Prepared By:- Dinesh Sharma Asstt. Professor, CSE & IT Deptt. ITM Gurgaon
|
|
|
- Bruno Powers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Data Structures &Al Algorithms Prepared By:- Dinesh Sharma Asstt. Professor, CSE & IT Deptt. ITM Gurgaon
2 What is Data Structure Data Structure is a logical relationship existing between individual elements of data the logical or mathematical model of a particular organization of data is called "Data Structure". A means of storing collection of data. It is the specification of the elements of the structure, the relationship between them, and the operations that may be performed on them.
3 Data Structure Continued... Data may be organized in many different ways; The choice of a particular data model depends on two considerations: 1. It must be rich enough in structure to reflect the actual relationships of the data in the real world. 2. The structure should be simple enough that one can effectively ec eyprocess the data a when necessary. Algorithm + Data structure Program
4 Classification of Data Structure Data Structure Primitive Data Structure Non primitive data structure integer Float Character Pointer Array Lists Files Linear List Non linear List Stacks Queues Graphs Trees
5 Classification of Data Structure Primitive Data Structure: These are Basic structures and are directly operated upon by machine instuructions, Have different representation on different computers. Examples : Real, Float, integer, character, pointer etc.
6 Classification of Data Structure Non primitive Data Structures: These are more sophisticated data structures. they are derived from the primitive data structure. The non primitive data structure emphasize on structuring of a group of homogeneous or heterogeneous data items. Examples: Arrays, List and Files.
7 Operations on Data Structures The particular data structure t thatt one chooses for a given situation depends largely on the nature of specific operations to be performed. The following are the four major operations associated with any data structure: 1. Traversing 2. Searching 3. Insertion 4. Deletion 5. Sorting 6. Merging
8 Operations on Data Structure Traversing : Accessing each record exactly once so that certain items in the record may be processed. Searching : Finding the location of the record with a given key value, or finding the locations of all records which satisfy one or more conditions. Inserting : Adding a new record to the structure. Deleting : Removing a record from the structure. Sorting : Arranging the record in some logical order. Merging : Combining the records in two sorted files into a single file.
9 Abstract Data Type ADT is a mathematically specified entity that defines a set of its instances, with: A specific interface a collection of signatures of operations, that can be invoked on an instance. A set of axioms (preconditions & Postconditions) that defines the semantics of operation(i.ee what the operations do to instances of ADT, not how)
10 Abstract Data Types Types of Operations: Constructors Manipulation Procedures Access Functions
11 Abstract Data Type Why do we need to talk about ADT in data structure??? They serve as specifications of requirements for the building blocks of solution to algorithmic problems. Provides a language to talk of on a higher level of abstraction. ADT s encapsulate data structures and Algorithms that implement them. Separates the issues of correctness and efficiency.
12 Memory Allocation in C There are two types of memory allocation possible in C language 1. Compile time/static 2. Run-time/Dynamic
13 Memory Allocation in C C provides four dynamic allocation and de-allocation functions: 1. Malloc() 2. Calloc() 3. Free() 4. Realloc()
14 Memory Allocation in C Malloc() Eg int ptr; Calloc() eg Free() Realloc() Ptr=(int *)malloc(10*sizeof(int)) int *ptr; ptr=(int *)calloc(10,2); Eg free(ptr) Eg ptr=realloc(ptr,new_size)
15 Example to show use of Malloc() Void main() { } int *ptr, I,n; printf( enter no of element u want to store in array ); Scanf( %d,&n) ptr=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*n); n); printf( \n Enter the elements ); For(i=0;i<n;i++) scanf( %d,ptr+i); printf( u have entered\n ); for(i=0;i<n;i++) printf( %d \t,*(ptr+i)); getch();
16 Stacks Non primitive linear data structure
17 Stacks Outline Stacks Definition Basic Stack Operations Array Implementation of Stacks
18 What is a stack? It is an ordered group of homogeneous items of elements. Elements are added to and removed from the top of the stack (the most recently added items are at the top of the stack). The last element to be added is the first to be removed (LIFO: Last In, First Out).
19 BASIC STACK OPERATIONS 1. Push(): the process of adding a new element to the top of the stack is called PUSH operation. 2. POP(): the process of deleting an element from the top of the stack is called pop operation.
20 Stack Terminology Overflow: This is the situation when stack becomes full and no more elements can be pushed on to the stacks. at this point the stack top is present at the highest location of the stack. Underflow: When stack contains no element. The TOP is present at the bottom of the stack.
21 Stack Terminology TOP: this term refers to the top of the stack. The stack TOP is used to check stack overflow and underflow. Initially the TOP stores -1. We use this term to refer to the maximum size of the stack. MAXSIZE:
22 Array Implementation of the Stacks The stacks can be implemented by the use of arrays and linked lists. One way to implement the stack is to have a data structure where a variable called top keeps the location of the elements in the stack (array) An array is used to store the elements in the stack
23 Stacks
24 Push Operation Push an item onto the top of the stack (insert an item)
25 Pop operation Pop an item off the top of the stack (delete an item)
26 Function To Implement PUSH() void push() { int pushed_item; if(top == (MAX-1)) printf("stack Overflow\n"); else { printf("enter t the item to be pushed in stack : "); scanf("%d",&pushed_item); top=top+1; top+1; stack_arr[top] = pushed_item; } }/*End of push()*/
27 Function to implement POP() void pop() { if(top == -1) printf("stack Underflow\n"); else { printf("popped element is : %d\n",stack_arr[top]); top=top-1; } }/*End of pop()*/
28 Function to display the Stack elements void display() { int i; if(top == -1) printf("stack is empty\n"); else { printf("stack elements :\n"); for(i = top; i >=0; i--) printf("%d\n", stack_arr[i] ); } }/*End of display()*/
29 Main Program in C #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> #define MAX 5 int top = -1; int stack_arr[max]; main() { int choice; while(1) { printf("1.push\n"); printf("2.pop\n"); printf("3.display\n"); printf("4.quit\n"); it\ ") printf("enter your choice : "); scanf("%d",&choice); switch(choice) { case 1 : push(); break; case 2: pop(); break; case 3: display(); break; case 4: exit(1); default: printf("wrong choice\n"); }/*End of switch*/ }/*End of while*/ }/*End of main()*/
30 EXAMPLE The following program implements stack of size 10 using array representation. The 10 elements entered by the user are pushed into the stack and then the elements are popped back and displayed.
