Timing GMP s Integer Multiplication Algorithm
|
|
|
- Miles McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Applied Symbolic Computation (CS 567) Assignment 3 Zexi Liu 12/08/ NxN limb 1 multiplications and squares are done using one of seven algorithms, as the size N increases Algorithm Basecase Karatsuba Toom 3 Toom 4 Toom 6.5 Toom 8.5 FFT Threshold (none) MUL_TOOM22_THRESHOLD MUL_TOOM33_THRESHOLD MUL_TOOM44_THRESHOLD MUL_TOOM6H_THRESHOLD MUL_TOOM8H_THRESHOLD MUL_FFT_THRESHOLD 1. A limb means the part of a multi precision number that fits in a single machine word. 2 1
2 Environment Information Ubuntu 10.10, Linux generic, 64 bit gcc version CPU: Intel core i MHz (idle 1600 MHz) 6 GB memory Performance Optimization In GMP package, build and run the tuneup program in the tune subdirectory cd tune make tuneup./tuneup 3 Results from running tuneup #define MUL_TOOM22_THRESHOLD THRESHOLD 18 #define MUL_TOOM33_THRESHOLD 65 #define MUL_TOOM44_THRESHOLD 166 #define MUL_TOOM6H_THRESHOLD 226 #define MUL_TOOM8H_THRESHOLD 336 #define MUL_FFT_THRESHOLD 4100 Occasional error when running tuneup speed_measure() could not get 4 results within 0.5% 05% tuneup will be aborted with this error. Have to re run it several times to get the results. 1. A limb means the part of a multi precision number that fits in a single machine word. 4 2
3 Verify the calculated thresholds #define MUL_TOOM22_THRESHOLD THRESHOLD 18 #define MUL_TOOM33_THRESHOLD 65 #define MUL_TOOM44_THRESHOLD 166 #define MUL_TOOM6H_THRESHOLD 226 #define MUL_TOOM8H_THRESHOLD 336 #define MUL_FFT_THRESHOLD 4100 In GMP package, build and run the speed program in the tune subdirectory./speed s t 100 c P P1 mpn_basecase s : multiply from 1x1 to 4000x4000 (limbs) t 100: step size 100, i.e., 1x1, 100x100, 200x200, c: times in cpu cycles P: plot using gnuplot 5 An overview 6 3
4 MUL_TOOM22_THRESHOLD 18 Threshold between basecase and karatsuba 18 Karatsuba n/a 7 MUL_TOOM33_THRESHOLD 65 Threshold between karatsuba and Toom
5 MUL_TOOM33_THRESHOLD 166 Threshold between Toom 3 and Toom MUL_FFT_THRESHOLD
6 MUL_FFT_THRESHOLD 4100 mpn_mul_fft Schoenhage Strassen s Algorithm Schoenhage Strassen s fast multiplication modulo 2 N +1 mpn_nussbaumer_mul Nussbaumer Negacyclic Convolution Multiply {ap, an and {bp, bn using Nussbaumer Negacyclic Convolution. It calls mpn_mul_fft. 11 void mpn_mul_n (mp_ptr p, mp_srcptr a, mp_srcptr b, mp_size_t n) { if (BELOW_THRESHOLD (n, MUL_TOOM22_THRESHOLD)) { mpn_mul_basecase (p, a, n, b, n); else if (BELOW_THRESHOLD (n, MUL_TOOM33_THRESHOLD)) { mpn_toom22_mul (p, a, n, b, n, ws); else if (BELOW_THRESHOLD (n, MUL_TOOM44_THRESHOLD)) { mpn_toom33_mul (p, a, n, b, n, ws); else if (BELOW_THRESHOLD (n, MUL_TOOM6H_THRESHOLD)) { mpn_toom44_mul (p, a, n, b, n, ws); else if (BELOW_THRESHOLD (n, MUL_TOOM8H_THRESHOLD)) _ { mpn_toom6h_mul (p, a, n, b, n, ws); else if (BELOW_THRESHOLD (n, MUL_FFT_THRESHOLD)) { mpn_toom8h_mul (p, a, n, b, n, ws); else { mpn_fft_mul (p, a, n, b, n); // mpn_nussbaumer_mul 12 6
7 Improvement 1 Arithmetic Modulo 2 n +1 The addition of two semi normalized representations (residue mod 2 n +1) /* r < a+b mod 2^(n*GMP_NUMB_BITS)+1. Assumes a and b are semi normalized. */ static inline void mpn_fft_add_modf (mp_ptr r, mp_srcptr a, mp_srcptr b, int n) { mp_limb_t c, x; c = a[n] + b[n] + mpn_add_n (r, a, b, n); /* 0 <= c <= 3 */ x = (c 1) & (c!= 0); r[n] = c x; MPN_DECR_U (r, n + 1, x); 13 Improvement 1 Arithmetic Modulo 2 n +1 The multiplication by 2 e /* r < a*2^d mod 2^(n*GMP_NUMB_BITS)+1 with a = {a, n+1 Assumes a is semi normalized, i.e. a[n] <= 1. r and a must have n+1 limbs, and not overlap. */ static void mpn_fft_mul_2exp_modf (mp_ptr r, mp_srcptr a, unsigned int d, mp_size_t n) {... sh = d % GMP_NUMB_BITS; d /= GMP_NUMB_BITS; if (d >= n) /* negate */ { /* r[0..d 1] < lshift(a[n d]..a[n 1], ], sh) r[d..n 1] < lshift(a[0]..a[n d 1], s d ], sh) */ d = n; if (sh!= 0) { /* no out shift below since a[n] <= 1 */ mpn_lshift (r, a + n d, d + 1, sh); rd = r[d]; cc = mpn_lshiftc (r + d, a, n d, sh);
8 Improvement 2 Cache Locality During the Transforms The Belgian Transform One solution is to perform the trees of butterflies following the BitReverse order. Higher Radix Transforms The principle of higher radix transforms is to use an atomic operation which groups several butterflies. Bailey's 4 step Algorithm A threshold is setup for activating Bailey's algorithm only for large sizes. Mixing Serveral Phases Another way to improve locality is to mix different phases of the algorithm in order to do as much work as possible on the data while they are in the cache. 15 Improvement 3 Fermat and Mersenne Transforms Power of two roots of unity are needed only at the "lower level", i.e., in Rn+. Therefore one can replace RN by RN i.e., the ring of integers modulo 2^N 1 in the original algorithm, and replace the weighted transform by a classical cyclic convolution, to compute a product mod 2 N 1. Improvement 4 The 2 Trick 3n n 2 k 2 We can use as a root of unity of order in the transform to double the possible transform length for a given n. 16 8
9 Improvement 5 Harley's and Granlund's Tricks Assume 2M + k is just above an integer multiple of K, say λk. Then we have to use n = (λ + 1)K, which gives an efficiency of only about λ /(λ +1). Harley s idea is to use n = λ K instead, and recover λ+1 the missing information from a CRT reconstruction with an additional computation modulo the machine word 2^w. Improvement 6 Improved Tuning Tuning the Fermat and Mersenne Transforms Tuning the Plain Integer Multiplication TODO In fact, some of these improvements are still on their TODO list: Implement some of the tricks published at ISSAC'2007 by Gaudry, Kruppa, and Zimmermann. It might be possible to avoid a small number of MPN_COPYs by using arotating temporary or two. Cleanup and simplify the code! 17 9
A GMP-BASED IMPLEMENTATION OF SCHÖNHAGE-STRASSEN S LARGE INTEGER MULTIPLICATION ALGORITHM
 A GMP-BASED IMPLEMENTATION OF SCHÖNHAGE-STRASSEN S LARGE INTEGER MULTIPLICATION ALGORITHM PIERRICK GAUDRY, ALEXANDER KRUPPA, AND PAUL ZIMMERMANN Abstract. Schönhage-Strassen s algorithm is one of the best
A GMP-BASED IMPLEMENTATION OF SCHÖNHAGE-STRASSEN S LARGE INTEGER MULTIPLICATION ALGORITHM PIERRICK GAUDRY, ALEXANDER KRUPPA, AND PAUL ZIMMERMANN Abstract. Schönhage-Strassen s algorithm is one of the best
A GMP-based implementation of Schönhage-Strassen s large integer multiplication algorithm
 A GMP-based implementation of Schönhage-Strassen s large integer multiplication algorithm Pierrick Gaudry, Alexander Kruppa, Paul Zimmermann To cite this version: Pierrick Gaudry, Alexander Kruppa, Paul
A GMP-based implementation of Schönhage-Strassen s large integer multiplication algorithm Pierrick Gaudry, Alexander Kruppa, Paul Zimmermann To cite this version: Pierrick Gaudry, Alexander Kruppa, Paul
Chapter Two MIPS Arithmetic
 Chapter Two MIPS Arithmetic Computer Organization Review Binary Representation Used for all data and instructions Fixed size values: 8, 16, 32, 64 Hexadecimal Sign extension Base and virtual machines.
