VNF Guidelines. Network Cloud. OpenECOMP
|
|
|
- Everett May
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VNF Guidelines for Network Cloud and OpenECOMP Version 1.0 February 1, 2017 You may obtain a copy of the License at Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License. ECOMP and OpenECOMP are trademarks and service marks of AT&T Intellectual Property
2 Document Revision History Date Revision Description 2/1/ Initial public release of VNF Guidelines for Network Cloud and OpenECOMP Page i
3 Table of Contents 1 Abstract Introduction Motivation Audience Program and Document Structure VNF Context Business Process Impacts ETSI Network Function Virtualization (NFV) comparison Evolving VNF Related Industry Activities Evolving towards VNFs VNF Characteristics Cloud Readiness OpenECOMP Ready Virtualization Environment Ready Summary Appendix A - Glossary Appendix B - References Appendix C - Comparison between VNF Guidelines and ETSI GS NFV-SWA Page ii
4 1 Abstract This white paper and the accompanying reference documents set forth guidelines and requirements for Virtual Network Functions (VNFs) that run in Network Clouds 1 and are managed by OpenECOMP 2. This document set is part of the OpenECOMP community and focuses on setting and evolving VNF standards that will facilitate industry discussion, participation, alignment and evolution toward comprehensive and actionable VNF best practices and standard interfaces. The goal is to accelerate adoption of VNF best practices which will increase innovation, minimize customization needed to onboard VNFs as well as reduce implementation complexity, time and cost for all impacted stakeholders. The intent is to drive harmonization of VNFs across VNF providers, Network Cloud Service Providers (NCSPs) and the overall Network Function Virtualization (NFV) ecosystem by providing both long term vision as well as short term focus and clarity where no current open source implementations exist today. This first release of the guidelines and requirements, although applicable in many implementations, is targeted for those implementations that consist of Network Clouds based on OpenStack. Future versions of these guidelines are envisioned to include other targeted virtualization environments, such as Customer Premises or other single-tenant small scale cloud implementations. In addition, given the relative maturity of key technologies involved, rapid innovation of NFV/SDN and virtualization technologies as well as the evolving OpenECOMP roadmap, this will be a living package that will evolve over time. These documents will become part of the OpenECOMP related requirements documents. The following enhancements are anticipated to be addressed in the next set of releases: Open source software and demos of simple reference VNFs; Automation of VNF onboarding and other aspects of VNF lifecycle as supported by OpenECOMP; Consistent VNF packaging for automated onboarding using OpenECOMP; Other implementation examples for targeted virtualization environments beyond OpenStack based Network Clouds; Incubation and certification environment to provide a self-service program to gauge maturity and readiness of VNFs. 1 Network Clouds are built on a framework containing these essential elements: refactoring hardware elements into software functions running on commodity cloud computing infrastructure; aligning access, core, and edge networks with the traffic patterns created by IP based services; integrating the network and cloud technologies on a software platform that enables rapid, highly automated, deployment and management of services, and software defined control so that both infrastructure and functions can be optimized across change in service demand and infrastructure availability; and increasing competencies in software integration and a DevOps operations model. 2 OpenECOMP is an open source initiative for ECOMP, Page 1
5 2 Introduction 2.1 Motivation The requirements and guidelines defined herein are intended to facilitate industry discussion, participation alignment and evolution toward comprehensive and actionable VNF best practices. Integration costs are a significant impediment to the development and deployment of new services. We envision developing open source industry processes and best practices leading eventually to VNF standards supporting commercial acquisition of VNFs with minimal integration costs. Traditional PNFs have all been unique like snowflakes and required expensive custom integration, whereas VNF products and services should be designed for easier integration just like Lego TM blocks. For example, by standardizing on common actions and related APIs supported by VNFs, plug and play integration is assured, jumpstarting automation with management frameworks. Onboarding VNFs would no longer require complex and protracted integration or development activities thus maximizing automation and minimizing integration cost. Creating VNF open source environments, best practices and standards provides additional benefits to the NFV ecosystems such as: Larger market for VNF providers Rapid introduction and integration of new capabilities into the services providers environment Reduced development times and costs for VNF providers Better availability of new capabilities to NCSPs Better distribution of new capabilities to end-user consumers Reduced integration cost (capex) for NCSPs Usage based software licensing for end-user consumers and NCSPs 2.2 Audience The industry transformation associated with softwarization 3 results in a number of changes in traditional approaches for industry collaboration. Changes from hardware to software, from waterfall to agile processes and the emergence of industry supported open source communities imply corresponding changes in processes at many industry collaboration bodies. With limited operational experience and much more dynamic requirements, open source communities are expected to evolve these VNF guidelines further before final documentation of those aspects necessary for standardization. This white paper and accompanying reference documents provides VNF providers, NCSPs and other interested 3rd parties a set of guidelines and requirements for the design, build and overall lifecycle management of VNFs. VNF Providers Both suppliers transitioning from providing physical network functions (PNFs) to providing VNFs as well as new market entrants should find these VNF requirements and guidelines a useful introduction to the requirements to be able to develop VNFs for deployment into a Network Cloud. VNF Providers may also be interested to test their VNFs in the context of an open source implementation of the environment. Network Cloud Service Providers (NCSPs) A NCSP provides services based on Network Cloud infrastructure as well as services above the infrastructure layer, e.g., platform service, end-to-end services. 3 Softwarization is the transformation of business processes to reflect characteristics of software centric products, services, lifecycles and methods. Page 2
6 Common approaches to packaging of VNFs enable economies of scale in their development. As suitable infrastructure becomes deployed, NCSPs have a common interest in guidelines that support the ease of deployment of VNFs in each other s Network Cloud. After reading these VNF guidelines, NCSPs should be motivated to join AT&T in evolving these guidelines in the OpenECOMP open source community to meet the industry s collective needs. Other interested parties Other parties such as solution providers, open source community, industry standard bodies, students and researchers of network technologies, as well as enterprise customers may also be interested in the VNF Guidelines. Solution Providers focused on specific industry verticals may find these VNF guidelines useful in the development of specialized VNFs that can better address the needs of their industry through deployment of these VNFs in NCSP infrastructure. Open Source developers can use these VNF guidelines to facilitate the automation of VNF ingestion and deployment. The emergence of a market for VNFs enables NCSPs to more rapidly deliver increased functionality, for execution on white box hardware on customer s premises such functionality may be of particular interest to enterprises supporting similar infrastructure. 2.3 Program and Document Structure This document is part of a hierarchy of documents that describes the overall Requirements and Guidelines for OpenECOMP. The diagram below identifies where this document fits in the hierarchy. OpenECOMP Requirements and Guidelines VNF Cloud Readiness Requirements for OpenECOMP VNF Guidelines for Network Cloud and OpenECOMP VNF Management Requirements for OpenECOMP VNF Heat Template Requirements for OpenECOMP Future VNF Requirements Documents Future OpenECOMP Subject Documents Future Requirements Documents Document summary: VNF Guidelines for Network Cloud and OpenECOMP Describes VNF environment and overview of requirements VNF Cloud Readiness Requirements for OpenECOMP Cloud readiness requirements for VNFs (Design, Resiliency, Security, and DevOps) VNF Management Requirements for OpenECOMP Requirements for how VNFs interact and utilize OpenECOMP VNF Heat Template Requirements for OpenECOMP Provides recommendations and standards for building Heat templates compatible with OpenECOMP initial implementations of Network Cloud are assumed to be OpenStack based. Page 3
7 3 VNF Context A technology trend towards softwarization is impacting the communications industry as it has already impacted a number of other industries. This trend is expected to have some significant impacts on the products and processes of this industry. The transformation from products primarily based on hardware to products primarily based on software has a number of impacts. The completeness of the software packages to ease integration, usage based licensing to reflect scaling properties, independence from hardware and location and software resilience in the presence of underlying hardware failure all gain in importance compared to prior solutions. The processes supporting software products and services are also expected to transform from traditional waterfall methodologies to agile methods. In agile processes, characteristics such as versioned APIs, rolling upgrades, automated testing and deployment support with incremental release schedules become important for these software products and services. Industry process related to software products and services also change with the rise of industrially supported open source communities. Engagement with these open source communities enables sharing of best practices and collaborative development of open source testing and integration regimes, open source APIs and open source code bases. The term VNF is inspired by the work 4 of the ETSI 5 Network Functions Virtualization (NFV) Industry Specification Group (ISG). ETSI s VNF definition includes both historically network functions, such as Virtual Provider Edge (VPE), Virtual Customer Edge (VCE), and Session Border Controller (SBC), as well as historically non-network functions when used to support network services, such as network-supporting web servers and databases. The VNF discussion in these guidelines applies to all types of virtualized workloads, not just network appliance workloads. Having a consistent approach to virtualizing any workload provides more industry value than just virtualizing some workloads. 6 VNFs are functions that are implemented in Network Clouds. Network Clouds must support end-to-end high-bandwidth low latency network flows through VNFs running in virtualization environments. For example, a Network Cloud is able to provide a firewall service to be created such that all Internet traffic to a customer premise passes through a virtual firewall running in the Network Cloud. A data center may be the most common target for a virtualization environment, but it is not the only target. Virtualization environments are also supported by more constrained resources e.g., Enterprise Customer Premise Equipment (CPE). Virtualization environments are also expected to be available at more distributed network locations by architecting central offices as data centers, or virtualizing functions located at the edge of the operator infrastructure (e.g., virtualized Optical Line Termination (volt) or xran 7 ) and in constrained resource Access Nodes. Expect detailed requirements to evolve with these additional virtualization environments. Some VNFs may scale across all these environments, but all VNFs should onboard through the same process before deployment to the targeted virtualization environment. 4 Virtual Network Functions Architecture ETSI GS NFV-SWA 001 v1.1.1 (Dec 2012) 5 European Telecommunications Standards Institute or ETSI ( is a respected standards body providing standards for information and communications technologies. 6 Full set of capabilities of Network Cloud and/or OpenECOMP might not be needed to support traditional IT like workloads. 7 xran ( Page 4
