Constructors and Destructors. Chapter 6
|
|
|
- Owen Day
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computer and Information, Zagazig University
2 Constructors and Destructors Chapter 6
3 6.1 Introduction Constructors and destructors are member functions of any class. They are automatically called when a class object is created or destroyed, respectively.
4 6.2 Constructor functions The constructor function is executed when a class object is defined. It can be argumentless or with arguments. It should have the following: No return data type, The same name as the class name, An optional initialization list may follow the name and arguments of the constructor, Public declaration within the class.
5 Example: // name.h class name { private: variable declarations public: name(); // constructor }; // name.cpp name::name(arguments):initialization list { statements }
6 Example: //declaration within a class account class account { public: account(); }; //definition in a cpp source file account::account():balance(0.0),accountnumber(-1) {}
7 Example: // declaration within a class account account(float newbalance=0.0,int newaccount=-1); // definition in a cpp source file account::account(float newbalance, int newaccount) : Balance(newBalance), AccountNumber(newAccount) {}
8 Example // test.h class test { private: float a; float b; public: test(float a=0,float b=0); }; // test.cpp #include "test.h #include <iostream.h> test::test(float c, float d):a(c),b(d) { cout << "a = "<<a<<endl; cout << "b = "<<b<<endl; }
9 // main.cpp #include "test.h #include <iostream.h> main(){ test obj1; test obj2(1); test obj3(1,1); return; }
10 6.3 Dynamic Memory Allocation Pointers in C++ // definition of a pointer to int int * IntPointer; int Integer_variable; Integer_variable=5; IntPointer=& Integer_variable; cout << "the address of integer variable is "<< IntPointer<< "but the quantity of this variable is "<<*IntPointer;
11 The new operator The way of declaring and assigning value and memory locations to pointers in the previous example is static. To declare and assign values and memory locations to pointers dynamically the new operator should be used. Example: float * RealPointer = new float; int * IntPointer = new int(24); *RealPointer = 3.34; cout << "pointer: "<< RealPointer << " ; value: "<< *RealPointer << endl; cout << " Pointer: "<< IntPointer << " ; value: "<< *IntPointer <<endl; In this example, RealPointer is assigned an address of a location in memory that is reserved for a float number. Also, IntPointer is assigned an address of a location in memory that is reserved for an int number whose value is 24.
12 Dynamic allocation of arrays int * IntArray = new int[100]; This statement reserves a memory space for 100 int values and returns the address of the first memory location to be assigned to IntArray. It is equivalent to: // static definition int IntArray[100]; but the size of the array can be a variable determined during program running in the dynamic memory assignment. Arrays can be initialized statically but not dynamically. int Num[10]={1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
13 6.4 Argument passing in function calls Passing by value /*definition of a function that receives its arguments by value.*/ int IntFunction(int Arg1, float Arg2) { } /*function calling for passing variables by value.*/ ReturnInt=IntFunction(Int1,Float2);
14 Passing by reference There are two ways for passing arguments by reference: int RefFunction(int &Arg1, float &Arg2){ } ReturnInt=RefFunction(Int1, Float2); Or int PointerFunction(int *Arg1, float *Arg2){ } ReturnInt=PointerFunction(&Int1, &Float2); The second way is clearer and more understandable from code. Passing variable by reference saves memory and time but requires attention about accessing the variables.
15 The const keyword Defining a constant int variable. const int Num = 10; Defining read only variables in a function. int ConstArgs(const int &Arg1,const float &Arg2){ }
16 6.5 Destructors It is necessary to release any memory allocated using the new operator. This can be done using the C++ delete keyword. This process could be done in the destructor function of every class.
17 Example: class Atm { private: variable declarations public: atm(); ~atm(); }; atm::atm() { int * intpointer=new int[10]; } atm::~atm() { delete [] intpointer; }
18 A destructor function: has no return type, takes no arguments, The operand of the delete keyword must be a pointer.
19 6.6 Function and operator overloading Object Oriented Programming (OOP) and its implementation with C++ allow the programmer to define several functions and operators that have the same names but do different tasks. These functions and operators should have the same return type but different argument list (either in the number or the type of arguments or both). This OOP feature is called function and operator overloading.
20 Example: the overloaded assignment (=) operator // main.cpp int main() { atm Atm1,Atm2; Atm1=Atm2; }
21 // atm.h class atm { public: atm operator = (const atm & sourceatm); };
22 // atm.cpp atm atm::operator=(const atm& SourceAtm) { if (this == &SourceAtm) return (*this); if (NumAccounts!= SourceAtm.NumAccounts) { cout «"Error in assignment: different array sizes.\n"; return 0; } else { EnteredCode = SourceAtm.EnteredCode; CardCode = SourceAtm.CardCode; for (int i = 0; i < NumAccounts; i++) Account[i] = SourceAtm.Account[i]; return (*this); } }
Object Oriented Programming CS250
 Object Oriented Programming CS250 Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computers & Informatics, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg Object Oriented Programming Principles
Object Oriented Programming CS250 Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computers & Informatics, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg Object Oriented Programming Principles
Object-Oriented Programming. Chapter 4
 Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computer and Information, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Object-Oriented Programming Chapter
Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computer and Information, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Object-Oriented Programming Chapter
Stacks and Queues. Chapter 8 (Cont.)
 Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computer and Information, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Stacks and Queues Chapter 8 (Cont.)
Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computer and Information, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Stacks and Queues Chapter 8 (Cont.)
KOM3191 Object Oriented Programming Dr Muharrem Mercimek OPERATOR OVERLOADING. KOM3191 Object-Oriented Programming
 KOM3191 Object Oriented Programming Dr Muharrem Mercimek 1 OPERATOR OVERLOADING KOM3191 Object-Oriented Programming KOM3191 Object Oriented Programming Dr Muharrem Mercimek 2 Dynamic Memory Management
KOM3191 Object Oriented Programming Dr Muharrem Mercimek 1 OPERATOR OVERLOADING KOM3191 Object-Oriented Programming KOM3191 Object Oriented Programming Dr Muharrem Mercimek 2 Dynamic Memory Management
Data Structures and Algorithms. Chapter 1
 Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computer and Information, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Data Structures and Algorithms
Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computer and Information, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Data Structures and Algorithms
3.Constructors and Destructors. Develop cpp program to implement constructor and destructor.
