HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS FEBRUARY Subject: Computing Form: 4 Time: 1 ½ hours MARKING SCHEME
|
|
|
- Leslie Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS FEBRUARY 2017 Subject: Computing Form: 4 Time: 1 ½ hours MARKING SCHEME 1
2 Section A Answer all the questions in the space provided. 1. Use 5 (five) of the following terms to identify the areas described below. Computer Process Control Teleshopping POS Terminals DBMS E-Commerce Robotics Medical Diagnosis Programming Intelligent Cars a. A digital computer is used to direct the operations of a manufacturing process. b. Sensors and actuators built into the mechanical body with computer software to execute the desired tasks. c. The idea of doing business electronically over the Internet. d. Managing a database to assist health providers in reaching a conclusion. e. In the future, collision-avoidance will be advanced enough to totally drive a car without any driver assistance. Computer Process Control Robotics E-Commerce Medical Diagnosis Intelligent Cars 2. Identify whether the below are properties of Off-the-Shelf or Tailor-Made software. a. Cheaper in price Off-the-Shelf b. Does not contain extra options other than those needed Tailor-Made c. Saves time and effort of development Off-the-Shelf d. May come with poor printed documentation Off-the-Shelf e. Developed for some specific organisation Tailor-Made 3. Two's complement is a clever way of storing integers so that common math problems are very simple to implement. a. Convert 83 to 8-bit 2 s complement binary. Award 1 mark for a completely correct answer. Space for working Answer: b. Convert -60 to 8-bit 2 s complement binary Award 1 mark for a completely correct answer. Space for working Answer:
3 4. This question is about ranges and binary addition. a. What is the smallest negative number that can be represented in a 2 s complement 8-bit register? -128 b. What is the largest negative number that can be represented in a 2 s complement 8-bit register? -1 c. Using an 8-bit unsigned register, perform binary addition for [1 mark for correct conversions to binary, 1 mark for correct answer] 75 = , 44 = , 119 = d. What is the technical term used to describe a situation where the result of an 8-bit binary addition contains 9 bits? Numeric Overflow 5. Identify whether the below are examples of a Syntax, Logical or Runtime error. a. Caused by incorrect use of the programming language. Syntax b. Caused by inaccurately reasoning out the solution. Logical c. Caused by an unexpected event during execution. Runtime d. Easiest error to identify. Syntax e. Attempting to read a file which does not exist. Runtime 6. The Java program below does not compile. Identify the line where there is: public class Prog1 { } public static void main(string[] args) { } int num = Keyboard.readInt(); if (num % 2 = 0) { System.out.println("ODD"); } else { System.out.println("EVEN"); } a. An input Line 5 b. An output Line 7 / Line 10 c. A Syntax Error Line 6 d. A Logical Error Line 6 e. The possibility of a Runtime Error Line 5 3
4 7. Put the following Systems Analysis in order. The first and last step have been done for you. [5] Present Systems Study and Analysis 2 Problem Selection and Feasibility Study 1 Implementation and Changeover Methods 5 Programming and Documentation 4 System Maintenance 7 Control and Review 6 Design of New Computerised System 3 8. Most software must be installed to disk before it can be used. a. Mention 3 things that happen during the installation process. i) The user is presented with the license agreement to accept or decline. ii) Parts of the software are copied to disk. iii) System is configured to be aware that a new program has been installed. b. Software is said to be user-friendly if it satisfies certain criteria. Mention 2 (two) such criteria. i) Easy to use, robust ii) Attractive interface, Helpful 9. Using Java syntax, write a single line statement to perform the following: a. Declare a private attribute named mark of type int. private int mark; b. Add the Scanner class declaration to a Java Class. import java.util.scanner; c. Store the result of the value of num1 and num2 into answer. answer = num1 + num2; d. Output Thanks for using the program! on screen. System.out.println( Thanks for using the program! ); 4
5 10. What do the following acronyms stand for? a. ATM Automated Teller Machines b. GPS Global Positioning System c. CAD Computer Aided Design d. CAL Computer Aided Learning e. POS Point of Sale 11. Work out the following: [5] Binary Decimal Hexadecimal CA D9 Space for working 12. The Systems Analyst has a very important role in the System Lifecycle. a. Why is a detailed systems analysis necessary during the development of a new system? To develop an efficient, easily-updatable system that caters for user s needs. b. Name two duties of the Systems Analyst. i. Draws up feasibility report. ii. Gathers data during Systems Analysis stage. c. Answer True or False i. The first step in developing a new system is the definition True of the problem. ii. Test data is supplied by the customer ordering the new system. False 5
