Geog, IES 377/Cee 357 Exercise 5 Page: 1/6. GEOG, IES 377/CEE 357: An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems
|
|
|
- Rodney Jenkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Geog, IES 377/Cee 357 Exercise 5 Page: 1/6 1. Introduction: GEOG, IES 377/CEE 357: An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Exercise 5 Compiling Spatial Database: Getting the other data layers into ARC/INFO Due Dates: November 6, 2000 (Lab 301) November 7, 2000 (Lab 302) November 8, 2000 (Lab 303) November 9, 2000 (Lab 304) (Total of 20 points) You have completed the conversion of the landuse coverage into ARC/INFO and made it ready to be used (Table 1). There are still other data layers which are not yet in a usable form or not in your workspace (which you named as sitedata in Exercise 3. In this exercise, you will get the rest of the data layers listed in Table 1 into a usable form and into the workspace. NOTE: Please remember to read slowly and carefully and watch out for typos. Also, remember that command syntax can be examined by using the usage command at any Arc/Info module prompt. Table 1: Current Status of the Data Layers Data Layer Format Coordinate System Status Landuse Map Arc/Info UTM Done Road Map Arc/Info UTM Not in workspace Sewer Line Map Arc/Info UTM Not in workspace Soil Map Arc/Info Interchange UTM Not yet Stream Network Map Arc/Info Generate UTM Not yet 2. Your Exercise 5: 2.1 Copying the sewer line and roads (existing ARC/INFO coverages): The road map and the sewer line map are already in the ARC/INFO format and in the UTM coordinate system. You can simply copy them over into your workspace. These two data layers are served over the network. Use ARC/INFO command COPY to copy these two data layers into your workspace. First, you need to be in your workspace (d:\sitedata). For copying the sewer line data layer, enter COPY s:\g377\lab5\sewers sewers at the Arc: prompt. To copy the road map, substitute sewers in the above command with roads. Use the listcoverages command to see if you have them in your workspace or use ARCPLOT or Arctools to display the coverages on screen. Use describe to obtain information about coverage sewers. You should study the information listed on screen carefully and also think about why we need this information. 2.2 Getting the soil data layer ready (ARC/INFO interchange format data): ARC/INFO interchange files normally would have.e00 as extensions. Often the data in ARC/INFO interchange format would already be in a usable form, which means that spatial topology has been built and attribute data have linked with spatial data. The data may have been projected into a known coordinate system. However, these may not be true all the times. So you should still check if the data
2 Geog, IES 377/Cee 357 Exercise 5 Page: 2/6 layer is usable yet by running the DESCRIBE command on the coverage after you have imported the data. The soil data layer in the interchange format is not yet in a usable form. You will perform the following tasks in this section to make it usable: a) import it into Arc/Info internal format; b) construct topology; 3) attach attribute data to it Importing from the ARC/INFO interchange format: Since the soil map layer of the area is in ARC/INFO interchange format, you need to import this data layer from ARC/INFO interchange format into ARC/INFO internal format. The command to import the data in the interchange format is IMPORT. Using the help system to find out more about this command. To import the soil data layer, enter IMPORT cover s:\g377\lab5\soils.e00 soils at the Arc: prompt. ARC/INFO should respond to you with Importing soils from interchange file s:\g377\lab5\soils.e00 Run DESCRIBE on the newly created coverage soils and you will find that the topology for the polygons is preliminary, which means that the spatial data have been changed since the last time the topology was built. This also means that you need to rebuild the topology (you will do it in Section below). If you enter LIST soils.pat, you will find that there are only four columns of data: Record ID (first column), AREA, PERIMETER, SOILS# (internal ID). This means that whoever created this soil data layer did not complete the job and you will have to enter the soil attribute data (such as soil type and suitability for construction) (You do this in Section 2.2.3) Constructing the polygon topology: As you have found out, the polygon topology of the soils data layer needs to be reconstructed. Let s now construct the topology of coverage SOILS. There are two basic commands for constructing topology: build and clean. We are going to use build this time. Type build alone at the Arc: prompt. The usage of build comes up. By now you should be comfortable with the syntax (synopsis) of the usage message. Since soils are represented by polygons we are going to construct polygon topology. Type build soils POLY and the computer will respond to you with the message of building polygons It will return you to the Arc: prompt once it is finished. You may be wondering what POLY is doing in the command build soils POLY. POLY here specifies that you are constructing polygon topology, which means that ARC/INFO will produce a PAT table (SOILS.PAT in this case) Getting soil polygon attributes in: You have learned how to get attribute data into ARC/INFO and link them with the spatial data in Exercise 4. The basic steps are: create an info table by defining the items (fields) needed, enter the attribute data into this info table, and finally link the info table with the pat table. Now let s put what you have learned in Exercise 4 into use. Table 2 contains the soil attribute information for the soil polygons. SOILS# is the internal soil polygon number created by ARC/INFO. The column labeled as SOILS-ID contains the polygon number (user defined polygon IDs), SOIL-CODE contains the names of soil types, and the fourth column (SUIT) contains the code indicating the suitability for construction. You may need to DEFINE (specifying item parameters width & output width can be the same as landuse.dat) a table in INFO and ADD and UPDATE records. After creating the table, and entering the data, link the soils attributes to the soil polygons! * Be careful to use the correct item to join SOILS.DAT and SOILS.PAT *
3 Geog, IES 377/Cee 357 Exercise 5 Page: 3/6 Table 2: A List of Soil Attributes SOILS# SOILS-ID SOIL-CODE SUIT Id Sg Id Id Ns Tn Sg Ns Id Tn Ns Ns Ns Sg Ns Ns Ko Sg Ns Ns Ns Ns Ns Sg Sg Ns Ns Ns Ns Ns Ns Sg Ns Id Id Ns Id Ss Ss Id Ns Ss 2
4 Geog, IES 377/Cee 357 Exercise 5 Page: 4/6 2.3 Getting the stream data layer ready (ARC/INFO Generate format): Importing from the ARC/INFO Generate format: The ARC/INFO Generate format is very simple (See the ARC/INFO on-line documentation on command GENERATE for detailed description). To import data in the Generate format, you need to run command GENERATE momentarily. To import the stream data layer, enter GENERATE STREAMS at the Arc: prompt. GENERATE has its own prompt and its own set of subcommands. You are now in the GENERATE subsystem (indicated by the Generate: prompt). To obtain a list of GENERATE subcommands, enter COMMANDS at the Generate: prompt. For now, you only need the INPUT, LINES, and QUIT subcommands. The INPUT subcommand tells the GENERATE subsystem where to read data. In your case, the subsystem will be reading the data s:\g377\lab5\streams.lin. Enter INPUT s:\g377\lab5\streams.lin at the Generate: prompt to tell the subsystem to read from the above specified file. At this point, the subsystem has not yet read the coordinates from the file. The LINES command tells the subsystem that it should read the data as linear features and should start reading the data right away. The subsystem responds with Creating Lines with coordinates loaded from s:\g377\lab5\streams.lin after you enter LINES at the Generate: prompt. Once the subsystem finishes reading the data, the Generate: prompt will return to you, which means that you have imported the data. Issue QUIT to leave the subsystem. You may want to use ARCPLOT or arctools to see the newly imported data layer. In order to register the imported streams data layer to any other data layers (such as ROADS and SEWERS) in the database, STREAMS must have the same tics as the other data layers. Since the STREAMS coverage is also in UTM, you can borrow the tics from ROADS. To do this, you need to use the GENERATE subsystem again. Issue GENERATE STREAMS, which will put you in the GENERATE subsystem for adding features to coverage STREAMS. At the Generate: prompt (indicator of being in the GENERATE subsystem), type COPYTICS ROADS. Once the Generate: prompt returns, type QUIT to exit from the GENERATE subsystem. Run DESCRIBE on STREAMS and study the information provided by DESCRIBE on this data layer. You should notice that the coordinate system for STREAMS is not known to ARC/INFO although we know that is in UTM and all other parameters are the same as those for the ROADS coverage. Issue the following commands to enter the coordinate information for STREAMS: projectdefine cover streams projection utm units meters zone 18 xshift yshift parameters You should study what these commands mean so that you will be able to use them properly in the future.