Chapter Two MIPS Arithmetic Computer Organization Review Binary Representation Used for all data and instructions Fixed size values: 8, 16, 32, 64 Hexadecimal Sign extension Base and virtual machines.
My 2 hours today: 1. Efficient arithmetic in finite fields minute break 3. Elliptic curves. My 2 hours tomorrow:
 My 2 hours today: 1. Efficient arithmetic in finite fields 2. 10-minute break 3. Elliptic curves My 2 hours tomorrow: 4. Efficient arithmetic on elliptic curves 5. 10-minute break 6. Choosing curves Efficient
My 2 hours today: 1. Efficient arithmetic in finite fields 2. 10-minute break 3. Elliptic curves My 2 hours tomorrow: 4. Efficient arithmetic on elliptic curves 5. 10-minute break 6. Choosing curves Efficient
Lecture 7: Divide & Conquer 2. Integer Multiplication. & Matrix Multiplication. CS 341: Algorithms. Tuesday, Jan 29 th 2019
 Lecture 7: Divide & Conquer 2 Integer Multiplication & Matrix Multiplication CS 341: Algorithms Tuesday, Jan 29 th 2019 1 Outline For Today 1. Integer Multiplication 2. Matrix Multiplication 2 Outline
Lecture 7: Divide & Conquer 2 Integer Multiplication & Matrix Multiplication CS 341: Algorithms Tuesday, Jan 29 th 2019 1 Outline For Today 1. Integer Multiplication 2. Matrix Multiplication 2 Outline
Optimized Binary64 and Binary128 Arithmetic with GNU MPFR (common work with Vincent Lefèvre)
 Arith 24 conference, London, July 24, 2017 Optimized Binary64 and Binary128 Arithmetic with GNU MPFR (common work with Vincent Lefèvre) Paul Zimmermann Introducing the GNU MPFR library a software implementation
Arith 24 conference, London, July 24, 2017 Optimized Binary64 and Binary128 Arithmetic with GNU MPFR (common work with Vincent Lefèvre) Paul Zimmermann Introducing the GNU MPFR library a software implementation
Missing a trick: Karatsuba variations
 Missing a trick: Karatsuba variations Michael Scott MIRACL Labs mike.scott@miracl.com Abstract. There are a variety of ways of applying the Karatsuba idea to multi-digit multiplication. These apply particularly
Missing a trick: Karatsuba variations Michael Scott MIRACL Labs mike.scott@miracl.com Abstract. There are a variety of ways of applying the Karatsuba idea to multi-digit multiplication. These apply particularly
Montgomery Multiplication Using Vector Instructions
 Montgomery Multiplication Using Vector Instructions Joppe W. Bos, Peter L. Montgomery, Daniel Shumow, and Gregory M. Zaverucha SAC 2013 E.g. ECDSA, ECDH Motivation E(F p ) Point arithmetic E.g. DH, DSA,
Montgomery Multiplication Using Vector Instructions Joppe W. Bos, Peter L. Montgomery, Daniel Shumow, and Gregory M. Zaverucha SAC 2013 E.g. ECDSA, ECDH Motivation E(F p ) Point arithmetic E.g. DH, DSA,
CS216: Spring 2005 Problem Set 5 Comments
 CS216: Spring 2005 Problem Set 5 Comments Question 1: Consider a simple hypothetical smart card with one 8-bit register using big-endian encoding. The current used for each operation scales linearly with
CS216: Spring 2005 Problem Set 5 Comments Question 1: Consider a simple hypothetical smart card with one 8-bit register using big-endian encoding. The current used for each operation scales linearly with
CHAPTER V NUMBER SYSTEMS AND ARITHMETIC
 CHAPTER V-1 CHAPTER V CHAPTER V NUMBER SYSTEMS AND ARITHMETIC CHAPTER V-2 NUMBER SYSTEMS RADIX-R REPRESENTATION Decimal number expansion 73625 10 = ( 7 10 4 ) + ( 3 10 3 ) + ( 6 10 2 ) + ( 2 10 1 ) +(
CHAPTER V-1 CHAPTER V CHAPTER V NUMBER SYSTEMS AND ARITHMETIC CHAPTER V-2 NUMBER SYSTEMS RADIX-R REPRESENTATION Decimal number expansion 73625 10 = ( 7 10 4 ) + ( 3 10 3 ) + ( 6 10 2 ) + ( 2 10 1 ) +(
Modular Arithmetic. Marizza Bailey. December 14, 2015
 Modular Arithmetic Marizza Bailey December 14, 2015 Introduction to Modular Arithmetic If someone asks you what day it is 145 days from now, what would you answer? Would you count 145 days, or find a quicker
Modular Arithmetic Marizza Bailey December 14, 2015 Introduction to Modular Arithmetic If someone asks you what day it is 145 days from now, what would you answer? Would you count 145 days, or find a quicker
IMPLEMENTATION OF THE. Alexander J. Yee University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign
 SINGLE-TRANSPOSE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE OUT-OF-ORDER 3D-FFT Alexander J. Yee University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign The Problem FFTs are extremely memory-intensive. Completely bound by memory access. Memory
SINGLE-TRANSPOSE IMPLEMENTATION OF THE OUT-OF-ORDER 3D-FFT Alexander J. Yee University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign The Problem FFTs are extremely memory-intensive. Completely bound by memory access. Memory
EC500. Design of Secure and Reliable Hardware. Lecture 9. Mark Karpovsky
 EC500 Design of Secure and Reliable Hardware Lecture 9 Mark Karpovsky 1 1 Arithmetical Codes 1.1 Detection and Correction of errors in arithmetical channels (adders, multipliers, etc) Let = 0,1,,2 1 and
EC500 Design of Secure and Reliable Hardware Lecture 9 Mark Karpovsky 1 1 Arithmetical Codes 1.1 Detection and Correction of errors in arithmetical channels (adders, multipliers, etc) Let = 0,1,,2 1 and
! Addition! Multiplication! Bigger Example - RSA cryptography
 ! Addition! Multiplication! Bigger Example - RSA cryptography Modular Arithmetic Modular Exponentiation Primality Testing (Fermat s little theorem) Probabilistic algorithm Euclid s Algorithm for gcd (greatest
! Addition! Multiplication! Bigger Example - RSA cryptography Modular Arithmetic Modular Exponentiation Primality Testing (Fermat s little theorem) Probabilistic algorithm Euclid s Algorithm for gcd (greatest
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 195 ( 2015 ) World Conference on Technology, Innovation and Entrepreneurship
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 195 ( 2015 ) 1959 1965 World Conference on Technology, Innovation and Entrepreneurship Investigation of
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 195 ( 2015 ) 1959 1965 World Conference on Technology, Innovation and Entrepreneurship Investigation of
Beating Hand-Tuned Assembly. David Richardson
 Beating Hand-Tuned Assembly David Richardson d.g.richardson@gmail.com Outline Problem Hand tuned assembly Faster than assembly All optimization is like this 2 Multi Precision Arithmetic 11111111111111
Beating Hand-Tuned Assembly David Richardson d.g.richardson@gmail.com Outline Problem Hand tuned assembly Faster than assembly All optimization is like this 2 Multi Precision Arithmetic 11111111111111
