Stating Your Preferences
|
|
|
- Osborn Griffin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Stating Your Preferences James W. Cooper Sometimes you don t remember what you prefer. For example, when you dine at the famous French restaurant Picholine, and are confronted with their mammoth cheese trolley, did you prefer the Perail over the Coolea? It would be nice if we had written this down in our Pomme Pilot, but we probably didn t. Java programmers have frequently faced the same problem. Short of hard coding a bunch of constants, how can we write an application that remembers data from one application to another. This is particularly difficult, when different users may have different preferences or requirements (such as Abbaye de Belloc or Zamorano). The recent release of JDK 1.4 has provided us with an excellent new API for solving such preference problems. Specifically, you can save data in a global database, labeled by user and application and retrieve it at another time. The structure and location of that database are not specified, and it is designed for robust access, but not necessarily for speed. In Windows, for example, these data are stored in the Registry, and in Linux, the data are stored in the file system. All of this is carried out below your eye level, and from the point of view of the Java programmer, it is unimportant how it is stored. The API The java.util.prefs package contains just a few classes, most notably the abstract Preferences class. While this class is abstract, it does contain a few concrete static methods for obtaining a Preference object. Preferences are organized into two trees: System and User, which could contain related information. The idea, of course, is that some program data is global, and regardless of who runs it the some constant values apply. And, on the other hand, some data is user specific, and each user should be able to store and retrieve his own unique values. Data in the Preferences database can be strings, just as it can in Properties files and inifiles, but the data can also be integer, long, float, double, Boolean or a byte array. Each entry is limited to 8192 bytes, however. To begin using Preferences, you need to get an instance of either the usernode or the systemnode for your program package: Preferences prefs = Preferences.userNodeForPackage(getClass()); Note that the Preferences API acts a Factory and returns an instance of a Preferences object using the current class as an argument. What it actually does is look at that class s package and return a Preferences object for that package. The Preference system then stores each tag name you select prefixed with the package name. So, let us suppose we want to store the final size of the window when we close it, so it will be that size when we re-open it in a later session. When the system closes, we just get the current size and store it in the Preferences database: private final String stxsize="xsize";
2 private final String stysize="ysize"; private final String apptitle ="prefdemo"; public void WindowClose() { Dimension dim = frame.getsize(); prefs.putint(apptitle + xsize, dim.width); prefs.putint(apptitle + ysize, dim.height); System.exit(0); Note that we are prefixing the name of the tag with the title of the actual application. This helps make each entry unique. So in this example, the tags are actually named prefdemoxsize and prefdemoysize You can name a tag anything you want, although it is conventional to prefix the variable name with the name of the application. Names may be any set of numbers and characters, but cannot contain the forward slash / character. Since you name the variables by application program name, you could access and change these variable from other applications as long as you know the program name you are looking for. This allows you to write an administration program that could set default parameters for other programs in the same package by simply using the names of those programs. In this example, we are storing integer values. For other types of data there are analogous methods: put Boolean, putbytearray, putdouble, putfloat, and putlong. Not every small program is put into a package, however. If you simply write a program as part of the default package, (the unnamed package), the data are stored as part of a package called <unnamed>. To get the values back again, when you restart the program, you just reverse this process: public int getxsize() { return prefs.getint(apptitle + stxsize, 400); Note that the get methods always require a default value as a second argument in case no value has yet been entered in the Preferences database. In Figure 1, we show how the Registry stores these data. You will see our program preference under the com.javapro.javatecture package.
3 Figure 1 - Preference data for our simple demo program Chacun a son Gout Now, every user may have his own preferences, even for something as simple as window size and position. So the preference system allows for this, by keeping the user branch of the Preference tree by user. So it is possible to store your favorite preferences for window size and then log off and log back on as a different user and set them differently. Note that there is nothing specifically in our application code to switch between users: this is handled automatically by the Preferences system. If instead of accessing the User preferences, you access the System preferences, these are truly user-independent and will save return the same values regardless of which user ID they are obtained from. Preferences pref = systemnodeforpackage(getclass()); Since you might conceivably keep around 2 or more Preferences objects, some user and some system, the API cleverly provides an isusernode() method so you can determine which kind of Preferences object you are dealing with. More Preferences I write Java applications all the time that do reasonably useful things within my work. Very frequently, these programs operate using some set of data parameters which I like to vary over time. For example, the name of the database I interact with could well be a user-level Preference parameter, but the value of some computation parameters like, for instance, a data smoothing constant, could vary from run to run within a single day. I call this third kind of preference an application-level preference, and would like to be able to change a number of these between program runs without either building an excessively complex user interface, or saving and restoring a lot of data in the Registry.
4 It is this sort of application-level data that I would normally store in a initialization file. Such a file is a pure text file that I can easily edit between runs to affect the outcome of my computation. The way I handle this using the Preferences API is to specify a Configuration filename and path from within the program one time when we first run it and then get that filename from the Preferences database each time the program starts. Let s consider the following simple program which can read in Windows-style ini-files as configuration files. When it first starts, it looks in the Preferences database for a configuration filename, and not finding one, it displays a message that it has no configuration file, as we see in Figure 2. Figure 2 - Our application before a configuration file is specified You can see us selecting the menu item to obtain a configuration file in Figure 3 Figure 3 - The menu item to select a configuration file. And the JFileChooser box where we select it in Figure 4.