6 Section B Answer BOTH questions in the space provided. 13. A local library is replacing its old computerised system with a new one. a. Name two reasons why the old system might need to be replaced. i. New functionality is needed. ii. New technology is available that can improve the system s efficiency if implemented. b. In the early stages of the development of the new system, a feasibility report is drawn up. Name two things you expect to find in such a report. i. The cost of the proposed system. ii. The time taken to develop the proposed system. c. Suggest two reasons why a client might wish to abort the project after being presented with the feasibility report. i. The system might be too expensive for his budget. ii. The timescale for developing the system might be unsuitable for the client. d. Suggest two ways in which data can be gathered during the systems analysis stage. i. Interviews with different people in the company. ii. Observation of the existent system in operation. e. After the system analysis is complete, there s a further step that needs to be taken before the coding of the new system starts. Name and briefly describe this stage. Name Description System Design System flowcharts, file formats, security measures and lists of input and output to the system are drawn up. f. Name and briefly describe two changeover methods the company may opt for. Name one advantage of each changeover method. Name Description Advantage Name Description Advantage g. With which stage of the system lifecycle would you associate the following? [4] i. The implemented system is observed in Control and review operation. ii. The client first outlines his needs to the Definition of the problem software house. iii. The user manuals are produced. Programming, testing and documentation iv. Users receive training on the new system. Implementation, training and changeover [6] 6
7 14. This question is about the Java programming language. a. Match [5] i. Java is A. A symbolic name in a program associated with a changeable value. ii. An object is B. A collection of statements grouped together to perform an operation. iii. A method is C. an object-oriented programming language. iv. A variable is D. A blueprint for one or many objects. v. An application is E. An instance of a class. vi. A class is F. A program designed to perform a group of tasks. i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. C E B A F D b. A zoo is expecting new-born giant pandas soon, as one of their pandas is having young. New-born giant pandas are just around 100g but, if they are healthy, they gain weight very rapidly after birth. The zoo plans to monitor the baby pandas weight carefully for the first months of their lives. An application is being created to help the zoo monitor the pandas weight gain. One of the classes in this application is called Panda. i. The class Panda has a property called weightatbirth that stores the weight (in kg) of the panda at birth. Show how this property would be declared in Java. double weightatbirth; [Accept also float. Do not accept int, byte etc] ii. The class Panda also has a property called ageindays that stores the age of a panda in days. Show how this property would be declared in Java. int ageindays; [Accept all integer data types] ii. Write Java code to create an object of class Panda called panda1. Panda panda1 = new Panda(); iii. Method weighin() asks the user to enter the age and weight of a given panda and then outputs the weight gained to date. Write method weighin(). Assume that classes needed for this method, if any, are already imported. Relevant objects of this/these classes (if any) are to be declared in method weighin() 1 mark for correct calculation 1 mark for correct output 1 mark for input from keyboard 1 mark for overall functionality iv. Write Java code to call method weighin() for your object panda1. panda1.weighin(); [1 for partially correct answer] v. After thirty days the panda should weigh around 2kg. Write method isprogressok() that returns false if a panda s weight is less than 1.8kg and otherwise returns true. 1 mark for correct method declaration 1 mark for implementation of decision structure 1 mark for correct decision 1 mark for return of correct value 1 mark for overall functionality 7 [4] [5]
8 8
HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS FEBRUARY
 HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS FEBRUARY 2016 Subject: Computing Form: 4 Time: 1½ hrs MARKING SCHEME Computing Form 4 Half Yearly Exams 2016 Page 1 Section A Answer ALL questions. Each questions carries 5 marks.
