Wireless Data Acquisition in. LabVIEW
|
|
|
- Lee Shields
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University College of Southeast Norway Wireless Data Acquisition in Hans-Petter Halvorsen, LabVIEW
2 Preface It's not just phones and computers that can communicate wirelessly with the outside world. Wireless sensors appear both in medicine, in buildings and especially in industrial applications. It is developed more standardized radio network for wireless sensors. Zigbee is probably the most famous, where more than 300 large and small companies working to develop solutions. For industrial use requires special safety requirements. Radio network must have sufficient coverage to obtain an acceptable error rate. The network should have redundancy so that the random outcome can be repaired automatically. It is achieved in that messages can go several ways from the sensors to the centers. Also, the network for error handling and error correction so that random errors are corrected. Because of these requirements it has been shown that ZigBee is not always suitable for use in the industrial context. This particularly applies it in process control, where resistance to electromagnetic noise and encryption of the signals is important. A wireless standard specifically designed to satisfy industrial requirements is Wireless HART. This is based on the same physical radio technology such as ZigBee, but specifies additional frequency hopping to mitigate interference, better encryption and that provides for lower power consumption. Currently, the wireless sensors have been used for monitoring, where a human operator must decide whether the process parameters should be changed or not. The objective is that the technology will prove to be robust enough to also be used to process control where the changes in the industrial processes should happen automatically without human intervention. This will be the next major challenge for systems based on wireless technology. Wireless technology has many potential benefits for remote monitoring applications; however, it has been slow to see adoption in industry because of the complexities of programming and deploying a reliable, secure, and high-performance wireless system. NI Wi-Fi data acquisition (DAQ) devices meet these challenges by combining IEEE wireless or Ethernet communication, direct sensor connectivity, and the flexibility of NI LabVIEW software. Some Application Areas for Wireless technology such as Wi-Fi monitoring: ii
3 Challenges with wireless data acquisition technology: Proprietary protocols and network hardware Incomplete I/O offerings High-speed waveform measurements Lack of interoperability between suppliers Integration with existing wired systems Non-standard vendor-defined solutions National Instruments (NI), the vendor of the LabVIEW programming environment delivers several solutions for wireless monitoring and data acquisition. NI Wi-Fi data acquisition (NI Wi-Fi DAQ) devices combine IEEE b/g wireless or Ethernet communication, direct sensor connectivity, and the flexibility of NI-DAQmx software for remote monitoring of electrical, physical, mechanical, and acoustic signals
4 This document introduces wireless data acquisition features and teaches you how you can simplify wireless remote measurements without compromising on the security or performance of a cabled data acquisition solution.
5 Table of Contents Preface... ii Table of Contents... v 1 Wireless Technology Bluetooth Wireless USB ZigBee (IEEE ) Wi-Fi (IEEE ) Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) Wireless Standards ZigBee (IEEE ) IEEE WirelessHART Wireless Mesh Network (WMN) Introduction to LabVIEW Dataflow programming Graphical programming Benefits Introduction to Data Acquisition (DAQ) Introduction to DAQ - Data Acquisition Physical input/output signals DAQ device/hardware Driver software Your software application (Application software) v
6 vi Table of Contents 4.2 MAX Measurement and Automation Explorer NI-DAQmx DAQ Assistant Introduction to Wireless Data Acquisition NI Wireless DAQ Devices NI WLS NI WAP NI UES PS-5 Power Supply NI WSN Devices Devices NI WSN WSN Ethernet Gateway NI WSN Thermocouple Input Node NI WSN Analog Input Node LabVIEW Drivers... 25
7 1 Wireless Technology Wireless technology and wireless networks are widely used today, but it s quite new in industrial automation systems. There are different technologies and wireless standards available: Bluetooth Wireless USB ZigBee (IEEE ) Wi-Fi (IEEE ) 1
8 2 Wireless Technology Different wireless technologies: The Figure below compare the different wireless technologies: Wi-Fi and ZigBee are the primary wireless technologies for measurement and control systems. 1.1 Bluetooth
9 3 Wireless Technology 1.2 Wireless USB
10 4 Wireless Technology 1.3 ZigBee (IEEE )
11 5 Wireless Technology 1.4 Wi-Fi (IEEE )
12 2 Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) Source: A wireless sensor network (WSN) consists of spatially distributed autonomous sensors to cooperatively monitor physical or environmental conditions, such as temperature, sound, vibration, pressure, motion or pollutants. The development of wireless sensor networks was motivated by military applications such as battlefield surveillance. They are now used in many industrial and civilian application areas, including industrial process monitoring and control, machine health monitoring, environment and habitat monitoring, healthcare applications, home automation, and traffic control. In addition to one or more sensors, each node in a sensor network is typically equipped with a radio transceiver or other wireless communications device, a small microcontroller, and an energy source, usually a battery. [Wikipedia] The applications for WSNs are varied, typically involving some kind of monitoring, tracking, or controlling. Specific applications include habitat monitoring, object tracking, nuclear reactor control, fire detection, and traffic monitoring. In a typical application, a WSN is scattered in a region where it is meant to collect data through its sensor nodes. 2.1 Wireless Standards Several standards are currently either ratified or under development for wireless sensor networks. ZigBee is a proprietary mesh-networking specification intended for uses such as 1
13 2 Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) embedded sensing, medical data collection, consumer devices like television remote controls, and home automation. Zigbee is promoted by a large consortium of industry players. WirelessHART is an extension of the HART Protocol and is specifically designed for Industrial applications like Process Monitoring and Control ZigBee (IEEE ) ZigBee is a low-cost, low-power, wireless mesh networking proprietary standard. The low cost allows the technology to be widely deployed in wireless control and monitoring applications, the low power-usage allows longer life with smaller batteries, and the mesh networking provides high reliability and larger range.
14 3 Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) Read more about ZigBee: ZigBee Alliance: Wikipedia: IEEE Wireless DAQ Products form National Instruments use the Wi-Fi IEEE standard. NI WSN Measurement Systems use the ZigBee (IEEE ) standard. Read more about wireless technology and products from National Instruments: NI Wireless Data Acquisition: NI Wireless Remote Monitoring: NI Wireless Devices: NI Wireless Sensor Networks: WirelessHART WirelessHART is an open-standard wireless networking technology developed by HART Communication Foundation.
15 4 Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) Developed as a multi-vendor, interoperable wireless standard, WirelessHART was defined specifically for the requirements of Process field device networks Read more about WirelessHART: HART Communication Foundation: Wikipedia: Wireless Mesh Network (WMN) Mesh networking is a type of networking where each node in the network may act as an independent router, regardless of whether it is connected to another network or not. It allows for continuous connections and reconfiguration around broken or blocked paths by hopping from node to node until the destination is reached. A mesh network whose nodes are all connected to each other is a fully connected network. Mesh networks differ from other networks in that the component parts can all connect to each other via multiple hops. A wireless mesh network (WMN) is a communications network made up of radio nodes organized in a mesh topology. Wireless mesh networks often consist of mesh clients, mesh routers and gateways. The mesh clients are often laptops, cell phones and other wireless devices while the mesh routers forward traffic to and from the gateways which may but need not connect to the Internet. The coverage area of the radio nodes working as a single network is sometimes called a mesh cloud. Access to this mesh cloud is dependent on the radio nodes working in harmony with each other to create a radio network. A mesh network is reliable and offers redundancy. When one node can no longer operate, the rest of the nodes can still communicate with each other, directly or through one or more intermediate nodes. Wireless mesh architecture is a first step towards providing high-bandwidth network over a specific coverage area. Wireless mesh architecture s infrastructure is, in effect, a router network minus the cabling between nodes. It's built of peer radio devices that don't have to be cabled to a wired port like traditional WLAN access points (AP) do. Mesh architecture sustains signal strength by breaking long distances into a series of shorter hops Below we see an example of a Wireless Mesh Topology:
16 5 Wireless Sensor Network (WSN) Wireless Mess Networks (WMN) is widely used in Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN).
