Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of
|
|
|
- Jasmine Stephens
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt
2 Dr. Michael Eichberg Fachgebiet Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Introduction to Software Engineering Domain Model and
3 Domain Model 3 A Handbook of Software and Systems Engineering Curtis law: [ ] Good designs require deep application knowledge. Albert Endres and Dieter Rombach; Addison Wesley, 2003
4 The Domain Model illustrates noteworthy concepts in a domain. Domain Model =dt. Analysemodell (Konzeptmodell) Domain Model 4 It is the basis for the design of the software The domain model is created during object-oriented analysis to decompose the domain into concepts or objects in the real world The model should identify the set of conceptual classes (The domain model is iteratively completed.) The domain model is also called conceptual model, domain object models or analysis object models.
5 Domain Model 5 Conceptual Classes Conceptual classes are ideas, things or objects in the domain. A conceptual class has a symbol representing the class, an intension and an extension that defines the set of examples to which the conceptual class applies. Domain concepts / conceptual classes are not software objects as e.g. in Java, C# or.net! intension =dt.(hier) Bedeutung extension =dt.(hier) Ausprägung
6 To visualize domain models the UML class diagram notation is used. Visualization of the Domain Model using UML Class Diagrams 6 However, no operations are defined only: domain objects or conceptual classes associations between them and attributes of conceptual classes are shown The result is a conceptual perspective model.
7 A class describes a set of objects with the same semantics, properties and behavior. When used for domain modeling, it is a visualization of a real world concept. UML Class Diagrams 7 Sale Shop Payment...
8 Attributes are logical data values of an object. UML Class Diagrams 8 attributes Sale date / total : Money derived attribute ("/") It is useful to identify those attributes of conceptual classes that are needed to satisfy the information requirements of the current scenarios under development.
9 Attributes are logical data values of an object. UML Class Diagrams 9 Full syntax for an attribute in the UML: visibility name : type multiplicity = default {property string} Math + pi: Real = 3.14 {readonly} Person firstname middlename : [0..1] lastname
10 An association is a relationship between classes. The ends of an association are called roles. Roles optionally have a multiplicity, name and navigability. UML Class Diagrams 10 name multiplicity Payment amount 1 PaysFor! 1 Sale date time association
11 The multiplicity defines how many instances of a class A can be associated with one instance of a class B at any particular moment. multiplicity =dt. Vielheit / Vielfachheit UML Class Diagrams 11 * T zero or more 1..* T one or more 5,10 T exactly 5 or 10
12 Two classes can have multiple associations. UML Class Diagrams 12 multiplicity =dt. Vielheit / Vielfachheit Flight * Flies-from 1 Airport * Flies-to 1
13 Excerpt Of the Domain Model For the POS System 13? Which are noteworthy domain concepts / domain objects?
14 How to create the domain model? Find the conceptual classes Strategies: a. Reuse or modify an existing model explained b. Use a category list in the }following c. Identify noun phrases 2. Draw them as classes in a UML class diagram 3. Add associations and attributes Use the domain vocabulary; e.g. a model for a library should use names like Borrower instead of customer.
15 How to create the domain model? Find the conceptual classes - Strategy: reuse or modify an existing model. 15 Example: existing model for bank accounts and associated entries. {balance = sum(entries.amount)} Acount balance: Quantity 1 0..* Entry amount: Quantity whenchanged: Timepoint A possible source: Analysis Patterns - Reusable Object Models; Martin Fowler; Addison-Wesley, 1997
16 How to create the domain model? Find the conceptual classes - Strategy: use a category list. 16 Business transactions... Conceptual Class Category Classes (for the POS system) Sale, Payment Transaction line items... Product or service related to a transaction or transaction line item. Where is the transaction recorded? Roles of people or organizations related to the transaction; actors in use cases. Place of transactions. Noteworthy events, often with a time or place that need to be remembered. SalesLineItem Item Register Cashier, Customer, Store Store Sale, Payment line item =dt. Einzelposten transaction =dt. Abwicklung / Durchführung; Geschäftsvorfall
17 How to create the domain model? Find the conceptual classes - Strategy: identify noun phrases (linguistic analysis). 17 Identify the nouns and noun phrases in textual descriptions of a domain and consider them as candidate conceptual classes or attributes. A mechanical noun-to-class mapping isn t possible; words in natural languages are ambiguous; i.e. the same noun can mean multiple things and multiple nouns can actually mean the same thing.
18 How to create the domain model? Find the conceptual classes - Strategy: identify noun phrases. Example: Using the Process Sale use case as the source for identification. 18 Process Sale: A customer arrives at a checkout with items to purchase. The cashier uses the POS system to record each item. The system present a running total and line-item details. The customer enters payment information, which the system validates and records. The system updates the inventory. The customer receives a receipt from the system and then leaves the store with the items.
19 How to create the domain model? Find the conceptual classes - Strategy: identify noun phrases. Example: Using the Process Sale use case as the source for identification. 19 Process Sale: A customer arrives at a checkout with items to purchase. The cashier uses the POS system to record each item. The system present a running total and line-item details. The customer enters payment information, which the system validates and records. The system updates the inventory. The customer receives a receipt from the system and then leaves the store with the items.
20 Strategy: identify noun phrases. 20 Process Sale: A customer arrives at a checkout with items to purchase. The cashier uses the POS system to record each item. The system present a running total and line-item details. The customer enters payment information, which the system validates and records. The system updates the inventory. The customer receives a receipt from the system and then leaves the store with the items. Identified candidate conceptual classes: Customer, Item, Cashier, Store, Payment, Sales Line Item, Inventory, Receipt, Sale. Should Receipt be in the domain model?
21 Guidelines when to include a candidate conceptual class that reports Information into the domain model 21 In general, it is not useful since all information is derived or duplicated from other sources. If it has a specific semantics w.r.t. the business, then it should be included. Should Receipt be in the domain model? A receipt is just a report of a sale and a payment...
22 Guidelines when to include a candidate conceptual class that reports information into the domain model 22 Should Receipt be in the domain model? A receipt is just a report of a sale and a payment... Well, it depends. if we just consider the Process Sale use case then receipt should not be part of the domain model; a receipt is just a report if we consider a Handle Return use case then a receipt represents an important concept on its own BTW, how about legal restrictions...? Domain Requirements
23 Guidelines when to include a description class into the domain model 23 A description class contains information that describes something else Examples: a product description records the price, picture and text of an item a flight description contains information about the flight (number) and the source and target destinations.