5 Geog, IES 377/Cee 357 Exercise 5 Page: 5/ Constructing streams topology: Constructing topology for linear features in ARC/INFO is not very different from constructing topology for polygon features. The only difference is that you specify LINE instead of POLY for the option of feature class type to be built. Here is the command to build topology for the stream data layer: BUILD STREAMS LINE. The other difference is that with the LINE option value, ARC/INFO will produce a AAT table (STREAMS.AAT in this case) instead of a PAT table Getting the stream attribute in: For the stream data layer, you are going to use a different way to get the attribute data into an info table (you may certainly use this method for importing attribute data into an info table for polygonal data layers). The attribute data for the stream data layer is stored s:\g377\lab5\streams.tab. That file is a text file which contains two columns (the first few records are shown in Figure 1). The first column contains the stream ID and second column contains the type (1 or 2) of stream. 1 refers to a major stream and 2 refers to a minor stream. Although the stream attribute data is in digital format already, it not yet in an info table format. First you create an info table containing two fields (items). The first item is used to contain the stream ID and second item is used to hold the stream type. Name these items STREAMS-ID and STREAMS- TYPE, respectively. Once you have created the info table, import the attribute data from s:\g377\lab5\streams.tab to the info table in INFO using the following command: add from s:\g377\lab5\streams.tab The computer should report 106 RECORD(S) ADDED after you have enter the above command. Use the LIST command in INFO to take a look of these records. Now you are ready to link the attribute data to STREAMS.AAT. You may want to review what we did in exercise 4 in order to execute this step. Up to this point, you have completed the compilation of a spatial database in ARC/INFO consisting of the following data layers: Landuse, Soils, Sewers, Roads, and Streams. You are set to perform some spatial analysis. 200,2 201,2 202,2 203,2 204,2 205,2 206,2 207,2 208,2 209,2 210,2 211,2 212,2 213,2 214,2 215,2 216,2 217,2 218,2 219,2 220,2 221,2 Figure 1: The First Few Records of the Stream Attribute Data
6 Geog, IES 377/Cee 357 Exercise 5 Page: 6/6 2.4 Printing the Data Layers Created in this Exercise: You have learned how to create a simple map in ARC/INFO in Exercise 4. Use similar ARCPLOT commands to produce a map for each of the new created data layers (use different map names for different data layers). 3. Questions: Write a one-paragraph summary of lab exercises. Be sure to include reasons for the procedures performed. 1) When you are creating the info table for the stream attribute data, why must you use the same stream ID name in the info table as that in STREAMS.AAT? 2) List the attribute definitions for each field used in the info table for holding the soil polygon attributes. Explain the reasons for defining the fields in such a way. 3) List and discuss some general steps (not Arc/Info commands) you would take to make a foreign data set, like a paper map, usable for your specific project. (Hint: What have we done so far?) 4. Things to Be Handed In: 1) Summary of lab exercises 2) Answers to the above questions and their supporting materials. 3) OPTIONAL A hardcopy of each of the four data layers created in this exercise OPTIONAL
Exercise 4 Compiling a Spatial Database: Adding and Linking Attribute Data
 Geog, IES 377/Cee 357 Exercise 4 Page: 1/9 GEOG 377/CEE 357: An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Exercise 4 Compiling a Spatial Database: Adding and Linking Attribute Data 1. Introduction
Geog, IES 377/Cee 357 Exercise 4 Page: 1/9 GEOG 377/CEE 357: An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems Exercise 4 Compiling a Spatial Database: Adding and Linking Attribute Data 1. Introduction
A Hands-on Experience with Arc/Info 8 Desktop
 Demo of Arc/Info 8 Desktop page 1 of 17 A Hands-on Experience with Arc/Info 8 Desktop Prepared by Xun Shi and Ted Quinby Geography 377 December 2000 In this DEMO, we introduce a brand new edition of ArcInfo,
Demo of Arc/Info 8 Desktop page 1 of 17 A Hands-on Experience with Arc/Info 8 Desktop Prepared by Xun Shi and Ted Quinby Geography 377 December 2000 In this DEMO, we introduce a brand new edition of ArcInfo,
IF YOU SAVED THE ArcMAP PROJECT FROM LAB#2 OPEN IT!
 Lab #4 Working with Fireatlas Regions in ArcInfo and ArcGIS NR506 Advanced GIS Applications in Fire Ecology and Management Objectives Understanding the Regions concept in GIS Learn a few regions commands
Lab #4 Working with Fireatlas Regions in ArcInfo and ArcGIS NR506 Advanced GIS Applications in Fire Ecology and Management Objectives Understanding the Regions concept in GIS Learn a few regions commands
Geospatial Technologies Student Training Manual
 Long Term Resource Monitoring Program Program Report 98-P010 Geospatial Technologies Student Training Manual 8S psbl'50 seieiis.; September 1998 WIG QUALITY INSPECTED 4 The Environmental Management Technical
Long Term Resource Monitoring Program Program Report 98-P010 Geospatial Technologies Student Training Manual 8S psbl'50 seieiis.; September 1998 WIG QUALITY INSPECTED 4 The Environmental Management Technical
Lab.4 & Assignment 2. Lab4. Conversion of Hardcopy Map to ArcGIS Map
 EATS4400 GIS Lab.4 & Assignment 2 Lab4 Conversion of Hardcopy Map to ArcGIS Map In this lab exercise you will have chance to go through the steps to convert hardcopy map into digital map for ArcGIS. Digitizing
EATS4400 GIS Lab.4 & Assignment 2 Lab4 Conversion of Hardcopy Map to ArcGIS Map In this lab exercise you will have chance to go through the steps to convert hardcopy map into digital map for ArcGIS. Digitizing
Coverage data model. Vector-Based Spatial Analysis: Tools Processes. Topological Data Model. Polygons Files. Geographic Information Systems.
