Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol
|
|
|
- Cecily Maxwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
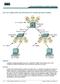
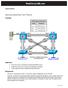
1 Lab 5-1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Diagram Objective Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault tolerant routing to the internal network. Scenario Step 1 HSRP provides a transparent failover mechanism to the end stations on the network. This provides users with uninterrupted service to the network in the event of a router failure. Power up the switches and use the standard process for establishing a HyperTerminal console connection from a workstation to each switch in your pod CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
2 Step 2 Remove all VLAN information and configurations that were previously entered into your switches. (Refer to Lab 2.0a or 2.0b if needed.) Cable the lab according to the diagram. Configure management IP addresses in VLAN 1, hostname, password, and telnet access on all four switches. The following is a sample configuration for the 2960 switch ALS1: Switch# configure terminal Switch(config)# hostname ALS1 ALS1(config)# enable secret cisco ALS1(config)# line vty 0 15 ALS1(config-line)# password cisco ALS1(config-line)# login ALS1(config-line)# exit ALS1(config)# interface vlan 1 ALS1(config-if)# ip address ALS1(config-if)# ALS1(config-if)# end The following is a sample configuration for the 2960 switch ALS2: Switch# configure terminal Switch(config)# hostname ALS2 ALS2(config)# enable secret cisco ALS2(config)# line vty 0 15 ALS2(config-line)# password cisco ALS2(config-line)# login ALS2(config-line)# exit ALS2(config)# interface vlan 1 ALS2(config-if)# ip address ALS2(config-if)# ALS2(config-if)# end The following is a sample configuration for the 3560 switch DLS1: Switch# configure terminal Switch(config)# hostname DLS1 DLS1(config)# enable secret cisco DLS1(config)# line vty 0 15 DLS1(config-line)# password cisco DLS1(config-line)# login DLS1(config-line)# exit DLS1(config)# interface vlan 1 DLS1(config-if)# ip address DLS1(config-if)# DLS1(config-if)# end The following is a sample configuration for the 3560 switch DLS2.: Switch# configure terminal 2-18 CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
3 Switch(config)# hostname DLS2 DLS2(config)# enable secret cisco DLS2(config)# line vty 0 15 DLS2(config-line)# password cisco DLS2(config-line)# login DLS2(config-line)# exit DLS2(config)# interface vlan 1 DLS2(config-if)# ip address DLS2(config-if)# DLS2(config-if)# end Configure default gateways on the access layer switches. The distribution layer switchs will not use a default gateway, because they act as Layer 3 devices. The access layer switches act as Layer 2 devices and need a default gateway to send traffic off of the local subnet for the management VLAN. The following is a sample configuration for the 2960 switch ALS1: ALS1# configure terminal ALS1(config)# ip default-gateway ALS1(config)# end The following is a sample configuration for the 2960 switch ALS2: ALS2# configure terminal ALS2(config)# ip default-gateway ALS2(config)# end Step 3 Configure trunks and EtherChannels between switches according to the diagram. EtherChannel is used for these trunks. EtherChannel allows you to utilize both Fast Ethernet interfaces that are available between each device, thereby doubling the bandwidth. The following is a sample configuration for the trunks and EtherChannel from DLS1 to the other three switches. The switchport trunk encapsulation [isl dot1q] command is used because this switch also supports ISL encapsulation. DLS1# configure terminal DLS1(config)# interface range fastethernet 0/7-8 DLS1(config-if-range)# DLS1(config-if-range)# DLS1(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1 DLS1(config-if-range)# interface range fastethernet 0/9-10 DLS1(config-if-range)# DLS1(config-if-range)# DLS1(config-if-range)# channel-group 2 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
4 DLS1(config-if-range)# interface range fastethernet 0/11-12 DLS1(config-if-range)# DLS1(config-if-range)# DLS1(config-if-range)# channel-group 3 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 3 DLS1(config-if-range)# end The following is a sample configuration for the trunks and EtherChannels from DLS2 to the other three switches: DLS2# configure terminal DLS2(config)# interface range fastethernet 0/7-8 DLS2(config-if-range)# DLS2(config-if-range)# DLS2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1 DLS2(config-if-range)# interface range fastethernet 0/9-10 DLS2(config-if-range)# DLS2(config-if-range)# DLS2(config-if-range)# channel-group 2 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 2 DLS2(config-if-range)# interface range fastethernet 0/11-12 DLS2(config-if-range)# DLS2(config-if-range)# DLS2(config-if-range)# channel-group 3 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 3 DLS2(config-if-range)# end The following is a sample configuration for the trunks and EtherChannel from ALS1 and ALS2 to the other switches. Notice that no encapsulation type is needed because the 2960 supports only 802.1q trunks. ALS1# configure terminal ALS1(config)# interface range fastethernet 0/7-8 ALS1(config-if-range)# ALS1(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1 ALS1(config-if-range)# interface range fastethernet 0/9-10 ALS1(config-if-range)# ALS1(config-if-range)# channel-group 2 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 2 ALS1(config-if-range)# interface range fastethernet 0/11-12 ALS1(config-if-range)# ALS1(config-if-range)# channel-group 3 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