8 3.1 Business Process Impacts Business process changes need to occur in order to realize full benefits of VNF characteristics: efficiency via automation, open source reliance, and improved cycle time through careful design. Efficiency via Automation Systems reliant on human labor for critical operational tasks don t scale. By aggressively automating all VNF operational procedures, VNFs have lower operational cost, are more rapidly deployed at scale and are more consistent in their operation. OpenECOMP provides the automation framework which VNFs can take advantage of simply by implementing OpenECOMP compatible interfaces and lifecycle models. This enables automation which drives operational efficiencies and delivers the corresponding benefits. Open Source VNFs are expected to run on infrastructure largely enabled by open source software. For example, OpenStack 8 is often used to provide the virtualized compute, network, and storage capabilities used to host VNFs. OpenDaylight (ODL) 9 can provide the network control plane. The OPNFV community 10 provides a reference platform through integration of ODL, OpenStack and other relevant open source projects. VNFs also run in open source operating systems like Linux. VNFs might also utilize open source software libraries to take advantage of required common but critical software capabilities where community support is available. Automation becomes easier, overall costs go down and time to market can decrease when VNFs can be developed and tested in an open source reference platform environment prior to onboarding by the NCSP. All of these points contribute to a lower cost structure for both VNF providers and NCSPs. Improved Cycle Time through Careful Design Today s fast paced world requires businesses to evolve rapidly in order to stay relevant and competitive. To a large degree VNFs, when used with the same control, orchestration, management and policy framework (e.g., OpenECOMP), will improve service development and composition. VNFs should enable NCSPs to exploit recursive nesting of VNFs to acquire VNFs at the smallest appropriate granularity so that new VNFs and network services can be composed. The ETSI NFV Framework 11 envisages such recursive assembly of VNFs, but many current implementations fail to support such features. Designing for VNF reuse often requires that traditional appliance based PNFs be refactored into multiple individual VNFs where each does one thing particularly well. While the original appliance based PNF can be replicated virtually by the right combination and organization of lower level VNFs, the real advantage comes in creating new services composed of different combinations of lower level VNFs (possibly from many providers) organized in new ways. Easier and faster service creation often generates real value for businesses. As softwarization trends progress towards more agile processes, VNFs, OpenECOMP and Network Clouds are all expected to evolve towards continuous integration, testing and deployment of small incremental changes to de-risk the upgrade process. 3.2 ETSI Network Function Virtualization (NFV) comparison ETSI defines a VNF as an implementation of a network function that can be deployed on a Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure (NFVI). Service instances may be composed of an assembly of VNFs. 8 OpenStack ( 9 OpenDaylight ( 10 OPNFV ( 11 See, e.g., Figure 3 of GS NFV 002, Architectural Framework Page 5
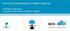
9 In turn, a VNF may also be assembled from VNF components (VNFCs) that each provide a reusable set of functionality. VNFs are expected to take advantage of platform provided common services. VNF management and control under OpenECOMP is different than management and control exposed in the ETSI MANO model. With OpenECOMP, there is only a single management and control plane. In ETSI s Framework 12, architectural options exist for preserving legacy systems that increase integration costs e.g., different VNFs can be controlled by VNF Managers (VNFMs) and Element Management Systems (EMSs) provided by different software providers. OpenECOMP addresses the concern that multiple VNFMs in this space will hinder VNF reuse and increase VNF and service integration costs. Asking all VNF providers to take advantage of and interoperate with common control software mitigates related reuse and integration challenges. The common, SDN based, control platform (OpenECOMP) is being made available as an open source project to reduce friction for VNF providers and enable new network functions to get to market faster and with lower costs. Also under OpenECOMP, VNF providers do not provide their own proprietary VNF Managers (VNFM) or Element Management Systems (EMS). Those capabilities are provided by OpenECOMP. Hence, VNFs are required to consume open interfaces to OpenECOMP in support of management and control. The VNF Package must include the appropriate data models for integration with OpenECOMP to enable management and control of the VNFCs. Figure 1 shows a simplified OpenECOMP and Infrastructure view to highlight how individual Virtual Network Functions plug into the OpenECOMP control loops. Figure 1. Control Loop In the control loop view in Figure 1, the VNF provides an event data stream via an API to Data Collection, Analytics and Events (DCAE). DCAE analyzes and aggregates the data stream and when particular conditions are detected, uses policy to enable what, if any, action should be triggered. Some of the triggered actions may require a controller to make changes to the VNF through a VNF provided API. 12 Architectural Framework, ETSI GS NFV 002 (v1.1.1) Oct. 2013) Page 6
10 For a detailed comparison between ETSI NFV and OpenECOMP, refer to Appendix C - Comparison between VNF Guidelines and ETSI GS NFV-SWA Evolving VNF Related Industry Activities Many existing industry collaboration bodies are structured around a particular service or segment of the network. VNFs are intended to operate across multiple services and execute on commodity targeted virtualization environments. With the NCSPs transformation to acquiring products and services based on location and hardware independent VNFs, the opportunity exists for instances of those VNFs to be deployed across multiple network locations and services where suitable virtualization infrastructure is available. The rise of industry-supported open source communities has created new opportunities for collaboration and challenges for existing industry communities such as Standards Developing Organizations (SDOs). Collaboration in many SDOs defers intellectual property issues. Most industrially-supported open source communities resolve intellectual property issues between collaborators through explicit contribution licensing agreements. Common infrastructure software components (e.g., SDN Controllers, Cloud Management Systems) are expected to be available through industrially supported open source communities (e.g., Open Daylight and OpenStack). Whether VNFs are open or proprietary, they should use open APIs, test and integration capabilities developed in industrially supported open source communities (e.g., OpenECOMP, OPNFV). The migration path for operator s existing processes and services to effectively utilize VNFs may be operator specific. The requirements for VNFs may be expected to evolve rapidly as the industry develops experience with operational and development best practices for VNFs. In particular, industry operations procedures are expected to evolve towards agile software methodologies, DevOps, continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD). In this environment of changing and context-dependent VNF requirements, agile, pragmatic approaches focused on delivering functionality in the near term and evolving it towards targeted VNF characteristics are preferred over lengthy waterfall industry standardization processes. Demonstrating functionality and interoperability of appropriate VNF-related APIs in open source communities is considered a pre-requisite to starting industry specification work documenting stable interfaces. While multiple open source communities exist supporting particular infrastructure software options, the market success of any particular option combination cannot be assured. Integration communities such as OPNFV provide an approach enabling VNF providers to test their products and services against a variety of expected configurations available in the industry. 3.4 Evolving towards VNFs In order to deploy VNFs, a target virtualization environment must already be in place. The NCSPs scale necessitates a phased rollout of virtualization infrastructure and then of VNFs upon that infrastructure. Some VNF use cases may require greenfield infrastructure deployments, others may start brownfield deployments in centralized data centers and then scale deployment more widely as infrastructure becomes available. Some service providers have been very public and proactive in setting transformation targets associated with VNFs 13. Because of the complexity of migration and integration issues, the requirements for VNFs in the short term may need to be contextualized to the specific service and transition planning. Much of the existing VNF work has been based on corresponding network function definitions and requirements developed for PNFs. Many of the assumptions about PNFs do not apply to VNFs and the modularity of the functionality is expected to be significantly different. In addition, the increased service velocity objectives of NFV are based on new types of VNFs being developed to support new services 13 AT&T, for instance, has announced that it seeks to virtualize and control 75% of its network functionality by 2020 and that 50% of AT&T s software be coming from open source. For AT&T, VNFs have already been placed in service in the Network Cloud and enterprise CPE whiteboxes. Page 7
11 being deployed in virtualized environments. Much of the functionality associated with 5G (e.g., IoT, augmented reality/virtual reality) is thus expected to be deployed as VNFs in targeted virtualization infrastructure towards the edge of the network. 4 VNF Characteristics VNFs need to be constructed using a distributed systems architecture that we will call "Network Cloud Ready". They need to interact with the orchestration and control platform provided by OpenECOMP and address the new security challenges that come in this environment. The main goal of a Network Cloud Ready VNF is to run well on any Network Cloud (public or private) over any network (carrier or enterprise). In addition, for optimal performance and efficiency, VNFs will be designed to take advantage of Network Clouds. This requires careful engineering in both VNFs and candidate Network Cloud computing frameworks. To ensure Network Cloud capabilities are leveraged and VNF resource consumption meets engineering and economic targets, VNF performance and efficiency will be benchmarked in a controlled lab environment. In line with the principles and practices laid out in ETSI GS NFV-PER 001, efficiency testing will consist of benchmarking VNF performance with a reference workload and associated performance metrics on a reference Network Cloud (or, when appropriate, additional benchmarking on a bare metal reference platform). Network Cloud Ready VNF characteristics and design consideration can be grouped into three areas: Cloud Readiness OpenECOMP Ready Virtualization Environment Ready Detailed requirements are contained in the reference documents that are listed in Appendix B - References. 4.1 Cloud Readiness VNFs should be designed to operate within a cloud environment from the first stages of the development. The VNF provider should think clearly about how the VNF should be decomposed into various modules. Resiliency within a cloud environment is very different than in a physical environment and the developer should give early thought as to how the Network Cloud Service Provider will ensure the level of resiliency required by the VNF and then provide the capabilities needed within that VNF. Scaling and Security should also be well thought out at design time so that the VNF runs well in a virtualized environment. Finally, the VNF Provider also needs to think about how they will integrate and deploy new versions of the VNF. Since the cloud environment is very dynamic, the developer should utilize DevOps practices to deploy new software. Requirements for Cloud Readiness can be found in the VNF Common Requirements for OpenECOMP document VNF Design A VNF may be a large construct and therefore when designing it, it is important to think about the components from which it will be composed. The ETSI SWA 001 document gives a good overview of the architecture of a VNF in Chapter 4 as well as some good examples of how to compose a VNF in its Annex B. When laying out the components of the VNF it is important to keep in mind the following principles: Single Capability, Independence, State and the APIs. Many Network Clouds will use Heat to describe orchestration templates for instantiating VNFs and VNFCs. Heat has a useful abstraction called a module that can contain one or more VNFCs. A module can be thought of as a deployment unit. In general the goal should be for each module to contain a single VNFC. Page 8
12 Single Capability VNFs should be carefully decomposed into loosely coupled, granular, re-usable VNFCs that can be distributed and scaled on a Network Cloud. VNFCs should be responsible for a single capability. The Network Cloud will define several flavors of VMs for a VNF designer to choose from for instantiating a VNFC. The best practice is to keep the VNFCs as lightweight as possible while still fulfilling the business requirements for the "single capability", however the VNFC should not be so small that the overhead of constructing, maintaining, and operating the service outweighs its utility Independence VNFCs should be independently deployed, configured, upgraded, scaled, monitored, and administered (by OpenECOMP). The VNFC must be a standalone executable process. API versioning is one of the biggest enablers of independence. To be able to independently evolve a component, versioning must ensure existing clients of the component are not forced to flash-cut with each interface change. API versioning enables smoother evolution while preserving backward compatibility Scaling Each VNFC within a VNF must support independent horizontal scaling, by adding/removing instances, in response to demand loads on that VNFC. The Network Cloud is not expected to support adding/removing resources (compute, memory, storage) to an existing instance of a VNFC (vertical scaling). A VNF should be designed such that its components can scale independently of each other. Scaling one component should not require another component to be scaled at the same time. All scaling will be controlled by OpenECOMP Managing State VNFCs and their interfaces should isolate and manage state to allow for high-reliability, scalability, and performance in a Network Cloud environment. The use of state should be minimized as much as possible to facilitate the movement of traffic from one instance of a VNFC to another. Where state is required it should be maintained in a geographically redundant data store that may in fact be its own VNFC. This concept of decoupling state data can be extended to all persistent data. Persistent data should be held in a loosely coupled database. These decoupled databases need to be engineered and placed correctly to still meet all the performance and resiliency requirements of the service Lightweight and Open APIs Key functions are accessible via open APIs, which align to Industry API Standards and supported by an open and extensible information/data model Reusability Properly (de)composing a VNF requires thinking about reusability. Components should be designed to be reusable within the VNF as well as by other VNFs. The single capability principle aids in this requirement. If a VNFC could be reusable by other VNFs then it should be designed as its own single component VNF that may then be chained with other VNFs. Likewise, a VNF provider should make use of other common platform VNFs such as firewalls and load balancers, instead of building their own Resiliency The VNF is responsible for meeting its resiliency goals and must factor in expected availability of the targeted virtualization environment. This is likely to be much lower than found in a traditional data center. The VNF developer should design the function in such a way that if there is a platform problem the VNF will continue working as needed and meet the SLAs of that function. VNFs should be designed to survive single failure platform problems including: hypervisor, server, datacenter outages, etc. There will also be significant planned downtime for the Network Cloud as the infrastructure goes through hardware and software upgrades. The VNF should support tools for gracefully meeting the service needs such as Page 9