 GEOG4340 Geographic Information Systems Lecture Four 2013winter Vector-Based Spatial Analysis: Tools Processes Reading materials: Chapter 6 of Intro GIS by J. R. Jensen and R.R. Jensen Cheng. Q., Earth
GEOG4340 Geographic Information Systems Lecture Four 2013winter Vector-Based Spatial Analysis: Tools Processes Reading materials: Chapter 6 of Intro GIS by J. R. Jensen and R.R. Jensen Cheng. Q., Earth
Lab 2. Vector and raster data.
 Lab 2. Vector and raster data. The goal: To learn about the structure of the vector and raster data types. Objective: Create vector and raster datasets and visualize them. Software for the lab: ARCINFO,
Lab 2. Vector and raster data. The goal: To learn about the structure of the vector and raster data types. Objective: Create vector and raster datasets and visualize them. Software for the lab: ARCINFO,
ANNEX V RASTER TO VECTOR CONVERSION MANUAL
 ANNEX V RASTER TO VECTOR CONVERSION MANUAL Table of Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. Software used...1 3. Methodology Flow chart...1 4. Scanning hard copy map...1 5. Working with Photo-editor environment
ANNEX V RASTER TO VECTOR CONVERSION MANUAL Table of Contents 1. Introduction...1 2. Software used...1 3. Methodology Flow chart...1 4. Scanning hard copy map...1 5. Working with Photo-editor environment
Working with Attribute Data and Clipping Spatial Data. Determining Land Use and Ownership Patterns associated with Streams.
 GIS LAB 3 Working with Attribute Data and Clipping Spatial Data. Determining Land Use and Ownership Patterns associated with Streams. One of the primary goals of this course is to give you some hands-on
GIS LAB 3 Working with Attribute Data and Clipping Spatial Data. Determining Land Use and Ownership Patterns associated with Streams. One of the primary goals of this course is to give you some hands-on
presented by: Tim Haithcoat University of Missouri Columbia with materials from: Environmental Systems Research Institute
 presented by: Tim Haithcoat University of Missouri Columbia with materials from: Environmental Systems Research Institute 2 Help you decrease time and resource use in arc/info tasks Give you ideas on how
presented by: Tim Haithcoat University of Missouri Columbia with materials from: Environmental Systems Research Institute 2 Help you decrease time and resource use in arc/info tasks Give you ideas on how
Data Assembling Topics:
 Topics: 1. GPX to Shape file 2. Data conversion with FME 3. Create a polygon feature 4. Merging /Appending data into a new dataset 5. Reproject data from one coordinate system to another 6. Data clipping
Topics: 1. GPX to Shape file 2. Data conversion with FME 3. Create a polygon feature 4. Merging /Appending data into a new dataset 5. Reproject data from one coordinate system to another 6. Data clipping
Contents. Functions and capabilities
 Contents Chapter 1 Introduction What is PC ARCEDIT? 1-2 PC ARCEDIT design 1-2 Edit environments 1-3 Feature-oriented editing 1-3 Database integrity 1-3 PC ARCEDIT workstation requirements 1-4 Limitations
Contents Chapter 1 Introduction What is PC ARCEDIT? 1-2 PC ARCEDIT design 1-2 Edit environments 1-3 Feature-oriented editing 1-3 Database integrity 1-3 PC ARCEDIT workstation requirements 1-4 Limitations
ArcLink. Bidirectional Conversion Utility for MapInfo and ARC/INFO Files. for Windows
 ArcLink Bidirectional Conversion Utility for MapInfo and ARC/INFO Files for Windows Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of the
ArcLink Bidirectional Conversion Utility for MapInfo and ARC/INFO Files for Windows Information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not represent a commitment on the part of the
Exercise 1: Introduction to MapInfo
 Geog 578 Exercise 1: Introduction to MapInfo Page: 1/22 Geog 578: GIS Applications Exercise 1: Introduction to MapInfo Assigned on January 25 th, 2006 Due on February 1 st, 2006 Total Points: 10 0. Convention
Geog 578 Exercise 1: Introduction to MapInfo Page: 1/22 Geog 578: GIS Applications Exercise 1: Introduction to MapInfo Assigned on January 25 th, 2006 Due on February 1 st, 2006 Total Points: 10 0. Convention
Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model Learn how to setup a MODClark model using distributed rainfall data Objectives Read an existing
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling Using NEXRAD Rainfall Data in an HEC-HMS (MODClark) Model Learn how to setup a MODClark model using distributed rainfall data Objectives Read an existing
Lab 1: Exploring data format
 Geog 458: Map Sources and Errors January 13, 2006 Lab 1: Exploring data format Data format supported by ArcGIS There are many file types supported by ArcGIS, in addition to specific cartographic objects.
Geog 458: Map Sources and Errors January 13, 2006 Lab 1: Exploring data format Data format supported by ArcGIS There are many file types supported by ArcGIS, in addition to specific cartographic objects.
GIS LAB 1. Basic GIS Operations with ArcGIS. Calculating Stream Lengths and Watershed Areas.
