Feasibility of Laser Induced Plasma Micro-machining (LIP-MM)
|
|
|
- Arthur Page
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Feasibility of Laser Induced Plasma Micro-machining (LIP-MM) Kumar Pallav 1, Kornel F. Ehmann 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering Northwestern University Evanston, IL 60208, USA {kumarpallav2008@u.northwestern.edu, k-ehmann@northwestern.edu} Abstract. The paper offers evidence on the feasibility of a newly proposed micro-machining process, which is motivated by the need to overcome the various limitations associated with µ-edm and conventional ultra-short laser micro-machining processes. The limitations in µ-edm and laser micromachining processes are mainly due to the requirement of a conductive electrode and workpiece, electrode wear and compensation strategies, and complex process control mechanisms respectively. The new process uses a laser beam to generate plasma in a dielectric near the workpiece surface whose explosive expansion results in material removal by mechanisms similar to those that occur in µ-edm. Keywords: µ-edm, Laser, Dielectric, Plasma, Micro-machining. 1.0 Introduction Micro-manufacturing encompasses the creation of high precision 3D products with feature sizes ranging from a few microns to a few millimeters. While micro-scale technologies are well established in the semiconductor and micro-electronics fields, the same cannot be said for manufacturing products involving highly accurate complex 3D geometries in materials such as metals, ceramics and polymers. Micro-EDM (µ-edm) has been one of the frontrunners for material removal in the aforementioned size range. Material removal is facilitated by the plasma created when the electric field generated due to high voltage between the electrode and the workpiece exceeds the threshold value for dielectric breakdown. The created plasma explosively expands and sends shock waves to the surface of the workpiece at very high speed that lead to localized heating and ablation. It has been widely recognized that the major limitations of µ-edm are [1-3]: (1) the inability to micro-machine nonconductive materials and metals with low conductivity, (2) non-productive time and cost associated with on-machine electrode manufacturing, (3) frequent electrode replacements due to high electrode wear, (4) flushing of debris from the small electrode-workpiece gap (< 5 µm), and (5) low MRR (0.6-6 mm 3 /hr).
2 A competing process is ultra-short laser pulse-based micro-machining. Ultrashort pulsed lasers have pulse durations ranging from (ps) to few (fs) at pulse frequencies ranging up to 500 khz, and very low average power (up to 10 W). However, since pulse duration is very short, the peak power is very high [4, 5]. With ultra-short laser pulses, the ablation process is dependant on a wide number of parameters including the type of polarization, type of material, peak pulse power, pulse repetition rate, pulse duration, environmental conditions and pressure, and wavelength. The ablation process is also accompanied by electron heat conduction and formation of a molten zone inside the metal target which reduces precision when machining metals [7]. The dependence of the ablation process on so many parameters makes conventional ultra-short laser micro-machining a very complex process and controlling all of these parameters is a major challenge [7]. The new micro-machining process described in this paper is motivated by the need to overcome the limitations of µ-edm and of conventional ultra-short laser micro-machining. The new micro-machining process, to be termed Laser Induced Plasma Micro-machining (LIP-MM) uses an alternative mechanism for plasma creation to facilitate material removal. 1.1 The Laser-induced Plasma Micromachining (LIP-MM) Process The underlying principle of the proposed LIP-MM process rests on the fact that when an ultra-short pulsed laser beam is tightly focused in a transparent dielectric medium, extremely high peak power densities are reached at the focal spot [6, 8, 9]. And, when the peak power density exceeds the threshold irradiance required for dielectric breakdown, rapid ionization of the medium occurs leading to plasma formation. The plasma formed is optically opaque and causes a drastic increase in the absorption coefficient, which, in turn, gives rise to a rapid energy transfer from the radiation field to the medium [6, 8]. This process is, in essence, an optical breakdown when the free electron density at the focal spot exceeds the critical value of cm -3. At this value, the plasma absorbs nearly all of the incoming laser beam s energy leading to rapid heating of the material in the focal volume [9]. The plasma results in a liquid-gas phase change and causes cavitation accompanied by the generation of shock waves. If the focal volume is slightly above the surface of the workpiece, the explosive expansion of the plasma that is followed by the generation of shock waves, like in the case of a µ-edm discharge, results in material removal. Plasma generation by ultra-short pulsed lasers, as described above does not require a conductive electrode and workpiece [9]. Actually, there is no need for an electrode. Even more importantly, the plasma s properties can be controlled by controlling the laser process parameters. Hence, many of the limitations of µ-edm and conventional laser micro-machining can be potentially circumvented through the LIP-MM process. In the subsequent sections initial results aimed at confirming the viability of the proposed material removal mechanism are presented.
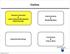
3 2.0 Experimental Setup and Results For the experimental realization of the LIP-MM process, a commercial, Nd:YVO 4 laser system (Lumera laser, Rapid) emitting laser pulses of 8 pico-seconds pulse duration at 532 nm wavelength was used. The beam profile of the (ps) pulses was Gaussian (TEM 00 ) and the beam was linearly polarized. The pulse repetition rate for the laser system varied from 10 khz to 500 khz. For plasma generation, since very high peak power density is required, low repetition rates ranging from 10 khz to 50 khz were used. The laser machine is capable of producing a peak power density level of several W/cm 2 at a spot size of 21 µm in diameter. It is also equipped with a 5- axis programmable motion controller that directs the beam, has a resolution of 0.01 µm and feed rates ranging from 0.01 µm/s to 10 cm/s, allowing a very precise control of the relative motion between the beam/plasma and the workpiece. The laser beam was brought to the focusing lens through a beam delivery system comprising of various mirrors and a 3X beam expander. The beam expander expands the beam diameter from 0.6 mm to 1.8 mm before it reaches the focusing triplet lens. The focusing triplet lens focuses the laser beam to a diffraction limited spot size of 21 µm at the focal spot. Water was selected as the dielectric for the LIP-MM process. The laser pulses were focused into a glass beaker filled with water. Fig. 1 shows the experimental setup used in the LIP-MM process. 1.8 mm Laser 532 nm Focusing Lens Plasma Water Pico-second - Laser NU Fig. 1. Schematics of the LIP-MM Process 2.1 Determination of Breakdown Threshold and Plasma Occurrence Probability The peak power density reached at the focal spot with ultra-short lasers generally ranges from several 10 9 W/cm 2 to few W/cm 2. Ionization starts as soon as the peak power density exceeds the threshold ionization potential for the dielectric medium that depends on a number of factors including: laser wavelength, laser and
4 dielectric media interaction time, and additional conditions such as the number of seed electrons, the type of dielectric, and the type of polarization of the laser beam [9]. Dielectric breakdown resulting in plasma generation can only be achieved when the peak power density exceeds the threshold value required to initiate ionization [6]. For plasma generation and control, the breakdown threshold corresponding to different pulse repetition rates was determined by imaging the plasma formed with a CCD camera (Edmund Optics, Guppy F-146 FireWire A 1/2" CCD Monochrome Camera) with a X magnification (Edmund Optics, VZM 1000i Video Lens) as the peak power density was varied from superthreshold values to subthreshold values. During each laser exposure, the output average power of the incident laser irradiation was measured using an external laser power meter (Gentec SOLO 2(R2)). Plasma generation due to dielectric breakdown was visually detected in a darkened room with the CCD camera and was recorded at a frame rate of 15 frames per second. Fig. 2 shows the plasma images obtained through the CCD camera at different average power levels and pulse repetition rates. For each peak power density value at every pulse repetition rate, at least 20 laser exposures were evaluated for determining the plasma occurrence probability. As shown in Fig. 2, with a decrease in peak power density levels at all repetition rates, the intensity of the plasma image decreases until it reaches the dielectric ionization threshold value where the plasma occurrence probability drops to below 10% and the plasma image cannot be obtained through the CCD camera. The mean breakdown threshold intensity corresponding to 10% plasma occurrence probability was experimentally measured to be 1.10x1011 W/cm2. However, the plasma size remained independent of the average power levels at all pulse repetition rates. Fig. 3 shows the dependence of the plasma occurrence probability at different pulse repetition rates on peak power density. It shows that the breakdown threshold in water, corresponding to 10 % plasma occurrence probability is approximately constant for all pulse repetition rates. Fig.2. Plasma Image at 10 khz, 63 mw and 38 mw Average Power