31 #include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> #define STACKSIZE 10 typedef struct{ int count; int top; int items[stacksize]; /*stack can contain up to 10 integers*/ }STACK; void push(stack *, int); int pop(stack *); int main() { int p, i; STACK s; s.top = -1; /*indicates that the stack is empty at the beginning*/ s.count = 0; /* 0 items are in the stack*/
32 /*reading and pushing items into the stack*/ printf("enter the %d stack items\n",stacksize); for(i=0;i<= i< STACKSIZE-1;i++){ scanf("%d",&p); push(&s,p); } /*popping and printing the items in the stack*/ printf("\n\nstack contains the following items\n"); for(i=0;i<= STACKSIZE-1;i++){ p=pop(&s); pop(&s); printf("%d\t",p); } return 0; }
33 void push(stack *Sptr, int ps) /*pushes ps into stack*/ { if(sptr->top == STACKSIZE-1){ printf("stack is full\n"); printf("there are %d items in the stack\n", Sptr- >count); return; /*return back to main function*/ } else { Sptr->top++; Sptr->items[Sptr->top]= ps; Sptr->count++; } }
34 int pop(stack *Sptr) { int pp; if(sptr->top == -1){ printf("stack is empty\n"); return -1 /*exit from the function*/ } else { pp = Sptr->items[Sptr->top]; Sptr->top--; } } Sptr->count--; return pp;
35 void display() { int i; if(top == -1) printf("stack is empty\n"); else { printf("stack elements :\n"); for(i = top; i >=0; i--) printf("%d\n", stack_arr[i] ); } }/*End of display()*/
36 Applications Of Stack
37 Problems That Uses Stack The runtime stack used by a process (running program) to keep track of methods in progress Search problems Undo, redo, back, forward
38 Problems That Uses Stack Contd... Recursion Reversing R i A string Calculation of a Postfix Expression.
39 Types of Notations Infix Notation eg e.g A+B Prefix Notation(Polish notation) e.g +AB Postfix P Notation ti (Reverse( Polish Notation) e.g AB+
40 Advantages of Postfix Notation No parenthesis required Simple Algo to evaluate a postfix expression No need to remember precedence and associativity rules of various operators.
41 Infix to Postfix Conversion Q 1 A+B/C-D Ans: Step 1: A+(BC/)-D Step 2: A+T-D Step 3: (A+T)-D Step 4: (AT+)- D Step 5: S D Step 6: SD- Step 7: AT+D- Step 8: ABC/+D- Q 2 (A+B) * C/D Ans: Step 1: (AB+) * C/D Step 2: T* C/D Step 3: (T*C)/D Step 4: (TC*)/D Step 5: S/D Step 6: SD/ Step 7: TC*D/ Step 8: AB+C*D/
42 Algo: Postfix(Q, P) [Suppose Q is an arithmatic expression written in infix notation. This algo finds the equivalent postfix expression P] 1. Push ( on to the stack and add ) to the end of expression. 2. Scan Q from left to right,repeat step 3 to 6 untill stack is empty 3. If operend ADD it to P 4. If (, push it onto thestack. 5. If operator then 1. Repeatedly pop from stack and add P each operator that has the same precedence or higher precedence then the operator encountered. 2. Add operator to stack 6. If ) then 7. Exit (a) Pop from stack and add to P each operator untill a left parenthesis is encountered. (b) remove left parenthesis.
43 Convert A+B/C D to postfix Sr. Symbol Stack Postfix No scanned Expr 1 ( 2 A ( A 3 + ( + A 4 B (+ AB 5 / ( + / AB 6 C ( +/ ABC 7 - ( - ABC / + 8 D ( - ABC/ + D 9 ) ABC/ + D -
44 Exercise Covert the following infix expression to Postfix. Show the Contents of the stack at various steps: P= A+(B * C-( D / E^F) * G ) * H
45 Evaluation of Postfix Expression Algo: [To evaluate a Postfix expression] 1. Add a right parenthesis ) at the end of P. 2. Scan P from left to right and repeat step 3 to 6 untill ) is encountered. 3. If an operend is encountered, put it on the stack. 4. If operator is encountered a) Pop top two elements from the stack A,B b) Evaluate A op B c) Push the result of(b) back on the stack (end of if) (end of step 2 loop) 5. Set value equal to the top element of the stack. 6. Exit.
46 Binary Search The binary search algorithm is naturally recursive. That is, the action that we perform on the original list is the very same as the action that we perform on the sublists. As a consequence, it is very easy to write a recursive binary search function.
47 Binary Search Binary search uses a recursive method to search an array to find a specified value The array must be asorted array: a[0] a[1] a[2]... a[finalindex] If the value is found, its index is returned If the value is not found, -1 is returned Note: Each execution of the recursive method reduces the search space by about a half
48 Binary Search An algorithm to solve this task looks at the middle of the array or array segment first If the value looked for is smaller than the value in the middle of the array Then the second half of the array or array segment can be ignored This strategy is then applied to the first half of the array or array segment
49 Binary Search If the value looked for is larger than the value in the middle of the array or array segment Then the first half of the arrayor array segment can be ignored This strategy is then applied to the second half of This strategy is then applied to the second half of the array or array segment If the value looked for is at the middle of the array or array segment, then it has been found If the entire array (or array segment) has been searched in this way without finding the value, then it is not in the array
50 Binary search Algo 1. [initialize i i variables] Set beg=0,end=ub, mid=(beg+end)/2 2. Repeat 3 and 4 while(beg<=end) and a[mid]!=item. 3. If(item<a[mid]) Set end=mid-1; Else Set beg-mid+1 4. Set mid=int(beg+end)/2 5. if(a[mid]==item) Set loc=mid Else loc=null 6. Exit
51 Iterative Binary Search #include<stdio.h> #include<conio.h> void main() { int a[10],item,beg,end; end; Int n,loc,mid,i,f=0; clrscr(); printf("enter the array size"); scanf("%d",&n); printf("\n enter array elements"); for(i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); printf("\n eneter item to be searched"); scanf("%d",&item); loc=0;beg=0;end=n-1; while((beg<=end)&&(a[mid]!=item)) { mid=(beg+end)/2; if (item==a[mid]) { loc=mid; f=1; printf("\n element found at position %d",loc+1); break; } else if(item< a[mid]) end=mid-1; else beg=mid+1; } if(f==0) printf("element not found"); getch(); }
52 Execution of Binary search
53 Execution of Binary search
54 BinarySearch(int a[], int value, int left, int right) { // See if the search has failed if (left > right) return 1; // See if the value is in the first half int middle = (left + right)/2; if (value < a[middle]) return BinarySearch(a, value, left, middle 1); // See if the value is in the second half else if (value > a[middle]) return BinarySearch(a, value, middle + 1, right); // The value has been found elsemiddle; }
55 Recursive Binary Search In C int bsearch(int a[ ], Int lb, I nt ub, int item) { int mid; if(lb>ub) return(-1); mid=(int) (lb+ub)/2; if(a[mid]==item) return(mid); if(a[mid]>item) bsearch(a,lb,mid-1,item); 1item); else bsearch(a,mid+1,ub,item);,, return; }
56 Binary Search in C void main() { int n,i,item,loc; int a[10]; printf("enter the size of array"); scanf("%d",&n); printf("\n enter elements"); for(i=0;i<n;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]); printf("\nenter item to be searched"); scanf("%d",&item); loc= bsearch(a,0,n- 1,item); if( loc<0) printf("element not found"); else printf("element found at location %d",loc); getch(); }
57 Array Representation in Memory 1. Row Major Representation 2. Column Major Representation
58 Composites: Arrays Implementation: ti 2D array (1) Storage Layout var A : array[l 1..U 1 ] of [L 2..U 2 ] of T (a) ROW-Major Layout A[L 1 ] A[L 1 +1]... A[U 1 ] [L 2 ] [L 2 +1] [L 2 +2]... [U 2-1] [U 2 ] Memory is a contiguous block Base 58
59 Composites: Arrays Implementation: 2D array (1) Storage Layout (b) COLUMN-Major Layout var A : array[l 1..U 1 ] of [L 2..U 2 ] of T A[L 1 ] A[L 1 +1]... A[U 1 ] [L 2 ] [L 2 +1] [L 2 +2]... [U 2-1] [U 2 ] Base Memory is a contiguous block 59
60 Row Major representation Address of A[i][j]= B + W(n(i-l1)+(j-l2)) Where B base address W size of each array element N number of columns(u2-l2+1)
61 Implementation: 2D array (2) Operation: Array subscripting. Eg. ROW-major j Layout var A : array[l 1..U 1 ] of [L 2..U 2 ] of T A[L 1 ] A[L 1 +1]... A[U 1 ] 1 [L 2 ] [L 2 +1] [L 2 +2]... [U 2-1] [U 2 ] Memory is a contiguous block Base address Skip # of rows row size Skip # of L-value of A[i,j] + (i-l 1 1) )*(U( 2 -L 2 +1)*cellsize ) + (j-l 2 )*cellsize Go to the correct row Go to the correct 61 cell
62 Example: Given Array Int a[4..7,-1..3]. Calculate the address of element at location a[6][[2]. Given that base address is 100. Base address B=100 Size of each array element n=2 Lower bound of row L1=4 Lower bound of column L2=-1 Upper bound of row U1=7 Upper bound of row U2=3 i=6, j=2 N=u2-l2+1 Address of A[i][j]= B + W(n(i-L1)+(j-L2)) ANS=?????