13 methods for migrating traffic between instances and draining traffic from an instance. The VNF needs to rapidly respond to the changing conditions of the underlying infrastructure. VNF resiliency can typically be met through redundancy often supported by distributed systems architectures. This is another reason for favoring smaller VNFCs. By having more instances of smaller VNFCs it is possible to spread the instance out across servers, racks, datacenters, and geographic regions. This level of redundancy can mitigate most failure scenarios and has the potential to provide a service with even greater availability than the old model. Careful consideration of VNFC modularity also minimizes the impact of failures when an instance does fail Security Security must be integral to the VNF through its design, development, instantiation, operation, and retirement phases. VNF architectures deliver new security capabilities that make it easier to maximize responsiveness during a cyber-attack and minimize service interruption to the customers. SDN enables the environment to expand and adapt for additional traffic and incorporation of security solutions. Further, additional requirements will exist to support new security capabilities as well as provide checks during the development and production stages to assure the expected advantages are present and compensating controls exist to mitigate new risks. New security requirements will evolve along with the new architecture. Initially, these requirements will fall into the following categories: VNF General Security Requirements VNF Identity and Access Management Requirements VNF API Security Requirements VNF Security Analytics Requirements VNF Data Protection Requirements DevOps The OpenECOMP software development and deployment methodology is evolving toward a DevOps model. VNF development and deployment should evolve in the same direction, enabling agile delivering of end-to-end services. Following these same principles better positions OpenECOMP and VNF development to coevolve in the same direction Testing VNF packages should provide comprehensive automated regression, performance and reliability testing with VNFs based on open industry standard testing tools and methodologies. VNF packages should provide acceptance and diagnostic tests and in-service instrumentation to be used in production to validate VNF operation Build and Deployment Processes VNF packages should include continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD) software artifacts that utilize automated open industry standard system and container build tools. The VNF package should include parameterized configuration variables to enable automated build customization. Don t create unique (snowflake) VNFs requiring any manual work or human attention to deploy. Do create standardized (Lego ) VNFs that can be deployed in a fully automated way. OpenECOMP will orchestrate updates and upgrades of VNFs. The target method for updates and upgrades is to onboard and validate the new version, then build a new instance with the new version of software, transfer traffic to that instance and kill the old instance. There should be no need for the VNF or its components to provide an update/upgrade mechanism. Page 10
14 Automation Increased automation is enabled by VNFs and VNF design and composition. VNF and VNFCs should provide the following automation capabilities, as triggered or managed via OpenECOMP: Events and alarms Lifecycle events Zero-Touch rolling upgrades and downgrades Configuration 4.2 OpenECOMP Ready OpenECOMP is the brain providing the lifecycle management and control of software-centric network resources, infrastructure and services. OpenECOMP is critical in achieving the objectives to increase the value of the Network Cloud to customers by rapidly on-boarding new services, enabling the creation of a new ecosystem of consumer and enterprise services, reducing capital and operational expenditures, and providing operations efficiencies. It delivers enhanced customer experience by allowing them in near realtime to reconfigure their network, services, and capacity. For more details, refer to the ECOMP Architecture White Paper 14. One of the main OpenECOMP responsibilities is to rapidly onboard and enrich VNFs to be cataloged as resources to allow composition and deployment of services in a multi-vendor plug and play environment. It is also extremely important to be able to automatically manage the VNF run-time lifecycle to fully realize benefits of NFV. The VNF run-time lifecycle includes aspects such as instantiation, configuration, elastic scaling, automatic recovery from resource failures, and resource allocation. It is therefore imperative to provide VNFs that are equipped with well-defined capabilities that comply with OpenECOMP standards to allow rapid onboarding and automatic lifecycle management of these resources when deploying services as depicted in Figure 2. Figure 2. VNF Complete Lifecycle Stages In order to realize these capabilities within the OpenECOMP platform, it is important to adhere to a set of key principles (listed below) for VNFs to integrate into OpenECOMP. 14 ECOMP (Enhanced Control Orchestration, Management & Policy) Architecture White Paper ( Page 11
15 Requirements for OpenECOMP Ready can be found in the VNF Management Requirements for OpenECOMP document Design Definition Onboarding automation will be facilitated by applying standards-based approaches to VNF packaging to describe the VNF s infrastructure resource requirements, topology, licensing model, design constraints, and other dependencies to enable successful VNF deployment and management of VNF configuration and operational behavior. The current VNF Package Requirement is based on a subset of the Requirements contained in the ETSI Document: ETSI GS NFV-MAN 001 v1.1.1 and GS NFV IFA011 V0.3.0 ( ) - Network Functions Virtualization (NFV), Management and Orchestration, VNF Packaging Specification Configuration Management OpenECOMP must be able to orchestrate and manage the VNF configuration to provide fully automated environment for rapid service provisioning and modification. VNF configuration/reconfiguration must be allowed directly through standardized APIs without the need for an EMS Monitoring and Management The end-to-end service reliability and availability in a virtualized environment will greatly depend on the ability to monitor and manage the behavior of Virtual Network Functions in real-time. OpenECOMP platform must be able to monitor the health of the network and VNFs through collection of event and performance data directly from network resources utilizing standardized APIs without the need for an EMS. The VNF provider must provide visibility into VNF performance and fault at the VNFC level (VNFC is the smallest granularity of functionality in our architecture) to allow OpenECOMP to proactively monitor, test, diagnose and trouble shoot the health and behavior of VNFs at their source. 4.3 Virtualization Environment Ready Every Network Cloud Service Provider will have a different set of resources and capabilities for their Network Cloud, but there are some common resources and capabilities that nearly every NCSP will offer Network Cloud VNFCs should be agnostic to the details of the Network Cloud (such as hardware, host OS, Hypervisor or container technology) and must run on the Network Cloud with acknowledgement to the paradigm that the Network Cloud will continue to rapidly evolve and the underlying components of the platform will change regularly. VNFs should be prepared to move VNFCs across VMs, hosts, locations or datacenters, or Network Clouds Overlay Network VNFs should be compliant with the Network Cloud network virtualization platform including the specific set of characteristics and features. The Network Cloud is expected to be tuned to support VNF performance requirements. Initially, specifics may differ per Network Cloud implementation and are expected to evolve over time, especially as the technology matures Guest Operating Systems VNFs should use the NCSP s standard set of OS images to enable compliance with security, audit, regulatory and other needs. Page 12
16 4.3.4 Compute Flavors VNFs should take advantage of the standard Network Cloud capabilities in terms of VM characteristics (often referred to as VM Flavors), VM sizes and cloud acceleration capabilities aimed at VNFs such as Intel s Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK). 5 Summary The intent of these guidelines and requirements is to provide long term vision as well as short term focus and clarity where no current open source implementation exists today. The goal is to accelerate the adoption of VNFs which will increase innovation, minimize customization to onboard VNFs, reduce implementation time and complexity as well as lower overall costs for all stakeholders. It is critical for the Industry to align on a set of standards and interfaces to quickly realize the benefits of NFV. AT&T is contributing these guidelines to the OpenECOMP open source community as a step in moving toward standards. These guidelines are based on our experience with large scale deployment and operations of VNFs over the past several years. This VNF guidelines document provides a general overview and points to more detailed requirements documents. The subtending documents provide more detailed requirements and are listed in Appendix B - References. All documents are expected to evolve. Some of these VNF guidelines may be more broadly applicable in the industry, e.g., in other open source communities or standards bodies. The art of VNF architecture and development is expected to mature rapidly with practical deployment and operations experience from a broader ecosystem of types of VNFs and different VNF providers. Individual operators may also choose to provide their own extensions and enhancements to support their particular operational processes, but these guidelines are expected to remain broadly applicable across a number of service providers interested in acquiring VNFs. We invite feedback on these VNF Guidelines in the context of the OpenECOMP Project. We anticipate an ongoing project within the OpenECOMP Community to maintain similar guidance for VNF developers to enable them to more easily develop VNFs which are compatible with the evolving releases of OpenECOMP. Comments on these guidelines should be discussed there. Page 13
17 Heat Network Clouds Network Cloud Service Provider SDOs Softwarization Targeted Virtualization Environment VM VNF VNFC Appendix A - Glossary Heat is a service to orchestrate composite cloud applications using a declarative template format through an OpenStack-native REST API. Network Clouds are built on a framework containing these essential elements: refactoring hardware elements into software functions running on commodity cloud computing infrastructure; aligning access, core, and edge networks with the traffic patterns created by IP based services; integrating the network and cloud technologies on a software platform that enables rapid, highly automated, deployment and management of services, and software defined control so that both infrastructure and functions can be optimized across change in service demand and infrastructure availability; and increasing competencies in software integration and a DevOps operations model. Network Cloud Service Provider (NCSP) is a company or organization, making use of a communications network to provide Network Cloud services on a commercial basis to third parties. Standards Developing Organizations are organizations which are active in the development of standards intended to address the needs of a group of affected adopters. Softwarization is the transformation of business processes to reflect characteristics of software centric products, services, lifecycles and methods. Targeted Virtualization Environment is the execution environment for VNFs. While Network Clouds located in datacenters are a common execution environment, VNFs can and will be deployed in various locations (e.g., non-datacenter environments) and form factors (e.g., enterprise Customer Premise Equipment). Non-datacenter environments are expected to be available at more distributed network locations including central offices and at the edge of the NCSP s infrastructure. Virtual Machine (VM) is a virtualized computation environment that behaves very much like a physical computer/server. A VM has all its ingredients (processor, memory/storage, interfaces/ports) of a physical computer/server and is generated by a hypervisor, which partitions the underlying physical resources and allocates them to VMs. Virtual Machines are capable of hosting a virtual network function component (VNFC). Virtual Network Function (VNF) is the software implementation of a function that can be deployed on a Network Cloud. It includes network functions that provide transport and forwarding. It also includes other functions when used to support network services, such as network-supporting web servers and database. Virtual Network Function Component (VNFC) are the sub-components of a VNF providing a VNF Provider a defined sub-set of that VNF's functionality, with the main characteristic that a single instance of this component maps 1:1 against a single Virtualization Container. See Figure 3 for the relationship between VNFC and VNFs. Page 14
