Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series
|
|
|
- Eugenia Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
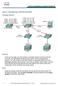
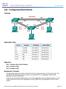
1 Lab 9.1.5a Trunking with ISL 2924XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an ISL trunk line between the two switches to allow communication between paired VLANs. Test the VLANs functionality by moving a workstation from one VLAN to another. Background/Preparation Note: The use of Catalyst 2950 switches is not appropriate for this lab as they only support 802.1q trunking. Trunking changes the formatting of the packets. The ports need to be in agreement as to which format is being used to transmit data on the trunk or no data will be passed. If there is different trunking encapsulation on the two ends of the link they will not able to communicate. Similar situation will occur if one of the ports is configured in trunking mode, unconditionally, and the other one is in access mode, unconditionally. When managing a switch, the Management Domain is always VLAN 1. The Network Administrator's workstation must have access to a port in the VLAN 1 Management Domain. All ports are assigned CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab 9.1.5a Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
2 to VLAN 1 by default. This lab will also help demonstrate how VLANs can be used to separate traffic and reduce broadcast domains. Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram. The configuration output used in this lab is produced from a 2900 series switch. Any other switch used may produce different output. The following steps are to be executed on each switch unless specifically instructed otherwise. Start a HyperTerminal session. Note: Go to the erase and reload instructions at the end of this lab. Perform those steps on all switches in this lab assignment before continuing. Step 1 Configure the switch Configure the hostname, access and command mode passwords, as well as the management LAN settings. These values are shown in the chart. If problems occur while performing this configuration, refer to the Basic Switch Configuration lab. Step 2 Configure the hosts attached to the switch Configure the IP address, mask, and default gateway on each host. Be sure to choose addresses that are on the same subnet as the switch. Step 3 Verify connectivity a. To verify that the host and switch are correctly configured, ping the switches from the host. b. Were the pings successful? Yes c. If the answer is no, troubleshoot the host and switches configurations. Step 4 Display the VLAN interface information On Switch_A, type the command show vlan at the Privileged EXEC prompt as follows: Switch_A#show vlan Note: There should be an entry for VLAN 1 and the default VLANs (1002 +). If other VLANs appear, they could be deleted as instructed in Step 2 of the Erasing and Reloading instructions at the end of this lab or refer to the Lab Exercise: Deleting VLAN Configurations. Step 5 Create and name three VLANs Enter the following commands to create and name three VLANs: Switch_A#vlan database Switch_A(vlan)#vlan 10 name Accounting Switch_A(vlan)#vlan 20 name Marketing Switch_A(vlan)#vlan 30 name Engineering Switch_A(vlan)#exit Use the show vlan command to verify that the VLANs have been created correctly. Step 6 Assign ports to a VLAN 10 Assigning ports to VLANs must be done from the interface mode. Enter the following commands to add ports 0/4 to 0/6 to VLAN 10: Switch_A#configure terminal CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab 9.1.5a Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
3 Switch_A(config)#interface fastethernet 0/4 Switch_A(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10 Switch_A(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/5 Switch_A(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10 Switch_A(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/6 Switch_A(config-if)#switchport access vlan 10 Switch_A(config-if)#end Step 7 Assign ports to VLAN 20 Enter the following commands to add ports 0/7 to 0/9 to VLAN 20: Switch_A#configure terminal Switch_A(config)#interface fastethernet 0/7 Switch_A(config-if)#switchport access vlan 20 Switch_A(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/8 Switch_A(config-if)#switchport access vlan 20 Switch_A(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/9 Switch_A(config-if)#switchport access vlan 20 Switch_A(config-if)#end Step 8 Assign ports to VLAN 30 Enter the following commands to add ports 0/10 to 0/12 to VLAN 30: Switch_A#configure terminal Switch_A(config)#interface fastethernet 0/10 Switch_A(config-if)#switchport access vlan 30 Switch_A(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/11 Switch_A(config-if)#switchport access vlan 30 Switch_A(config-if)#interface fastethernet 0/12 Switch_A(config-if)#switchport access vlan 30 Switch_A(config-if)#end Step 9 Create VLANs on Switch_B Repeat Steps 5 through 8 on Switch_B to create its VLANs. Step 10 Display he VLAN interface information a. On Switch_A, type the command show vlan at the Privileged EXEC prompt as follows: Switch_A#show vlan b. Are ports 0/10 through 0/12 assigned to VLAN 30? Yes CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab 9.1.5a Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
4 Step 11 Test the VLANs Ping from the host in Switch_A port 0/12 to the host in Switch_B port 0/12. a. Was the ping successful? No b. Why? No trunk has been configured Ping from the host in Switch_A port 0/12 to the switch IP c. Was the ping successful? No d. Why? Interfaces are in different VLANs Step 12 Create the ISL trunk On both switches, Switch_A and Switch_B, type the following command at the fastethernet 0/1 interface command prompt Switch_A(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1 Switch_A(config-if)#switchport mode trunk Switch_A(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation isl Switch_A(config-if)#end Switch_B(config)#interface fastethernet 0/1 Switch_B(config-if)#switchport mode trunk Switch_B(config-if)#switchport trunk encapsulation isl Switch_B(config-if)#end Step 13 Verify the ISL trunk a. To verify that port fastethernet 0/1 has been established as a trunk port, type show interface fastethernet 0/1 switchport at the Privileged EXEC mode prompt. b. What