63 Queries
64
The program simply pushes all of the characters of the string into the stack. Then it pops and display until the stack is empty.
 EENG212 Algorithms & Data Structures Fall 0/07 Lecture Notes # Outline Stacks Application of Stacks Reversing a String Palindrome Example Infix, Postfix and Prefix Notations APPLICATION OF STACKS Stacks
EENG212 Algorithms & Data Structures Fall 0/07 Lecture Notes # Outline Stacks Application of Stacks Reversing a String Palindrome Example Infix, Postfix and Prefix Notations APPLICATION OF STACKS Stacks
STACKS 3.1 INTRODUCTION 3.2 DEFINITION
 STACKS 3 3.1 INTRODUCTION A stack is a linear data structure. It is very useful in many applications of computer science. It is a list in which all insertions and deletions are made at one end, called
STACKS 3 3.1 INTRODUCTION A stack is a linear data structure. It is very useful in many applications of computer science. It is a list in which all insertions and deletions are made at one end, called
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit 3
 Linear and Non-Linear Data Structures Linear data structure: Linear data structures are those data structure in which data items are arranged in a linear sequence by physically or logically or both the
Linear and Non-Linear Data Structures Linear data structure: Linear data structures are those data structure in which data items are arranged in a linear sequence by physically or logically or both the
MODULE V: POINTERS & PREPROCESSORS
 MODULE V: POINTERS & PREPROCESSORS INTRODUCTION As you know, every variable is a memory-location and every memory-location has its address defined which can be accessed using ampersand(&) operator, which
MODULE V: POINTERS & PREPROCESSORS INTRODUCTION As you know, every variable is a memory-location and every memory-location has its address defined which can be accessed using ampersand(&) operator, which
Guide for The C Programming Language Chapter 5
 1. Differentiate between primitive data type and non-primitive data type. Primitive data types are the basic data types. These data types are used to represent single values. For example: Character, Integer,
1. Differentiate between primitive data type and non-primitive data type. Primitive data types are the basic data types. These data types are used to represent single values. For example: Character, Integer,
UNIT 2: STACK & RECURSION Programs demonstrated in class. Tojo Mathew Asst. Professor CSE Dept., NIE Mysuru.
 UNIT 2: STACK & RECURSION Programs demonstrated in class. Tojo Mathew Asst. Professor CSE Dept., NIE Mysuru. Table of Contents 1. C Program to Check for balanced parenthesis by using Stacks...3 2. Program
UNIT 2: STACK & RECURSION Programs demonstrated in class. Tojo Mathew Asst. Professor CSE Dept., NIE Mysuru. Table of Contents 1. C Program to Check for balanced parenthesis by using Stacks...3 2. Program
Data Structures Week #3. Stacks
 Data Structures Week #3 Stacks Outline Stacks Operations on Stacks Array Implementation of Stacks Linked List Implementation of Stacks Stack Applications October 5, 2015 Borahan Tümer, Ph.D. 2 Stacks (Yığınlar)
Data Structures Week #3 Stacks Outline Stacks Operations on Stacks Array Implementation of Stacks Linked List Implementation of Stacks Stack Applications October 5, 2015 Borahan Tümer, Ph.D. 2 Stacks (Yığınlar)
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in themodel answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in themodel answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate may
NCS 301 DATA STRUCTURE USING C
 NCS 301 Data Structure Using C NCS 301 DATA STRUCTURE USING C Unit-1 Part-1 Intro to Data Structures Hammad Mashkoor Lari Assistant Professor Allenhouse Institute of Technolgy www.ncs301ds.wordpress.com
NCS 301 Data Structure Using C NCS 301 DATA STRUCTURE USING C Unit-1 Part-1 Intro to Data Structures Hammad Mashkoor Lari Assistant Professor Allenhouse Institute of Technolgy www.ncs301ds.wordpress.com
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 18 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure using C Model wer Subject Code: 22317 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given
WINTER 18 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure using C Model wer Subject Code: 22317 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given
NCS 301 DATA STRUCTURE USING C
 NCS Data Structure Using C -8- NCS DATA STRUCTURE USING C Unit- Part- Stack Hammad Mashkoor Lari Assistant Professor Allenhouse Institute of Technology www.ncsds.wordpress.com Introduction Stack is a non
NCS Data Structure Using C -8- NCS DATA STRUCTURE USING C Unit- Part- Stack Hammad Mashkoor Lari Assistant Professor Allenhouse Institute of Technology www.ncsds.wordpress.com Introduction Stack is a non
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 18 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure Model wer Subject Code: 17330 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in
WINTER 18 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure Model wer Subject Code: 17330 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in
 Class / Sem: I CSE / II Semester Subject Code: CS 6202 Subject: Programming and Data Structures I Prepared by T. Vithya Unit IV - LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES STACKS AND QUEUES Stack ADT Evaluating arithmetic
Class / Sem: I CSE / II Semester Subject Code: CS 6202 Subject: Programming and Data Structures I Prepared by T. Vithya Unit IV - LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES STACKS AND QUEUES Stack ADT Evaluating arithmetic
CSE101-lec#19. Array searching and sorting techniques. Created By: Amanpreet Kaur & Sanjeev Kumar SME (CSE) LPU. LPU CSE101 C Programming
 CSE101-lec#19 Array searching and sorting techniques Created By: Amanpreet Kaur & Sanjeev Kumar SME (CSE) LPU Outline Introduction Linear search Binary search Bubble sort Introduction The process of finding
CSE101-lec#19 Array searching and sorting techniques Created By: Amanpreet Kaur & Sanjeev Kumar SME (CSE) LPU Outline Introduction Linear search Binary search Bubble sort Introduction The process of finding
Linked List in Data Structure. By Prof. B J Gorad, BECSE, M.Tech CST, PHD(CSE)* Assistant Professor, CSE, SITCOE, Ichalkaranji,Kolhapur, Maharashtra
 Linked List in Data Structure By Prof. B J Gorad, BECSE, M.Tech CST, PHD(CSE)* Assistant Professor, CSE, SITCOE, Ichalkaranji,Kolhapur, Maharashtra Linked List Like arrays, Linked List is a linear data
Linked List in Data Structure By Prof. B J Gorad, BECSE, M.Tech CST, PHD(CSE)* Assistant Professor, CSE, SITCOE, Ichalkaranji,Kolhapur, Maharashtra Linked List Like arrays, Linked List is a linear data
Types of Data Structures
 DATA STRUCTURES material prepared by: MUKESH BOHRA Follow me on FB : http://www.facebook.com/mukesh.sirji4u The logical or mathematical model of data is called a data structure. In other words, a data
DATA STRUCTURES material prepared by: MUKESH BOHRA Follow me on FB : http://www.facebook.com/mukesh.sirji4u The logical or mathematical model of data is called a data structure. In other words, a data
VTU NOTES QUESTION PAPERS NEWS RESULTS FORUMS THE STACK
 Contents: Definition and Examples Representing stacks in C Example: infix, prefix, and postfix Exercises THE STACK Definition and Examples A stack is an ordered collection of items into which new items
Contents: Definition and Examples Representing stacks in C Example: infix, prefix, and postfix Exercises THE STACK Definition and Examples A stack is an ordered collection of items into which new items