18 VNFC2 VNF1 VNFC1 Service 1 VNFC4 VNF3 VNFC5 Service 2 VNF2 VNFC3 VNF2 VNFC3 Service 3 Virtual Network Function Component (VNFC) Virtual Network Function Service Figure 3. Virtual Network Function Entity Relationship Page 15
19 Appendix B - References 1. VNF Cloud Readiness Requirements for OpenECOMP 2. VNF Management Requirements for OpenECOMP 3. VNF Heat Template Requirements for OpenECOMP Page 16
20 Appendix C - Comparison between VNF Guidelines and ETSI GS NFV-SWA 001 The VNF guidelines presented in this document (VNF Guidelines) overlap with the ETSI GS NFV-SWA 001 (Network Functions Virtualization (NFV); Virtual Network Function Architecture) document. For convenience we will just refer to this document as SWA 001. The SWA 001 document is a survey of the landscape for architecting a VNF. It includes many different options for building a VNF that take advantage of the ETSI MANO architecture. The Network Cloud and OpenECOMP have similarities to ETSI s MANO, but also have differences described in earlier sections. The result is differences in the VNF requirements. Since these VNF Guidelines are for a specific implementation of an architecture they are narrower in scope than what is specified in the SWA 001 document. The VNF Guidelines primarily overlaps the SWA 001 in Sections 4 and 5. The other sections of the SWA 001 document lie outside the scope of the VNF Guidelines. This appendix will describe the differences between these two documents indexed on the SWA 001 sections Section 4 Overview of VNF in the NFV Architecture This section provides an overview of the ETSI NFVI architecture and how it interfaces with the VNF architecture. Because of the differences between infrastructure architectures there will naturally be some differences in how it interfaces with the VNF. A high level view of the differences in architecture can be found in the main body of this document and a more detailed analysis can be found in the ECOMP Architecture White Paper 15. Section 4.3 Interfaces Since OpenECOMP provides the VNFM and EMS functionality for all VNFs the SWA-3 and SWA-4 interfaces are OpenECOMP interfaces. All OpenECOMP interfaces are described in this package of documents. Section 5 VNF Design Patterns and Properties This section of the SWA 001 document gives a broad view of all the possible design patterns of VNFs. The VNF Guidelines do not generally differ from this section. The VNF Guidelines address a more specific scope than what is allowed in the SWA 001 document. Section 5.1 VNF Design Patterns The following are differences between the VNF Guidelines and SWA-001: The Network Cloud does not recognize the distinction between parallelizable and nonparallelizable VNFCs, where parallelizable means that there can be multiple instances of the VNFC. In the VNF Guidelines, all VNFCs should support multiple instances and therefore be parallelizable The VNF Guidelines encourages the use of stateless VNFCs. However, where state is needed it should be kept external to the VNFC to enable easier failover The VNF Guidelines only accepts horizontal scaling (scale out/in) by VNFC. Vertical scaling (scale up/down) is not supported by OpenECOMP. 15 ECOMP (Enhanced Control Orchestration, Management & Policy) Architecture White Paper ( Page 17
21 Since OpenECOMP provides all EMS and VNFM functionality On-Demand scaling is accomplished through OpenECOMP and not directly by the VNF Section 5.2 VNF Update and Upgrade OpenECOMP will orchestrate updates and upgrades. The preferred method for updates and upgrades is to build a new instance with the new version of software, transfer traffic to that instance and kill the old instance Section 5.3 VNF Properties The following are differences between the VNF Guidelines and SWA-001: In a Network Cloud all VNFs must be only COTS-Ready. The VNF Guidelines does not support Partly COTS-READY or Hardware Dependent The only virtualization environment currently supported by OpenECOMP is Virtual Machines. The VNF Guidelines state that all VNFs should be hypervisor agnostic. Other virtualized environment options such as containers are not currently supported. However, container technology is targeted to be supported in the future All VNFs must scale horizontally (scale out/in) within the Network Cloud. Vertical (scale up/down) is not supported The VNF Guidelines state that OpenECOMP will provide full policy management for all VNFs. The VNF will not provide its own policy management for provisioning and management The VNF Guidelines recognizes both stateless and stateful VNFCs but it encourages the minimization of stateful VNFCs The VNF Guidelines only allows for OpenECOMP management of the VNF. It does not allow a proprietary management interface for use with a 3rd party EMS Section 5.4 Attributes describing VNF Requirements Attributes described in the VNF Guidelines and reference documents include those attributes defined in this section of the SWA 001 document but also include additional attributes. Page 18
22 Copyright 2017 AT&T Intellectual Property. All Rights Reserved. This paper is licensed to you under the Creative Commons License: Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International Public License You may obtain a copy of the License at: You are free to: Share copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format Adapt remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, even commercially. The licensor cannot revoke these freedoms as long as you follow the license terms. Under the following terms: Attribution You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use. ShareAlike If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same license as the original. No additional restrictions You may not apply legal terms or technological measures that legally restrict others from doing anything the license permits. Notices: You do not have to comply with the license for elements of the material in the public domain or where your use is permitted by an applicable exception or limitation. No warranties are given. The license may not give you all of the permissions necessary for your intended use. For example, other rights such as publicity, privacy, or moral rights may limit how you use the material. Page 19
PAVING THE WAY TO OPEN SOURCE NFV. A Linux Foundation Collaborative Project
 PAVING THE WAY TO OPEN SOURCE NFV A Linux Foundation Collaborative Project 1. AN OVERVIEW OF OPNFV The Open Platform for Network Functions Virtualization (OPNFV) project was introduced in September 2014
PAVING THE WAY TO OPEN SOURCE NFV A Linux Foundation Collaborative Project 1. AN OVERVIEW OF OPNFV The Open Platform for Network Functions Virtualization (OPNFV) project was introduced in September 2014
Accelerate Your Enterprise Private Cloud Initiative
 Cisco Cloud Comprehensive, enterprise cloud enablement services help you realize a secure, agile, and highly automated infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) environment for cost-effective, rapid IT service
Cisco Cloud Comprehensive, enterprise cloud enablement services help you realize a secure, agile, and highly automated infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) environment for cost-effective, rapid IT service
Cloud Systems 2018 Training Programs. Catalog of Course Descriptions
 Cloud Systems 2018 Training Programs Catalog of Course Descriptions Catalog of Course Descriptions INTRODUCTION...3 Open 2 2018 Introduction Ericsson has developed a comprehensive Training Programs service
Cloud Systems 2018 Training Programs Catalog of Course Descriptions Catalog of Course Descriptions INTRODUCTION...3 Open 2 2018 Introduction Ericsson has developed a comprehensive Training Programs service
ONAP VoLTE Use Case Solution Brief
 ONAP VoLTE Use Case Solution Brief ONAP Voice over LTE Improves Agility and Slashes Costs for Communication Service Providers ONAP VoLTE Use Case Solution Brief 1 By using ONAP to support the VoLTE use
ONAP VoLTE Use Case Solution Brief ONAP Voice over LTE Improves Agility and Slashes Costs for Communication Service Providers ONAP VoLTE Use Case Solution Brief 1 By using ONAP to support the VoLTE use
Casa Systems Axyom Software Platform
 Solution Brief Casa Systems Axyom Software Platform Over the last few years and continuing through the next decade, all broadband networks will be transformed by Network Functions Virtualization (NFV)
Solution Brief Casa Systems Axyom Software Platform Over the last few years and continuing through the next decade, all broadband networks will be transformed by Network Functions Virtualization (NFV)
WIND RIVER TITANIUM CLOUD FOR TELECOMMUNICATIONS
 WIND RIVER TITANIUM CLOUD FOR TELECOMMUNICATIONS Carrier networks are undergoing their biggest transformation since the beginning of the Internet. The ability to get to market quickly and to respond to
WIND RIVER TITANIUM CLOUD FOR TELECOMMUNICATIONS Carrier networks are undergoing their biggest transformation since the beginning of the Internet. The ability to get to market quickly and to respond to
ONUG SDN Federation/Operability
 ONUG SDN Federation/Operability Orchestration A white paper from the ONUG SDN Federation/Operability Working Group May, 2016 Definition of Open Networking Open networking is a suite of interoperable software
ONUG SDN Federation/Operability Orchestration A white paper from the ONUG SDN Federation/Operability Working Group May, 2016 Definition of Open Networking Open networking is a suite of interoperable software
Introduction. Delivering Management as Agile as the Cloud: Enabling New Architectures with CA Technologies Virtual Network Assurance Solution
 Delivering Management as Agile as the Cloud: Enabling New Architectures with CA Technologies Virtual Network Assurance Solution Introduction Service providers and IT departments of every type are seeking
Delivering Management as Agile as the Cloud: Enabling New Architectures with CA Technologies Virtual Network Assurance Solution Introduction Service providers and IT departments of every type are seeking
ONAP CCVPN Blueprint Overview. ONAP CCVPN Blueprint Improves Agility and Provides Cross-Domain Connectivity. ONAP CCVPN Blueprint Overview 1
 ONAP CCVPN Blueprint Overview ONAP CCVPN Blueprint Improves Agility and Provides Cross-Domain Connectivity ONAP CCVPN Blueprint Overview 1 OVERVIEW: Build high-bandwidth, flat OTN (Optical Transport Networks)
ONAP CCVPN Blueprint Overview ONAP CCVPN Blueprint Improves Agility and Provides Cross-Domain Connectivity ONAP CCVPN Blueprint Overview 1 OVERVIEW: Build high-bandwidth, flat OTN (Optical Transport Networks)
UNIVERSITY OF CAGLIARI
 UNIVERSITY OF CAGLIARI DIEE - Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Infrastrutture ed Applicazioni Avanzate nell Internet NFV ACK: content taken from Foundations of Modern Networking, SDN,
UNIVERSITY OF CAGLIARI DIEE - Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Infrastrutture ed Applicazioni Avanzate nell Internet NFV ACK: content taken from Foundations of Modern Networking, SDN,
Systems Engineering for Software-Defined Network Virtualisation. John Risson, Solutions Engineering Manager IP and Transport Engineering, Telstra
 Systems Engineering for Software-Defined Network Virtualisation John Risson, Solutions Engineering Manager IP and Transport Engineering, Telstra Agenda Motivation Case Studies Opportunities and Challenges
Systems Engineering for Software-Defined Network Virtualisation John Risson, Solutions Engineering Manager IP and Transport Engineering, Telstra Agenda Motivation Case Studies Opportunities and Challenges
NEC Virtualized Evolved Packet Core vepc
 TE-524262 NEC Virtualized Evolved Packet Core vepc Design Concepts and Benefits INDEX Leading the transformation into Mobile Packet Core Virtualization P.3 vepc System Architecture Overview P.4 Elastic
TE-524262 NEC Virtualized Evolved Packet Core vepc Design Concepts and Benefits INDEX Leading the transformation into Mobile Packet Core Virtualization P.3 vepc System Architecture Overview P.4 Elastic
I D C T E C H N O L O G Y S P O T L I G H T. V i r t u a l and Cloud D a t a Center Management
 I D C T E C H N O L O G Y S P O T L I G H T Orchestration S i m p l i f i es and Streamlines V i r t u a l and Cloud D a t a Center Management January 2013 Adapted from Systems Management Software Purchasing
I D C T E C H N O L O G Y S P O T L I G H T Orchestration S i m p l i f i es and Streamlines V i r t u a l and Cloud D a t a Center Management January 2013 Adapted from Systems Management Software Purchasing
Bringing DevOps to Service Provider Networks & Scoping New Operational Platform Requirements for SDN & NFV
 White Paper Bringing DevOps to Service Provider Networks & Scoping New Operational Platform Requirements for SDN & NFV Prepared by Caroline Chappell Practice Leader, Cloud & NFV, Heavy Reading www.heavyreading.com
White Paper Bringing DevOps to Service Provider Networks & Scoping New Operational Platform Requirements for SDN & NFV Prepared by Caroline Chappell Practice Leader, Cloud & NFV, Heavy Reading www.heavyreading.com
Simplified service creation and delivery. Branch. SOHO Data Center. Control Center / NOC Packet Muse Service & Network Applications
 ElastiNET FOR SERVICE PROVIDERS DEAL CONFIDENTLY WITH A CHANGING WORLD In today s world change is the only constant. Enabling technologies are changing, as is competition and customer expectations. Service
ElastiNET FOR SERVICE PROVIDERS DEAL CONFIDENTLY WITH A CHANGING WORLD In today s world change is the only constant. Enabling technologies are changing, as is competition and customer expectations. Service
Modelos de Negócio na Era das Clouds. André Rodrigues, Cloud Systems Engineer
 Modelos de Negócio na Era das Clouds André Rodrigues, Cloud Systems Engineer Agenda Software and Cloud Changed the World Cisco s Cloud Vision&Strategy 5 Phase Cloud Plan Before Now From idea to production:
Modelos de Negócio na Era das Clouds André Rodrigues, Cloud Systems Engineer Agenda Software and Cloud Changed the World Cisco s Cloud Vision&Strategy 5 Phase Cloud Plan Before Now From idea to production:
DevOps CICD for VNF a NetOps Approach
 DevOps CICD for VNF a NetOps Approach Renato Fichmann Senior Solutions Architect Cisco Advanced Services Cisco Spark How Questions? Use Cisco Spark to communicate with the speaker after the session 1.