type of trunking encapsulation is shown on the output results? ISL c. According to the output with show interface fastethernet 0/1 switchport on Switch_B, is there a difference from the Administrative Trunking Encapsulation from the Operational Trunking Encapsulation? No, both encapsulation types are ISL. d. On the fragment Trunking VLANs Enable from the output, what does the word ALL mean? It means that traffic from all VLANs are allowed to cross the trunked link What would happen if the two ports of the trunk were using different encapsulation? It wouldn t form a trunk. e. Explain. The encapsulation must match on both sides of the link in order for the trunk to form. Step 14 Test the VLANS and the trunk Ping from the host in Switch_A port 0/12 to the host in Switch_B port 0/12. a. Was the ping successful? Yes b. Why? Hosts are on the same VLAN with trunking enabled on port 0/1. Ping from the host in Switch_A port 0/12 to the switch IP c. Was the ping successful? No d. Why? The interfaces are on different VLANs. Step 15 Move host CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab 9.1.5a Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
5 Move the host in Switch_A from port 0/12 to port 0/8. Wait until the port LED goes green and then go to the next step. Step 16 Test the VLANS and the trunk Ping from the host in Switch_A port 0/8 to the host in Switch_B port 0/12. a. Was the ping successful? No b. Why? The hosts are on different VLANs Ping from the host in Switch_A port 0/8 to the switch IP c. Was the ping successful? No d. Why? The hosts are on different VLANs Step 17 Move host Move the host in Switch_B from port 0/12 to port 0/7. Wait until the port LED goes green and then go to the next step. Step 18 Test the VLANS and the trunk Ping from the host in Switch_A port 0/8 to the host in Switch_B port 0/7. a. Was the ping successful? Yes b. Why? The hosts are now on the same VLAN (VLAN 20) Ping from the host in Switch_A port 0/8 to the switch IP c. Was the ping successful? No d. Why? The interfaces are on different VLANs. Step 19 Move host Move the host in Switch_A from port 0/8 to port 0/2. Wait until the port LED goes green and then go to the next step. Step 20 Test the VLANS and the trunk Ping from the host in Switch_A port 0/2 to the host in Switch_B port 0/7. a. Was the ping successful? No Ping from the host in Switch_A port 0/2 to the switch IP b. Was the ping successful? Yes c. Why? Both interfaces are assigned to the same VLAN (VLAN 1) Step 21 Move host Move the host in Switch_B from port 0/7 to port 0/3. Wait until the port LED goes green and then go to the next step. Step 22 Test the VLANS and the trunk Ping from the host in Switch_A port 0/2 to the host in Switch_B port 0/3. a. Was the ping successful? Yes b. Why? Both hosts now belong to the same VLAN Ping from the host in Switch_B port 0/3 to the switch IP c. Was the ping successful? Yes CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab 9.1.5a Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
6 d. Why? Both interfaces are assigned to the same VLAN (VLAN 1). Ping from the host in Switch_B port 0/3 to the switch IP e. Was the ping successful? Yes f. Why? Both interfaces are assigned to the same VLAN. (VLAN 1). g. What conclusions can be drawn from the testing that was just performed in regards to VLAN membership and VLANs across a trunk? Hosts must be grouped together into the same VLAN before they can communicate with each other. Trunk links carry VLAN traffic across switches. Once the steps are complete, logoff by typing exit, and turn all the devices off. Then remove and store the cables and adapter. Switch_A#show vlan VLAN Name Status Ports default active Fa0/1, Fa0/2, Fa0/3 10 Accounting active Fa0/4, Fa0/5, Fa0/6 20 Marketing active Fa0/7, Fa0/8, Fa0/9 30 Engineering active Fa0/10, Fa0/11, Fa0/ fddi-default active 1003 token-ring-default active 1004 fddinet-default active 1005 trnet-default active VLAN Type SAID MTU Parent RingNo BridgeNo Stp BrdgMode Trans1 Trans enet enet enet enet fddi tr fdnet ieee trnet ibm Switch_A#show interface fastethernet 0/1 switchport Name: Fa0/1 Switchport: Enabled Administrative mode: trunk Operational Mode: trunk Administrative Trunking Encapsulation: isl Operational Trunking Encapsulation: isl Negotiation of Trunking: Disabled Access Mode VLAN: 0 ((Inactive)) Trunking Native Mode VLAN: 1 (default) Trunking VLANs Enabled: ALL Trunking VLANs Active: 1,10,20,30 Pruning VLANs Enabled: Priority for untagged frames: 0 Override vlan tag priority: FALSE Voice VLAN: none Appliance trust: none Self Loopback: No C:\>ping CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab 9.1.5a Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
7 Pinging with 32 bytes of data: Reply from : bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128 Reply from : bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128 Reply from : bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128 Reply from : bytes=32 time<1ms TTL=128 Ping statistics for : Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss), Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds: Minimum = 0ms, Maximum = 0ms, Average = 0ms C:\>ping Pinging with 32 bytes of data: Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out. Request timed out. Ping statistics for : Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 0, Lost = 4 (100% loss), Switch_A#show running-config Building configuration... Current configuration: version 12.0 no service pad service timestamps debug uptime service timestamps log uptime no service password-encryption hostname Switch_A enable secret 5 $1$Spup$4rLiyqQseDcu2xWzhd9Ko. ip subnet-zero interface FastEthernet0/1 switchport mode trunk interface FastEthernet0/2 interface FastEthernet0/3 interface FastEthernet0/4 switchport access vlan 10 interface FastEthernet0 switchport access vlan CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab 9.1.5a Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
8 interface FastEthernet0/6 switchport access vlan 10 interface FastEthernet0/7 switchport access vlan 20 interface FastEthernet0/8 switchport access vlan 20 interface FastEthernet0/9 switchport access vlan 20 interface FastEthernet0/10 switchport access vlan 30 interface FastEthernet0/11 switchport access vlan 30 interface FastEthernet0/12 switchport access vlan 30 interface VLAN1 ip address no ip directed-broadcast no ip route-cache ip default-gateway line con 0 password cisco login transport input none stopbits 1 line vty 0 4 password cisco login line vty 5 15 password cisco login end CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab 9.1.5a Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