24 Guidelines when to include a description class into the domain model 24 A description class should be added to the domain mode when: There needs to be a description about an item or service, independent of the current existence of any examples of those items or services Deleting instances of things they describe results in a loss of information that needs to be maintained, but was incorrectly associated with the deleted thing It reduces redundant or duplicated information
25 When should I model something as an attribute or a class? 25 Rule of Thumb: If we do not think of some conceptual class X as a number or text in the real world, X is probably a conceptual class, not an attribute. class attribute Sale date time
26 When should I model something as an attribute or a class? 26 Let s assume that we develop an airline reservation system. Should destination be an attribute of flight, or a conceptual class airport? A destination airport is building at a specific place, it is not just a number or some text. Hence, it should be a conceptual class. How about the name of the airport?
27 When should I add an association to the domain model? 27 Rule of Thumb: Include associations in the domain model for which knowledge of the relationship needs to be preserved for some duration. We are working on the conceptual model; we are not modeling associations at the software level.
28 When should I add an association to the domain model? 28 When an association is among the common associations list: A is a transaction related to another transaction B A is a line item of a transaction B A is a product or service for a transaction B A is a role related to a transaction B A is physical or logical part of B...
29 When should I add an association to the domain model? 29 E.g. the relation between a Sale and a SalesLineItem needs to be remembered However, it is not necessary to store the relation between a Cashier and a ProductDescription that he looks up
30 Name an association based on a ClassName- VerbPhrase-ClassName format where the verb phrase creates a sequence that is readable and meaningful. 30 Good examples: Player Is-on Square Sale Paid-by CashPayment Bad examples: Sale Uses CashPayment (Uses is usually generic and doesn t tell us anything.) Player Has Square (Has is usually generic and doesn t tell us anything)
31 The attributes in a domain model should preferably be primitive data types. 31 Very common data types include: Boolean, Date, Number, Character, String, Address, Color, Phone Number, avoid: recommended: Cashier name currentregister Cashier name Consider modeling quantities as classes to associated units; e.g. the data type of the amount attribute of payment should indicate the currency Register number Use associations to model dependencies between conceptual classes; do not use attributes.
32 Consider defining a new data type class for something that is initially considered a string. 32 If the string is composed of separate sections e.g., phone number, name of person,... Different operations are associated with the string e.g., social security number The string has other attributes The string is a quantity with a unit e.g., money has a unit for currency avoid: recommended: ProductDescription itemid : ItemId ProductDescription 1 1 ItemId id countrycode
33 Excerpt Of the Domain Model For the POS System 33? Which are noteworthy domain concepts / domain objects?
34 Excerpt Of the Domain Model For the POS System 34 Sales LineItem quantity 1..* Contained-in Records-sale-of Item * Stocked-in Sale date time Paid-by Captured-on! 1 Store address name Houses Payment amount 1 Register
35 The domain model serves as a source of inspiration for the design model. Purpose of 35 Domain Model Payment amount 1 1 Sale date time inspiration / basis Design Model Payment amount: Money getbalance():money 1 1 Sale date: Date starttime: Time gettotal(): Money By using the domain model as a direct inspiration for software classes the representational gap between the domain concepts and the program is (relatively) small.
Domain Model and Domain Modeling
 Dr. Michael Eichberg Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Software Engineering Domain Model and Domain Modeling Resources: Craig Larman; Applying UML and
Dr. Michael Eichberg Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Software Engineering Domain Model and Domain Modeling Resources: Craig Larman; Applying UML and
Domain Modeling: Associations and Attributes
 Domain Modeling: Associations and Attributes CSSE 574: Week 2, Part Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (82) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu Q Description Classes A description class
Domain Modeling: Associations and Attributes CSSE 574: Week 2, Part Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (82) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu Q Description Classes A description class
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of
 Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Dr.
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Dr.
Domain Modeling. CSSE 574: Week 1, Part 3. Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) Cell (937)
 Domain Modeling CSSE 574: Week 1, Part 3 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu s g Where we re going Sample UP Artifact Relationships date...
Domain Modeling CSSE 574: Week 1, Part 3 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu s g Where we re going Sample UP Artifact Relationships date...
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of
 Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt What
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt What
CTIS 359 Principles of Software Engineering SOFTWARE DESIGN OO(A)D
 CTIS 359 Principles of Software Engineering SOFTWARE DESIGN OO(A)D Today s Objectives To explain the basic concepts of OO(A)D To describe some best practices regarding to OO(A)D What is NOT UML? The UML
CTIS 359 Principles of Software Engineering SOFTWARE DESIGN OO(A)D Today s Objectives To explain the basic concepts of OO(A)D To describe some best practices regarding to OO(A)D What is NOT UML? The UML
Goal: build an object-oriented model of the realworld system (or imaginary world) Slicing the soup: OOA vs. OOD
 Domain analysis Goal: build an object-oriented model of the realworld system (or imaginary world) Slicing the soup: OOA vs. OOD OOA concerned with what, not how OOA activities focus on the domain layer
Domain analysis Goal: build an object-oriented model of the realworld system (or imaginary world) Slicing the soup: OOA vs. OOD OOA concerned with what, not how OOA activities focus on the domain layer
Object-Oriented Functional Analysis and Design for POS Example
 Object-Oriented Functional Analysis and Design for POS Example Focus in Analysis, Design, Implementation Analysis Investigation to the problem in problem domain Design Logical solution(model) for implementation
Object-Oriented Functional Analysis and Design for POS Example Focus in Analysis, Design, Implementation Analysis Investigation to the problem in problem domain Design Logical solution(model) for implementation
Constantinos Constantinides Computer Science and Software Engineering Concordia University Montreal, Canada
 1 Disclaimer: These slides are based on the 2 nd edition of Applying UML and Patterns; An introduction to OOAD and the Unified process by Craig Larman (2002). I take responsibility for any errors. Constantinos
1 Disclaimer: These slides are based on the 2 nd edition of Applying UML and Patterns; An introduction to OOAD and the Unified process by Craig Larman (2002). I take responsibility for any errors. Constantinos
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of
 Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Dr.
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Dr.
Information Expert (or Expert)
 Page 2 Page 3 Pattern or Principle? Information Expert (or Expert) Class Responsibility Sale Knows Sale total SalesLineItem Knows line item total ProductDescription Knows product price The GRASP patterns
Page 2 Page 3 Pattern or Principle? Information Expert (or Expert) Class Responsibility Sale Knows Sale total SalesLineItem Knows line item total ProductDescription Knows product price The GRASP patterns
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of
 Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Dr.