Some Applications of Stack. Spring Semester 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1
 Some Applications of Stack Spring Semester 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1 Arithmetic Expressions Polish Notation Spring Semester 2007 Programming and Data Structure 2 What is Polish Notation? Conventionally,
Some Applications of Stack Spring Semester 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1 Arithmetic Expressions Polish Notation Spring Semester 2007 Programming and Data Structure 2 What is Polish Notation? Conventionally,
Lecture Data Structure Stack
 Lecture Data Structure Stack 1.A stack :-is an abstract Data Type (ADT), commonly used in most programming languages. It is named stack as it behaves like a real-world stack, for example a deck of cards
Lecture Data Structure Stack 1.A stack :-is an abstract Data Type (ADT), commonly used in most programming languages. It is named stack as it behaves like a real-world stack, for example a deck of cards
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified) WINTER 16 EXAMINATION Model Answer Subject Code:
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
1 P a g e A r y a n C o l l e g e \ B S c _ I T \ C \
 BSc IT C Programming (2013-2017) Unit I Q1. What do you understand by type conversion? (2013) Q2. Why we need different data types? (2013) Q3 What is the output of the following (2013) main() Printf( %d,
BSc IT C Programming (2013-2017) Unit I Q1. What do you understand by type conversion? (2013) Q2. Why we need different data types? (2013) Q3 What is the output of the following (2013) main() Printf( %d,
Linked List. April 2, 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1
 Linked List April 2, 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1 Introduction head A linked list is a data structure which can change during execution. Successive elements are connected by pointers. Last element
Linked List April 2, 2007 Programming and Data Structure 1 Introduction head A linked list is a data structure which can change during execution. Successive elements are connected by pointers. Last element
The time and space are the two measure for efficiency of an algorithm.
 There are basically six operations: 5. Sorting: Arranging the elements of list in an order (either ascending or descending). 6. Merging: combining the two list into one list. Algorithm: The time and space
There are basically six operations: 5. Sorting: Arranging the elements of list in an order (either ascending or descending). 6. Merging: combining the two list into one list. Algorithm: The time and space
MAHARASHTRA STATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 WINTER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure Using C Model Answer Subject Code: 17330 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
WINTER 17 EXAMINATION Subject Name: Data Structure Using C Model Answer Subject Code: 17330 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as
Application of Stack (Backtracking)
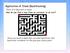 Application of Stack (Backtracking) Think of a labyrinth or maze How do you find a way from an entrance to an exit? Once you reach a dead end, you must backtrack. But backtrack to where? to the previous
Application of Stack (Backtracking) Think of a labyrinth or maze How do you find a way from an entrance to an exit? Once you reach a dead end, you must backtrack. But backtrack to where? to the previous
Stack. 4. In Stack all Operations such as Insertion and Deletion are permitted at only one end. Size of the Stack 6. Maximum Value of Stack Top 5
 What is Stack? Stack 1. Stack is LIFO Structure [ Last in First Out ] 2. Stack is Ordered List of Elements of Same Type. 3. Stack is Linear List 4. In Stack all Operations such as Insertion and Deletion
What is Stack? Stack 1. Stack is LIFO Structure [ Last in First Out ] 2. Stack is Ordered List of Elements of Same Type. 3. Stack is Linear List 4. In Stack all Operations such as Insertion and Deletion
An array is a collection of similar elements that is all the elements in an array should have same data type. This means that an array can store
 An array is a collection of similar elements that is all the elements in an array should have same data type. This means that an array can store either all integers, all floating point numbers, all characters,
An array is a collection of similar elements that is all the elements in an array should have same data type. This means that an array can store either all integers, all floating point numbers, all characters,
Revision Statement while return growth rate asymptotic notation complexity Compare algorithms Linear search Binary search Preconditions: sorted,
 [1] Big-O Analysis AVERAGE(n) 1. sum 0 2. i 0. while i < n 4. number input_number(). sum sum + number 6. i i + 1 7. mean sum / n 8. return mean Revision Statement no. of times executed 1 1 2 1 n+1 4 n
[1] Big-O Analysis AVERAGE(n) 1. sum 0 2. i 0. while i < n 4. number input_number(). sum sum + number 6. i i + 1 7. mean sum / n 8. return mean Revision Statement no. of times executed 1 1 2 1 n+1 4 n
Bangalore South Campus
 USN: 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before ElectronicCity, Bengaluru -100 Department of Basic Science and Humanities INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Date: 22/11/2017 Time:11:30am- 1.00 pm
USN: 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before ElectronicCity, Bengaluru -100 Department of Basic Science and Humanities INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 3 Date: 22/11/2017 Time:11:30am- 1.00 pm
Introduction. Problem Solving on Computer. Data Structures (collection of data and relationships) Algorithms
 Introduction Problem Solving on Computer Data Structures (collection of data and relationships) Algorithms 1 Objective of Data Structures Two Goals: 1) Identify and develop useful high-level data types
Introduction Problem Solving on Computer Data Structures (collection of data and relationships) Algorithms 1 Objective of Data Structures Two Goals: 1) Identify and develop useful high-level data types
Stacks, Queues (cont d)
 Stacks, Queues (cont d) CSE 2011 Winter 2007 February 1, 2007 1 The Adapter Pattern Using methods of one class to implement methods of another class Example: using List to implement Stack and Queue 2 1
Stacks, Queues (cont d) CSE 2011 Winter 2007 February 1, 2007 1 The Adapter Pattern Using methods of one class to implement methods of another class Example: using List to implement Stack and Queue 2 1
STACKS. A stack is defined in terms of its behavior. The common operations associated with a stack are as follows:
 STACKS A stack is a linear data structure for collection of items, with the restriction that items can be added one at a time and can only be removed in the reverse order in which they were added. The
STACKS A stack is a linear data structure for collection of items, with the restriction that items can be added one at a time and can only be removed in the reverse order in which they were added. The
A. Year / Module Semester Subject Topic 2016 / V 2 PCD Pointers, Preprocessors, DS
 Syllabus: Pointers and Preprocessors: Pointers and address, pointers and functions (call by reference) arguments, pointers and arrays, address arithmetic, character pointer and functions, pointers to pointer,initialization
Syllabus: Pointers and Preprocessors: Pointers and address, pointers and functions (call by reference) arguments, pointers and arrays, address arithmetic, character pointer and functions, pointers to pointer,initialization
DEEPIKA KAMBOJ UNIT 2. What is Stack?