5 Fig. 3. Plasma Occurrence Probability at Different Peak power Densities and Pulse Repetition Rates 2.2 Laser Induced Plasma Micro-machining of Steel and Quartz For making micro channels in steel using the LIP-MM process, a pulse repetition rate of 10 khz and a peak power density corresponding to a 70% plasma occurrence probability were selected. The laser beam traverse speed was kept at two levels of 100 µm/sec and 500 µm/sec for machining single pass channels. The depths of the micro-machined channels in steel were examined at various locations through a white light interferometer (Zygo NewView 7300). It was observed that the depth of the channels varied inversely with variation in the laser beam traverse speed. With the lower laser beam traverse speed of 100 µm/s, the depth of the channel was approximately 30 µm, whereas with the higher laser beam traverse speed of 500 µm/s, the depth of the channel was only 6 µm. Fig. 4. Channels Made by LIP-MM in Steel at an Average Power of 59 mw, Pulse Repetition Rate of 10 khz and Laser Beam Traverse Speed of 100 µm/s Fig. 4 shows the image of a single pass channel made in steel with the LIP-MM process at a laser beam traverse speed of 100 µm/sec and peak power density corresponding to 70% plasma occurrence probability at 10 khz pulse repetition rate. The channel has an approximately 30 µm depth at various cross-sections and the walls of the channel are not vertical. Fig. 5 shows the images obtained through a SEM
6 (Hitachi S3400N II) of channels machined in steel with different number of passes. The other process parameters were similar to the channel shown in Fig. 4. Fig. 5. SEM Images of Channels Made in Steel Through LIP-MM Process with 1, 5 and 10 Passes, 10 khz Pulse Repetition Rate, Peak Power Density Level Corresponding to 70% Plasma Occurrence Probability and Laser Beam Traverse Speed of 100 µm/s As shown in Fig. 5, with single pass micro-machining the channel had a significant recast layer and inclined walls. However with an increase in the number of passes, the walls became vertical and the recast layer decreased significantly. The depth of the channel became more uniform and also increased with an increase in the number of passes. Hence, with an increase in the number of passes, the surface features of the channel improve due to the vertical walls, uniform depth, and significant reduction in the recast layer. Fig. 6. Depth of Channel (2 Passes) in Quartz, Average Power 59 mw, Pulse Repetition Rate 10 khz, and Laser Beam Traverse Speed of 1µm/s Since, quartz is transparent to incident laser irradiation at most wavelengths, it is very difficult to machine by the conventional laser micro-machining process. During the conventional laser micro-machining process, almost all the incident laser irradiation passes through the quartz workpiece with a very negligible portion being absorbed. Quartz is also a non-conductive material and cannot be machined using the µ-edm process. Since, in LIP-MM the plasma physically interacts with the target material, the problem of negligible absorption is not encountered. Single pass and multiple pass channels were made in a quartz workpiece by the LIP-MM process at different peak power density levels and laser beam traverse speeds. Fig. 6 shows the depth of a typical multiple pass channel made in quartz, measured through an interferometer (Zygo NewView 7300). Fig. 7 shows the dependence of the depth of a single pass channel on laser beam traverse speed at different peak power density values in quartz. It shows that irrespective of the peak
7 power density level, significant reduction in channel depth occurs with an increase in the laser beam traverse speed. Fig. 7. Dependence of Channel Depth (Single Pass) in Quartz on Laser Beam Traverse Speed at Different Peak Power Density Levels 3.0 Results and Discussion The breakdown threshold for water corresponding to 10% plasma occurrence probability was found to be equal to 1.10 x W/cm 2. The peak power density depends on the average power, pulse repetition rate, pulse duration, and the focal spot size. With 8 ps pulses and a diffraction limited spot size of 21 µm, a strong dependence of the plasma occurrence probability and its intensity on the peak power density was observed. At near threshold values of the peak power density at all pulse repetition rates, the plasma intensity decreased significantly and could not be observed by the CCD camera. However, no systematic dependence between the breakdown threshold and the pulse repetition rate was observed. Channels were machined in steel and quartz at different values of peak power densities, laser beam traverse speeds and pulse repetition rates. At a peak power density level corresponding to 100 % plasma occurrence probability, significant recast layer was observed in the micro-machined channels. Irrespective of the pulse repetition rate, recast layer was also observed at very low laser beam traverse speeds, such as 1 µm/s. The best quality surface features with a minimal recast layer, uniform depth and vertical walls was observed when channels were machined in multiple passes at peak power density levels corresponding to 50%-70% of plasma occurrence probability and laser beam traverse speeds corresponding to a few 100 µm/s. The channel depth varied significantly with variation in the laser beam traverse speed. At lower values of the laser beam traverse speed, e.g., 100 µm/s, the depth was approximately 30 µm at all pulse repetition rates. However, with an increase in the laser beam traverse speed to values such as 500 µm/s, the channel depth was found to decrease significantly.
8 4.0 Conclusion The feasibility of a new micro-machining process called Laser-Induced Plasma Micro-Machining has been demonstrated. The limitations of µ-edm and of conventional ultra-short laser micro-machining are not observed with the LIP-MM process. Hence, the LIP-MM process attempts to provide a plausible alternative to the many existing limitations associated with both the µ-edm and ultra-short laser micro-machining processes. The LIP-MM process is a very novel process for material removal at the microscale. It removes material by plasma-matter interaction. As a matter of fact, it can be postulated that the material removal regime in LIP-MM is very similar to that in µ- EDM. The LIP-MM process also helps in reducing the costs associated with electrode manufacture and dressing in µ-edm. Finally, it also has the capability to micromachine materials ranging from quartz which is non-conductive and transparent to metals such as steel, nickel, aluminum, etc. 5.0 References [1] D. T. Pham, S. S. Dimov, S. Bigot, A. Ivanov, and K. Popov, "Micro-EDM-- recent developments and research issues," Journal of Materials Processing Technology, vol. 149, pp , [2] K. H. Ho and S. T. Newman, "State of the art electrical discharge machining (EDM)," International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, vol. 43, pp , [3] Z. Y. Yu, J. Kozak, and K. P. Rajurkar, "Modelling and Simulation of Micro EDM Process," CIRP Annals - Manufacturing Technology, vol. 52, pp , [4] C. Momma, S. Nolte, B. N. Chichkov, F. v. Alvensleben, and A. Tünnermann, "Precise laser ablation with ultrashort pulses," Applied Surface Science, vol , pp , [5] X. Liu, D. Du, and G. Mourou, "Laser ablation and micromachining with ultrashort laser pulses," Quantum Electronics, IEEE Journal of, vol. 33, pp , [6] J. Noack and A. Vogel, "Laser-induced plasma formation in water at nanosecond to femtosecond time scales: calculation of thresholds, absorption coefficients, and energy density," Quantum Electronics, IEEE Journal of, vol. 35, pp , [7] M. D. Shirk and P. A. Molian, "A review of ultrashort pulsed laser ablation of materials," Journal of Laser Applications, vol. 10, pp , [8] C. A. Sacchi, "Laser-Induced Electric Breakdown in Water," Journal of the Optical Society of America B-Optical Physics, vol. 8, pp , [9] A. Vogel, K. Nahen, D. Theisen, and J. Noack, "Plasma formation in water by picosecond and nanosecond Nd:YAG laser pulses. I. Optical breakdown at threshold and superthreshold irradiance," Selected Topics in Quantum Electronics, IEEE Journal of, vol. 2, pp , 1996.