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Dr.
Modeling Dynamic Behavior
 Dr. Michael Eichberg Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Software Engineering Modeling Dynamic Behavior The following slides use material from: Craig Larman;
Dr. Michael Eichberg Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Software Engineering Modeling Dynamic Behavior The following slides use material from: Craig Larman;
Äriprotsesside modelleerimine ja automatiseerimine Loeng 7 Valdkonna mudel
 Äriprotsesside modelleerimine ja automatiseerimine Loeng 7 Valdkonna mudel Enn Õunapuu enn.ounapuu@ttu.ee What is a domain model? A domain model captures the most important types of objects in the context
Äriprotsesside modelleerimine ja automatiseerimine Loeng 7 Valdkonna mudel Enn Õunapuu enn.ounapuu@ttu.ee What is a domain model? A domain model captures the most important types of objects in the context
COMP 354: INTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE ENGINEERING
 COMP 354: INTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Introduction to UML d_sinnig@cs.concordia.ca Department for Computer Science and Software Engineering 28-May-14 Unified Modeling Language Structural Diagrams
COMP 354: INTRODUCTION TO SOFTWARE ENGINEERING Introduction to UML d_sinnig@cs.concordia.ca Department for Computer Science and Software Engineering 28-May-14 Unified Modeling Language Structural Diagrams
On to Object-oriented Design
 Dr. Michael Eichberg Software Technology Group Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Introduction to Software Engineering On to Object-oriented Design Object-oriented Design 2
Dr. Michael Eichberg Software Technology Group Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Introduction to Software Engineering On to Object-oriented Design Object-oriented Design 2
Modeling Dynamic Behavior
 Dr. Michael Eichberg Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Software Engineering Modeling Dynamic Behavior The following slides use material from: Craig Larman;
Dr. Michael Eichberg Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Software Engineering Modeling Dynamic Behavior The following slides use material from: Craig Larman;
Domain Modeling- 2. Generalization
 Generalization Domain Modeling- 2 Conceptual superclasses and subclasses When to create a subclass? A superclass? Abstract classes Modeling state changes Operation contracts Attaching pre- /post-conditions
Generalization Domain Modeling- 2 Conceptual superclasses and subclasses When to create a subclass? A superclass? Abstract classes Modeling state changes Operation contracts Attaching pre- /post-conditions
System Analysis & design
 Assiut University Faculty of Computers and Information System Analysis & design Year 2 Academic Year 2014/ 2015 Term (2) 5 A PICTURE IS WORTH A 1,000 WORDS A process model is a graphical way of representing
Assiut University Faculty of Computers and Information System Analysis & design Year 2 Academic Year 2014/ 2015 Term (2) 5 A PICTURE IS WORTH A 1,000 WORDS A process model is a graphical way of representing
ADVANCED SOFTWARE DESIGN LECTURE 7 GRASP
 ADVANCED SOFTWARE DESIGN LECTURE 7 GRASP Dave Clarke 1 TODAY S LECTURE We will discuss 7 of the GRASP design patterns cohesion and coupling were covered earlier. These provide principles for evaluating
ADVANCED SOFTWARE DESIGN LECTURE 7 GRASP Dave Clarke 1 TODAY S LECTURE We will discuss 7 of the GRASP design patterns cohesion and coupling were covered earlier. These provide principles for evaluating
Object-Oriented Software Engineering Practical Software Development using UML and Java
 Object-Oriented Software Engineering Practical Software Development using UML and Java Chapter 5: Modelling with Classes Lecture 5 5.1 What is UML? The Unified Modelling Language is a standard graphical
Object-Oriented Software Engineering Practical Software Development using UML and Java Chapter 5: Modelling with Classes Lecture 5 5.1 What is UML? The Unified Modelling Language is a standard graphical
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency
 Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Designing (sub-) systems A formal design process Charlie Garrod Michael Hilton School of Computer Science 1 Administrivia Optional
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Designing (sub-) systems A formal design process Charlie Garrod Michael Hilton School of Computer Science 1 Administrivia Optional
Software Modeling & Analysis
 Software Modeling & Analysis OOPT (Object Oriented Process with Trace) Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr What is OOPT? OOPT (Object Oriented Process with Trace) A software process based on RUP Revision
Software Modeling & Analysis OOPT (Object Oriented Process with Trace) Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr What is OOPT? OOPT (Object Oriented Process with Trace) A software process based on RUP Revision
A - 1. CS 494 Object-Oriented Analysis & Design. UML Class Models. Overview. Class Model Perspectives (cont d) Developing Class Models
 CS 494 Object-Oriented Analysis & Design UML Class Models Overview How class models are used? Perspectives Classes: attributes and operations Associations Multiplicity Generalization and Inheritance Aggregation
CS 494 Object-Oriented Analysis & Design UML Class Models Overview How class models are used? Perspectives Classes: attributes and operations Associations Multiplicity Generalization and Inheritance Aggregation
Responsibilities. Using several specific design principles to guide OO design decisions.