5 Figure 4 - Selecting the configuration file. Here is the code the launches the JfileChoose and saves the filename: public void selectconfigfile() { JFileChooser chooser = new JFileChooser(); int returnval = chooser.showopendialog(frame); if (returnval == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) { configfile = chooser.getselectedfile().getabsolutepath() ; prefs.put(apptitle + configname, configfile); After this, our application displays the name of the file and the current value of the smoothing constant as you see in Figure 5. Figure 5 - The application showing the configuration file and the smoothing constant it contains. The actual configuration file just contains the following two lines: [data] smoothing=3.2
6 We read this file using the ini-file classes we developed in our November, 2001 column (Courage in Profiles). Here is an example: public float getsmoothing() { File fini = new File(configFile); IniFile ini = null; float smooth = 0.0f; if (fini.exists()) { try { ini = new IniFile(configFile); catch (IOException e) { smooth = 0.0f; smooth = new Float( ini.getprofile("data", "smoothing")).floatvalue(); return smooth; Using Our Application So every time we start up this application, it goes to the Preferences system and fetches the xsize and ysize and the configuration filename. Then if that filename exists it loads the current smoothing constant. This is very convenient, because I can now vary several application level parameters by just editing the configuration file, and running the application with these new values. I structured this program so all of the computations for manipulating preferences are in a simple PMediator class, that handles the reading and writing of Preferences and configuration file parameters. You can see the entire class in Listing 1. /** * Preferences file Mediator */ package com.javapro.javatecture; import java.util.prefs.*; import javax.swing.*; import java.awt.*; import java.io.*; public class PMediator { private Preferences prefs; private JFrame frame; private String apptitle; private String configfile; private final String configname = "configfile"; private final String stxsize="xsize"; private final String stysize="ysize"; public PMediator(JFrame frame, String apptitle) { prefs = Preferences.userNodeForPackage(getClass()); this.frame = frame; this.apptitle = apptitle; configfile = prefs.get(apptitle + configname, ""); public float getsmoothing() {
7 File fini = new File(configFile); IniFile ini = null; float smooth = 0.0f; if (fini.exists()) { try { ini = new IniFile(configFile); catch (IOException e) { smooth = 0.0f; smooth = new Float(ini.getProfile("Data", "smoothing")).floatvalue(); return smooth; public void forgetconfig() { configfile = ""; prefs.remove(apptitle + configname); public String getconfigfilename() { if (configfile.length() < 1) return "No config file selected"; else return configfile; public void selectconfigfile() { JFileChooser chooser = new JFileChooser(); int returnval = chooser.showopendialog(frame); if (returnval == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION) { configfile = chooser.getselectedfile().getabsolutepath() ; prefs.put(apptitle + configname, configfile); public void WindowClose() { Dimension dim = frame.getsize(); prefs.putint(apptitle + stxsize, dim.width); prefs.putint(apptitle + stysize, dim.height); System.exit(0); public int getxsize() { return prefs.getint(apptitle + stxsize, 400); public int getysize() { return prefs.getint(apptitle + stysize, 300); Listing 1 The PMediator class for manipulating Preferences and the configuration file.
8 You can see how we use this class in the fragment of the main Swing application show in Listing 2. public PDemo() { super("preferences demo"); //set title bar med = new PMediator(this, "prefdemo"); super.setmediator(med); //tell frame about mediator int xsize = med.getxsize(); //get the window sizes int ysize = med.getysize(); setsize(xsize, ysize); setgui(); //set up the display setvisible(true); //display the window ---- private void setgui() { setmenus(); //create the menus //layout the screen getcontentpane().setlayout(new BorderLayout()); JPanel jp = new JPanel(); jp.setlayout(new GridLayout(3, 1)); getcontentpane().add(jp); //display the configuration time label = new JLabel(med.getConfigFilename()); label.setfont( new Font("SansSerif", Font.BOLD,14 )); label.setforeground( Color.red); jp.add("center", label); //display the current smoothing constant smooth = new JLabel(); smooth.setfont( new Font("SansSerif", Font.BOLD,16 )); smooth.setforeground(color.blue); jp.add("center", smooth); jp.setbackground(color.white); loadsmooth(); //get the smoothing function //get the current smoothing constant and display it private void loadsmooth() { smooth.settext("smoothing value: " + new Float(med.getSmoothing()).toString()); Listing 2 A section of the main application showing how the PMediator class is used. Summary You can store any kind of preference information in the Preferences system, whether you know a Camembert from a ComboBox. You can even use it effectively to provide parameters to JSP beans and servlets more conveniently. I m already using it every day.
Eclipsing Your IDE. Figure 1 The first Eclipse screen.
 Eclipsing Your IDE James W. Cooper I have been hearing about the Eclipse project for some months, and decided I had to take some time to play around with it. Eclipse is a development project (www.eclipse.org)
Eclipsing Your IDE James W. Cooper I have been hearing about the Eclipse project for some months, and decided I had to take some time to play around with it. Eclipse is a development project (www.eclipse.org)
Class 16: The Swing Event Model
 Introduction to Computation and Problem Solving Class 16: The Swing Event Model Prof. Steven R. Lerman and Dr. V. Judson Harward 1 The Java Event Model Up until now, we have focused on GUI's to present
Introduction to Computation and Problem Solving Class 16: The Swing Event Model Prof. Steven R. Lerman and Dr. V. Judson Harward 1 The Java Event Model Up until now, we have focused on GUI's to present
Frames, GUI and events. Introduction to Swing Structure of Frame based applications Graphical User Interface (GUI) Events and event handling
 Frames, GUI and events Introduction to Swing Structure of Frame based applications Graphical User Interface (GUI) Events and event handling Introduction to Swing The Java AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit)
Frames, GUI and events Introduction to Swing Structure of Frame based applications Graphical User Interface (GUI) Events and event handling Introduction to Swing The Java AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit)
CS506 Web Design & Development Final Term Solved MCQs with Reference
 with Reference I am student in MCS (Virtual University of Pakistan). All the MCQs are solved by me. I followed the Moaaz pattern in Writing and Layout this document. Because many students are familiar
with Reference I am student in MCS (Virtual University of Pakistan). All the MCQs are solved by me. I followed the Moaaz pattern in Writing and Layout this document. Because many students are familiar
I VE GOT A LITTLE LIST
 1 I VE GOT A LITTLE LIST James W. Cooper As someday it may happen that a sorted list must be found, Java s got the list. I was thinking about the problem of sorted terms in a list box when I was writing
1 I VE GOT A LITTLE LIST James W. Cooper As someday it may happen that a sorted list must be found, Java s got the list. I was thinking about the problem of sorted terms in a list box when I was writing
Swing from A to Z Using Focus in Swing, Part 2. Preface
 Swing from A to Z Using Focus in Swing, Part 2 By Richard G. Baldwin Java Programming, Lecture Notes # 1042 November 27, 2000 Preface Introduction Sample Program Interesting Code Fragments Summary What's
Swing from A to Z Using Focus in Swing, Part 2 By Richard G. Baldwin Java Programming, Lecture Notes # 1042 November 27, 2000 Preface Introduction Sample Program Interesting Code Fragments Summary What's
Swing from A to Z Some Simple Components. Preface
 By Richard G. Baldwin baldwin.richard@iname.com Java Programming, Lecture Notes # 1005 July 31, 2000 Swing from A to Z Some Simple Components Preface Introduction Sample Program Interesting Code Fragments
By Richard G. Baldwin baldwin.richard@iname.com Java Programming, Lecture Notes # 1005 July 31, 2000 Swing from A to Z Some Simple Components Preface Introduction Sample Program Interesting Code Fragments
CSEN401 Computer Programming Lab. Topics: Graphical User Interface Window Interfaces using Swing
 CSEN401 Computer Programming Lab Topics: Graphical User Interface Window Interfaces using Swing Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher 22.3.2015 c S. Abdennadher 1 Swing c S. Abdennadher 2 AWT versus Swing Two basic
CSEN401 Computer Programming Lab Topics: Graphical User Interface Window Interfaces using Swing Prof. Dr. Slim Abdennadher 22.3.2015 c S. Abdennadher 1 Swing c S. Abdennadher 2 AWT versus Swing Two basic
CS 251 Intermediate Programming GUIs: Components and Layout
 CS 251 Intermediate Programming GUIs: Components and Layout Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Fall 2017 import javax. swing.*; Hello GUI public class HelloGUI extends JFrame { public HelloGUI ()
CS 251 Intermediate Programming GUIs: Components and Layout Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Fall 2017 import javax. swing.*; Hello GUI public class HelloGUI extends JFrame { public HelloGUI ()
Topic 9: Swing. Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more
 Swing = Java's GUI library Topic 9: Swing Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more Assignment 5: Will be an open-ended Swing project. "Programming Contest"
Swing = Java's GUI library Topic 9: Swing Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more Assignment 5: Will be an open-ended Swing project. "Programming Contest"
Topic 9: Swing. Why are we studying Swing? GUIs Up to now: line-by-line programs: computer displays text user types text. Outline. 1. Useful & fun!