9
Recent Advances in Ultrafast Laser Subtractive and Additive Manufacturing
 Industrial Affiliates Symposium March 16-18, 2017 Recent Advances in Ultrafast Laser Subtractive and Additive Manufacturing Xiaoming Yu Assistant Professor Ultrafast Laser Processing Group CREOL, The College
Industrial Affiliates Symposium March 16-18, 2017 Recent Advances in Ultrafast Laser Subtractive and Additive Manufacturing Xiaoming Yu Assistant Professor Ultrafast Laser Processing Group CREOL, The College
Short pulse laser milling effects on surface integrity. P V Petkov, S S Dimov, R. Minev and D T Pham
 Short pulse laser milling effects on surface integrity P V Petkov, S S Dimov, R. Minev and D T Pham Presentation Outline 2 Overview Process description Experiments & Results Conclusions Overview 3 Pictures
Short pulse laser milling effects on surface integrity P V Petkov, S S Dimov, R. Minev and D T Pham Presentation Outline 2 Overview Process description Experiments & Results Conclusions Overview 3 Pictures
A Comparative Study of Laser Induced Plasma Micro-Machining and Laser Ablation of Low Melting Point Polymers
 IWMF2014, 9 th INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON MICROFACTORIES OCTOBER 5-8, 2014, HONOLULU, U.S.A. / 1 A Comparative Study of Laser Induced Plasma Micro-Machining and Laser Ablation of Low Melting Point Polymers
IWMF2014, 9 th INTERNATIONAL WORKSHOP ON MICROFACTORIES OCTOBER 5-8, 2014, HONOLULU, U.S.A. / 1 A Comparative Study of Laser Induced Plasma Micro-Machining and Laser Ablation of Low Melting Point Polymers
Company Pioneer in Ytterbium ultrafast lasers High quality manufacturing Intense and active R&D Located in Bordeaux and Paris US offices in Boston and
 High power ultrafast lasers Eric Mottay High Brightness Laser sources Burgdorf, November 26, 2009 Company Pioneer in Ytterbium ultrafast lasers High quality manufacturing Intense and active R&D Located
High power ultrafast lasers Eric Mottay High Brightness Laser sources Burgdorf, November 26, 2009 Company Pioneer in Ytterbium ultrafast lasers High quality manufacturing Intense and active R&D Located
Development of a Simulation Method of Three-Dimensional Ultrafine Processing by Femtosecond Laser Shunsuke Nabetani 1, a, Hideki Aoyama 1, b * 1, 2, c
 Development of a Simulation Method of Three-Dimensional Ultrafine Processing by Femtosecond Laser Shunsuke Nabetani 1, a, Hideki Aoyama 1, b * 1,, c, Masahiro Ueda Yoshinori Ogawa 1,, d 1,, 3, e, and Kazuo
Development of a Simulation Method of Three-Dimensional Ultrafine Processing by Femtosecond Laser Shunsuke Nabetani 1, a, Hideki Aoyama 1, b * 1,, c, Masahiro Ueda Yoshinori Ogawa 1,, d 1,, 3, e, and Kazuo
Study of Laser Induced Plasma Using Two Focusing Techniques
 Study of Laser Induced Plasma Using Two Focusing Techniques Ahmad Hadi Ali 1, * and Noriah Bidin 2 1 Science Department, Centre for Science Studies, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia 2 Physics Department,
Study of Laser Induced Plasma Using Two Focusing Techniques Ahmad Hadi Ali 1, * and Noriah Bidin 2 1 Science Department, Centre for Science Studies, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia 2 Physics Department,
Laser milling for micro tooling
 Laser milling for micro tooling D T Pham, S S Dimov, P V Petkov and T Dobrev Manufacturing Engineering Centre,Cardiff University, UK Abstract Laser milling provides a new method of producing components
Laser milling for micro tooling D T Pham, S S Dimov, P V Petkov and T Dobrev Manufacturing Engineering Centre,Cardiff University, UK Abstract Laser milling provides a new method of producing components
MICROMACHINING OF OPTICAL FIBRES WITH A NANOSECOND LASER FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION AND SENSOR APPLICATIONS
 58 SOUTH AFRICAN INSTITUTE OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERS Vol.102(3) September 2011 MICROMACHINING OF OPTICAL FIBRES WITH A NANOSECOND LASER FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION AND SENSOR APPLICATIONS D. Schmieder, R.
58 SOUTH AFRICAN INSTITUTE OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERS Vol.102(3) September 2011 MICROMACHINING OF OPTICAL FIBRES WITH A NANOSECOND LASER FOR OPTICAL COMMUNICATION AND SENSOR APPLICATIONS D. Schmieder, R.
High-Accuracy LIBS with Nanosecond and Picosecond Time Resolution Enabled by Ultrasensitive emiccd Technology
 2015 Princeton Instruments, Inc. All rights reserved. High-Accuracy LIBS with Nanosecond and Picosecond Time Resolution Enabled by Ultrasensitive emiccd Technology The PI-MAX4:1024EMB emiccd camera seamlessly
2015 Princeton Instruments, Inc. All rights reserved. High-Accuracy LIBS with Nanosecond and Picosecond Time Resolution Enabled by Ultrasensitive emiccd Technology The PI-MAX4:1024EMB emiccd camera seamlessly
Tutorial: Instantaneous Measurement of M 2 Beam Propagation Ratio in Real-Time
 Tutorial: Instantaneous Measurement of M 2 Beam Propagation Ratio in Real-Time By Allen M. Cary, Jeffrey L. Guttman, Razvan Chirita, Derrick W. Peterman, Photon Inc A new instrument design allows the M
Tutorial: Instantaneous Measurement of M 2 Beam Propagation Ratio in Real-Time By Allen M. Cary, Jeffrey L. Guttman, Razvan Chirita, Derrick W. Peterman, Photon Inc A new instrument design allows the M
Sensor based adaptive laser micromachining using ultrashort pulse lasers for zero-failure manufacturing
 Sensor based adaptive laser micromachining using ultrashort pulse lasers for zero-failure manufacturing Fraunhofer Institute for Production Technology, Aachen M. Sc. Guilherme Mallmann Prof. Dr.-Ing. Robert
Sensor based adaptive laser micromachining using ultrashort pulse lasers for zero-failure manufacturing Fraunhofer Institute for Production Technology, Aachen M. Sc. Guilherme Mallmann Prof. Dr.-Ing. Robert
MEMS SENSOR FOR MEMS METROLOGY
 MEMS SENSOR FOR MEMS METROLOGY IAB Presentation Byungki Kim, H Ali Razavi, F. Levent Degertekin, Thomas R. Kurfess 9/24/24 OUTLINE INTRODUCTION Motivation Contact/Noncontact measurement Optical interferometer
MEMS SENSOR FOR MEMS METROLOGY IAB Presentation Byungki Kim, H Ali Razavi, F. Levent Degertekin, Thomas R. Kurfess 9/24/24 OUTLINE INTRODUCTION Motivation Contact/Noncontact measurement Optical interferometer
Applications of adaptive optics in femtosecond laser material processing
 Applications of adaptive optics in femtosecond laser material processing STFC / Photonics KTN - Laser Applications of Adaptive Optics Professor Derryck T. Reid Ultrafast Optics Group School of Engineering
Applications of adaptive optics in femtosecond laser material processing STFC / Photonics KTN - Laser Applications of Adaptive Optics Professor Derryck T. Reid Ultrafast Optics Group School of Engineering
Outline. Nuclear Forensics & Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy. Interferometry & Shadowgraphy. Conclusion & Future Work. Experimental Setup
 Outline Nuclear Forensics Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Interferometry Shadowgraphy Experimental Setup Conclusion Future Work 1 Nuclear forensics The analysis of nuclear materials recovered from
Outline Nuclear Forensics Laser-Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy Interferometry Shadowgraphy Experimental Setup Conclusion Future Work 1 Nuclear forensics The analysis of nuclear materials recovered from
Micro structuring with highly repetitive ultra short laser pulses
 Proceedings of LPM008-the 9th International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication Micro structuring with highly repetitive ultra short laser pulses Joerg SCHILLE, Robby EBERT, Udo LOESCHNER, Peter
Proceedings of LPM008-the 9th International Symposium on Laser Precision Microfabrication Micro structuring with highly repetitive ultra short laser pulses Joerg SCHILLE, Robby EBERT, Udo LOESCHNER, Peter
2011 Optical Science & Engineering PhD Qualifying Examination Optical Sciences Track: Advanced Optics Time allowed: 90 minutes
 2011 Optical Science & Engineering PhD Qualifying Examination Optical Sciences Track: Advanced Optics Time allowed: 90 minutes Answer all four questions. All questions count equally. 3(a) A linearly polarized
2011 Optical Science & Engineering PhD Qualifying Examination Optical Sciences Track: Advanced Optics Time allowed: 90 minutes Answer all four questions. All questions count equally. 3(a) A linearly polarized
New concepts in ultra-short pulse laser ablation using digital tools
 10 th CIRP Conference on Photonic Technologies [LANE 2018] Industrial Paper New concepts in ultra-short pulse laser ablation using digital tools Alexander Pernizki a, Stephan Eifel a,* a Pulsar Photonics
10 th CIRP Conference on Photonic Technologies [LANE 2018] Industrial Paper New concepts in ultra-short pulse laser ablation using digital tools Alexander Pernizki a, Stephan Eifel a,* a Pulsar Photonics
4. Recommended alignment procedure:
 4. Recommended alignment procedure: 4.1 Introduction The described below procedure presents an example of alignment of beam shapers Shaper and Focal- Shaper (F- Shaper) with using the standard Shaper Mount