 Designing Objects with Responsibilities Using several specific design principles to guide OO design decisions. Challenge Old-school advice on OOD After identifying i your requirements and creating a domain
Designing Objects with Responsibilities Using several specific design principles to guide OO design decisions. Challenge Old-school advice on OOD After identifying i your requirements and creating a domain
References: Applying UML and patterns Craig Larman
 References: Applying UML and patterns Craig Larman 1 2 What are patterns? Principles and solutions codified in a structured format describing a problem and a solution A named problem/solution pair that
References: Applying UML and patterns Craig Larman 1 2 What are patterns? Principles and solutions codified in a structured format describing a problem and a solution A named problem/solution pair that
Assigning Responsibilities (Patterns of Responsibility Assignment Principles: GRASP)
 Subsystem design basics Assigning Responsibilities (Patterns of Responsibility Assignment Principles: GRASP) Dept. of Computer Science Baylor University Focus on modeling how subsystems accomplish goals
Subsystem design basics Assigning Responsibilities (Patterns of Responsibility Assignment Principles: GRASP) Dept. of Computer Science Baylor University Focus on modeling how subsystems accomplish goals
SE 1: Software Requirements Specification and Analysis
 SE 1: Software Requirements Specification and Analysis Lecture 9: UML Class (Concept), Object, Communication Diagrams Nancy Day, Davor Svetinović http://www.student.cs.uwaterloo.ca/ cs445/winter2006 uw.cs.cs445
SE 1: Software Requirements Specification and Analysis Lecture 9: UML Class (Concept), Object, Communication Diagrams Nancy Day, Davor Svetinović http://www.student.cs.uwaterloo.ca/ cs445/winter2006 uw.cs.cs445
Class Diagrams in Analysis
 3.2 Subject/Topic/Focus: Introduction to Classes Summary: Conceptual Modeling Notation: Classes Associations: Multiplicity, Roles, Aggregation, Composition Generalization Objects Analysis Process Literature:
3.2 Subject/Topic/Focus: Introduction to Classes Summary: Conceptual Modeling Notation: Classes Associations: Multiplicity, Roles, Aggregation, Composition Generalization Objects Analysis Process Literature:
Object Oriented Software Development CIS Today: Object Oriented Analysis
 Object Oriented Software Development CIS 50-3 Marc Conrad D104 (Park Square Building) Marc.Conrad@luton.ac.uk Today: Object Oriented Analysis The most single important ability in object oriented analysis
Object Oriented Software Development CIS 50-3 Marc Conrad D104 (Park Square Building) Marc.Conrad@luton.ac.uk Today: Object Oriented Analysis The most single important ability in object oriented analysis
On to Object-oriented Design
 Dr. Michael Eichberg Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Software Engineering On to Object-oriented Design Object-oriented Design 2 A popular way of thinking
Dr. Michael Eichberg Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Software Engineering On to Object-oriented Design Object-oriented Design 2 A popular way of thinking
COMP 6471 Software Design Methodologies
 COMP 6471 Software Design Methodologies Fall 2011 Dr Greg Butler http://www.cs.concordia.ca/~gregb/home/comp6471-fall2011.html Page 2 Sample UP Artifact Relationships Domain Model Context Business Modeling
COMP 6471 Software Design Methodologies Fall 2011 Dr Greg Butler http://www.cs.concordia.ca/~gregb/home/comp6471-fall2011.html Page 2 Sample UP Artifact Relationships Domain Model Context Business Modeling
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of
 Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Dr.
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Dr.
OO Design2. Design Artifacts
 OO Design2 POS example - revisited LAR Ch 8 has entire POS design explained READ THIS CHAPTER and ASK Q s in class Design class diagrams Kinds of visibility of objects to one another Navigability of associations
OO Design2 POS example - revisited LAR Ch 8 has entire POS design explained READ THIS CHAPTER and ASK Q s in class Design class diagrams Kinds of visibility of objects to one another Navigability of associations
OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN SYLLABUS
 OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN SYLLABUS CS6502 - OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN L T P C 3 0 0 3 UNIT I- UML DIAGRAMS Introduction to OOAD Unified Process - UML diagrams Use Case Class Diagrams
OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN SYLLABUS CS6502 - OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN L T P C 3 0 0 3 UNIT I- UML DIAGRAMS Introduction to OOAD Unified Process - UML diagrams Use Case Class Diagrams
Software Engineering Prof.N.L.Sarda IIT Bombay. Lecture-11 Data Modelling- ER diagrams, Mapping to relational model (Part -II)
 Software Engineering Prof.N.L.Sarda IIT Bombay Lecture-11 Data Modelling- ER diagrams, Mapping to relational model (Part -II) We will continue our discussion on process modeling. In the previous lecture
Software Engineering Prof.N.L.Sarda IIT Bombay Lecture-11 Data Modelling- ER diagrams, Mapping to relational model (Part -II) We will continue our discussion on process modeling. In the previous lecture
MSO Lecture 3. Wouter Swierstra. September 14, 2015
 1 MSO Lecture 3 Wouter Swierstra September 14, 2015 2 Haven t found a lab partner yet? Come talk to me in the break. 3 LAST LECTURE How can I manage the process of constructing complex software? How do
1 MSO Lecture 3 Wouter Swierstra September 14, 2015 2 Haven t found a lab partner yet? Come talk to me in the break. 3 LAST LECTURE How can I manage the process of constructing complex software? How do
IMS1002/CSE1205 Lectures 1
 IMS1002/CSE1205 Systems Analysis and Design Lecture 2 & 3 Introduction to Data Modelling Entity Relationship Modelling Data Modelling Focus on the information aspects of the organisation In a database
IMS1002/CSE1205 Systems Analysis and Design Lecture 2 & 3 Introduction to Data Modelling Entity Relationship Modelling Data Modelling Focus on the information aspects of the organisation In a database
CS6502-OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN Two Marks Question with Answers Unit-I Introduction to OOAD
 CS6502-OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN Two Marks Question with Answers Unit-I Introduction to OOAD 1. What is Object-Oriented Analysis? Nov/Dec 2016 During object-oriented analysis there is an emphasis
CS6502-OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN Two Marks Question with Answers Unit-I Introduction to OOAD 1. What is Object-Oriented Analysis? Nov/Dec 2016 During object-oriented analysis there is an emphasis
System Sequence Diagrams. Based on Craig Larman, Chapter 10 and Anuradha Dharani s notes