 GIS LAB 1 Basic GIS Operations with ArcGIS. Calculating Stream Lengths and Watershed Areas. ArcGIS offers some advantages for novice users. The graphical user interface is similar to many Windows packages
GIS LAB 1 Basic GIS Operations with ArcGIS. Calculating Stream Lengths and Watershed Areas. ArcGIS offers some advantages for novice users. The graphical user interface is similar to many Windows packages
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations,
 Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Welcome to NR402 GIS Applications in Natural Resources. This course consists of 9 lessons, including Power point presentations, demonstrations, readings, and hands on GIS lab exercises. Following the last
Analysis of Change in Polygon Distribution
 Analysis of Change in Polygon Distribution t 1 t 2 These instructions enable you to analyze the change in polygon distribution between two time periods using ArcGIS 8.1 (ArcInfo licensed) software. The
Analysis of Change in Polygon Distribution t 1 t 2 These instructions enable you to analyze the change in polygon distribution between two time periods using ArcGIS 8.1 (ArcInfo licensed) software. The
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling HEC-1 Interface Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-1 model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic parameters
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Learn how to setup a basic HEC-1 model using WMS Objectives Build a basic HEC-1 model from scratch using a DEM, land use, and soil data. Compute the geometric and hydrologic parameters
v SMS 13.0 Tutorial GIS P Prerequisites Time Requirements Objectives
 v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to import data, visualize it, and convert it into SMS coverage data that could be used to build a numeric model. This tutorial will instruct
v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to import data, visualize it, and convert it into SMS coverage data that could be used to build a numeric model. This tutorial will instruct
4 OPERATION MANUAL FOR ARC/INFO
 4 OPERATION MANUAL FOR ARC/INFO 4-1 Final Report (Volume IV) 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction The ARC/INFO is GIS software based on topological data structure. This software is different in this point from
4 OPERATION MANUAL FOR ARC/INFO 4-1 Final Report (Volume IV) 1 Introduction 1.1 Introduction The ARC/INFO is GIS software based on topological data structure. This software is different in this point from
SVY2001: Databases for GIS
 SVY2001: Databases for GIS Lecture 15: Introduction to GIS and Attribute Data Management. Dr Stuart Barr School of Civil Engineering & Geosciences University of Newcastle upon Tyne. Email: S.L.Barr@ncl.ac.uk
SVY2001: Databases for GIS Lecture 15: Introduction to GIS and Attribute Data Management. Dr Stuart Barr School of Civil Engineering & Geosciences University of Newcastle upon Tyne. Email: S.L.Barr@ncl.ac.uk
v Prerequisite Tutorials GSSHA Modeling Basics Stream Flow GSSHA WMS Basics Creating Feature Objects and Mapping their Attributes to the 2D Grid
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial GSSHA Modeling Basics Developing a GSSHA Model Using the Hydrologic Modeling Wizard in WMS Learn how to setup a basic GSSHA model using the hydrologic modeling wizard Objectives
GEOG4017 Geographical Information Systems Lab 3 Data Collection and Integration (I)
 DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIVERSITY Prof. Q. Zhou GEOG4017 Geographical Information Systems Lab 3 Data Collection and Integration (I) Objectives Before we can use GIS for any analysis
DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIVERSITY Prof. Q. Zhou GEOG4017 Geographical Information Systems Lab 3 Data Collection and Integration (I) Objectives Before we can use GIS for any analysis
An Example of Regional Web Resources: Massachusetts, USA Digital Data
 An Example of Regional Web Resources: Massachusetts, USA Digital Data Author Attribution Major contributors to this curriculum include (alphabetical): Maria Fernandez Michael Hamel Quentin Lewis Maili
An Example of Regional Web Resources: Massachusetts, USA Digital Data Author Attribution Major contributors to this curriculum include (alphabetical): Maria Fernandez Michael Hamel Quentin Lewis Maili
Exercise 1: An Overview of ArcMap and ArcCatalog
 Exercise 1: An Overview of ArcMap and ArcCatalog Introduction: ArcGIS is an integrated collection of GIS software products for building a complete GIS. ArcGIS enables users to deploy GIS functionality
Exercise 1: An Overview of ArcMap and ArcCatalog Introduction: ArcGIS is an integrated collection of GIS software products for building a complete GIS. ArcGIS enables users to deploy GIS functionality
Using ArcToolbox. GIS by ESRI
 Using ArcToolbox GIS by ESRI Copyright 1999, 2000 ESRI All rights reserved Printed in the United States of America The information contained in this document is the exclusive property of ESRI This work
Using ArcToolbox GIS by ESRI Copyright 1999, 2000 ESRI All rights reserved Printed in the United States of America The information contained in this document is the exclusive property of ESRI This work
Lab 7: Tables Operations in ArcMap
 Lab 7: Tables Operations in ArcMap What You ll Learn: This Lab provides more practice with tabular data management in ArcMap. In this Lab, we will view, select, re-order, and update tabular data. You should
Lab 7: Tables Operations in ArcMap What You ll Learn: This Lab provides more practice with tabular data management in ArcMap. In this Lab, we will view, select, re-order, and update tabular data. You should
Finding and Using Spatial Data
 Finding and Using Spatial Data Introduction In this lab, you will download two different versions of the National Wetlands Inventory (NWI) dataset for a region of Massachusetts, from a source on the internet.
Finding and Using Spatial Data Introduction In this lab, you will download two different versions of the National Wetlands Inventory (NWI) dataset for a region of Massachusetts, from a source on the internet.
GIS LAB 8. Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation
 GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
GIS LAB 8 Raster Data Applications Watershed Delineation This lab will require you to further your familiarity with raster data structures and the Spatial Analyst. The data for this lab are drawn from
Object modeling and geodatabases. GEOG 419: Advanced GIS
 Object modeling and geodatabases GEOG 419: Advanced GIS CAD Data Model 1960s and 1970s Geographic data stored as points, lines, and areas No attributes; each feature type stored on a different layer No
Object modeling and geodatabases GEOG 419: Advanced GIS CAD Data Model 1960s and 1970s Geographic data stored as points, lines, and areas No attributes; each feature type stored on a different layer No
LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8
 LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8 Outline Introduction Purpose Lab Basics o About the Computers o About the software o Additional information Data ArcGIS Applications o Starting ArcGIS o o o Conclusion To
LAB 1: Introduction to ArcGIS 8 Outline Introduction Purpose Lab Basics o About the Computers o About the software o Additional information Data ArcGIS Applications o Starting ArcGIS o o o Conclusion To
v SMS 11.1 Tutorial GIS Requirements GIS Module Map Module ArcGis (Optional) Time minutes Prerequisites None Objectives
 v. 11.1 SMS 11.1 Tutorial GIS Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how you can read in GIS data, visualize it, and convert it into SMS coverage data that could be used to build a numeric model. We will
v. 11.1 SMS 11.1 Tutorial GIS Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how you can read in GIS data, visualize it, and convert it into SMS coverage data that could be used to build a numeric model. We will
Lab 1: Exploring ArcMap and ArcCatalog In this lab, you will explore the ArcGIS applications ArcCatalog and ArcMap. You will learn how to use
 Lab 1: Exploring ArcMap and ArcCatalog In this lab, you will explore the ArcGIS applications ArcCatalog and ArcMap. You will learn how to use ArcCatalog to find maps and data and how to display maps in
Lab 1: Exploring ArcMap and ArcCatalog In this lab, you will explore the ArcGIS applications ArcCatalog and ArcMap. You will learn how to use ArcCatalog to find maps and data and how to display maps in
ArcCatalog or the ArcCatalog tab in ArcMap ArcCatalog or the ArcCatalog tab in ArcMap ArcCatalog or the ArcCatalog tab in ArcMap
 ArcGIS Procedures NUMBER OPERATION APPLICATION: TOOLBAR 1 Import interchange file to coverage 2 Create a new 3 Create a new feature dataset 4 Import Rasters into a 5 Import tables into a PROCEDURE Coverage
ArcGIS Procedures NUMBER OPERATION APPLICATION: TOOLBAR 1 Import interchange file to coverage 2 Create a new 3 Create a new feature dataset 4 Import Rasters into a 5 Import tables into a PROCEDURE Coverage