4. Recommended alignment procedure: 4.1 Introduction The described below procedure presents an example of alignment of beam shapers Shaper and Focal- Shaper (F- Shaper) with using the standard Shaper Mount
Emission characteristics of debris from Nd:YAG LPP and CO 2 LPP
 Emission characteristics of debris from Nd:YAG LPP and CO 2 LPP A Takahashi 1, K Tamaru 2, T Akiyama 2, D Nakamura 2 and T Okada 2 1 Department of Health Sciences, Kyushu University, 3-1-1, Maidashi, Fukuoka
Emission characteristics of debris from Nd:YAG LPP and CO 2 LPP A Takahashi 1, K Tamaru 2, T Akiyama 2, D Nakamura 2 and T Okada 2 1 Department of Health Sciences, Kyushu University, 3-1-1, Maidashi, Fukuoka
PGx01 series. High Peak Power. Available models
 Picosecond Lasers Nanosecond Lasers Nanosecond Tunable Lasers High Energy Lasers Ultrafast Fiber Lasers Other Ekspla Products PGx1 PGx3 PGx11 PT2 Travelling Wave Optical Parametric Generators (TWOPG) are
Picosecond Lasers Nanosecond Lasers Nanosecond Tunable Lasers High Energy Lasers Ultrafast Fiber Lasers Other Ekspla Products PGx1 PGx3 PGx11 PT2 Travelling Wave Optical Parametric Generators (TWOPG) are
Sample Introduction Systems SOLID LASER ABLATION
 Sample Introduction Systems SOLID LASER ABLATION Laser ablation Benefits: spatial resolution of < 10 um little to no sample preparation required Drawbacks: transient signal reduced precision/accuracy relative
Sample Introduction Systems SOLID LASER ABLATION Laser ablation Benefits: spatial resolution of < 10 um little to no sample preparation required Drawbacks: transient signal reduced precision/accuracy relative
Range Sensors (time of flight) (1)
 Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Large range distance measurement -> called range sensors Range information: key element for localization and environment modeling Ultrasonic sensors, infra-red sensors
Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Large range distance measurement -> called range sensors Range information: key element for localization and environment modeling Ultrasonic sensors, infra-red sensors
Mikro-und Nanostrukturierung mit Ultrakurzpulslasern für Werkzeugtechnik und funktionale Oberflächen
 Micro and Nano Structuring with Ultra Short Pulsed Lasers for Tool Technology and Functional Surfaces Mikro-und Nanostrukturierung mit Ultrakurzpulslasern für Werkzeugtechnik und funktionale Oberflächen
Micro and Nano Structuring with Ultra Short Pulsed Lasers for Tool Technology and Functional Surfaces Mikro-und Nanostrukturierung mit Ultrakurzpulslasern für Werkzeugtechnik und funktionale Oberflächen
Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 2, MATHEMATICAL MODELLING OF THE LASER MACHINING PROCESS OF SAPPHIRE CRYSTAL Al 2 O 3
 Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 2, 2012 laser beam machining micromachining, sapphire Dominik WYSZYNSKI 1 Sebastian SKOCZYPIEC 1 Karolina FURYK 1 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING OF THE LASER MACHINING
Journal of Machine Engineering, Vol. 12, No. 2, 2012 laser beam machining micromachining, sapphire Dominik WYSZYNSKI 1 Sebastian SKOCZYPIEC 1 Karolina FURYK 1 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING OF THE LASER MACHINING
OPSE FINAL EXAM Fall CLOSED BOOK. Two pages (front/back of both pages) of equations are allowed.
 CLOSED BOOK. Two pages (front/back of both pages) of equations are allowed. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED.
CLOSED BOOK. Two pages (front/back of both pages) of equations are allowed. YOU MUST SHOW YOUR WORK. ANSWERS THAT ARE NOT JUSTIFIED WILL BE GIVEN ZERO CREDIT. ALL NUMERICAL ANSERS MUST HAVE UNITS INDICATED.
Experimental studies on effects at micro-structuring of highly reflecting metals using nano- and picosecond-lasers
 Physics Procedia 5 (21) 245 253 LANE 21 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia Experimental studies on effects at micro-structuring of highly reflecting metals using nano- and picosecond-lasers Yvonne Reg a
Physics Procedia 5 (21) 245 253 LANE 21 www.elsevier.com/locate/procedia Experimental studies on effects at micro-structuring of highly reflecting metals using nano- and picosecond-lasers Yvonne Reg a
Supplementary Figure 1 Optimum transmissive mask design for shaping an incident light to a desired
 Supplementary Figure 1 Optimum transmissive mask design for shaping an incident light to a desired tangential form. (a) The light from the sources and scatterers in the half space (1) passes through the
Supplementary Figure 1 Optimum transmissive mask design for shaping an incident light to a desired tangential form. (a) The light from the sources and scatterers in the half space (1) passes through the
Precision Engineering
 Precision Engineering 37 (2013) 753 757 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Precision Engineering jou rnal h om epage: www.elsevier.com/locate/precision Tool wear compensation in 3D micro
Precision Engineering 37 (2013) 753 757 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Precision Engineering jou rnal h om epage: www.elsevier.com/locate/precision Tool wear compensation in 3D micro
Machining and metrology systems for free-form laser printer mirrors
 Sādhan ā Vol. 28, Part 5, October 2003, pp. 925 932. Printed in India Machining and metrology systems for free-form laser printer mirrors DWDAVIS 1, M WALTER 1, M TAKAHASHI 2 and T MASAKI 2 1 Precitech
Sādhan ā Vol. 28, Part 5, October 2003, pp. 925 932. Printed in India Machining and metrology systems for free-form laser printer mirrors DWDAVIS 1, M WALTER 1, M TAKAHASHI 2 and T MASAKI 2 1 Precitech
Ultrafast Scan Techniques for 3D-µm Structuring of Metal Surfaces with high repetitive ps-laser pulses
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 1 (11) 15 115 LiM 11 Ultrafast Scan Techniques for 3D-µm Structuring of Metal Surfaces with high repetitive ps-laser pulses Stephan Bruening a,
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Physics Procedia 1 (11) 15 115 LiM 11 Ultrafast Scan Techniques for 3D-µm Structuring of Metal Surfaces with high repetitive ps-laser pulses Stephan Bruening a,
Dielectric Optical-Controllable Magnifying Lens. by Nonlinear Negative Refraction
 Dielectric Optical-Controllable Magnifying Lens by Nonlinear Negative Refraction Jianjun Cao 1, Ce Shang 2, Yuanlin Zheng 1,Yaming Feng, Xianfeng Chen 1,3, Xiaogan Liang 4 and Wenjie Wan 1,2,3* 1 Key Laboratory
Dielectric Optical-Controllable Magnifying Lens by Nonlinear Negative Refraction Jianjun Cao 1, Ce Shang 2, Yuanlin Zheng 1,Yaming Feng, Xianfeng Chen 1,3, Xiaogan Liang 4 and Wenjie Wan 1,2,3* 1 Key Laboratory
High-Power Femtosecond Lasers
 High-Power Femtosecond Lasers FEATURES 190 fs ps tunable pulse duration Up to 2 mj pulse energy Up to 20 W average power Single pulse 1 MHz tunable repetition rate Includes pulse picker for pulse-on-demand
High-Power Femtosecond Lasers FEATURES 190 fs ps tunable pulse duration Up to 2 mj pulse energy Up to 20 W average power Single pulse 1 MHz tunable repetition rate Includes pulse picker for pulse-on-demand
Multiple optical traps from a single laser beam using a mechanical element
 Multiple optical traps from a single laser beam using a mechanical element J.A. Dharmadhikari, A.K. Dharmadhikari, and D. Mathur * Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, 1 Homi Bhabha Road, Mumbai 400
Multiple optical traps from a single laser beam using a mechanical element J.A. Dharmadhikari, A.K. Dharmadhikari, and D. Mathur * Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, 1 Homi Bhabha Road, Mumbai 400
Physics 625 Femtosecond laser Project
 Physics 625 Femtosecond laser Project The purpose of this project is for each person to gain experience in designing part of a femtosecond laser system for pump-probe experiments. The system diagram is
Physics 625 Femtosecond laser Project The purpose of this project is for each person to gain experience in designing part of a femtosecond laser system for pump-probe experiments. The system diagram is
Error Detection and Correction Methodology for Laser Milling Processes on Biocompatible Ceramic Materials
 KES Transactions on Sustainable Design and Manufacturing I Sustainable Design and Manufacturing 2014 : pp.574-582 : Paper sdm14-044 Error Detection and Correction Methodology for Laser Milling Processes
KES Transactions on Sustainable Design and Manufacturing I Sustainable Design and Manufacturing 2014 : pp.574-582 : Paper sdm14-044 Error Detection and Correction Methodology for Laser Milling Processes
NEAR-IR BROADBAND POLARIZER DESIGN BASED ON PHOTONIC CRYSTALS
 U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 77, Iss. 3, 2015 ISSN 1223-7027 NEAR-IR BROADBAND POLARIZER DESIGN BASED ON PHOTONIC CRYSTALS Bogdan Stefaniţă CALIN 1, Liliana PREDA 2 We have successfully designed a
U.P.B. Sci. Bull., Series A, Vol. 77, Iss. 3, 2015 ISSN 1223-7027 NEAR-IR BROADBAND POLARIZER DESIGN BASED ON PHOTONIC CRYSTALS Bogdan Stefaniţă CALIN 1, Liliana PREDA 2 We have successfully designed a
10/5/09 1. d = 2. Range Sensors (time of flight) (2) Ultrasonic Sensor (time of flight, sound) (1) Ultrasonic Sensor (time of flight, sound) (2) 4.1.
 Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Range Sensors (time of flight) (2) arge range distance measurement -> called range sensors Range information: key element for localization and environment modeling Ultrasonic
Range Sensors (time of flight) (1) Range Sensors (time of flight) (2) arge range distance measurement -> called range sensors Range information: key element for localization and environment modeling Ultrasonic
Development of automated ultraviolet laser beam profiling system using fluorometric technique
 Development of automated ultraviolet laser beam profiling system using fluorometric technique BB Shrivastava*, NS Benerji, P Bhatnagar, HS Vora a and U Nundy Chemical and Excimer Laser Section a Laser
Development of automated ultraviolet laser beam profiling system using fluorometric technique BB Shrivastava*, NS Benerji, P Bhatnagar, HS Vora a and U Nundy Chemical and Excimer Laser Section a Laser
Artisan Technology Group is your source for quality new and certified-used/pre-owned equipment
 Artisan Technology Group is your source for quality new and certified-used/pre-owned equipment FAST SHIPPING AND DELIVERY TENS OF THOUSANDS OF IN-STOCK ITEMS EQUIPMENT DEMOS HUNDREDS OF MANUFACTURERS SUPPORTED
Artisan Technology Group is your source for quality new and certified-used/pre-owned equipment FAST SHIPPING AND DELIVERY TENS OF THOUSANDS OF IN-STOCK ITEMS EQUIPMENT DEMOS HUNDREDS OF MANUFACTURERS SUPPORTED
NEW OPTICAL MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUE FOR SI WAFER SURFACE DEFECTS USING ANNULAR ILLUMINATION WITH CROSSED NICOLS
 NEW OPTICAL MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUE FOR SI WAFER SURFACE DEFECTS USING ANNULAR ILLUMINATION WITH CROSSED NICOLS Satoru Takahashi 1, Takashi Miyoshi 1, Yasuhiro Takaya 1, and Takahiro Abe 2 1 Department of
NEW OPTICAL MEASUREMENT TECHNIQUE FOR SI WAFER SURFACE DEFECTS USING ANNULAR ILLUMINATION WITH CROSSED NICOLS Satoru Takahashi 1, Takashi Miyoshi 1, Yasuhiro Takaya 1, and Takahiro Abe 2 1 Department of
Enhanced optical absorptance of metals using interferometric femtosecond ablation
 Enhanced optical absorptance of metals using interferometric femtosecond ablation K. Paivasaari, J. J. J. Kaakkunen, M. Kuittinen and T. Jaaskelainen Department of Physics and Mathematics, University of
Enhanced optical absorptance of metals using interferometric femtosecond ablation K. Paivasaari, J. J. J. Kaakkunen, M. Kuittinen and T. Jaaskelainen Department of Physics and Mathematics, University of
Vision Based Metal Spectral Analysis using
 1/27 Vision Based Metal Spectral Analysis using Eranga Ukwatta Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Western Ontario May 25, 2009 2/27 Outline 1 Overview of Element Spectroscopy
1/27 Vision Based Metal Spectral Analysis using Eranga Ukwatta Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering The University of Western Ontario May 25, 2009 2/27 Outline 1 Overview of Element Spectroscopy
Time-Resolved measurements by FEL spontaneous emission: A proposal for sub-picosecond pumps & probe structural and spectrometric investigations
 Time-Resolved measurements by FEL spontaneous emission: A proposal for sub-picosecond pumps & probe structural and spectrometric investigations V. Rossi Albertini, B. Paci & P. Perfetti Istituto di Struttura
Time-Resolved measurements by FEL spontaneous emission: A proposal for sub-picosecond pumps & probe structural and spectrometric investigations V. Rossi Albertini, B. Paci & P. Perfetti Istituto di Struttura
Single Photon Interference
 December 19, 2006 D. Lancia P. McCarthy Classical Interference Intensity Distribution Overview Quantum Mechanical Interference Probability Distribution Which Path? The Effects of Making a Measurement Wave-Particle
December 19, 2006 D. Lancia P. McCarthy Classical Interference Intensity Distribution Overview Quantum Mechanical Interference Probability Distribution Which Path? The Effects of Making a Measurement Wave-Particle
Particle Image Velocimetry for Fluid Dynamics Measurements
 Particle Image Velocimetry for Fluid Dynamics Measurements Lyes KADEM, Ph.D; Eng kadem@encs.concordia.ca Laboratory for Cardiovascular Fluid Dynamics MIE Concordia University Presentation - A bit of history
Particle Image Velocimetry for Fluid Dynamics Measurements Lyes KADEM, Ph.D; Eng kadem@encs.concordia.ca Laboratory for Cardiovascular Fluid Dynamics MIE Concordia University Presentation - A bit of history
Lab2: Single Photon Interference
 Lab2: Single Photon Interference Xiaoshu Chen* Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Rochester, NY, 14623 ABSTRACT The wave-particle duality of light was verified by multi and single photon
Lab2: Single Photon Interference Xiaoshu Chen* Department of Mechanical Engineering, University of Rochester, NY, 14623 ABSTRACT The wave-particle duality of light was verified by multi and single photon
Increasing laser processing efficiency using multibeam and tailored beam profiles
 Increasing laser processing efficiency using multibeam and tailored beam profiles Ulrich Rädel TOPAG Lasertechnik GmbH, Darmstadt Overview Presentation of company Topag Increasing processing efficiency
Increasing laser processing efficiency using multibeam and tailored beam profiles Ulrich Rädel TOPAG Lasertechnik GmbH, Darmstadt Overview Presentation of company Topag Increasing processing efficiency
A. K. Srivastava, K.C. Sati, Satyander Kumar alaser Science and Technology Center, Metcalfe House, Civil Lines, Delhi , INDIA
 International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 8, Issue 7, July-2017 1752 Optical method for measurement of radius of curvature of large diameter mirrors A. K. Srivastava, K.C. Sati,
International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research Volume 8, Issue 7, July-2017 1752 Optical method for measurement of radius of curvature of large diameter mirrors A. K. Srivastava, K.C. Sati,
Analysis of Cornell Electron-Positron Storage Ring Test Accelerator's Double Slit Visual Beam Size Monitor
 Analysis of Cornell Electron-Positron Storage Ring Test Accelerator's Double Slit Visual Beam Size Monitor Senior Project Department of Physics California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo By:
Analysis of Cornell Electron-Positron Storage Ring Test Accelerator's Double Slit Visual Beam Size Monitor Senior Project Department of Physics California Polytechnic State University San Luis Obispo By:
Optical diffraction gratings embedded in BK-7 glass by low-density plasma formation using femtosecond laser
 Optical diffraction gratings embedded in BK-7 glass by low-density plasma formation using femtosecond laser Jung-Kyu PARK 1, Sung-Hak CHO 1, Kwang-Ho KIM 2, Myung-Chang KANG 2 1. Nano Machining Laboratory,