5 ALS1(config-if-range)# end The following is a sample configuration from ALS2: ALS2# configure terminal ALS2(config)# interface range fastethernet 0/7-8 ALS2(config-if-range)# ALS2(config-if-range)# channel-group 1 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 1 ALS2(config-if-range)# interface range fastethernet 0/9-10 ALS2(config-if-range)# ALS2(config-if-range)# channel-group 2 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 2 ALS2(config-if-range)# interface range fastethernet 0/11-12 ALS2(config-if-range)# ALS2(config-if-range)# channel-group 3 mode desirable Creating a port-channel interface Port-channel 3 ALS2(config-if-range)# end Verify trunking between DLS1, ALS1, and ALS2 using the show interface trunk command on all switches. DLS1# show interface trunk Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan Po1 on 802.1q trunking 1 Po2 on 802.1q trunking 1 Po3 on 802.1q trunking 1 Port Vlans allowed on trunk Po Po Po Port Vlans allowed and active in management domain Po1 1 Po2 1 Po3 1 Port Vlans in spanning tree forwarding state and not pruned Po1 1 Po2 1 Po3 1 Issue the show etherchannel summary command on each switch to verify the EtherChannels. In the following sample output from ALS1, notice the three EtherChannels on the access and distribution layer switches. Your output may vary depending on which ports have been placed in blocking by the Spanning Tree Protocol. ALS1# show etherchannel summary Flags: D - down P - in port-channel 5-18 CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
6 I - stand-alone s - suspended H - Hot-standby (LACP only) R - Layer3 S - Layer2 U - in use f - failed to allocate aggregator u - unsuitable for bundling w - waiting to be aggregated d - default port Number of channel-groups in use: 3 Number of aggregators: 3 Group Port-channel Protocol Ports Po1(SU) PAgP Fa0/7(P) Fa0/8(P) 2 Po2(SU) PAgP Fa0/9(P) Fa0/10(P) 3 Po3(SU) PAgP Fa0/11(P) Fa0/12(P) 1. Which EtherChannel negotiation protocol is in use here? Step 4 Change the VTP mode of ALS1 and ALS2 to client. ALS1# configure terminal ALS1(config)# vtp mode client Setting device to VTP CLIENT mode. ALS1(config)# end ALS2# configure terminal ALS2(config)# vtp mode client Setting device to VTP CLIENT mode. ALS2(config)# end Verify the VTP changes with the show vtp status command. ALS2# show vtp status VTP Version : 2 Configuration Revision : 0 Maximum VLANs supported locally : 1005 Number of existing VLANs : 5 VTP Operating Mode : Client VTP Domain Name : VTP Pruning Mode : Disabled VTP V2 Mode : Disabled VTP Traps Generation : Disabled MD5 digest : 0xC8 0xAB 0x3C 0x3B 0xAB 0xDD 0x34 0xCF Configuration last modified by at :47:34 2. How many VLANs can be supported locally on the 2960 switch? 6-18 CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
7 Step 5 Create the VTP domain on DLS1 and create VLANs 100, 200, 300, and 400 for the domain. DLS1# configure terminal DLS1(config)# vtp domain SWPOD DLS1(config)# vlan 10 DLS1(config-vlan)# name Finance DLS1(config-vlan)# exit DLS1(config)# vlan 20 DLS1(config-vlan)# name Engineering DLS1(config-vlan)# exit DLS1(config)# vlan 30 DLS1(config-vlan)# name Server-Farm1 DLS1(config-vlan)# exit DLS1(config)# vlan 40 DLS1(config-vlan)# name Server-Farm2 DLS1(config-vlan)# end Verify VTP information throughout the domain using the show vlan and show vtp status commands. 3. How many existing VLANs are in the VTP domain? Step 6 Configure your hosts with IP addresses and default gateways according to the diagram. Configure the host ports of all four switches. The following commands set up access as the switchport mode, place the port in the proper VLANs, and turn Spanning Tree Portfast on for the ports. DLS1# configure terminal DLS1(config)# interface fastethernet 0/6 DLS1(config-if)# switchport mode access DLS1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 30 DLS1(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast DLS1(config-if)# end DLS2# configure terminal DLS2(config)# interface fastethernet 0/6 DLS2(config-if)# switchport mode access DLS2(config-if)# switchport access vlan 40 DLS2(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast DLS2(config-if)# end 7-18 CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
8 ALS1# configure terminal ALS1(config)# interface fastethernet 0/6 ALS1(config-if)# switchport mode access ALS1(config-if)# switchport access vlan 10 ALS1(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast ALS1(config-if)# end ALS2# configure terminal ALS2(config)# interface fastethernet 0/6 ALS2(config-if)# switchport mode access ALS2(config-if)# switchport access vlan 20 ALS2(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast ALS2(config-if)# end 4. Ping from the host on VLAN 10 to the host on VLAN 40. The ping should fail. Are these results expected at this point? Why? Step 7 Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) provides redundancy in the network. You can also load balance the VLANs by using the standby group priority priority command. The ip routing command is used on DLS1 and DLS2 to activate routing capabilities on the switch. Each route processor can route between the various SVIs configured on its switch. Assign a third IP address in each subnet to be used as a virtual gateway address. HSRP negotiates and handles which switch accepts information forwarded to the virtual gateway IP address. The standby command configures the IP address of the virtual gateway, sets the priority for each VLAN, and configures the router for preempt. Preemption allows the router with the higher priority to become the active router after a network failure has been resolved. In the following configurations, the priority for VLANs 1, 10, and 20 is 150 on DLS1, making it the active router for those VLANs. VLANs 30 and 40 have a priority of 100 on DLS1, making DLS1 the standby router for these VLANs. DLS2 is configured to be the active router for VLANs 30 and 40, and the standby router for VLANs 1, 10, and 20. HSRP configuration for DLS1: DLS1# config t DLS1(config)# ip routing DLS1(config)# interface vlan CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