9 Erasing and Reloading the Switch For the majority of the labs in CCNA 3 and CCNA 4 it is necessary to start with an unconfigured switch. Use of a switch with an existing configuration may produce unpredictable results. These instructions allow preparation of the switch prior to performing the lab so previous configuration options do not interfere. The following is the procedure for clearing out previous configurations and starting with an unconfigured switch. Instructions are provided for the 2900, 2950, and 1900 Series switches and 2950 Series Switches 1. Enter into the Privileged EXEC mode by typing enable. Switch>enable If prompted for a password, enter class, if that does not work, ask the instructor. 2. Remove the VLAN database information file. Switch#delete flash:vlan.dat Delete filename [vlan.dat]?[enter] Delete flash:vlan.dat? [confirm] [Enter] If there was no VLAN file, this message is displayed. %Error deleting flash:vlan.dat (No such file or directory) 3. Remove the switch startup configuration file from NVRAM. Switch#erase startup-config The responding line prompt will be: Erasing the nvram filesystem will remove all files Continue? [confirm] Press Enter to confirm. The response should be: Erase of nvram: complete 4. Check that VLAN information was deleted. Verify that the VLAN configuration was deleted in Step 2 using the show vlan command. If previous VLAN configuration information (other than the default management VLAN 1) is still present it will be necessary to power cycle the switch (hardware restart) instead of issuing the reload command. To power cycle the switch, remove the power cord from the back of the switch or unplug it. Then plug it back in. If the VLAN information was successfully deleted in Step 2, go to Step 5 and restart the switch using the reload command CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab 9.1.5a Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
10 5. Software restart (using the reload command) Note: This step is not necessary if the switch was restarted using the power cycle method. a. At the Privileged EXEC mode enter the command reload. Switch#reload The responding line prompt will be: System configuration has been modified. Save? [yes/no]: b. Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Proceed with reload? [confirm] [Enter] The first line of the response will be: Reload requested by console. After the switch has reloaded, the line prompt will be: Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: c. Type n and then press Enter. The responding line prompt will be: Press RETURN to get started [Enter] 1900 Series Switches 1. Remove VLAN Trunking Protocol (VTP) information. #delete vtp This command resets the switch with VTP parameters set to factory defaults. All other parameters will be unchanged. Reset system with VTP parameters set to factory defaults, [Y]es or [N]o? Enter y and press Enter. 2. Remove the switch startup configuration from NVRAM. #delete nvram This command resets the switch with factory defaults. All system parameters will revert to their default factory settings. All static and dynamic addresses will be removed. Reset system with factory defaults, [Y]es or [N]o? Enter y and press Enter CCNA 3: Switching Basics and Intermediate Routing v Lab 9.1.5a Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Lab 9.1.5b Trunking with 802.1q
 Lab 9.1.5b Trunking with 802.1q Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an 802.1q trunk line between
Lab 9.1.5b Trunking with 802.1q Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create an 802.1q trunk line between
Lab VTP Client and Server Configurations
 Lab 9.2.5 VTP Client and Server Configurations Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Configure the VTP
Lab 9.2.5 VTP Client and Server Configurations Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Configure the VTP
Lab Verifying VLAN Configurations
 Lab 8.2.4 Verifying VLAN Configurations Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create two VLANs. Name the VLANs and assign multiple member ports to them. Test functionality by moving
Lab 8.2.4 Verifying VLAN Configurations Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create two VLANs. Name the VLANs and assign multiple member ports to them. Test functionality by moving
Lab Configuring Static VLANs
 Lab 8.2.3 Configuring Static VLANs Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine the switch firmware version. Create two VLANs, name them and assign member ports to them. Background/Preparation
Lab 8.2.3 Configuring Static VLANs Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine the switch firmware version. Create two VLANs, name them and assign member ports to them. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing
 Lab 9.3.6 Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create a basic configuration
Lab 9.3.6 Configuring Inter-VLAN Routing Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Create multiple VLANs, name them and assign multiple member ports to them. Create a basic configuration
Lab Spanning-Tree Recalculation
 Lab 7.2.6 Spanning-Tree Recalculation Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Observe the behavior of spanning-tree algorithm in presence of switched network topology changes. Background/Preparation
Lab 7.2.6 Spanning-Tree Recalculation Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Observe the behavior of spanning-tree algorithm in presence of switched network topology changes. Background/Preparation
Lab Selecting the Root Bridge
 Lab 7.2.4 Selecting the Root Bridge Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other
Lab 7.2.4 Selecting the Root Bridge Objective Create a basic switch configuration and verify it. Determine which switch is selected as the root switch with the factory default settings. Force the other
Lab Managing the MAC Address Table 2900XL Series
 Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table 2900XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram.