Optical diffraction gratings embedded in BK-7 glass by low-density plasma formation using femtosecond laser Jung-Kyu PARK 1, Sung-Hak CHO 1, Kwang-Ho KIM 2, Myung-Chang KANG 2 1. Nano Machining Laboratory,
Accurate alignment technique for nanoimprint lithography
 Accurate alignment technique for nanoimprint lithography Li Jiang and Martin Feldman * Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Louisiana State University Baton Rouge, LA 70803-5901 ABSTRACT The
Accurate alignment technique for nanoimprint lithography Li Jiang and Martin Feldman * Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Louisiana State University Baton Rouge, LA 70803-5901 ABSTRACT The
Laser readiness for all optical EUV FEL
 Laser readiness for all optical EUV FEL Akira Endo EUVA (Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography System Development Association) EUVL Source Workshop 19 October, 2006 Barcelona, Spain Acknowledgments This work
Laser readiness for all optical EUV FEL Akira Endo EUVA (Extreme Ultraviolet Lithography System Development Association) EUVL Source Workshop 19 October, 2006 Barcelona, Spain Acknowledgments This work
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti 1-4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Assume a black
 Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Assume a black body type emitter: uniform emission Total energy radiating
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Assume a black body type emitter: uniform emission Total energy radiating
Cold Cutting or Laser Dissociation Uses Eximer (UV) lasers to cut without melting UV photons ev Enough energy to break organic molecular
 Cold Cutting or Laser Dissociation Uses Eximer (UV) lasers to cut without melting UV photons 3.5-7.9 ev Enough energy to break organic molecular bonds eg C=H bond 3.5 ev Causes material to fall apart Does
Cold Cutting or Laser Dissociation Uses Eximer (UV) lasers to cut without melting UV photons 3.5-7.9 ev Enough energy to break organic molecular bonds eg C=H bond 3.5 ev Causes material to fall apart Does
Progress of the Thomson Scattering Experiment on HSX
 Progress of the Thomson Scattering Experiment on HSX K. Zhai, F.S.B. Anderson, D.T. Anderson HSX Plasma Laboratory, UW-Madison Bill Mason PSL, UW-Madison, The Thomson scattering system being constructed
Progress of the Thomson Scattering Experiment on HSX K. Zhai, F.S.B. Anderson, D.T. Anderson HSX Plasma Laboratory, UW-Madison Bill Mason PSL, UW-Madison, The Thomson scattering system being constructed
Scheme ASADOG for stretching or compressing short optical pulses
 Scheme ASADOG for stretching or compressing short optical pulses Sergiy Kaim 1, George Venus 1, Vadim Smirnov 2, Boris Ya. Zeldovich 1, Leon B. Glebov 1,2 1 CREOL, The College of Optics and Photonics,
Scheme ASADOG for stretching or compressing short optical pulses Sergiy Kaim 1, George Venus 1, Vadim Smirnov 2, Boris Ya. Zeldovich 1, Leon B. Glebov 1,2 1 CREOL, The College of Optics and Photonics,
Related topics Interference, wavelength, refractive index, speed of light, phase, virtuallight source.
 Determination of the refractive index TEP Overview Related topics Interference, wavelength, refractive index, speed of light, phase, virtuallight source. Principle Light is brought to interference by two
Determination of the refractive index TEP Overview Related topics Interference, wavelength, refractive index, speed of light, phase, virtuallight source. Principle Light is brought to interference by two
HOLOGRAPHIC FEMTOSECOND LASER PROCESSING AND THREE-DIMENSIONAL RECORDING IN BIOLOGICAL TISSUES
 Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 2, 115 123, 2008 HOLOGRAPHIC FEMTOSECOND LASER PROCESSING AND THREE-DIMENSIONAL RECORDING IN BIOLOGICAL TISSUES Y. Hayasaki Department of Optical Science
Progress In Electromagnetics Research Letters, Vol. 2, 115 123, 2008 HOLOGRAPHIC FEMTOSECOND LASER PROCESSING AND THREE-DIMENSIONAL RECORDING IN BIOLOGICAL TISSUES Y. Hayasaki Department of Optical Science
CinCam CCD - Technical Data -
 - Technical Data - SENSOR DATA CCD-1201 CCD-1301 CCD-2301 CCD-2302 Format: 1/2 1/3 2/3 2/3 Active area: 6.5mm x 4.8mm 4.8mm x 3.6mm 9.0mm x 6.7mm 8.5mm x 7.1mm Number of pixel: 1388 x 1038 (1.4MPixel)
- Technical Data - SENSOR DATA CCD-1201 CCD-1301 CCD-2301 CCD-2302 Format: 1/2 1/3 2/3 2/3 Active area: 6.5mm x 4.8mm 4.8mm x 3.6mm 9.0mm x 6.7mm 8.5mm x 7.1mm Number of pixel: 1388 x 1038 (1.4MPixel)
Laser Micro-Fabricator. Innovative Laser Technology KORTherm Science
 Laser Micro-Fabricator Innovative Laser Technology KORTherm Science Wavelength and material Interaction 10600n 1064nm 532nm 351nm 308nm 248nm 193nm 157nm N-H C-H O-H H-H O-O C-C N-O C-N N-N C-O THERMAL
Laser Micro-Fabricator Innovative Laser Technology KORTherm Science Wavelength and material Interaction 10600n 1064nm 532nm 351nm 308nm 248nm 193nm 157nm N-H C-H O-H H-H O-O C-C N-O C-N N-N C-O THERMAL
WAVELENGTH MANAGEMENT
 Camera Accessories WAVELENGTH MANAGEMENT UV CONVERTERS UV Converters take advantage of a phenomenon called fluorescence to extend the performance range of the Beamage beam profiling camera to ultraviolet
Camera Accessories WAVELENGTH MANAGEMENT UV CONVERTERS UV Converters take advantage of a phenomenon called fluorescence to extend the performance range of the Beamage beam profiling camera to ultraviolet
E x Direction of Propagation. y B y
 x E x Direction of Propagation k z z y B y An electromagnetic wave is a travelling wave which has time varying electric and magnetic fields which are perpendicular to each other and the direction of propagation,
x E x Direction of Propagation k z z y B y An electromagnetic wave is a travelling wave which has time varying electric and magnetic fields which are perpendicular to each other and the direction of propagation,
Text for the class, Pump-Probe Technique for Picosecond Time-resolved X-ray Diffraction at Cheiron School
 BL19LXU Yoshihito Tanaka, Oct. 2013 Text for the class, Pump-Probe Technique for Picosecond Time-resolved X-ray Diffraction at Cheiron School Abstract The pulsed time structure of synchrotron radiation
BL19LXU Yoshihito Tanaka, Oct. 2013 Text for the class, Pump-Probe Technique for Picosecond Time-resolved X-ray Diffraction at Cheiron School Abstract The pulsed time structure of synchrotron radiation
MATHEMATICAL MODELLING OF THE PRECISE LASER CUTTING PROCESS OF Al 2 O 3 (SAPPHIRE) CRYSTAL. 1. INTRODUCTION.
 Laser beam machining micromachining, sapphire Dominik WYSZYNSKI 1 Sebastian SKOCZYPIEC 1 Karolina FURYK 1 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING OF THE PRECISE LASER CUTTING PROCESS OF Al 2 O 3 (SAPPHIRE) CRYSTAL. Today
Laser beam machining micromachining, sapphire Dominik WYSZYNSKI 1 Sebastian SKOCZYPIEC 1 Karolina FURYK 1 MATHEMATICAL MODELLING OF THE PRECISE LASER CUTTING PROCESS OF Al 2 O 3 (SAPPHIRE) CRYSTAL. Today
specular diffuse reflection.
 Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Lesson 8 Light and Optics The Nature of Light Properties of Light: Reflection Refraction Interference Diffraction Polarization Dispersion and Prisms Total Internal Reflection Huygens s Principle The Nature
Chapter 2: Wave Optics
 Chapter : Wave Optics P-1. We can write a plane wave with the z axis taken in the direction of the wave vector k as u(,) r t Acos tkzarg( A) As c /, T 1/ and k / we can rewrite the plane wave as t z u(,)
Chapter : Wave Optics P-1. We can write a plane wave with the z axis taken in the direction of the wave vector k as u(,) r t Acos tkzarg( A) As c /, T 1/ and k / we can rewrite the plane wave as t z u(,)
Efficient metal processing using high average power ultrafast laser
 Efficient metal processing using high average power ultrafast laser Strasbourg, September 13 th, 2017 J. Lopez J. Lopez et al., Journal of Laser Micro and Nanofabrication, submitted (2017) G. Mincuzzi
Efficient metal processing using high average power ultrafast laser Strasbourg, September 13 th, 2017 J. Lopez J. Lopez et al., Journal of Laser Micro and Nanofabrication, submitted (2017) G. Mincuzzi
WAVELENGTH MANAGEMENT
 BEAM DIAGNOS TICS SPECIAL PRODUCTS OEM DETECTORS THZ DETECTORS PHOTO DETECTORS HIGH POWER SOLUTIONS POWER DETECTORS ENERGY DETECTORS MONITORS Camera Accessories WAVELENGTH MANAGEMENT UV CONVERTERS UV Converters
BEAM DIAGNOS TICS SPECIAL PRODUCTS OEM DETECTORS THZ DETECTORS PHOTO DETECTORS HIGH POWER SOLUTIONS POWER DETECTORS ENERGY DETECTORS MONITORS Camera Accessories WAVELENGTH MANAGEMENT UV CONVERTERS UV Converters
ratio of the volume under the 2D MTF of a lens to the volume under the 2D MTF of a diffraction limited
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES.9 Strehl ratio (a.u.).5 Singlet Doublet 2 Incident angle (degree) 3 Supplementary Figure. Strehl ratio of the singlet and doublet metasurface lenses. Strehl ratio is the ratio of
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES.9 Strehl ratio (a.u.).5 Singlet Doublet 2 Incident angle (degree) 3 Supplementary Figure. Strehl ratio of the singlet and doublet metasurface lenses. Strehl ratio is the ratio of
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11. Reflection and refraction
 Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Lecture 7 Notes: 07 / 11 Reflection and refraction When an electromagnetic wave, such as light, encounters the surface of a medium, some of it is reflected off the surface, while some crosses the boundary
Diffraction Diffraction occurs when light waves is passed by an aperture/edge Huygen's Principal: each point on wavefront acts as source of another
 Diffraction Diffraction occurs when light waves is passed by an aperture/edge Huygen's Principal: each point on wavefront acts as source of another circular wave Consider light from point source at infinity
Diffraction Diffraction occurs when light waves is passed by an aperture/edge Huygen's Principal: each point on wavefront acts as source of another circular wave Consider light from point source at infinity
Coherent Gradient Sensing Microscopy: Microinterferometric Technique. for Quantitative Cell Detection
 Coherent Gradient Sensing Microscopy: Microinterferometric Technique for Quantitative Cell Detection Proceedings of the SEM Annual Conference June 7-10, 010 Indianapolis, Indiana USA 010 Society for Experimental
Coherent Gradient Sensing Microscopy: Microinterferometric Technique for Quantitative Cell Detection Proceedings of the SEM Annual Conference June 7-10, 010 Indianapolis, Indiana USA 010 Society for Experimental
MACHINING SURFACE FINISH QUALITY USING 3D PROFILOMETRY
 MACHINING SURFACE FINISH QUALITY USING 3D PROFILOMETRY Prepared by Duanjie Li, PhD Morgan, Ste1, Irvine CA 91 P: 99.1.99 F: 99.1.93 nanovea.com Today's standard for tomorrow's materials. 1 NANOVEA INTRODUCTION
MACHINING SURFACE FINISH QUALITY USING 3D PROFILOMETRY Prepared by Duanjie Li, PhD Morgan, Ste1, Irvine CA 91 P: 99.1.99 F: 99.1.93 nanovea.com Today's standard for tomorrow's materials. 1 NANOVEA INTRODUCTION
2/26/2016. Chapter 23 Ray Optics. Chapter 23 Preview. Chapter 23 Preview
 Chapter 23 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 23-2 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-3 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-4 1 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-5 Chapter 23 Preview
Chapter 23 Ray Optics Chapter Goal: To understand and apply the ray model of light. Slide 23-2 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-3 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-4 1 Chapter 23 Preview Slide 23-5 Chapter 23 Preview
Real-world applications of intense light matter interaction beyond the scope of classical micromachining.
 Dr. Lukas Krainer lk@onefive.com CEO Real-world applications of intense light matter interaction beyond the scope of classical micromachining. 1 Management & Company Company Based in Zürich, Switzerland
Dr. Lukas Krainer lk@onefive.com CEO Real-world applications of intense light matter interaction beyond the scope of classical micromachining. 1 Management & Company Company Based in Zürich, Switzerland
MICRO FABRICATION BY UV LASER PHOTOPOLYMERIZATION
 Memoirs Micro of Fabrication the School by of UV Engineering, Laser Photopolymerization Nagoya University Vol.50, No.1/ (1998) 33 MICRO FABRICATION BY UV LASER PHOTOPOLYMERIZATION Katsumi YAMAGUCHI and
Memoirs Micro of Fabrication the School by of UV Engineering, Laser Photopolymerization Nagoya University Vol.50, No.1/ (1998) 33 MICRO FABRICATION BY UV LASER PHOTOPOLYMERIZATION Katsumi YAMAGUCHI and
dq dt I = Irradiance or Light Intensity is Flux Φ per area A (W/m 2 ) Φ =
 Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
Mirror Example Consider a concave mirror radius -10 cm then = = Now consider a 1 cm candle s = 15 cm from the vertex Where is the image.
 Mirror Example Consider a concave mirror radius -10 cm then r 10 f = = = 5 cm 2 2 Now consider a 1 cm candle s = 15 cm from the vertex Where is the image 1 s 2 1 = = r s 1 1 2 + = = s s r 1 1 = 0.13333
Mirror Example Consider a concave mirror radius -10 cm then r 10 f = = = 5 cm 2 2 Now consider a 1 cm candle s = 15 cm from the vertex Where is the image 1 s 2 1 = = r s 1 1 2 + = = s s r 1 1 = 0.13333
Vibration-assisted Surface Texturing Yanjie Yuan, Jian Cao, Kornel Ehmann
 Vibration-assisted Surface Texturing Yanjie Yuan, Jian Cao, Kornel Ehmann SmartManufacturingSeries.com Outline Introduction and Motivation Types of Vibration-assisted Cutting and Texturing 1D Methods Resonant
Vibration-assisted Surface Texturing Yanjie Yuan, Jian Cao, Kornel Ehmann SmartManufacturingSeries.com Outline Introduction and Motivation Types of Vibration-assisted Cutting and Texturing 1D Methods Resonant
Manual Infrared viewers ABRIS M series M1300 M1700 M2000
 Manual Infrared viewers ABRIS M series M1300 M1700 M2000 Content Content... 3 Safety requirements... 4 About... 4 Applications... 5 How does it work?... 5 Operation... 6 IR viewer in comparison with a
Manual Infrared viewers ABRIS M series M1300 M1700 M2000 Content Content... 3 Safety requirements... 4 About... 4 Applications... 5 How does it work?... 5 Operation... 6 IR viewer in comparison with a
Be careful not to leave your fingerprints on the optical surfaces of lenses or Polaroid sheets.