9 DLS1(config-if)# standby 1 ip DLS1(config-if)# DLS1(config-if)# standby 1 priority 150 DLS1(config-if)# exit DLS1(config)# interface vlan 10 DLS1(config-if)# ip address DLS1(config-if)# standby 1 ip DLS1(config-if)# DLS1(config-if)# standby 1 priority 150 DLS1(config-if)# DLS1(config-if)# exit DLS1(config)# interface vlan 20 DLS1(config-if)# ip address DLS1(config-if)# standby 1 ip DLS1(config-if)# DLS1(config-if)# standby 1 priority 150 DLS1(config-if)# exit DLS1(config)# interface vlan 30 DLS1(config-if)# ip address DLS1(config-if)# standby 1 ip DLS1(config-if)# DLS1(config-if)# standby 1 priority 100 DLS1(config-if)# exit DLS1(config)# interface vlan 40 DLS1(config-if)# ip address DLS1(config-if)# standby 1 ip DLS1(config-if)# DLS1(config-if)# standby 1 priority 100 DLS1(config-if)# end HSRP configuration for DLS2: DLS2# config t DLS2(config)# ip routing DLS2(config)# interface vlan 1 DLS2(config-if)# standby 1 ip DLS2(config-if)# DLS2(config-if)# standby 1 priority 150 DLS2(config-if)# exit DLS2(config)# interface vlan 10 DLS2(config-if)# ip address DLS2(config-if)# standby 1 ip DLS2(config-if)# DLS2(config-if)# standby 1 priority 150 DLS2(config-if)# DLS2(config-if)# exit DLS2(config)# interface vlan 20 DLS2(config-if)# ip address DLS2(config-if)# standby 1 ip DLS2(config-if)# DLS2(config-if)# standby 1 priority 150 DLS2(config-if)# exit DLS2(config)# interface vlan 30 DLS2(config-if)# ip address DLS2(config-if)# standby 1 ip DLS2(config-if)# DLS2(config-if)# standby 1 priority 100 DLS2(config-if)# exit DLS2(config)# interface vlan 40 DLS2(config-if)# ip address DLS2(config-if)# standby 1 ip DLS2(config-if)# 9-18 CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
10 Step 8 DLS2(config-if)# standby 1 priority 100 DLS2(config-if)# end Issue the show standby command on both DLS1 and DLS2. DLS1# show standby Vlan1 - Group 1 State is Active 5 state changes, last state change 00:02:48 Virtual IP address is Next hello sent in secs Active router is local Standby router is , priority 100 (expires in sec) Priority 150 (configured 150) IP redundancy name is "hsrp-vl1-1" (default) Vlan10 - Group 1 State is Active 5 state changes, last state change 00:02:50 Virtual IP address is Next hello sent in secs Active router is local Standby router is , priority 100 (expires in sec) Priority 150 (configured 150) IP redundancy name is "hsrp-vl10-1" (default) Vlan20 - Group 1 State is Active 5 state changes, last state change 00:02:55 Virtual IP address is Next hello sent in secs Active router is local Standby router is , priority 100 (expires in sec) Priority 150 (configured 150) IP redundancy name is "hsrp-vl20-1" (default) Vlan30 - Group 1 State is Standby 4 state changes, last state change 00:02:45 Virtual IP address is Next hello sent in secs Active router is , priority 150 (expires in sec) Standby router is local Priority 100 (default 100) IP redundancy name is "hsrp-vl30-1" (default) Vlan40 - Group 1 State is Standby CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
11 4 state changes, last state change 00:02:51 Virtual IP address is Next hello sent in secs Active router is , priority 150 (expires in sec) Standby router is local Priority 100 (default 100) IP redundancy name is "hsrp-vl40-1" (default) DLS2# show standby Vlan1 - Group 1 State is Standby 3 state changes, last state change 00:02:33 Virtual IP address is Next hello sent in secs Active router is , priority 150 (expires in sec) Standby router is local Priority 100 (default 100) IP redundancy name is "hsrp-vl1-1" (default) Vlan10 - Group 1 State is Standby 3 state changes, last state change 00:02:34 Virtual IP address is Next hello sent in secs Active router is , priority 150 (expires in sec) Standby router is local Priority 100 (default 100) IP redundancy name is "hsrp-vl10-1" (default) Vlan20 - Group 1 State is Standby 3 state changes, last state change 00:02:42 Virtual IP address is Next hello sent in secs Active router is , priority 150 (expires in sec) Standby router is local Priority 100 (default 100) IP redundancy name is "hsrp-vl20-1" (default) Vlan30 - Group 1 State is Active 2 state changes, last state change 00:02:52 Virtual IP address is Next hello sent in secs CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
12 Active router is local Standby router is , priority 100 (expires in sec) Priority 150 (configured 150) IP redundancy name is "hsrp-vl30-1" (default) Vlan40 - Group 1 State is Active 2 state changes, last state change 00:02:58 Virtual IP address is Next hello sent in secs Active router is local Standby router is , priority 100 (expires in sec) Priority 150 (configured 150) IP redundancy name is "hsrp-vl40-1" (default) 5. Which router is the active router for VLANs 1, 10, and 20? Which is the active router for 30 and 40? 6. What is the default hello time for each VLAN? What is the default hold time? 7. How is the active HSRP router selected? Use the show ip route command to verify routing on both DLS1 and DLS2. DLS1# show ip route Codes: C - connected, S - static, R - RIP, M - mobile, B - BGP D - EIGRP, EX - EIGRP external, O - OSPF, IA - OSPF inter area N1 - OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 - OSPF NSSA external type 2 E1 - OSPF external type 1, E2 - OSPF external type 2, E - EGP i - IS-IS, su - IS-IS summary, L1 - IS-IS level-1, L2 - IS-IS level-2 ia - IS-IS inter area, * - candidate default, U - per-user static route o - ODR, P - periodic downloaded static route Gateway of last resort is not set C C C C C /24 is subnetted, 5 subnets is directly connected, Vlan is directly connected, Vlan is directly connected, Vlan is directly connected, Vlan is directly connected, Vlan CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