Lab 6.2.3 Managing the MAC Address Table 2900XL Series Objective Create a basic switch configuration. Manage the switch MAC table. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in the diagram.
Lab Add, Move, and Change MAC Addresses
 Lab 6.2.6 Add, Move, and Change MAC Addresses Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Move a PC from one switch port to another and add a new PC to the switch. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.2.6 Add, Move, and Change MAC Addresses Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Move a PC from one switch port to another and add a new PC to the switch. Background/Preparation
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS
 Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Lab 2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Static VLANS Objective Create and maintain VLANs on a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Scenario
Lab 6.2.7a Managing Switch Operating System Files
 Lab 6.2.7a Managing Switch Operating System Files Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Backup the switch IOS to a TFTP server and then restore it. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Lab 6.2.7a Managing Switch Operating System Files Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Backup the switch IOS to a TFTP server and then restore it. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
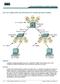 Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab 2.9.2 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch in
Lab Firmware Upgrade of a Catalyst 2950 Series Switch 2900XL Series
 Lab 6.2.9 Firmware Upgrade of a Catalyst 2950 Series Switch 2900XL Series Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Upgrade the IOS and HTML files from a file supplied by the instructor.
Lab 6.2.9 Firmware Upgrade of a Catalyst 2950 Series Switch 2900XL Series Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Upgrade the IOS and HTML files from a file supplied by the instructor.
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking
 Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab 2.3.7.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series VTP Domain and VLAN Trunking Objective Configure a VLAN trunk between two Cisco Catalyst WS-C2950T-24-EI switches and a Cisco Catalyst WS-C3550-24-EMI switch
Lab Password Recovery Procedure on a Catalyst 2950 Series Switch 2900XL Series
 Lab 6.2.8 Password Recovery Procedure on a Catalyst 2950 Series Switch 2900XL Series Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Change passwords and use the password recovery procedure.
Lab 6.2.8 Password Recovery Procedure on a Catalyst 2950 Series Switch 2900XL Series Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Change passwords and use the password recovery procedure.
Lab Firmware Upgrade of a Catalyst 2900 Series Switch
 Lab 6.2.9 Firmware Upgrade of a Catalyst 2900 Series Switch Objective Create a basic switch configuration verify it. Upgrade the IOS and HTML files from a file supplied by the instructor. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.2.9 Firmware Upgrade of a Catalyst 2900 Series Switch Objective Create a basic switch configuration verify it. Upgrade the IOS and HTML files from a file supplied by the instructor. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.1.6 Configuring Static Routes Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure static routes between routers to allow data transfer between routers without the use of dynamic routing protocols. Background/Preparation
Lab Password Recovery Procedure on a Catalyst 2900 Series Switches
 Lab 6.2.8 Password Recovery Procedure on a Catalyst 2900 Series Switches Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration verify it. Change passwords to the password recovery procedure be performed.
Lab 6.2.8 Password Recovery Procedure on a Catalyst 2900 Series Switches Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration verify it. Change passwords to the password recovery procedure be performed.
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3
Lab - Troubleshooting VLAN Configurations (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Netw 3000 VLAN 1 LAB Darlene Redmond Ryan Gamblin January 19 th 2012
 Netw 3000 VLAN 1 LAB Darlene Redmond Ryan Gamblin January 19 th 2012 3. Attach a workstation to the Management VLAN and demonstrate a successful login to the switch at the privileged exec mode, with a
Netw 3000 VLAN 1 LAB Darlene Redmond Ryan Gamblin January 19 th 2012 3. Attach a workstation to the Management VLAN and demonstrate a successful login to the switch at the privileged exec mode, with a
Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 1 192.168.1.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 1 192.168.1.12 255.255.255.0 N/A PC-A NIC 192.168.10.3 255.255.255.0
IEEE 802.1Q Configuration
 CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
CHAPTER15 This chapter describes: IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q InterVLAN Routing and 802.1Q Trunking IP Routing over IEEE 802.1Q This section provides procedures for configuring protocols supported with
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes
 Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Chapter 2 Lab 2-1, Static VLANS, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains and Modes Topology Objectives Background Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure ISL and 802.1Q trunking. VLANs logically
Lab Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure two routers and two workstations in a small WAN. Troubleshoot problems introduced by incorrect configurations. Background/Preparation
Lab 4.2.6 Troubleshooting IP Address Issues Instructor Version 2500 Objective Configure two routers and two workstations in a small WAN. Troubleshoot problems introduced by incorrect configurations. Background/Preparation
Question 5.1. Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain.
