Wi-Fi Scanner. Glossary. LizardSystems
|
|
|
- Junior Booth
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Wi-Fi Scanner Glossary LizardSystems
2 2
3 Table of Contents a b d e g h i j n X A 8 Ad-Hoc mode 8 AES 8 AP 8 Access Point 8 B 9 Bandwidth 9 bps 9 BSSID 9 C 10 Channel 10 D 11 Data rate 11 Device-to-device network 11 Two or more devices that connect using wireless network devices without the use of a centralized wireless access point. Also known as a peer-to-peer network. (See Ad-Hoc mode, Peer-to-peer network). 11 DHCP 11 Dual-band 11 E 12 EAP 12 3
4 Encryption 12 A mechanism for providing data confidentiality. (See i, RC4, TKIP, WEP, WPA, WPA2). 12 Ethernet 12 G 13 Gateway 13 H 14 Hz 14 I 15 IP address 15 M 16 MAC address 16 MAC layer 16 Mbps 16 Megabits per second. A measurement of data speed that is roughly equivalent to a million 16 bits per second. (See bps). MIC 16 MIMO 16 Modulation and Coding Index n 17 N 20 Network name 20 NIC 20 P 21 Packet 21 Pass phrase 21 PC Card 21 PCI 21 Peer-to-peer network 21 PHY 21 PHY layer 21 PSK 22 Q 23 QoS 23 R 24 Range 24 4
5 RC4 24 S 25 Site survey 25 SSID 25 T 26 TCP 26 TCP/IP 26 Throughput 26 TKIP 26 TLS 27 Tri-mode 27 V 28 Voice over Wi-Fi 28 VoIP services delivered over wireless networks. Sometimes referred to as wireless voice over IP. (See VoIP). 28 VoIP 28 W 29 WAN 29 WEP 29 WiMAX 29 Wireless network 29 WLAN 29 WMM 29 WMM Power Save 30 WPA - Enterprise 30 WPA - Personal 30 WPA 30 WPA2 - Enterprise 30 WPA2 - Personal 30 WPA2 31 WPS 31 5
6 IEEE is a set of medium access control (MAC layer) and physical layer (PHY layer) specifications for implementing wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication in the 2.4, 3.6, 5 and 60 GHz frequency bands (See Wi-Fi Generations) a An IEEE standard for a wireless network that operates at 5 GHz with rates up to 54Mbps b An IEEE standard for a wireless network that operates at 2.4 GHz with rates up to 11Mbps d An IEEE specification that allows for configuration changes at the Media Access Control layer (MAC layer) level to comply with the rules of the country in which the network is to be used. (See MAC address) e An IEEE standard that adds Quality of Service (QoS) features and multimedia support to the existing b, g, and a wireless networks. (See QoS, WMM) g An IEEE standard for a wireless network that operates at 2.4 GHz Wi-Fi with rates up to 54Mbps h h supports Dynamic Frequency Selection(DFS) and Transmit Power Control(TPC) requirements to ensure coexistence between Wi-Fi and other types of radio frequency devices in the 5 GHz band i An IEEE standard specifying security mechanisms for networks i makes use of the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) block cipher. The standard also includes improvements in key management, user authentication through 802.1X and data integrity of headers. (See 802.1X, AES, WPA2) j An IEEE specification for wireless networks that incorporates Japanese regulatory requirements concerning wireless transmitter output power, operational modes, channel arrangements and spurious emission levels. 6
7 802.11n A taskgroup of the IEEE committee whose goal is to define a standard for high throughput speeds of at least 100Mbps on wireless networks. The standard is expected to be ratified by Some proposals being fielded by the taskgroup include designs for up to 540 Mbps. Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output (MIMO) technology, using multiple receivers and multiple transmitters in both the client and access point to achieve improved performance is expected to form the basis of the final specification. (See Mbps, MIMO) X A standard for port-based authentication, first used in wired networks, that was adapted for use in enterprise WLANs to address security flaws in WEP, the original security specification for networks X provides a framework for authenticating users and controlling their access to a protected network and dynamic encryption keys to protect data privacy. (See EAP, WEP, WPA, WPA2) The standard defining wired Ethernet networks. (See Ethernet). 7
8 A Ad-Hoc mode An old term used to describe a device-to-device network. (See Device-to-device network, Peer-to-peer network). AES Advanced Encryption Standard. The preferred standard for the encryption of commercial and government data using a symmetric block data encryption technique. It is used in the implementation of WPA2. (See i, WPA2). AP Access point. Often a wireless router, a device that connects wireless devices to another network. Access Point Access Point. often a wireless router, a device that connects wireless devices to another network. (See AP.) 8
9 B Bandwidth The maximum transmission capacity of a communications channel at any point in time. Bandwidth, usually measured in bits per second (bps), determines the speed at which information can be sent across a network. If you compare the communications channel to a pipe, bandwidth represents the pipe width and determines how much data can flow through the pipe at any one time. The greater the bandwidth, the faster data can flow. (See bps). bps Bits per second. Network performance has traditionally been measured in units of bits per second (bps). BSSID Basic Service Set Identifier. A unique address that identifies the access point/router that creates the wireless network. LizardSystems Wi-Fi Scanner obtains BSSID and other information. 9
10 C Channel One portion of the available radio spectrum that all devices on a wireless network use to communicate. Changing the channel on the access point/router can help reduce interference. Wi-Fi Scanner make graphical visualization of channel allocation. 10
11 D Data rate Also known as the PHY rate, this number captures the speed at which all data bits pass over the Wi-Fi network. Many Wi-Fi devices will report this number as the speed at which your network is performing. Actual throughout rates will always be lower than the data rate, due to available network capacity and overhead in real-world environments. The data rate communicates the maximum possible rate at which a device can transmit data. See also Throughput, which is a real-world measure of performance and is always lower than data rate. Device-to-device network Two or more devices that connect using wireless network devices without the use of a centralized wireless access point. Also known as a peer-to-peer network. (See Ad-Hoc mode, Peer-to-peer network). DHCP Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. A protocol for dynamically assigning IP addresses from a pre-defined list to nodes on a network. When they log on, network nodes automatically receive an IP address from a pool of addresses served by a DHCP. The DHCP server provides (or leases) an IP address (to a client for a specific period of time. The client will automatically request a renewal of the lease when the lease is about to run out. If a lease renewal is not requested and it expires, the address is returned to the pool of available IP addresses. Using DHCP to manage IP addresses simplifies client configuration and efficiently utilizes IP addresses. (See IP address). Dual-band A device that is capable of operating in two frequencies. On a wireless network, dual-band devices are capable of operating in both the 2.4 GHz (802.11b/g) and 5 GHz (802.11a) bands. In cellular phone technology, dual-band devices typically operate in both the GSM900 and GSM1800 frequencies, allowing a greater number of roaming options. (See Tri-mode). 11
12 E EAP Extensible Authentication Protocol. A protocol that provides an authentication framework for both wireless and wired Ethernet enterprise networks. It is typically used with a RADIUS server to authenticate users on large networks. EAP protocol types are used in the 802.1X-based authentication in WPA-Enterprise and WPA2-Enterprise. (See 802.1X, EAP, TLS, WPA - Enterprise, WPA2 - Enterprise). Encryption A mechanism for providing data confidentiality. (See i, RC4, TKIP, WEP, WPA, WPA2). Ethernet The most popular international standard technology for wired Local Area Networks (LANs). It provides from 10 Mbps transmission speeds on basic 10BastT Ethernet networks to 100 Mbps transmission speeds on Fast Ethernet networks, 1000 Mbps on Gigabit Ethernet, and 10,000 Mbps on 10 Gigabit Ethernet. (See 802.3) 12
13 G Gateway In the wireless world, a gateway is an access point with additional software capabilities such as providing NAT and DHCP. Gateways may also provide VPN support, roaming, firewalls, various levels of security, etc. 13
14 H Hz Hertz, not the car rental company. The international unit for measuring frequency equivalent to the older unit of cycles per second. One megahertz (MHz) is one million hertz. One gigahertz (GHz) is one billion hertz. The standard US electrical power frequency is 60 Hz 14
15 I IP address Internet Protocol address. IP Version 4, the most widely used Internet protocol, provides 32-bit number that identifies the sender or receiver of information sent across the Internet. An IP address has two parts: The identifier of the particular network on the Internet and the identifier of the particular device (which can be a server or a workstation) within that network. The newer IP, Version 6, provides a 128-bit addressing scheme to support a much greater number of IP addresses. (See DHCP, IP). 15