Geography 476/676 (Spring 09)
 Geography 476/676 (Spring 09) GIS DATABASE CONVERSION: DEM, DLG, and DRG files An important consideration in the development of a GIS database is whether one should acquire readily available geographic
Geography 476/676 (Spring 09) GIS DATABASE CONVERSION: DEM, DLG, and DRG files An important consideration in the development of a GIS database is whether one should acquire readily available geographic
GEOG 487 Lesson 7: Step- by- Step Activity
 GEOG 487 Lesson 7: Step- by- Step Activity Part I: Review the Relevant Data Layers and Organize the Map Document In Part I, we will review the data and organize the map document for analysis. 1. Unzip
GEOG 487 Lesson 7: Step- by- Step Activity Part I: Review the Relevant Data Layers and Organize the Map Document In Part I, we will review the data and organize the map document for analysis. 1. Unzip
Programming in ArcGIS using ArcObjects and AML
 Guide 93 Version 3.0 Programming in ArcGIS using ArcObjects and AML ArcObjects is the development environment of the Desktop ArcGIS applications ArcMap, ArcCatalog and ArcScene. It is used to customise
Guide 93 Version 3.0 Programming in ArcGIS using ArcObjects and AML ArcObjects is the development environment of the Desktop ArcGIS applications ArcMap, ArcCatalog and ArcScene. It is used to customise
GRASS to ARC/INFO Data Conversion by Kelly Dilks Edward Delisio Mark Gibb Chris Rewerts Eric Bader Gail Taylor
 US Army Corps of Engineers Construction Engineering Research Laboratories USACERL Technical Report 98/66 April 1998 GRASS to ARC/INFO Data Conversion by Kelly Dilks Edward Delisio Mark Gibb Chris Rewerts
US Army Corps of Engineers Construction Engineering Research Laboratories USACERL Technical Report 98/66 April 1998 GRASS to ARC/INFO Data Conversion by Kelly Dilks Edward Delisio Mark Gibb Chris Rewerts
Using GIS to Site Minimal Excavation Helicopter Landings
 Using GIS to Site Minimal Excavation Helicopter Landings The objective of this analysis is to develop a suitability map for aid in locating helicopter landings in mountainous terrain. The tutorial uses
Using GIS to Site Minimal Excavation Helicopter Landings The objective of this analysis is to develop a suitability map for aid in locating helicopter landings in mountainous terrain. The tutorial uses
Lab 10: Raster Analyses
 Lab 10: Raster Analyses What You ll Learn: Spatial analysis and modeling with raster data. You will estimate the access costs for all points on a landscape, based on slope and distance to roads. You ll
Lab 10: Raster Analyses What You ll Learn: Spatial analysis and modeling with raster data. You will estimate the access costs for all points on a landscape, based on slope and distance to roads. You ll
Digging Into Autodesk Map 3D 2007 Level 1 Training Rick Ellis Michael Carris Russell Martin
 Digging Into Autodesk Map 3D 2007 Level 1 Training Rick Ellis Michael Carris Russell Martin PO Box 344 Canby Oregon 97013 www.cadapult-software.com training@cadapult-software.com (503) 829-8929 Table of
Digging Into Autodesk Map 3D 2007 Level 1 Training Rick Ellis Michael Carris Russell Martin PO Box 344 Canby Oregon 97013 www.cadapult-software.com training@cadapult-software.com (503) 829-8929 Table of
Chapter 17 Creating a New Suit from Old Cloth: Manipulating Vector Mode Cartographic Data
 Chapter 17 Creating a New Suit from Old Cloth: Manipulating Vector Mode Cartographic Data Imagine for a moment that digital cartographic databases were a perfect analog of the paper map. Once you digitized
Chapter 17 Creating a New Suit from Old Cloth: Manipulating Vector Mode Cartographic Data Imagine for a moment that digital cartographic databases were a perfect analog of the paper map. Once you digitized
layers in a raster model
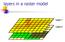 layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
layers in a raster model Layer 1 Layer 2 layers in an vector-based model (1) Layer 2 Layer 1 layers in an vector-based model (2) raster versus vector data model Raster model Vector model Simple data structure
v SMS 12.3 Tutorial GIS P Prerequisites Time Requirements Objectives
 v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to import data, visualize it, and convert it into SMS coverage data that could be used to build a numeric model. This tutorial will instruct
v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to import data, visualize it, and convert it into SMS coverage data that could be used to build a numeric model. This tutorial will instruct
v SMS 12.2 Tutorial GIS Requirements GIS Module Map Module ArcGis (Optional) Time minutes Prerequisites None Objectives
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to read in data, visualize it, and convert it into SMS coverage data that could be used to build a numeric model. This tutorial will
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to read in data, visualize it, and convert it into SMS coverage data that could be used to build a numeric model. This tutorial will
The GIS Spatial Data Model
 The GIS Spatial Data Model Introduction: Spatial data are what drive a GIS. Every piece of functionality that makes a GIS separate from another analytical environment is rooted in the spatially explicit
The GIS Spatial Data Model Introduction: Spatial data are what drive a GIS. Every piece of functionality that makes a GIS separate from another analytical environment is rooted in the spatially explicit
GMS 10.3 Tutorial Stratigraphy Modeling Horizon Coverages Use horizon coverages to help control the Horizons Solids operation
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Stratigraphy Modeling Horizon Coverages Use horizon coverages to help control the Horizons Solids operation Objectives Learn how to constrain the areal extent of the solids created
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Stratigraphy Modeling Horizon Coverages Use horizon coverages to help control the Horizons Solids operation Objectives Learn how to constrain the areal extent of the solids created
Compilation of GIS data for the Lower Brazos River basin
 Compilation of GIS data for the Lower Brazos River basin Prepared by Francisco Olivera, Ph.D., P.E., Srikanth Koka, and Lauren Walker Department of Civil Engineering October 2, 2006 Contents: Brief Overview
Compilation of GIS data for the Lower Brazos River basin Prepared by Francisco Olivera, Ph.D., P.E., Srikanth Koka, and Lauren Walker Department of Civil Engineering October 2, 2006 Contents: Brief Overview
Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model Learn how to setup an HEC-HMS model using WMS online spatial data Objectives This tutorial shows how to
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Using Online Spatial Data to Create an HEC-HMS Model Learn how to setup an HEC-HMS model using WMS online spatial data Objectives This tutorial shows how to
Minnesota Department of Natural Resources ArcView Utilities Extension User s Guide
 Introduction This document describes the functionality and use of the ArcView Utilities extension for the ArcView desktop GIS software. These tools were developed out of the need for additional geoprocessing
Introduction This document describes the functionality and use of the ArcView Utilities extension for the ArcView desktop GIS software. These tools were developed out of the need for additional geoprocessing
Heads-up Digitizing from Scanned Hard-Copy Maps Part II - Vector Point, Segment and Polygon Editing 1
 Data conversion/entry (GIS, databases) February 18-25, 2007 Freetown, Sierra Leone Heads-up Digitizing from Scanned Hard-Copy Maps Part II - Vector Point, Segment and Polygon Editing 1 Objectives: Create
Data conversion/entry (GIS, databases) February 18-25, 2007 Freetown, Sierra Leone Heads-up Digitizing from Scanned Hard-Copy Maps Part II - Vector Point, Segment and Polygon Editing 1 Objectives: Create
Unit 3: Proximity Analysis and Buffering. Lecture Outline
 Unit 3: Proximity Analysis and Buffering Lecture Outline I. Vector-Based Proximity 1. Proximity involves the calculation of distance between features in a single layer, or between features in multiple
Unit 3: Proximity Analysis and Buffering Lecture Outline I. Vector-Based Proximity 1. Proximity involves the calculation of distance between features in a single layer, or between features in multiple
Lab Exercise 6: Vector Spatial Analysis
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Urban Studies and Planning 11.520: A Workshop on Geographic Information Systems 11.188: Urban Planning and Social Science Laboratory Lab Exercise 6:
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Department of Urban Studies and Planning 11.520: A Workshop on Geographic Information Systems 11.188: Urban Planning and Social Science Laboratory Lab Exercise 6:
Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS.
 GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
GIS INTRODUCTION TO RASTER GRIDS AND VECTOR MAP ELEMENTS c:wou:nssi:vecrasex.wpd Purpose: To explore the raster grid and vector map element concepts in GIS. PART A. RASTER GRID NETWORKS Task A- Examine
v Modeling Orange County Unit Hydrograph GIS Learn how to define a unit hydrograph model for Orange County (California) from GIS data
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Unit Hydrograph GIS Learn how to define a unit hydrograph model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows how to define
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Modeling Orange County Unit Hydrograph GIS Learn how to define a unit hydrograph model for Orange County (California) from GIS data Objectives This tutorial shows how to define
Lab 5: Georeferencing, Digitization, and Processing
 Lab 5: Georeferencing, Digitization, and Processing Purpose: An introduction to georeferencing images, practice digitizing, and combine lesson up to this point. To Do: Register a scanned image, digitize
Lab 5: Georeferencing, Digitization, and Processing Purpose: An introduction to georeferencing images, practice digitizing, and combine lesson up to this point. To Do: Register a scanned image, digitize
In the previous lecture, we examined how to analyse a FSM using state table, state diagram and waveforms. In this lecture we will learn how to design
 1 In the previous lecture, we examined how to analyse a FSM using state table, state diagram and waveforms. In this lecture we will learn how to design a fininte state machine in order to produce the desired
1 In the previous lecture, we examined how to analyse a FSM using state table, state diagram and waveforms. In this lecture we will learn how to design a fininte state machine in order to produce the desired
In the previous lecture, we examined how to analyse a FSM using state table, state diagram and waveforms. In this lecture we will learn how to design
 In the previous lecture, we examined how to analyse a FSM using state table, state diagram and waveforms. In this lecture we will learn how to design a fininte state machine in order to produce the desired
In the previous lecture, we examined how to analyse a FSM using state table, state diagram and waveforms. In this lecture we will learn how to design a fininte state machine in order to produce the desired
v SMS 12.1 Tutorial GIS Requirements GIS Module Map Module ArcGis (Optional) Time minutes Prerequisites None Objectives
 v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to read in data, visualize it, and convert it into SMS coverage data that could be used to build a numeric model. This tutorial will
v. 12.1 SMS 12.1 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial demonstrates how to read in data, visualize it, and convert it into SMS coverage data that could be used to build a numeric model. This tutorial will
Notes: Notes: Notes: Notes:
 NR406 GIS Applications in Fire Ecology & Management Lesson 2 - Overlay Analysis in GIS Gathering Information from Multiple Data Layers One of the many strengths of a GIS is that you can stack several data
NR406 GIS Applications in Fire Ecology & Management Lesson 2 - Overlay Analysis in GIS Gathering Information from Multiple Data Layers One of the many strengths of a GIS is that you can stack several data
A New Approach for Data Conversion from CAD to GIS
 Esin Bitik (PhD) Dursun Zafer Şeker Ziyadin ÇAKIR Hakan DENLİ A New Approach for Data Conversion from CAD to GIS June 19, 2014 Contents 1. Aim of the study 2. Introduction 3. Vector Data Structure 4. Converting
Esin Bitik (PhD) Dursun Zafer Şeker Ziyadin ÇAKIR Hakan DENLİ A New Approach for Data Conversion from CAD to GIS June 19, 2014 Contents 1. Aim of the study 2. Introduction 3. Vector Data Structure 4. Converting
The WSC Data Users Guide
 Page 1 of 8 Mekong River Commission Secretariat GIS - Applications for Watershed Classification The WSC Data Users Guide Prepared by the Centre for Development and Environment (CDE), University of Berne,
Page 1 of 8 Mekong River Commission Secretariat GIS - Applications for Watershed Classification The WSC Data Users Guide Prepared by the Centre for Development and Environment (CDE), University of Berne,
Lab - Create User Accounts in Windows 8
 Introduction In this lab, you will create user accounts in Windows 8. Recommended Equipment The following equipment is required for this exercise: A computer with a new installation of Windows 8 Part 1:
Introduction In this lab, you will create user accounts in Windows 8. Recommended Equipment The following equipment is required for this exercise: A computer with a new installation of Windows 8 Part 1:
Vector-Based GIS Data Processing. Chapter 6
 Vector-Based GIS Data Processing Chapter 6 Vector Data Model Feature Classes points lines polygons Layers limited to one class of data Figure p. 186 Vector Data Model Shapefiles ArcView non-topological
Vector-Based GIS Data Processing Chapter 6 Vector Data Model Feature Classes points lines polygons Layers limited to one class of data Figure p. 186 Vector Data Model Shapefiles ArcView non-topological
GIS IN ECOLOGY: CREATING RESEARCH MAPS
 GIS IN ECOLOGY: CREATING RESEARCH MAPS Contents Introduction... 2 Elements of Cartography... 2 Course Data Sources... 3 Tasks... 3 Establishing the Map Document... 3 Laying Out the Map... 5 Exporting Your
GIS IN ECOLOGY: CREATING RESEARCH MAPS Contents Introduction... 2 Elements of Cartography... 2 Course Data Sources... 3 Tasks... 3 Establishing the Map Document... 3 Laying Out the Map... 5 Exporting Your
Lab 10: Raster Analyses
 Lab 10: Raster Analyses What You ll Learn: Spatial analysis and modeling with raster data. You will estimate the access costs for all points on a landscape, based on slope and distance to roads. You ll
Lab 10: Raster Analyses What You ll Learn: Spatial analysis and modeling with raster data. You will estimate the access costs for all points on a landscape, based on slope and distance to roads. You ll
OziExplorer Training and Help Manual
 Scientifically Valid Evaluations of Forest Practices under the Forest and Range Practices Act OziExplorer Training and Help Manual for use with Soil Effectiveness Evaluation Cards For the most current
Scientifically Valid Evaluations of Forest Practices under the Forest and Range Practices Act OziExplorer Training and Help Manual for use with Soil Effectiveness Evaluation Cards For the most current
Measure the Perimeter of Polygons Over a Surface. Operations. What Do I Need?