17 3 Introduction to LabVIEW Sources: LabVIEW (short for Laboratory Virtual Instrumentation Engineering Workbench) is a platform and development environment for a visual programming language from National Instruments. The graphical language is named "G". Originally released for the Apple Macintosh in 1986, LabVIEW is commonly used for data acquisition, instrument control, and industrial automation on a variety of platforms including Microsoft Windows, various flavors of UNIX, Linux, and Mac OS X. Visit National Instruments at The code files have the extension.vi, which is a abbreviation for Virtual Instrument. LabVIEW offers lots of additional Add-Ons and Toolkits. 3.1 Dataflow programming The programming language used in LabVIEW, also referred to as G, is a dataflow programming language. Execution is determined by the structure of a graphical block diagram (the LV-source code) on which the programmer connects different function-nodes by drawing wires. These wires propagate variables and any node can execute as soon as all its input data become available. Since this might be the case for multiple nodes simultaneously, G is inherently capable of parallel execution. Multi-processing and multithreading hardware is automatically exploited by the built-in scheduler, which multiplexes multiple OS threads over the nodes ready for execution. 3.2 Graphical programming LabVIEW ties the creation of user interfaces (called front panels) into the development cycle. LabVIEW programs/subroutines are called virtual instruments (VIs). Each VI has three components: a block diagram, a front panel, and a connector panel. The last is used to represent the VI in the block diagrams of other, calling VIs. Controls and indicators on the front panel allow an operator to input data into or extract data from a running virtual instrument. However, the front panel can also serve as a programmatic interface. Thus a virtual instrument can either be run as a program, with the front panel serving as a user interface, or, when dropped as a node onto the block diagram, the front panel defines the inputs and outputs for the given node through the connector pane. This implies each VI can be easily tested before being embedded as a subroutine into a larger program. 6
18 7 Introduction to LabVIEW The graphical approach also allows non-programmers to build programs simply by dragging and dropping virtual representations of lab equipment with which they are already familiar. The LabVIEW programming environment, with the included examples and the documentation, makes it simple to create small applications. This is a benefit on one side, but there is also a certain danger of underestimating the expertise needed for good quality "G" programming. For complex algorithms or large-scale code, it is important that the programmer possess an extensive knowledge of the special LabVIEW syntax and the topology of its memory management. The most advanced LabVIEW development systems offer the possibility of building stand-alone applications. Furthermore, it is possible to create distributed applications, which communicate by a client/server scheme, and are therefore easier to implement due to the inherently parallel nature of G-code. 3.3 Benefits One benefit of LabVIEW over other development environments is the extensive support for accessing instrumentation hardware. Drivers and abstraction layers for many different types of instruments and buses are included or are available for inclusion. These present themselves as graphical nodes. The abstraction layers offer standard software interfaces to communicate with hardware devices. The provided driver interfaces save program development time. The sales pitch of National Instruments is, therefore, that even people with limited coding experience can write programs and deploy test solutions in a reduced time frame when compared to more conventional or competing systems. A new hardware driver topology (DAQmxBase), which consists mainly of G-coded components with only a few register calls through NI Measurement Hardware DDK (Driver Development Kit) functions, provides platform independent hardware access to numerous data acquisition and instrumentation devices. The DAQmxBase driver is available for LabVIEW on Windows, Mac OS X and Linux platforms.
19 4 Introduction to Data Acquisition (DAQ) This chapter explains the basic concepts of using DAQ in LabVIEW. Topics: Introduction to DAQ - Data Acquisition MAX Measurement and Automation Explorer NI-DAQmx Driver software LabVIEW is very powerful when it comes to creating DAQ applications. LabVIEW includes a set of VIs that let you configure, acquire data from, and send data to DAQ devices. Often, one device can perform a variety of functions, such as analog-to-digital (A/D) conversion, digital-to-analog (D/A) conversion, digital I/O, and counter/timer operations. Each device supports different DAQ and signal generation speeds. Also, each DAQ device is designed for specific hardware, platforms and operating systems. National Instruments, the inventor of LabVIEW, also make DAQ devices, so the integration with the DAQ devices from NI and the LabVIEW software is seamless and makes it easy to do I/O operations from the LabVIEW environment. 4.1 Introduction to DAQ - Data Acquisition The purpose of data acquisition is to measure an electrical or physical phenomenon such as voltage, current, temperature, pressure, or sound. PC-based data acquisition uses a combination of modular hardware, application software, and a computer to take measurements. While each data acquisition system is defined by its application requirements, every system shares a common goal of acquiring, analyzing, and presenting information. Data acquisition systems incorporate signals, sensors, actuators, signal conditioning, data acquisition devices, and application software. So summing up, Data Acquisition is the process of: Acquiring signals from real-world phenomena Digitizing the signals Analyzing, presenting and saving the data 8
20 9 Introduction to Data Acquisition (DAQ) The DAQ system has the following parts involved, see Figure: The parts are: Physical input/output signals DAQ device/hardware Driver software Your software application (Application software) For an Introduction to Data Acquisition, see this webcast: Physical input/output signals A physical input/output signal is typically a voltage or current signal DAQ device/hardware DAQ hardware acts as the interface between the computer and the outside world. It primarily functions as a device that digitizes incoming analog signals so that the computer can interpret them A DAQ device (Data Acquisition Hardware) usually has these functions: Analog input Analog output Digital I/O Counter/timers We have different DAQ devices, such as:
21 10 Introduction to Data Acquisition (DAQ) Desktop DAQ devices where you need to plug a PCI DAQ board into your computer. The software is running on a computer. Portable DAQ devices for connection to the USB port, Wi-Fi connections, etc. The software is running on a computer Distributed DAQ devices where the software is developed on your computer and then later downloaded to the distributed DAQ device. Wi-Fi DAQ Devices Wireless: Driver software
22 11 Introduction to Data Acquisition (DAQ) Driver software is the layer of software for easily communicating with the hardware. It forms the middle layer between the application software and the hardware. Driver software also prevents a programmer from having to do register-level programming or complicated commands in order to access the hardware functions. Driver software from National Instruments: NI-DAQmx NI-DAQmx Base The DAQ Assistant, included with NI-DAQmx, is a graphical, interactive guide for configuring, testing, and acquiring measurement data. With a single click, you can even generate code based on your configuration, making it easier and faster to develop complex operations. Because DAQ Assistant is completely menu-driven, you will make fewer programming errors and drastically decrease the time from setting up your DAQ system to taking your first measurement. NI-DAQmx Base offers a subset of NI-DAQmx functionality on Windows and Linux, Mac OS X, Windows Mobile and Windows CE Your software application (Application software) Application software adds analysis and presentation capabilities to the driver software. Your software application normally does such tasks as: Real-time monitoring Data analysis Data logging Control algorithms Human machine interface (HMI) In order to create your DAQ application you need a programming development tool, such as LabVIEW. 4.2 MAX Measurement and Automation Explorer Measurement & Automation Explorer (MAX) provides access to your National Instruments devices and systems. With MAX, you can: Configure your National Instruments hardware and software Create and edit channels, tasks, interfaces, scales, and virtual instruments
23 12 Introduction to Data Acquisition (DAQ) Execute system diagnostics View devices and instruments connected to your system Update your National Instruments software In addition to the standard tools, MAX can expose item-specific tools you can use to configure, diagnose, or test your system, depending on which NI products you install. As you navigate through MAX, the contents of the application menu and toolbar change to reflect these new tools. 4.3 NI-DAQmx
24 13 Introduction to Data Acquisition (DAQ) The NI-DAQmx Driver software is the layer of software for easily communicating with the hardware. It forms the middle layer between the application software and the hardware. Driver software also prevents a programmer from having to do register-level programming or complicated commands in order to access the hardware functions. The DAQmx palette in LabVIEW: DAQ Assistant The DAQ Assistant, included with NI-DAQmx, is a graphical, interactive guide for configuring, testing, and acquiring measurement data. With a single click, you can even generate code based on your configuration, making it easier and faster to develop complex operations. Because DAQ Assistant is completely menu-driven, you will make fewer programming errors and drastically decrease the time from setting up your DAQ system to taking your first measurement.