HALF-YEARLY EXAMINATIONS FEBRUARY 2016 Subject: Computing Form: 4 Time: 1½ hrs MARKING SCHEME Computing Form 4 Half Yearly Exams 2016 Page 1 Section A Answer ALL questions. Each questions carries 5 marks.
FORM 4 (Option) COMPUTING TIME: 1 hr 30 min
 DIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION Department for Curriculum Management and elearning Educational Assessment Unit Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2013 Track 2 FORM 4 (Option)
DIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION Department for Curriculum Management and elearning Educational Assessment Unit Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2013 Track 2 FORM 4 (Option)
SECONDARY SCHOOL, L-IMRIEĦEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017
 SECONDARY SCHOOL, L-IMRIEĦEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017 YEAR: 10 Computing Time: 1½ Hr. Name: Class: Instructions: 1. Answer all the questions in the space provided on this paper. 2. Calculators
SECONDARY SCHOOL, L-IMRIEĦEL HALF YEARLY EXAMINATIONS 2016/2017 YEAR: 10 Computing Time: 1½ Hr. Name: Class: Instructions: 1. Answer all the questions in the space provided on this paper. 2. Calculators
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Programs Open DrJava. Under the File menu click on New Java Class and the window to the right should appear. Fill in the information as shown and click OK. This code is generated
KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Secondary School, Kirkop
 KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Secondary School, Kirkop Mark HALF YEARLY EXAMINATION 2014/2015 Level 5 6 7-8 Form 4 COMPUTING TIME: 1h 30min Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Global Mark Max. Mark 8 5 7 10 8 12 13 16
KULLEĠĠ SAN BENEDITTU Secondary School, Kirkop Mark HALF YEARLY EXAMINATION 2014/2015 Level 5 6 7-8 Form 4 COMPUTING TIME: 1h 30min Question 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Global Mark Max. Mark 8 5 7 10 8 12 13 16
FORM 5 COMPUTING TIME: 1h 45min
 DIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION Curriculum Management and elearning Department Educational Assessment Unit Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2014 Track 3 FORM 5 COMPUTING TIME:
DIRECTORATE FOR QUALITY AND STANDARDS IN EDUCATION Curriculum Management and elearning Department Educational Assessment Unit Annual Examinations for Secondary Schools 2014 Track 3 FORM 5 COMPUTING TIME:
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs
 Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
Introduction to Java Unit 1. Using BlueJ to Write Programs 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
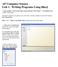 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS
 PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS Q1. Name any two Object Oriented Programming languages? Q2. Why is java called a platform independent language? Q3. Elaborate the java Compilation process. Q4. Why do we write
PROGRAMMING FUNDAMENTALS Q1. Name any two Object Oriented Programming languages? Q2. Why is java called a platform independent language? Q3. Elaborate the java Compilation process. Q4. Why do we write
Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79 Example Given a radius
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45 / 79 Example Given a radius
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods
 Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
Fundamentals of Programming Data Types & Methods By Budditha Hettige Overview Summary (Previous Lesson) Java Data types Default values Variables Input data from keyboard Display results Methods Operators
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Makeup Spring 2013 / 2014
 M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Makeup Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Java is. a. case
M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Makeup Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Java is. a. case
Getting started with Java
 Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
Getting started with Java Magic Lines public class MagicLines { public static void main(string[] args) { } } Comments Comments are lines in your code that get ignored during execution. Good for leaving
Formatting Output & Enumerated Types & Wrapper Classes
 Formatting Output & Enumerated Types & Wrapper Classes Quick review of last lecture September 8, 2006 ComS 207: Programming I (in Java) Iowa State University, FALL 2006 Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev
Formatting Output & Enumerated Types & Wrapper Classes Quick review of last lecture September 8, 2006 ComS 207: Programming I (in Java) Iowa State University, FALL 2006 Instructor: Alexander Stoytchev
World Inside a Computer is Binary
 C Programming 1 Representation of int data World Inside a Computer is Binary C Programming 2 Decimal Number System Basic symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 Radix-10 positional number system. The radix
C Programming 1 Representation of int data World Inside a Computer is Binary C Programming 2 Decimal Number System Basic symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 Radix-10 positional number system. The radix
CIS133J. Working with Numbers in Java
 CIS133J Working with Numbers in Java Contents: Using variables with integral numbers Using variables with floating point numbers How to declare integral variables How to declare floating point variables
CIS133J Working with Numbers in Java Contents: Using variables with integral numbers Using variables with floating point numbers How to declare integral variables How to declare floating point variables
1. [3 pts] What is your section number, the period your discussion meets, and the name of your discussion leader?