 POLARIZATION OF LIGHT REFERENCES Halliday, D. and Resnick, A., Physics, 4 th edition, New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1992, Volume II, Chapter 48-1, 48-2, 48-3. (2weights) (1weight-exercises 1 and 3
POLARIZATION OF LIGHT REFERENCES Halliday, D. and Resnick, A., Physics, 4 th edition, New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 1992, Volume II, Chapter 48-1, 48-2, 48-3. (2weights) (1weight-exercises 1 and 3
Philip E. Plantz. Application Note. SL-AN-08 Revision C. Provided By: Microtrac, Inc. Particle Size Measuring Instrumentation
 A Conceptual, Non-Mathematical Explanation on the Use of Refractive Index in Laser Particle Size Measurement (Understanding the concept of refractive index and Mie Scattering in Microtrac Instruments and
A Conceptual, Non-Mathematical Explanation on the Use of Refractive Index in Laser Particle Size Measurement (Understanding the concept of refractive index and Mie Scattering in Microtrac Instruments and
Lab 2 Report. Carlin Gettliffe
 Lab 2 Report Carlin Gettliffe Abstract: In this lab we investigated the wave-particle duality of light. We verified light s wave properties by conducting both a double slit experiment and constructing
Lab 2 Report Carlin Gettliffe Abstract: In this lab we investigated the wave-particle duality of light. We verified light s wave properties by conducting both a double slit experiment and constructing
The branch of physics which studies light
 Mr.V The branch of physics which studies light Geometric model XVI century by W Snell Wave Model XIX century by JC Maxwell Photon Model XX century by Planck, Einstein Models of Light Basic Concept Laws
Mr.V The branch of physics which studies light Geometric model XVI century by W Snell Wave Model XIX century by JC Maxwell Photon Model XX century by Planck, Einstein Models of Light Basic Concept Laws
SPIE Paper Number: SPIE Optics and Photonics August 2012 San Diego, California, USA 1. INTRODUCTION ABSTRACT
 SPIE Paper Number: 8519-21 SPIE Optics and Photonics 12-16 August 2012 San Diego, California, USA Femtosecond fiber laser based micro- and nano-processing (Invited talk) Huan Huang*, Lih-Mei Yang and Jian
SPIE Paper Number: 8519-21 SPIE Optics and Photonics 12-16 August 2012 San Diego, California, USA Femtosecond fiber laser based micro- and nano-processing (Invited talk) Huan Huang*, Lih-Mei Yang and Jian
The Importance of Refractive Index When using Laser Diffraction
 The Importance of Refractive Index When using Laser Diffraction Mark Bumiller mark.bumiller@horiba.com Fraunhofer Approximation Mie Theory RI 1.60 0.0i, in water, RI 1.33 Mie vs. Fraunhofer 1.E+05 1.E+04
The Importance of Refractive Index When using Laser Diffraction Mark Bumiller mark.bumiller@horiba.com Fraunhofer Approximation Mie Theory RI 1.60 0.0i, in water, RI 1.33 Mie vs. Fraunhofer 1.E+05 1.E+04
Section 2 PROGRESS IN LASER FUSION
 Section 2 PROGRESS IN LASER FUSION 2.A Optical Fiducials for X-Ray Streak Cameras X-ray streak cameras are the primary instruments for studying the transient nature of laser-produced plasmas. However,
Section 2 PROGRESS IN LASER FUSION 2.A Optical Fiducials for X-Ray Streak Cameras X-ray streak cameras are the primary instruments for studying the transient nature of laser-produced plasmas. However,
B R O A D B A N D P O L A R I Z I N G B E A M S P L I T T E R C U B E S I N 3 0 M M C A G E C U B E S
 B R O A D B A N D P O L A R I Z I N G B E A M S P L I T T E R C U B E S I N 3 0 M M C A G E C U B E S Transmitted Beam Extinction Ratio: >1000:1 Reflects S Polarization 90º SM1 and 30 mm Cage System Compatible
B R O A D B A N D P O L A R I Z I N G B E A M S P L I T T E R C U B E S I N 3 0 M M C A G E C U B E S Transmitted Beam Extinction Ratio: >1000:1 Reflects S Polarization 90º SM1 and 30 mm Cage System Compatible
UV-NIR LASER BEAM PROFILER
 - Technical Data - CCD-1201 CCD-2301 CCD-2302 Standard Series Standard Series Standard Series SENSOR DATA Format: 1/2 2/3 2/3 Active area (without cover glass): 6.5mm x 4.8mm 9.0mm x 6.7mm 8.5mm x 7.1mm
- Technical Data - CCD-1201 CCD-2301 CCD-2302 Standard Series Standard Series Standard Series SENSOR DATA Format: 1/2 2/3 2/3 Active area (without cover glass): 6.5mm x 4.8mm 9.0mm x 6.7mm 8.5mm x 7.1mm
New approach to jitter reduction of an x-ray streak camera in accumulation mode
 New approach to jitter reduction of an x-ray streak camera in accumulation mode J. Liu *a, A. G. MacPhee b, C. Liu a, B. Shan c, Z. Chang c and J. Wang a a Advanced Photon Source, Argonne National Laboratory,
New approach to jitter reduction of an x-ray streak camera in accumulation mode J. Liu *a, A. G. MacPhee b, C. Liu a, B. Shan c, Z. Chang c and J. Wang a a Advanced Photon Source, Argonne National Laboratory,
APPLICATIONS KEY FEATURES. High-speed intensified Camera Attachment
 HiCATT High-speed intensified Camera Attachment The HiCATT is an intensified camera attachment specifically designed for use in combination with high-speed cameras. It can be used to amplify low light
HiCATT High-speed intensified Camera Attachment The HiCATT is an intensified camera attachment specifically designed for use in combination with high-speed cameras. It can be used to amplify low light
SHEAR WAVE WEDGE FOR LASER ULTRASONICS INTRODUCTION
 SHEAR WAVE WEDGE FOR LASER ULTRASONICS INTRODUCTION R. Daniel Costleyl, Vimal Shah2, Krishnan Balasubramaniam2, and Jagdish Singhl 1 Diagnostic Instrumentation and Analysis Laboratories 2 Department of
SHEAR WAVE WEDGE FOR LASER ULTRASONICS INTRODUCTION R. Daniel Costleyl, Vimal Shah2, Krishnan Balasubramaniam2, and Jagdish Singhl 1 Diagnostic Instrumentation and Analysis Laboratories 2 Department of
Thread Mountable Cameo Laser Diode Module
 Thread Mountable Cameo Laser Diode Module Thread Mountable Cameo The Cameo is a unique, versatile, high quality industrial laser diode module widely used in alignment applications. Available in two models,
Thread Mountable Cameo Laser Diode Module Thread Mountable Cameo The Cameo is a unique, versatile, high quality industrial laser diode module widely used in alignment applications. Available in two models,
Text for the class, Pump and probe technique for picosecond time-resolved x-ray diffraction at the Cheiron School
 Yoshihito Tanaka, Kiminori Ito Oct. 3-4, 2011 Text for the class, Pump and probe technique for picosecond time-resolved x-ray diffraction at the Cheiron School 1. Introduction 1-1. Purpose The pulsed nature
Yoshihito Tanaka, Kiminori Ito Oct. 3-4, 2011 Text for the class, Pump and probe technique for picosecond time-resolved x-ray diffraction at the Cheiron School 1. Introduction 1-1. Purpose The pulsed nature
Measurement of period difference in grating pair based on analysis of grating phase shift
 Measurement of period difference in grating pair based on analysis of grating phase shift Chao Guo, Lijiang Zeng State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments Department of Precision
Measurement of period difference in grating pair based on analysis of grating phase shift Chao Guo, Lijiang Zeng State Key Laboratory of Precision Measurement Technology and Instruments Department of Precision
CHAPTER 2: THREE DIMENSIONAL TOPOGRAPHICAL MAPPING SYSTEM. Target Object
 CHAPTER 2: THREE DIMENSIONAL TOPOGRAPHICAL MAPPING SYSTEM 2.1 Theory and Construction Target Object Laser Projector CCD Camera Host Computer / Image Processor Figure 2.1 Block Diagram of 3D Areal Mapper
CHAPTER 2: THREE DIMENSIONAL TOPOGRAPHICAL MAPPING SYSTEM 2.1 Theory and Construction Target Object Laser Projector CCD Camera Host Computer / Image Processor Figure 2.1 Block Diagram of 3D Areal Mapper
Internal modification in transparent hybrid germanium-silica plates using plasma formation induced by a femtosecond laser
 Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) s808 s812 Internal modification in transparent hybrid germanium-silica plates using plasma formation induced by a femtosecond laser Ji-Wook YOON 1, Jung-Kyu PARK
Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 22(2012) s808 s812 Internal modification in transparent hybrid germanium-silica plates using plasma formation induced by a femtosecond laser Ji-Wook YOON 1, Jung-Kyu PARK
Chemistry Instrumental Analysis Lecture 6. Chem 4631
 Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 6 UV to IR Components of Optical Basic components of spectroscopic instruments: stable source of radiant energy transparent container to hold sample device
Chemistry 4631 Instrumental Analysis Lecture 6 UV to IR Components of Optical Basic components of spectroscopic instruments: stable source of radiant energy transparent container to hold sample device
High spatial resolution measurement of volume holographic gratings
 High spatial resolution measurement of volume holographic gratings Gregory J. Steckman, Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc., 8 E. Duarte Rd., Monrovia, CA, USA 9116 ABSTRACT The conventional approach for measuring
High spatial resolution measurement of volume holographic gratings Gregory J. Steckman, Frank Havermeyer Ondax, Inc., 8 E. Duarte Rd., Monrovia, CA, USA 9116 ABSTRACT The conventional approach for measuring
dq dt I = Irradiance or Light Intensity is Flux Φ per area A (W/m 2 ) Φ =
 Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
Radiometry (From Intro to Optics, Pedrotti -4) Radiometry is measurement of Emag radiation (light) Consider a small spherical source Total energy radiating from the body over some time is Q total Radiant