Groups of two-state devices are used to represent data in a computer. In general, we say the states are either: high/low, on/off, 1/0,...
 Chapter 9 Computer Arithmetic Reading: Section 9.1 on pp. 290-296 Computer Representation of Data Groups of two-state devices are used to represent data in a computer. In general, we say the states are
Chapter 9 Computer Arithmetic Reading: Section 9.1 on pp. 290-296 Computer Representation of Data Groups of two-state devices are used to represent data in a computer. In general, we say the states are
Arithmetic Processing
 CS/EE 5830/6830 VLSI ARCHITECTURE Chapter 1 Basic Number Representations and Arithmetic Algorithms Arithmetic Processing AP = (operands, operation, results, conditions, singularities) Operands are: Set
CS/EE 5830/6830 VLSI ARCHITECTURE Chapter 1 Basic Number Representations and Arithmetic Algorithms Arithmetic Processing AP = (operands, operation, results, conditions, singularities) Operands are: Set
CS 33. Data Representation (Part 3) CS33 Intro to Computer Systems VIII 1 Copyright 2018 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved.
 CS 33 Data Representation (Part 3) CS33 Intro to Computer Systems VIII 1 Copyright 2018 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Byte-Oriented Memory Organization 00 0 FF F Programs refer to data by address
CS 33 Data Representation (Part 3) CS33 Intro to Computer Systems VIII 1 Copyright 2018 Thomas W. Doeppner. All rights reserved. Byte-Oriented Memory Organization 00 0 FF F Programs refer to data by address
4. Number Representations
 Educational Objectives You have a good understanding how a computer represents numbers. You can transform integers in binary representation and perform computations. You understand how the value range
Educational Objectives You have a good understanding how a computer represents numbers. You can transform integers in binary representation and perform computations. You understand how the value range
Chapter 2. Positional number systems. 2.1 Signed number representations Signed magnitude
 Chapter 2 Positional number systems A positional number system represents numeric values as sequences of one or more digits. Each digit in the representation is weighted according to its position in the
Chapter 2 Positional number systems A positional number system represents numeric values as sequences of one or more digits. Each digit in the representation is weighted according to its position in the
CUDA. Schedule API. Language extensions. nvcc. Function type qualifiers (1) CUDA compiler to handle the standard C extensions.
 Schedule CUDA Digging further into the programming manual Application Programming Interface (API) text only part, sorry Image utilities (simple CUDA examples) Performace considerations Matrix multiplication
Schedule CUDA Digging further into the programming manual Application Programming Interface (API) text only part, sorry Image utilities (simple CUDA examples) Performace considerations Matrix multiplication
Multi-Precision Arithmetic for Cryptography in C++
 Multi-Precision Arithmetic for Cryptography in C++ at Run-Time and at Compile-Time Niek J. Bouman, PhD niekbouman@gmail.com 1 Secure Multiparty Computation (MPC) in Gartner s Hype Cycle (2017) 2 Secure
Multi-Precision Arithmetic for Cryptography in C++ at Run-Time and at Compile-Time Niek J. Bouman, PhD niekbouman@gmail.com 1 Secure Multiparty Computation (MPC) in Gartner s Hype Cycle (2017) 2 Secure
Decision Procedures. An Algorithmic Point of View. Bit-Vectors. D. Kroening O. Strichman. Version 1.0, ETH/Technion
 Decision Procedures An Algorithmic Point of View Bit-Vectors D. Kroening O. Strichman ETH/Technion Version 1.0, 2007 Part VI Bit-Vectors Outline 1 Introduction to Bit-Vector Logic 2 Syntax 3 Semantics
Decision Procedures An Algorithmic Point of View Bit-Vectors D. Kroening O. Strichman ETH/Technion Version 1.0, 2007 Part VI Bit-Vectors Outline 1 Introduction to Bit-Vector Logic 2 Syntax 3 Semantics
A Proposal 1 to add the Infinite Precision Integer and Rational to the C ++ Standard Library
 A Proposal 1 to add the Infinite Precision Integer and Rational to the C ++ Standard Library M.J. Kronenburg e-mail: M.Kronenburg@inter.nl.net 1 November 2004 1 Document number N1718=04-0138 ii Contents
A Proposal 1 to add the Infinite Precision Integer and Rational to the C ++ Standard Library M.J. Kronenburg e-mail: M.Kronenburg@inter.nl.net 1 November 2004 1 Document number N1718=04-0138 ii Contents
How to get an efficient yet verified arbitrary-precision integer library
 How to get an efficient yet verified arbitrary-precision integer library Raphaël Rieu-Helft (joint work with Guillaume Melquiond and Claude Marché) TrustInSoft Inria May 28, 2018 1/31 Context, motivation,
How to get an efficient yet verified arbitrary-precision integer library Raphaël Rieu-Helft (joint work with Guillaume Melquiond and Claude Marché) TrustInSoft Inria May 28, 2018 1/31 Context, motivation,
Expressions. Eric McCreath
 Expressions Eric McCreath 2 Expressions on integers There is the standard set of interger operators in c. We have: y = 4 + 7; // add y = 7-3; // subtract y = 3 * x; // multiply y = x / 3; // integer divide
Expressions Eric McCreath 2 Expressions on integers There is the standard set of interger operators in c. We have: y = 4 + 7; // add y = 7-3; // subtract y = 3 * x; // multiply y = x / 3; // integer divide
How to get an efficient yet verified arbitrary-precision integer library
 How to get an efficient yet verified arbitrary-precision integer library Raphaël Rieu-Helft TrustInSoft Inria March 13, 2018 March 13, 2018 1 / 36 Context, motivation, goals goal: efficient and formally
How to get an efficient yet verified arbitrary-precision integer library Raphaël Rieu-Helft TrustInSoft Inria March 13, 2018 March 13, 2018 1 / 36 Context, motivation, goals goal: efficient and formally
Programming Project, CS378, Spring 2013 Implementing ElGamal Encryption
 Programming Project, CS378, Spring 2013 Implementing ElGamal Encryption Andrew Klapper c Andrew Klapper, 2013 1 Overview The purpose of this project is to implement the ElGamal cryptosystem. This is a
Programming Project, CS378, Spring 2013 Implementing ElGamal Encryption Andrew Klapper c Andrew Klapper, 2013 1 Overview The purpose of this project is to implement the ElGamal cryptosystem. This is a
The LinBox Project for Linear Algebra Computation
 The LinBox Project for Linear Algebra Computation A Practical Tutorial Daniel S. Roche Symbolic Computation Group School of Computer Science University of Waterloo MOCAA 2008 University of Western Ontario