16 M MAC address Media Access Control address. A unique hardware number that identifies each device on a network. A device can be a computer, printer, etc. (See IP address). MAC layer In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, media access control (MAC) data communication protocol is a sublayer of the data link layer, which itself is layer 2. The MAC sublayer provides addressing and channel access control mechanisms that make it possible for several terminals or network nodes to communicate within a multiple access network that incorporates a shared medium, e.g. Ethernet. The hardware that implements the MAC is referred to as a medium access controller. The MAC sublayer acts as an interface between the logical link control (LLC) sublayer and the network's physical layer. The MAC layer emulates a full-duplex logical communication channel in a multi-point network. This channel may provide unicast, multicast or broadcast communication service. Mbps Megabits per second. A measurement of data speed that is roughly equivalent to a million bits per second. (See bps). MIC Message Integrity Check. A technology that is employed to prevent an attacker from capturing data packets, altering them and resending them. The MIC provides a strong mathematical function in which the receiver and the transmitter each compute and then compare the MIC. If it does not match, the data is assumed to have been tampered with and the packet is dropped. (See Packet, TKIP, WPA, WPA2). MIMO Multiple-Input-Multiple-Output. An advanced signal processing technology that uses multiple receivers and multiple transmitters in both the client and access point to achieve data throughput speeds of 100Mbps. (See n). 16
17 Modulation and Coding Index n Data Rate HT MCS Index Spatial Streams 20MHz 40MHz (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) 0 1 6,5 7,2 13, , ,5 21,7 40, , , , , , , Data Rate HT MCS Index Spatial Streams 20MHz 40MHz (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) , , , , , , , , Data Rate HT MCS Index Spatial Streams 20MHz 40MHz (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) ,5 21,7 40, , , , , , , , , Data Rate HT MCS Index Spatial Streams 20MHz 40MHz (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) , , , , , , ,
18 Data Rate HT MCS Index Spatial Streams 20MHz 40MHz (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) , Data Rate HT MCS Index Spatial Streams 20MHz 40MHz (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) , , , , , , ,5 108,3 202,5 225 Data Rate HT MCS Index Spatial Streams 20MHz 40MHz (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) , , , , , , , , ,5 108,3 202, ,5 108,3 202, ,5 151,7 283, ,5 151,7 283, , Data Rate HT MCS Index Spatial Streams 20MHz 40MHz (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) (GI = 800ns) (GI = 400ns) , , , , , , , , , , ,5 108,3 202,
19 ,5 151,7 283, ,5 151,7 283, , , , , , , , , ,5 238,3 445,
20 N Network name A name used to identify a wireless network. (See SSID) NIC Network Interface Card. A wireless or wired PC adapter card that allows the client computer to utilize network resources. Most office wired NICs operate at 100 Mbps. Wireless NICs operate at data rates defined by standards. 20
21 P Packet A unit of information transmitted from one device to another on a network. A packet typically contains a header with addressing information, data, and a checksum to insure data integrity. (See MIC). Pass phrase A series of characters used to create a key which is used by Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA). (See PSK, WPA). PC Card A removable, credit-card-sized memory or I/O device that fits into an expansion slot on a notebook computer or a personal digital assistant (PDA). PC Cards are used primarily in notebook computers and PDAs. PC Card peripherals include Wi-Fi network cards, memory cards, modems, wired NICs, and hard drives. (See NIC, PCI). PCI Peripheral Component Interconnect. A high-performance I/O (input/output) computer bus that allows expansion slots to be spaced closely for high-speed operation. (See NIC, PC Card). Peer-to-peer network A wireless or wired computer network that has no server or central hub or router. All the networked PCs are equally able to act as a network server or client, and each client computer can talk to all the other wireless computers without having to go through an access point or hub. However, since there is no central base station to monitor traffic or provide Internet access, the various signals can collide with each other, reducing overall performance. (See Ad-Hoc mode, Device-to-device network). PHY he physical, or lowest, layer of the OSI Network Model. In a wireless network, the PHY defines parameters such as data rates, modulation method, signaling parameters, transmitter/receiver synchronization, etc. Within an actual radio implementation, the PHY corresponds to the radio front end and baseband signal processing sections. Wi-Fi Scanner make graphical visualization PHY layer statistics. PHY layer In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first (lowest) layer. The implementation of this layer is often termed PHY. 21
22 The physical layer consists of the basic networking hardware transmission technologies of a network. It is a fundamental layer underlying the logical data structures of the higher level functions in a network. Due to the plethora of available hardware technologies with widely varying characteristics, this is perhaps the most complex layer in the OSI architecture. The physical layer defines the means of transmitting raw bits rather than logical data packets over a physical link connecting network nodes. The bit stream may be grouped into code words or symbols and converted to a physical signal that is transmitted over a hardware transmission medium. The physical layer provides an electrical, mechanical, and procedural interface to the transmission medium. The shapes and properties of the electrical connectors, the frequencies to broadcast on, the modulation scheme to use and similar low-level parameters, are specified here. Within the semantics of the OSI network architecture, the physical layer translates logical communications requests from the data link layer into hardware-specific operations to affect transmission or reception of electronic signals. PSK A mechanism in Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)-Personal that allows the use of manually entered keys or passwords to initiate WPA security. The PSK is entered on the access point or home wireless gateway and each PC that is on the Wi-Fi network. After entering the password, Wi-Fi Protected Access automatically takes over. It keeps out eavesdroppers and other unauthorized users by requiring all devices to have the matching password. The password also initiates the encryption process which, in WPA is Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) and in WPA2 is Advanced Encryption Standard (WPA2). (See TKIP, WPA - Personal, WPA2 - Personal). 22
23 Q QoS Quality of Service. Required to support wireless multimedia applications and advanced traffic management. QoS enables Wi-Fi access points to prioritize traffic and optimize the way shared network resources are allocated among different applications. Without QoS, all applications running on different devices have equal opportunity to transmit data frames. That works well for data traffic from applications such as web browsers, file transfers, or but it is inadequate for multimedia applications. Voice over Internet Protocol (VoIP), video streaming, and interactive gaming are highly sensitive to latency increases and throughput reductions and require QoS. QoS extensions for networks will be addressed in the upcoming IEEE e standard. (See e, WMM). 23
24 R Range The distance covered by a wireless network or radio device. Depending on the environment and the type of antenna used, Wi-Fi signals can have a range of up to a mile. RC4 An encryption cipher designed RSA Data Security. It allows key lengths up to 1024 bits and is a component in many encryption schemes, including SSL, WEP, and TKIP. (See WEP, TKIP). 24
25 S Site survey A comprehensive facility study performed by network managers to insure that planned service levels will be met when a new wireless LAN, or additional WLAN segments to an existing network, are deployed. Site survey's are usually performed by a radio frequency engineer and used by systems integrators to identify the optimum placements of access points to insure that planned levels of service are met. Site surveys are sometimes conducted following the deployment to insure that the WLAN is achieving the necessary level of coverage. Site surveys can also be used to detect rogue access points. SSID A unique 32-character network name, or identifier, that differentiates one wireless LAN from another. All access points and clients attempting to connect to a specific WLAN must use the same SSID. The SSID can be any alphanumeric entry up to a maximum of 32 characters. Wi-Fi Scanner obtains SSID and other information. (See Network name). 25
26 T TCP Transmission Control Protocol. The Transport level protocol used with the Internet Protocol (IP) to route data across the Internet. (See IP, TCP/IP). TCP/IP The underlying technology of Internet communications. While IP handles the actual delivery of data, TCP tracks the data packets to efficiently route a message through the Internet. Every computer in a TCP/IP network has its own IP address that is either dynamically assigned at startup (See DHCP) or permanently assigned as a static address. All TCP/IP messages contain the address of the destination network, as well as the address of the destination station. This enables TCP/IP messages to be transmitted to multiple networks (subnets) within an organization or worldwide. For example, when a user downloads a web page, TCP divides the page file on the web server into packets, numbers the packets, and forwards them individually to the user's IP address. The packets may be routed along different paths before reaching the user's address. At the destination, TCP reassembles the individual packets, waiting until they have all arrived to present them as a single file. (See IP, IP address, Packet, TCP). Throughput A real-world performance measure. The average rate of successful delivery over a wireless system. Throughput is usually measured in bits per second (bps) or Megabits per second (Mbps) and sometimes in data packets per second or data packets per time slot. Throughput of a particular device will always be lower than its stated Data rate. Throughput is the amount of data that can be sent from one location to another in a specific amount of time. (See bps, Mbps). TKIP Temporal Key Integrity Protocol. The wireless security encryption mechanism in Wi-Fi Protected Access. TKIP uses a key hierarchy and key management methodology that removes the predictability that intruders relied upon to exploit the WEP key. It increases the size of the key from 40 to 128 bits and replaces WEP's single static key with keys that are dynamically generated and distributed by an authentication server, providing some 500 trillion possible keys that can be used on a given data packet. It also includes a Message Integrity Check (MIC), designed to prevent an attacker from capturing data packets, altering them and resending them. By greatly expanding the size of keys, the number of keys in use, and by creating an integrity checking mechanism, TKIP magnifies the complexity and difficulty involved in decoding data on a Wi-Fi network. TKIP greatly increases the strength and complexity of wireless encryption, making it far more difficult-if not impossible-for a would-be intruder to break into a Wi-Fi network. (See AES, WPA, WPA2). 26