25 5 Introduction to Wireless Data Acquisition Source: Wi-Fi DAQ is: Simple Direct sensors connectivity and graphical programming Secure Highest commercially available data encryption and authentication Wireless g Wi-Fi data acquisition is an extension of PC-based data acquisition to measurement applications where cables are inconvenient or uneconomical. NI Wi-Fi data acquisition (DAQ) devices combine IEEE g wireless or Ethernet communication; direct sensor connectivity; and the flexibility of NI-DAQmx driver software for remote monitoring of electrical, physical, mechanical, and acoustical signals. NI Wi-Fi DAQ devices can stream data on each channel at up to 250 ks/s. In addition, built-in NIST-approved 128-bit AES encryption and advanced network authentication methods offer the highest commercially available network security. With the flexibility of NI LabVIEW graphical programming and the ubiquity of network infrastructure, NI Wi-Fi DAQ makes it easy to incorporate wireless connectivity into new or existing PC-based measurement or control systems. 14
26 15 Introduction to Wireless Data Acquisition The Data Flow in Wi-Fi DAQ is as follows: Unlike most wireless sensors or wireless sensor networks, wireless data acquisition devices are meant to stream data continuously back to a host PC or laptop. A wireless sensor node is typically a low-power, autonomous battery-operated device intended for long-term deployment in applications where measurements are needed only every few minutes, hours, or even days. Wi-Fi data acquisition devices, on the other hand, behave in much the same way as a USB data acquisition device a host PC collects data continuously (in real time) as the device acquires it. The data acquisition device may be battery-operated, but the focus is on the measurement versus the battery life. Also, Wi-Fi data acquisition devices use the nearubiquitous wireless networking standard, IEEE because of its higher bandwidth and
27 16 Introduction to Wireless Data Acquisition broader applicability. Finally, because NI Wi-Fi data acquisition uses the same NI-DAQmx driver software as other NI data acquisition devices, you can develop your applications using NI LabVIEW, LabWindows /CVI; ANSI C/C++; or Microsoft C#, Visual Basic, or Visual Basic.NET. More Information about Wi-Fi DAQ: Watch the Wi-Fi DAQ Tour: wv-795 Wi-Fi DAQ Webcast:
28 6 NI Wireless DAQ Devices Common components in Wi-Fi DAQ are as follows: DAQ Devices Wireless Access Points (WAP) or a Wireless Router Network Switches How do I connect to an NI Wi-Fi DAQ device? When setting up your NI Wi-Fi DAQ device, you may choose to connect to an existing enterprise network through a wireless access point or set up your own network with a wireless router. For existing IT infrastructure, NI Wi-Fi DAQ devices support WPA Enterprise and WPA2 Enterprise (IEEE i). If you set up your own network, you may use WEP, WPA Personal (WPA-PSK), or WPA2 Personal (WPA2-PSK) security. NI Wi-Fi DAQ devices also support ad hoc or peer-to-peer networks, which do not require any routers or access points. However, ad hoc support is inconsistent across wireless network interface cards and is not secure. Communication through a wireless access point or wireless router is the preferred mode of operation. How do I program NI Wi-Fi DAQ devices? All NI Wi-Fi and Ethernet DAQ devices use the same NI-DAQmx measurement services and driver software as other National Instruments PCI, PXI, and USB DAQ devices. NI-DAQmx measurement services software controls every aspect of your data acquisition system from configuration to programming. With NI-DAQmx software, you can quickly configure and acquire measurements using the DAQ Assistant and automatically generate code to get your application started quickly. NI-DAQmx also features virtual channels that automatically scale raw data into engineering units. Because you can use the same driver API to program new NI Wi-Fi DAQ devices, incorporating wireless connectivity into your existing applications is easy. Wi-Fi DAQ Devices from National Instruments: 17
29 18 NI Wireless DAQ Devices TUC have the following wireless DAQ devices available: NI WLS Wireless 4-Channel Accelerometer and Microphone Input NI WAP Wireless access points (WAPs) add wireless connectivity to all Ethernet-based NI programmable automation NI UES An eight-port unmanaged entry-level switch for networking between NI Ethernet-based controllers and devices using standard Ethernet protocols PS-5 Power Supply 6.1 NI WLS-9234 The NI WLS-9234 is a four-channel IEEE wireless or Ethernet C Series dynamic signal acquisition module for making high-accuracy audio frequency measurements from integrated electronic piezoelectric (IEPE) and non-iepe sensors. 4-Channel, 51.2 ks/s/ch, 24-Bit, ±5 V IEPE Input IEEE b/g (Wi-Fi) wireless and Ethernet communications interfaces 51.2 ks/s per-channel maximum sampling rate; ±5 V input
30 19 NI Wireless DAQ Devices 24-bit resolution; 102 db dynamic range; antialiasing filters Software-selectable AC/DC coupling; AC-coupled (0.5 Hz) Software-selectable IEPE signal conditioning (0 or 2 ma) The NI WLS-9234 is a four-channel IEEE wireless or Ethernet C Series dynamic signal acquisition module for making high-accuracy audio frequency measurements from integrated electronic piezoelectric (IEPE) and non-iepe sensors. The WLS-9234 delivers 102 db of dynamic range and incorporates software-selectable AC/DC coupling and IEPE signal conditioning for accelerometers and microphones. The four input channels simultaneously digitize signals at rates up to 51.2 khz per channel with built-in antialiasing filters that automatically adjust to your sampling rate. The WLS-9234 is well-suited for noise and vibration analysis applications. The NI Sound and Vibration Measurement Suite, which specifically addresses these applications, has two components: the NI Sound and Vibration Assistant and LabVIEW Analysis VIs (functions) for power spectra, frequency response (FRF), fractional octave analysis, sound-level measurements, order spectra, order maps, order extraction, sensor calibration, human vibration filters, and torsional vibration. WLS-9234 has 4 BNC connectors. The BNC connector is used for RF signal connections. The BNC connector is one of several radio frequency (RF) connectors on the market today. 6.2 NI WAP-3701
31 20 NI Wireless DAQ Devices WAP Wireless Access Point The NI WAP-3701 wireless access points (WAPs) add wireless connectivity to all Ethernetbased NI programmable automation controllers (PACs). A WAP-37x1 can connect wireless devices to a wired network and has an IP address so other wireless clients can access the device. A WAP-37x1 can also serve as a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server and configure other WAP-37x1 devices as wireless clients. A single WAP-37x1 typically supports up to 30 client devices, with the range depending on the wireless antennae selection. It also serves as a wireless bridge and allows two devices to talk to each other. EEE g/b wireless access point, client, and bridge Web-based management software included 64- and 128-bit wired equivalent privacy (WEP) security Redundant dual 24 VDC power inputs Metal enclosure, IP30 rated; Class I, Division 2 hazardous locations DIN-rail mounting support 6.3 NI UES-3880 UES Unmanaged Ethernet Switch The NI UES-3880 is an eight-port unmanaged entry-level switch for networking between NI Ethernet-based controllers and devices using standard Ethernet protocols. To network with NI programmable automation controllers (PACs), the UES-3880 provides industrial features including -40 to 70 C operating temperature; Class I, Division 2 and ATEX Class 1, Zone 2 certifications for hazardous locations; and redundant dual 24 VDC power inputs.
32 21 NI Wireless DAQ Devices 6.4 PS-5 Power Supply PS Power Supply The PS-5 is a DIN-rail-mountable 24 VDC power supply that provides 5 A of current and is rated for operation from -25C to 60C. Two PS-5 supplies can be wired in parallel to provide up to 10 A. The PS-5 is recommended for industrial installations. The PS-4 is a DIN-railmountable 24 V power supply in FieldPoint packaging. The PS-3 and PS-2 are power supply "bricks" with a universal IEC power input. The PS-3 can also operate as a float charger for 12 VDC batteries. The PS-1 is a wall-mount power supply.
33 7 NI WSN Devices A wireless sensor network (WSN) is a wireless network consisting of spatially distributed autonomous devices that use sensors to monitor physical or environmental conditions. These autonomous devices, or nodes, combine with routers and a gateway to create a typical WSN system. The distributed measurement nodes communicate wirelessly to a central gateway, which provides a connection to the wired world where you can collect, process, analyze, and present your measurement data. To extend distance and reliability in a WSN, you can use routers to gain an additional communication link between end nodes and the gateway. The proprietary NI WSN protocol is based on IEEE and ZigBee technology. The IEEE communication standard defines the Physical and Medium Access Control layers in the networking model, providing communication in three frequency bands including the 2.4 GHz ISM band. ZigBee builds on the standard with the network and application layers, offering features such as device coordination, reliability through mesh networking topologies, and the functionality to create user-defined profiles that allow for customization and flexibility within the protocol. What is the difference between NI Wi-Fi data acquisition (DAQ) and NI WSN devices? NI Wi-Fi DAQ devices combine IEEE b/g (Wi-Fi) wireless or Ethernet communication, direct sensor connectivity, and the flexibility of NI-DAQmx software for a breadth of remote measurement and control options. Externally powered, NI Wi-Fi DAQ devices can stream continuous waveform data on each channel at more than 50 ks/s and offer the highest commercially available network security (WPA2 Enterprise). NI WSN devices deliver low-power measurement nodes that operate for up to three years on 4 AA batteries and can be deployed for long-term, remote operation. The wireless measurement nodes communicate with a central gateway using a protocol based on IEEE (ZigBee) to offer mesh routing capabilities that extend network distance and reliability. NI WSN systems support lower data rates to preserve power, are easily programmed using I/O variables, and currently accommodate thermocouple and ±10 V measurements. 22
34 23 NI WSN Devices Many of the WSN systems today are based on ZigBee or IEEE protocols due to their low-power consumption. ZigBee builds on the layers to provide security, reliability through mesh networking topologies, and interoperability with other devices and standards.
35 24 NI WSN Devices 7.1 Devices NI WSN WSN Ethernet Gateway The NI WSN-9791 Ethernet gateway coordinates communication between distributed measurement nodes and the host controller in your NI wireless sensor network (WSN). The gateway has a 2.4 GHz, IEEE radio based on ZigBee technology to collect measurement data from the sensor network and a 10/100 Mbits/s Ethernet port to provide flexible connectivity to a Windows or LabVIEW Real-Time OS host controller NI WSN Thermocouple Input Node The NI WSN-3212 measurement node is a wireless device that provides four 24-bit thermocouple input channels and four bidirectional digital channels that you can configure on a per-channel basis for input, sinking output, or sourcing output.
36 25 NI WSN Devices NI WSN Analog Input Node The NI WSN-3202 measurement node is a wireless device that provides four ±10 V analog input channels and four bidirectional digital channels that you can configure on a perchannel basis for input, sinking output, or sourcing output. 7.2 LabVIEW Drivers National Instruments offer the NI-WSN software.