 Swing = Java's GUI library Topic 9: Swing Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more Why are we studying Swing? 1. Useful & fun! 2. Good application of OOP techniques
Swing = Java's GUI library Topic 9: Swing Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more Why are we studying Swing? 1. Useful & fun! 2. Good application of OOP techniques
School of Computer Science CPS109 Course Notes 5 Alexander Ferworn Updated Fall 15
 Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 1 2 IF... 1 2.1 BOOLEAN EXPRESSIONS... 3 2.2 BLOCKS... 3 2.3 IF-ELSE... 4 2.4 NESTING... 5 3 SWITCH (SOMETIMES KNOWN AS CASE )... 6 3.1 A BIT ABOUT BREAK... 7 4 CONDITIONAL
AP CS Unit 11: Graphics and Events
 AP CS Unit 11: Graphics and Events This packet shows how to create programs with a graphical interface in a way that is consistent with the approach used in the Elevens program. Copy the following two
AP CS Unit 11: Graphics and Events This packet shows how to create programs with a graphical interface in a way that is consistent with the approach used in the Elevens program. Copy the following two
CS Exam 1 Review Suggestions
 CS 235 - Fall 2015 - Exam 1 Review Suggestions p. 1 last modified: 2015-09-30 CS 235 - Exam 1 Review Suggestions You are responsible for material covered in class sessions, lab exercises, and homeworks;
CS 235 - Fall 2015 - Exam 1 Review Suggestions p. 1 last modified: 2015-09-30 CS 235 - Exam 1 Review Suggestions You are responsible for material covered in class sessions, lab exercises, and homeworks;
Lesson 3: Accepting User Input and Using Different Methods for Output
 Lesson 3: Accepting User Input and Using Different Methods for Output Introduction So far, you have had an overview of the basics in Java. This document will discuss how to put some power in your program
Lesson 3: Accepting User Input and Using Different Methods for Output Introduction So far, you have had an overview of the basics in Java. This document will discuss how to put some power in your program
COMP 1006/1406 Assignment 1 Carleton Foodorama (Part 1) Due: Friday, July 14 th 2006, before 11h55 pm
 COMP 006/406 Assignment Carleton Foodorama (Part ) Due: Friday, July 4 th 2006, before h55 pm In this assignment, you will review basic concepts from COMP 005. You will get to design a simple text-based
COMP 006/406 Assignment Carleton Foodorama (Part ) Due: Friday, July 4 th 2006, before h55 pm In this assignment, you will review basic concepts from COMP 005. You will get to design a simple text-based
First Name: AITI 2004: Exam 2 July 19, 2004
 First Name: AITI 2004: Exam 2 July 19, 2004 Last Name: JSP Track Read Instructions Carefully! This is a 3 hour closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. Please write clearly if we cannot understand
First Name: AITI 2004: Exam 2 July 19, 2004 Last Name: JSP Track Read Instructions Carefully! This is a 3 hour closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. Please write clearly if we cannot understand
Outline. Topic 9: Swing. GUIs Up to now: line-by-line programs: computer displays text user types text AWT. A. Basics
 Topic 9: Swing Outline Swing = Java's GUI library Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more Assignment 7: Expand moving shapes from Assignment 4 into game. "Programming
Topic 9: Swing Outline Swing = Java's GUI library Swing is a BIG library Goal: cover basics give you concepts & tools for learning more Assignment 7: Expand moving shapes from Assignment 4 into game. "Programming
Welcome to CIS 068! 1. GUIs: JAVA Swing 2. (Streams and Files we ll not cover this in this semester, just a review) CIS 068
 Welcome to! 1. GUIs: JAVA Swing 2. (Streams and Files we ll not cover this in this semester, just a review) Overview JAVA and GUIs: SWING Container, Components, Layouts Using SWING Streams and Files Text
Welcome to! 1. GUIs: JAVA Swing 2. (Streams and Files we ll not cover this in this semester, just a review) Overview JAVA and GUIs: SWING Container, Components, Layouts Using SWING Streams and Files Text
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388)
 Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Introduction to Programming Using Java (98-388) Understand Java fundamentals Describe the use of main in a Java application Signature of main, why it is static; how to consume an instance of your own class;
Educational Fusion. Implementing a Production Quality User Interface With JFC
 Educational Fusion Implementing a Production Quality User Interface With JFC Kevin Kennedy Prof. Seth Teller 6.199 May 1999 Abstract Educational Fusion is a online algorithmic teaching program implemented
Educational Fusion Implementing a Production Quality User Interface With JFC Kevin Kennedy Prof. Seth Teller 6.199 May 1999 Abstract Educational Fusion is a online algorithmic teaching program implemented
Pace University. Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1
 Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
CS 11 java track: lecture 3
 CS 11 java track: lecture 3 This week: documentation (javadoc) exception handling more on object-oriented programming (OOP) inheritance and polymorphism abstract classes and interfaces graphical user interfaces
CS 11 java track: lecture 3 This week: documentation (javadoc) exception handling more on object-oriented programming (OOP) inheritance and polymorphism abstract classes and interfaces graphical user interfaces
Lecture 28. Exceptions and Inner Classes. Goals. We are going to talk in more detail about two advanced Java features:
 Lecture 28 Exceptions and Inner Classes Goals We are going to talk in more detail about two advanced Java features: Exceptions supply Java s error handling mechanism. Inner classes ease the overhead of
Lecture 28 Exceptions and Inner Classes Goals We are going to talk in more detail about two advanced Java features: Exceptions supply Java s error handling mechanism. Inner classes ease the overhead of
CSSE 220 Day 19. Object-Oriented Design Files & Exceptions. Check out FilesAndExceptions from SVN
 CSSE 220 Day 19 Object-Oriented Design Files & Exceptions Check out FilesAndExceptions from SVN A practical technique OBJECT-ORIENTED DESIGN Object-Oriented Design We won t use full-scale, formal methodologies
CSSE 220 Day 19 Object-Oriented Design Files & Exceptions Check out FilesAndExceptions from SVN A practical technique OBJECT-ORIENTED DESIGN Object-Oriented Design We won t use full-scale, formal methodologies
Building a GUI in Java with Swing. CITS1001 extension notes Rachel Cardell-Oliver
 Building a GUI in Java with Swing CITS1001 extension notes Rachel Cardell-Oliver Lecture Outline 1. Swing components 2. Building a GUI 3. Animating the GUI 2 Swing A collection of classes of GUI components
Building a GUI in Java with Swing CITS1001 extension notes Rachel Cardell-Oliver Lecture Outline 1. Swing components 2. Building a GUI 3. Animating the GUI 2 Swing A collection of classes of GUI components