DevOps CICD for VNF a NetOps Approach Renato Fichmann Senior Solutions Architect Cisco Advanced Services Cisco Spark How Questions? Use Cisco Spark to communicate with the speaker after the session 1.
VMWARE AND NETROUNDS ACTIVE ASSURANCE SOLUTION FOR COMMUNICATIONS SERVICE PROVIDERS
 SOLUTION OVERVIEW VMWARE AND NETROUNDS ACTIVE ASSURANCE SOLUTION FOR COMMUNICATIONS SERVICE PROVIDERS Combined solution provides end-to-end service and infrastructure visibility, service monitoring and
SOLUTION OVERVIEW VMWARE AND NETROUNDS ACTIVE ASSURANCE SOLUTION FOR COMMUNICATIONS SERVICE PROVIDERS Combined solution provides end-to-end service and infrastructure visibility, service monitoring and
Guide to SDN, SD-WAN, NFV, and VNF
 Evalu- ation Guide Technical Brief SD-WAN, NFV, and With so many acronyms and each one building on another, it can be confusing about how they work together. This guide describes the difference. 006180206
Evalu- ation Guide Technical Brief SD-WAN, NFV, and With so many acronyms and each one building on another, it can be confusing about how they work together. This guide describes the difference. 006180206
UNIFY SUBSCRIBER ACCESS MANAGEMENT AND EXPLOIT THE BUSINESS BENEFITS OF NOKIA REGISTERS ON VMWARE vcloud NFV
 SOLUTION OVERVIEW UNIFY SUBSCRIBER ACCESS MANAGEMENT AND EXPLOIT THE BUSINESS BENEFITS OF NOKIA REGISTERS ON VMWARE vcloud NFV Subscriber data management (SDM) plays a significant role in network evolution
SOLUTION OVERVIEW UNIFY SUBSCRIBER ACCESS MANAGEMENT AND EXPLOIT THE BUSINESS BENEFITS OF NOKIA REGISTERS ON VMWARE vcloud NFV Subscriber data management (SDM) plays a significant role in network evolution
A Better Approach to Leveraging an OpenStack Private Cloud. David Linthicum
 A Better Approach to Leveraging an OpenStack Private Cloud David Linthicum A Better Approach to Leveraging an OpenStack Private Cloud 1 Executive Summary The latest bi-annual survey data of OpenStack users
A Better Approach to Leveraging an OpenStack Private Cloud David Linthicum A Better Approach to Leveraging an OpenStack Private Cloud 1 Executive Summary The latest bi-annual survey data of OpenStack users
Virtualization of Customer Premises Equipment (vcpe)
 Case Study Virtualization of Customer Premises Equipment (vcpe) Customer Profile Customer: A Cloud Service Provider Reach: Global Industry: Telecommunications The Challenge A Cloud Service Provider serving
Case Study Virtualization of Customer Premises Equipment (vcpe) Customer Profile Customer: A Cloud Service Provider Reach: Global Industry: Telecommunications The Challenge A Cloud Service Provider serving
When (and how) to move applications from VMware to Cisco Metacloud
 White Paper When (and how) to move applications from VMware to Cisco Metacloud What You Will Learn This white paper will explain when to migrate various applications running in VMware virtual machines
White Paper When (and how) to move applications from VMware to Cisco Metacloud What You Will Learn This white paper will explain when to migrate various applications running in VMware virtual machines
Accelerating SDN and NFV Deployments. Malathi Malla Spirent Communications
 Accelerating SDN and NFV Deployments Malathi Malla Spirent Communications 2 Traditional Networks Vertically integrated Closed, proprietary Slow innovation 3 Infinite Complexity of Testing Across virtual
Accelerating SDN and NFV Deployments Malathi Malla Spirent Communications 2 Traditional Networks Vertically integrated Closed, proprietary Slow innovation 3 Infinite Complexity of Testing Across virtual
Benefits of SD-WAN to the Distributed Enterprise
 WHITE PAPER Benefits of SD-WAN to the Distributed Enterprise 1 B enefits of SD-WAN to the Distributed Enterprise Branch Networking Today More Bandwidth, More Complexity Branch or remote office network
WHITE PAPER Benefits of SD-WAN to the Distributed Enterprise 1 B enefits of SD-WAN to the Distributed Enterprise Branch Networking Today More Bandwidth, More Complexity Branch or remote office network
Cisco Unified Computing System Delivering on Cisco's Unified Computing Vision
 Cisco Unified Computing System Delivering on Cisco's Unified Computing Vision At-A-Glance Unified Computing Realized Today, IT organizations assemble their data center environments from individual components.
Cisco Unified Computing System Delivering on Cisco's Unified Computing Vision At-A-Glance Unified Computing Realized Today, IT organizations assemble their data center environments from individual components.
7 Things ISVs Must Know About Virtualization
 7 Things ISVs Must Know About Virtualization July 2010 VIRTUALIZATION BENEFITS REPORT Table of Contents Executive Summary...1 Introduction...1 1. Applications just run!...2 2. Performance is excellent...2
7 Things ISVs Must Know About Virtualization July 2010 VIRTUALIZATION BENEFITS REPORT Table of Contents Executive Summary...1 Introduction...1 1. Applications just run!...2 2. Performance is excellent...2
Upgrading Your System a Telco User Perspective. Ulrich Kleber San Francisco November 2015
 Upgrading Your System a Telco User Perspective Ulrich Kleber San Francisco November 2015 Outline Introduction and Requirements Upgrade Scenarios OPNFV Escalator Project 2 Outline Introduction and Requirements
Upgrading Your System a Telco User Perspective Ulrich Kleber San Francisco November 2015 Outline Introduction and Requirements Upgrade Scenarios OPNFV Escalator Project 2 Outline Introduction and Requirements
Ending the Confusion About Software- Defined Networking: A Taxonomy
 Ending the Confusion About Software- Defined Networking: A Taxonomy This taxonomy cuts through confusion generated by the flood of vendor SDN announcements. It presents a framework that network and server
Ending the Confusion About Software- Defined Networking: A Taxonomy This taxonomy cuts through confusion generated by the flood of vendor SDN announcements. It presents a framework that network and server
Service Delivery Platform
 Solution Brief Service Delivery Platform Enabling the transition to high-value and more differentiated network services with new consumption models for deploying VNFs. Keeping Up With Cloud Expectations
Solution Brief Service Delivery Platform Enabling the transition to high-value and more differentiated network services with new consumption models for deploying VNFs. Keeping Up With Cloud Expectations
Increasing Network Agility through Intelligent Orchestration
 Increasing Network Agility through Intelligent Orchestration The Oracle Communications Application Orchestrator advantage ORACLE WHITE PAPER OCTOBER 2015 Table of Contents Introduction 1 Network Virtualization
Increasing Network Agility through Intelligent Orchestration The Oracle Communications Application Orchestrator advantage ORACLE WHITE PAPER OCTOBER 2015 Table of Contents Introduction 1 Network Virtualization
UNLOCKING THE FULL POTENTIAL OF NFV
 SERVICE PROVIDER SOLUTIONS WHITE PAPER UNLOCKING THE FULL POTENTIAL OF NFV Helping Communications Service Providers (CoSP) achieve the most out of NFV through a microservices architecture 1 Unlocking the
SERVICE PROVIDER SOLUTIONS WHITE PAPER UNLOCKING THE FULL POTENTIAL OF NFV Helping Communications Service Providers (CoSP) achieve the most out of NFV through a microservices architecture 1 Unlocking the
The CORD reference architecture addresses the needs of various communications access networks with a wide array of use cases including:
 Introduction Today s Mobile Network Operator (MNO) infrastructure is built with proprietary vertically integrated Network Elements (NEs), leading to inefficient utilization of network resources. Further,
Introduction Today s Mobile Network Operator (MNO) infrastructure is built with proprietary vertically integrated Network Elements (NEs), leading to inefficient utilization of network resources. Further,
BUILDING the VIRtUAL enterprise
 BUILDING the VIRTUAL ENTERPRISE A Red Hat WHITEPAPER www.redhat.com As an IT shop or business owner, your ability to meet the fluctuating needs of your business while balancing changing priorities, schedules,
BUILDING the VIRTUAL ENTERPRISE A Red Hat WHITEPAPER www.redhat.com As an IT shop or business owner, your ability to meet the fluctuating needs of your business while balancing changing priorities, schedules,
Network Edge Innovation With Virtual Routing
 Independent market research and competitive analysis of next-generation business and technology solutions for service providers and vendors Network Edge Innovation With Virtual Routing A Heavy Reading
Independent market research and competitive analysis of next-generation business and technology solutions for service providers and vendors Network Edge Innovation With Virtual Routing A Heavy Reading
STRATEGIC WHITE PAPER. Securing cloud environments with Nuage Networks VSP: Policy-based security automation and microsegmentation overview
 STRATEGIC WHITE PAPER Securing cloud environments with Nuage Networks VSP: Policy-based security automation and microsegmentation overview Abstract Cloud architectures rely on Software-Defined Networking
STRATEGIC WHITE PAPER Securing cloud environments with Nuage Networks VSP: Policy-based security automation and microsegmentation overview Abstract Cloud architectures rely on Software-Defined Networking
ONAP ETSI NFV ARCHITECTURE ALIGNEMENT
 ONAP ETSI NFV ARCHITECTURE ALIGNEMENT Bruno Chatras, NFV ISG Vice-Chairman on behalf of the ISG leadership team ETSI 2017. All rights reserved 2 PART 1 ETSI NFV CONCEPTS ETSI NFV Architecture, and NFV-MANO
ONAP ETSI NFV ARCHITECTURE ALIGNEMENT Bruno Chatras, NFV ISG Vice-Chairman on behalf of the ISG leadership team ETSI 2017. All rights reserved 2 PART 1 ETSI NFV CONCEPTS ETSI NFV Architecture, and NFV-MANO
A guide for IT professionals. implementing the hybrid cloud
 A guide for IT professionals implementing the hybrid cloud A guide for IT professionals implementing the hybrid cloud Cloud technology is maturing and advancing rapidly. And for schools today, hybrid cloud