13 Step 9 Verify connectivity between VLANs using the ping command from the SQL Server (VLAN 40) to the other hosts and servers on the network. The following is from the SQL Server to the Engineering host: C:\> ping Pinging with 32 bytes of data: Reply from : bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=255 Reply from : bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=255 Reply from : bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=255 Reply from : bytes=32 time=2ms TTL=255 Ping statistics for : Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 2ms, Maximum = 2ms, Average = 2ms Step 10 Verify HSRP by disconnecting the trunks to DLS2. If you have physical access to the routers, unplug the cables to FastEthernet0/7 through FastEthernet0/12. If you do not have physical access, use the shutdown command on those interfaces. DLS2# configure terminal DLS2(config)# interface range fastethernet 0/7-12 DLS2(config-if-range)# shutdown DLS2(config-if-range)# end Output to the terminal should reflect DLS1 becoming the active router for VLANs 30 and 40. 1w3d: %HSRP-6-STATECHANGE: Vlan30 Grp 1 state Standby -> Active 1w3d: %HSRP-6-STATECHANGE: Vlan40 Grp 1 state Standby -> Active If the trunks are disconnected, reconnect the cables to FastEthernet0/7 through FastEthernet0/12 on DLS2. Repeat this step by disconnecting the trunks for DLS1 and use the show standby command to see the results. Final Configurations DLS1# show run hostname DLS1 enable secret cisco ip routing interface Port-channel CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
14 interface Port-channel2 interface Port-channel3 interface FastEthernet0/6 switchport access vlan 300 switchport mode access interface FastEthernet0/7 channel-group 1 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/8 channel-group 1 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/9 channel-group 2 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/10 channel-group 2 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/11 channel-group 3 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/12 channel-group 3 mode desirable interface Vlan1 ip address standby 1 ip standby 1 priority 150 interface Vlan10 ip address standby 1 ip standby 1 priority 150 interface Vlan20 ip address standby 1 ip standby 1 priority CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
15 interface Vlan30 ip address standby 1 ip interface Vlan40 ip address standby 1 ip line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login end DLS2# show run hostname DLS2 enable secret cisco ip routing interface Port-channel1 interface Port-channel2 interface Port-channel3 interface FastEthernet0/6 switchport access vlan 400 switchport mode access interface FastEthernet0/7 channel-group 1 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/8 channel-group 1 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/9 channel-group 2 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/ CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
16 channel-group 2 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/11 channel-group 3 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/12 channel-group 3 mode desirable interface Vlan1 ip address standby 1 ip interface Vlan10 ip address standby 1 ip interface Vlan20 ip address standby 1 ip interface Vlan30 ip address standby 1 ip standby 1 priority 150 interface Vlan40 ip address standby 1 ip standby 1 priority 150 line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login end ALS1# show run hostname ALS1 enable secret cisco interface Port-channel CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
17 interface Port-channel2 interface Port-channel3 interface FastEthernet0/6 switchport access vlan 100 switchport mode access interface FastEthernet0/7 channel-group 1 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/8 channel-group 1 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/9 channel-group 2 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/10 channel-group 2 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/11 channel-group 3 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/12 channel-group 3 mode desirable interface Vlan1 ip address ip default-gateway line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login end ALS2# show run hostname ALS2 enable secret cisco interface Port-channel1 interface Port-channel CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
18 interface Port-channel3 interface FastEthernet0/6 switchport access vlan 200 switchport mode access interface FastEthernet0/7 channel-group 1 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/8 channel-group 1 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/9 channel-group 2 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/10 channel-group 2 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/11 channel-group 3 mode desirable interface FastEthernet0/12 channel-group 3 mode desirable interface Vlan1 ip address ip default-gateway line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login end CCNP: Building Multilayer Switched Networks v5.0 - Lab 5-1 Copyright 2006, Cisco Systems, Inc
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network. Hot
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Hot Standby Router Protocol Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP to provide redundant, fault-tolerant routing to the internal network. Hot
RealCiscoLAB.com. Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions Topology Objective Background Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Inter-VLAN Routing with an Internal Route Processor and Monitoring CEF Functions Topology Objective Background Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route
Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF).
 Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller
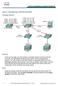 Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario Step 1 In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless access points,
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario Step 1 In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless access points,
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller
 Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless access points, and a switched
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless access points, and a switched
Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, First Hop Redundancy Protocols HSRP and VRRP INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, First Hop Redundancy Protocols HSRP and VRRP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP and load balancing Configure HSRP authentication
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, First Hop Redundancy Protocols HSRP and VRRP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP and load balancing Configure HSRP authentication
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
RealCiscoLAB.com. Configuring EtherChannel. Topology. Objective. Background. Required Resources. CCNPv6 Switch. Configure EtherChannel.
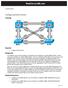 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 Switch Configuring EtherChannel Topology Objective Background Configure EtherChannel. Four switches have just been installed. The distribution layer switches are Catalyst 3560 switches,
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
CCNA Semester 3 labs Part 1 of 1 Labs for chapters 1 8 2.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant Links 2.3.2.3 Lab - Configuring Rapid PVST+, PortFast and BPDU Guard 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring
Note: Use two 2960 switches for ALS1 and ALS2 and two 3560 switches for DLS1 and DLS2
 LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
Lab Configuring EtherChannel
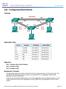 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1
 CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
CCNA Routing & Switching Lab Workbook - Full-Scale Lab 1 Task 1.1 Tasks You must load the initial configuration files for the section, FS Lab-1 Initial, which can be found in CCNA Routing & Switching Topology
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller
 Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a router with a built-in WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a router with a built-in WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security
 ABOUT CONTACT FAQ JOIN HOME CCNA CCNP COMPTIA DESIGN You are here: Home / 101 CCNP Labs Solutions / CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security Lab Objective:
ABOUT CONTACT FAQ JOIN HOME CCNA CCNP COMPTIA DESIGN You are here: Home / 101 CCNP Labs Solutions / CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security CCNP Lab 006 Solution: HSRP and Switch Security Lab Objective:
VLANs. Traditional Campus Networks. Performance Issues. Broadcast Issues. Bridges terminate collision domains
 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Lab Hot Standby Router Protocol
 Lab 6.5.1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Objective Scenario Step 1 Step 2 Configure Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) on a pair of routers to provide redundant router services to a network. Two routers are
Lab 6.5.1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Objective Scenario Step 1 Step 2 Configure Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) on a pair of routers to provide redundant router services to a network. Two routers are
Lab Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Lab Configuring Fast EtherChannel
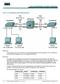 Lab 3.7.5 Configuring Fast EtherChannel Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to provide more bandwidth between Ethernet switches. Two 100-Mb links will be combined together to form a full duplex
Lab 3.7.5 Configuring Fast EtherChannel Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to provide more bandwidth between Ethernet switches. Two 100-Mb links will be combined together to form a full duplex
Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure trunking, VTP, and inter-vlan routing using router-on-a stick Configure GLBP Configure
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-3, Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure trunking, VTP, and inter-vlan routing using router-on-a stick Configure GLBP Configure
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol
 Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
Lab 8-2 Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Learning Objectives Secure the Layer 2 spanning tree topology with BPDU guard Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with root guard Protect switchports from
CCNA Semester 3 labs. Labs for chapters 2 10
 CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
CCNA Semester 3 labs Labs for chapters 2 10 2.1.4.5 Lab - Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP 2.2.2.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing 3.1.2.12 Lab - Building a Switched Network with Redundant
Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Synchronizing Campus Network Devices using Network Time Protocol (NTP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Synchronizing Campus Network Devices using Network Time Protocol (NTP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objective Background Configure network to synchronize time using the
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 7 Lab 7-1, Synchronizing Campus Network Devices using Network Time Protocol (NTP) INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objective Background Configure network to synchronize time using the
Lab Configuring HSRP and GLBP Topology
 Topology 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Topology 2014 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 1 of 9 Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab Troubleshooting VTP Configuration
 Lab 4.4.3 Troubleshooting VTP Configuration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Lab 4.4.3 Troubleshooting VTP Configuration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA ( )
 STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA (640-802) Developed By, Router Infotech Career Academy LAB: 09 Static Route Configuration Objective: To configure & implement Static Route successfully on said devices and test its
STUDENT LAB GUIDE CCNA (640-802) Developed By, Router Infotech Career Academy LAB: 09 Static Route Configuration Objective: To configure & implement Static Route successfully on said devices and test its
Lab 3.3 Configuring Wireshark and SPAN
 Lab 3.3 Configuring Wireshark and SPAN Learning Objectives Install Wireshark on a host PC Configure a switch to use the SPAN monitoring tool. Topology Diagram Scenario In this lab, you will configure a
Lab 3.3 Configuring Wireshark and SPAN Learning Objectives Install Wireshark on a host PC Configure a switch to use the SPAN monitoring tool. Topology Diagram Scenario In this lab, you will configure a
BraindumpsIT. BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf!