 3.Constructors and Destructors Develop cpp program to implement constructor and destructor. Constructors A constructor is a special member function whose task is to initialize the objects of its class.
3.Constructors and Destructors Develop cpp program to implement constructor and destructor. Constructors A constructor is a special member function whose task is to initialize the objects of its class.
Lecture-5. Miscellaneous topics Templates. W3101: Programming Languages C++ Ramana Isukapalli
 Lecture-5 Miscellaneous topics Templates W3101: Programming Languages C++ Miscellaneous topics Miscellaneous topics const member functions, const arguments Function overloading and function overriding
Lecture-5 Miscellaneous topics Templates W3101: Programming Languages C++ Miscellaneous topics Miscellaneous topics const member functions, const arguments Function overloading and function overriding
Review: C++ Basic Concepts. Dr. Yingwu Zhu
 Review: C++ Basic Concepts Dr. Yingwu Zhu Outline C++ class declaration Constructor Overloading functions Overloading operators Destructor Redundant declaration A Real-World Example Question #1: How to
Review: C++ Basic Concepts Dr. Yingwu Zhu Outline C++ class declaration Constructor Overloading functions Overloading operators Destructor Redundant declaration A Real-World Example Question #1: How to
THE NAME OF THE CONSTRUCTOR AND DESTRUCTOR(HAVING (~) BEFORE ITS NAME) FUNCTION MUST BE SAME AS THE NAME OF THE CLASS IN WHICH THEY ARE DECLARED.
 Constructor and Destructor Member Functions Constructor: - Constructor function gets invoked automatically when an object of a class is constructed (declared). Destructor:- A destructor is a automatically
Constructor and Destructor Member Functions Constructor: - Constructor function gets invoked automatically when an object of a class is constructed (declared). Destructor:- A destructor is a automatically
Constructors.
 Constructors Initializing New Objects Fraction g(4, 5); Initializing New Objects Fraction g(4, 5); Initializing New Objects Fraction g(4, 5); Initializing New Objects Fraction g(4, 5); Initializing New
Constructors Initializing New Objects Fraction g(4, 5); Initializing New Objects Fraction g(4, 5); Initializing New Objects Fraction g(4, 5); Initializing New Objects Fraction g(4, 5); Initializing New
Passing arguments to functions by. const member functions const arguments to a function. Function overloading and overriding Templates
 Lecture-4 Inheritance review. Polymorphism Virtual functions Abstract classes Passing arguments to functions by Value, pointers, refrence const member functions const arguments to a function Function overloading
Lecture-4 Inheritance review. Polymorphism Virtual functions Abstract classes Passing arguments to functions by Value, pointers, refrence const member functions const arguments to a function Function overloading
Searching Algorithms. Chapter 11
 Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computer and Information, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Searching Algorithms Chapter 11
Data Structures Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computer and Information, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Searching Algorithms Chapter 11
CS201- Introduction to Programming Current Quizzes
 CS201- Introduction to Programming Current Quizzes Q.1 char name [] = Hello World ; In the above statement, a memory of characters will be allocated 13 11 12 (Ans) Q.2 A function is a block of statements
CS201- Introduction to Programming Current Quizzes Q.1 char name [] = Hello World ; In the above statement, a memory of characters will be allocated 13 11 12 (Ans) Q.2 A function is a block of statements
Intermediate Programming & Design (C++) Classes in C++
 Classes in C++ A class is a data type similar to a C structure. It includes various local data (called data members) together with constructors, destructors and member functions. All of them are called
Classes in C++ A class is a data type similar to a C structure. It includes various local data (called data members) together with constructors, destructors and member functions. All of them are called
C++ 8. Constructors and Destructors
 8. Constructors and Destructors C++ 1. When an instance of a class comes into scope, the function that executed is. a) Destructors b) Constructors c) Inline d) Friend 2. When a class object goes out of
8. Constructors and Destructors C++ 1. When an instance of a class comes into scope, the function that executed is. a) Destructors b) Constructors c) Inline d) Friend 2. When a class object goes out of
SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR
 SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & APPLICATIONS QUESTION BANK (2017-2018) Course / Branch : M.Sc CST Semester / Year : EVEN / II Subject Name
SRM ARTS AND SCIENCE COLLEGE SRM NAGAR, KATTANKULATHUR 603203 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & APPLICATIONS QUESTION BANK (2017-2018) Course / Branch : M.Sc CST Semester / Year : EVEN / II Subject Name
Midterm Review. PIC 10B Spring 2018
 Midterm Review PIC 10B Spring 2018 Q1 What is size t and when should it be used? A1 size t is an unsigned integer type used for indexing containers and holding the size of a container. It is guarenteed
Midterm Review PIC 10B Spring 2018 Q1 What is size t and when should it be used? A1 size t is an unsigned integer type used for indexing containers and holding the size of a container. It is guarenteed
Intermediate Programming, Spring 2017*
 600.120 Intermediate Programming, Spring 2017* Misha Kazhdan *Much of the code in these examples is not commented because it would otherwise not fit on the slides. This is bad coding practice in general
600.120 Intermediate Programming, Spring 2017* Misha Kazhdan *Much of the code in these examples is not commented because it would otherwise not fit on the slides. This is bad coding practice in general
EINDHOVEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mathematics and Computer Science
 EINDHOVEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Written examination Homologation C++ and Computer Organization (2DMW00) Part I: C++ - on Tuesday, November 1st 2016, 9:00h-12:00h.
EINDHOVEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Written examination Homologation C++ and Computer Organization (2DMW00) Part I: C++ - on Tuesday, November 1st 2016, 9:00h-12:00h.
Constructor - example
 Constructors A constructor is a special member function whose task is to initialize the objects of its class. It is special because its name is same as the class name. The constructor is invoked whenever
Constructors A constructor is a special member function whose task is to initialize the objects of its class. It is special because its name is same as the class name. The constructor is invoked whenever
CISC 2200 Data Structure Fall, C++ Review:3/3. 1 From last lecture:
 CISC 2200 Data Structure Fall, 2016 C++ Review:3/3 1 From last lecture: pointer type and pointer variable (stores memory addresses of a variable (of any type, local or global, automatic/static/dynamic)
CISC 2200 Data Structure Fall, 2016 C++ Review:3/3 1 From last lecture: pointer type and pointer variable (stores memory addresses of a variable (of any type, local or global, automatic/static/dynamic)
Short Notes of CS201
 #includes: Short Notes of CS201 The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with < and > if the file is a system
#includes: Short Notes of CS201 The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with < and > if the file is a system
Exam 3 Chapters 7 & 9
 Exam 3 Chapters 7 & 9 CSC 2100-002/003 29 Mar 2017 Read through the entire test first BEFORE starting Put your name at the TOP of every page The test has 4 sections worth a total of 100 points o True/False
Exam 3 Chapters 7 & 9 CSC 2100-002/003 29 Mar 2017 Read through the entire test first BEFORE starting Put your name at the TOP of every page The test has 4 sections worth a total of 100 points o True/False
C++_ MARKS 40 MIN
 C++_16.9.2018 40 MARKS 40 MIN https://tinyurl.com/ya62ayzs 1) Declaration of a pointer more than once may cause A. Error B. Abort C. Trap D. Null 2Whice is not a correct variable type in C++? A. float
C++_16.9.2018 40 MARKS 40 MIN https://tinyurl.com/ya62ayzs 1) Declaration of a pointer more than once may cause A. Error B. Abort C. Trap D. Null 2Whice is not a correct variable type in C++? A. float
CS201 - Introduction to Programming Glossary By
 CS201 - Introduction to Programming Glossary By #include : The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with
CS201 - Introduction to Programming Glossary By #include : The #include directive instructs the preprocessor to read and include a file into a source code file. The file name is typically enclosed with
CS304 Object Oriented Programming Final Term
 1. Which of the following is the way to extract common behaviour and attributes from the given classes and make a separate class of those common behaviours and attributes? Generalization (pg 29) Sub-typing
1. Which of the following is the way to extract common behaviour and attributes from the given classes and make a separate class of those common behaviours and attributes? Generalization (pg 29) Sub-typing
Page. No. 1/15 CS201 Introduction to Programmming Solved Subjective Questions From spring 2010 Final Term Papers By vuzs Team
 Page. No. 1/15 CS201 Introduction to Programmming Solved Subjective Questions From spring 2010 Final Term Papers By vuzs Team Question No: 1 ( Marks: 2 ) Write a declaration statement for an array of 10
Page. No. 1/15 CS201 Introduction to Programmming Solved Subjective Questions From spring 2010 Final Term Papers By vuzs Team Question No: 1 ( Marks: 2 ) Write a declaration statement for an array of 10
UEE1303(1070) S12: Object-Oriented Programming Advanced Topics of Class
 UEE1303(1070) S12: Object-Oriented Programming Advanced Topics of Class What you will learn from Lab 6 In this laboratory, you will learn the advance topics of object-oriented programming using class.
UEE1303(1070) S12: Object-Oriented Programming Advanced Topics of Class What you will learn from Lab 6 In this laboratory, you will learn the advance topics of object-oriented programming using class.
(5 2) Introduction to Classes in C++ Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 7, 2018) Washington State University
 (5 2) Introduction to Classes in C++ Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 7, 2018) Washington State University Key Concepts Function templates Defining classes with member functions The Rule
(5 2) Introduction to Classes in C++ Instructor - Andrew S. O Fallon CptS 122 (February 7, 2018) Washington State University Key Concepts Function templates Defining classes with member functions The Rule
Abstract Data Types (ADT) and C++ Classes
 Abstract Data Types (ADT) and C++ Classes 1-15-2013 Abstract Data Types (ADT) & UML C++ Class definition & implementation constructors, accessors & modifiers overloading operators friend functions HW#1
Abstract Data Types (ADT) and C++ Classes 1-15-2013 Abstract Data Types (ADT) & UML C++ Class definition & implementation constructors, accessors & modifiers overloading operators friend functions HW#1
Object Oriented Programming. Assistant Lecture Omar Al Khayat 2 nd Year
 Object Oriented Programming Assistant Lecture Omar Al Khayat 2 nd Year Syllabus Overview of C++ Program Principles of object oriented programming including classes Introduction to Object-Oriented Paradigm:Structures
Object Oriented Programming Assistant Lecture Omar Al Khayat 2 nd Year Syllabus Overview of C++ Program Principles of object oriented programming including classes Introduction to Object-Oriented Paradigm:Structures
Chapter 10 Pointers and Dynamic Arrays. GEDB030 Computer Programming for Engineers Fall 2017 Euiseong Seo
 Chapter 10 Pointers and Dynamic Arrays 1 Learning Objectives Pointers Pointer variables Memory management Dynamic Arrays Creating and using Pointer arithmetic Classes, Pointers, Dynamic Arrays The this
Chapter 10 Pointers and Dynamic Arrays 1 Learning Objectives Pointers Pointer variables Memory management Dynamic Arrays Creating and using Pointer arithmetic Classes, Pointers, Dynamic Arrays The this
public : int min, hour ; T( ) //here constructor is defined inside the class definition, as line function. { sec = min = hour = 0 ; }