 What is Stack? UNIT 2 Stack is an important data structure which stores its elements in an ordered manner. You must have seen a pile of plates where one plate is placed on top of another. Now, when you
What is Stack? UNIT 2 Stack is an important data structure which stores its elements in an ordered manner. You must have seen a pile of plates where one plate is placed on top of another. Now, when you
Linear Data Structure
 Linear Data Structure Definition A data structure is said to be linear if its elements form a sequence or a linear list. Examples: Array Linked List Stacks Queues Operations on linear Data Structures Traversal
Linear Data Structure Definition A data structure is said to be linear if its elements form a sequence or a linear list. Examples: Array Linked List Stacks Queues Operations on linear Data Structures Traversal
C Language Part 2 Digital Computer Concept and Practice Copyright 2012 by Jaejin Lee
 C Language Part 2 (Minor modifications by the instructor) 1 Scope Rules A variable declared inside a function is a local variable Each local variable in a function comes into existence when the function
C Language Part 2 (Minor modifications by the instructor) 1 Scope Rules A variable declared inside a function is a local variable Each local variable in a function comes into existence when the function
Data Structure using C++ Lecture 04. Data Structures and algorithm analysis in C++ Chapter , 3.2, 3.2.1
 Data Structure using C++ Lecture 04 Reading Material Data Structures and algorithm analysis in C++ Chapter. 3 3.1, 3.2, 3.2.1 Summary Stack Operations on a stack Representing stacks Converting an expression
Data Structure using C++ Lecture 04 Reading Material Data Structures and algorithm analysis in C++ Chapter. 3 3.1, 3.2, 3.2.1 Summary Stack Operations on a stack Representing stacks Converting an expression
FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- OCTOBER, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE
 TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- OCTOBER, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours (Maximum marks: 100)
TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- OCTOBER, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours (Maximum marks: 100)
Stacks. CONTENTS 3.1 Introduction 1. Stack as an abstract data type 2. Representation of a Stack as an array 3.2Applications of Stack.
 Stacks CONTENTS 3.1 Introduction 1. Stack as an abstract data type 2. Representation of a Stack as an array 3.2Applications of Stack Hours: 12 Marks: 18 3.1 Introduction to Stacks 1. Stack as Abstract
Stacks CONTENTS 3.1 Introduction 1. Stack as an abstract data type 2. Representation of a Stack as an array 3.2Applications of Stack Hours: 12 Marks: 18 3.1 Introduction to Stacks 1. Stack as Abstract
DATA STRUCTURE : A MCQ QUESTION SET Code : RBMCQ0305
 Q.1 If h is any hashing function and is used to hash n keys in to a table of size m, where n
Q.1 If h is any hashing function and is used to hash n keys in to a table of size m, where n
Formal Languages and Automata Theory, SS Project (due Week 14)
 Formal Languages and Automata Theory, SS 2018. Project (due Week 14) 1 Preliminaries The objective is to implement an algorithm for the evaluation of an arithmetic expression. As input, we have a string
Formal Languages and Automata Theory, SS 2018. Project (due Week 14) 1 Preliminaries The objective is to implement an algorithm for the evaluation of an arithmetic expression. As input, we have a string
Subject: Fundamental of Computer Programming 2068
 Subject: Fundamental of Computer Programming 2068 1 Write an algorithm and flowchart to determine whether a given integer is odd or even and explain it. Algorithm Step 1: Start Step 2: Read a Step 3: Find
Subject: Fundamental of Computer Programming 2068 1 Write an algorithm and flowchart to determine whether a given integer is odd or even and explain it. Algorithm Step 1: Start Step 2: Read a Step 3: Find
Content: Learning Objectives
 1 BLOOM PUBLIC CHOOL Vasant Kunj, New Delhi Lesson Plan Class: XII ubject: Computer cience Month : July No of s: 21 Chapter:Data structure: Linked List TTT: 8 WT: 12 Content: Learning Objectives At the
1 BLOOM PUBLIC CHOOL Vasant Kunj, New Delhi Lesson Plan Class: XII ubject: Computer cience Month : July No of s: 21 Chapter:Data structure: Linked List TTT: 8 WT: 12 Content: Learning Objectives At the
UNIT-2 Stack & Queue
 UNIT-2 Stack & Queue 59 13. Stack A stack is an Abstract Data Type (ADT), commonly used in most programming languages. It is named stack as it behaves like a real-world stack, for example a deck of cards
UNIT-2 Stack & Queue 59 13. Stack A stack is an Abstract Data Type (ADT), commonly used in most programming languages. It is named stack as it behaves like a real-world stack, for example a deck of cards
MODULE 5: Pointers, Preprocessor Directives and Data Structures
 MODULE 5: Pointers, Preprocessor Directives and Data Structures 1. What is pointer? Explain with an example program. Solution: Pointer is a variable which contains the address of another variable. Two
MODULE 5: Pointers, Preprocessor Directives and Data Structures 1. What is pointer? Explain with an example program. Solution: Pointer is a variable which contains the address of another variable. Two
Computer Science BS Degree - Data Structures (I2206) Abstract Data Types (ADT)
 Abstract Data Types (ADT) 70 Hierarchy of types Each type is implemented in terms if the types lower in the hierarchy Level 0 Bit Byte Word Level 1 Integer Real Char Boolean Pointer Level 2 Array Record
Abstract Data Types (ADT) 70 Hierarchy of types Each type is implemented in terms if the types lower in the hierarchy Level 0 Bit Byte Word Level 1 Integer Real Char Boolean Pointer Level 2 Array Record
Outline. Introduction Stack Operations Stack Implementation Implementation of Push and Pop operations Applications. ADT for stacks
 Stack Chapter 4 Outline Introduction Stack Operations Stack Implementation Implementation of Push and Pop operations Applications Recursive Programming Evaluation of Expressions ADT for stacks Introduction
Stack Chapter 4 Outline Introduction Stack Operations Stack Implementation Implementation of Push and Pop operations Applications Recursive Programming Evaluation of Expressions ADT for stacks Introduction
Stacks. stacks of dishes or trays in a cafeteria. Last In First Out discipline (LIFO)
 Outline stacks stack ADT method signatures array stack implementation linked stack implementation stack applications infix, prefix, and postfix expressions 1 Stacks stacks of dishes or trays in a cafeteria
Outline stacks stack ADT method signatures array stack implementation linked stack implementation stack applications infix, prefix, and postfix expressions 1 Stacks stacks of dishes or trays in a cafeteria
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING
 INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch DATA STRUCTURES ACS002 B. Tech
INSTITUTE OF AERONAUTICAL ENGINEERING (Autonomous) Dundigal, Hyderabad - 500 043 COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING TUTORIAL QUESTION BANK Course Name Course Code Class Branch DATA STRUCTURES ACS002 B. Tech
Frequently asked Data Structures Interview Questions
 Frequently asked Data Structures Interview Questions Queues Data Structure Interview Questions How is queue different from a stack? The difference between stacks and queues is in removing. In a stack we
