points): State a definition for the term "programming language". In the slides, a programming language is said to be "a notation for
Midterm 2. Replace by cover page.
 Midterm 2 Replace by cover page. Replace by conduct during examinations page. WRITE UGRAD IDs HERE (-1 mark if any missing or incorrect; use only the boxes you need) UGRAD ID #1: UGRAD ID #2: UGRAD ID
Midterm 2 Replace by cover page. Replace by conduct during examinations page. WRITE UGRAD IDs HERE (-1 mark if any missing or incorrect; use only the boxes you need) UGRAD ID #1: UGRAD ID #2: UGRAD ID
1 Static-to-Dynamic Transformations
 You re older than you ve ever been and now you re even older And now you re even older And now you re even older You re older than you ve ever been and now you re even older And now you re older still
You re older than you ve ever been and now you re even older And now you re even older And now you re even older You re older than you ve ever been and now you re even older And now you re older still
CS 106X, Lecture 7 Introduction to Recursion
 CS 106X, Lecture 7 Introduction to Recursion reading: Programming Abstractions in C++, Chapter 7 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Nick Troccoli, licensed under Creative Commons
CS 106X, Lecture 7 Introduction to Recursion reading: Programming Abstractions in C++, Chapter 7 This document is copyright (C) Stanford Computer Science and Nick Troccoli, licensed under Creative Commons
Collections, Maps and Generics
 Collections API Collections, Maps and Generics You've already used ArrayList for exercises from the previous semester, but ArrayList is just one part of much larger Collections API that Java provides.
Collections API Collections, Maps and Generics You've already used ArrayList for exercises from the previous semester, but ArrayList is just one part of much larger Collections API that Java provides.
Queues and Unit Testing
 Queues and Unit Testing Shreya Shankar Stanford CS 106B 3 July 2018 Based on slides created by Ashley Taylor, Marty Stepp, Chris Gregg, Keith Schwarz, Julie Zelenski, Jerry Cain, Eric Roberts, Mehran Sahami,
Queues and Unit Testing Shreya Shankar Stanford CS 106B 3 July 2018 Based on slides created by Ashley Taylor, Marty Stepp, Chris Gregg, Keith Schwarz, Julie Zelenski, Jerry Cain, Eric Roberts, Mehran Sahami,