 . CONSTRUCTOR If the name of the member function of a class and the name of class are same, then the member function is called constructor. Constructors are used to initialize the object of that class
. CONSTRUCTOR If the name of the member function of a class and the name of class are same, then the member function is called constructor. Constructors are used to initialize the object of that class
Object Oriented Programming. Solved MCQs - Part 2
 Object Oriented Programming Solved MCQs - Part 2 Object Oriented Programming Solved MCQs - Part 2 It is possible to declare as a friend A member function A global function A class All of the above What
Object Oriented Programming Solved MCQs - Part 2 Object Oriented Programming Solved MCQs - Part 2 It is possible to declare as a friend A member function A global function A class All of the above What
Example : class Student { int rollno; float marks; public: student( ) //Constructor { rollno=0; marks=0.0; } //other public members };
 Constructors A Member function with the same name as its classis called Constructor and it is used to initilize the objects of that class type with a legal value. A Constructor is a special member function
Constructors A Member function with the same name as its classis called Constructor and it is used to initilize the objects of that class type with a legal value. A Constructor is a special member function
Quiz Start Time: 09:34 PM Time Left 82 sec(s)
 Quiz Start Time: 09:34 PM Time Left 82 sec(s) Question # 1 of 10 ( Start time: 09:34:54 PM ) Total Marks: 1 While developing a program; should we think about the user interface? //handouts main reusability
Quiz Start Time: 09:34 PM Time Left 82 sec(s) Question # 1 of 10 ( Start time: 09:34:54 PM ) Total Marks: 1 While developing a program; should we think about the user interface? //handouts main reusability
Introduction Of Classes ( OOPS )
 Introduction Of Classes ( OOPS ) Classes (I) A class is an expanded concept of a data structure: instead of holding only data, it can hold both data and functions. An object is an instantiation of a class.
Introduction Of Classes ( OOPS ) Classes (I) A class is an expanded concept of a data structure: instead of holding only data, it can hold both data and functions. An object is an instantiation of a class.
Engineering Problem Solving with C++, 3e Chapter 2 Test Bank
 1. Match each of the following data types with literal constants of that data type. A data type can be used more than once. A. integer B 1.427E3 B. double D "Oct" C. character B -63.29 D. string F #Hashtag
1. Match each of the following data types with literal constants of that data type. A data type can be used more than once. A. integer B 1.427E3 B. double D "Oct" C. character B -63.29 D. string F #Hashtag
POLYMORPHISM 2 PART. Shared Interface. Discussions. Abstract Base Classes. Abstract Base Classes and Pure Virtual Methods EXAMPLE
 Abstract Base Classes POLYMORPHISM 2 PART Abstract Classes Static and Dynamic Casting Common Programming Errors class B { // base class virtual void m( ) =0; // pure virtual function class D1 : public
Abstract Base Classes POLYMORPHISM 2 PART Abstract Classes Static and Dynamic Casting Common Programming Errors class B { // base class virtual void m( ) =0; // pure virtual function class D1 : public
 POINTERS - Pointer is a variable that holds a memory address of another variable of same type. - It supports dynamic allocation routines. - It can improve the efficiency of certain routines. C++ Memory
POINTERS - Pointer is a variable that holds a memory address of another variable of same type. - It supports dynamic allocation routines. - It can improve the efficiency of certain routines. C++ Memory
CS201 Latest Solved MCQs
 Quiz Start Time: 09:34 PM Time Left 82 sec(s) Question # 1 of 10 ( Start time: 09:34:54 PM ) Total Marks: 1 While developing a program; should we think about the user interface? //handouts main reusability
Quiz Start Time: 09:34 PM Time Left 82 sec(s) Question # 1 of 10 ( Start time: 09:34:54 PM ) Total Marks: 1 While developing a program; should we think about the user interface? //handouts main reusability
POLYMORPHISM 2 PART Abstract Classes Static and Dynamic Casting Common Programming Errors
 POLYMORPHISM 2 PART Abstract Classes Static and Dynamic Casting Common Programming Errors CSC 330 OO Software Design 1 Abstract Base Classes class B { // base class virtual void m( ) =0; // pure virtual
POLYMORPHISM 2 PART Abstract Classes Static and Dynamic Casting Common Programming Errors CSC 330 OO Software Design 1 Abstract Base Classes class B { // base class virtual void m( ) =0; // pure virtual
Makefiles Makefiles should begin with a comment section of the following form and with the following information filled in:
 CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II C++ Programming Style Guideline Most of a programmer's efforts are aimed at the development of correct and efficient programs. But the readability of programs is also
CS 215 Fundamentals of Programming II C++ Programming Style Guideline Most of a programmer's efforts are aimed at the development of correct and efficient programs. But the readability of programs is also
More About Classes. Gaddis Ch. 14, CS 2308 :: Fall 2015 Molly O'Neil
 More About Classes Gaddis Ch. 14, 13.3 CS 2308 :: Fall 2015 Molly O'Neil Pointers to Objects Just like pointers to structures, we can define pointers to objects Time t1(12, 20, true); Time *tptr; tptr
More About Classes Gaddis Ch. 14, 13.3 CS 2308 :: Fall 2015 Molly O'Neil Pointers to Objects Just like pointers to structures, we can define pointers to objects Time t1(12, 20, true); Time *tptr; tptr
Chapter 10. Pointers and Dynamic Arrays. Copyright 2016 Pearson, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 10 Pointers and Dynamic Arrays Copyright 2016 Pearson, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives Pointers Pointer variables Memory management Dynamic Arrays Creating and using Pointer arithmetic
Chapter 10 Pointers and Dynamic Arrays Copyright 2016 Pearson, Inc. All rights reserved. Learning Objectives Pointers Pointer variables Memory management Dynamic Arrays Creating and using Pointer arithmetic