A guide for IT professionals implementing the hybrid cloud A guide for IT professionals implementing the hybrid cloud Cloud technology is maturing and advancing rapidly. And for schools today, hybrid cloud
Hybrid Cloud (Telco & IT) - en fleksibel og optimal implementering
 Hybrid Cloud (Telco & IT) - en fleksibel og optimal implementering June 6th, 2017 1 Nokia 2016 Drivers - Agility is the prime reason to move to the Cloud 16% New revenues 16% Fluctuating demand 13% Customer
Hybrid Cloud (Telco & IT) - en fleksibel og optimal implementering June 6th, 2017 1 Nokia 2016 Drivers - Agility is the prime reason to move to the Cloud 16% New revenues 16% Fluctuating demand 13% Customer
Migrating Session Border Controllers to the Cloud
 Migrating Session Border Controllers to the Cloud An IHS Markit Technology Webinar #CloudifySBC Today s Speakers Migrating Session Border Controllers to the Cloud #CloudifySBC Diane Myers Senior Research
Migrating Session Border Controllers to the Cloud An IHS Markit Technology Webinar #CloudifySBC Today s Speakers Migrating Session Border Controllers to the Cloud #CloudifySBC Diane Myers Senior Research
Airship A New Open Infrastructure Project for OpenStack
 Airship A New Open Infrastructure Project for OpenStack Declaratively define your OpenStack & Kubernetes Infrastructure Airship A New Open Infrastructure Project for OpenStack Declaratively define your
Airship A New Open Infrastructure Project for OpenStack Declaratively define your OpenStack & Kubernetes Infrastructure Airship A New Open Infrastructure Project for OpenStack Declaratively define your
Transformation Through Innovation
 Transformation Through Innovation A service provider strategy to prosper from digitization People will have 11.6 billion mobile-ready devices and connections by 2020. For service providers to thrive today
Transformation Through Innovation A service provider strategy to prosper from digitization People will have 11.6 billion mobile-ready devices and connections by 2020. For service providers to thrive today
Networking for a smarter data center: Getting it right
 IBM Global Technology Services October 2011 Networking for a smarter data center: Getting it right Planning the network needed for a dynamic infrastructure 2 Networking for a smarter data center: Getting
IBM Global Technology Services October 2011 Networking for a smarter data center: Getting it right Planning the network needed for a dynamic infrastructure 2 Networking for a smarter data center: Getting
Making hybrid IT simple with Capgemini and Microsoft Azure Stack
 Making hybrid IT simple with Capgemini and Microsoft Azure Stack The significant evolution of cloud computing in the last few years has encouraged IT leaders to rethink their enterprise cloud strategy.
Making hybrid IT simple with Capgemini and Microsoft Azure Stack The significant evolution of cloud computing in the last few years has encouraged IT leaders to rethink their enterprise cloud strategy.
Survey of ETSI NFV standardization documents BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING FEBRUARY 26, 2016
 Survey of ETSI NFV standardization documents BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING FEBRUARY 26, 2016 VNFaaS (Virtual Network Function as a Service) In our present work, we consider the VNFaaS use-case
Survey of ETSI NFV standardization documents BY ABHISHEK GUPTA FRIDAY GROUP MEETING FEBRUARY 26, 2016 VNFaaS (Virtual Network Function as a Service) In our present work, we consider the VNFaaS use-case
Architecting a vcloud NFV Platform R E F E R E N C E A R C H I T E C T U RE V E R S I O N 2. 0
 Architecting a vcloud NFV Platform R E F E R E N C E A R C H I T E C T U RE V E R S I O N 2. 0 Table of Contents 1. Network Function Virtualization Overview... 6 1.1 NFV Infrastructure Working Domain...
Architecting a vcloud NFV Platform R E F E R E N C E A R C H I T E C T U RE V E R S I O N 2. 0 Table of Contents 1. Network Function Virtualization Overview... 6 1.1 NFV Infrastructure Working Domain...
SDN+NFV Next Steps in the Journey
 SDN+NFV Next Steps in the Journey Margaret T. Chiosi AT&T Labs Distinguished Architect SDN-NFV Realization 2015 AT&T Intellectual Property. All rights reserved. AT&T, the AT&T logo and all other AT&T marks
SDN+NFV Next Steps in the Journey Margaret T. Chiosi AT&T Labs Distinguished Architect SDN-NFV Realization 2015 AT&T Intellectual Property. All rights reserved. AT&T, the AT&T logo and all other AT&T marks
Oracle Solaris 11: No-Compromise Virtualization
 Oracle Solaris 11: No-Compromise Virtualization Oracle Solaris 11 is a complete, integrated, and open platform engineered for large-scale enterprise environments. Its built-in virtualization provides a
Oracle Solaris 11: No-Compromise Virtualization Oracle Solaris 11 is a complete, integrated, and open platform engineered for large-scale enterprise environments. Its built-in virtualization provides a
Evolution of connectivity in the era of cloud
 Evolution of connectivity in the era of cloud Phil Harris SVP and GM SP Market Vertical Riverbed Technology 1 2017 Riverbed Technology. All rights reserved. Transformational Services Span The Business
Evolution of connectivity in the era of cloud Phil Harris SVP and GM SP Market Vertical Riverbed Technology 1 2017 Riverbed Technology. All rights reserved. Transformational Services Span The Business
ELASTIC SERVICES PLATFORM
 ELASTIC SERVICES PLATFORM SIMPLIFYING SERVICE DELIVERY The telecom industry is at the dawn of a bright new era - one in which new services and technologies, such as 5G, IoT, and smart cities, hold promise
ELASTIC SERVICES PLATFORM SIMPLIFYING SERVICE DELIVERY The telecom industry is at the dawn of a bright new era - one in which new services and technologies, such as 5G, IoT, and smart cities, hold promise
The Interoperability Challenge in. Telecom and NFV Environments. Carsten Rossenhövel, EANTC Chris Price, Ericsson Ildikó Váncsa, OpenStack Foundation
 The Interoperability Challenge in Telecom and NFV Environments Carsten Rossenhövel, EANTC Chris Price, Ericsson Ildikó Váncsa, OpenStack Foundation Open source testing Commercial implementation testing
The Interoperability Challenge in Telecom and NFV Environments Carsten Rossenhövel, EANTC Chris Price, Ericsson Ildikó Váncsa, OpenStack Foundation Open source testing Commercial implementation testing
Redefining Networking with Network Virtualization
 WHITE PAPER Redefining Networking with Network ization Why Networking Is Ripe for a Change Table of Contents Overcoming the Obstacle Blocking the Benefits of a Hybrid Cloud... 3 What Is Network ization?...4
WHITE PAPER Redefining Networking with Network ization Why Networking Is Ripe for a Change Table of Contents Overcoming the Obstacle Blocking the Benefits of a Hybrid Cloud... 3 What Is Network ization?...4
DEFINING SECURITY FOR TODAY S CLOUD ENVIRONMENTS. Security Without Compromise
 DEFINING SECURITY FOR TODAY S CLOUD ENVIRONMENTS Security Without Compromise CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 1 SECTION 1: STRETCHING BEYOND STATIC SECURITY 2 SECTION 2: NEW DEFENSES FOR CLOUD ENVIRONMENTS 5 SECTION
DEFINING SECURITY FOR TODAY S CLOUD ENVIRONMENTS Security Without Compromise CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 1 SECTION 1: STRETCHING BEYOND STATIC SECURITY 2 SECTION 2: NEW DEFENSES FOR CLOUD ENVIRONMENTS 5 SECTION
SD-WAN Solution How to Make the Best Choice for Your Business
 HOW-TO GUIDE Choosing the Right SD-WAN Solution How to Make the Best Choice for Your Business Section Title - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 3 CH. 1 Why Organizations are Choosing SD-WAN 4 CH. 2 What
HOW-TO GUIDE Choosing the Right SD-WAN Solution How to Make the Best Choice for Your Business Section Title - 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction 3 CH. 1 Why Organizations are Choosing SD-WAN 4 CH. 2 What
End-to-End Cloudification of Mobile Telecoms. The MCN Consortium Presenter: Andy Edmonds ZHAW
 End-to-End Cloudification of Mobile Telecoms The MCN Consortium Presenter: Andy Edmonds (@dizz), ZHAW Goals of MCN Architecture Modularity, reusability Creation of composed (end-to-end) services Adhere
End-to-End Cloudification of Mobile Telecoms The MCN Consortium Presenter: Andy Edmonds (@dizz), ZHAW Goals of MCN Architecture Modularity, reusability Creation of composed (end-to-end) services Adhere
The Top Five Reasons to Deploy Software-Defined Networks and Network Functions Virtualization
 The Top Five Reasons to Deploy Software-Defined Networks and Network Functions Virtualization May 2014 Prepared by: Zeus Kerravala The Top Five Reasons to Deploy Software-Defined Networks and Network Functions
The Top Five Reasons to Deploy Software-Defined Networks and Network Functions Virtualization May 2014 Prepared by: Zeus Kerravala The Top Five Reasons to Deploy Software-Defined Networks and Network Functions
Media Processing in NFV Architectures
 White Paper December 2014 Media Processing in NFV Architectures Introduction Across the IT industry, providers are rapidly moving towards the benefits of agility, flexibility, and cost savings offered
White Paper December 2014 Media Processing in NFV Architectures Introduction Across the IT industry, providers are rapidly moving towards the benefits of agility, flexibility, and cost savings offered
Introducing Avaya SDN Fx with FatPipe Networks Next Generation SD-WAN
 Avaya-FatPipe Solution Overview Introducing Avaya SDN Fx with FatPipe Networks Next Generation SD-WAN The Avaya SDN-Fx and FatPipe Networks solution provides a fabric-based SDN architecture for simplicity
Avaya-FatPipe Solution Overview Introducing Avaya SDN Fx with FatPipe Networks Next Generation SD-WAN The Avaya SDN-Fx and FatPipe Networks solution provides a fabric-based SDN architecture for simplicity
Deployment Case Study of SDN and NFV Transformation. Marcela Blanco-Luna Solutions Architect Advanced Services