 Question 5.1 Q 5.1.1 Number of Collision Domains: = 14 Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain. Number of Broadcast Domains: = 5 Every port on a router
Question 5.1 Q 5.1.1 Number of Collision Domains: = 14 Every port on a switch is a collision domain. Every port on a router is a collision domain. Number of Broadcast Domains: = 5 Every port on a router
Note: Use two 2960 switches for ALS1 and ALS2 and two 3560 switches for DLS1 and DLS2
 LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
LAB 2 - Part I - VLANs, VLAN Trunking, and VTP Domains Topology: Objectives Set up a VTP domain. Create and maintain VLANs. Configure 802.1Q trunking. Background VLANs logically segment a network by function,
Lab Troubleshooting RIP
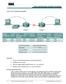 Lab 7.2.6 Troubleshooting RIP Objective Set up an IP addressing scheme using class B networks. Configure RIP on routers. Observe routing activity using the debug ip rip command. Examine routes using the
Lab 7.2.6 Troubleshooting RIP Objective Set up an IP addressing scheme using class B networks. Configure RIP on routers. Observe routing activity using the debug ip rip command. Examine routes using the
1 of :22
 Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Feedback: Help us help you Please rate this document. Excellent Good Average Fair Poor This document solved my problem. Yes No Just Browsing Suggestions to improve this document. (512 character limit)
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping
 Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab 4.2.5a Connectivity Tests Ping Objective Use the ping command to send ICMP datagrams to target host. Verify that the network layer between source and destination is working properly. Retrieve information
Lab Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.2 Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500 Objective Establish a Telnet connection to a remote router. Verify that the application layer between source and destination
Lab 4.2.2 Establishing and Verifying a Telnet Connection Instructor Version 2500 Objective Establish a Telnet connection to a remote router. Verify that the application layer between source and destination
Lab Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab 9.3.4 Troubleshooting Using traceroute Instructor Version 2500 294-833 CCNA 2: Routers and Routing Basics v 3.1 - Lab 9.3.4 Copyright 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. Objective Use the traceroute Cisco IOS
Lab Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
Lab 5.3.4.1 Inter-VLAN Routing with the Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure Inter-VLAN routing using a switch with an internal route processor. The network
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.2.7a Managing Switch Operating System Files 2900XL Series
 Lab 6.2.7a Managing Switch Operating System Files 2900XL Series Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Backup the switch IOS to a TFTP server and then restore it. Background/Preparation
Lab 6.2.7a Managing Switch Operating System Files 2900XL Series Objective Create and verify a basic switch configuration. Backup the switch IOS to a TFTP server and then restore it. Background/Preparation
Lab Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor
 Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
Lab 5.3.4.2 Routing Between an External Router and an Internal Route Processor Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to configure routing between an internal route processor and an external router.
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual
 CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
CCNP SWITCH 6.0 Student Lab Manual This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by
Lab Powering Up a Switch
 Lab 5.5.2 Powering Up a Switch Objectives Set up a new Cisco LAN switch. Connect a computer to the router console interface. Configure HyperTerminal so that the computer can communicate with the router.
Lab 5.5.2 Powering Up a Switch Objectives Set up a new Cisco LAN switch. Connect a computer to the router console interface. Configure HyperTerminal so that the computer can communicate with the router.