Initializing and Finalizing Objects
 4 Initializing and Finalizing Objects 147 Content Initializing and Finalizing Objects 4 Constructors Default Constructor Copy Constructor Destructor 148 Initializing Objects: Constructors Initializing
4 Initializing and Finalizing Objects 147 Content Initializing and Finalizing Objects 4 Constructors Default Constructor Copy Constructor Destructor 148 Initializing Objects: Constructors Initializing
CS201 Some Important Definitions
 CS201 Some Important Definitions For Viva Preparation 1. What is a program? A program is a precise sequence of steps to solve a particular problem. 2. What is a class? We write a C++ program using data
CS201 Some Important Definitions For Viva Preparation 1. What is a program? A program is a precise sequence of steps to solve a particular problem. 2. What is a class? We write a C++ program using data
Function Overloading
 Function Overloading C++ supports writing more than one function with the same name but different argument lists How does the compiler know which one the programmer is calling? They have different signatures
Function Overloading C++ supports writing more than one function with the same name but different argument lists How does the compiler know which one the programmer is calling? They have different signatures
Object-Oriented Programming, Iouliia Skliarova
 Object-Oriented Programming, Iouliia Skliarova CBook a = CBook("C++", 2014); CBook b = CBook("Physics", 1960); a.display(); b.display(); void CBook::Display() cout
Object-Oriented Programming, Iouliia Skliarova CBook a = CBook("C++", 2014); CBook b = CBook("Physics", 1960); a.display(); b.display(); void CBook::Display() cout
CS250 Final Review Questions
 CS250 Final Review Questions The following is a list of review questions that you can use to study for the final. I would first make sure you review all previous exams and make sure you fully understand
CS250 Final Review Questions The following is a list of review questions that you can use to study for the final. I would first make sure you review all previous exams and make sure you fully understand
Come and join us at WebLyceum
 Come and join us at WebLyceum For Past Papers, Quiz, Assignments, GDBs, Video Lectures etc Go to http://www.weblyceum.com and click Register In Case of any Problem Contact Administrators Rana Muhammad
Come and join us at WebLyceum For Past Papers, Quiz, Assignments, GDBs, Video Lectures etc Go to http://www.weblyceum.com and click Register In Case of any Problem Contact Administrators Rana Muhammad
IS0020 Program Design and Software Tools Midterm, Fall, 2004
 IS0020 Program Design and Software Tools Midterm, Fall, 2004 Name: Instruction There are two parts in this test. The first part contains 22 questions worth 40 points you need to get 20 right to get the
IS0020 Program Design and Software Tools Midterm, Fall, 2004 Name: Instruction There are two parts in this test. The first part contains 22 questions worth 40 points you need to get 20 right to get the
AN OVERVIEW OF C++ 1
 AN OVERVIEW OF C++ 1 OBJECTIVES Introduction What is object-oriented programming? Two versions of C++ C++ console I/O C++ comments Classes: A first look Some differences between C and C++ Introducing function
AN OVERVIEW OF C++ 1 OBJECTIVES Introduction What is object-oriented programming? Two versions of C++ C++ console I/O C++ comments Classes: A first look Some differences between C and C++ Introducing function
cout << "How many numbers would you like to type? "; cin >> memsize; p = new int[memsize];
![cout << How many numbers would you like to type? ; cin >> memsize; p = new int[memsize]; cout << How many numbers would you like to type? ; cin >> memsize; p = new int[memsize];](/thumbs/77/75038547.jpg) 1 C++ Dynamic Allocation Memory needs were determined before program execution by defining the variables needed. Sometime memory needs of a program can only be determined during runtime, or the memory
1 C++ Dynamic Allocation Memory needs were determined before program execution by defining the variables needed. Sometime memory needs of a program can only be determined during runtime, or the memory
Chapter 13: Introduction to Classes Procedural and Object-Oriented Programming
 Chapter 13: Introduction to Classes 1 13.1 Procedural and Object-Oriented Programming 2 Procedural and Object-Oriented Programming Procedural programming focuses on the process/actions that occur in a
Chapter 13: Introduction to Classes 1 13.1 Procedural and Object-Oriented Programming 2 Procedural and Object-Oriented Programming Procedural programming focuses on the process/actions that occur in a
class Array; // Class template declaration class Array public: // T="type",e.g.,int or float Array(int n); // Create array of n elements Array(); // C
 LECTURE 5 Templates We have written a simple array class of oat variables. But suppose we want to have arrays of integers, or doubles, or something else. It's a pain to write a separate array class for
LECTURE 5 Templates We have written a simple array class of oat variables. But suppose we want to have arrays of integers, or doubles, or something else. It's a pain to write a separate array class for
Polymorphism. Zimmer CSCI 330
 Polymorphism Polymorphism - is the property of OOP that allows the run-time binding of a function's name to the code that implements the function. (Run-time binding to the starting address of the code.)
Polymorphism Polymorphism - is the property of OOP that allows the run-time binding of a function's name to the code that implements the function. (Run-time binding to the starting address of the code.)
Module 1. C++ Classes Exercises
 Module 1. C++ Classes Exercises 1. The ZooAnimal class definition below is missing a prototype for the Create function. It should have parameters so that a character string and three integer values (in
Module 1. C++ Classes Exercises 1. The ZooAnimal class definition below is missing a prototype for the Create function. It should have parameters so that a character string and three integer values (in
Classes and Objects. Class scope: - private members are only accessible by the class methods.