![1. [3 pts] What is your section number, the period your discussion meets, and the name of your discussion leader? 1. [3 pts] What is your section number, the period your discussion meets, and the name of your discussion leader?](/thumbs/74/69673120.jpg) CIS 3022 Prog for CIS Majors I February 10, 2009 Exam I Print Your Name Your Section # Total Score Your work is to be done individually. The exam is worth 105 points (five points of extra credit are available
CIS 3022 Prog for CIS Majors I February 10, 2009 Exam I Print Your Name Your Section # Total Score Your work is to be done individually. The exam is worth 105 points (five points of extra credit are available
Do not open this examination paper until instructed to do so. Section A: answer all the questions. Section B: answer all the questions.
 M09/5/COMSC/SP1/ENG/TZ0/XX 22097013 Computer science Standard level Paper 1 Tuesday 19 May 2009 (afternoon) 1 hour 30 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed
M09/5/COMSC/SP1/ENG/TZ0/XX 22097013 Computer science Standard level Paper 1 Tuesday 19 May 2009 (afternoon) 1 hour 30 minutes INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES Do not open this examination paper until instructed
CS16 Exam #1 7/17/ Minutes 100 Points total
 CS16 Exam #1 7/17/2012 75 Minutes 100 Points total Name: 1. (10 pts) Write the definition of a C function that takes two integers `a` and `b` as input parameters. The function returns an integer holding
CS16 Exam #1 7/17/2012 75 Minutes 100 Points total Name: 1. (10 pts) Write the definition of a C function that takes two integers `a` and `b` as input parameters. The function returns an integer holding
Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler are denoted using a. Two
Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.2 Your First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler are denoted using a. Two
false, import, new 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 45
Selections. EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG
 Selections EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes The Boolean Data Type if Statement Compound vs. Primitive Statement Common Errors
Selections EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG Learning Outcomes The Boolean Data Type if Statement Compound vs. Primitive Statement Common Errors
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I. Midterm Examination February 24, Name: KEY 1
 CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 24, 2014 Name: KEY 1 Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
CSC 1051 Algorithms and Data Structures I Midterm Examination February 24, 2014 Name: KEY 1 Question Value Score 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 6 10 7 10 8 10 9 10 10 10 TOTAL 100 Please answer questions in
COMP-202B - Introduction to Computing I (Winter 2011) - All Sections Example Questions for In-Class Quiz
 COMP-202B - Introduction to Computing I (Winter 2011) - All Sections Example Questions for In-Class Quiz The in-class quiz is intended to give you a taste of the midterm, give you some early feedback about
COMP-202B - Introduction to Computing I (Winter 2011) - All Sections Example Questions for In-Class Quiz The in-class quiz is intended to give you a taste of the midterm, give you some early feedback about
Midterm Examination (MTA)
 M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
M105: Introduction to Programming with Java Midterm Examination (MTA) Spring 2013 / 2014 Question One: [6 marks] Choose the correct answer and write it on the external answer booklet. 1. Compilers and
Internal Data Representation
 Introduction to Computer Science, Shimon Schocken, IDC Herzliya Lecture 7. Internal Data Representation Internal Data Representation, Shimon Schocken, IDC Herzliya, www.introcs.com slide 1 Why binary representation
Introduction to Computer Science, Shimon Schocken, IDC Herzliya Lecture 7. Internal Data Representation Internal Data Representation, Shimon Schocken, IDC Herzliya, www.introcs.com slide 1 Why binary representation
CSc 2010 Principles of Computer Science, Fall 2013 Practice Problems for Midterm 3* * 3 17 % 9-20 % (26 / 7) "2"