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic Switch Configuration
 Topology NOTE TO USER: This activity is a variation of Lab 2.5.1. Packet Tracer may not support all the tasks specified in the hands-on lab. This activity should not be considered equivalent to completing
Topology NOTE TO USER: This activity is a variation of Lab 2.5.1. Packet Tracer may not support all the tasks specified in the hands-on lab. This activity should not be considered equivalent to completing
Lab Configuring Basic Switch Settings (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1 PC-A NIC 192.168.1.10 255.255.255.0 192.168.1.1
Lab Using the Boot System Command. Objective. Background/Preparation
 Lab 5.1.3 Using the Boot System Command Objective Display information about the Cisco IOS Image (software) that is currently running. Determine where the IOS is booting from. Check the amount of RAM, Flash
Lab 5.1.3 Using the Boot System Command Objective Display information about the Cisco IOS Image (software) that is currently running. Determine where the IOS is booting from. Check the amount of RAM, Flash
Lab Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic
 Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab 1.2.2 Capturing and Analyzing Network Traffic Host Name IP Address Fa0/0 Subnet Mask IP Address S0/0/0 Subnet Mask Default Gateway RouterA 172.17.0.1 255.255.0.0 192.168.1.1 (DCE) 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab Well-Known Port Numbers and Multiple Sessions
 Lab 10.2.5 Well-Known Port Numbers and Multiple Sessions Objective Enable HTTP services on a router. Show multiple HTTP and Telnet sessions on a single host. Observe well-known TCP port numbers on the
Lab 10.2.5 Well-Known Port Numbers and Multiple Sessions Objective Enable HTTP services on a router. Show multiple HTTP and Telnet sessions on a single host. Observe well-known TCP port numbers on the
Table of Contents. isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ
 king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
king Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running isco Configuring 802.1q Trunking Between a Catalyst 3550 and Catalyst Switches Running Integrated Cisco IOS (Nativ Table of Contents Configuring
Lab Configuring Fast EtherChannel
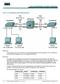 Lab 3.7.5 Configuring Fast EtherChannel Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to provide more bandwidth between Ethernet switches. Two 100-Mb links will be combined together to form a full duplex
Lab 3.7.5 Configuring Fast EtherChannel Objective Scenario The purpose of this lab is to provide more bandwidth between Ethernet switches. Two 100-Mb links will be combined together to form a full duplex
Lab Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab 7.3.5 Configuring IGRP Instructor Version 2500 Objective Setup IP an addressing scheme using class C networks. Configure IGRP on routers. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one in
Lab Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test
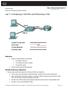 Lab 7.1.6 Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test Objectives Analyze a sample test plan to determine: The subject of the test The methods and tools for testing The potential results Perform the test
Lab 7.1.6 Analyzing a Test Plan and Performing a Test Objectives Analyze a sample test plan to determine: The subject of the test The methods and tools for testing The potential results Perform the test
Lab Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 2.2.1 Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the System Configuration dialog (setup). Establish some basic router configurations. Background/Preparation A new router
Lab 2.2.1 Router Configuration Using Setup Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the System Configuration dialog (setup). Establish some basic router configurations. Background/Preparation A new router
Lab Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series
 Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.5 Configuring OSPF Timers 2500 Series Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF interface timers to adjust efficiency of network. Background/Preparation
Lab Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
Lab 9.3.5 Troubleshooting Routing Issues with show ip route and show ip protocols Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the show ip route and show ip protocol commands to diagnose a routing configuration
Lab VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
Lab 11.2.6 VTY Restriction Instructor Version 2500 NOTE: The loopback entry in this graphic is not required in the lab. Objective Scenario Use the access-class and line commands to control Telnet access
VLANs. Traditional Campus Networks. Performance Issues. Broadcast Issues. Bridges terminate collision domains
 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain VLANs Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router
 Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
Chapter 4 Lab 4-1, Inter-VLAN Routing with an External Router Topology Objective Background Configure inter-vlan routing using an external router, also known as a router on a stick. Inter-VLAN routing
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs. CCNA Exploration Semester 3 Chapter Sep-13
 VLANs CCNA Exploration Semester 3 Chapter 3 1 Topics The role of VLANs in a network Trunking VLANs Configure VLANs on switches Troubleshoot common VLAN problems 2 Semester 3 LAN Design Basic Switch Concepts
VLANs CCNA Exploration Semester 3 Chapter 3 1 Topics The role of VLANs in a network Trunking VLANs Configure VLANs on switches Troubleshoot common VLAN problems 2 Semester 3 LAN Design Basic Switch Concepts
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Solution)
 (Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
(Solution) Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/0 192.168.20.1 255.255.255.0 N/A G0/1 192.168.10.1 255.255.255.0 N/A S1 VLAN 10 192.168.10.11
VLANs. 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1
 VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
VLANs 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. 2-1 Traditional Campus Networks Broadcast Domain Collision Domain 1 Collision Domain 2 Bridges terminate collision domains 2003, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Lab Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version)
 (Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
(Instructor Version) Instructor Note: Red font color or Gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask
Lab 1. CLI Navigation. Scenario. Initial Configuration for R1
 Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Lab 1 CLI Navigation This lab covers the most basic skills for accessing and using the command-line interface (CLI) on a Cisco router or switch. Many of the small, picky details of how the CLI works cannot
Lab 6.4.1: Basic Inter-VLAN Routing
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 172.17.99.1
Lab Troubleshooting VTP Configuration
 Lab 4.4.3 Troubleshooting VTP Configuration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
Lab 4.4.3 Troubleshooting VTP Configuration Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0
All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example
 All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 81682 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