 Class Declaration Classes and Objects class class-tag //data members & function members ; Information hiding in C++: Private Used to hide class member data and methods (implementation details). Public
Class Declaration Classes and Objects class class-tag //data members & function members ; Information hiding in C++: Private Used to hide class member data and methods (implementation details). Public
Distributed Real-Time Control Systems. Lecture 17 C++ Programming Intro to C++ Objects and Classes
 Distributed Real-Time Control Systems Lecture 17 C++ Programming Intro to C++ Objects and Classes 1 Bibliography Classical References Covers C++ 11 2 What is C++? A computer language with object oriented
Distributed Real-Time Control Systems Lecture 17 C++ Programming Intro to C++ Objects and Classes 1 Bibliography Classical References Covers C++ 11 2 What is C++? A computer language with object oriented
Come and join us at WebLyceum
 Come and join us at WebLyceum For Past Papers, Quiz, Assignments, GDBs, Video Lectures etc Go to http://www.weblyceum.com and click Register In Case of any Problem Contact Administrators Rana Muhammad
Come and join us at WebLyceum For Past Papers, Quiz, Assignments, GDBs, Video Lectures etc Go to http://www.weblyceum.com and click Register In Case of any Problem Contact Administrators Rana Muhammad
COMS W3101 Programming Language: C++ (Fall 2016) Ramana Isukapalli
 COMS W3101 Programming Language: C++ (Fall 2016) ramana@cs.columbia.edu Lecture-2 Overview of C C++ Functions Structures Pointers Design, difference with C Concepts of Object oriented Programming Concept
COMS W3101 Programming Language: C++ (Fall 2016) ramana@cs.columbia.edu Lecture-2 Overview of C C++ Functions Structures Pointers Design, difference with C Concepts of Object oriented Programming Concept
14.1. Chapter 14: static member variable. Instance and Static Members 8/23/2014. Instance and Static Members
 Chapter 14: More About Classes 14.1 Instance and Static Members Instance and Static Members instance variable: a member variable in a class. Each object has its own copy. static variable: one variable
Chapter 14: More About Classes 14.1 Instance and Static Members Instance and Static Members instance variable: a member variable in a class. Each object has its own copy. static variable: one variable
C++ (Non for C Programmer) (BT307) 40 Hours
 C++ (Non for C Programmer) (BT307) 40 Hours Overview C++ is undoubtedly one of the most widely used programming language for implementing object-oriented systems. The C++ language is based on the popular
C++ (Non for C Programmer) (BT307) 40 Hours Overview C++ is undoubtedly one of the most widely used programming language for implementing object-oriented systems. The C++ language is based on the popular
CMSC202 Computer Science II for Majors
 CMSC202 Computer Science II for Majors Lecture 17 and 18 Bits & Pieces and Templates Dr. Katherine Gibson Last Class We Covered Error handling Exceptions Try Throw Catch Went over Exam 2 2 Any Questions
CMSC202 Computer Science II for Majors Lecture 17 and 18 Bits & Pieces and Templates Dr. Katherine Gibson Last Class We Covered Error handling Exceptions Try Throw Catch Went over Exam 2 2 Any Questions
CS250 Final Review Questions
 CS250 Final Review Questions The following is a list of review questions that you can use to study for the final. I would first make sure you review all previous exams and make sure you fully understand
CS250 Final Review Questions The following is a list of review questions that you can use to study for the final. I would first make sure you review all previous exams and make sure you fully understand
Faculty of Information and Communication Technologies
 Swinburne University Of Technology Faculty of Information and Communication Technologies ASSIGNMENT COVER SHEET Subject Code: Subject Title: Assignment number and title: Due date: Lecturer: HIT3303 Data
Swinburne University Of Technology Faculty of Information and Communication Technologies ASSIGNMENT COVER SHEET Subject Code: Subject Title: Assignment number and title: Due date: Lecturer: HIT3303 Data
! A class in C++ is similar to a structure. ! A class contains members: - variables AND. - public: accessible outside the class.
 Classes and Objects Week 5 Gaddis:.2-.12 14.3-14.4 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman The Class! A class in C++ is similar to a structure.! A class contains members: - variables AND - functions (often called
Classes and Objects Week 5 Gaddis:.2-.12 14.3-14.4 CS 5301 Spring 2015 Jill Seaman The Class! A class in C++ is similar to a structure.! A class contains members: - variables AND - functions (often called
1. Match each of the following data types with literal constants of that data type. A data type can be used more than once. A.
 Engineering Problem Solving With C++ 4th Edition Etter TEST BANK Full clear download (no error formating) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/engineering-problem-solving-with-c-4thedition-etter-test-bank/
Engineering Problem Solving With C++ 4th Edition Etter TEST BANK Full clear download (no error formating) at: https://testbankreal.com/download/engineering-problem-solving-with-c-4thedition-etter-test-bank/
C++ Review. CptS 223 Advanced Data Structures. Larry Holder School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University
 C++ Review CptS 223 Advanced Data Structures Larry Holder School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University 1 Purpose of Review Review some basic C++ Familiarize us with
C++ Review CptS 223 Advanced Data Structures Larry Holder School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University 1 Purpose of Review Review some basic C++ Familiarize us with
CSCE 110 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS
 CSCE 110 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS WITH C++ Prof. Amr Goneid AUC Part 15. Dictionaries (1): A Key Table Class Prof. amr Goneid, AUC 1 Dictionaries(1): A Key Table Class Prof. Amr Goneid, AUC 2 A Key Table
CSCE 110 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS WITH C++ Prof. Amr Goneid AUC Part 15. Dictionaries (1): A Key Table Class Prof. amr Goneid, AUC 1 Dictionaries(1): A Key Table Class Prof. Amr Goneid, AUC 2 A Key Table
C:\Temp\Templates. Download This PDF From The Web Site