 Deployment Case Study of SDN and NFV Transformation Marcela Blanco-Luna Solutions Architect Advanced Services Future Network Platform Service Creation Service Design Service Assurance Cloud Optimization
Deployment Case Study of SDN and NFV Transformation Marcela Blanco-Luna Solutions Architect Advanced Services Future Network Platform Service Creation Service Design Service Assurance Cloud Optimization
Government IT Modernization and the Adoption of Hybrid Cloud
 Government IT Modernization and the Adoption of Hybrid Cloud An IDC InfoBrief, Sponsored by VMware June 2018 Federal and National Governments Are at an Inflection Point Federal and national governments
Government IT Modernization and the Adoption of Hybrid Cloud An IDC InfoBrief, Sponsored by VMware June 2018 Federal and National Governments Are at an Inflection Point Federal and national governments
The intelligence of hyper-converged infrastructure. Your Right Mix Solution
 The intelligence of hyper-converged infrastructure Your Right Mix Solution Applications fuel the idea economy SLA s, SLA s, SLA s Regulations Latency Performance Integration Disaster tolerance Reliability
The intelligence of hyper-converged infrastructure Your Right Mix Solution Applications fuel the idea economy SLA s, SLA s, SLA s Regulations Latency Performance Integration Disaster tolerance Reliability
The Virtual Brick Road Achievements and Challenges in NFV Space. Diego R. Lopez Telefónica NFV ISG Technical Manager October 2013
 The Virtual Brick Road Achievements and Challenges in NFV Space Diego R. Lopez Telefónica NFV ISG Technical Manager October 2013 The NFV Concept A means to make the network more flexible and simple by
The Virtual Brick Road Achievements and Challenges in NFV Space Diego R. Lopez Telefónica NFV ISG Technical Manager October 2013 The NFV Concept A means to make the network more flexible and simple by
SDN for Multi-Layer IP & Optical Networks
 SDN for Multi-Layer IP & Optical Networks Sterling d Perrin Senior Analyst, Heavy Reading Agenda Definitions for SDN and NFV SDN Drivers and Barriers SDN Use Cases and Applications General Uses Specific
SDN for Multi-Layer IP & Optical Networks Sterling d Perrin Senior Analyst, Heavy Reading Agenda Definitions for SDN and NFV SDN Drivers and Barriers SDN Use Cases and Applications General Uses Specific
Introduction to Cisco and Intel NFV Quick Start
 Quick Start Cisco Intel NFV Quick Start. Simplify Virtualization, Encourage Innovation for Service Providers Introduction Customer expectations for network services have evolved markedly. Customers want
Quick Start Cisco Intel NFV Quick Start. Simplify Virtualization, Encourage Innovation for Service Providers Introduction Customer expectations for network services have evolved markedly. Customers want
FROM A RIGID ECOSYSTEM TO A LOGICAL AND FLEXIBLE ENTITY: THE SOFTWARE- DEFINED DATA CENTRE
 FROM A RIGID ECOSYSTEM TO A LOGICAL AND FLEXIBLE ENTITY: THE SOFTWARE- DEFINED DATA CENTRE The demand for cloud infrastructure is rapidly increasing, the world of information is becoming application and
FROM A RIGID ECOSYSTEM TO A LOGICAL AND FLEXIBLE ENTITY: THE SOFTWARE- DEFINED DATA CENTRE The demand for cloud infrastructure is rapidly increasing, the world of information is becoming application and
MASERGY S MANAGED SD-WAN
 MASERGY S MANAGED New Performance Options for Hybrid Networks Business Challenges WAN Ecosystem Features and Benefits Use Cases INTRODUCTION Organizations are leveraging technology to transform the way
MASERGY S MANAGED New Performance Options for Hybrid Networks Business Challenges WAN Ecosystem Features and Benefits Use Cases INTRODUCTION Organizations are leveraging technology to transform the way
Hyper-Converged Infrastructure: Providing New Opportunities for Improved Availability
 Hyper-Converged Infrastructure: Providing New Opportunities for Improved Availability IT teams in companies of all sizes face constant pressure to meet the Availability requirements of today s Always-On
Hyper-Converged Infrastructure: Providing New Opportunities for Improved Availability IT teams in companies of all sizes face constant pressure to meet the Availability requirements of today s Always-On
The Five Phases of Virtualization: From Hardware Rigidity to Web-Scale Flexibility
 WHITE PAPER The Five Phases of Virtualization: From Hardware Rigidity to Web-Scale Flexibility It s a harsh reality that today s networks are still burdened by hardware-based rigidity. At the same time,
WHITE PAPER The Five Phases of Virtualization: From Hardware Rigidity to Web-Scale Flexibility It s a harsh reality that today s networks are still burdened by hardware-based rigidity. At the same time,
Progress report on NFV standardization in ETSI.
 Progress report on NFV standardization in ETSI. NetV: IRISA / Technicolor Workshop on Network Virtualization Bruno CHATRAS, Orange, ETSI NFV ISG Vice-Chairman 1 Agenda Overview Selected technical items
Progress report on NFV standardization in ETSI. NetV: IRISA / Technicolor Workshop on Network Virtualization Bruno CHATRAS, Orange, ETSI NFV ISG Vice-Chairman 1 Agenda Overview Selected technical items
DNA Automation Services Offerings
 DNA Automation Services Offerings Jamie Owen, Solutions Architect, Cisco Advanced Services Cisco Spark How Questions? Use Cisco Spark to communicate with the speaker after the session 1. Find this session
DNA Automation Services Offerings Jamie Owen, Solutions Architect, Cisco Advanced Services Cisco Spark How Questions? Use Cisco Spark to communicate with the speaker after the session 1. Find this session
Cloud Services. Infrastructure-as-a-Service
 Cloud Services Infrastructure-as-a-Service Accelerate your IT and business transformation with our networkcentric, highly secure private and public cloud services - all backed-up by a 99.999% availability
Cloud Services Infrastructure-as-a-Service Accelerate your IT and business transformation with our networkcentric, highly secure private and public cloud services - all backed-up by a 99.999% availability
TALK THUNDER SOFTWARE FOR BARE METAL HIGH-PERFORMANCE SOFTWARE FOR THE MODERN DATA CENTER WITH A10 DATASHEET YOUR CHOICE OF HARDWARE
 DATASHEET THUNDER SOFTWARE FOR BARE METAL YOUR CHOICE OF HARDWARE A10 Networks application networking and security solutions for bare metal raise the bar on performance with an industryleading software
DATASHEET THUNDER SOFTWARE FOR BARE METAL YOUR CHOICE OF HARDWARE A10 Networks application networking and security solutions for bare metal raise the bar on performance with an industryleading software
Network Virtualisation Vision and Strategy_ (based on lesson learned) Telefónica Global CTO
 Network Virtualisation Vision and Strategy_ (based on lesson learned) Telefónica I+D @ Global CTO 18.03.2014 Business development requires a continuous evolution of our network but it still seems unable
Network Virtualisation Vision and Strategy_ (based on lesson learned) Telefónica I+D @ Global CTO 18.03.2014 Business development requires a continuous evolution of our network but it still seems unable
SD-WAN orchestrated by Amdocs
 SD-WAN orchestrated by Amdocs What is software-defined wide area network? SD-WAN determines the most cost-effective and efficient way to route enterprise traffic to remote locations over ubiquitous broadband
SD-WAN orchestrated by Amdocs What is software-defined wide area network? SD-WAN determines the most cost-effective and efficient way to route enterprise traffic to remote locations over ubiquitous broadband
EUROPEAN ICT PROFESSIONAL ROLE PROFILES VERSION 2 CWA 16458:2018 LOGFILE
 EUROPEAN ICT PROFESSIONAL ROLE PROFILES VERSION 2 CWA 16458:2018 LOGFILE Overview all ICT Profile changes in title, summary, mission and from version 1 to version 2 Versions Version 1 Version 2 Role Profile
EUROPEAN ICT PROFESSIONAL ROLE PROFILES VERSION 2 CWA 16458:2018 LOGFILE Overview all ICT Profile changes in title, summary, mission and from version 1 to version 2 Versions Version 1 Version 2 Role Profile
Network Functions Virtualisation. Kazuaki OBANA Media Innovation Laboratory, NTT Network Innovation Laboratories
 Network Functions Virtualisation Looking to the Future NFV ETSI Industry Specification Group Kazuaki OBANA Media Innovation Laboratory, NTT Network Innovation Laboratories Network Functions Virtualisation:
Network Functions Virtualisation Looking to the Future NFV ETSI Industry Specification Group Kazuaki OBANA Media Innovation Laboratory, NTT Network Innovation Laboratories Network Functions Virtualisation:
VMWARE PIVOTAL CONTAINER SERVICE
 DATASHEET VMWARE PIVOTAL CONTAINER SERVICE AT A GLANCE VMware Pivotal Container Service (PKS) is a production-grade Kubernetes-based container solution equipped with advanced networking, a private container
DATASHEET VMWARE PIVOTAL CONTAINER SERVICE AT A GLANCE VMware Pivotal Container Service (PKS) is a production-grade Kubernetes-based container solution equipped with advanced networking, a private container
CT and IT architecture reconstruction based on software_. Global CTO
 CT and IT architecture reconstruction based on software_ Global CTO 09.09.2015 We are evolving towards a Hyper Connected and Intelligent Digital World* The explosion of digital services makes connectivity
CT and IT architecture reconstruction based on software_ Global CTO 09.09.2015 We are evolving towards a Hyper Connected and Intelligent Digital World* The explosion of digital services makes connectivity
THE JOURNEY OVERVIEW THREE PHASES TO A SUCCESSFUL MIGRATION ADOPTION ACCENTURE IS 80% IN THE CLOUD
 OVERVIEW Accenture is in the process of transforming itself into a digital-first enterprise. Today, Accenture is 80 percent in a public cloud. As the journey continues, Accenture shares its key learnings
OVERVIEW Accenture is in the process of transforming itself into a digital-first enterprise. Today, Accenture is 80 percent in a public cloud. As the journey continues, Accenture shares its key learnings
Practical Guide to Hybrid Cloud Computing. Cloud-Computing.