The LinBox Project for Linear Algebra Computation A Practical Tutorial Daniel S. Roche Symbolic Computation Group School of Computer Science University of Waterloo MOCAA 2008 University of Western Ontario
CS 376b Computer Vision
 CS 376b Computer Vision 09 / 25 / 2014 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? / Comments? Enhancing images / masks Cross correlation Convolution C++ Cross-correlation Cross-correlation involves
CS 376b Computer Vision 09 / 25 / 2014 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? / Comments? Enhancing images / masks Cross correlation Convolution C++ Cross-correlation Cross-correlation involves
A Guide. DSP Library
 DSP A Guide To The DSP Library SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive, Suite 150 Norcross, GA 30092 USA
DSP A Guide To The DSP Library SystemView by ELANIX Copyright 1994-2005, Eagleware Corporation All rights reserved. Eagleware-Elanix Corporation 3585 Engineering Drive, Suite 150 Norcross, GA 30092 USA
Numeric-Symbolic Exact Rational Linear System Solver
 Numeric-Symbolic Exact Rational Linear System Solver B David Saunders, David Wood, and Bryan Youse University of Delaware June 10, 2011 Motivation Ax = b Given A Z m n and b Z m, compute x Q n Core problem
Numeric-Symbolic Exact Rational Linear System Solver B David Saunders, David Wood, and Bryan Youse University of Delaware June 10, 2011 Motivation Ax = b Given A Z m n and b Z m, compute x Q n Core problem
Algorithm Design and Analysis
 Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 16 Dynamic Programming (plus FFT Recap) Adam Smith 9/24/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne Discrete Fourier Transform
Algorithm Design and Analysis LECTURE 16 Dynamic Programming (plus FFT Recap) Adam Smith 9/24/2008 A. Smith; based on slides by E. Demaine, C. Leiserson, S. Raskhodnikova, K. Wayne Discrete Fourier Transform
36 Modular Arithmetic
 36 Modular Arithmetic Tom Lewis Fall Term 2010 Tom Lewis () 36 Modular Arithmetic Fall Term 2010 1 / 10 Outline 1 The set Z n 2 Addition and multiplication 3 Modular additive inverse 4 Modular multiplicative
36 Modular Arithmetic Tom Lewis Fall Term 2010 Tom Lewis () 36 Modular Arithmetic Fall Term 2010 1 / 10 Outline 1 The set Z n 2 Addition and multiplication 3 Modular additive inverse 4 Modular multiplicative
A Study of High Performance Multiple Precision Arithmetic on Graphics Processing Units
 University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Doctoral Dissertations Dissertations and Theses 2018 A Study of High Performance Multiple Precision Arithmetic on Graphics Processing Units
University of Massachusetts Amherst ScholarWorks@UMass Amherst Doctoral Dissertations Dissertations and Theses 2018 A Study of High Performance Multiple Precision Arithmetic on Graphics Processing Units
The Basic Polynomial Algebra Subprograms
 The Basic Polynomial Algebra Subprograms Changbo Chen 1, Svyatoslav Covanov 2, Farnam Mansouri 2, Marc Moreno Maza 2, Ning Xie 2, and Yuzhen Xie 2 1 Chongqing Key Laboratory of Automated Reasoning and
The Basic Polynomial Algebra Subprograms Changbo Chen 1, Svyatoslav Covanov 2, Farnam Mansouri 2, Marc Moreno Maza 2, Ning Xie 2, and Yuzhen Xie 2 1 Chongqing Key Laboratory of Automated Reasoning and
Comp 335 File Structures. Hashing
 Comp 335 File Structures Hashing What is Hashing? A process used with record files that will try to achieve O(1) (i.e. constant) access to a record s location in the file. An algorithm, called a hash function
Comp 335 File Structures Hashing What is Hashing? A process used with record files that will try to achieve O(1) (i.e. constant) access to a record s location in the file. An algorithm, called a hash function
Computer Architecture /
 Computer Architecture 02-201 / 02-601 The Conceptual Architecture of a Computer PC CPU register 0 register 1 register 2 registers hold small amounts of data for processing by the CPU Reading / writing
Computer Architecture 02-201 / 02-601 The Conceptual Architecture of a Computer PC CPU register 0 register 1 register 2 registers hold small amounts of data for processing by the CPU Reading / writing
Introduction to HPC. Lecture 21
 443 Introduction to HPC Lecture Dept of Computer Science 443 Fast Fourier Transform 443 FFT followed by Inverse FFT DIF DIT Use inverse twiddles for the inverse FFT No bitreversal necessary! 443 FFT followed
443 Introduction to HPC Lecture Dept of Computer Science 443 Fast Fourier Transform 443 FFT followed by Inverse FFT DIF DIT Use inverse twiddles for the inverse FFT No bitreversal necessary! 443 FFT followed
High-Performance Modular Multiplication on the Cell Broadband Engine
 High-Performance Modular Multiplication on the Cell Broadband Engine Joppe W. Bos Laboratory for Cryptologic Algorithms EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland joppe.bos@epfl.ch 1 / 21 Outline Motivation and previous
High-Performance Modular Multiplication on the Cell Broadband Engine Joppe W. Bos Laboratory for Cryptologic Algorithms EPFL, Lausanne, Switzerland joppe.bos@epfl.ch 1 / 21 Outline Motivation and previous
IEEE 754 Floating-Point Format
 PDS: CS 11002 Computer Sc & Engg: IIT Kharagpur 1 IEEE 754 Floating-Point Format PDS: CS 11002 Computer Sc & Engg: IIT Kharagpur 2 Floating-Point Decimal Number 123456. 10 1 = 12345.6 10 0 = 1234.56 10
PDS: CS 11002 Computer Sc & Engg: IIT Kharagpur 1 IEEE 754 Floating-Point Format PDS: CS 11002 Computer Sc & Engg: IIT Kharagpur 2 Floating-Point Decimal Number 123456. 10 1 = 12345.6 10 0 = 1234.56 10
AP Computer Science Principles Exam Reference Sheet
 AP Computer Science Principles Exam Reference Sheet July 2015 As AP Computer Science Principles does not designate any particular programming language, this reference sheet provides instructions and explanations
AP Computer Science Principles Exam Reference Sheet July 2015 As AP Computer Science Principles does not designate any particular programming language, this reference sheet provides instructions and explanations
Instructions: Language of the Computer
 CS359: Computer Architecture Instructions: Language of the Computer Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering 1 The Language a Computer Understands Word a computer understands: instruction
CS359: Computer Architecture Instructions: Language of the Computer Yanyan Shen Department of Computer Science and Engineering 1 The Language a Computer Understands Word a computer understands: instruction
CS 265. Computer Architecture. Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng.
 CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. 1 Part 1: Data Representation Our goal: revisit and re-establish fundamental of mathematics for the computer architecture course Overview: what are bits
CS 265 Computer Architecture Wei Lu, Ph.D., P.Eng. 1 Part 1: Data Representation Our goal: revisit and re-establish fundamental of mathematics for the computer architecture course Overview: what are bits
Advanced Computing Research Laboratory. Adaptive Scientific Software Libraries
 Adaptive Scientific Software Libraries and Texas Learning and Computation Center and Department of Computer Science University of Houston Challenges Diversity of execution environments Growing complexity
Adaptive Scientific Software Libraries and Texas Learning and Computation Center and Department of Computer Science University of Houston Challenges Diversity of execution environments Growing complexity
Binary Adders. Ripple-Carry Adder
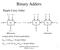 Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Image Compression System on an FPGA
 Image Compression System on an FPGA Group 1 Megan Fuller, Ezzeldin Hamed 6.375 Contents 1 Objective 2 2 Background 2 2.1 The DFT........................................ 3 2.2 The DCT........................................
Image Compression System on an FPGA Group 1 Megan Fuller, Ezzeldin Hamed 6.375 Contents 1 Objective 2 2 Background 2 2.1 The DFT........................................ 3 2.2 The DCT........................................
Efficient Implementation of Public Key Cryptosystems on Mote Sensors (Short Paper)
 Efficient Implementation of Public Key Cryptosystems on Mote Sensors (Short Paper) Haodong Wang and Qun Li Department of Computer Science College of William and Mary {wanghd, liqun}@cs.wm.edu Abstract.
Efficient Implementation of Public Key Cryptosystems on Mote Sensors (Short Paper) Haodong Wang and Qun Li Department of Computer Science College of William and Mary {wanghd, liqun}@cs.wm.edu Abstract.
CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security
 CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 7 January 30, 2012 CPSC 467b, Lecture 7 1/44 Public-key cryptography RSA Factoring Assumption Computing with Big Numbers Fast Exponentiation
CPSC 467b: Cryptography and Computer Security Michael J. Fischer Lecture 7 January 30, 2012 CPSC 467b, Lecture 7 1/44 Public-key cryptography RSA Factoring Assumption Computing with Big Numbers Fast Exponentiation
Unit-2 Divide and conquer 2016
 2 Divide and conquer Overview, Structure of divide-and-conquer algorithms, binary search, quick sort, Strassen multiplication. 13% 05 Divide-and- conquer The Divide and Conquer Paradigm, is a method of
2 Divide and conquer Overview, Structure of divide-and-conquer algorithms, binary search, quick sort, Strassen multiplication. 13% 05 Divide-and- conquer The Divide and Conquer Paradigm, is a method of
Synthesizable variable bit-width floating-point SystemC Class. Richard Walke Real-Time Systems Lab, QinetiQ LTD, Malvern UK.
 Synthesizable variable bit-width floating-point SystemC Class Richard Walke Real-Time Systems Lab, QinetiQ LTD, Malvern UK. walke@signal.qinetiq.com Contents 3 1 Advantages of floating-point arithmetic
Synthesizable variable bit-width floating-point SystemC Class Richard Walke Real-Time Systems Lab, QinetiQ LTD, Malvern UK. walke@signal.qinetiq.com Contents 3 1 Advantages of floating-point arithmetic
a) Do exercise (5th Edition Patterson & Hennessy). Note: Branches are calculated in the execution stage.
 CS3410 Spring 2015 Problem Set 2 (version 3) Due Saturday, April 25, 11:59 PM (Due date for Problem-5 is April 20, 11:59 PM) NetID: Name: 200 points total. Start early! This is a big problem set. Problem
CS3410 Spring 2015 Problem Set 2 (version 3) Due Saturday, April 25, 11:59 PM (Due date for Problem-5 is April 20, 11:59 PM) NetID: Name: 200 points total. Start early! This is a big problem set. Problem
Tutorial 3 Sample Answer
 Tutorial 3 Sample Answer Q1 Variables assigned to registers in line with RISC-1 register usage before code generation. // int g = 4 ; global variable g:r9 add r0, #4, r9 ; need to initialise r9 // int
Tutorial 3 Sample Answer Q1 Variables assigned to registers in line with RISC-1 register usage before code generation. // int g = 4 ; global variable g:r9 add r0, #4, r9 ; need to initialise r9 // int
CSCI 402: Computer Architectures
 CSCI 402: Computer Architectures Instructions: Language of the Computer (2) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI Memory Operands Two tribes: Big Endian: Most-significant byte
CSCI 402: Computer Architectures Instructions: Language of the Computer (2) Fengguang Song Department of Computer & Information Science IUPUI Memory Operands Two tribes: Big Endian: Most-significant byte
Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data
 Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data CSCI 2400: Computer Architecture ECE 3217: Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: David Ferry Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides
Arithmetic and Bitwise Operations on Binary Data CSCI 2400: Computer Architecture ECE 3217: Computer Architecture and Organization Instructor: David Ferry Slides adapted from Bryant & O Hallaron s slides
Turbo Charge CPU Utilization in Fork/Join Using the ManagedBlocker
 1 Turbo Charge CPU Utilization in Fork/Join Using the ManagedBlocker 2017 Heinz Kabutz, All Rights Reserved Dr Heinz M. Kabutz Last Updated 2017-01-24 2 Regular 3 ManagedBlocker 4 Speeding Up Fibonacci
1 Turbo Charge CPU Utilization in Fork/Join Using the ManagedBlocker 2017 Heinz Kabutz, All Rights Reserved Dr Heinz M. Kabutz Last Updated 2017-01-24 2 Regular 3 ManagedBlocker 4 Speeding Up Fibonacci
Cryptology complementary. Finite fields the practical side (1)
 Cryptology complementary Finite fields the practical side (1) Pierre Karpman pierre.karpman@univ-grenoble-alpes.fr https://www-ljk.imag.fr/membres/pierre.karpman/tea.html 2018 03 15 Finite Fields in practice
Cryptology complementary Finite fields the practical side (1) Pierre Karpman pierre.karpman@univ-grenoble-alpes.fr https://www-ljk.imag.fr/membres/pierre.karpman/tea.html 2018 03 15 Finite Fields in practice
1. Introduction. Raj Kishore Kumar 1, Vikram Kumar 2
 ASIC Implementation and Comparison of Diminished-one Modulo 2 n +1 Adder Raj Kishore Kumar 1, Vikram Kumar 2 1 Shivalik Institute of Engineering & Technology 2 Assistant Professor, Shivalik Institute of