 System Sequence Diagrams Based on Craig Larman, Chapter 10 and Anuradha Dharani s notes Dynamic behaviors Class diagrams represent static relationships. Why? What about modeling dynamic behavior? Interaction
System Sequence Diagrams Based on Craig Larman, Chapter 10 and Anuradha Dharani s notes Dynamic behaviors Class diagrams represent static relationships. Why? What about modeling dynamic behavior? Interaction
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design and Concurrency. Just enough UML. toad
 Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design and Concurrency Just enough UML 15-214 toad Christian Kästner Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science With slides from Klaus Ostermann Learning Goals
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design and Concurrency Just enough UML 15-214 toad Christian Kästner Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science With slides from Klaus Ostermann Learning Goals
VEL TECH HIGH TECH Dr. RANGARAJAN Dr. SAKUNTHALA ENGINEERING COLLEGE UNIT 1 UML DIAGRAMS
 UNIT 1 UML DIAGRAMS Introduction to OOAD Unified Process - UML diagrams Use Case Class Diagrams Interaction Diagrams State Diagrams Activity Diagrams Package, component and Deployment Diagrams. INTRODUCTION
UNIT 1 UML DIAGRAMS Introduction to OOAD Unified Process - UML diagrams Use Case Class Diagrams Interaction Diagrams State Diagrams Activity Diagrams Package, component and Deployment Diagrams. INTRODUCTION
user.book Page 45 Friday, April 8, :05 AM Part 2 BASIC STRUCTURAL MODELING
 user.book Page 45 Friday, April 8, 2005 10:05 AM Part 2 BASIC STRUCTURAL MODELING user.book Page 46 Friday, April 8, 2005 10:05 AM user.book Page 47 Friday, April 8, 2005 10:05 AM Chapter 4 CLASSES In
user.book Page 45 Friday, April 8, 2005 10:05 AM Part 2 BASIC STRUCTURAL MODELING user.book Page 46 Friday, April 8, 2005 10:05 AM user.book Page 47 Friday, April 8, 2005 10:05 AM Chapter 4 CLASSES In
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency
 Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency A formal design process Josh Bloch Charlie Garrod Darya Melicher 1 Administrivia Homework 2 feedback in your GitHub repository Homework
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency A formal design process Josh Bloch Charlie Garrod Darya Melicher 1 Administrivia Homework 2 feedback in your GitHub repository Homework
UML Modeling I. Instructor: Yongjie Zheng September 3, CS 490MT/5555 Software Methods and Tools
 UML Modeling I Instructor: Yongjie Zheng September 3, 2015 CS 490MT/5555 Software Methods and Tools Object-Oriented Design: Topics & Skills Rational Unified Process Unified Modeling Languages (UML) Provide
UML Modeling I Instructor: Yongjie Zheng September 3, 2015 CS 490MT/5555 Software Methods and Tools Object-Oriented Design: Topics & Skills Rational Unified Process Unified Modeling Languages (UML) Provide
S T R U C T U R A L M O D E L I N G ( M O D E L I N G A S Y S T E M ' S L O G I C A L S T R U C T U R E U S I N G C L A S S E S A N D C L A S S D I A
 S T R U C T U R A L M O D E L I N G ( M O D E L I N G A S Y S T E M ' S L O G I C A L S T R U C T U R E U S I N G C L A S S E S A N D C L A S S D I A G R A M S ) WHAT IS CLASS DIAGRAM? A class diagram
S T R U C T U R A L M O D E L I N G ( M O D E L I N G A S Y S T E M ' S L O G I C A L S T R U C T U R E U S I N G C L A S S E S A N D C L A S S D I A G R A M S ) WHAT IS CLASS DIAGRAM? A class diagram
Lesson 11. W.C.Udwela Department of Mathematics & Computer Science
 Lesson 11 INTRODUCING UML W.C.Udwela Department of Mathematics & Computer Science Why we model? Central part of all the activities We build model to Communicate Visualize and control Better understand
Lesson 11 INTRODUCING UML W.C.Udwela Department of Mathematics & Computer Science Why we model? Central part of all the activities We build model to Communicate Visualize and control Better understand
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency. Assigning Responsibilities to Objects. toad. Jonathan Aldrich Charlie Garrod
 Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Assigning Responsibilities to Objects toad Fall 2014 Jonathan Aldrich Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science Key concepts from Thursday
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Assigning Responsibilities to Objects toad Fall 2014 Jonathan Aldrich Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science Key concepts from Thursday
Object-Oriented Software Engineering Practical Software Development using UML and Java. Chapter 5: Modelling with Classes
 Object-Oriented Software Engineering Practical Software Development using UML and Java Chapter 5: Modelling with Classes 5.1 What is UML? The Unified Modelling Language is a standard graphical language
Object-Oriented Software Engineering Practical Software Development using UML and Java Chapter 5: Modelling with Classes 5.1 What is UML? The Unified Modelling Language is a standard graphical language
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design and Concurrency. Object-Oriented Design: Assigning Responsibilities.
 Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design and Concurrency 15-214 toad Object-Oriented Design: Assigning Responsibilities Christian Kästner Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science With slides
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design and Concurrency 15-214 toad Object-Oriented Design: Assigning Responsibilities Christian Kästner Charlie Garrod School of Computer Science With slides
Object-Oriented Design. Module UFC016QM. and Programming. Objects and Classes. O-O Design Unit 2: Faculty of Computing, Engineering
 Module UFC016QM Object-Oriented Design and Programming O-O Design Unit 2: Objects and Classes Faculty of Computing, Engineering and Mathematical Sciences Schedule Quick recap on Use Case diagrams UWE Flix
Module UFC016QM Object-Oriented Design and Programming O-O Design Unit 2: Objects and Classes Faculty of Computing, Engineering and Mathematical Sciences Schedule Quick recap on Use Case diagrams UWE Flix
Operations Contracts and Preliminaries on Design
 Operations Contracts and Preliminaries on Design CSSE 574: Week 2, Part 3 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu We are at System Operation Contracts
Operations Contracts and Preliminaries on Design CSSE 574: Week 2, Part 3 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu We are at System Operation Contracts
Chapter 10. Object-Oriented Analysis and Modeling Using the UML. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 Chapter 10 Object-Oriented Analysis and Modeling Using the UML McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 10-2 Define object modeling and explain
Chapter 10 Object-Oriented Analysis and Modeling Using the UML McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2007 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 10-2 Define object modeling and explain