 Measure the Perimeter of Polygons Over a Surface Operations What Do I Need? Incremental Frontage Score To measure the perimeter of polygons over a surface you need to have two input map layers. The first
Measure the Perimeter of Polygons Over a Surface Operations What Do I Need? Incremental Frontage Score To measure the perimeter of polygons over a surface you need to have two input map layers. The first
Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models
 Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
Geography 38/42:286 GIS 1 Topic 5: Raster and Vector Data Models Chapters 3 & 4: Chang (Chapter 4: DeMers) 1 The Nature of Geographic Data Most features or phenomena occur as either: discrete entities
v Map Module Operations SMS Tutorials Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial describes the fundamental tools in the Map module of the SMS. This tutorial provides information that is useful when constructing any type of geometric
v. 12.3 SMS 12.3 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial describes the fundamental tools in the Map module of the SMS. This tutorial provides information that is useful when constructing any type of geometric
Feature Analyst Quick Start Guide
 Feature Analyst Quick Start Guide Change Detection Change Detection allows you to identify changes in images over time. By automating the process, it speeds up a acquisition of data from image archives.
Feature Analyst Quick Start Guide Change Detection Change Detection allows you to identify changes in images over time. By automating the process, it speeds up a acquisition of data from image archives.
Creating Your Own Student Accounts On Central UNIX and OpenMail
 Creating Your Own Student Accounts On Central UNIX and OpenMail SYNOPSIS This section describes how Cal Poly students may create their own account on Cal Poly's Central UNIX. When the UNIX account is created
Creating Your Own Student Accounts On Central UNIX and OpenMail SYNOPSIS This section describes how Cal Poly students may create their own account on Cal Poly's Central UNIX. When the UNIX account is created
4.0 DIGITIZATION, EDITING AND STRUCTURING OF MAP DATA
 .0 DIGITIZATION, EDITING AND STRUCTURING OF MAP DATA The process of digitizing existing maps is a transformation from one analog) form of information to another digital) form. Data input is the operation
.0 DIGITIZATION, EDITING AND STRUCTURING OF MAP DATA The process of digitizing existing maps is a transformation from one analog) form of information to another digital) form. Data input is the operation
Feature Extraction. Contents. 1. Installing Feature Extraction. 2. Using Feature Extraction
 1 Feature Extraction Contents 1. Installing Feature Extraction 2. Using Feature Extraction Adding an image to a view Converting image to grid Resample a grid Connecting to Arc/Info Server Calculating the
1 Feature Extraction Contents 1. Installing Feature Extraction 2. Using Feature Extraction Adding an image to a view Converting image to grid Resample a grid Connecting to Arc/Info Server Calculating the
SPECS FOR G.I.S. DATA PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL
 SPECS FOR G.I.S. DATA PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL DIGITAL MAPPING FILES (very efficient/extremely accurate): 1. G.I.S. dataset formats that we can accept: FORMAT FILE EXT(S) FORMAT FILE EXT(S) AutoCAD (*.dwg,
SPECS FOR G.I.S. DATA PROVIDED TO ONE-CALL DIGITAL MAPPING FILES (very efficient/extremely accurate): 1. G.I.S. dataset formats that we can accept: FORMAT FILE EXT(S) FORMAT FILE EXT(S) AutoCAD (*.dwg,
GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems
 v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems Learn how to work with DEMs and images and to convert between projection systems in the WMS interface
v. 10.0 WMS 10.0 Tutorial GSSHA WMS Basics Loading DEMs, Contour Options, Images, and Projection Systems Learn how to work with DEMs and images and to convert between projection systems in the WMS interface
Data Models and Data processing in GIS
 PDHonline Course L155G (5 PDH) Data Models and Data processing in GIS Instructor: Steve Ramroop, Ph.D. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088
PDHonline Course L155G (5 PDH) Data Models and Data processing in GIS Instructor: Steve Ramroop, Ph.D. 2012 PDH Online PDH Center 5272 Meadow Estates Drive Fairfax, VA 22030-6658 Phone & Fax: 703-988-0088
Spatial Data Models. Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities
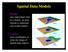 Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Spatial Data Models Raster uses individual cells in a matrix, or grid, format to represent real world entities Vector uses coordinates to store the shape of spatial data objects David Tenenbaum GEOG 7
Answer the following general questions: 1. What happens when you right click on an icon on your desktop? When you left double click on an icon?
 Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Practical: Explore ArcGIS 10 Desktop Tools and functionality Day_1 Lecture 1 Sources: o ArcGIS Desktop help o ESRI website o Getting to Know ArcGIS
Name: Date: June 27th, 2011 GIS Boot Camps For Educators Practical: Explore ArcGIS 10 Desktop Tools and functionality Day_1 Lecture 1 Sources: o ArcGIS Desktop help o ESRI website o Getting to Know ArcGIS
Geography 104 Instructors: Judd Curran & Mark Goodman. LAB EXERCISE #3 Data Analysis - Buffering (25pts)
 Instructors: Judd Curran & Mark Goodman Name: LAB EXERCISE #3 Data Analysis - Buffering (25pts) Transformations in GIS are methods that transform GIS objects and databases into more useful products using
Instructors: Judd Curran & Mark Goodman Name: LAB EXERCISE #3 Data Analysis - Buffering (25pts) Transformations in GIS are methods that transform GIS objects and databases into more useful products using
Raster Data Model & Analysis
 Topics: 1. Understanding Raster Data 2. Adding and displaying raster data in ArcMap 3. Converting between floating-point raster and integer raster 4. Converting Vector data to Raster 5. Querying Raster
Topics: 1. Understanding Raster Data 2. Adding and displaying raster data in ArcMap 3. Converting between floating-point raster and integer raster 4. Converting Vector data to Raster 5. Querying Raster
Lab 2.1: Fixing a C++ program
 CS 150 Lab 2 Introduction to Compiler Errors, Variables, Assignments and Output The purpose of today s lab session is to allow you to gain experience using primitive data types, constants, assignment statements
CS 150 Lab 2 Introduction to Compiler Errors, Variables, Assignments and Output The purpose of today s lab session is to allow you to gain experience using primitive data types, constants, assignment statements
QGIS LAB SERIES GST 102: Spatial Analysis Lab 3: Advanced Attributes and Spatial Queries for Data Exploration
 QGIS LAB SERIES GST 102: Spatial Analysis Lab 3: Advanced Attributes and Spatial Queries for Data Exploration Objective Understanding Attribute Queries and Spatial Queries Document Version: 2014-06-19
QGIS LAB SERIES GST 102: Spatial Analysis Lab 3: Advanced Attributes and Spatial Queries for Data Exploration Objective Understanding Attribute Queries and Spatial Queries Document Version: 2014-06-19