Frequently asked Data Structures Interview Questions Queues Data Structure Interview Questions How is queue different from a stack? The difference between stacks and queues is in removing. In a stack we
FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- MARCH, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours
 TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) (Maximum marks: 100) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- MARCH, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours PART
TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) (Maximum marks: 100) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- MARCH, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours PART
AE52/AC52/AT52 C & Data Structures JUNE 2014
 Q.2 a. Write a program to add two numbers using a temporary variable. #include #include int main () int num1, num2; clrscr (); printf( \n Enter the first number : ); scanf ( %d, &num1);
Q.2 a. Write a program to add two numbers using a temporary variable. #include #include int main () int num1, num2; clrscr (); printf( \n Enter the first number : ); scanf ( %d, &num1);
March 13/2003 Jayakanth Srinivasan,
 Statement Effort MergeSort(A, lower_bound, upper_bound) begin T(n) if (lower_bound < upper_bound) Θ(1) mid = (lower_bound + upper_bound)/ 2 Θ(1) MergeSort(A, lower_bound, mid) T(n/2) MergeSort(A, mid+1,
Statement Effort MergeSort(A, lower_bound, upper_bound) begin T(n) if (lower_bound < upper_bound) Θ(1) mid = (lower_bound + upper_bound)/ 2 Θ(1) MergeSort(A, lower_bound, mid) T(n/2) MergeSort(A, mid+1,
Data Structures. Chapter 06. 3/10/2016 Md. Golam Moazzam, Dept. of CSE, JU
 Data Structures Chapter 06 1 Stacks A stack is a list of elements in which an element may be inserted or deleted only at one end, called the top of the stack. This means that elements are removed from
Data Structures Chapter 06 1 Stacks A stack is a list of elements in which an element may be inserted or deleted only at one end, called the top of the stack. This means that elements are removed from
Outline. Stacks. 1 Chapter 5: Stacks and Queues. favicon. CSI33 Data Structures
 Outline Chapter 5: and Queues 1 Chapter 5: and Queues Chapter 5: and Queues The Stack ADT A Container Class for Last-In-First-Out Access A stack is a last in, first out (LIFO) structure, i.e. a list-like
Outline Chapter 5: and Queues 1 Chapter 5: and Queues Chapter 5: and Queues The Stack ADT A Container Class for Last-In-First-Out Access A stack is a last in, first out (LIFO) structure, i.e. a list-like
Cpt S 122 Data Structures. Data Structures
 Cpt S 122 Data Structures Data Structures Nirmalya Roy School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Topics Introduction Self Referential Structures Dynamic Memory Allocation
Cpt S 122 Data Structures Data Structures Nirmalya Roy School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science Washington State University Topics Introduction Self Referential Structures Dynamic Memory Allocation
DATA STRUCUTRES. A data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently.
 DATA STRUCUTRES A data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. An algorithm, which is a finite sequence of instructions, each of which
DATA STRUCUTRES A data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently. An algorithm, which is a finite sequence of instructions, each of which
Solution for Data Structure
 Solution for Data Structure May 2016 INDEX Q1 a 2-3 b 4 c. 4-6 d 7 Q2- a 8-12 b 12-14 Q3 a 15-18 b 18-22 Q4- a 22-35 B..N.A Q5 a 36-38 b N.A Q6- a 39-42 b 43 1 www.brainheaters.in Q1) Ans: (a) Define ADT
Solution for Data Structure May 2016 INDEX Q1 a 2-3 b 4 c. 4-6 d 7 Q2- a 8-12 b 12-14 Q3 a 15-18 b 18-22 Q4- a 22-35 B..N.A Q5 a 36-38 b N.A Q6- a 39-42 b 43 1 www.brainheaters.in Q1) Ans: (a) Define ADT
CS11001/CS11002 Programming and Data Structures (PDS) (Theory: 3-0-0)
 CS11001/CS11002 Programming and Data Structures (PDS) (Theory: 3-0-0) Class Teacher: Pralay Mitra Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Conceptual Idea
CS11001/CS11002 Programming and Data Structures (PDS) (Theory: 3-0-0) Class Teacher: Pralay Mitra Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur Conceptual Idea
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES
 DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT III LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES PART A 1. What is meant by data
DHANALAKSHMI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING EC6301 OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES UNIT III LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES PART A 1. What is meant by data
Answers. 1. (A) Attempt any five : 20 Marks
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
STACKS AND QUEUES. Problem Solving with Computers-II
 STACKS AND QUEUES Problem Solving with Computers-II 2 Stacks container class available in the C++ STL Container class that uses the Last In First Out (LIFO) principle Methods i. push() ii. iii. iv. pop()
STACKS AND QUEUES Problem Solving with Computers-II 2 Stacks container class available in the C++ STL Container class that uses the Last In First Out (LIFO) principle Methods i. push() ii. iii. iv. pop()
ESC101N: Fundamentals of Computing End-sem st semester
 ESC101N: Fundamentals of Computing End-sem 2010-11 1st semester Instructor: Arnab Bhattacharya 8:00-11:00am, 15th November, 2010 Instructions 1. Please write your name, roll number and section below. 2.
ESC101N: Fundamentals of Computing End-sem 2010-11 1st semester Instructor: Arnab Bhattacharya 8:00-11:00am, 15th November, 2010 Instructions 1. Please write your name, roll number and section below. 2.
Write a C program to add two Complex numbers using functions illustrating-
 Scheme of valuvation Date : 29/8/2017 Marks: 40 Subject & Code : Data Structures and Applications (15CS33) Class : III A&B Name of Faculty : Ms. Saritha Time : 8:30 am to 10 am NOTE: ANSWER All FIVE QUESTIONS
Scheme of valuvation Date : 29/8/2017 Marks: 40 Subject & Code : Data Structures and Applications (15CS33) Class : III A&B Name of Faculty : Ms. Saritha Time : 8:30 am to 10 am NOTE: ANSWER All FIVE QUESTIONS
#06 More Structures LIFO FIFO. Contents. Queue vs. Stack 3. Stack Operations. Pop. Push. Stack Queue Hash table
 Contents #06 More Structures -07 FUNDAMENTAL PROGRAMMING I Stack Queue Hash table DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING, PSU v. Queue vs. Stack Stack Operations IN IN OUT Push: add an item to the top Pop:
Contents #06 More Structures -07 FUNDAMENTAL PROGRAMMING I Stack Queue Hash table DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER ENGINEERING, PSU v. Queue vs. Stack Stack Operations IN IN OUT Push: add an item to the top Pop:
Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis. Lecturer: Souad Alonazi
 Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis Lec(3) Stacks Lecturer: Souad Alonazi What is a stack? Stores a set of elements in a particular order Stack principle: LAST IN FIRST OUT = LIFO It means: the last element
Data Structures & Algorithm Analysis Lec(3) Stacks Lecturer: Souad Alonazi What is a stack? Stores a set of elements in a particular order Stack principle: LAST IN FIRST OUT = LIFO It means: the last element
Downloaded from
 Unit-II Data Structure Arrays, Stacks, Queues And Linked List Chapter: 06 In Computer Science, a data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently.