37 26 NI WSN Devices With NI-WSN software you can easily configure your network in the Measurement & Automation Explorer (MAX) utility. MAX provides an intuitive user interface to add and remove measurement nodes and configure wireless settings. NI-WSN software provides seamless LabVIEW integration so that you can quickly and easily extract measurement data from your WSN. After adding the NI WSN Ethernet gateway to a LabVIEW Project, the nodes configured with the gateway in MAX automatically populate in the LabVIEW Project, giving you instant access to their I/O and properties. Simply drag and drop I/O variables from the LabVIEW Project to a LabVIEW Block Diagram for data extraction, analysis, and presentation. National Instruments also offer WSN drivers for WSN equipments from other vendors:
38 Hans-Petter Halvorsen, M.Sc. Blog: University College of Southeast Norway
Data Acquisition in LabVIEW
 University College of Southeast Norway Data Acquisition in LabVIEW Hans-Petter Halvorsen, 2016.10.28 http://home.hit.no/~hansha Preface This tutorial explains the basic concepts of a Data Acquisition in
University College of Southeast Norway Data Acquisition in LabVIEW Hans-Petter Halvorsen, 2016.10.28 http://home.hit.no/~hansha Preface This tutorial explains the basic concepts of a Data Acquisition in
Datalogging in LabVIEW
 Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics Datalogging in LabVIEW HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN, 2011.01.04 Faculty of Technology, Postboks 203, Kjølnes
Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics Datalogging in LabVIEW HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN, 2011.01.04 Faculty of Technology, Postboks 203, Kjølnes
DAQ in MATLAB HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN,
 Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics DAQ in MATLAB HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN, 2011.06.07 Faculty of Technology, Postboks 203, Kjølnes ring
Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics DAQ in MATLAB HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN, 2011.06.07 Faculty of Technology, Postboks 203, Kjølnes ring
Høgskolen i Telemark Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics.
 Høgskolen i Telemark Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics Wi- Fi DAQ Hardware Setup Cuong Nguyen, Hans- Petter Halvorsen, 2013.08.07
Høgskolen i Telemark Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics Wi- Fi DAQ Hardware Setup Cuong Nguyen, Hans- Petter Halvorsen, 2013.08.07
How to Choose the Right Bus for Your Measurement System
 1 How to Choose the Right Bus for Your Measurement System Overview When you have hundreds of different data acquisition (DAQ) devices to choose from on a wide variety of buses, it can be difficult to select
1 How to Choose the Right Bus for Your Measurement System Overview When you have hundreds of different data acquisition (DAQ) devices to choose from on a wide variety of buses, it can be difficult to select
Introduction to LabVIEW
 University College of Southeast Norway Introduction to LabVIEW Hans-Petter Halvorsen, 2016-09-07 http://home.hit.no/~hansha Preface This document explains the basic concepts of LabVIEW. You find additional
University College of Southeast Norway Introduction to LabVIEW Hans-Petter Halvorsen, 2016-09-07 http://home.hit.no/~hansha Preface This document explains the basic concepts of LabVIEW. You find additional
Virtual Instruments with LabVIEW
 Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics Virtual Instruments with LabVIEW HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN, 2011.01.04 Faculty of Technology, Postboks
Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics Virtual Instruments with LabVIEW HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN, 2011.01.04 Faculty of Technology, Postboks
Wireless DAQ using ZigBee
 Høgskolen i Telemark Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics Wireless DAQ using ZigBee Cuong Nguyen, Hans- Petter Halvorsen 2013.10.29 Hardware
Høgskolen i Telemark Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics Wireless DAQ using ZigBee Cuong Nguyen, Hans- Petter Halvorsen 2013.10.29 Hardware
Linear Algebra in LabVIEW
 https://www.halvorsen.blog Linear Algebra in LabVIEW Hans-Petter Halvorsen, 2018-04-24 Preface This document explains the basic concepts of Linear Algebra and how you may use LabVIEW for calculation of
https://www.halvorsen.blog Linear Algebra in LabVIEW Hans-Petter Halvorsen, 2018-04-24 Preface This document explains the basic concepts of Linear Algebra and how you may use LabVIEW for calculation of
CompactDAQ Chassis PRODUCT FLYER CONTENTS. Цены и срок поставки уточняйте на сайте по телефону: или
 PRODUCT FLYER CompactDAQ Chassis CONTENTS CompactDAQ Chassis Detailed View of cdaq-9189 Key Features NI-DAQmx Application Programming Interface (API) Platform-Based Approach to Conditioned Measurements
PRODUCT FLYER CompactDAQ Chassis CONTENTS CompactDAQ Chassis Detailed View of cdaq-9189 Key Features NI-DAQmx Application Programming Interface (API) Platform-Based Approach to Conditioned Measurements
Overcoming Concerns about Wireless PACs and I/O in Industrial Automation
 Overcoming Concerns about Wireless PACs and I/O in Industrial Automation Industrial Automation Flirts with Wireless The automation industry increasingly finds wireless attractive, and for several reasons.
Overcoming Concerns about Wireless PACs and I/O in Industrial Automation Industrial Automation Flirts with Wireless The automation industry increasingly finds wireless attractive, and for several reasons.
Hands-On Seminar. Evaluate CompactDAQ and LabVIEW for Your Application 09/05/2017. ni.com
 Hands-On Seminar Evaluate CompactDAQ and LabVIEW for Your Application 09/05/2017 ni.com Jason Strydom Technical Sales Engineer CLD Let s Talk About You What type of applications are you going to be working
Hands-On Seminar Evaluate CompactDAQ and LabVIEW for Your Application 09/05/2017 ni.com Jason Strydom Technical Sales Engineer CLD Let s Talk About You What type of applications are you going to be working
Wireless Field Data Backhaul
 Service Data Sheet Wireless Field Data Backhaul Scalable Reduced cost Safer deployment Secure and reliable communications Full support service An Emerson Smart Wireless Field Data Backhaul Solution integrates
Service Data Sheet Wireless Field Data Backhaul Scalable Reduced cost Safer deployment Secure and reliable communications Full support service An Emerson Smart Wireless Field Data Backhaul Solution integrates
What s New in Data Acquisition
 What s New in Data Acquisition NEW! New DAQ Products and Demos NEW! USB DAQ Multifunction Intelligent DAQ DAQ Software New DAQ Products and Demos NEW! USB DAQ Multifunction Intelligent DAQ DAQ Software
What s New in Data Acquisition NEW! New DAQ Products and Demos NEW! USB DAQ Multifunction Intelligent DAQ DAQ Software New DAQ Products and Demos NEW! USB DAQ Multifunction Intelligent DAQ DAQ Software
Data Acquisition HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN,
 Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics Data Acquisition HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN, 2011.10.14 Faculty of Technology, Postboks 203, Kjølnes
Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics Data Acquisition HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN, 2011.10.14 Faculty of Technology, Postboks 203, Kjølnes
OPC and Real-Time Systems. in LabVIEW
 University College of Southeast Norway OPC and Real-Time Systems Hans-Petter Halvorsen, 2016.10.31 in LabVIEW http://home.hit.no/~hansha Preface OPC (OLE for process control) is a standard interface between
University College of Southeast Norway OPC and Real-Time Systems Hans-Petter Halvorsen, 2016.10.31 in LabVIEW http://home.hit.no/~hansha Preface OPC (OLE for process control) is a standard interface between
Wireless technology Principles of Security
 Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing. Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology
 CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Sensor Networks A wireless sensor network (WSN) is a wireless network consisting
CSC344 Wireless and Mobile Computing Department of Computer Science COMSATS Institute of Information Technology Wireless Sensor Networks A wireless sensor network (WSN) is a wireless network consisting
Naveen Kumar. 1 Wi-Fi Technology
 Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
Datasheet ac Dual-Radio Access Points. Models: UAP-AC-LITE, UAP-AC-LR, UAP-AC, UAP-AC-EDU, UAP-AC-PRO, UAP-AC-Outdoor
 802.11ac Dual-Radio Access Points Models: UAP-AC-LITE, UAP-AC-LR, UAP-AC, UAP-AC-EDU, UAP-AC-PRO, UAP-AC-Outdoor Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Breakthrough Speeds
802.11ac Dual-Radio Access Points Models: UAP-AC-LITE, UAP-AC-LR, UAP-AC, UAP-AC-EDU, UAP-AC-PRO, UAP-AC-Outdoor Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Breakthrough Speeds
NI Technical Symposium ni.com
 NI Technical Symposium 2016 1 New Hardware Technologies for DAQ Applications Nicholas Haripersad Field Sales Engineer Session Objectives Introduce the three major NI DAQ platforms Present future trends
NI Technical Symposium 2016 1 New Hardware Technologies for DAQ Applications Nicholas Haripersad Field Sales Engineer Session Objectives Introduce the three major NI DAQ platforms Present future trends
Datasheet ac Dual-Radio Access Points. Models: UAP-AC-LITE, UAP-AC-LR, UAP-AC-EDU, UAP-AC-PRO, UAP-AC-Outdoor, UAP-AC
 802.11ac Dual-Radio Access Points Models: UAP-AC-LITE, UAP-AC-LR, UAP-AC-EDU, UAP-AC-PRO, UAP-AC-Outdoor, UAP-AC Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Breakthrough Speeds
802.11ac Dual-Radio Access Points Models: UAP-AC-LITE, UAP-AC-LR, UAP-AC-EDU, UAP-AC-PRO, UAP-AC-Outdoor, UAP-AC Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Breakthrough Speeds
Presented by Viraj Anagal Kaushik Mada. Presented to Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud. ECE 6900 Fall 2014 Date: 09/29/2014 1
 Presented by Viraj Anagal Kaushik Mada Presented to Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud ECE 6900 Fall 2014 Date: 09/29/2014 1 Outline Motivation Overview Wireless Sensor Network Components Characteristics of Wireless
Presented by Viraj Anagal Kaushik Mada Presented to Dr. Mohamed Mahmoud ECE 6900 Fall 2014 Date: 09/29/2014 1 Outline Motivation Overview Wireless Sensor Network Components Characteristics of Wireless
University College of Southeast Norway. LM-900 Level Tank. Hans-Petter Halvorsen,
 University College of Southeast Norway LM-900 Level Tank Hans-Petter Halvorsen, 2016.10.26 http://home.hit.no/~hansha Table of Contents Table of Contents... ii 1 Introduction... 1 2 System Description...