 Practical Guide to Hybrid Cloud Computing http://www.cloud-council.org/deliverables/cscc-practical-guide-to-hybrid- Cloud-Computing.pdf April 21, 2016 The Cloud Standards Customer Council THE Customer
Practical Guide to Hybrid Cloud Computing http://www.cloud-council.org/deliverables/cscc-practical-guide-to-hybrid- Cloud-Computing.pdf April 21, 2016 The Cloud Standards Customer Council THE Customer
VVD for Cloud Providers: Scale and Performance Guidelines. October 2018
 VVD for Cloud Providers: Scale and Performance Guidelines October 2018 2018 VMware, Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and intellectual property laws.
VVD for Cloud Providers: Scale and Performance Guidelines October 2018 2018 VMware, Inc. All rights reserved. This product is protected by U.S. and international copyright and intellectual property laws.
Virtual Private Networks with Cisco Network Services Orchestrator Enabled by Tail-f - Fast, Simple, and Automated
 Solution Overview Virtual Private Networks with Cisco Network Services Orchestrator Enabled by Tail-f - Fast, Simple, and Automated BENEFITS Accelerate new VPN services with automated, self-service, on-demand
Solution Overview Virtual Private Networks with Cisco Network Services Orchestrator Enabled by Tail-f - Fast, Simple, and Automated BENEFITS Accelerate new VPN services with automated, self-service, on-demand
TRANSFORM YOUR NETWORK
 TRANSFORM YOUR NETWORK SIMPLIFY MODERNIZATION WITH AN INNOVATIVE ECOSYSTEM OF CERTIFIED SOLUTIONS AND PARTNERS TELECOMMUNICATIONS ECOSYSTEM E-BOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS Adapt to growing network demand...3
TRANSFORM YOUR NETWORK SIMPLIFY MODERNIZATION WITH AN INNOVATIVE ECOSYSTEM OF CERTIFIED SOLUTIONS AND PARTNERS TELECOMMUNICATIONS ECOSYSTEM E-BOOK TABLE OF CONTENTS Adapt to growing network demand...3
Pasiruoškite ateičiai: modernus duomenų centras. Laurynas Dovydaitis Microsoft Azure MVP
 Pasiruoškite ateičiai: modernus duomenų centras Laurynas Dovydaitis Microsoft Azure MVP 2016-05-17 Tension drives change The datacenter today Traditional datacenter Tight coupling between infrastructure
Pasiruoškite ateičiai: modernus duomenų centras Laurynas Dovydaitis Microsoft Azure MVP 2016-05-17 Tension drives change The datacenter today Traditional datacenter Tight coupling between infrastructure
and public cloud infrastructure, including Amazon Web Services (AWS) and AWS GovCloud, Microsoft Azure and Azure Government Cloud.
 DATA SHEET vthunder SOFTWARE FOR VIRTUAL & CLOUD INFRASTRUCTURE A10 vthunder software appliances enable organizations to SUPPORTED SOLUTIONS gain flexible, easy-to-deploy and high-performance secure application
DATA SHEET vthunder SOFTWARE FOR VIRTUAL & CLOUD INFRASTRUCTURE A10 vthunder software appliances enable organizations to SUPPORTED SOLUTIONS gain flexible, easy-to-deploy and high-performance secure application
Mobile Edge Computing
 Mobile Edge Computing A key technology towards 5G 1 Nurit Sprecher (Chair of ETSI MEC ISG) 5G World 2016, London, UK 5G Use Cases and Requirements 5G Use Cases Families and Related Examples Build a virtual
Mobile Edge Computing A key technology towards 5G 1 Nurit Sprecher (Chair of ETSI MEC ISG) 5G World 2016, London, UK 5G Use Cases and Requirements 5G Use Cases Families and Related Examples Build a virtual
Wireless Network Virtualization: Ensuring Carrier Grade Availability
 AN INTEL COMPANY Wireless Network Virtualization: Ensuring Carrier Grade Availability WHEN IT MATTERS, IT RUNS ON WIND RIVER EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The wireless industry s battle to acquire new subscribers
AN INTEL COMPANY Wireless Network Virtualization: Ensuring Carrier Grade Availability WHEN IT MATTERS, IT RUNS ON WIND RIVER EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The wireless industry s battle to acquire new subscribers
Telco Perceptions of OPNFV. Roz Roseboro, Senior Analyst, Heavy Reading
 Telco Perceptions of OPNFV Roz Roseboro, Senior Analyst, Heavy Reading CSP Info (1) Source: Heavy Reading Service Provider Survey, June 2017 n=98 CSP info (2) Source: Heavy Reading Service Provider Survey,
Telco Perceptions of OPNFV Roz Roseboro, Senior Analyst, Heavy Reading CSP Info (1) Source: Heavy Reading Service Provider Survey, June 2017 n=98 CSP info (2) Source: Heavy Reading Service Provider Survey,
ETSI Zero touch network and Service Management (ZSM)
 ETSI Zero touch network and Service Management (ZSM) Enabling agile service delivery and new business opportunities Presented by: Klaus Martiny, Chair, ETSI ISG ZSM For: NFV SDN World Congress 2018 11.10.2018
ETSI Zero touch network and Service Management (ZSM) Enabling agile service delivery and new business opportunities Presented by: Klaus Martiny, Chair, ETSI ISG ZSM For: NFV SDN World Congress 2018 11.10.2018
WHITE PAPER. Applying Software-Defined Security to the Branch Office
 Applying Software-Defined Security to the Branch Office Branch Security Overview Increasingly, the branch or remote office is becoming a common entry point for cyber-attacks into the enterprise. Industry
Applying Software-Defined Security to the Branch Office Branch Security Overview Increasingly, the branch or remote office is becoming a common entry point for cyber-attacks into the enterprise. Industry
Choosing the Right Cloud Computing Model for Data Center Management
 Choosing the Right Cloud Computing Model for Data Center Management www.nsi1.com NETWORK SOLUTIONS INCOPORATED NS1.COM UPDATING YOUR NETWORK SOLUTION WITH CISCO DNA CENTER 1 Section One Cloud Computing
Choosing the Right Cloud Computing Model for Data Center Management www.nsi1.com NETWORK SOLUTIONS INCOPORATED NS1.COM UPDATING YOUR NETWORK SOLUTION WITH CISCO DNA CENTER 1 Section One Cloud Computing
ITU-T Y Next generation network evolution phase 1 Overview
 I n t e r n a t i o n a l T e l e c o m m u n i c a t i o n U n i o n ITU-T Y.2340 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (09/2016) SERIES Y: GLOBAL INFORMATION INFRASTRUCTURE, INTERNET PROTOCOL
I n t e r n a t i o n a l T e l e c o m m u n i c a t i o n U n i o n ITU-T Y.2340 TELECOMMUNICATION STANDARDIZATION SECTOR OF ITU (09/2016) SERIES Y: GLOBAL INFORMATION INFRASTRUCTURE, INTERNET PROTOCOL
Data Protection for Virtualized Environments
 Technology Insight Paper Data Protection for Virtualized Environments IBM Spectrum Protect Plus Delivers a Modern Approach By Steve Scully, Sr. Analyst February 2018 Modern Data Protection for Virtualized
Technology Insight Paper Data Protection for Virtualized Environments IBM Spectrum Protect Plus Delivers a Modern Approach By Steve Scully, Sr. Analyst February 2018 Modern Data Protection for Virtualized
Virtualization & On-Premise Cloud
 Key Solutions Virtualization & On-Premise Cloud Hive Fabric provides the economics and simplicity of the Public Cloud in your data center. No more VMware Tax or proprietary HCI hardware. Expensive, proprietary,
Key Solutions Virtualization & On-Premise Cloud Hive Fabric provides the economics and simplicity of the Public Cloud in your data center. No more VMware Tax or proprietary HCI hardware. Expensive, proprietary,
Cisco CloudCenter Solution with Cisco ACI: Common Use Cases
 Cisco CloudCenter Solution with Cisco ACI: Common Use Cases Cisco ACI increases network security, automates communication policies based on business-relevant application requirements, and decreases developer
Cisco CloudCenter Solution with Cisco ACI: Common Use Cases Cisco ACI increases network security, automates communication policies based on business-relevant application requirements, and decreases developer
How the WAN is Driving Digital Transformation. An IDC InfoBrief, Sponsored by
 How the WAN is Driving Digital Transformation Executive Summary Digital transformation needs to go hand in hand with an evolution of the wide area network (WAN). IDC has built a comparison framework to
How the WAN is Driving Digital Transformation Executive Summary Digital transformation needs to go hand in hand with an evolution of the wide area network (WAN). IDC has built a comparison framework to
Optimisation drives digital transformation
 January 2017 Executive summary Forward-thinking business leaders are challenging their organisations to achieve transformation by harnessing digital technologies with organisational, operational, and business
January 2017 Executive summary Forward-thinking business leaders are challenging their organisations to achieve transformation by harnessing digital technologies with organisational, operational, and business
SOLUTION BRIEF NETWORK OPERATIONS AND ANALYTICS. How Can I Predict Network Behavior to Provide for an Exceptional Customer Experience?
 SOLUTION BRIEF NETWORK OPERATIONS AND ANALYTICS How Can I Predict Network Behavior to Provide for an Exceptional Customer Experience? SOLUTION BRIEF CA DATABASE MANAGEMENT FOR DB2 FOR z/os DRAFT When used
SOLUTION BRIEF NETWORK OPERATIONS AND ANALYTICS How Can I Predict Network Behavior to Provide for an Exceptional Customer Experience? SOLUTION BRIEF CA DATABASE MANAGEMENT FOR DB2 FOR z/os DRAFT When used
Migration and Building of Data Centers in IBM SoftLayer
 Migration and Building of Data Centers in IBM SoftLayer Advantages of IBM SoftLayer and RackWare Together IBM SoftLayer offers customers the advantage of migrating and building complex environments into
Migration and Building of Data Centers in IBM SoftLayer Advantages of IBM SoftLayer and RackWare Together IBM SoftLayer offers customers the advantage of migrating and building complex environments into
Orchestrated Assurance enabled by NFV 1 NFV ISG PoC Proposal
 Orchestrated Assurance enabled by NFV 1 NFV ISG PoC Proposal 1.1 PoC Team Members PoC Project Name: Orchestrated Assurance enabled by NFV Network Operators/ Service Providers: Orange Contact: Christos
Orchestrated Assurance enabled by NFV 1 NFV ISG PoC Proposal 1.1 PoC Team Members PoC Project Name: Orchestrated Assurance enabled by NFV Network Operators/ Service Providers: Orange Contact: Christos