27 TLS Transport Layer Security. A newer version of the SSL protocol, It supports more cryptographic algorithms than SSL. TLS is designed to authenticate and encrypt data communications, preventing eavesdropping, message forgery and interference. (See EAP). Tri-mode In the Wi-Fi context, tri-mode refers to devices which are b, a, and g-compatible. In the mobile context, tri-mode describes a cellular phone that is capable of using analog, digital and GSM frequencies. (See Dual-band). 27
28 V Voice over Wi-Fi VoIP services delivered over wireless networks. Sometimes referred to as wireless voice over IP. (See VoIP). VoIP Voice over Internet Protocol. A technology for transmitting ordinary telephone calls over the Internet using packet-based networks instead of standard public switched telephone networks or Plain Old Telephone Service (POTS). (See Voice over Wi-Fi). 28
29 W WAN Wide Area Network. A data communications network that spans large local, regional, national or international areas and is usually provided by a public carrier (such as a telephone company or service provider).the term is used to distinguish between phone-based data networks and Wi-Fi networks. Phone networks are considered WANs and Wi-Fi networks are considered Wireless Local Area Networks. WEP The original security standard used in wireless networks to encrypt the wireless network traffic. (See WPA). WiMAX Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access. Refers to the standard being developed by the IEEE to provide a wireless coverage of up to 31 miles. It operates in the 2 to 11 GHz bands and enables connectivity without a direct line-of-sight to a base station although line-of-site is probably required to achieve connectivity at the distance of 31 miles.. It provides shared data rates up to 70 Mbps, which, according to WiMAX proponents, is enough bandwidth to simultaneously support more than 60 businesses and hundreds of homes. Wireless network Devices connected to a network using a centralized wireless access point. Wi-Fi Scanner allows you to scan the Wireless networks.(see WLAN). WLAN Wireless Local Area Network. A type of local-area network in which data is sent and received via high-frequency radio waves rather than cables or wires. Wi-Fi Scanner allows you to scan the WLAN (See Wireless network). WMM Wi-Fi Multimedia. A group of features for wireless networks that improve the user experience for audio, video and voice applications. WMM is based on a subset of the IEEE e WLAN QoS draft standard. WMM adds prioritized capabilities to Wi-Fi networks and optimizes their performance when multiple concurring applications, each with different latency and throughput requirements, compete for network resources. By using WMM, end-user satisfaction is maintained in a wider variety of environments and traffic conditions. WMM makes it possible for home network users and enterprise network managers to decide which data streams are most important and assign them a higher traffic priority. (See e, QoS). 29
30 WMM Power Save WMM Power Save is a set of features for Wi-Fi networks that increase the efficiency and flexibility of data transmission in order to conserve power. WMM Power Save has been optimized for mobile devices running latency-sensitive applications such as voice, audio, or video, but can benefit any Wi-Fi device. WMM Power Save uses mechanisms included in the IEEE e standard and is an enhancement of IEEE legacy power save. With WMM Power Save, the same amount of data can be transmitted in a shorter time while allowing the Wi-Fi device to remain longer in a low-power dozing state. WPA - Enterprise Wi-Fi Protected Access-Enterprise. A wireless security method that provides strong data protection for multiple users and large managed networks. It uses the 802.1X authentication framework with TKIP encryption and prevents unauthorized network access by verifying network users through an authentication server. (See 802.1X, TKIP, WPA). WPA - Personal Wi-Fi Protected Access-Personal. A wireless security method that provides strong data protection and prevents unauthorized network access for small networks. It uses TKIP encryption and protects against unauthorized network access through the use of a pre-shared key (PSK). (See WPA, PSK). WPA Wi-Fi Protected Access. An improved security standard for wireless networks that provides strong data protection and network access control. WPA was developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance and addresses all known WEP vulnerabilities. It provides strong data protection by using encryption, as well as strong access controls and 802.1X-based user authentication which was largely missing in WEP. WPA is designed to secure all versions of devices, including b, a, and g, dual-band and tri-mode. WPA can be enabled in two versions, WPA-Personal and WPA-Enterprise. WPA-Personal protects against unauthorized network access by utilizing a set-up pass phrase, or pre-shared key. WPA-Enterprise verifies network users through an authentication server. In either mode, WPA utilizes 128-bit encryption keys and dynamic session keys to ensure the wireless network's privacy and security. (See PSK, WEP, WPA2). WPA2 - Enterprise Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 - Enterprise. The follow on wireless security method to WPA that provides stronger data protection for multiple users and large managed networks. It prevents unauthorized network access by verifying network users through an authentication server. (See WPA2). WPA2 - Personal Wi-Fi Protected Access 2 - Personal. The follow on wireless security method to WPA that provides stronger data protection and prevents unauthorized network access for small networks. (See WPA2, PSK). 30
31 WPA2 Wi-Fi Protected Access 2. The follow on security method to WPA for wireless networks that provides stronger data protection and network access control. It provides enterprise and consumer Wi-Fi users with a high level of assurance that only authorized users can access their wireless networks. Based on the ratified IEEE i standard, WPA2 provides government grade security by implementing the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) FIPS compliant AES encryption algorithm and 802.1X-based authentication. There are two versions of WPA2: WPA2-Personal, and WPA2-Enterprise. WPA2-Personal protects unauthorized network access by utilizing a set-up password. WPA2-Enterprise verifies network users through a server. WPA2 is backward compatible with WPA. Like WPA, WPA2 uses the 802.1X/EAP framework as part of the infrastructure that ensures centralized mutual authentication and dynamic key management and offers a pre-shared key for use in home and small office environments. Like WPA, WPA2 is designed to secure all versions of devices, including b, a, and g, multi-band and multi-mode. (See WPA2 - Enterprise, WPA2 - Personal). WPS Wi-Fi Protected Setup is an optional certification program developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance designed to ease set up of security-enabled Wi-Fi networks in the home and small office environment. Wi-Fi Protected Setup supports methods (pushing a button or entering a PIN into a wizard-type application) that are familiar to most consumers to configure a network and enable security. LizardSystems lizardsystems.com 31
Wireless technology Principles of Security
 Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Wireless technology Principles of Security 1 Wireless technologies 2 Overview This module provides an introduction to the rapidly evolving technology of wireless LANs (WLANs). WLANs redefine the way the
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications. Objectives
 Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 8 High-Speed WLANs and WLAN Security Objectives Describe how IEEE 802.11a networks function and how they differ from 802.11 networks Outline how 802.11g
Wireless# Guide to Wireless Communications Chapter 8 High-Speed WLANs and WLAN Security Objectives Describe how IEEE 802.11a networks function and how they differ from 802.11 networks Outline how 802.11g
EnGenius Quick Start Guide
 T he operates seamlessly in the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum supporting the 802.11b (2.4GHz, 11Mbps) and the newer, faster 802.11g (2.4GHz, 54Mbpswireless standard. High output power and high sensitivity
T he operates seamlessly in the 2.4 GHz frequency spectrum supporting the 802.11b (2.4GHz, 11Mbps) and the newer, faster 802.11g (2.4GHz, 54Mbpswireless standard. High output power and high sensitivity
Basic Wireless Settings on the CVR100W VPN Router
 Basic Wireless Settings on the CVR100W VPN Router Objective A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) utilizes radio communication to connect wireless devices to a LAN. An example is a Wi-Fi hotspot at a cafe.