University College of Southeast Norway LM-900 Level Tank Hans-Petter Halvorsen, 2016.10.26 http://home.hit.no/~hansha Table of Contents Table of Contents... ii 1 Introduction... 1 2 System Description...
Thread in Commercial Backgrounder
 Thread in Commercial Backgrounder September 2018 An introduction to Thread, its Network Topology and Application Support 1 What is Thread Thread is an open standard for wireless communication providing
Thread in Commercial Backgrounder September 2018 An introduction to Thread, its Network Topology and Application Support 1 What is Thread Thread is an open standard for wireless communication providing
New Technologies in Data Acquisition
 New Technologies in Data Acquisition Agenda Introduction to PC Based Data Acquisition New Technologies in Data Acquisition 1. New Bus Technologies 2. Signal Conditioning, Timing and Synchronization Introduction
New Technologies in Data Acquisition Agenda Introduction to PC Based Data Acquisition New Technologies in Data Acquisition 1. New Bus Technologies 2. Signal Conditioning, Timing and Synchronization Introduction
Enterprise WiFi System. Datasheet. Models: UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-PRO, UAP-AC, UAP-Outdoor+, UAP-Outdoor5, UAP-AC Outdoor
 Enterprise WiFi System Models: UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-PRO, UAP-AC, UAP-Outdoor+, UAP-Outdoor5, UAP-AC Outdoor Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Breakthrough Speeds up to
Enterprise WiFi System Models: UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-PRO, UAP-AC, UAP-Outdoor+, UAP-Outdoor5, UAP-AC Outdoor Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Breakthrough Speeds up to
Madrid, 25 y 26 de mayo de 2015 ABB Automation Days Wireless Instrumentation
 Madrid, 25 y 26 de mayo de 2015 ABB Automation Days Wireless Instrumentation Discovering the Unknown Rising demand for monitoring of process values by Increasing efficiency, reducing waste (raw materials,
Madrid, 25 y 26 de mayo de 2015 ABB Automation Days Wireless Instrumentation Discovering the Unknown Rising demand for monitoring of process values by Increasing efficiency, reducing waste (raw materials,
Designing Next Generation Test Systems An In-Depth Developers Guide
 An In-Depth Developers Guide Designing Next Generation Test Systems An In-depth Developers Guide Contents Section 1 Executive Summary Chapter 1 Increasing Design Complexity...1-1 Shorter Product Development
An In-Depth Developers Guide Designing Next Generation Test Systems An In-depth Developers Guide Contents Section 1 Executive Summary Chapter 1 Increasing Design Complexity...1-1 Shorter Product Development
Enterprise WiFi System. Datasheet. Tel: +44 (0) Fax: +44 (0)
 Enterprise WiFi System Models: UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-PRO, UAP-AC, UAP-Outdoor+, UAP-Outdoor5, UAP-AC Outdoor Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Breakthrough Speeds up to
Enterprise WiFi System Models: UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-PRO, UAP-AC, UAP-Outdoor+, UAP-Outdoor5, UAP-AC Outdoor Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Breakthrough Speeds up to
NI mydaq HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN, Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics
 Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics NI mydaq HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN, 2012.01.20 Faculty of Technology, Postboks 203, Kjølnes ring 56,
Telemark University College Department of Electrical Engineering, Information Technology and Cybernetics NI mydaq HANS-PETTER HALVORSEN, 2012.01.20 Faculty of Technology, Postboks 203, Kjølnes ring 56,
Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs
 Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wireless Transmission for LAN Radio Frequency Transmission (RF) Infrared Transmission 2 1
Chapter 10: Wireless LAN & VLANs Abdullah Konak School of Information Sciences and Technology Penn State Berks Wireless Transmission for LAN Radio Frequency Transmission (RF) Infrared Transmission 2 1
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Index
 Index Symbols and Numbers $ (dollar sign), in folder share names, 117 802.11a standard definition, 22 speed, 26 802.11b standard 802.11g standard 802.11i standard, 23 A access points compatibility, 45
Index Symbols and Numbers $ (dollar sign), in folder share names, 117 802.11a standard definition, 22 speed, 26 802.11b standard 802.11g standard 802.11i standard, 23 A access points compatibility, 45
Ethernet/Serial Interfaces for Compact FieldPoint
 NI cfp-180x Distributed I/O interfaces for Ethernet and RS232 networks 4 or 8-slot Compact FieldPoint distributed Ethernet/serial network interfaces FieldPoint software for rapid distributed I/O access
NI cfp-180x Distributed I/O interfaces for Ethernet and RS232 networks 4 or 8-slot Compact FieldPoint distributed Ethernet/serial network interfaces FieldPoint software for rapid distributed I/O access
Add a Wireless Network to an Existing Wired Network using a Wireless Access Point (WAP)
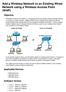 Add a Wireless Network to an Existing Wired Network using a Wireless Access Point (WAP) Objective A Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a networking device that allows wireless-capable devices to connect to
Add a Wireless Network to an Existing Wired Network using a Wireless Access Point (WAP) Objective A Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a networking device that allows wireless-capable devices to connect to
WirelessHART, Technology and Deployment ( ETSI Nov. 09 ) Jean-Luc Griessmann, HART Communication Foundation Europe
 WirelessHART, Technology and Deployment ( ETSI Nov. 09 ) Jean-Luc Griessmann, HART Communication Foundation Europe Introduction Wireless devices are everywhere! We use wireless devices in everyday life.
WirelessHART, Technology and Deployment ( ETSI Nov. 09 ) Jean-Luc Griessmann, HART Communication Foundation Europe Introduction Wireless devices are everywhere! We use wireless devices in everyday life.
Datasheet ac Wave 2 Enterprise Wi-Fi Access Point. Model: UAP-AC-HD. Simultaneous Dual-Band 4x4 Multi-User MIMO
 802.11ac Wave 2 Enterprise Wi-Fi Access Point Model: UAP-AC-HD Simultaneous Dual-Band 4x4 Multi-User MIMO Four-Stream 802.11ac Wave 2 Technology 802.3at PoE+ Compatibility Scalable Enterprise Wi-Fi Management
802.11ac Wave 2 Enterprise Wi-Fi Access Point Model: UAP-AC-HD Simultaneous Dual-Band 4x4 Multi-User MIMO Four-Stream 802.11ac Wave 2 Technology 802.3at PoE+ Compatibility Scalable Enterprise Wi-Fi Management
Wireless and Mobile Networks
 Monash University Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering Wireless and Mobile Networks Present and Future Y. Ahmet Şekercioğlu August 2007wireless-nets.tex,v1.5 Y. Ahmet Şekercioğlu:
Monash University Department of Electrical and Computer Systems Engineering Wireless and Mobile Networks Present and Future Y. Ahmet Şekercioğlu August 2007wireless-nets.tex,v1.5 Y. Ahmet Şekercioğlu:
LabVIEW Basics I: Introduction Course
 www.ni.com/training LabVIEW Basics I Page 1 of 4 LabVIEW Basics I: Introduction Course Overview The LabVIEW Basics I course prepares you to develop test and measurement, data acquisition, instrument control,
www.ni.com/training LabVIEW Basics I Page 1 of 4 LabVIEW Basics I: Introduction Course Overview The LabVIEW Basics I course prepares you to develop test and measurement, data acquisition, instrument control,
Introduction to LabVIEW and NI Hardware Platform
 Introduction to LabVIEW and NI Hardware Platform Corrie Botha Platform-Based Approach 2 With LabVIEW, You Can Program the Way You Think 3 With LabVIEW, You Can Program the Way You Think The graphical,
Introduction to LabVIEW and NI Hardware Platform Corrie Botha Platform-Based Approach 2 With LabVIEW, You Can Program the Way You Think 3 With LabVIEW, You Can Program the Way You Think The graphical,
SDCI Student Project 6 Sensing Capabilites Go Wireless. Mario Caruso Francesco Leotta Leonardo Montecchi Marcello Pietri
 SDCI 2012 Student Project 6 Sensing Capabilites Go Wireless Mario Caruso Francesco Leotta Leonardo Montecchi Marcello Pietri Overview Wireless Sensor Network Is a collection of nodes organized into a cooperative
SDCI 2012 Student Project 6 Sensing Capabilites Go Wireless Mario Caruso Francesco Leotta Leonardo Montecchi Marcello Pietri Overview Wireless Sensor Network Is a collection of nodes organized into a cooperative
Wireless IoT Sensing Solutions
 Wireless IoT Sensing Solutions Modularized and Ready-to-Use Solutions High Adaptability for IoT Sensing IoT Sensing Applications LPWAN and Wireless Ethernet IoT Architecture IoT Technology Product Highlights
Wireless IoT Sensing Solutions Modularized and Ready-to-Use Solutions High Adaptability for IoT Sensing IoT Sensing Applications LPWAN and Wireless Ethernet IoT Architecture IoT Technology Product Highlights
 Wireless Networking WiFi Standards 802.11a 5GHz 54MB 802.11b 2.4 GHz 11MB 802.11g 2.4GHz 52MB 802.11n 2.4/5GHz 108MB 802.11b The 802.11b standard has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s, and uses
Wireless Networking WiFi Standards 802.11a 5GHz 54MB 802.11b 2.4 GHz 11MB 802.11g 2.4GHz 52MB 802.11n 2.4/5GHz 108MB 802.11b The 802.11b standard has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s, and uses
Wireless Networking. Chapter The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