CSSE 220 Day 19. Object-Oriented Design Files & Exceptions. Check out FilesAndExceptions from SVN
 CSSE 220 Day 19 Object-Oriented Design Files & Exceptions Check out FilesAndExceptions from SVN A practical technique OBJECT-ORIENTED DESIGN Object-Oriented Design We won t use full-scale, formal methodologies
CSSE 220 Day 19 Object-Oriented Design Files & Exceptions Check out FilesAndExceptions from SVN A practical technique OBJECT-ORIENTED DESIGN Object-Oriented Design We won t use full-scale, formal methodologies
Java Programming Lecture 6
 Java Programming Lecture 6 Alice E. Fischer Feb 15, 2013 Java Programming - L6... 1/32 Dialog Boxes Class Derivation The First Swing Programs: Snow and Moving The Second Swing Program: Smile Swing Components
Java Programming Lecture 6 Alice E. Fischer Feb 15, 2013 Java Programming - L6... 1/32 Dialog Boxes Class Derivation The First Swing Programs: Snow and Moving The Second Swing Program: Smile Swing Components
Java Help Files. by Peter Lavin. May 22, 2004
 Java Help Files by Peter Lavin May 22, 2004 Overview Help screens are a necessity for making any application user-friendly. This article will show how the JEditorPane and JFrame classes, along with HTML
Java Help Files by Peter Lavin May 22, 2004 Overview Help screens are a necessity for making any application user-friendly. This article will show how the JEditorPane and JFrame classes, along with HTML
CS 3 Introduction to Software Engineering. 3: Exceptions
 CS 3 Introduction to Software Engineering 3: Exceptions Questions? 2 Objectives Last Time: Procedural Abstraction This Time: Procedural Abstraction II Focus on Exceptions. Starting Next Time: Data Abstraction
CS 3 Introduction to Software Engineering 3: Exceptions Questions? 2 Objectives Last Time: Procedural Abstraction This Time: Procedural Abstraction II Focus on Exceptions. Starting Next Time: Data Abstraction
A Simple Text Editor Application
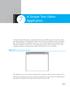 CASE STUDY 7 A Simple Text Editor Application To demonstrate the JTextArea component, fonts, menus, and file choosers we present a simple text editor application. This application allows you to create
CASE STUDY 7 A Simple Text Editor Application To demonstrate the JTextArea component, fonts, menus, and file choosers we present a simple text editor application. This application allows you to create
Week 7 - More Java! this stands for the calling object:
 Week 7 - More Java! Variable Scoping, Revisited this Parameter Encapsulation & Principles of Information Hiding: Use of public and private within class API, ADT javadoc Variables of class Type Wrapper
Week 7 - More Java! Variable Scoping, Revisited this Parameter Encapsulation & Principles of Information Hiding: Use of public and private within class API, ADT javadoc Variables of class Type Wrapper
Introduction to the JAVA UI classes Advanced HCI IAT351
 Introduction to the JAVA UI classes Advanced HCI IAT351 Week 3 Lecture 1 17.09.2012 Lyn Bartram lyn@sfu.ca About JFC and Swing JFC Java TM Foundation Classes Encompass a group of features for constructing
Introduction to the JAVA UI classes Advanced HCI IAT351 Week 3 Lecture 1 17.09.2012 Lyn Bartram lyn@sfu.ca About JFC and Swing JFC Java TM Foundation Classes Encompass a group of features for constructing
Text Input and Conditionals
 Text Input and Conditionals Text Input Many programs allow the user to enter information, like a username and password. Python makes taking input from the user seamless with a single line of code: input()
Text Input and Conditionals Text Input Many programs allow the user to enter information, like a username and password. Python makes taking input from the user seamless with a single line of code: input()
Project #1 rev 2 Computer Science 2334 Fall 2013 This project is individual work. Each student must complete this assignment independently.
 Project #1 rev 2 Computer Science 2334 Fall 2013 This project is individual work. Each student must complete this assignment independently. User Request: Create a simple magazine data system. Milestones:
Project #1 rev 2 Computer Science 2334 Fall 2013 This project is individual work. Each student must complete this assignment independently. User Request: Create a simple magazine data system. Milestones:
Application Development in JAVA. Data Types, Variable, Comments & Operators. Part I: Core Java (J2SE) Getting Started
 Application Development in JAVA Duration Lecture: Specialization x Hours Core Java (J2SE) & Advance Java (J2EE) Detailed Module Part I: Core Java (J2SE) Getting Started What is Java all about? Features
Application Development in JAVA Duration Lecture: Specialization x Hours Core Java (J2SE) & Advance Java (J2EE) Detailed Module Part I: Core Java (J2SE) Getting Started What is Java all about? Features
Part 3: Graphical User Interface (GUI) & Java Applets
 1,QWURGXFWLRQWR-DYD3URJUDPPLQJ (( Part 3: Graphical User Interface (GUI) & Java Applets EE905-GUI 7RSLFV Creating a Window Panels Event Handling Swing GUI Components ƒ Layout Management ƒ Text Field ƒ
1,QWURGXFWLRQWR-DYD3URJUDPPLQJ (( Part 3: Graphical User Interface (GUI) & Java Applets EE905-GUI 7RSLFV Creating a Window Panels Event Handling Swing GUI Components ƒ Layout Management ƒ Text Field ƒ
Introduction to Java
 Introduction to Java Module 1: Getting started, Java Basics 22/01/2010 Prepared by Chris Panayiotou for EPL 233 1 Lab Objectives o Objective: Learn how to write, compile and execute HelloWorld.java Learn
Introduction to Java Module 1: Getting started, Java Basics 22/01/2010 Prepared by Chris Panayiotou for EPL 233 1 Lab Objectives o Objective: Learn how to write, compile and execute HelloWorld.java Learn
Software Engineering Large Practical: Preferences, storage, and testing
 Software Engineering Large Practical: Preferences, storage, and testing Stephen Gilmore (Stephen.Gilmore@ed.ac.uk) School of Informatics November 9, 2016 Contents A simple counter activity Preferences
Software Engineering Large Practical: Preferences, storage, and testing Stephen Gilmore (Stephen.Gilmore@ed.ac.uk) School of Informatics November 9, 2016 Contents A simple counter activity Preferences
State Application Using MVC
 State Application Using MVC 1. Getting ed: Stories and GUI Sketch This example illustrates how applications can be thought of as passing through different states. The code given shows a very useful way
State Application Using MVC 1. Getting ed: Stories and GUI Sketch This example illustrates how applications can be thought of as passing through different states. The code given shows a very useful way
1Z Java SE 5 and 6, Certified Associate Exam Summary Syllabus Questions
 1Z0-850 Java SE 5 and 6, Certified Associate Exam Summary Syllabus Questions Table of Contents Introduction to 1Z0-850 Exam on Java SE 5 and 6, Certified Associate... 2 Oracle 1Z0-850 Certification Details:...