ASIC Implementation and Comparison of Diminished-one Modulo 2 n +1 Adder Raj Kishore Kumar 1, Vikram Kumar 2 1 Shivalik Institute of Engineering & Technology 2 Assistant Professor, Shivalik Institute of
Cryptography and Network Security
 Cryptography and Network Security CRYPTOGRAPHY AND NETWORK SECURITY PRAKASH C. GUPTA Former Head Department of Information Technology Maharashtra Institute of Technology Pune Delhi-110092 2015 CRYPTOGRAPHY
Cryptography and Network Security CRYPTOGRAPHY AND NETWORK SECURITY PRAKASH C. GUPTA Former Head Department of Information Technology Maharashtra Institute of Technology Pune Delhi-110092 2015 CRYPTOGRAPHY
Add Subtract Multiply Divide
 ARITHMETIC OPERATORS if AND if/else AND while LOOP Order of Operation (Precedence Part 1) Copyright 2014 Dan McElroy Add Subtract Multiply Divide + Add - Subtract * Multiply / Divide = gives the quotient
ARITHMETIC OPERATORS if AND if/else AND while LOOP Order of Operation (Precedence Part 1) Copyright 2014 Dan McElroy Add Subtract Multiply Divide + Add - Subtract * Multiply / Divide = gives the quotient
A Rigorous Extension of the Schönhage-Strassen Integer Multiplication Algorithm Using Complex Interval Arithmetic
 A Rigorous Extension of the Schönhage-Strassen Integer Multiplication Algorithm Using Complex Interval Arithmetic Thomas Steinke Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Canterbury Christchurch,
A Rigorous Extension of the Schönhage-Strassen Integer Multiplication Algorithm Using Complex Interval Arithmetic Thomas Steinke Department of Mathematics and Statistics University of Canterbury Christchurch,
Introduction Presentation A
 CSE 2421/5042: Systems I Low-Level Programming and Computer Organization Introduction Presentation A Read carefully: Bryant Chapter 1 Study: Reek Chapter 2 Skim: Reek Chapter 1 08/22/2018 Gojko Babić Some
CSE 2421/5042: Systems I Low-Level Programming and Computer Organization Introduction Presentation A Read carefully: Bryant Chapter 1 Study: Reek Chapter 2 Skim: Reek Chapter 1 08/22/2018 Gojko Babić Some
Consider the actions taken on positive integers when considering decimal values shown in Table 1 where the division discards the remainder.
 9.3 Mapping Down to 0,..., M 1 In our previous step, we discussed methods for taking various objects and deterministically creating a 32- bit hash value based on the properties of the object. Hash tables,
9.3 Mapping Down to 0,..., M 1 In our previous step, we discussed methods for taking various objects and deterministically creating a 32- bit hash value based on the properties of the object. Hash tables,
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ARCHITECTURE
 COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ARCHITECTURE Instructions Sets Architecture Lesson 5a 1 What are Instruction Sets The complete collection of instructions that are understood by a CPU Can be considered as a functional
COMPUTER ORGANIZATION & ARCHITECTURE Instructions Sets Architecture Lesson 5a 1 What are Instruction Sets The complete collection of instructions that are understood by a CPU Can be considered as a functional
EEC 483 Computer Organization
 EEC 483 Computer Organization Chapter 3. Arithmetic for Computers Chansu Yu Table of Contents Ch.1 Introduction Ch. 2 Instruction: Machine Language Ch. 3-4 CPU Implementation Ch. 5 Cache and VM Ch. 6-7
EEC 483 Computer Organization Chapter 3. Arithmetic for Computers Chansu Yu Table of Contents Ch.1 Introduction Ch. 2 Instruction: Machine Language Ch. 3-4 CPU Implementation Ch. 5 Cache and VM Ch. 6-7
REFERENCE MATERIALS. Assignment, Display, and Input Evaluates expression and assigns the result to the variable a.
 a expression Assignment, Display, and Input Evaluates expression and assigns the result to the variable a. DISPLAY (expression) Displays the value of expression, followed by a space. INPUT () Accepts a
a expression Assignment, Display, and Input Evaluates expression and assigns the result to the variable a. DISPLAY (expression) Displays the value of expression, followed by a space. INPUT () Accepts a
On a 64-bit CPU. Size/Range vary by CPU model and Word size.
 On a 64-bit CPU. Size/Range vary by CPU model and Word size. unsigned short x; //range 0 to 65553 signed short x; //range ± 32767 short x; //assumed signed There are (usually) no unsigned floats or doubles.
On a 64-bit CPU. Size/Range vary by CPU model and Word size. unsigned short x; //range 0 to 65553 signed short x; //range ± 32767 short x; //assumed signed There are (usually) no unsigned floats or doubles.
Pomcor JavaScript Cryptographic Library (PJCL)
 Pomcor JavaScript Cryptographic Library (PJCL) Version 0.9 (beta test version) Contents 1 Functionality provided in Version 0.9 6 2 Requirements 7 3 License 8 4 Downloadable zip archive 8 5 Data encodings
Pomcor JavaScript Cryptographic Library (PJCL) Version 0.9 (beta test version) Contents 1 Functionality provided in Version 0.9 6 2 Requirements 7 3 License 8 4 Downloadable zip archive 8 5 Data encodings
Topics in computer architecture
 Topics in computer architecture Sun Microsystems SPARC P.J. Drongowski SandSoftwareSound.net Copyright 1990-2013 Paul J. Drongowski Sun Microsystems SPARC Scalable Processor Architecture Computer family
Topics in computer architecture Sun Microsystems SPARC P.J. Drongowski SandSoftwareSound.net Copyright 1990-2013 Paul J. Drongowski Sun Microsystems SPARC Scalable Processor Architecture Computer family
Computer Arithmetic. L. Liu Department of Computer Science, ETH Zürich Fall semester, Reconfigurable Computing Systems ( L) Fall 2012
 Reconfigurable Computing Systems (252-2210-00L) all 2012 Computer Arithmetic L. Liu Department of Computer Science, ETH Zürich all semester, 2012 Source: ixed-point arithmetic slides come from Prof. Jarmo
Reconfigurable Computing Systems (252-2210-00L) all 2012 Computer Arithmetic L. Liu Department of Computer Science, ETH Zürich all semester, 2012 Source: ixed-point arithmetic slides come from Prof. Jarmo
But first, encode deck of cards. Integer Representation. Two possible representations. Two better representations WELLESLEY CS 240 9/8/15
 Integer Representation Representation of integers: unsigned and signed Sign extension Arithmetic and shifting Casting But first, encode deck of cards. cards in suits How do we encode suits, face cards?