ISSN (PRINT): , (ONLINE): , VOLUME-6, ISSUE-1,
 DESIGN OF MULTIMODE GATEWAY FOR DATA ACQUISITION TO HIGH END DATA MONITORING USING IEEE802.15.4 Madhhav G.Raut 1 & Pradip B.Dahikar 2 Hislop College,Civil Lines, Nagpur & Kamala Nehru Mahavidyalaya,Nagpur,India
DESIGN OF MULTIMODE GATEWAY FOR DATA ACQUISITION TO HIGH END DATA MONITORING USING IEEE802.15.4 Madhhav G.Raut 1 & Pradip B.Dahikar 2 Hislop College,Civil Lines, Nagpur & Kamala Nehru Mahavidyalaya,Nagpur,India
Datasheet AC Dual-Radio Access Points. Models: UAP-AC-IW, UAP-AC-IW-PRO, UAP-AC-LITE, UAP-AC-LR, UAP-AC-PRO, UAP-AC-EDU
 802.11AC Dual-Radio Access Points Models: UAP-AC-IW, UAP-AC-IW-PRO, UAP-AC-LITE, UAP-AC-LR, UAP-AC-PRO, UAP-AC-EDU Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Breakthrough Speeds
802.11AC Dual-Radio Access Points Models: UAP-AC-IW, UAP-AC-IW-PRO, UAP-AC-LITE, UAP-AC-LR, UAP-AC-PRO, UAP-AC-EDU Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Breakthrough Speeds
INTEGRATION OF AD HOC WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS IN A VIRTUAL INSTRUMENTATION CONFIGURATION
 Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 7 (56) No. 2-2014 Series I: Engineering Sciences INTEGRATION OF AD HOC WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS IN A VIRTUAL INSTRUMENTATION CONFIGURATION Mihai MACHEDON-PISU
Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Braşov Vol. 7 (56) No. 2-2014 Series I: Engineering Sciences INTEGRATION OF AD HOC WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS IN A VIRTUAL INSTRUMENTATION CONFIGURATION Mihai MACHEDON-PISU
Advanced NI-DAQmx Programming Techniques with LabVIEW
 Advanced NI-DAQmx Programming Techniques with LabVIEW Agenda Understanding Your Hardware Data Acquisition Systems Data Acquisition Device Subsystems Advanced Programming with NI-DAQmx Understanding Your
Advanced NI-DAQmx Programming Techniques with LabVIEW Agenda Understanding Your Hardware Data Acquisition Systems Data Acquisition Device Subsystems Advanced Programming with NI-DAQmx Understanding Your
Case study of Wireless Technologies in Industrial Applications
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 1, January 2017 257 Case study of Wireless Technologies in Industrial Applications Rahul Hanumanth Rao Computer Information
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 1, January 2017 257 Case study of Wireless Technologies in Industrial Applications Rahul Hanumanth Rao Computer Information
What do we expect from Wireless in the Factory?
 What do we expect from Wireless in the Factory? And what are we doing about it? ETSI Wireless Factory Workshop, 15 December 2008 Tim Whittaker System Architect, Wireless Division 11 December 2008 S4989-P-188
What do we expect from Wireless in the Factory? And what are we doing about it? ETSI Wireless Factory Workshop, 15 December 2008 Tim Whittaker System Architect, Wireless Division 11 December 2008 S4989-P-188
EAGLE Smart Wireless Solution Condition monitoring installation has never been so easy!!
 EAGLE Smart Wireless Solution Condition monitoring installation has never been so easy!! oneprod.com EAGLE is ONEPROD s easy-to-deploy continuous monitoring system for conditionbased maintenance. EAGLE
EAGLE Smart Wireless Solution Condition monitoring installation has never been so easy!! oneprod.com EAGLE is ONEPROD s easy-to-deploy continuous monitoring system for conditionbased maintenance. EAGLE
Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit. Manual
 Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit Manual Dear Customer, Thanks for choosing Hamlet. Please carefully follow the instructions for its use and maintenance and, once this item has run its life span, we kindly
Wireless LAN USB Super G 108 Mbit Manual Dear Customer, Thanks for choosing Hamlet. Please carefully follow the instructions for its use and maintenance and, once this item has run its life span, we kindly
WZRDnet. A Low-Power Wireless Ad-Hoc Mesh Network for Austere Tactical Environments. February 14, 2018
 White Paper TELEGRID Technologies, Inc. WZRDnet A Low-Power Wireless Ad-Hoc Mesh Network for Austere Tactical Environments February 14, 2018 23 Vreeland Road Suite 290 Florham Park, NJ 07932 www.telegrid.com
White Paper TELEGRID Technologies, Inc. WZRDnet A Low-Power Wireless Ad-Hoc Mesh Network for Austere Tactical Environments February 14, 2018 23 Vreeland Road Suite 290 Florham Park, NJ 07932 www.telegrid.com
VIBBOX. 32, 48, or 64-Channel Sound & Vibration Solution Expansion to 256 Channels. Key Feature of Each VIBbox: Table 1. Key Features of VIBbox Models
 VIBBOX 32, 48, or 64-Channel Sound & Vibration Solution Expansion to 256 Channels VIBbox is a high-accuracy, high channel count, dynamic signal analyzer system for sound and vibration applications. Each
VIBBOX 32, 48, or 64-Channel Sound & Vibration Solution Expansion to 256 Channels VIBbox is a high-accuracy, high channel count, dynamic signal analyzer system for sound and vibration applications. Each
Wireless Networks. Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas. Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov.
 Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
Datasheet. Enterprise WiFi System. Models: UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-Pro, UAP-Outdoor, UAP-Outdoor5. Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a
 Enterprise WiFi System Models: UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-Pro, UAP-Outdoor, UAP-Outdoor5 Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a 1 The UniFi Enterprise WiFi System is a scalable enterprise access point solution
Enterprise WiFi System Models: UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-Pro, UAP-Outdoor, UAP-Outdoor5 Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a 1 The UniFi Enterprise WiFi System is a scalable enterprise access point solution
DATASHEET Pepwave Mesh Connector
 Features Vendor Neutral Repeater, Interoperability Certified The allows you to seamlessly extend the coverage of an existing Wi-Fi network, without messy configurations or having to run cables! Simply
Features Vendor Neutral Repeater, Interoperability Certified The allows you to seamlessly extend the coverage of an existing Wi-Fi network, without messy configurations or having to run cables! Simply
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN)
 Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) Introduction M. Schölzel Difference to existing wireless networks Infrastructure-based networks e.g., GSM, UMTS, Base stations connected to a wired backbone network Mobile
Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN) Introduction M. Schölzel Difference to existing wireless networks Infrastructure-based networks e.g., GSM, UMTS, Base stations connected to a wired backbone network Mobile
Ubiquiti UniFi AC Dual-Radio Access Point with 1300Mbps / 600ft range / 24V Passive PoE
 Innovative Antenna Design Designed for Optimal RF Performance Scalable Enterprise Wi-Fi Management Overview UQ-UAP-AC-LR 1/5 Scalable Enterprise Wi-Fi Management UniFi is the revolutionary Wi-Fi system
Innovative Antenna Design Designed for Optimal RF Performance Scalable Enterprise Wi-Fi Management Overview UQ-UAP-AC-LR 1/5 Scalable Enterprise Wi-Fi Management UniFi is the revolutionary Wi-Fi system
ICP DAS. ICP DAS 2015 M2M WLAN Wireless Solutions
 ICP DAS 2015 M2M WLAN Wireless Solutions Industrial Computer Industrial Product Data Computer Acquisition Product System Data Acquisition System PAC WLAN Wireless Solutions Wi-Fi Products WLAN Converter
ICP DAS 2015 M2M WLAN Wireless Solutions Industrial Computer Industrial Product Data Computer Acquisition Product System Data Acquisition System PAC WLAN Wireless Solutions Wi-Fi Products WLAN Converter
NI-DAQmx Basic Course NITS John Shannon
 NI-DAQmx Basic Course NITS 2005 John Shannon Agenda Intro to DAQMX Difference between traditional / DaqMX MAX and DAQ Assistance Analog Input / Output Property Nodes Buffered / Continuous Acquisition Analog
NI-DAQmx Basic Course NITS 2005 John Shannon Agenda Intro to DAQMX Difference between traditional / DaqMX MAX and DAQ Assistance Analog Input / Output Property Nodes Buffered / Continuous Acquisition Analog
Software-Defined Test Fundamentals. Understanding the Architecture of Modular, High-Performance Test Systems
 Software-Defined Test Fundamentals Understanding the Architecture of Modular, High-Performance Test Systems Contents Executive Summary 4 Architecture Layer No. 5: System Management/Test Executive 5 Architecture
Software-Defined Test Fundamentals Understanding the Architecture of Modular, High-Performance Test Systems Contents Executive Summary 4 Architecture Layer No. 5: System Management/Test Executive 5 Architecture
Applying Plantwide Industrial Wireless Communications for Cost Savings. Copyright 2012 Rockwell Automation, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Applying Plantwide Industrial Wireless Communications for Cost Savings Rev 5058-CO900C Abstract New cost savings across multiple industries are now possible by leveraging recent developments in both Integrated
Applying Plantwide Industrial Wireless Communications for Cost Savings Rev 5058-CO900C Abstract New cost savings across multiple industries are now possible by leveraging recent developments in both Integrated
Wireless Sensor Networks CS742