Basic Wireless Settings on the CVR100W VPN Router Objective A Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN) utilizes radio communication to connect wireless devices to a LAN. An example is a Wi-Fi hotspot at a cafe.
 Wireless Networking WiFi Standards 802.11a 5GHz 54MB 802.11b 2.4 GHz 11MB 802.11g 2.4GHz 52MB 802.11n 2.4/5GHz 108MB 802.11b The 802.11b standard has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s, and uses
Wireless Networking WiFi Standards 802.11a 5GHz 54MB 802.11b 2.4 GHz 11MB 802.11g 2.4GHz 52MB 802.11n 2.4/5GHz 108MB 802.11b The 802.11b standard has a maximum raw data rate of 11 Mbit/s, and uses
Wireless Router at Home
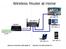 Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Wireless Router at Home 192.168.1.2 192.168.1.1 Modem 192.168.1.3 120.6.46.15 telephone line to ISP 192.168.1.4 Internet connection with public IP internal LAN with private IPs 192.168.1.5 Wireless All-in-one
Appendix E Wireless Networking Basics
 Appendix E Wireless Networking Basics This chapter provides an overview of Wireless networking. Wireless Networking Overview The FWG114P v2 Wireless Firewall/Print Server conforms to the Institute of Electrical
Appendix E Wireless Networking Basics This chapter provides an overview of Wireless networking. Wireless Networking Overview The FWG114P v2 Wireless Firewall/Print Server conforms to the Institute of Electrical
IEEE n Wireless PCI Adapter. User s Manual
 IEEE 802.11n Wireless PCI Adapter User s Manual October, 2008 FCC Warning This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class C digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC
IEEE 802.11n Wireless PCI Adapter User s Manual October, 2008 FCC Warning This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class C digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC
Outline : Wireless Networks Lecture 10: Management. Management and Control Services : Infrastructure Reminder.
 Outline 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 10: 802.11 Management Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2016 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss16/
Outline 18-759: Wireless Networks Lecture 10: 802.11 Management Peter Steenkiste Departments of Computer Science and Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring Semester 2016 http://www.cs.cmu.edu/~prs/wirelesss16/
Chapter 3 Wireless Configuration
 Chapter 3 Wireless Configuration This chapter describes how to configure the wireless features of your WNR854T router. In planning your wireless network, you should consider the level of security required.
Chapter 3 Wireless Configuration This chapter describes how to configure the wireless features of your WNR854T router. In planning your wireless network, you should consider the level of security required.
Wireless MAXg Technology
 Wireless MAXg Technology MAXimizing range, performance, security and simplicity for 802.11g networks Technology Note Wireless technology has undoubtedly become a ubiquitous presence in our computing environment,
Wireless MAXg Technology MAXimizing range, performance, security and simplicity for 802.11g networks Technology Note Wireless technology has undoubtedly become a ubiquitous presence in our computing environment,
IP network that supports DHCP or manual assignment of IP address, gateway, and subnet mask
 Network Requirements, page 1 Wireless LAN, page 2 Wi-Fi Network Components, page 3 802.11 Standards for WLAN Communications, page 6 Security for Communications in WLANs, page 9 WLANs and Roaming, page
Network Requirements, page 1 Wireless LAN, page 2 Wi-Fi Network Components, page 3 802.11 Standards for WLAN Communications, page 6 Security for Communications in WLANs, page 9 WLANs and Roaming, page
Wireless-N Business Notebook Adapter
 Wireless-N Business Notebook Adapter USER GUIDE BUSINESS SERIES Model No. WPC4400N Model Model No. No. Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered
Wireless-N Business Notebook Adapter USER GUIDE BUSINESS SERIES Model No. WPC4400N Model Model No. No. Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered
U S E R M A N U A L b/g PC CARD
 U S E R M A N U A L 802.11b/g PC CARD Table of Content CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 WIRELESS LAN FEATURE FUNCTIONS... 1 1.2 REGULATORY NOTICE... 1 1.2.1 FCC Class B Statement...1 1.2.2 Canadian Regulatory
U S E R M A N U A L 802.11b/g PC CARD Table of Content CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 1.1 WIRELESS LAN FEATURE FUNCTIONS... 1 1.2 REGULATORY NOTICE... 1 1.2.1 FCC Class B Statement...1 1.2.2 Canadian Regulatory
Version /01/2013. User Manual. DAP-1665 Wireless AC1200 Dual Band Access Point DAP-1665
 Version 1.0 10/01/2013 User Manual DAP-1665 Wireless AC1200 Dual Band Access Point DAP-1665 Table of Contents Product Overview... 4 Package Contents... 4 System Requirements... 5 Introduction... 6 Features...
Version 1.0 10/01/2013 User Manual DAP-1665 Wireless AC1200 Dual Band Access Point DAP-1665 Table of Contents Product Overview... 4 Package Contents... 4 System Requirements... 5 Introduction... 6 Features...
Wireless Networks. Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas. Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov.
 Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
Wireless Networks Authors: Marius Popovici Daniel Crişan Zagham Abbas Technical University of Cluj-Napoca Group 3250 Cluj-Napoca, 24 Nov. 2003 Presentation Outline Wireless Technology overview The IEEE
Exam HP2-Z32 Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks Version: 7.1 [ Total Questions: 115 ]
![Exam HP2-Z32 Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks Version: 7.1 [ Total Questions: 115 ] Exam HP2-Z32 Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks Version: 7.1 [ Total Questions: 115 ]](/thumbs/89/97686506.jpg) s@lm@n HP Exam HP2-Z32 Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks Version: 7.1 [ Total Questions: 115 ] HP HP2-Z32 : Practice Test Question No : 1 What is a proper use for an ingress VLAN in an HP MSM VSC?
s@lm@n HP Exam HP2-Z32 Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks Version: 7.1 [ Total Questions: 115 ] HP HP2-Z32 : Practice Test Question No : 1 What is a proper use for an ingress VLAN in an HP MSM VSC?
A POLYCOM WHITEPAPER Deploying Enterprise-Grade Wi-Fi Telephony : Coverage, Capacity, Quality of Service, and Security Considerations for Delivering
 Deploying Enterprise-Grade Wi-Fi Telephony : Coverage, Capacity, Quality of Service, and Security Considerations for Delivering Excellent Voice Quality on Enterprise Wi-Fi Networks November 2010 Coverage,
Deploying Enterprise-Grade Wi-Fi Telephony : Coverage, Capacity, Quality of Service, and Security Considerations for Delivering Excellent Voice Quality on Enterprise Wi-Fi Networks November 2010 Coverage,
Chapter 2 Installation and Configuration
 Chapter 2 Installation and Configuration This chapter describes how to set up your NETGEAR Wireless-N Access Point WN802T v2 for wireless connectivity to your LAN. This basic configuration will enable
Chapter 2 Installation and Configuration This chapter describes how to set up your NETGEAR Wireless-N Access Point WN802T v2 for wireless connectivity to your LAN. This basic configuration will enable
Vendor: HP. Exam Code: HP2-Z32. Exam Name: Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks. Version: Demo
 Vendor: HP Exam Code: HP2-Z32 Exam Name: Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks Version: Demo QUESTION 1 A network administrator deploys several HP MSM APs and an HP MSM Controller. The APs discover the
Vendor: HP Exam Code: HP2-Z32 Exam Name: Implementing HP MSM Wireless Networks Version: Demo QUESTION 1 A network administrator deploys several HP MSM APs and an HP MSM Controller. The APs discover the
Designing AirPort Extreme n Networks
 Designing AirPort Extreme 802.11n Networks 1 Contents Chapter 1 3 Getting Started 5 Configuring the AirPort Extreme Base Station for Internet Access Using AirPort Utility 6 Extending the Range of Your
Designing AirPort Extreme 802.11n Networks 1 Contents Chapter 1 3 Getting Started 5 Configuring the AirPort Extreme Base Station for Internet Access Using AirPort Utility 6 Extending the Range of Your
WL 5011s g Wireless Network Adapter Client Utility User Guide
 WL 5011s 802.11g Wireless Network Adapter Client Utility User Guide 10/2005 1 1. Introduction WL5011s client utility is a clean, straightforward GUI (Graphic User Interface) tool, which is designed for
WL 5011s 802.11g Wireless Network Adapter Client Utility User Guide 10/2005 1 1. Introduction WL5011s client utility is a clean, straightforward GUI (Graphic User Interface) tool, which is designed for
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2, g. Wireless-G. User Guide. Access Point WIRELESS WAP54G (EU/LA/UK) Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2,4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G Access Point User Guide Model No. WAP54G (EU/LA/UK) Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2,4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G Access Point User Guide Model No. WAP54G (EU/LA/UK) Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
Table of Contents. Chapter 1 Product Overview Features Package Contents LED Indicator and Panel Description...
 Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Monoprice. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. Copyright of the
Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Monoprice. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective holders. Copyright of the
Naveen Kumar. 1 Wi-Fi Technology
 Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
Naveen Kumar 1 Contents 2 Introduction Need of Purpose History How a Wi-Fi Network Works Topologies & Configurations Applications Wi-Fi Security Advantages & Limitations Innovations Introduction 3 Wireless
Configuring a VAP on the WAP351, WAP131, and WAP371
 Article ID: 5072 Configuring a VAP on the WAP351, WAP131, and WAP371 Objective Virtual Access Points (VAPs) segment the wireless LAN into multiple broadcast domains that are the wireless equivalent of
Article ID: 5072 Configuring a VAP on the WAP351, WAP131, and WAP371 Objective Virtual Access Points (VAPs) segment the wireless LAN into multiple broadcast domains that are the wireless equivalent of
11N Wireless PCI Adapter User Guide -6-
 -6- Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Shenzhen Tenda Technology Co., Ltd. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
-6- Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Shenzhen Tenda Technology Co., Ltd. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
Computer to Network Connection
 Computer to Network Connection Network Installation Steps Having a clear understanding of all the steps required to physically building a network improves the success of a project. You may need to install
Computer to Network Connection Network Installation Steps Having a clear understanding of all the steps required to physically building a network improves the success of a project. You may need to install
11N Wireless PCI Adapter User Guide
 -- 1 -- Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Shenzhen Tenda Technology Co., Ltd. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
-- 1 -- Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Shenzhen Tenda Technology Co., Ltd. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 10 Networking Essentials
 A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
LevelOne User Manual WNC-0600USB N_One Wireless USB Adapter
 LevelOne User Manual WNC-0600USB N_One Wireless USB Adapter V2.0.0-0712 i Safety FCC WARNING This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
LevelOne User Manual WNC-0600USB N_One Wireless USB Adapter V2.0.0-0712 i Safety FCC WARNING This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to
Security SSID Selection: Broadcast SSID:
 69 Security SSID Selection: Broadcast SSID: WMM: Encryption: Select the SSID that the security settings will apply to. If Disabled, then the device will not be broadcasting the SSID. Therefore it will
69 Security SSID Selection: Broadcast SSID: WMM: Encryption: Select the SSID that the security settings will apply to. If Disabled, then the device will not be broadcasting the SSID. Therefore it will
11N Wireless USB Adapter User Guide
 -- 1 -- Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Shenzhen Tenda Technology Co., Ltd. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
-- 1 -- Copyright Statement is the registered trademark of Shenzhen Tenda Technology Co., Ltd. All the products and product names mentioned herein are the trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective
Configuring the Xirrus Array
 Configuring the Xirrus Array This chapter covers configuration and management tasks using the product s embedded Web Management Interface (WMI). It also includes a procedure for logging in to the XS-3900/XS-3700/XS-3500
Configuring the Xirrus Array This chapter covers configuration and management tasks using the product s embedded Web Management Interface (WMI). It also includes a procedure for logging in to the XS-3900/XS-3700/XS-3500
CSNT 180 Wireless Networking. Chapter 7 WLAN Terminology and Technology
 CSNT 180 Wireless Networking Chapter 7 WLAN Terminology and Technology Norman McEntire norman.mcentire@servin.com Founder, Servin Corporation, http://servin.com Technology Training for Technology Professionals
CSNT 180 Wireless Networking Chapter 7 WLAN Terminology and Technology Norman McEntire norman.mcentire@servin.com Founder, Servin Corporation, http://servin.com Technology Training for Technology Professionals
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e. Chapter 10 Networking Essentials
 A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
A+ Guide to Hardware: Managing, Maintaining, and Troubleshooting, 5e Chapter 10 Networking Essentials Objectives Learn about hardware devices used for networking Learn about the different types of networks
CS-435 spring semester Network Technology & Programming Laboratory. Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis
 CS-435 spring semester 2016 Network Technology & Programming Laboratory University of Crete Computer Science Department Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis CS-435 Lecture preview 802.11 Security IEEE
CS-435 spring semester 2016 Network Technology & Programming Laboratory University of Crete Computer Science Department Stefanos Papadakis & Manolis Spanakis CS-435 Lecture preview 802.11 Security IEEE
GHz g. Wireless A+G. User Guide. Notebook Adapter. Dual-Band. Dual-Band WPC55AG a. A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Dual-Band 5 GHz 802.11a + GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Dual-Band Wireless A+G Notebook Adapter User Guide Model No. WPC55AG Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Dual-Band 5 GHz 802.11a + GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Dual-Band Wireless A+G Notebook Adapter User Guide Model No. WPC55AG Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject
Wireless Networking. Chapter The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved
 Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
Wireless Networking Chapter 23 Overview In this chapter, you will learn how to Discuss wireless networking components Analyze and explain wireless networking standards Install and configure wireless networks
Networking interview questions
 Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
Networking interview questions What is LAN? LAN is a computer network that spans a relatively small area. Most LANs are confined to a single building or group of buildings. However, one LAN can be connected
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Dual-Band. GHz g a. Dual-Band. Wireless A+G. Access Point. User Guide WIRELESS WAP55AG. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Dual-Band 5 GHz 802.11a + GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Dual-Band Wireless A+G Access Point User Guide Model No. WAP55AG Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. Dual-Band 5 GHz 802.11a + GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Dual-Band Wireless A+G Access Point User Guide Model No. WAP55AG Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject
NWD2705. User s Guide. Quick Start Guide. Dual-Band Wireless N450 USB Adapter. Version 1.00 Edition 1, 09/2012
 NWD2705 Dual-Band Wireless N450 USB Adapter Version 1.00 Edition 1, 09/2012 Quick Start Guide User s Guide www.zyxel.com Copyright 2012 ZyXEL Communications Corporation IMPORTANT! READ CAREFULLY BEFORE
NWD2705 Dual-Band Wireless N450 USB Adapter Version 1.00 Edition 1, 09/2012 Quick Start Guide User s Guide www.zyxel.com Copyright 2012 ZyXEL Communications Corporation IMPORTANT! READ CAREFULLY BEFORE
Configuring the Wireless Parameters (CPE and WBS)
 Configuring the Wireless Parameters (CPE and WBS) CHAPTERS 1. Configure Basic Wireless Parameters 2. Configure Wireless Client Parameters 3. Configure Wireless AP Parameters 4. Configure Multi-SSID 5.
Configuring the Wireless Parameters (CPE and WBS) CHAPTERS 1. Configure Basic Wireless Parameters 2. Configure Wireless Client Parameters 3. Configure Wireless AP Parameters 4. Configure Multi-SSID 5.
User Manual. OT-1044ns
 User Manual OT-1044ns CONTENTS Chapter 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Features... 3 1.2 Environments... 3 1.3 System Requirement... 4 Chapter 2 Hardware Installation... 4 2.1 Led indicators... 4 2.2 Back Panel
User Manual OT-1044ns CONTENTS Chapter 1 Introduction... 3 1.1 Features... 3 1.2 Environments... 3 1.3 System Requirement... 4 Chapter 2 Hardware Installation... 4 2.1 Led indicators... 4 2.2 Back Panel
Wireless 300N Gigabit Gaming Router 2.4GHz Gigabit Ethernet / Stream Engine 11N 2x2 (300Mbps)
 Wireless 300N Gigabit Gaming Router ESR9855G 2.4GHz Gigabit Ethernet / Stream Engine 11N 2x2 (300Mbps) PRODUCT DESCRIPTION ESR9855G is a Media Enhanced 11N Gaming Router. ESR9855G supports home network
Wireless 300N Gigabit Gaming Router ESR9855G 2.4GHz Gigabit Ethernet / Stream Engine 11N 2x2 (300Mbps) PRODUCT DESCRIPTION ESR9855G is a Media Enhanced 11N Gaming Router. ESR9855G supports home network
QuickSpecs. Models HP V110 Cable/DSL Wireless-N Router HP V110 ADSL-B Wireless-N Router
 Overview Models HP V110 Cable/DSL Wireless-N Router HP V110 ADSL-A Wireless-N Router HP V110 ADSL-B Wireless-N Router JE468A JE459A JE461A Key features Robust routing and security features WDS support
Overview Models HP V110 Cable/DSL Wireless-N Router HP V110 ADSL-A Wireless-N Router HP V110 ADSL-B Wireless-N Router JE468A JE459A JE461A Key features Robust routing and security features WDS support
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz g. Wireless-G. PCI Adapter with SRX 400. User Guide WIRELESS WMP54GX4. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter with SRX 400 User Guide Model No. WMP54GX4 Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice.