TUFLOW 1D/2D SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM. 1 Introduction. 2 Background Data
 SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM TUFLOW 1D/2D 1 Introduction This tutorial describes the generation of a 1D TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. It is recommended that the TUFLOW 2D tutorial be done before
SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM TUFLOW 1D/2D 1 Introduction This tutorial describes the generation of a 1D TUFLOW project using the SMS interface. It is recommended that the TUFLOW 2D tutorial be done before
Spatial Hydrologic Modeling HEC-HMS Distributed Parameter Modeling with the MODClark Transform
 v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling HEC-HMS Distributed Parameter Modeling with the MODClark Transform Setup a basic distributed MODClark model using the WMS interface Objectives In this
v. 9.0 WMS 9.0 Tutorial Spatial Hydrologic Modeling HEC-HMS Distributed Parameter Modeling with the MODClark Transform Setup a basic distributed MODClark model using the WMS interface Objectives In this
Module 10 Data-action models
 Introduction Geo-Information Science Practical Manual Module 10 Data-action models 10. INTRODUCTION 10-1 DESIGNING A DATA-ACTION MODEL 10-2 REPETITION EXERCISES 10-6 10. Introduction Until now you have
Introduction Geo-Information Science Practical Manual Module 10 Data-action models 10. INTRODUCTION 10-1 DESIGNING A DATA-ACTION MODEL 10-2 REPETITION EXERCISES 10-6 10. Introduction Until now you have
1 INTRODUCTION WAYPOINT MANAGEMENT ROUTE DIGITIZING...12
 1 INTRODUCTION...1 2 WAYPOINT MANAGEMENT...2 3 ROUTE DIGITIZING...12 4 GARMIN TO SHAPE...17 4.1 How to Make a Simple Shape from Garmin MapSource for Free...18 4.2 Complex Polygons From Garmin...26 1 Introduction
1 INTRODUCTION...1 2 WAYPOINT MANAGEMENT...2 3 ROUTE DIGITIZING...12 4 GARMIN TO SHAPE...17 4.1 How to Make a Simple Shape from Garmin MapSource for Free...18 4.2 Complex Polygons From Garmin...26 1 Introduction
CSCI 1100L: Topics in Computing Lab Lab 11: Programming with Scratch
 CSCI 1100L: Topics in Computing Lab Lab 11: Programming with Scratch Purpose: We will take a look at programming this week using a language called Scratch. Scratch is a programming language that was developed
CSCI 1100L: Topics in Computing Lab Lab 11: Programming with Scratch Purpose: We will take a look at programming this week using a language called Scratch. Scratch is a programming language that was developed
Module 7 Raster operations
 Introduction Geo-Information Science Practical Manual Module 7 Raster operations 7. INTRODUCTION 7-1 LOCAL OPERATIONS 7-2 Mathematical functions and operators 7-5 Raster overlay 7-7 FOCAL OPERATIONS 7-8
Introduction Geo-Information Science Practical Manual Module 7 Raster operations 7. INTRODUCTION 7-1 LOCAL OPERATIONS 7-2 Mathematical functions and operators 7-5 Raster overlay 7-7 FOCAL OPERATIONS 7-8
GY301 Geomorphology Lab 5 Topographic Map: Final GIS Map Construction
 GY301 Geomorphology Lab 5 Topographic Map: Final GIS Map Construction Introduction This document describes how to take the data collected with the total station for the campus topographic map project and
GY301 Geomorphology Lab 5 Topographic Map: Final GIS Map Construction Introduction This document describes how to take the data collected with the total station for the campus topographic map project and
2. The histogram. class limits class boundaries frequency cumulative frequency
 MA 115 Lecture 03 - Some Standard Graphs Friday, September, 017 Objectives: Introduce some standard statistical graph types. 1. Some Standard Kinds of Graphs Last week, we looked at the Frequency Distribution
MA 115 Lecture 03 - Some Standard Graphs Friday, September, 017 Objectives: Introduce some standard statistical graph types. 1. Some Standard Kinds of Graphs Last week, we looked at the Frequency Distribution
Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox
 v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox Learn how to design inlet grates, detention basins, channels, and riprap using the FHWA Hydraulic Toolbox
v. 9.1 WMS 9.1 Tutorial Hydraulics and Floodplain Modeling Modeling with the Hydraulic Toolbox Learn how to design inlet grates, detention basins, channels, and riprap using the FHWA Hydraulic Toolbox
Introduction to GeoServer
 Tutorial ID: This tutorial has been developed by BVIEER as part of the IGET web portal intended to provide easy access to geospatial education. This tutorial is released under the Creative Commons license.
Tutorial ID: This tutorial has been developed by BVIEER as part of the IGET web portal intended to provide easy access to geospatial education. This tutorial is released under the Creative Commons license.
Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation
 v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation Techniques Model manmade and natural drainage features Objectives Learn to manipulate the default watershed boundaries by assigning
v. 10.1 WMS 10.1 Tutorial Watershed Modeling Advanced DEM Delineation Techniques Model manmade and natural drainage features Objectives Learn to manipulate the default watershed boundaries by assigning
An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) using ArcGIS 9.2
 An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) using ArcGIS 9.2 by Marcel Fortin, GIS and Map Librarian, University of Toronto Libraries, 2009 gis.maps@utoronto.ca http://www.library.utoronto.ca/maplib/
An Introduction to Geographic Information Systems (GIS) using ArcGIS 9.2 by Marcel Fortin, GIS and Map Librarian, University of Toronto Libraries, 2009 gis.maps@utoronto.ca http://www.library.utoronto.ca/maplib/
Lab - Designing and Implementing a Subnetted IPv4 Addressing Scheme
 Lab - Designing and Implementing a Subnetted IPv4 Addressing Scheme Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G00 NA G01 NA Lo0 Lo1 NA NA S1 VLAN 1
Lab - Designing and Implementing a Subnetted IPv4 Addressing Scheme Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G00 NA G01 NA Lo0 Lo1 NA NA S1 VLAN 1
Adding Existing Source Code in NetBeans CS288, Autumn 2005 Lab 002
 Adding Existing Source Code in NetBeans CS288, Autumn 2005 Lab 002 Purpose This document will show how to incorporate existing source code within a NetBeans project. It will also introduce the concept
Adding Existing Source Code in NetBeans CS288, Autumn 2005 Lab 002 Purpose This document will show how to incorporate existing source code within a NetBeans project. It will also introduce the concept
Stratigraphy Modeling Horizons and Solids
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Stratigraphy Modeling Horizons and Solids Create solids from boreholes using the Horizons Solids tool. Objectives Learn how to construct a set of solid models using the horizon
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial Stratigraphy Modeling Horizons and Solids Create solids from boreholes using the Horizons Solids tool. Objectives Learn how to construct a set of solid models using the horizon