1Z0-850 Java SE 5 and 6, Certified Associate Exam Summary Syllabus Questions Table of Contents Introduction to 1Z0-850 Exam on Java SE 5 and 6, Certified Associate... 2 Oracle 1Z0-850 Certification Details:...
Queen s University Faculty of Arts and Science School of Computing CISC 124 Final Examination December 2004 Instructor: M. Lamb
 Queen s University Faculty of Arts and Science School of Computing CISC 124 Final Examination December 2004 Instructor: M. Lamb HAND IN Answers recorded on Examination paper This examination is THREE HOURS
Queen s University Faculty of Arts and Science School of Computing CISC 124 Final Examination December 2004 Instructor: M. Lamb HAND IN Answers recorded on Examination paper This examination is THREE HOURS
Introduction to Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) Lecture 10 CS2110 Fall 2008
 Introduction to Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) Lecture 10 CS2110 Fall 2008 Announcements A3 is up, due Friday, Oct 10 Prelim 1 scheduled for Oct 16 if you have a conflict, let us know now 2 Interactive
Introduction to Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) Lecture 10 CS2110 Fall 2008 Announcements A3 is up, due Friday, Oct 10 Prelim 1 scheduled for Oct 16 if you have a conflict, let us know now 2 Interactive
1.00 Lecture 14. Lecture Preview
 1.00 Lecture 14 Introduction to the Swing Toolkit Lecture Preview Over the next 5 lectures, we will introduce you to the techniques necessary to build graphic user interfaces for your applications. Lecture
1.00 Lecture 14 Introduction to the Swing Toolkit Lecture Preview Over the next 5 lectures, we will introduce you to the techniques necessary to build graphic user interfaces for your applications. Lecture
Window Interfaces Using Swing Objects
 Chapter 12 Window Interfaces Using Swing Objects Event-Driven Programming and GUIs Swing Basics and a Simple Demo Program Layout Managers Buttons and Action Listeners Container Classes Text I/O for GUIs
Chapter 12 Window Interfaces Using Swing Objects Event-Driven Programming and GUIs Swing Basics and a Simple Demo Program Layout Managers Buttons and Action Listeners Container Classes Text I/O for GUIs
First Name: AITI 2004: Exam 2 July 19, 2004
 First Name: AITI 2004: Exam 2 July 19, 2004 Last Name: Standard Track Read Instructions Carefully! This is a 3 hour closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. Please write clearly if we cannot understand
First Name: AITI 2004: Exam 2 July 19, 2004 Last Name: Standard Track Read Instructions Carefully! This is a 3 hour closed book exam. No calculators are allowed. Please write clearly if we cannot understand
Java Review Outline. basics exceptions variables arrays modulo operator if statements, booleans, comparisons loops: while and for
 Java Review Outline basics exceptions variables arrays modulo operator if statements, booleans, comparisons loops: while and for Java basics write a simple program, e.g. hello world http://www2.hawaii.edu/~esb/2017fall.ics211/helloworl
Java Review Outline basics exceptions variables arrays modulo operator if statements, booleans, comparisons loops: while and for Java basics write a simple program, e.g. hello world http://www2.hawaii.edu/~esb/2017fall.ics211/helloworl
KF5008 Program Design & Development. Lecture 1 Usability GUI Design and Implementation
 KF5008 Program Design & Development Lecture 1 Usability GUI Design and Implementation Types of Requirements Functional Requirements What the system does or is expected to do Non-functional Requirements
KF5008 Program Design & Development Lecture 1 Usability GUI Design and Implementation Types of Requirements Functional Requirements What the system does or is expected to do Non-functional Requirements
Chapter 12 GUI Basics
 Chapter 12 GUI Basics 1 Creating GUI Objects // Create a button with text OK JButton jbtok = new JButton("OK"); // Create a label with text "Enter your name: " JLabel jlblname = new JLabel("Enter your
Chapter 12 GUI Basics 1 Creating GUI Objects // Create a button with text OK JButton jbtok = new JButton("OK"); // Create a label with text "Enter your name: " JLabel jlblname = new JLabel("Enter your
Classes, interfaces, & documentation. Review of basic building blocks
 Classes, interfaces, & documentation Review of basic building blocks Objects Data structures literally, storage containers for data constitute object knowledge or state Operations an object can perform
Classes, interfaces, & documentation Review of basic building blocks Objects Data structures literally, storage containers for data constitute object knowledge or state Operations an object can perform
Part I: Learn Common Graphics Components
 OOP GUI Components and Event Handling Page 1 Objectives 1. Practice creating and using graphical components. 2. Practice adding Event Listeners to handle the events and do something. 3. Learn how to connect
OOP GUI Components and Event Handling Page 1 Objectives 1. Practice creating and using graphical components. 2. Practice adding Event Listeners to handle the events and do something. 3. Learn how to connect
VARIABLES. 1. STRINGS Data with letters and/or characters 2. INTEGERS Numbers without decimals 3. FLOATING POINT NUMBERS Numbers with decimals
 VARIABLES WHAT IS A VARIABLE? A variable is a storage location in the computer s memory, used for holding information while the program is running. The information that is stored in a variable may change,
VARIABLES WHAT IS A VARIABLE? A variable is a storage location in the computer s memory, used for holding information while the program is running. The information that is stored in a variable may change,
RAIK 183H Examination 2 Solution. November 10, 2014
 RAIK 183H Examination 2 Solution November 10, 2014 Name: NUID: This examination consists of 5 questions and you have 110 minutes to complete the test. Show all steps (including any computations/explanations)
RAIK 183H Examination 2 Solution November 10, 2014 Name: NUID: This examination consists of 5 questions and you have 110 minutes to complete the test. Show all steps (including any computations/explanations)
CS 3331 Advanced Object-Oriented Programming Final Exam
 Fall 2015 (Thursday, December 3) Name: CS 3331 Advanced Object-Oriented Programming Final Exam This test has 5 questions and pages numbered 1 through 10. Reminders This test is closed-notes and closed-book.