 11 2 2 2 3 3 3 C:\Temp\Templates Download This PDF From The Web Site 4 5 Use This Main Program Copy-Paste Code From The Next Slide? Compile Program 6 Copy/Paste Main # include "Utilities.hpp" # include
11 2 2 2 3 3 3 C:\Temp\Templates Download This PDF From The Web Site 4 5 Use This Main Program Copy-Paste Code From The Next Slide? Compile Program 6 Copy/Paste Main # include "Utilities.hpp" # include
Solved Exercises from exams: Midterm(1)
 Solved Exercises from exams: Midterm(1) 1431-1432 1. What is the output of the following program: #include void fun(int *b) *b = *b+10; main() int a=50; fun(&a); cout
Solved Exercises from exams: Midterm(1) 1431-1432 1. What is the output of the following program: #include void fun(int *b) *b = *b+10; main() int a=50; fun(&a); cout
Recap: Pointers. int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff
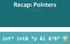 Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
Recap: Pointers IFMP 18, M. Schwerhoff int* int& *p &i &*&* ** * * * * A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i int* p; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5 5 i p int* p; p = &i; A 0 A 1 A 2 A 3 A 4 A 5
OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING. Ms. Ajeta Nandal C.R.Polytechnic,Rohtak
 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING Ms. Ajeta Nandal C.R.Polytechnic,Rohtak OBJECT ORIENTED PARADIGM Object 2 Object 1 Data Data Function Function Object 3 Data Function 2 WHAT IS A MODEL? A model is an abstraction
OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING Ms. Ajeta Nandal C.R.Polytechnic,Rohtak OBJECT ORIENTED PARADIGM Object 2 Object 1 Data Data Function Function Object 3 Data Function 2 WHAT IS A MODEL? A model is an abstraction
2 2
 1 2 2 3 3 C:\Temp\Templates 4 5 Use This Main Program 6 # include "Utilities.hpp" # include "Student.hpp" Copy/Paste Main void MySwap (int Value1, int Value2); int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { int A
1 2 2 3 3 C:\Temp\Templates 4 5 Use This Main Program 6 # include "Utilities.hpp" # include "Student.hpp" Copy/Paste Main void MySwap (int Value1, int Value2); int main(int argc, char * argv[]) { int A
Introduction to C++ Friends, Nesting, Static Members, and Templates Topic #7
 Introduction to C++ Friends, Nesting, Static Members, and Templates Topic #7 CS202 7-1 Relationship of Objects Friends, Nesting Static Members Template Functions and Classes Reusing Code Template Specializations
Introduction to C++ Friends, Nesting, Static Members, and Templates Topic #7 CS202 7-1 Relationship of Objects Friends, Nesting Static Members Template Functions and Classes Reusing Code Template Specializations
21. Exceptions. Advanced Concepts: // exceptions #include <iostream> using namespace std;
 - 147 - Advanced Concepts: 21. Exceptions Exceptions provide a way to react to exceptional circumstances (like runtime errors) in our program by transferring control to special functions called handlers.
- 147 - Advanced Concepts: 21. Exceptions Exceptions provide a way to react to exceptional circumstances (like runtime errors) in our program by transferring control to special functions called handlers.
Topics. Constructor. Constructors
 Topics 1) How can we initialize an object when it's created? 2) How can we do things when an object is destroyed? 3) How can we write functions with different parameters? Slides #11 - Text 7.6-7.7 Constructors
Topics 1) How can we initialize an object when it's created? 2) How can we do things when an object is destroyed? 3) How can we write functions with different parameters? Slides #11 - Text 7.6-7.7 Constructors
6.096 Introduction to C++ January (IAP) 2009
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.096 Introduction to C++ January (IAP) 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Welcome to 6.096 Lecture
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 6.096 Introduction to C++ January (IAP) 2009 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. Welcome to 6.096 Lecture
Object oriented programming with C++
 http://uranchimeg.com/ Object oriented programming with C++ T.Uranchimeg Prof. Dr. Email uranchimeg@must.edu.mn Power Engineering School M.EC203* -- OOP (C++) -- Lecture 10 Subjects Overloading operators
http://uranchimeg.com/ Object oriented programming with C++ T.Uranchimeg Prof. Dr. Email uranchimeg@must.edu.mn Power Engineering School M.EC203* -- OOP (C++) -- Lecture 10 Subjects Overloading operators
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 13
 G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 13 Dr Jason Atkin http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~jaa/cpp/ g52cpp.html 1 Last lecture Function pointers Arrays of function pointers Virtual and non-virtual functions vtable and
G52CPP C++ Programming Lecture 13 Dr Jason Atkin http://www.cs.nott.ac.uk/~jaa/cpp/ g52cpp.html 1 Last lecture Function pointers Arrays of function pointers Virtual and non-virtual functions vtable and
OOP THROUGH C++(R16) int *x; float *f; char *c;
 What is pointer and how to declare it? Write the features of pointers? A pointer is a memory variable that stores the address of another variable. Pointer can have any name that is legal for other variables,
What is pointer and how to declare it? Write the features of pointers? A pointer is a memory variable that stores the address of another variable. Pointer can have any name that is legal for other variables,
the gamedesigninitiative at cornell university Lecture 7 C++ Overview
 Lecture 7 Lecture 7 So You Think You Know C++ Most of you are experienced Java programmers Both in 2110 and several upper-level courses If you saw C++, was likely in a systems course Java was based on
Lecture 7 Lecture 7 So You Think You Know C++ Most of you are experienced Java programmers Both in 2110 and several upper-level courses If you saw C++, was likely in a systems course Java was based on
CS304 Object Oriented Programming
 1 CS304 Object Oriented Programming 1. Which of the following is the way to extract common behaviour and attributes from the given classes and make a separate class of those common behaviours and attributes?
1 CS304 Object Oriented Programming 1. Which of the following is the way to extract common behaviour and attributes from the given classes and make a separate class of those common behaviours and attributes?