Integer Representation Representation of integers: unsigned and signed Sign extension Arithmetic and shifting Casting But first, encode deck of cards. cards in suits How do we encode suits, face cards?
DIGITAL ARITHMETIC. Miloš D. Ercegovac Computer Science Department University of California Los Angeles and
 1 DIGITAL ARITHMETIC Miloš D. Ercegovac Computer Science Department University of California Los Angeles and Tomás Lang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California at Irvine
1 DIGITAL ARITHMETIC Miloš D. Ercegovac Computer Science Department University of California Los Angeles and Tomás Lang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California at Irvine
Double-precision General Matrix Multiply (DGEMM)
 Double-precision General Matrix Multiply (DGEMM) Parallel Computation (CSE 0), Assignment Andrew Conegliano (A0) Matthias Springer (A00) GID G-- January, 0 0. Assumptions The following assumptions apply
Double-precision General Matrix Multiply (DGEMM) Parallel Computation (CSE 0), Assignment Andrew Conegliano (A0) Matthias Springer (A00) GID G-- January, 0 0. Assumptions The following assumptions apply
Introduction to the new AES Standard: Rijndael
 Introduction to the new AES Standard: Rijndael Paul Donis This paper will explain how the Rijndael Cipher Reference Code in C works. Rijndael is a block cipher that encrypts and decrypts 128, 192, and
Introduction to the new AES Standard: Rijndael Paul Donis This paper will explain how the Rijndael Cipher Reference Code in C works. Rijndael is a block cipher that encrypts and decrypts 128, 192, and
Monte Carlo Integration and Random Numbers
 Monte Carlo Integration and Random Numbers Higher dimensional integration u Simpson rule with M evaluations in u one dimension the error is order M -4! u d dimensions the error is order M -4/d u In general
Monte Carlo Integration and Random Numbers Higher dimensional integration u Simpson rule with M evaluations in u one dimension the error is order M -4! u d dimensions the error is order M -4/d u In general
Supercomputing in Plain English
 Supercomputing in Plain English An Introduction to High Performance Computing Part III: Instruction Level Parallelism and Scalar Optimization Henry Neeman, Director OU Supercomputing Center for Education
Supercomputing in Plain English An Introduction to High Performance Computing Part III: Instruction Level Parallelism and Scalar Optimization Henry Neeman, Director OU Supercomputing Center for Education
We would like to find the value of the right-hand side of this equation. We know that
 CS 61 Scribe Notes Computer Arithmetic II, Structured Data, Memory Layout (Th 9/13) Renzo Lucioni, Weishen Mead, Kat Zhou Unsigned Computer Arithmetic II Consider the following: We would like to find the
CS 61 Scribe Notes Computer Arithmetic II, Structured Data, Memory Layout (Th 9/13) Renzo Lucioni, Weishen Mead, Kat Zhou Unsigned Computer Arithmetic II Consider the following: We would like to find the
Hashing. Manolis Koubarakis. Data Structures and Programming Techniques
 Hashing Manolis Koubarakis 1 The Symbol Table ADT A symbol table T is an abstract storage that contains table entries that are either empty or are pairs of the form (K, I) where K is a key and I is some
Hashing Manolis Koubarakis 1 The Symbol Table ADT A symbol table T is an abstract storage that contains table entries that are either empty or are pairs of the form (K, I) where K is a key and I is some
Integers II. CSE 351 Autumn Instructor: Justin Hsia
 Integers II CSE 351 Autumn 2016 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Chris Ma Hunter Zahn John Kaltenbach Kevin Bi Sachin Mehta Suraj Bhat Thomas Neuman Waylon Huang Xi Liu Yufang Sun http://xkcd.com/571/
Integers II CSE 351 Autumn 2016 Instructor: Justin Hsia Teaching Assistants: Chris Ma Hunter Zahn John Kaltenbach Kevin Bi Sachin Mehta Suraj Bhat Thomas Neuman Waylon Huang Xi Liu Yufang Sun http://xkcd.com/571/
Vectorized implementations of post-quantum crypto
 Vectorized implementations of post-quantum crypto Peter Schwabe January 12, 2015 DIMACS Workshop on the Mathematics of Post-Quantum Cryptography The multicore revolution Until early years 2000 each new
Vectorized implementations of post-quantum crypto Peter Schwabe January 12, 2015 DIMACS Workshop on the Mathematics of Post-Quantum Cryptography The multicore revolution Until early years 2000 each new
Basic Assignment and Arithmetic Operators
 C Programming 1 Basic Assignment and Arithmetic Operators C Programming 2 Assignment Operator = int count ; count = 10 ; The first line declares the variable count. In the second line an assignment operator
C Programming 1 Basic Assignment and Arithmetic Operators C Programming 2 Assignment Operator = int count ; count = 10 ; The first line declares the variable count. In the second line an assignment operator
In case you didn t get it (or you were too lazy to check)
 15213 Recitation 1 In case you didn t get it (or you were too lazy to check) Class Web page: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~213 No Blackboard, no Piazza Questions? Email 15 213 staff@cs.cmu.edu Office hours: MTWR,
15213 Recitation 1 In case you didn t get it (or you were too lazy to check) Class Web page: http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~213 No Blackboard, no Piazza Questions? Email 15 213 staff@cs.cmu.edu Office hours: MTWR,
An Efficient Elliptic Curve Cryptography Arithmetic Using Nikhilam Multiplication
 The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (IJES) Volume 4 Issue 4 Pages PP.45-50 2015 ISSN (e): 2319 1813 ISSN (p): 2319 1805 An Efficient Elliptic Curve Cryptography Arithmetic Using Nikhilam
The International Journal Of Engineering And Science (IJES) Volume 4 Issue 4 Pages PP.45-50 2015 ISSN (e): 2319 1813 ISSN (p): 2319 1805 An Efficient Elliptic Curve Cryptography Arithmetic Using Nikhilam
- 0 - CryptoLib: Cryptography in Software John B. Lacy 1 Donald P. Mitchell 2 William M. Schell 3 AT&T Bell Laboratories ABSTRACT
 - 0 - CryptoLib: Cryptography in Software John B. Lacy 1 Donald P. Mitchell 2 William M. Schell 3 AT&T Bell Laboratories ABSTRACT With the capacity of communications channels increasing at the current
- 0 - CryptoLib: Cryptography in Software John B. Lacy 1 Donald P. Mitchell 2 William M. Schell 3 AT&T Bell Laboratories ABSTRACT With the capacity of communications channels increasing at the current
Algorithms and arithmetic for the implementation of cryptographic pairings
 Cairn seminar November 29th, 2013 Algorithms and arithmetic for the implementation of cryptographic pairings Nicolas Estibals CAIRN project-team, IRISA Nicolas.Estibals@irisa.fr What is an elliptic curve?