Fall 2015 (Thursday, December 3) Name: CS 3331 Advanced Object-Oriented Programming Final Exam This test has 5 questions and pages numbered 1 through 10. Reminders This test is closed-notes and closed-book.
Introduction to Graphical Interface Programming in Java. Introduction to AWT and Swing
 Introduction to Graphical Interface Programming in Java Introduction to AWT and Swing GUI versus Graphics Programming Graphical User Interface (GUI) Graphics Programming Purpose is to display info and
Introduction to Graphical Interface Programming in Java Introduction to AWT and Swing GUI versus Graphics Programming Graphical User Interface (GUI) Graphics Programming Purpose is to display info and
Chapter 1 Getting Started
 Chapter 1 Getting Started The C# class Just like all object oriented programming languages, C# supports the concept of a class. A class is a little like a data structure in that it aggregates different
Chapter 1 Getting Started The C# class Just like all object oriented programming languages, C# supports the concept of a class. A class is a little like a data structure in that it aggregates different
Graphical User Interface (GUI)
 Graphical User Interface (GUI) Layout Managment 1 Hello World Often have a static method: createandshowgui() Invoked by main calling invokelater private static void createandshowgui() { } JFrame frame
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Layout Managment 1 Hello World Often have a static method: createandshowgui() Invoked by main calling invokelater private static void createandshowgui() { } JFrame frame
An array is a type of variable that is able to hold more than one piece of information under a single variable name.
 Arrays An array is a type of variable that is able to hold more than one piece of information under a single variable name. Basically you are sub-dividing a memory box into many numbered slots that can
Arrays An array is a type of variable that is able to hold more than one piece of information under a single variable name. Basically you are sub-dividing a memory box into many numbered slots that can
Do not turn to the next page until the start of the exam.
 Principles of Java Language with Applications, PIC20a E. Ryu Winter 2017 Final Exam Monday, March 20, 2017 3 hours, 8 questions, 100 points, 11 pages While we don t expect you will need more space than
Principles of Java Language with Applications, PIC20a E. Ryu Winter 2017 Final Exam Monday, March 20, 2017 3 hours, 8 questions, 100 points, 11 pages While we don t expect you will need more space than
CS 180 Final Exam Review 12/(11, 12)/08
 CS 180 Final Exam Review 12/(11, 12)/08 Announcements Final Exam Thursday, 18 th December, 10:20 am 12:20 pm in PHYS 112 Format 30 multiple choice questions 5 programming questions More stress on topics
CS 180 Final Exam Review 12/(11, 12)/08 Announcements Final Exam Thursday, 18 th December, 10:20 am 12:20 pm in PHYS 112 Format 30 multiple choice questions 5 programming questions More stress on topics
Simple Java Input/Output
 Simple Java Input/Output Prologue They say you can hold seven plus or minus two pieces of information in your mind. I can t remember how to open files in Java. I ve written chapters on it. I ve done it
Simple Java Input/Output Prologue They say you can hold seven plus or minus two pieces of information in your mind. I can t remember how to open files in Java. I ve written chapters on it. I ve done it
Systems Programming Graphical User Interfaces
 Systems Programming Graphical User Interfaces Julio Villena Román (LECTURER) CONTENTS ARE MOSTLY BASED ON THE WORK BY: José Jesús García Rueda Systems Programming GUIs based on Java
Systems Programming Graphical User Interfaces Julio Villena Román (LECTURER) CONTENTS ARE MOSTLY BASED ON THE WORK BY: José Jesús García Rueda Systems Programming GUIs based on Java
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Methods and Classes
 CS 251 Intermediate Programming Methods and Classes Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Fall 2018 Methods An operation that can be performed on an object Has return type and parameters Method with
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Methods and Classes Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Fall 2018 Methods An operation that can be performed on an object Has return type and parameters Method with
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Methods and More
 CS 251 Intermediate Programming Methods and More Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Methods An operation that can be performed on an object Has return type and parameters Method with
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Methods and More Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Methods An operation that can be performed on an object Has return type and parameters Method with
Accurate study guides, High passing rate! Testhorse provides update free of charge in one year!
 Accurate study guides, High passing rate! Testhorse provides update free of charge in one year! http://www.testhorse.com Exam : 1Z0-850 Title : Java Standard Edition 5 and 6, Certified Associate Exam Version
Accurate study guides, High passing rate! Testhorse provides update free of charge in one year! http://www.testhorse.com Exam : 1Z0-850 Title : Java Standard Edition 5 and 6, Certified Associate Exam Version
Heap Arrays and Linked Lists. Steven R. Bagley
 Heap Arrays and Linked Lists Steven R. Bagley Recap Data is stored in variables Can be accessed by the variable name Or in an array, accessed by name and index Variables and arrays have a type Create our
Heap Arrays and Linked Lists Steven R. Bagley Recap Data is stored in variables Can be accessed by the variable name Or in an array, accessed by name and index Variables and arrays have a type Create our
Window Interfaces Using Swing Objects
 Chapter 12 Window Interfaces Using Swing Objects Event-Driven Programming and GUIs Swing Basics and a Simple Demo Program Layout Managers Buttons and Action Listeners Container Classes Text I/O for GUIs
Chapter 12 Window Interfaces Using Swing Objects Event-Driven Programming and GUIs Swing Basics and a Simple Demo Program Layout Managers Buttons and Action Listeners Container Classes Text I/O for GUIs
Graphical User Interfaces. Swing. Jose Jesus García Rueda
 Graphical User Interfaces. Swing Jose Jesus García Rueda Introduction What are the GUIs? Well known examples Basic concepts Graphical application. Containers. Actions. Events. Graphical elements: Menu
Graphical User Interfaces. Swing Jose Jesus García Rueda Introduction What are the GUIs? Well known examples Basic concepts Graphical application. Containers. Actions. Events. Graphical elements: Menu
5/29/2006. Announcements. Last Time. Today. Text File I/O Sample Programs. The File Class. Without using FileReader. Reviewed method overloading.
 Last Time Reviewed method overloading. A few useful Java classes: Other handy System class methods Wrapper classes String class StringTokenizer class Assn 3 posted. Announcements Final on June 14 or 15?
Last Time Reviewed method overloading. A few useful Java classes: Other handy System class methods Wrapper classes String class StringTokenizer class Assn 3 posted. Announcements Final on June 14 or 15?