Software Modeling & Analysis
 Software Modeling & Analysis KUPE (Konkuk Unified Process for Education) With Case Study -OOPT (Object Oriented Process with Trace) Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr What is KUPE? KUPE (Konkuk Unified
Software Modeling & Analysis KUPE (Konkuk Unified Process for Education) With Case Study -OOPT (Object Oriented Process with Trace) Lecturer: JUNBEOM YOO jbyoo@konkuk.ac.kr What is KUPE? KUPE (Konkuk Unified
Premium POS Pizza Order Entry Module. Introduction and Tutorial
 Premium POS Pizza Order Entry Module Introduction and Tutorial Overview The premium POS Pizza module is a replacement for the standard order-entry module. The standard module will still continue to be
Premium POS Pizza Order Entry Module Introduction and Tutorial Overview The premium POS Pizza module is a replacement for the standard order-entry module. The standard module will still continue to be
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency
 Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Designing (sub-) systems Responsibility assignment Charlie Garrod Michael Hilton School of Computer Science 1 Administrivia Reading
Principles of Software Construction: Objects, Design, and Concurrency Designing (sub-) systems Responsibility assignment Charlie Garrod Michael Hilton School of Computer Science 1 Administrivia Reading
Object-Oriented Analysis and Design
 Analysis and Design To develop an application, it is necessary a description of the problem and requirements: what the problem is about and what a system must do high-level and detailed descriptions of
Analysis and Design To develop an application, it is necessary a description of the problem and requirements: what the problem is about and what a system must do high-level and detailed descriptions of
Process Modelling. Data flow Diagrams. Process Modelling Data Flow Diagrams. CSE Information Systems 1
 CSE104 - Information s 1 Process Modelling Data Flow Diagrams Process Modelling Process modelling aims to graphically represent the processes which capture, manipulate, store and distribute data. data
CSE104 - Information s 1 Process Modelling Data Flow Diagrams Process Modelling Process modelling aims to graphically represent the processes which capture, manipulate, store and distribute data. data
Final Exam CISC 475/675 Fall 2004
 True or False [2 pts each]: Final Exam CISC 475/675 Fall 2004 1. (True/False) All software development processes contain at least separate planning, testing, and documentation phases. 2. (True/False) The
True or False [2 pts each]: Final Exam CISC 475/675 Fall 2004 1. (True/False) All software development processes contain at least separate planning, testing, and documentation phases. 2. (True/False) The
A Conceptual Model of the UML
 CONTENT A Conceptual Model of the UML Building Blocks of the UML 1. Things [1.1] Structural Things (1.1.1) Class (1.1.2) Interface (1.1.3) Collaboration: (1.1.4) Use case (1.1.5) Components: (1.1.6) Node:
CONTENT A Conceptual Model of the UML Building Blocks of the UML 1. Things [1.1] Structural Things (1.1.1) Class (1.1.2) Interface (1.1.3) Collaboration: (1.1.4) Use case (1.1.5) Components: (1.1.6) Node:
Lecture 8: Use Case -Driven Design. Where UML fits in
 Lecture 8: Use Case -Driven Design The Role of UML in the Software Process E.g. ICONIX Domain Models Use Cases 2008 Steve Easterbrook. This presentation is available free for non-commercial use with attribution
Lecture 8: Use Case -Driven Design The Role of UML in the Software Process E.g. ICONIX Domain Models Use Cases 2008 Steve Easterbrook. This presentation is available free for non-commercial use with attribution
17. GRASP: Designing Objects with Responsibilities
 17. GRASP: Designing Objects with Responsibilities Objectives Learn to apply five of the GRASP principles or patterns for OOD. Dr. Ziad Kobti School of Computer Science University of Windsor Understanding
17. GRASP: Designing Objects with Responsibilities Objectives Learn to apply five of the GRASP principles or patterns for OOD. Dr. Ziad Kobti School of Computer Science University of Windsor Understanding
System Analysis and Design. Data Flow Diagram. System Analysis and Design
 Data Flow Diagram 1 Data Flow diagram The dataflow diagram is a modeling tool that allows us to picture a system as a network of functional processes, connected to one another by pipelines and holding
Data Flow Diagram 1 Data Flow diagram The dataflow diagram is a modeling tool that allows us to picture a system as a network of functional processes, connected to one another by pipelines and holding
ROEVER ENGINEERING COLLEGE DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY CS2353-OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN. Unit-I. Introduction to OOAD
 ROEVER ENGINEERING COLLEGE CS2353-OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN 1. What is Object-Oriented Analysis? Unit-I Introduction to OOAD PART-A During object-oriented analysis there is an emphasis on finding
ROEVER ENGINEERING COLLEGE CS2353-OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN 1. What is Object-Oriented Analysis? Unit-I Introduction to OOAD PART-A During object-oriented analysis there is an emphasis on finding
Mapping Designs to Code
 Mapping Designs to Code Creating Class Definitions from DCDs public class SalesLineItem private int quantity; private ProductDescription description ; public SalesLineItem(ProductDescription desc, int
Mapping Designs to Code Creating Class Definitions from DCDs public class SalesLineItem private int quantity; private ProductDescription description ; public SalesLineItem(ProductDescription desc, int
Object Design II: Design Patterns
 Object-Oriented Software Engineering Using UML, Patterns, and Java Object Design II: Design Patterns Bernd Bruegge Applied Software Engineering Technische Universitaet Muenchen A Game: Get-15 The game
Object-Oriented Software Engineering Using UML, Patterns, and Java Object Design II: Design Patterns Bernd Bruegge Applied Software Engineering Technische Universitaet Muenchen A Game: Get-15 The game
22/09/2012 INFO2110. Copyright Warning. Revision of class diagram. Overview. Purpose of class diagram. Generalization Relationship
 22/09/202 INFO20 Copyright Warning System Analysis and Modelling Semester 2, 202 Lecture 8, Structural Modelling (II) COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 969 WARNING This material has been
22/09/202 INFO20 Copyright Warning System Analysis and Modelling Semester 2, 202 Lecture 8, Structural Modelling (II) COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 969 WARNING This material has been
What is a Model? Copyright hebley & Associates
 Modeling Overview... as we know, there are known knowns; there are things we know we know. We also know there are known unknowns; that is to say we know there are some things we do not know. But there