 Wireless Sensor Networks CS742 Outline Overview Environment Monitoring Medical application Data-dissemination schemes Media access control schemes Distributed algorithms for collaborative processing Architecture
Wireless Sensor Networks CS742 Outline Overview Environment Monitoring Medical application Data-dissemination schemes Media access control schemes Distributed algorithms for collaborative processing Architecture
Industrial IOT Gateway Family Datasheet
 Industrial IOT Gateway Family Datasheet GW-Series Overview Samsara IoT gateways securely connect sensor data to the Samsara cloud. All models include WiFi and built-in cellular connectivity, storage, and
Industrial IOT Gateway Family Datasheet GW-Series Overview Samsara IoT gateways securely connect sensor data to the Samsara cloud. All models include WiFi and built-in cellular connectivity, storage, and
Cisco Edge 300 Series
 Data Sheet Cisco Edge 300 Series Product Overview The Cisco Edge 300 Series (as shown in Figure 1) is an all-in-one access platform for enterprise next-generation connected room deployments that provide
Data Sheet Cisco Edge 300 Series Product Overview The Cisco Edge 300 Series (as shown in Figure 1) is an all-in-one access platform for enterprise next-generation connected room deployments that provide
Troubleshooting Microsoft Windows XP-based Wireless Networks in the Small Office or Home Office
 Operating System Troubleshooting Microsoft Windows XP-based Wireless Networks in the Small Office or Home Office Microsoft Corporation Published: December 2004 Update: May 2005 Abstract Because small office/home
Operating System Troubleshooting Microsoft Windows XP-based Wireless Networks in the Small Office or Home Office Microsoft Corporation Published: December 2004 Update: May 2005 Abstract Because small office/home
Increase Your Test Capabilities with Reconfigurable FPGA Technology
 Increase Your Test Capabilities with Reconfigurable FPGA Technology CTEA Electronics Symposium Ryan Verret Senior Product Manager FPGA Technology for Test National Instruments Graphical System Design A
Increase Your Test Capabilities with Reconfigurable FPGA Technology CTEA Electronics Symposium Ryan Verret Senior Product Manager FPGA Technology for Test National Instruments Graphical System Design A
Enterprise WiFi System. Datasheet. Models: UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-PRO, UAP-AC, UAP-Outdoor+, UAP-Outdoor5, UAP-AC Outdoor
 Enterprise WiFi System Models: UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-PRO, UAP-AC,, UAP-Outdoor5, UAP-AC Outdoor Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Breakthrough Speeds up to 1300 Mbps (802.11ac)
Enterprise WiFi System Models: UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-PRO, UAP-AC,, UAP-Outdoor5, UAP-AC Outdoor Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Breakthrough Speeds up to 1300 Mbps (802.11ac)
By Ambuj Varshney & Akshat Logar
 By Ambuj Varshney & Akshat Logar Wireless operations permits services, such as long range communications, that are impossible or impractical to implement with the use of wires. The term is commonly used
By Ambuj Varshney & Akshat Logar Wireless operations permits services, such as long range communications, that are impossible or impractical to implement with the use of wires. The term is commonly used
Seminar: Mobile Systems. Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht
 Personal Area Networks Seminar: Mobile Systems November 19th 2009 Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht Agenda Motivation Application areas Historical and technical overview Security issues Discussion
Personal Area Networks Seminar: Mobile Systems November 19th 2009 Krzysztof Dabkowski Supervisor: Fabio Hecht Agenda Motivation Application areas Historical and technical overview Security issues Discussion
Product Brief: SDC-PE15N n PCIe Module with Antenna Connectors
 Product Brief: SDC-PE15N 802.11n PCIe Module with Antenna Connectors The SDC-PE15N PCI Express Mini Card (PCIe) radio module from Summit Data Communications combines a high-performance, dual-band 802.11n
Product Brief: SDC-PE15N 802.11n PCIe Module with Antenna Connectors The SDC-PE15N PCI Express Mini Card (PCIe) radio module from Summit Data Communications combines a high-performance, dual-band 802.11n
1.0 Basic RF Characteristics (15%) 1.1 Describe RF signal characteristics Frequency Amplitude Phase 1.1.
 CWT 100 Objectives The Certified Wireless Technician (CWT) is an individual who can install APs based on a design document, configure the AP for initial operations and ensure connectivity. The individual
CWT 100 Objectives The Certified Wireless Technician (CWT) is an individual who can install APs based on a design document, configure the AP for initial operations and ensure connectivity. The individual
Honeywell OneWireless Network and Multinode Specifications EP November 2007
 Honeywell OneWireless Network and Multinode Specifications EP03-610-100 1 November 2007 Honeywell s OneWireless Network is a universal and multi-functional wireless mesh network that supports field I/O,
Honeywell OneWireless Network and Multinode Specifications EP03-610-100 1 November 2007 Honeywell s OneWireless Network is a universal and multi-functional wireless mesh network that supports field I/O,
Product Brief: SDC-PC22AG a/g PCMCIA Card with Integrated Antenna
 Product Brief: SDC-PC22AG 802.11a/g PCMCIA Card with Integrated Antenna The SDC-PC22AG PC Card (PCMCIA) radio card from Summit Data Communications combines a high-performance 802.11a/g radio with customized
Product Brief: SDC-PC22AG 802.11a/g PCMCIA Card with Integrated Antenna The SDC-PC22AG PC Card (PCMCIA) radio card from Summit Data Communications combines a high-performance 802.11a/g radio with customized
802.11ac FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS. May 2012
 802.11ac FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS May 2012 Table of Contents General Questions:... 3 1. What is 802.11ac?... 3 2. When will 802.11ac be ratified into a standard?... 3 5. Will 802.11ac come out before
802.11ac FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS May 2012 Table of Contents General Questions:... 3 1. What is 802.11ac?... 3 2. When will 802.11ac be ratified into a standard?... 3 5. Will 802.11ac come out before
Main objectives or functions can be modelled like different blocks or components that can be observed in Figure 1. Figure 1: HOPE System Architecture
 Overall Approach HOPE system can be modelled as a distributed system where many agents (subsystem located in each patient 's home) are connected to a main agent, the HOPE server, using IP communication
Overall Approach HOPE system can be modelled as a distributed system where many agents (subsystem located in each patient 's home) are connected to a main agent, the HOPE server, using IP communication
Engineering Project-I. Module 1: Familiarization of LabVIEW and the Vernier Toolkit
 Engineering Project-I Module 1: Familiarization of LabVIEW and the Vernier Toolkit PREPARED BY Academic Services Unit January 2012 Applied Technology High Schools, 2012 Module 1: Familiarization of LabVIEW
Engineering Project-I Module 1: Familiarization of LabVIEW and the Vernier Toolkit PREPARED BY Academic Services Unit January 2012 Applied Technology High Schools, 2012 Module 1: Familiarization of LabVIEW
IEEE n Wireless PCI Adapter. User s Manual
 IEEE 802.11n Wireless PCI Adapter User s Manual October, 2008 FCC Warning This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class C digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC
IEEE 802.11n Wireless PCI Adapter User s Manual October, 2008 FCC Warning This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class C digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC
Datasheet AC AP with Plug & Play Mesh. Models: UAP-AC-M, UAP-AC-M-PRO. High-Performance Wide-Area Wi-Fi with UniFi Mesh Technology
 802.11AC AP with Plug & Play Mesh Models: UAP-AC-M, UAP-AC-M-PRO High-Performance Wide-Area Wi-Fi with UniFi Mesh Technology Breakthrough Speeds up to 1300 Mbps in the 5 GHz Band 802.3af PoE Compatibility
802.11AC AP with Plug & Play Mesh Models: UAP-AC-M, UAP-AC-M-PRO High-Performance Wide-Area Wi-Fi with UniFi Mesh Technology Breakthrough Speeds up to 1300 Mbps in the 5 GHz Band 802.3af PoE Compatibility
Hybrid Coax-Wireless Multimedia Home Networks Using Technology. Noam Geri, Strategic Marketing Manager
 White Paper Hybrid Coax-Wireless Multimedia Home Networks Noam Geri, Strategic Marketing Manager Cable Broadband Communications Group, Texas Instruments Introduction Wireless home networking has emerged
White Paper Hybrid Coax-Wireless Multimedia Home Networks Noam Geri, Strategic Marketing Manager Cable Broadband Communications Group, Texas Instruments Introduction Wireless home networking has emerged
AC1200 Mesh Wi-Fi Range Extender
 AC1200 Mesh Wi-Fi Range Extender Stable Dual Band Wi-Fi Extension RE300 Wi-Fi Dead-Zone Killer Supports Smart Roaming Easy Setup via Tether App Highlights Extend AC1200 Wi-Fi to Your Whole Home The AC1200
AC1200 Mesh Wi-Fi Range Extender Stable Dual Band Wi-Fi Extension RE300 Wi-Fi Dead-Zone Killer Supports Smart Roaming Easy Setup via Tether App Highlights Extend AC1200 Wi-Fi to Your Whole Home The AC1200
Data Acquisition Laboratory
 Session 2559 Data Acquisition Laboratory Asad Yousuf Savannah State University Abstract The essential element to automate your system for data collection and analysis is termed as the data acquisition.