Class 14: Introduction to the Swing Toolkit
 Introduction to Computation and Problem Solving Class 14: Introduction to the Swing Toolkit Prof. Steven R. Lerman and Dr. V. Judson Harward 1 Class Preview Over the next 5 lectures, we will introduce
Introduction to Computation and Problem Solving Class 14: Introduction to the Swing Toolkit Prof. Steven R. Lerman and Dr. V. Judson Harward 1 Class Preview Over the next 5 lectures, we will introduce
Inheritance (cont) Abstract Classes
 Inheritance (cont) Abstract Classes 1 Polymorphism inheritance allows you to define a base class that has fields and methods classes derived from the base class can use the public and protected base class
Inheritance (cont) Abstract Classes 1 Polymorphism inheritance allows you to define a base class that has fields and methods classes derived from the base class can use the public and protected base class
5/3/2006. Today! HelloWorld in BlueJ. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont. HelloWorld in BlueJ, Cont.
 Today! Build HelloWorld yourself in BlueJ and Eclipse. Look at all the Java keywords. Primitive Types. HelloWorld in BlueJ 1. Find BlueJ in the start menu, but start the Select VM program instead (you
Today! Build HelloWorld yourself in BlueJ and Eclipse. Look at all the Java keywords. Primitive Types. HelloWorld in BlueJ 1. Find BlueJ in the start menu, but start the Select VM program instead (you
Object Oriented Programming: In this course we began an introduction to programming from an object-oriented approach.
 CMSC 131: Chapter 28 Final Review: What you learned this semester The Big Picture Object Oriented Programming: In this course we began an introduction to programming from an object-oriented approach. Java
CMSC 131: Chapter 28 Final Review: What you learned this semester The Big Picture Object Oriented Programming: In this course we began an introduction to programming from an object-oriented approach. Java
cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 topics: introduction to java, part 1
 topics: introduction to java, part 1 cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 cis20.1-fall2007-sklar-leci.2 1 Java. Java is an object-oriented language: it is
topics: introduction to java, part 1 cis20.1 design and implementation of software applications I fall 2007 lecture # I.2 cis20.1-fall2007-sklar-leci.2 1 Java. Java is an object-oriented language: it is
Final Examination Semester 2 / Year 2011
 Southern College Kolej Selatan 南方学院 Final Examination Semester 2 / Year 2011 COURSE COURSE CODE TIME DEPARTMENT LECTURER : JAVA PROGRAMMING : PROG1114 : 2 1/2 HOURS : COMPUTER SCIENCE : LIM PEI GEOK Student
Southern College Kolej Selatan 南方学院 Final Examination Semester 2 / Year 2011 COURSE COURSE CODE TIME DEPARTMENT LECTURER : JAVA PROGRAMMING : PROG1114 : 2 1/2 HOURS : COMPUTER SCIENCE : LIM PEI GEOK Student
Gracefulness of TP-Tree with Five Levels Obtained by Java Programming
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 12, December 2012 1 Gracefulness of TP-Tree with Five Levels Obtained by Java Programming A.Solairaju 1, N. Abdul Ali 2 and
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 2, Issue 12, December 2012 1 Gracefulness of TP-Tree with Five Levels Obtained by Java Programming A.Solairaju 1, N. Abdul Ali 2 and
CS112 Lecture: Primitive Types, Operators, Strings
 CS112 Lecture: Primitive Types, Operators, Strings Last revised 1/24/06 Objectives: 1. To explain the fundamental distinction between primitive types and reference types, and to introduce the Java primitive
CS112 Lecture: Primitive Types, Operators, Strings Last revised 1/24/06 Objectives: 1. To explain the fundamental distinction between primitive types and reference types, and to introduce the Java primitive
CSE wi Final Exam 3/12/18. Name UW ID#
 Name UW ID# There are 13 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes,
Name UW ID# There are 13 questions worth a total of 100 points. Please budget your time so you get to all of the questions. Keep your answers brief and to the point. The exam is closed book, closed notes,
CS61B Lecture #12. Today: Various odds and ends in support of abstraction.
 CS61B Lecture #12 Today: Various odds and ends in support of abstraction. Readings: At this point, we have looked at Chapters 1 9 of Head First Java. Today s lecture is about Chapters 9 and 11. For Friday,
CS61B Lecture #12 Today: Various odds and ends in support of abstraction. Readings: At this point, we have looked at Chapters 1 9 of Head First Java. Today s lecture is about Chapters 9 and 11. For Friday,
Type Conversion. and. Statements
 and Statements Type conversion changing a value from one type to another Void Integral Floating Point Derived Boolean Character Integer Real Imaginary Complex no fractional part fractional part 2 tj Suppose
and Statements Type conversion changing a value from one type to another Void Integral Floating Point Derived Boolean Character Integer Real Imaginary Complex no fractional part fractional part 2 tj Suppose
G52PGP. Lecture oo3 Java (A real object oriented language)
 G52PGP Lecture oo3 Java (A real object oriented language) 1 Last lecture Associating functions with data into objects is an alternative way to decompose a program Can then consider each object on its own
G52PGP Lecture oo3 Java (A real object oriented language) 1 Last lecture Associating functions with data into objects is an alternative way to decompose a program Can then consider each object on its own
Today. Book-keeping. File I/O. Subscribe to sipb-iap-java-students. Inner classes. Debugging tools
 Today Book-keeping File I/O Subscribe to sipb-iap-java-students Inner classes http://sipb.mit.edu/iap/java/ Debugging tools Problem set 1 questions? Problem set 2 released tomorrow 1 2 So far... Reading
Today Book-keeping File I/O Subscribe to sipb-iap-java-students Inner classes http://sipb.mit.edu/iap/java/ Debugging tools Problem set 1 questions? Problem set 2 released tomorrow 1 2 So far... Reading
Programming. Syntax and Semantics
 Programming For the next ten weeks you will learn basic programming principles There is much more to programming than knowing a programming language When programming you need to use a tool, in this case
Programming For the next ten weeks you will learn basic programming principles There is much more to programming than knowing a programming language When programming you need to use a tool, in this case
Virtualians.ning.pk. 2 - Java program code is compiled into form called 1. Machine code 2. native Code 3. Byte Code (From Lectuer # 2) 4.
 1 - What if the main method is declared as private? 1. The program does not compile 2. The program compiles but does not run 3. The program compiles and runs properly ( From Lectuer # 2) 4. The program
1 - What if the main method is declared as private? 1. The program does not compile 2. The program compiles but does not run 3. The program compiles and runs properly ( From Lectuer # 2) 4. The program
Project #3. Computer Science 2334 Fall Create a Graphical User Interface and import/export software for a Hurricane Database.