 BraindumpsIT http://www.braindumpsit.com BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf! Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
BraindumpsIT http://www.braindumpsit.com BraindumpsIT - IT Certification Company provides Braindumps pdf! Exam : 300-115 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
Lab Hot Standby Router Protocol
 Lab 6.2.2.1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Objective Scenario Configure Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) on a pair of routers to provide redundant fault tolerant router services to a network. Two routers
Lab 6.2.2.1 Hot Standby Router Protocol Objective Scenario Configure Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP) on a pair of routers to provide redundant fault tolerant router services to a network. Two routers
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS
 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and Catalyst Switches Running CatOS Document ID: 23408 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab Multigroup Hot Standby Router Protocol
 Lab 6.2.2.2 Multigroup Hot Standby Router Protocol Objective Scenario Step 1 Configure Multigroup Hot Standby Router Protocol (MHSRP) on a pair of routers to provide redundant router services to a network.
Lab 6.2.2.2 Multigroup Hot Standby Router Protocol Objective Scenario Step 1 Configure Multigroup Hot Standby Router Protocol (MHSRP) on a pair of routers to provide redundant router services to a network.
Lab Configuring Static NAT
 Lab 10.5.1 Configuring Static NAT Objective Configure Network Address Translation (NAT) static translation to provide reliable outside access to three shared company servers. Scenario Step 1 The International
Lab 10.5.1 Configuring Static NAT Objective Configure Network Address Translation (NAT) static translation to provide reliable outside access to three shared company servers. Scenario Step 1 The International
Configuring Secure (Router) Mode, Redundancy, Fault Tolerance, and HSRP
 CHAPTER 4 Configuring Secure (Router) Mode, Redundancy, Fault Tolerance, and HSRP This chapter describes how to configure the following aspects of content switching that are necessary for the Content Services
CHAPTER 4 Configuring Secure (Router) Mode, Redundancy, Fault Tolerance, and HSRP This chapter describes how to configure the following aspects of content switching that are necessary for the Content Services
Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing
 Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN
Lab 6.4.2: Challenge Inter-VLAN Routing Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 192.168.99.1 S2 VLAN
Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Secure the server farm using private VLANs. Secure the staff VLAN from the student VLAN. Secure the
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 10 Lab 10-2, Securing VLANs INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Secure the server farm using private VLANs. Secure the staff VLAN from the student VLAN. Secure the
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS
 QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
QUAID-E-AWAM UNIVERSITY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY, NAWABSHAH TELECOMMUNICATION MANAGEMENT AND NETWORKS LAB # 3 CONFIGURING INTERFACES OF ROUTER AND SWITCH Topology Diagram Addressing Table
Lecture (06) Design and Configuration LAN Practicing, working on CISCO equipment. By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee
 Lecture (06) Design and Configuration LAN Practicing, working on CISCO equipment By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Fall 2015, Practical App. Networks II Part I ٢ ٣ SW01 steps firstly connect
Lecture (06) Design and Configuration LAN Practicing, working on CISCO equipment By: Dr. Ahmed ElShafee ١ Dr. Ahmed ElShafee, ACU : Fall 2015, Practical App. Networks II Part I ٢ ٣ SW01 steps firstly connect
Lab VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
PracticeDump. Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam
 PracticeDump http://www.practicedump.com Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam Instant Download - Best Exam Practice Material - 100% Money Back Guarantee IT Certification Guaranteed,
PracticeDump http://www.practicedump.com Free Practice Dumps - Unlimited Free Access of practice exam Instant Download - Best Exam Practice Material - 100% Money Back Guarantee IT Certification Guaranteed,
Table of Contents. isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ
 king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Scaling Networks
 CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Scaling Networks As a business grows, so does its networking requirements. To keep pace with a business s expansion and new emerging technologies, a network must be designed to
CHAPTER 1 Introduction to Scaling Networks As a business grows, so does its networking requirements. To keep pace with a business s expansion and new emerging technologies, a network must be designed to
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 일년무료업데이트서비스제공
 itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
itexamdump 최고이자최신인 IT 인증시험덤프 http://www.itexamdump.com 일년무료업데이트서비스제공 Exam : 642-813 Title : Implementing Cisco IP Switched Networks Vendor : Cisco Version : DEMO Get Latest & Valid 642-813 Exam's Question
Lab 1. CLI Navigation. Scenario. Initial Configuration for R1
 Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
CHAPTER 37 Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
LAN Troubleshooting. Ethernet Troubleshooting
 CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
CCIE Routing & Switching Advanced Troubleshooting Bootcamp LAN Troubleshooting http:// Ethernet Troubleshooting No Ethernet switching troubleshooting in Troubleshooting Section, but it can be included
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
35 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 and Layer 3 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover
 28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
28 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Layer 2 Trunk Failover This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed links
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS. Cisco Lab Øvelse Af Kim Donnerborg / RTS. Side 0 af 8
 KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
KIM DONNERBORG / RTS Side 0 af 8 INDHOLDSFORTEGNELSE Lab: Basic Router Configuration... 2 Topology Diagram... 2 Addressing Table... 2 Learning Objectives... 2 Scenario... 2 Task 1: Cable the Network....