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter with SRX 400 User Guide Model No. WMP54GX4 Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice.
802.11ac Wireless Access Point Model WAC104
 Point Model WAC104 User Manual October 2016 202-11698-01 350 E. Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for purchasing this NETGEAR product. You can visit www.netgear.com/support to register
Point Model WAC104 User Manual October 2016 202-11698-01 350 E. Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for purchasing this NETGEAR product. You can visit www.netgear.com/support to register
WNRT-627. Data Sheet. Europe/ ETSI: 2.412~2.472GHz (13 Channels) Japan/ TELEC: 2.412~2.484GHz (14 Channels) RF Power.
 300Mbps 802.11n Wireless Broadband Router Ultra High Speed 802.11n Wireless The WNRT-627 features latest IEEE 802.11n radio with 2T2R MIMO antenna technology to provide improved wireless speed and coverage
300Mbps 802.11n Wireless Broadband Router Ultra High Speed 802.11n Wireless The WNRT-627 features latest IEEE 802.11n radio with 2T2R MIMO antenna technology to provide improved wireless speed and coverage
ECB N Multi-Function Gigabit Client Bridge
 ECB9500 is a powerful and multi-functioned 11n product with 7 major multi-functions, is designed to operate in every working environment for enterprises. ECB9500 is a Wireless Network device that delivers
ECB9500 is a powerful and multi-functioned 11n product with 7 major multi-functions, is designed to operate in every working environment for enterprises. ECB9500 is a Wireless Network device that delivers
WL-5420AP. User s Guide
 WL-5420AP User s Guide Table of contents INTRODUCTION... 1 About the Operation Modes...2 LED Indicators...5 Solid...5 Ports on the Rear Panel...7 GETTING CONNECTED... 8 WPA AP -CONFIGURATION VIA WEB...
WL-5420AP User s Guide Table of contents INTRODUCTION... 1 About the Operation Modes...2 LED Indicators...5 Solid...5 Ports on the Rear Panel...7 GETTING CONNECTED... 8 WPA AP -CONFIGURATION VIA WEB...
Viewing Status and Statistics
 CHAPTER 7 This chapter explains how to use ADU to view the client adapter s status and its transmit and receive statistics. The following topics are covered in this chapter: Overview of ADU and Statistics
CHAPTER 7 This chapter explains how to use ADU to view the client adapter s status and its transmit and receive statistics. The following topics are covered in this chapter: Overview of ADU and Statistics
Configure n on the WLC
 Configure 802.11n on the WLC Document ID: 108184 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions 802.11n An Overview How Does 802.11n Provide Greater Throughput
Configure 802.11n on the WLC Document ID: 108184 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions 802.11n An Overview How Does 802.11n Provide Greater Throughput
Unit title: Mobile Technology: Device Connectivity (SCQF level 5) Outcome 1
 1 Outcome 1 A description of mobile device internet connectivity using two current Wi-Fi methods. A description of mobile device internet connectivity using two current GSM mobile telephony methods. A
1 Outcome 1 A description of mobile device internet connectivity using two current Wi-Fi methods. A description of mobile device internet connectivity using two current GSM mobile telephony methods. A
Chapter 4 Advanced Settings and Features
 Chapter 4 Advanced Settings and Features This chapter describes the features you can configure or view under Advanced in the main menu of your WiFi range extender. Advanced Wireless Settings Note: The
Chapter 4 Advanced Settings and Features This chapter describes the features you can configure or view under Advanced in the main menu of your WiFi range extender. Advanced Wireless Settings Note: The
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition. Chapter 8 Wireless Networking
 Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 8 Wireless Networking Objectives Explain how nodes exchange wireless signals Identify potential obstacles to successful wireless transmission and their repercussions,
Network+ Guide to Networks 6 th Edition Chapter 8 Wireless Networking Objectives Explain how nodes exchange wireless signals Identify potential obstacles to successful wireless transmission and their repercussions,
Wireless Security Protocol Analysis and Design. Artoré & Bizollon : Wireless Security Protocol Analysis and Design
 Protocol Analysis and Design 1 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 2 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 1.1 WiFi 802.11 3 Networks OSI Structure 4 Networks Infrastructure Networks BSS : Basic Set Service ESS : Extended
Protocol Analysis and Design 1 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 2 Networks 1. WIRELESS NETWORKS 1.1 WiFi 802.11 3 Networks OSI Structure 4 Networks Infrastructure Networks BSS : Basic Set Service ESS : Extended
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition. Objectives
 Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
Guide to Wireless Communications, Third Edition Chapter 7 Low-Speed Wireless Local Area Networks Objectives Describe how WLANs are used List the components and modes of a WLAN Describe how an RF WLAN works
QuickSpecs. Models HP 110 ADSL-B Wireless-N Router
 Overview Models HP 110 ADSL-A Wireless-N Router HP 110 ADSL-B Wireless-N Router JE459A JE461A Key features Robust routing and security features WDS support for simplified network setup Advanced MIMO technology
Overview Models HP 110 ADSL-A Wireless-N Router HP 110 ADSL-B Wireless-N Router JE459A JE461A Key features Robust routing and security features WDS support for simplified network setup Advanced MIMO technology
Add a Wireless Network to an Existing Wired Network using a Wireless Access Point (WAP)
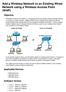 Add a Wireless Network to an Existing Wired Network using a Wireless Access Point (WAP) Objective A Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a networking device that allows wireless-capable devices to connect to
Add a Wireless Network to an Existing Wired Network using a Wireless Access Point (WAP) Objective A Wireless Access Point (WAP) is a networking device that allows wireless-capable devices to connect to
Configuring Wireless Security Settings on the RV130W
 Article ID: 5021 Configuring Wireless Security Settings on the RV130W Objective Wireless networking operates by sending information over radio waves, which can be more vulnerable to intruders than a traditional
Article ID: 5021 Configuring Wireless Security Settings on the RV130W Objective Wireless networking operates by sending information over radio waves, which can be more vulnerable to intruders than a traditional
Wireless Terms. Uses a Chipping Sequence to Provide Reliable Higher Speed Data Communications Than FHSS
 How to Set Up a Secure Home Wireless Network What you don t know about setting up a home wireless network can hurt you. 2008 APCUG Convention Session Tom Jones, P.E., RCDD-NTS CQS-CWLSS AGENDA Some Terms
How to Set Up a Secure Home Wireless Network What you don t know about setting up a home wireless network can hurt you. 2008 APCUG Convention Session Tom Jones, P.E., RCDD-NTS CQS-CWLSS AGENDA Some Terms
Wireless Technologies
 Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
Wireless Technologies Networking for Home and Small Businesses Chapter 7 Manju. V. Sankar 1 Objectives Describe wireless technologies. Describe the various components and structure of a WLAN Describe wireless
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz g. Wireless-G. USB Network Adapter. User Guide WIRELESS WUSB54G. Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G USB Network Adapter User Guide Model No. WUSB54G Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2.4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G USB Network Adapter User Guide Model No. WUSB54G Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys
Wireless LAN, WLAN Security, and VPN
 Wireless LAN, WLAN Security, and VPN 麟瑞科技台南辦事處技術經理張晃崚 WLAN & VPN FAQ What is WLAN?802.11a?802.11b?802.11g? Which standard (product) should we use? How to deploy WLAN? How to block intruders? How to authenticate