Modeling Overview... as we know, there are known knowns; there are things we know we know. We also know there are known unknowns; that is to say we know there are some things we do not know. But there
COMP 6471 Software Design Methodologies
 COMP 647 Software Design Methodologies Fall 20 Dr Greg Butler http://www.cs.concordia.ca/~gregb/home/comp647-fall20.html Course Introduction Course People Course Components What the course is What the
COMP 647 Software Design Methodologies Fall 20 Dr Greg Butler http://www.cs.concordia.ca/~gregb/home/comp647-fall20.html Course Introduction Course People Course Components What the course is What the
Object Analysis & Design in the textbook. Introduction to GRASP: Assigning Responsibilities to Objects. Responsibility-Driven Design
 Object Analysis & Design in the textbook Chapter 2 Object Oriented Design Process Introduction to GRASP: Assigning Responsibilities to Objects CS 4354 Summer II 2016 Jill Seaman Much of the material in
Object Analysis & Design in the textbook Chapter 2 Object Oriented Design Process Introduction to GRASP: Assigning Responsibilities to Objects CS 4354 Summer II 2016 Jill Seaman Much of the material in
THE UNIVERSITY OF THE WEST INDIES. Answer ALL questions. Marks for each question are given in the margin. This exam is worth 60 marks
 THE UNIVERSITY OF THE WEST INDIES EXAMINATIONS OF MAY 2004 Code and Name of Course: EE29B Introduction to Software Engineering Paper: Date and Time: Duration: Three Hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: This
THE UNIVERSITY OF THE WEST INDIES EXAMINATIONS OF MAY 2004 Code and Name of Course: EE29B Introduction to Software Engineering Paper: Date and Time: Duration: Three Hours INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES: This
SIF8035. Events and System Requirements
 SIF8035 Lecture 4 DFD and PrM Events and System Requirements Events Occurrences at a specific time and place Trigger all system processing Requirement definition Determine relevant events External events
SIF8035 Lecture 4 DFD and PrM Events and System Requirements Events Occurrences at a specific time and place Trigger all system processing Requirement definition Determine relevant events External events
Software Engineering I (02161)
 Software Engineering I (02161) Week 2 Assoc. Prof. Hubert Baumeister DTU Compute Technical University of Denmark Spring 2017 Contents What are software requirements? Requirements Engineering Process Domain
Software Engineering I (02161) Week 2 Assoc. Prof. Hubert Baumeister DTU Compute Technical University of Denmark Spring 2017 Contents What are software requirements? Requirements Engineering Process Domain
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING CS2353-OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN. Unit-I. Introduction to OOAD
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING CS2353-OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN 1. What is Object-Oriented Analysis? Unit-I Introduction to OOAD PART-A (UML Notations has to be used wherever necessary)
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING CS2353-OBJECT ORIENTED ANALYSIS AND DESIGN 1. What is Object-Oriented Analysis? Unit-I Introduction to OOAD PART-A (UML Notations has to be used wherever necessary)
CSSE 374: UML Activity Diagrams. Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812)
 CSSE 374: UML Activity Diagrams Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Patterns, Tradeoffs Identify criteria for the design of a software
CSSE 374: UML Activity Diagrams Shawn Bohner Office: Moench Room F212 Phone: (812) 877-8685 Email: bohner@rose-hulman.edu Learning Outcomes: Patterns, Tradeoffs Identify criteria for the design of a software
Domain-Driven Development with Ontologies and Aspects
 Domain-Driven Development with Ontologies and Aspects Submitted for Domain-Specific Modeling workshop at OOPSLA 2005 Latest version of this paper can be downloaded from http://phruby.com Pavel Hruby Microsoft
Domain-Driven Development with Ontologies and Aspects Submitted for Domain-Specific Modeling workshop at OOPSLA 2005 Latest version of this paper can be downloaded from http://phruby.com Pavel Hruby Microsoft
Design First ITS Instructor Tool
 Design First ITS Instructor Tool The Instructor Tool allows instructors to enter problems into Design First ITS through a process that creates a solution for a textual problem description and allows for
Design First ITS Instructor Tool The Instructor Tool allows instructors to enter problems into Design First ITS through a process that creates a solution for a textual problem description and allows for
On to Iteration 3, and Activity Diagrams CSSE 574: Session 6, Part 1
 On to Iteration 3, and Activity Diagrams CSSE 574: Session 6, Part 1 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu On to Iteration 3: NextGen POS Failover
On to Iteration 3, and Activity Diagrams CSSE 574: Session 6, Part 1 Steve Chenoweth Phone: Office (812) 877-8974 Cell (937) 657-3885 Email: chenowet@rose-hulman.edu On to Iteration 3: NextGen POS Failover
Domain Analysis. SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering. Department of Software Engineering Rochester Institute of Technology.
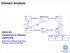 Domain Analysis Die 2 played with Monopoly Game played on Board Count 2 takes turn defines a using location on SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Player 2..8 represents Piece Character 0..8
Domain Analysis Die 2 played with Monopoly Game played on Board Count 2 takes turn defines a using location on SWEN-261 Introduction to Software Engineering Player 2..8 represents Piece Character 0..8
21. Document Component Design
 Page 1 of 17 1. Plan for Today's Lecture Methods for identifying aggregate components 21. Document Component Design Bob Glushko (glushko@sims.berkeley.edu) Document Engineering (IS 243) - 11 April 2005
Page 1 of 17 1. Plan for Today's Lecture Methods for identifying aggregate components 21. Document Component Design Bob Glushko (glushko@sims.berkeley.edu) Document Engineering (IS 243) - 11 April 2005
The Zachman Framework
 member of The Zachman Framework Introduction to Business-IT Alignment and Enterprise Architecture 1 Zachman Framework Regarded the origin of enterprise architecture frameworks (originally called "Framework
member of The Zachman Framework Introduction to Business-IT Alignment and Enterprise Architecture 1 Zachman Framework Regarded the origin of enterprise architecture frameworks (originally called "Framework
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of
 Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Dr.
Introduction to Software Engineering (2+1 SWS) Winter Term 2009 / 2010 Dr. Michael Eichberg Vertretungsprofessur Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Dr.