Session 2559 Data Acquisition Laboratory Asad Yousuf Savannah State University Abstract The essential element to automate your system for data collection and analysis is termed as the data acquisition.
Product Brief: SDC-PC10AG a/g Compact Flash Module with Antenna Connectors
 Product Brief: SDC-PC10AG 802.11a/g Compact Flash Module with Antenna Connectors The SDC PC10AG PC Card (PCMCIA) radio module from Summit Data Communications combines a high performance 802.11a/g radio
Product Brief: SDC-PC10AG 802.11a/g Compact Flash Module with Antenna Connectors The SDC PC10AG PC Card (PCMCIA) radio module from Summit Data Communications combines a high performance 802.11a/g radio
Wireless Technologies
 Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
A Wireless Process Monitoring And Control System With Zigbee
 American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-7, Issue-2, pp-177-183 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access A Wireless Process Monitoring And Control System
American Journal of Engineering Research (AJER) e-issn: 2320-0847 p-issn : 2320-0936 Volume-7, Issue-2, pp-177-183 www.ajer.org Research Paper Open Access A Wireless Process Monitoring And Control System
Datasheet. Enterprise Wi-Fi System. Models: UAP-IW, UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-PRO, UAP-Outdoor+, UAP-Outdoor5
 Enterprise Wi-Fi System Models: UAP-IW, UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-PRO, UAP-Outdoor+, UAP-Outdoor5 Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Reliable Throughput up to 750 Mbps Intuitive
Enterprise Wi-Fi System Models: UAP-IW, UAP, UAP-LR, UAP-PRO, UAP-Outdoor+, UAP-Outdoor5 Unlimited Indoor/Outdoor AP Scalability in a Unified Management System Reliable Throughput up to 750 Mbps Intuitive
SG B b/g/n Wireless USB Module
 SG901-1059B 802.11 b/g/n Wireless USB Module Overview The SG901-1059B is a high speed module supporting all data rates of the latest standards including Wi-Fi 802.11B/G/N using a USB 2.0 interface. This
SG901-1059B 802.11 b/g/n Wireless USB Module Overview The SG901-1059B is a high speed module supporting all data rates of the latest standards including Wi-Fi 802.11B/G/N using a USB 2.0 interface. This
IP67 Certified 2T2R 5GHz Outdoor Wireless-N Access Point - PoE-Powered 300Mbps a/n WiFi AP
 IP67 Certified 2T2R 5GHz Outdoor Wireless-N Access Point - PoE-Powered 300Mbps 802.11a/n WiFi AP Product ID: R300WN22MO5E The R300WN22MO5E Outdoor Wireless Access Point lets you add 5GHz Wireless-N network
IP67 Certified 2T2R 5GHz Outdoor Wireless-N Access Point - PoE-Powered 300Mbps 802.11a/n WiFi AP Product ID: R300WN22MO5E The R300WN22MO5E Outdoor Wireless Access Point lets you add 5GHz Wireless-N network
N o W i r e s. N o W a i t i n g
 N o W i r e s N o W a i t i n g N E T W O R K S W I T H O U T W I R E S Sales: Computer Service Corp 644 Strander Blvd #11 Seattle, Wa 98188 (866) 7209-7771 Toll Free www.csc-service.com T h e B e s t
N o W i r e s N o W a i t i n g N E T W O R K S W I T H O U T W I R E S Sales: Computer Service Corp 644 Strander Blvd #11 Seattle, Wa 98188 (866) 7209-7771 Toll Free www.csc-service.com T h e B e s t
Radiocrafts Embedded Wireless Solutions
 Selecting an IEEE 802.15.4, 2.4 GHz wireless solution By Ø.Nottveit Abstract Companies searching for a low power 2.45 GHz wireless solution will find many different technical solutions. This white paper
Selecting an IEEE 802.15.4, 2.4 GHz wireless solution By Ø.Nottveit Abstract Companies searching for a low power 2.45 GHz wireless solution will find many different technical solutions. This white paper
WLAN Products 2.1 Overview P WLAN Remote Maintenance Device P WLAN Converter P Applications P2-4-1
 WLAN Products.1 Overview P-1-1. WLAN Remote Maintenance Device P--1.3 WLAN Converter P-3-1.4 Applications P-4-1 Overview.1. Overview WLAN Products Overview 1 WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) links devices
WLAN Products.1 Overview P-1-1. WLAN Remote Maintenance Device P--1.3 WLAN Converter P-3-1.4 Applications P-4-1 Overview.1. Overview WLAN Products Overview 1 WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) links devices
Part I. Wireless Communication
 1 Part I. Wireless Communication 1.5 Topologies of cellular and ad-hoc networks 2 Introduction Cellular telephony has forever changed the way people communicate with one another. Cellular networks enable
1 Part I. Wireless Communication 1.5 Topologies of cellular and ad-hoc networks 2 Introduction Cellular telephony has forever changed the way people communicate with one another. Cellular networks enable
Cisco Edge 300 Series
 Data Sheet Cisco Edge 300 Series Product Overview The Cisco Edge 300 Series (as shown in Figure 1) is an all-in-one access platform for enterprise next-generation connected room deployments that provide
Data Sheet Cisco Edge 300 Series Product Overview The Cisco Edge 300 Series (as shown in Figure 1) is an all-in-one access platform for enterprise next-generation connected room deployments that provide
Features. RoHS COMPLIANT 2002/95/EC
 PCIE-1730 32-ch TTL and 32-ch Isolated Digital I/O PCI Express Card 32-ch isolated DI/O (16-ch digital input, 16-ch digital output) 32-ch TTL DI/O (16-ch digital input,16-ch digital output) High output
PCIE-1730 32-ch TTL and 32-ch Isolated Digital I/O PCI Express Card 32-ch isolated DI/O (16-ch digital input, 16-ch digital output) 32-ch TTL DI/O (16-ch digital input,16-ch digital output) High output
NT1210 Introduction to Networking. Unit 6: Chapter 6, Wireless LANs
 NT1210 Introduction to Networking Unit 6: Chapter 6, Wireless LANs Objectives Identify the major needs and stakeholders for computer networks and network applications. Identify the classifications of networks
NT1210 Introduction to Networking Unit 6: Chapter 6, Wireless LANs Objectives Identify the major needs and stakeholders for computer networks and network applications. Identify the classifications of networks
PC-based data acquisition I
 FYS3240 PC-based instrumentation and microcontrollers PC-based data acquisition I Spring 2016 Lecture #8 Bekkeng, 20.01.2016 General-purpose computer With a Personal Computer (PC) we mean a general-purpose
FYS3240 PC-based instrumentation and microcontrollers PC-based data acquisition I Spring 2016 Lecture #8 Bekkeng, 20.01.2016 General-purpose computer With a Personal Computer (PC) we mean a general-purpose
Chapter 5 Ad Hoc Wireless Network. Jang Ping Sheu
 Chapter 5 Ad Hoc Wireless Network Jang Ping Sheu Introduction Ad Hoc Network is a multi-hop relaying network ALOHAnet developed in 1970 Ethernet developed in 1980 In 1994, Bluetooth proposed by Ericsson
Chapter 5 Ad Hoc Wireless Network Jang Ping Sheu Introduction Ad Hoc Network is a multi-hop relaying network ALOHAnet developed in 1970 Ethernet developed in 1980 In 1994, Bluetooth proposed by Ericsson
Wireless for Process Automation. Alex Nisbett (ABB) & Gareth Johnston (ABB)
 Wireless for Process Automation Alex Nisbett (ABB) & Gareth Johnston (ABB) 1. Introduction: Stepping towards wireless The transfer of data within a process plant has seen several evolutionary steps over
Wireless for Process Automation Alex Nisbett (ABB) & Gareth Johnston (ABB) 1. Introduction: Stepping towards wireless The transfer of data within a process plant has seen several evolutionary steps over
Feature. What exactly is WLAN? More reading:
 The WLAN Roadmap Wireless Local Area Networking (WLAN) is a simple concept, but one that entails a wide, sometimes confusing, variety of standards, implementations, and future plans for development. This
The WLAN Roadmap Wireless Local Area Networking (WLAN) is a simple concept, but one that entails a wide, sometimes confusing, variety of standards, implementations, and future plans for development. This