 User Request: Project #3 Computer Science 2334 Fall 2007 Milestones: Create a Graphical User Interface and import/export software for a Hurricane Database. 1. Create import software that can read the output
User Request: Project #3 Computer Science 2334 Fall 2007 Milestones: Create a Graphical User Interface and import/export software for a Hurricane Database. 1. Create import software that can read the output
Exception Handling. Run-time Errors. Methods Failure. Sometimes when the computer tries to execute a statement something goes wrong:
 Exception Handling Run-time errors The exception concept Throwing exceptions Handling exceptions Declaring exceptions Creating your own exception 22 November 2007 Ariel Shamir 1 Run-time Errors Sometimes
Exception Handling Run-time errors The exception concept Throwing exceptions Handling exceptions Declaring exceptions Creating your own exception 22 November 2007 Ariel Shamir 1 Run-time Errors Sometimes
2.4 Choose method names carefully
 2.4 Choose method names carefully We ve already discussed how to name a class in Section 1.1. Now it s time to name methods properly. I m suggesting this simple rule of thumb: builders are nouns, manipulators
2.4 Choose method names carefully We ve already discussed how to name a class in Section 1.1. Now it s time to name methods properly. I m suggesting this simple rule of thumb: builders are nouns, manipulators
Exam Questions 1Z0-895
 Exam Questions 1Z0-895 Java Platform, Enterprise Edition 6 Enterprise JavaBeans Developer Certified Expert Exam https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/1z0-895/ QUESTION NO: 1 A developer needs to deliver a large-scale
Exam Questions 1Z0-895 Java Platform, Enterprise Edition 6 Enterprise JavaBeans Developer Certified Expert Exam https://www.2passeasy.com/dumps/1z0-895/ QUESTION NO: 1 A developer needs to deliver a large-scale
Information Technology for Industrial Engineers 15 November ISE 582: Information Technology for Industrial Engineers
 ISE 582: Information Technology for Industrial Engineers University of Southern California Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Lecture 10 JAVA Cup 9: Images, Interactive Forms Handouts & Announcements
ISE 582: Information Technology for Industrial Engineers University of Southern California Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering Lecture 10 JAVA Cup 9: Images, Interactive Forms Handouts & Announcements
Java Graphical User Interfaces AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) & Swing
 Java Graphical User Interfaces AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) & Swing Rui Moreira Some useful links: http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/uiswing/toc.html http://www.unix.org.ua/orelly/java-ent/jfc/
Java Graphical User Interfaces AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) & Swing Rui Moreira Some useful links: http://java.sun.com/docs/books/tutorial/uiswing/toc.html http://www.unix.org.ua/orelly/java-ent/jfc/
Procedures, Parameters, Values and Variables. Steven R. Bagley
 Procedures, Parameters, Values and Variables Steven R. Bagley Recap A Program is a sequence of statements (instructions) Statements executed one-by-one in order Unless it is changed by the programmer e.g.
Procedures, Parameters, Values and Variables Steven R. Bagley Recap A Program is a sequence of statements (instructions) Statements executed one-by-one in order Unless it is changed by the programmer e.g.
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Java Basics
 CS 251 Intermediate Programming Java Basics Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Prerequisites These are the topics that I assume that you have already seen: Variables Boolean expressions
CS 251 Intermediate Programming Java Basics Brooke Chenoweth University of New Mexico Spring 2018 Prerequisites These are the topics that I assume that you have already seen: Variables Boolean expressions
Java E-Commerce Martin Cooke,
 Java E-Commerce Martin Cooke, 2002 1 Java technologies for presentation: JSP Today s lecture in the presentation tier Java Server Pages Tomcat examples Presentation How the web tier interacts with the
Java E-Commerce Martin Cooke, 2002 1 Java technologies for presentation: JSP Today s lecture in the presentation tier Java Server Pages Tomcat examples Presentation How the web tier interacts with the
CSE 143 SAMPLE MIDTERM
 CSE 143 SAMPLE MIDTERM 1. (5 points) In some methods, you wrote code to check if a certain precondition was held. If the precondition did not hold, then you threw an exception. This leads to robust code
CSE 143 SAMPLE MIDTERM 1. (5 points) In some methods, you wrote code to check if a certain precondition was held. If the precondition did not hold, then you threw an exception. This leads to robust code
CS Exam 3 - Spring 2010
 CS 1316 - Exam 3 - Spring 2010 Name: Grading TA: Section: INTEGRITY: By taking this exam, you pledge that this is your work and you have neither given nor received inappropriate help during the taking
CS 1316 - Exam 3 - Spring 2010 Name: Grading TA: Section: INTEGRITY: By taking this exam, you pledge that this is your work and you have neither given nor received inappropriate help during the taking
CS 335 Graphics and Multimedia. Image Manipulation
 CS 335 Graphics and Multimedia Image Manipulation Image Manipulation Independent pixels: image subtraction image averaging grey level mapping thresholding Neighborhoods of pixels: filtering, convolution,
CS 335 Graphics and Multimedia Image Manipulation Image Manipulation Independent pixels: image subtraction image averaging grey level mapping thresholding Neighborhoods of pixels: filtering, convolution,
Chapter 13 Lab Advanced GUI Applications
 Gaddis_516907_Java 4/10/07 2:10 PM Page 113 Chapter 13 Lab Advanced GUI Applications Objectives Be able to add a menu to the menu bar Be able to use nested menus Be able to add scroll bars, giving the
Gaddis_516907_Java 4/10/07 2:10 PM Page 113 Chapter 13 Lab Advanced GUI Applications Objectives Be able to add a menu to the menu bar Be able to use nested menus Be able to add scroll bars, giving the
Project 1 Computer Science 2334 Spring 2016 This project is individual work. Each student must complete this assignment independently.
 Project 1 Computer Science 2334 Spring 2016 This project is individual work. Each student must complete this assignment independently. User Request: Create a simple movie data system. Milestones: 1. Use
Project 1 Computer Science 2334 Spring 2016 This project is individual work. Each student must complete this assignment independently. User Request: Create a simple movie data system. Milestones: 1. Use
A JavaBean is a class file that stores Java code for a JSP
 CREATE A JAVABEAN A JavaBean is a class file that stores Java code for a JSP page. Although you can use a scriptlet to place Java code directly into a JSP page, it is considered better programming practice
CREATE A JAVABEAN A JavaBean is a class file that stores Java code for a JSP page. Although you can use a scriptlet to place Java code directly into a JSP page, it is considered better programming practice
Strategy Pattern. What is it?
 Strategy Pattern 1 What is it? The Strategy pattern is much like the State pattern in outline, but a little different in intent. The Strategy pattern consists of a number of related algorithms encapsulated
Strategy Pattern 1 What is it? The Strategy pattern is much like the State pattern in outline, but a little different in intent. The Strategy pattern consists of a number of related algorithms encapsulated