Wireless LAN, WLAN Security, and VPN 麟瑞科技台南辦事處技術經理張晃崚 WLAN & VPN FAQ What is WLAN?802.11a?802.11b?802.11g? Which standard (product) should we use? How to deploy WLAN? How to block intruders? How to authenticate
Multi-Function Gigabit Wireless-N Client Bridge 2.4GHz 300Mbps Client Bridge/AP/ WDS/Repeater
 Multi-Function Gigabit Wireless-N Client Bridge 2.4GHz 300Mbps Client Bridge/AP/ WDS/Repeater ECB-9750 ECB-9750 is a powerful and multi-functioned 11n product with 7 major multi-functions, is designed
Multi-Function Gigabit Wireless-N Client Bridge 2.4GHz 300Mbps Client Bridge/AP/ WDS/Repeater ECB-9750 ECB-9750 is a powerful and multi-functioned 11n product with 7 major multi-functions, is designed
Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures
 Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures Wireless Network Technology Wireless network refers to any type of computer network which is wireless, and is commonly associated with a network whose interconnections
Wireless Attacks and Countermeasures Wireless Network Technology Wireless network refers to any type of computer network which is wireless, and is commonly associated with a network whose interconnections
WAP3205 v2. User s Guide. Quick Start Guide. Wireless N300 Access Point. Default Login Details. Version 1.00 Edition 2, 12/2012
 WAP3205 v2 Wireless N300 Access Point Version 1.00 Edition 2, 12/2012 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details LAN IP Address http://192.168.1.2 Password 1234 www.zyxel.com Copyright 2012 ZyXEL
WAP3205 v2 Wireless N300 Access Point Version 1.00 Edition 2, 12/2012 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details LAN IP Address http://192.168.1.2 Password 1234 www.zyxel.com Copyright 2012 ZyXEL
Product Brief: SDC-PE15N n PCIe Module with Antenna Connectors
 Product Brief: SDC-PE15N 802.11n PCIe Module with Antenna Connectors The SDC-PE15N PCI Express Mini Card (PCIe) radio module from Summit Data Communications combines a high-performance, dual-band 802.11n
Product Brief: SDC-PE15N 802.11n PCIe Module with Antenna Connectors The SDC-PE15N PCI Express Mini Card (PCIe) radio module from Summit Data Communications combines a high-performance, dual-band 802.11n
M a/b/g Outdoor Layer-2 MESH AP
 802.11a/b/g Outdoor Layer-2 MESH AP 2.4GHz / 5GHz 802.11 a/b/g MESH PRODUCT DESCRIPTION EnGenius Mesh AP is designed with IEEE802.11a/b/g standards and addressed on providing high performance mesh network.
802.11a/b/g Outdoor Layer-2 MESH AP 2.4GHz / 5GHz 802.11 a/b/g MESH PRODUCT DESCRIPTION EnGenius Mesh AP is designed with IEEE802.11a/b/g standards and addressed on providing high performance mesh network.
Data Communication. Introduction of Communication. Data Communication. Elements of Data Communication (Communication Model)
 Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
Data Communication Introduction of Communication The need to communicate is part of man s inherent being. Since the beginning of time the human race has communicated using different techniques and methods.
Wireless AC1750 Wave 2 Dual-Band PoE Access Point
 Product Highlights Enjoy High-Performance Wireless Connectivity Harness the power of IEEE 802.11ac Wave 2 wireless and experience wireless speeds of up to 1750 Mbps 1, perfect for high-demand business
Product Highlights Enjoy High-Performance Wireless Connectivity Harness the power of IEEE 802.11ac Wave 2 wireless and experience wireless speeds of up to 1750 Mbps 1, perfect for high-demand business
IEEE a/ac/n/b/g Outdoor Stand-Alone Access Point. Management Guide. ECWO Series. Software Release v1.0.1.
 IEEE 802.11a/ac/n/b/g Outdoor Stand-Alone Access Point ECWO Series Management Guide Software Release v1.0.1.1 www.edge-core.com Management Guide ECWO Series Outdoor Stand-Alone Access Points 2.4 GHz, 5
IEEE 802.11a/ac/n/b/g Outdoor Stand-Alone Access Point ECWO Series Management Guide Software Release v1.0.1.1 www.edge-core.com Management Guide ECWO Series Outdoor Stand-Alone Access Points 2.4 GHz, 5
Outdoor High Power Wireless N Access Point
 Outdoor High Power Wireless N Access Point Model WND930 User Manual December 2017 202-11483-02 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for purchasing this NETGEAR product. You
Outdoor High Power Wireless N Access Point Model WND930 User Manual December 2017 202-11483-02 350 East Plumeria Drive San Jose, CA 95134 USA Support Thank you for purchasing this NETGEAR product. You
Chapter 1: Introduction
 Chapter 1: Introduction Welcome Thank you for choosing the Linksys Wireless-G Broadband Router with SpeedBooster. The Wireless-G Broadband Router with SpeedBooster will allow you to network wirelessly
Chapter 1: Introduction Welcome Thank you for choosing the Linksys Wireless-G Broadband Router with SpeedBooster. The Wireless-G Broadband Router with SpeedBooster will allow you to network wirelessly
802.11b+g Wireless LAN USB Adapter. User Manual
 802.11b+g Wireless LAN USB Adapter User Manual REGULATORY STATEMENTS FCC Certification The United States Federal Communication Commission (FCC) and the Canadian Department of Communications have established
802.11b+g Wireless LAN USB Adapter User Manual REGULATORY STATEMENTS FCC Certification The United States Federal Communication Commission (FCC) and the Canadian Department of Communications have established
02/21/08 TDC Branch Offices. Headquarters SOHO. Hot Spots. Home. Wireless LAN. Customer Sites. Convention Centers. Hotel
 TDC 363 Introductions to LANs Lecture 7 Wireless LAN 1 Outline WLAN Markets and Business Cases WLAN Standards WLAN Physical Layer WLAN MAC Layer WLAN Security WLAN Design and Deployment 2 The Mobile Environment
TDC 363 Introductions to LANs Lecture 7 Wireless LAN 1 Outline WLAN Markets and Business Cases WLAN Standards WLAN Physical Layer WLAN MAC Layer WLAN Security WLAN Design and Deployment 2 The Mobile Environment
Wireless AC1200 Concurrent Dual Band PoE Access Point
 DAP-2660 Version 1.00 AirPremier Wireless AC1200 Concurrent Dual Band PoE Access Point Product Overview...5 Introduction... 5 Features... 6 Package Contents... 7 System Requirements... 7 Hardware Overview...8
DAP-2660 Version 1.00 AirPremier Wireless AC1200 Concurrent Dual Band PoE Access Point Product Overview...5 Introduction... 5 Features... 6 Package Contents... 7 System Requirements... 7 Hardware Overview...8
EnGenius EAP-9550 Indoor Access Point
 Product Name: Manufacturer: - Model Number: NET-EL-EAP9550 Please Note the has been discontinued, for alternative wireless equipment please check out Ubiquiti UniFi UAP LR EnGenius EAP9550 Indoor Access
Product Name: Manufacturer: - Model Number: NET-EL-EAP9550 Please Note the has been discontinued, for alternative wireless equipment please check out Ubiquiti UniFi UAP LR EnGenius EAP9550 Indoor Access
802.11N Wireless Broadband Router
 802.11N Wireless Broadband Router Pre-N Wireless Access Point Broadband Internet Access WPS 4-Port Switching Hub User's Guide Table of Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Wireless Router Features... 1
802.11N Wireless Broadband Router Pre-N Wireless Access Point Broadband Internet Access WPS 4-Port Switching Hub User's Guide Table of Contents CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 Wireless Router Features... 1
b/g/n 1T1R Wireless USB Adapter. User s Manual
 802.11 b/g/n 1T1R Wireless USB Adapter User s Manual Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
802.11 b/g/n 1T1R Wireless USB Adapter User s Manual Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
WLAN Mesh Architectures and IEEE s
 WLAN Architectures and IEEE 802.11s Abstract WLAN mesh networks using 802.11 Access Points (APs) to relay traffic among each other to increase the RF coverage of the networks are becoming very popular
WLAN Architectures and IEEE 802.11s Abstract WLAN mesh networks using 802.11 Access Points (APs) to relay traffic among each other to increase the RF coverage of the networks are becoming very popular
Wireless-N. User Guide. USB Network Adapter WUSB300N WIRELESS. Model No.