Programming, numerics and optimization
 Programming, numerics and optimization Lecture A-4: Object-oriented programming Łukasz Jankowski ljank@ippt.pan.pl Institute of Fundamental Technological Research Room 4.32, Phone +22.8261281 ext. 428
Programming, numerics and optimization Lecture A-4: Object-oriented programming Łukasz Jankowski ljank@ippt.pan.pl Institute of Fundamental Technological Research Room 4.32, Phone +22.8261281 ext. 428
Financial computing with C++
 Financial Computing with C++, Lecture 4 - p1/19 Financial computing with C++ LG Gyurkó University of Oxford Michaelmas Term 2015 Financial Computing with C++, Lecture 4 - p2/19 Outline General properties
Financial Computing with C++, Lecture 4 - p1/19 Financial computing with C++ LG Gyurkó University of Oxford Michaelmas Term 2015 Financial Computing with C++, Lecture 4 - p2/19 Outline General properties
CMPT 117: Tutorial 1. Craig Thompson. 12 January 2009
 CMPT 117: Tutorial 1 Craig Thompson 12 January 2009 Administrivia Coding habits OOP Header Files Function Overloading Class info Tutorials Review of course material additional examples Q&A Labs Work on
CMPT 117: Tutorial 1 Craig Thompson 12 January 2009 Administrivia Coding habits OOP Header Files Function Overloading Class info Tutorials Review of course material additional examples Q&A Labs Work on
C++ PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE: DYNAMIC MEMORY ALLOCATION AND EXCEPTION IN C++. CAAM 519, CHAPTER 15
 C++ PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE: DYNAMIC MEMORY ALLOCATION AND EXCEPTION IN C++. CAAM 519, CHAPTER 15 This chapter introduces the notion of dynamic memory allocation of variables and objects in a C++ program.
C++ PROGRAMMING LANGUAGE: DYNAMIC MEMORY ALLOCATION AND EXCEPTION IN C++. CAAM 519, CHAPTER 15 This chapter introduces the notion of dynamic memory allocation of variables and objects in a C++ program.
Lab 2: ADT Design & Implementation
 Lab 2: ADT Design & Implementation By Dr. Yingwu Zhu, Seattle University 1. Goals In this lab, you are required to use a dynamic array to design and implement an ADT SortedList that maintains a sorted
Lab 2: ADT Design & Implementation By Dr. Yingwu Zhu, Seattle University 1. Goals In this lab, you are required to use a dynamic array to design and implement an ADT SortedList that maintains a sorted
CSE 303: Concepts and Tools for Software Development
 CSE 303: Concepts and Tools for Software Development Hal Perkins Autumn 2008 Lecture 24 Introduction to C++ CSE303 Autumn 2008, Lecture 24 1 C++ C++ is an enormous language: All of C Classes and objects
CSE 303: Concepts and Tools for Software Development Hal Perkins Autumn 2008 Lecture 24 Introduction to C++ CSE303 Autumn 2008, Lecture 24 1 C++ C++ is an enormous language: All of C Classes and objects
Dynamic Data Structures
 Dynamic Data Structures We have seen that the STL containers vector, deque, list, set and map can grow and shrink dynamically. We now examine how some of these containers can be implemented in C++. To
Dynamic Data Structures We have seen that the STL containers vector, deque, list, set and map can grow and shrink dynamically. We now examine how some of these containers can be implemented in C++. To
What does it mean by information hiding? What are the advantages of it? {5 Marks}
 SECTION ONE (COMPULSORY) Question #1 [30 Marks] a) Describe the main characteristics of object-oriented programming. {5 Marks Encapsulation the ability to define a new type and a set of operations on that
SECTION ONE (COMPULSORY) Question #1 [30 Marks] a) Describe the main characteristics of object-oriented programming. {5 Marks Encapsulation the ability to define a new type and a set of operations on that
内存管理. Memory management
 内存管理 Memory management Review: Constructors Method that is called when an instance is created class Integer { public: int val; Integer() { val = 0; cout
内存管理 Memory management Review: Constructors Method that is called when an instance is created class Integer { public: int val; Integer() { val = 0; cout
Constructors & Destructors
 Constructors & Destructors Constructor It is a member function which initializes a class. A constructor has: (i) the same name as the class itself (ii) no return type class rectangle private: float height;
Constructors & Destructors Constructor It is a member function which initializes a class. A constructor has: (i) the same name as the class itself (ii) no return type class rectangle private: float height;
ADTs & Classes. An introduction
 ADTs & Classes An introduction Quick review of OOP Object: combination of: data structures (describe object attributes) functions (describe object behaviors) Class: C++ mechanism used to represent an object
ADTs & Classes An introduction Quick review of OOP Object: combination of: data structures (describe object attributes) functions (describe object behaviors) Class: C++ mechanism used to represent an object
CSC 330 Object-Oriented Programming. Exception Handling CSC 330
 Object-Oriented Programming Exception Handling 1 C++ Exception Handling Topics Exception Handling C++ Exception Handling Basics Throwing and Catching Exceptions Constructors, Destructors and Exceptions
Object-Oriented Programming Exception Handling 1 C++ Exception Handling Topics Exception Handling C++ Exception Handling Basics Throwing and Catching Exceptions Constructors, Destructors and Exceptions
And Even More and More C++ Fundamentals of Computer Science
 And Even More and More C++ Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline C++ Classes Special Members Friendship Classes are an expanded version of data structures (structs) Like structs, the hold data members
And Even More and More C++ Fundamentals of Computer Science Outline C++ Classes Special Members Friendship Classes are an expanded version of data structures (structs) Like structs, the hold data members
Comp151. Inheritance: Initialization & Substitution Principle
 Comp151 Inheritance: Initialization & Substitution Principle Initializing Base Class Objects If class C is derived from class B which is in turn derived from class A, then C will contain data members of
Comp151 Inheritance: Initialization & Substitution Principle Initializing Base Class Objects If class C is derived from class B which is in turn derived from class A, then C will contain data members of
W3101: Programming Languages C++ Ramana Isukapalli
 Lecture-6 Operator overloading Namespaces Standard template library vector List Map Set Casting in C++ Operator Overloading Operator overloading On two objects of the same class, can we perform typical
Lecture-6 Operator overloading Namespaces Standard template library vector List Map Set Casting in C++ Operator Overloading Operator overloading On two objects of the same class, can we perform typical