INTRODUCTION TO UNIFIED MODELING MODEL (UML) & DFD. Slides by: Shree Jaswal
 INTRODUCTION TO UNIFIED MODELING MODEL (UML) & DFD Slides by: Shree Jaswal What is UML? 2 It is a standard graphical language for modeling object oriented software. It was developed in mid 90 s by collaborative
INTRODUCTION TO UNIFIED MODELING MODEL (UML) & DFD Slides by: Shree Jaswal What is UML? 2 It is a standard graphical language for modeling object oriented software. It was developed in mid 90 s by collaborative
MIS2502: Data Analytics Relational Data Modeling - 1. JaeHwuen Jung
 MIS2502: Data Analytics Relational Data Modeling - 1 JaeHwuen Jung jaejung@temple.edu http://community.mis.temple.edu/jaejung Where we are Now we re here Data entry Transactional Database Data extraction
MIS2502: Data Analytics Relational Data Modeling - 1 JaeHwuen Jung jaejung@temple.edu http://community.mis.temple.edu/jaejung Where we are Now we re here Data entry Transactional Database Data extraction
Interaction Modelling: Use Cases
 Interaction Modelling: Use Cases Fabrizio Maria Maggi Institute of Computer Science (these slides are derived from the book Object-oriented modeling and design with UML ) Interaction Modelling: INPUT 1
Interaction Modelling: Use Cases Fabrizio Maria Maggi Institute of Computer Science (these slides are derived from the book Object-oriented modeling and design with UML ) Interaction Modelling: INPUT 1
Introduction to UML. (Unified Modeling Language)
 Introduction to UML (Unified Modeling Language) What Is the UML? UML stands for Unified Modeling Language. UML is a family of graphical notations that help in describing and designing software systems
Introduction to UML (Unified Modeling Language) What Is the UML? UML stands for Unified Modeling Language. UML is a family of graphical notations that help in describing and designing software systems
MIS2502: Data Analytics Relational Data Modeling. Jing Gong
 MIS2502: Data Analytics Relational Data Modeling Jing Gong gong@temple.edu http://community.mis.temple.edu/gong Where we are Now we re here Data entry Transactional Database Data extraction Analytical
MIS2502: Data Analytics Relational Data Modeling Jing Gong gong@temple.edu http://community.mis.temple.edu/gong Where we are Now we re here Data entry Transactional Database Data extraction Analytical
Information Technology Audit & Cyber Security
 Information Technology Audit & Cyber Security Structured Data Requirements Systems & Infrastructure Lifecycle Management with E-R LEARNING OBJECTIVES Explain the role of conceptual data modeling in the
Information Technology Audit & Cyber Security Structured Data Requirements Systems & Infrastructure Lifecycle Management with E-R LEARNING OBJECTIVES Explain the role of conceptual data modeling in the
Topics. Overview- The UML Functional Model. Structural Model. Behavioral Models. Use Case Diagram (essential and system)
 Topics Overview- The UML Functional Model Use Case Diagram (essential and system) Structural Model Class/object, Component and Deployment Diagram Behavioral Models Activity, State chart, sequence /collaboration
Topics Overview- The UML Functional Model Use Case Diagram (essential and system) Structural Model Class/object, Component and Deployment Diagram Behavioral Models Activity, State chart, sequence /collaboration
User Guide. Document Version: 1.0. Solution Version: 365_102017_3_4
 User Guide Document Version: 1.0 Solution Version: 365_102017_3_4 Table of Contents How to Install Purchase Manager in your Dynamics 365?... 3 How to Configure Purchase Manager Security Roles in your Dynamics
User Guide Document Version: 1.0 Solution Version: 365_102017_3_4 Table of Contents How to Install Purchase Manager in your Dynamics 365?... 3 How to Configure Purchase Manager Security Roles in your Dynamics
MIS2502: Data Analytics Relational Data Modeling. Jing Gong
 MIS2502: Data Analytics Relational Data Modeling Jing Gong gong@temple.edu http://community.mis.temple.edu/gong Where we are Now we re here Data entry Transactional Database Data extraction Analytical
MIS2502: Data Analytics Relational Data Modeling Jing Gong gong@temple.edu http://community.mis.temple.edu/gong Where we are Now we re here Data entry Transactional Database Data extraction Analytical
From Analysis to Design. LTOOD/OOAD Verified Software Systems
 From Analysis to Design 1 Use Cases: Notation Overview Actor Use case System X System boundary UCBase «extend» UCExt Actor A UCVar1 UCVar2 Extending case Generalization «include» Actor B UCIncl Included
From Analysis to Design 1 Use Cases: Notation Overview Actor Use case System X System boundary UCBase «extend» UCExt Actor A UCVar1 UCVar2 Extending case Generalization «include» Actor B UCIncl Included
Assigning Responsibilities by Larman
 Assigning Responsibilities by Larman Core design activity: The identification of objects and responsibilities and providing a solution in terms of an interaction diagram this is the creative part where
Assigning Responsibilities by Larman Core design activity: The identification of objects and responsibilities and providing a solution in terms of an interaction diagram this is the creative part where
From designing to coding
 From designing to coding l st step: sensibly split work among team members Choose splits along thin interfaces l Probably not equal parts; split biggest parts again later Formalize the interfaces think
From designing to coding l st step: sensibly split work among team members Choose splits along thin interfaces l Probably not equal parts; split biggest parts again later Formalize the interfaces think
2 GRASP Patterns and basic OO Design. Roel Wuyts OASS
 2 GRASP Patterns and basic OO Design Roel Wuyts OASS1 2009-2010 Patterns 2 Bit of history... Christoffer Alexander The Timeless Way of Building, Christoffer Alexander, Oxford University Press, 1979, ISBN
2 GRASP Patterns and basic OO Design Roel Wuyts OASS1 2009-2010 Patterns 2 Bit of history... Christoffer Alexander The Timeless Way of Building, Christoffer Alexander, Oxford University Press, 1979, ISBN
Requirements Engineering
 Dr. Michael Eichberg Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Software Engineering Engineering The following slides are primarily based on the contents of the
Dr. Michael Eichberg Software Engineering Department of Computer Science Technische Universität Darmstadt Software Engineering Engineering The following slides are primarily based on the contents of the
Chapter 6 Structuring System Requirements: Process Modeling 6.1
 Chapter 6 Structuring System Requirements: Process Modeling 6.1 Learning Objectives Explain process modeling Discuss data-flow diagramming mechanics, definitions, and rules Discuss balancing data-flow
Chapter 6 Structuring System Requirements: Process Modeling 6.1 Learning Objectives Explain process modeling Discuss data-flow diagramming mechanics, definitions, and rules Discuss balancing data-flow
The Object-Oriented Design Process
 The Object-Oriented Design Process Part 1: Techniques & Tools OOdesignProcess 1 Program development In theory, 3 phase development process: Analysis: figure out the problem Design: develop the solution
The Object-Oriented Design Process Part 1: Techniques & Tools OOdesignProcess 1 Program development In theory, 3 phase development process: Analysis: figure out the problem Design: develop the solution
Basic Structural Modeling. Copyright Joey Paquet,
 Basic Structural Modeling Copyright Joey Paquet, 2000 1 Part I Classes Copyright Joey Paquet, 2000 2 Classes Description of a set of objects sharing the same attributes, operations and semantics Abstraction
Basic Structural Modeling Copyright Joey Paquet, 2000 1 Part I Classes Copyright Joey Paquet, 2000 2 Classes Description of a set of objects sharing the same attributes, operations and semantics Abstraction
(Murlidhar Group of Institutions,Bhavnagar Road, Rajkot) by:-assit. Prof. Vijay Vora (SOOADM) MCA-III
 Analysis Modeling What is Analysis Modeling? Analysis modeling uses a combination of text and diagrammatic forms to depict(represent) requirements for data, function, and behavior These text and diagrammatic
Analysis Modeling What is Analysis Modeling? Analysis modeling uses a combination of text and diagrammatic forms to depict(represent) requirements for data, function, and behavior These text and diagrammatic