 2.4 GHz WIRELESS Wireless-N USB Network Adapter User Guide Model No. WUSB300N Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark
2.4 GHz WIRELESS Wireless-N USB Network Adapter User Guide Model No. WUSB300N Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change without notice. Linksys is a registered trademark or trademark
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2, g. Wireless-G. User Guide. PCI Adapter WIRELESS. with SpeedBooster WMP54GS (EU/UK/LA) Model No.
 A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2,4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter with SpeedBooster User Guide Model No. WMP54GS (EU/UK/LA) Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change
A Division of Cisco Systems, Inc. GHz 2,4 802.11g WIRELESS Wireless-G PCI Adapter with SpeedBooster User Guide Model No. WMP54GS (EU/UK/LA) Copyright and Trademarks Specifications are subject to change
Light Mesh AP. User s Guide. 2009/2/20 v1.0 draft
 Light Mesh AP User s Guide 2009/2/20 v1.0 draft i FCC Certifications This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
Light Mesh AP User s Guide 2009/2/20 v1.0 draft i FCC Certifications This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules.
OWL630 OUTDOOR ACCESS POINT
 OWL630 OUTDOOR ACCESS POINT Wireless INTRODUCTION The OWL630 is an enterprise-grade, concurrent dual-band 802.11ac outdoor access point, designed specifically to withstand harsh weather conditions in outdoor
OWL630 OUTDOOR ACCESS POINT Wireless INTRODUCTION The OWL630 is an enterprise-grade, concurrent dual-band 802.11ac outdoor access point, designed specifically to withstand harsh weather conditions in outdoor
HP V110 Wireless-N Router Series
 Data sheet Product overview The HP V110 Wireless-N Router Series IEEE 802.11n wireless LAN (WLAN) routers are ideal first networking devices for building a small business data network with a secure connection
Data sheet Product overview The HP V110 Wireless-N Router Series IEEE 802.11n wireless LAN (WLAN) routers are ideal first networking devices for building a small business data network with a secure connection
1. INTRODUCTION. Wi-Fi 1
 Wi-Fi 1 1. INTRODUCTION Wi-Fi, or Wireless Fidelity, is freedom: it allows you to connect to the Internet from your home, a bed in a hotel room or at a conference room at work without wires. How? Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi 1 1. INTRODUCTION Wi-Fi, or Wireless Fidelity, is freedom: it allows you to connect to the Internet from your home, a bed in a hotel room or at a conference room at work without wires. How? Wi-Fi
WUG2690 User s Manual
 802.11b+g Wireless LAN USB Adapter WUG2690 User s Manual Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
802.11b+g Wireless LAN USB Adapter WUG2690 User s Manual Federal Communication Commission Interference Statement This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Index
 Index Symbols and Numbers $ (dollar sign), in folder share names, 117 802.11a standard definition, 22 speed, 26 802.11b standard 802.11g standard 802.11i standard, 23 A access points compatibility, 45
Index Symbols and Numbers $ (dollar sign), in folder share names, 117 802.11a standard definition, 22 speed, 26 802.11b standard 802.11g standard 802.11i standard, 23 A access points compatibility, 45
Wireless 450N Dual-Band Gigabit Router 450 Mbps Wireless a/b/g/n, GHz, 3T3R MIMO, QoS, 4-Port Gigabit LAN Switch Part No.
 Wireless 450N Dual-Band Gigabit Router 450 Mbps Wireless 802.11a/b/g/n, 2.4 + 5 GHz, 3T3R MIMO, QoS, 4-Port Gigabit LAN Switch Part No.: 524988 Wireless 450N Dual-Band Router - The Ultimate in Wireless
Wireless 450N Dual-Band Gigabit Router 450 Mbps Wireless 802.11a/b/g/n, 2.4 + 5 GHz, 3T3R MIMO, QoS, 4-Port Gigabit LAN Switch Part No.: 524988 Wireless 450N Dual-Band Router - The Ultimate in Wireless
Everybody s connecting.
 Everybody s connecting. The ABGs of Wireless LAN Technology Overview February 2003 Introduction Wireless LANs (WLANs) using the 802.11 standard offer compelling value in office, public, and home LAN environments.
Everybody s connecting. The ABGs of Wireless LAN Technology Overview February 2003 Introduction Wireless LANs (WLANs) using the 802.11 standard offer compelling value in office, public, and home LAN environments.
Cisco WAP131 Wireless-N Dual Radio Access Point with PoE
 Data Sheet Cisco WAP131 Wireless-N Dual Radio Access Point with PoE Improved Coverage, Easy to Deploy, Secure Business-Class Wireless-N Connectivity Highlights Provides cost-effective 802.11n connectivity
Data Sheet Cisco WAP131 Wireless-N Dual Radio Access Point with PoE Improved Coverage, Easy to Deploy, Secure Business-Class Wireless-N Connectivity Highlights Provides cost-effective 802.11n connectivity
LP-2396K Outdoor 2.4GHz Wireless AP/CPE/Bridge
 User Manual LP-2396K Outdoor 2.4GHz Wireless AP/CPE/Bridge 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Product Introduction... 4 1.2 Package Content... 5 1.3 Product Features... 6 1.4 Application... 6
User Manual LP-2396K Outdoor 2.4GHz Wireless AP/CPE/Bridge 1 Table of Contents 1. Introduction... 3 1.1 Product Introduction... 4 1.2 Package Content... 5 1.3 Product Features... 6 1.4 Application... 6
Chapter 5 Local Area Networks. Computer Concepts 2013
 Chapter 5 Local Area Networks Computer Concepts 2013 5 Chapter Contents Section A: Network Building Blocks Section B: Wired and Wireless Technologies Section C: Network Setup Section D: Sharing Files Section
Chapter 5 Local Area Networks Computer Concepts 2013 5 Chapter Contents Section A: Network Building Blocks Section B: Wired and Wireless Technologies Section C: Network Setup Section D: Sharing Files Section
WAP3205 v3. User s Guide. Quick Start Guide. Wireless N300 Access Point. Default Login Details. Version 1.0 Edition 1, 05/2016
 WAP3205 v3 Wireless N300 Access Point Version 1.0 Edition 1, 05/2016 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details LAN IP Address http://192.168.1.2 User Name www.zyxel.com admin Password 1234 Copyright
WAP3205 v3 Wireless N300 Access Point Version 1.0 Edition 1, 05/2016 Quick Start Guide User s Guide Default Login Details LAN IP Address http://192.168.1.2 User Name www.zyxel.com admin Password 1234 Copyright
A Configuration Protocol for Embedded Devices on Secure Wireless Networks
 A Configuration Protocol for Embedded Devices on Secure Wireless Networks Larry Sanders lsanders@ittc.ku.edu 6 May 2003 Introduction Wi-Fi Alliance Formally Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA)
A Configuration Protocol for Embedded Devices on Secure Wireless Networks Larry Sanders lsanders@ittc.ku.edu 6 May 2003 Introduction Wi-Fi Alliance Formally Wireless Ethernet Compatibility Alliance (WECA)
Wireless LAN Security. Gabriel Clothier
 Wireless LAN Security Gabriel Clothier Timeline 1997: 802.11 standard released 1999: 802.11b released, WEP proposed [1] 2003: WiFi alliance certifies for WPA 2004: 802.11i released 2005: 802.11w task group
Wireless LAN Security Gabriel Clothier Timeline 1997: 802.11 standard released 1999: 802.11b released, WEP proposed [1] 2003: WiFi alliance certifies for WPA 2004: 802.11i released 2005: 802.11w task group
Outdoor High Power b/g/n Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL 4.0
 Outdoor High Power 802.11b/g/n Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL 4.0 2012 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Hardware Installation... 4 3 Driver Installation... 6 3.1 Windows XP... 6 3.2 Windows Vista... 9
Outdoor High Power 802.11b/g/n Wireless USB Adapter USER MANUAL 4.0 2012 Contents 1 Introduction... 3 2 Hardware Installation... 4 3 Driver Installation... 6 3.1 Windows XP... 6 3.2 Windows Vista... 9
Chapter 24 Wireless Network Security
 Chapter 24 Wireless Network Security Wireless Security Key factors contributing to higher security risk of wireless networks compared to wired networks include: o Channel Wireless networking typically
Chapter 24 Wireless Network Security Wireless Security Key factors contributing to higher security risk of wireless networks compared to wired networks include: o Channel Wireless networking typically