CHAPTER 1 LAN Design
 CHAPTER 1 LAN Design As a business grows, so does its networking requirements. To keep pace with a business s expansion and new emerging technologies, a network must be designed to scale. A network that
CHAPTER 1 LAN Design As a business grows, so does its networking requirements. To keep pace with a business s expansion and new emerging technologies, a network must be designed to scale. A network that
Configuring the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch
 APPENDIXA Configuring the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch The Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch is an integrated Catalyst 3750 switch and Cisco 4400 series
APPENDIXA Configuring the Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch The Catalyst 3750G Integrated Wireless LAN Controller Switch is an integrated Catalyst 3750 switch and Cisco 4400 series
Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking
 30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
30 CHAPTER Configuring EtherChannels and Link-State Tracking This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels on Layer 2 ports on the Catalyst 2960 switch. EtherChannel provides fault-tolerant high-speed
Lab Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routes (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.0.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/1 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 N/A R3 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 10 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring Link Aggregation
 Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 1 (GUI), page 3 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 4 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 1 (GUI), page 3 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 4 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Setup a VTP v2 Domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q Trunking. Setup a VTP v3 Domain.
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 3 Lab 3-1 Static VLANS, Trunking, and VTP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Setup a VTP v2 Domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q Trunking. Setup a VTP v3 Domain.
Lab Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
Lab Configure Extended VLANs, VTP, and DTP
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Part 1: Configure VTP Part 2: Configure DTP Table Heading Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.1 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.2 255.255.255.0
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution
 Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Case Study 2: Frame Relay and OSPF Solution Objective In this case study, you troubleshoot a complex scenario involving Frame Relay and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF). Figure 2-1 shows the topology for
Configuring VLAN Trunks
 Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLAN Trunks, page 1 Information About VLAN Trunks, page 2 How to Configure VLAN Trunks, page 5 Configuration Examples for VLAN Trunking, page 20 Where
Finding Feature Information, page 1 Prerequisites for VLAN Trunks, page 1 Information About VLAN Trunks, page 2 How to Configure VLAN Trunks, page 5 Configuration Examples for VLAN Trunking, page 20 Where
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series
 Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line
Configuring InterVLAN Routing
 CHAPTER 2 Configuring InterVLAN Routing This chapter describes how to configure the Multilayer Switch Feature Card (MSFC) for intervlan routing on the Catalyst 6000 family switches and MSFC. Note For more
CHAPTER 2 Configuring InterVLAN Routing This chapter describes how to configure the Multilayer Switch Feature Card (MSFC) for intervlan routing on the Catalyst 6000 family switches and MSFC. Note For more
Lab 5: Basic VLAN Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Configuring EtherChannels
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of EtherChannels in Cisco NX-OS. This chapter
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure EtherChannels and to apply and configure the Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) for more efficient use of EtherChannels in Cisco NX-OS. This chapter
Chapter 8 Lab 8-1, IP Service Level Agreements and Remote SPAN in a Campus Environment INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 8 Lab 8-1, IP Service Level Agreements and Remote SPAN in a Campus Environment INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Configure trunking, VTP, and SVIs. Implement IP
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 8 Lab 8-1, IP Service Level Agreements and Remote SPAN in a Campus Environment INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Background Configure trunking, VTP, and SVIs. Implement IP
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
CHAPTER 9 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094). It includes information about VLAN membership modes, VLAN configuration
Describing the STP. Enhancements to STP. Configuring PortFast. Describing PortFast. Configuring. Verifying
 Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
Enhancements to STP Describing the STP PortFast Per VLAN Spanning Tree+ (PVST+) Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) MSTP is also known as Multi-Instance Spanning
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
CHAPTER 12 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the switch. It includes information about VLAN membership
Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router (InterVLAN Routing)
 Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
Cisco - Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Conf... Page 1 of 13 Configuring EtherChannel and 802.1Q Trunking Between Catalyst L2 Fixed Configuration Switches and a Router
Configuring HSRP. Global Knowledge Training LLC L5-1
 L5 Configuring HSRP Global Knowledge Training LLC L5-1 Objectives In this lab you will examine the hot standby router protocol (HSRP). First you will configure PxR2 similar to PxR1, so they are both possible
L5 Configuring HSRP Global Knowledge Training LLC L5-1 Objectives In this lab you will examine the hot standby router protocol (HSRP). First you will configure PxR2 similar to PxR1, so they are both possible
Lab 1-2Connecting to a Cisco Router or Switch via Console. Lab 1-6Basic Graphic Network Simulator v3 Configuration
 MODULE1 GETTING STARTED WITH YOUR CISCO LAB Lab 1-1Identifying Router Components and Accessories Lab 1-2Connecting to a Cisco Router or Switch via Console Lab 1-3Identifying Router & Switch IOS Software
MODULE1 GETTING STARTED WITH YOUR CISCO LAB Lab 1-1Identifying Router Components and Accessories Lab 1-2Connecting to a Cisco Router or Switch via Console Lab 1-3Identifying Router & Switch IOS Software
Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Internetwork Communications C:>ping 172.16.30.100 Can two hosts on different subnets communicate without a router? No
Implementing Inter-VLAN Routing 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Internetwork Communications C:>ping 172.16.30.100 Can two hosts on different subnets communicate without a router? No
Lab 2.8.1: Basic Static Route Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 Fa0/0 172.16.3.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S0/0/0 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 N/A Fa0/0 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R2
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on your Catalyst 3550 switch. It includes information about VLAN
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
RealCiscoLAB.com. Securing Spanning Tree Protocol. Topology. Objectives. Background. CCNPv6 SWITCH
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Securing Spanning Tree Protocol Topology Objectives Background Secure the Layer 2 spanning-tree topology with BPDU guard. Protect the primary and secondary root bridge with
RealCiscoLAB.com. Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified.
 RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
RealCiscoLAB.com CCNPv6 SWITCH Modifying Default Spanning Tree Behavior Topology Objective Background Observe what happens when the default spanning tree behavior is modified. Four switches have just been
Lab Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2
 Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Lab 8.5.2: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 2 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway Fa0/0 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A R1 Fa0/1 192.168.11.1 255.255.255.0
Understanding and Configuring Private VLANs
 CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes private VLANs on the Catalyst 4000 family switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major sections:
CHAPTER 8 This chapter describes private VLANs on the Catalyst 4000 family switches. It also provides guidelines, procedures, and configuration examples. This chapter includes the following major sections:
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
CHAPTER 11 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Cisco ME 3400 Ethernet Access switch. It includes information
Configuring Link Aggregation
 Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 2 (GUI), page 4 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 5 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
Information About Link Aggregation, page 1 Restrictions for Link Aggregation, page 2 (GUI), page 4 (CLI), page 4 Verifying Link Aggregation Settings (CLI), page 5 Configuring Neighbor Devices to Support
Basic Router Configuration
 This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
This section includes information about some basic router configuration, and contains the following sections: Default Configuration, on page 1 Configuring Global Parameters, on page 2 Configuring Gigabit
Chapter 6: Network Layer
 Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks Intro to Networks v5 Network Layer Intro to Networks v5 2 The Network Layer End to End Transport processes Addressing end devices Encapsulation of Packets
Chapter 6: Network Layer Introduction to Networks Intro to Networks v5 Network Layer Intro to Networks v5 2 The Network Layer End to End Transport processes Addressing end devices Encapsulation of Packets
Configuring Private VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CHAPTER 15 This chapter describes how to configure private VLANs on the Cisco 7600 series routers. Note For complete syntax and usage information for the commands used in this chapter, refer to the Cisco
CCNP Switch Questions/Answers Implementing VLANs in Campus Networks
 Refer to the exhibit. Given the configuration information of the CAT1 and CAT2 switches, which statement is true? A. LACP will form a channel between the switches. B. Because the port-channel numbers do
Refer to the exhibit. Given the configuration information of the CAT1 and CAT2 switches, which statement is true? A. LACP will form a channel between the switches. B. Because the port-channel numbers do
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
Assignment Six: Configure Hot Standby Router Protocol. Brian Dwyer. Morrisville State College
 Running head: ASSIGNMENT SIX: CONFIGURE HSRP Assignment Six: Configure Hot Standby Router Protocol Brian Dwyer Morrisville State College ASSIGNMENT SIX 1 Brian Dwyer CITA370 2/5/2010 Assignment Six: Configure
Running head: ASSIGNMENT SIX: CONFIGURE HSRP Assignment Six: Configure Hot Standby Router Protocol Brian Dwyer Morrisville State College ASSIGNMENT SIX 1 Brian Dwyer CITA370 2/5/2010 Assignment Six: Configure
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator
 Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Configuring Redundant Routing on the VPN 3000 Concentrator Document ID: 13354 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Configure Network Diagram Router Configurations
Pass-Through Technology
 CHAPTER 3 This chapter provides best design practices for deploying blade servers using pass-through technology within the Cisco Data Center Networking Architecture, describes blade server architecture,
CHAPTER 3 This chapter provides best design practices for deploying blade servers using pass-through technology within the Cisco Data Center Networking Architecture, describes blade server architecture,
Lab Network Baseline Discovery
 Lab 1.2.6 Network Baseline Discovery Objective In this lab, the student will establish the baseline for the configuration and operation of the network. The student will complete the following tasks: Job
Lab 1.2.6 Network Baseline Discovery Objective In this lab, the student will establish the baseline for the configuration and operation of the network. The student will complete the following tasks: Job
Configuring VLANs. Understanding VLANs CHAPTER
 CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
CHAPTER 14 This chapter describes how to configure normal-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1 to 1005) and extended-range VLANs (VLAN IDs 1006 to 4094) on the Catalyst 3750 switch. It includes information about VLAN