Unit-II Data Structure Arrays, Stacks, Queues And Linked List Chapter: 06 In Computer Science, a data structure is a particular way of storing and organizing data in a computer so that it can be used efficiently.
Top of the Stack. Stack ADT
 Module 3: Stack ADT Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Stack ADT Features (Logical View) A List that
Module 3: Stack ADT Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Stack ADT Features (Logical View) A List that
Chapter4: Data Structures. Data: It is a collection of raw facts that has implicit meaning.
 Chapter4: s Data: It is a collection of raw facts that has implicit meaning. Data may be single valued like ID, or multi valued like address. Information: It is the processed data having explicit meaning.
Chapter4: s Data: It is a collection of raw facts that has implicit meaning. Data may be single valued like ID, or multi valued like address. Information: It is the processed data having explicit meaning.
Solution: The examples of stack application are reverse a string, post fix evaluation, infix to postfix conversion.
 1. What is the full form of LIFO? The full form of LIFO is Last In First Out. 2. Give some examples for stack application. The examples of stack application are reverse a string, post fix evaluation, infix
1. What is the full form of LIFO? The full form of LIFO is Last In First Out. 2. Give some examples for stack application. The examples of stack application are reverse a string, post fix evaluation, infix
Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms S.GokulaKrishnan B.Tech.,M.Tech.,[Ph.D] Assistant Professor[Stage-I] Department of Computer Science and
![Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms S.GokulaKrishnan B.Tech.,M.Tech.,[Ph.D] Assistant Professor[Stage-I] Department of Computer Science and Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms S.GokulaKrishnan B.Tech.,M.Tech.,[Ph.D] Assistant Professor[Stage-I] Department of Computer Science and](/thumbs/88/115919367.jpg) Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms S.GokulaKrishnan B.Tech.,M.Tech.,[Ph.D] Assistant Professor[Stage-I] Department of Computer Science and Engineering Sri Chandrasekharendra Saraswathi Viswa
Introduction to Data Structures & Algorithms S.GokulaKrishnan B.Tech.,M.Tech.,[Ph.D] Assistant Professor[Stage-I] Department of Computer Science and Engineering Sri Chandrasekharendra Saraswathi Viswa
DC54 DATA STRUCTURES DEC 2014
 Q.2 a. Write a function that computes x^y using Recursion. The property that x^y is simply a product of x and x^(y-1 ). For example, 5^4= 5 * 5^3. The recursive definition of x^y can be represented as
Q.2 a. Write a function that computes x^y using Recursion. The property that x^y is simply a product of x and x^(y-1 ). For example, 5^4= 5 * 5^3. The recursive definition of x^y can be represented as
MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI KUALA LUMPUR
 STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION PSD2023 ALGORITHM & DATA STRUCTURE DSEW-E-F-2/13 25 MAY 2015 9.00 AM
STUDENT IDENTIFICATION NO MULTIMEDIA COLLEGE JALAN GURNEY KIRI 54100 KUALA LUMPUR FIFTH SEMESTER FINAL EXAMINATION, 2014/2015 SESSION PSD2023 ALGORITHM & DATA STRUCTURE DSEW-E-F-2/13 25 MAY 2015 9.00 AM
DS Assignment II. Full Sized Image
 DS Assignment II 1. A) For the Towers of Hanoi problem, show the call tree during the recursive call Towers(3, A, C, B). In the tree, label the root node as Towers (3, A, C, B) while marking all the intermediate
DS Assignment II 1. A) For the Towers of Hanoi problem, show the call tree during the recursive call Towers(3, A, C, B). In the tree, label the root node as Towers (3, A, C, B) while marking all the intermediate
Data Structure & Algorithms Laboratory Manual (CS 392)
 Institute of Engineering & Management Department of Computer Science & Engineering Data Structure Laboratory for 2 nd year 3 rd semester Code: CS 392 Data Structure & Algorithms Laboratory Manual (CS 392)
Institute of Engineering & Management Department of Computer Science & Engineering Data Structure Laboratory for 2 nd year 3 rd semester Code: CS 392 Data Structure & Algorithms Laboratory Manual (CS 392)
Stacks. Manolis Koubarakis. Data Structures and Programming Techniques
 Stacks Manolis Koubarakis 1 Stacks and Queues Linear data structures are collections of components arranged in a straight line. If we restrict the growth of a linear data structure so that new components
Stacks Manolis Koubarakis 1 Stacks and Queues Linear data structures are collections of components arranged in a straight line. If we restrict the growth of a linear data structure so that new components
EC8393FUNDAMENTALS OF DATA STRUCTURES IN C Unit 3
 UNIT 3 LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 1. Define Data Structures Data Structures is defined as the way of organizing all data items that consider not only the elements stored but also stores the relationship between
UNIT 3 LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 1. Define Data Structures Data Structures is defined as the way of organizing all data items that consider not only the elements stored but also stores the relationship between
PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before ElectronicCity, Bengaluru -100 Department of Basic Science and Humanities
 INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST-3 Date : 12-05-2016 Marks: 40 Subject & Code : Programming in C and data structures (15PCD23) Sec : F,G,H,I,J,K Name of faculty :Dr J Surya Prasad/Mr.Sreenath M V/Ms.Monika/ Time
INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST-3 Date : 12-05-2016 Marks: 40 Subject & Code : Programming in C and data structures (15PCD23) Sec : F,G,H,I,J,K Name of faculty :Dr J Surya Prasad/Mr.Sreenath M V/Ms.Monika/ Time
PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Computer Science and Engineering
 USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Computer Science and Engineering SOLUTION FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : 6/10/2017 Marks:
USN 1 P E PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of Computer Science and Engineering SOLUTION FOR INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : 6/10/2017 Marks:
Top of the Stack. Stack ADT
 Module 3: Stack ADT Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Stack ADT Features (Logical View) A List that
Module 3: Stack ADT Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Stack ADT Features (Logical View) A List that
BSc.(Hons.) Business Information Systems, BSc. (Hons.) Computer Science with Network Security, BSc.(Hons.) Software Engineering
 BSc.(Hons.) Business Information Systems, BSc. (Hons.) Computer Science with Network Security, BSc.(Hons.) Software Engineering Cohorts BIS/04 Full Time - BCNS/04 Full Time SE/04 Full Time Examinations
BSc.(Hons.) Business Information Systems, BSc. (Hons.) Computer Science with Network Security, BSc.(Hons.) Software Engineering Cohorts BIS/04 Full Time - BCNS/04 Full Time SE/04 Full Time Examinations
-The Hacker's Dictionary. Friedrich L. Bauer German computer scientist who proposed "stack method of expression evaluation" in 1955.
 Topic 15 Implementing and Using "stack n. The set of things a person has to do in the future. "I haven't done it yet because every time I pop my stack something new gets pushed." If you are interrupted
Topic 15 Implementing and Using "stack n. The set of things a person has to do in the future. "I haven't done it yet because every time I pop my stack something new gets pushed." If you are interrupted
Classification s of Data Structures
 Linear Data Structures using Sequential organization Classification s of Data Structures Types of Data Structures Arrays Declaration of arrays type arrayname [ arraysize ]; Ex-double balance[10]; Arrays
Linear Data Structures using Sequential organization Classification s of Data Structures Types of Data Structures Arrays Declaration of arrays type arrayname [ arraysize ]; Ex-double balance[10]; Arrays
MODULE 1. Introduction to Data Structures
 MODULE 1 Introduction to Data Structures Data Structure is a way of collecting and organizing data in such a way that we can perform operations on these data in an effective way. Data Structures is about
MODULE 1 Introduction to Data Structures Data Structure is a way of collecting and organizing data in such a way that we can perform operations on these data in an effective way. Data Structures is about
a) State the need of data structure. Write the operations performed using data structures.