Cairn seminar November 29th, 2013 Algorithms and arithmetic for the implementation of cryptographic pairings Nicolas Estibals CAIRN project-team, IRISA Nicolas.Estibals@irisa.fr What is an elliptic curve?
EE 486 Winter The role of arithmetic. EE 486 : lecture 1, the integers. SIA Roadmap - 2. SIA Roadmap - 1
 EE 486 Winter 2-3 The role of arithmetic EE 486 : lecture, the integers M. J. Flynn With increasing circuit density available with sub micron feature sizes, there s a corresponding broader spectrum of
EE 486 Winter 2-3 The role of arithmetic EE 486 : lecture, the integers M. J. Flynn With increasing circuit density available with sub micron feature sizes, there s a corresponding broader spectrum of
data within a computer system are stored in one of 2 physical states (hence the use of binary digits)
 Binary Digits (bits) data within a computer system are stored in one of 2 physical states (hence the use of binary digits) 0V and 5V charge / NO charge on a transistor gate ferrite core magnetised clockwise
Binary Digits (bits) data within a computer system are stored in one of 2 physical states (hence the use of binary digits) 0V and 5V charge / NO charge on a transistor gate ferrite core magnetised clockwise
c 2013 Alexander Jih-Hing Yee
 c 2013 Alexander Jih-Hing Yee A FASTER FFT IN THE MID-WEST BY ALEXANDER JIH-HING YEE THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Computer Science
c 2013 Alexander Jih-Hing Yee A FASTER FFT IN THE MID-WEST BY ALEXANDER JIH-HING YEE THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Computer Science
WYSE Academic Challenge 2002 Computer Science Test (Sectional) SOLUTION
 Computer Science - 1 WYSE Academic Challenge 2002 Computer Science Test (Sectional) SOLUTION 1. Access to moving head disks requires three periods of delay before information is brought into memory. The
Computer Science - 1 WYSE Academic Challenge 2002 Computer Science Test (Sectional) SOLUTION 1. Access to moving head disks requires three periods of delay before information is brought into memory. The
Recap. ANSI C Reserved Words C++ Multimedia Programming Lecture 2. Erwin M. Bakker Joachim Rijsdam
 Multimedia Programming 2004 Lecture 2 Erwin M. Bakker Joachim Rijsdam Recap Learning C++ by example No groups: everybody should experience developing and programming in C++! Assignments will determine
Multimedia Programming 2004 Lecture 2 Erwin M. Bakker Joachim Rijsdam Recap Learning C++ by example No groups: everybody should experience developing and programming in C++! Assignments will determine
7 Control Structures, Logical Statements
 7 Control Structures, Logical Statements 7.1 Logical Statements 1. Logical (true or false) statements comparing scalars or matrices can be evaluated in MATLAB. Two matrices of the same size may be compared,
7 Control Structures, Logical Statements 7.1 Logical Statements 1. Logical (true or false) statements comparing scalars or matrices can be evaluated in MATLAB. Two matrices of the same size may be compared,
Unit-2 (Operators) ANAND KR.SRIVASTAVA
 Unit-2 (Operators) ANAND KR.SRIVASTAVA 1 Operators in C ( use of operators in C ) Operators are the symbol, to perform some operation ( calculation, manipulation). Set of Operations are used in completion
Unit-2 (Operators) ANAND KR.SRIVASTAVA 1 Operators in C ( use of operators in C ) Operators are the symbol, to perform some operation ( calculation, manipulation). Set of Operations are used in completion
Finite Fields can be represented in various ways. Generally, they are most
 Using Fibonacci Cycles Modulo p to Represent Finite Fields 1 Caitlyn Conaway, Jeremy Porché, Jack Rebrovich, Shelby Robertson, and Trey Smith, PhD Abstract Finite Fields can be represented in various ways.
Using Fibonacci Cycles Modulo p to Represent Finite Fields 1 Caitlyn Conaway, Jeremy Porché, Jack Rebrovich, Shelby Robertson, and Trey Smith, PhD Abstract Finite Fields can be represented in various ways.
On The Computational Cost of FFT-Based Linear Convolutions. David H. Bailey 07 June 1996 Ref: Not published
 On The Computational Cost of FFT-Based Linear Convolutions David H. Bailey 07 June 1996 Ref: Not published Abstract The linear convolution of two n-long sequences x and y is commonly performed by extending
On The Computational Cost of FFT-Based Linear Convolutions David H. Bailey 07 June 1996 Ref: Not published Abstract The linear convolution of two n-long sequences x and y is commonly performed by extending
TABLES AND HASHING. Chapter 13
 Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computer and Information, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ TABLES AND HASHING Chapter 13
Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computer and Information, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ TABLES AND HASHING Chapter 13
3.1 Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts. 3.1 Dividing a Set into Fractional Parts. 3.2 Identifying Parts of Wholes.
 . Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts Fraction: represents a part of a whole object or unit Numerator: (top number) represents number of parts of the whole Denominator: (bottom number) represents how
. Dividing a Whole into Fractional Parts Fraction: represents a part of a whole object or unit Numerator: (top number) represents number of parts of the whole Denominator: (bottom number) represents how
Microprocessor and Assembly Language Week-5. System Programming, BCS 6th, IBMS (2017)
 Microprocessor and Assembly Language Week-5 System Programming, BCS 6th, IBMS (2017) High Speed Memory Registers CPU store data temporarily in these location CPU process, store and transfer data from one
Microprocessor and Assembly Language Week-5 System Programming, BCS 6th, IBMS (2017) High Speed Memory Registers CPU store data temporarily in these location CPU process, store and transfer data from one
CS 261 Fall Mike Lam, Professor Integer Encodings
 CS 261 Fall 2018 Mike Lam, Professor https://xkcd.com/571/ Integer Encodings Integers Topics C integer data types Unsigned encoding Signed encodings Conversions Integer data types in C99 1 byte 2 bytes
CS 261 Fall 2018 Mike Lam, Professor https://xkcd.com/571/ Integer Encodings Integers Topics C integer data types Unsigned encoding Signed encodings Conversions Integer data types in C99 1 byte 2 bytes
CS61C : Machine Structures
 inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #5 Memory Management; Intro MIPS 2007-7-2 Scott Beamer, Instructor iphone Draws Crowds www.sfgate.com CS61C L5 Memory Management; Intro
inst.eecs.berkeley.edu/~cs61c CS61C : Machine Structures Lecture #5 Memory Management; Intro MIPS 2007-7-2 Scott Beamer, Instructor iphone Draws Crowds www.sfgate.com CS61C L5 Memory Management; Intro