All Transparent VTP Domain to Server Client VTP Domain Migration Configuration Example Document ID: 81682 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Conventions Background Information
Lab Configuring 802.1Q Trunk-Based Inter-VLAN Routing (Instructor Version Optional Lab)
 (Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
(Instructor Version Optional Lab) Instructor Note: Red font color or gray highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only. Optional activities are designed to enhance understanding and/or
Lab Modifying OSPF Cost Metric
 Lab 2.3.3 Modifying OSPF Cost Metric Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF cost metric on an interface. Background/Preparation
Lab 2.3.3 Modifying OSPF Cost Metric Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Modify OSPF cost metric on an interface. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring DHCP
 Lab 1.2.6 Configuring DHCP Objective Configure a router for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to dynamically assign addresses to attached hosts. Background/Preparation Routing between the ISP
Lab 1.2.6 Configuring DHCP Objective Configure a router for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to dynamically assign addresses to attached hosts. Background/Preparation Routing between the ISP
Lab Verifying RIP v2 Configuration
 Lab 1.2.5 Verifying RIP v2 Configuration Objective Configure RIP v1 and v2 on routers. Use show commands to verify RIP v2 operation. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the
Lab 1.2.5 Verifying RIP v2 Configuration Objective Configure RIP v1 and v2 on routers. Use show commands to verify RIP v2 operation. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar to the one shown in the
Lab b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 11.2.1b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500 Objective Scenario Plan, configure, and apply a standard ACL to permit or deny specific traffic and test the ACL to determine if the desired results were
Lab 11.2.1b Standard ACLs Instructor Version 2500 Objective Scenario Plan, configure, and apply a standard ACL to permit or deny specific traffic and test the ACL to determine if the desired results were
Lab Configuring the OSPF Routing Process
 Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area 0. Configure and verify Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Lab 2.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Routing Process Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for OSPF area 0. Configure and verify Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing. Background/Preparation Cable a network
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT
 Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
Lab 1.1.4a Configuring NAT Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses. Background/Preparation
PT Activity 4.4.1: Basic VTP Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13 255.255.255.0
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13 255.255.255.0
Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using Cisco Express Forwarding (CEF).
 Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Lab 3- Part I Inter-VLAN routing with a Multilayer Switch Configuration and Management of Networks - 2014 Topology Objective Route between VLANs using a 3560 switch with an internal route processor using
Lab Configuring OSPF Authentication
 Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication into the area.
Lab 2.3.4 Configuring OSPF Authentication Objective Setup an IP addressing scheme for Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) area. Configure and verify OSPF routing. Introduce OSPF authentication into the area.
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing
 Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab 5: Inter-VLANs Routing Network Topology:- Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Gateway/Clock Rate Fa 0/0.10 10.5.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- R1 Fa 0/0.20 10.6.0.1 255.255.255.192 ----- Fa 0/0.30 10.10.0.1
Lab Command Modes and Router Identification. Objective. Background/Preparation. Step 1 Login to the router in user EXEC mode
 Lab 3.1.2 Command Modes and Router Identification Objective Identify basic router modes of user EXEC and privileged EXEC. Use commands to enter specific modes. Become familiar with the router prompt for
Lab 3.1.2 Command Modes and Router Identification Objective Identify basic router modes of user EXEC and privileged EXEC. Use commands to enter specific modes. Become familiar with the router prompt for
Lab Verifying PPP Configuration
 Lab 3.3.4 Verifying PPP Configuration Objective Configure a serial interface on two routers with the PPP protocol. Verify and test the link for connectivity. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar
Lab 3.3.4 Verifying PPP Configuration Objective Configure a serial interface on two routers with the PPP protocol. Verify and test the link for connectivity. Background/Preparation Cable a network similar
Lab Configuring a Serial Interface
 Lab 3.1.5 Configuring a Serial Interface Objective Configure a serial interface on each of two routers so they can communicate. Background/Preparation Any router that meets the interface requirements may
Lab 3.1.5 Configuring a Serial Interface Objective Configure a serial interface on each of two routers so they can communicate. Background/Preparation Any router that meets the interface requirements may
Table of Contents. co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern
 outing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2 co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern Table of Contents Configuring
outing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2 co Configuring InterVLAN Routing and ISL/802.1Q Trunking on a Catalyst 2900XL/3500XL/2950 Switch Using An Extern Table of Contents Configuring
Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software
 Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab Managing Router Configuration Files with Terminal Emulation Software Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway R1 G0/1 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 N/A
Lab Configuring the Management VLAN on a Single Switch
 Lab 7.5.6.4 Configuring the Management VLAN on a Single Switch Objective Equipment Scenario Step 1 In this lab, students will configure and use a non-default Management VLAN. This lab will use the config-vlan
Lab 7.5.6.4 Configuring the Management VLAN on a Single Switch Objective Equipment Scenario Step 1 In this lab, students will configure and use a non-default Management VLAN. This lab will use the config-vlan
CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual
 CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, Indiana 46240 USA ii CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual CCNA SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Copyright 2011
CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Cisco Press 800 East 96th Street Indianapolis, Indiana 46240 USA ii CCNP SWITCH Lab Manual CCNA SWITCH Lab Manual Cisco Networking Academy Copyright 2011
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses
 Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Lab 1.1.4c Configuring Static NAT Addresses Objective Configure a router to use network address translation (NAT) to convert internal IP addresses, typically private addresses, into outside public addresses.
Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on a router.
 Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on a router. Background/Preparation
Lab 5.2.5 Managing IOS Images with TFTP Objective Backup a copy of a router IOS from flash to a TFTP server. Reload the backup IOS software image from a TFTP server into flash on a router. Background/Preparation
Lab Configuring Router Passwords. Objective. Background/Preparation. Step 1 Login to the router in user EXEC mode
 Lab 3.1.3 Configuring Router Passwords Objective Configure a password for console login to user EXEC mode. Configure a password for virtual terminal (Telnet) sessions. Configure a secret password for privileged
Lab 3.1.3 Configuring Router Passwords Objective Configure a password for console login to user EXEC mode. Configure a password for virtual terminal (Telnet) sessions. Configure a secret password for privileged
Lab Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration
 Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
Lab 1.1.5 Verifying NAT and PAT Configuration Objective Configure a router for Network Address Translation (NAT) and Port Address Translation (PAT) Test the configuration and verify NAT/PAT statistics
Buy full file at
 14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
14 Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy Chapter 2 LAN Redundancy 2.0.1.2 Class Activity Stormy Traffic ( ) Objective Explain the purpose of the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) in a switched LAN environment with redundant
Lab Configuring ISDN BRI (U-Interface)
 Lab 4.2.1 Configuring ISDN BRI (U-Interface) Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a successful connection to a local ISDN switch. Background/Preparation This lab assumes that a router with an ISDN
Lab 4.2.1 Configuring ISDN BRI (U-Interface) Objective Configure an ISDN router to make a successful connection to a local ISDN switch. Background/Preparation This lab assumes that a router with an ISDN
Lab 5: Basic VLAN Configuration
 Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
Topology Diagram Addressing Table Device (Hostname) Interface IP Address Subnet Mask Default Gateway S1 VLAN 99 172.17.99.11 255.255.255.0 N/A S2 VLAN 99 172.17.99.12 255.255.255.0 N/A S3 VLAN 99 172.17.99.13
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example
 EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
EtherSwitch Service Module (ES) Configuration Example Document ID: 82288 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Related Products Conventions EtherSwitch Modules Concepts Configure
Lab Backing up Configuration Files Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Instructor Version 2500 Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the
Lab 3.2.9 Backing up Configuration Files Instructor Version 2500 Objective Demonstrate the capture of the running configuration of a router to an ASCII text file with HyperTerminal. Edit or modify the
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller
 Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario Step 1 In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless access points,
Lab 6-1 Configuring a WLAN Controller Topology Diagram Scenario Step 1 In the next two labs, you will configure a wireless solution involving a WLAN controller, two lightweight wireless access points,
Lab Configuring EtherChannel
 Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Topology Addressing Table Objectives Device Interface IP Address Subnet Mask S1 VLAN 99 192.168.99.11 255.255.255.0 S2 VLAN 99 192.168.99.12 255.255.255.0 S3 VLAN 99 192.168.99.13 255.255.255.0 PC-A NIC
Lab Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500
 Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
Lab 4.2.4 Advanced Telnet Operations Instructor Version 2500 Objective Use the telnet command to remotely access other routers. Verify that the application layer between the source and the destination
Configuring Routing CHAPTERS
 Configuring Routing CHAPTERS 1. Overview 2. IPv4 Static Routing Configuration 3. IPv6 Static Routing Configuration 4. Viewing Routing Table 5. Example for Static Routing This guide applies to: T1600G-52TS
Configuring Routing CHAPTERS 1. Overview 2. IPv4 Static Routing Configuration 3. IPv6 Static Routing Configuration 4. Viewing Routing Table 5. Example for Static Routing This guide applies to: T1600G-52TS
Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software
 Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software Document ID: 8759 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Theory Important
Configuring ISL Trunking Between Catalyst Switches Running CatOS and Cisco IOS System Software Document ID: 8759 Contents Introduction Prerequisites Requirements Components Used Background Theory Important
Configuring a LAN with DHCP and VLANs
 CHAPTER 15 The Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) support clients on both physical LANs and VLANs. The routers can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to enable
CHAPTER 15 The Cisco 860 and Cisco 880 series Integrated Services Routers (ISRs) support clients on both physical LANs and VLANs. The routers can use the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) to enable
Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, First Hop Redundancy Protocols HSRP and VRRP INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, First Hop Redundancy Protocols HSRP and VRRP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP and load balancing Configure HSRP authentication
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 6 Lab 6-1, First Hop Redundancy Protocols HSRP and VRRP INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Configure inter-vlan routing with HSRP and load balancing Configure HSRP authentication
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and
 This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy this document for non-commercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the CCNA Exploration:
Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION
 CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
CCNPv7.1 SWITCH Chapter 5 Lab 5-1 Inter-VLAN Routing INSTRUCTOR VERSION Topology Objectives Implement a Layer 3 EtherChannel Implement Static Routing Implement Inter-VLAN Routing Background Cisco's switching
Lab Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup
 Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
Lab 1.2.9.1 Catalyst 2950T and 3550 Series Basic Setup Objective Configure a Cisco Catalyst 2950T or 3550 series Ethernet switch for the first time using the command-line interface (CLI) mode. Basic first