 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model answer and the answer written by candidate
 CS6202 - PROGRAMMING & DATA STRUCTURES I Unit IV Part - A 1. Define Stack. A stack is an ordered list in which all insertions and deletions are made at one end, called the top. It is an abstract data type
CS6202 - PROGRAMMING & DATA STRUCTURES I Unit IV Part - A 1. Define Stack. A stack is an ordered list in which all insertions and deletions are made at one end, called the top. It is an abstract data type
Vivekananda College of Engineering & Technology. Data Structures and Applications
 Vivekananda College of Engineering & Technology [Sponsored by Vivekananda Vidyavardhaka Sangha, Puttur ] Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University Approved by AICTE New Delhi & Govt of Karnataka
Vivekananda College of Engineering & Technology [Sponsored by Vivekananda Vidyavardhaka Sangha, Puttur ] Affiliated to Visvesvaraya Technological University Approved by AICTE New Delhi & Govt of Karnataka
The Stack and Queue Types
 The Stack and Queue Types Hartmut Kaiser hkaiser@cct.lsu.edu http://www.cct.lsu.edu/ hkaiser/fall_2012/csc1254.html 2 Programming Principle of the Day Do the simplest thing that could possibly work A good
The Stack and Queue Types Hartmut Kaiser hkaiser@cct.lsu.edu http://www.cct.lsu.edu/ hkaiser/fall_2012/csc1254.html 2 Programming Principle of the Day Do the simplest thing that could possibly work A good
CSE202- Lec#6. (Operations on CSE202 C++ Programming
 Arrays CSE202- Lec#6 (Operations on Arrays) Outline To declare an array To initialize an array Operations on array Introduction Arrays Collection of related data items of same data type. Static entity
Arrays CSE202- Lec#6 (Operations on Arrays) Outline To declare an array To initialize an array Operations on array Introduction Arrays Collection of related data items of same data type. Static entity
MID TERM MEGA FILE SOLVED BY VU HELPER Which one of the following statement is NOT correct.
 MID TERM MEGA FILE SOLVED BY VU HELPER Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the elements may locate at far positions
MID TERM MEGA FILE SOLVED BY VU HELPER Which one of the following statement is NOT correct. In linked list the elements are necessarily to be contiguous In linked list the elements may locate at far positions
S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Data Structures. Primitive Linear Non Linear
![S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Data Structures. Primitive Linear Non Linear S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Data Structures. Primitive Linear Non Linear](/thumbs/93/111913146.jpg) S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Data Structures Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1(a) Explain different types of data structures with examples. [5] Ans.: Types of Data Structure : Data Structures
S.E. Sem. III [CMPN] Data Structures Time : 3 Hrs.] Prelim Paper Solution [Marks : 80 Q.1(a) Explain different types of data structures with examples. [5] Ans.: Types of Data Structure : Data Structures
Table of Contents. Chapter 1: Introduction to Data Structures... 1
 Table of Contents Chapter 1: Introduction to Data Structures... 1 1.1 Data Types in C++... 2 Integer Types... 2 Character Types... 3 Floating-point Types... 3 Variables Names... 4 1.2 Arrays... 4 Extraction
Table of Contents Chapter 1: Introduction to Data Structures... 1 1.1 Data Types in C++... 2 Integer Types... 2 Character Types... 3 Floating-point Types... 3 Variables Names... 4 1.2 Arrays... 4 Extraction
Preface... (vii) CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS
 Contents Preface... (vii) CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS 1.1. INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS... 1 1.2. HISTORY OF C & C++... 3 1.3. DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT AND EXECUTION OF A PROGRAM... 3 1.4 TESTING OF PROGRAMS...
Contents Preface... (vii) CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS 1.1. INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS... 1 1.2. HISTORY OF C & C++... 3 1.3. DESIGN, DEVELOPMENT AND EXECUTION OF A PROGRAM... 3 1.4 TESTING OF PROGRAMS...
This document can be downloaded from with most recent updates. 1 Data Structures using C: Module 4 (16MCA11) LINKED LISTS
 1 Data Structures using C: Module 4 (16MCA11) LINKED LISTS 4.1 MEMORY MANAGEMENT 4.1.1 Basics about Memory When a C program is compiled, the compiler translates the source code into machine code. Now the
1 Data Structures using C: Module 4 (16MCA11) LINKED LISTS 4.1 MEMORY MANAGEMENT 4.1.1 Basics about Memory When a C program is compiled, the compiler translates the source code into machine code. Now the
MAHARASHTRASTATE BOARD OF TECHNICAL EDUCATION (Autonomous) (ISO/IEC Certified)
 Subject Code: 17330 Model Answer Page 1/ 22 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Subject Code: 17330 Model Answer Page 1/ 22 Important Instructions to examiners: 1) The answers should be examined by key words and not as word-to-word as given in the model answer scheme. 2) The model
Stacks and Queues. CSE Data Structures April 12, 2002
 Stacks and Queues CSE 373 - Data Structures April 12, 2002 Readings and References Reading Section 3.3 and 3.4, Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in C, Weiss Other References 12-Apr-02 CSE 373 - Data
Stacks and Queues CSE 373 - Data Structures April 12, 2002 Readings and References Reading Section 3.3 and 3.4, Data Structures and Algorithm Analysis in C, Weiss Other References 12-Apr-02 CSE 373 - Data
dynamic memory allocation
 Dynamic memory allocation in C The concept of dynamic memory allocation in c language enables the C programmer to allocate memory at runtime. Dynamic memory allocation in c language is possible by 4 functions
Dynamic memory allocation in C The concept of dynamic memory allocation in c language enables the C programmer to allocate memory at runtime. Dynamic memory allocation in c language is possible by 4 functions
Procedural programming with C
 Procedural programming with C Dr. C. Constantinides Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering Concordia University Montreal, Canada August 11, 2016 1 / 77 Functions Similarly to its mathematical
Procedural programming with C Dr. C. Constantinides Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering Concordia University Montreal, Canada August 11, 2016 1 / 77 Functions Similarly to its mathematical
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit 1
 Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit 1 Introduction Computer is an electronic machine which is used for data processing and manipulation. In order to make computer work
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology for Diploma Studies Unit 1 Introduction Computer is an electronic machine which is used for data processing and manipulation. In order to make computer work
Stacks Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller
 Stacks 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Today Exam 2 is next Tuesday, October 30 Today: Quiz 5 solutions Recursive add from last week (see SinglyLinkedListR.java) Stacks ADT (Queues on Thursday) ArrayStack
Stacks 15-121 Fall 2018 Margaret Reid-Miller Today Exam 2 is next Tuesday, October 30 Today: Quiz 5 solutions Recursive add from last week (see SinglyLinkedListR.java) Stacks ADT (Queues on Thursday) ArrayStack