 CSc 2010 Principles of Computer Science, Fall 2013 Practice Problems for Midterm 1. For each Java expression in the left hand column, indicate its value in the right hand column. Be sure to show a constant
CSc 2010 Principles of Computer Science, Fall 2013 Practice Problems for Midterm 1. For each Java expression in the left hand column, indicate its value in the right hand column. Be sure to show a constant
BSc. (Hons.) Software Engineering. Examinations for / Semester 2
 BSc. (Hons.) Software Engineering Cohort: BSE/04/PT Examinations for 2005-2006 / Semester 2 MODULE: OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING MODULE CODE: BISE050 Duration: 2 Hours Reading Time: 5 Minutes Instructions
BSc. (Hons.) Software Engineering Cohort: BSE/04/PT Examinations for 2005-2006 / Semester 2 MODULE: OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING MODULE CODE: BISE050 Duration: 2 Hours Reading Time: 5 Minutes Instructions
Exercise: Using Numbers
 Exercise: Using Numbers Problem: You are a spy going into an evil party to find the super-secret code phrase (made up of letters and spaces), which you will immediately send via text message to your team
Exercise: Using Numbers Problem: You are a spy going into an evil party to find the super-secret code phrase (made up of letters and spaces), which you will immediately send via text message to your team
Supplementary Test 1
 Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2009 Supplementary Test 1 Question
Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2009 Supplementary Test 1 Question
1 Definitions & Short Answer (4 Points Each)
 Fall 013 Exam #1 Key COSC 117 1 Definitions & Short Answer ( Points Each) 1. Explain the difference between high-level languages and machine language. A high-level language is human readable code that
Fall 013 Exam #1 Key COSC 117 1 Definitions & Short Answer ( Points Each) 1. Explain the difference between high-level languages and machine language. A high-level language is human readable code that
Java Foundations: Introduction to Program Design & Data Structures, 4e John Lewis, Peter DePasquale, Joseph Chase Test Bank: Chapter 2
 Java Foundations Introduction to Program Design and Data Structures 4th Edition Lewis TEST BANK Full download at : https://testbankreal.com/download/java-foundations-introduction-toprogram-design-and-data-structures-4th-edition-lewis-test-bank/
Java Foundations Introduction to Program Design and Data Structures 4th Edition Lewis TEST BANK Full download at : https://testbankreal.com/download/java-foundations-introduction-toprogram-design-and-data-structures-4th-edition-lewis-test-bank/
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes
 AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
AP CS Unit 3: Control Structures Notes The if and if-else Statements. These statements are called control statements because they control whether a particular block of code is executed or not. Some texts
Data and Variables. Data Types Expressions. String Concatenation Variables Declaration Assignment Shorthand operators. Operators Precedence
 Data and Variables Data Types Expressions Operators Precedence String Concatenation Variables Declaration Assignment Shorthand operators Review class All code in a java file is written in a class public
Data and Variables Data Types Expressions Operators Precedence String Concatenation Variables Declaration Assignment Shorthand operators Review class All code in a java file is written in a class public
Binary Values. CSE 410 Lecture 02
 Binary Values CSE 410 Lecture 02 Lecture Outline Binary Decimal, Binary, and Hexadecimal Integers Why Place Value Representation Boolean Algebra 2 First: Why Binary? Electronic implementation Easy to store
Binary Values CSE 410 Lecture 02 Lecture Outline Binary Decimal, Binary, and Hexadecimal Integers Why Place Value Representation Boolean Algebra 2 First: Why Binary? Electronic implementation Easy to store
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes
 Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
Introduction to Computer Science Unit 2. Notes Name: Objectives: By the completion of this packet, students should be able to describe the difference between.java and.class files and the JVM. create and
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch.
![1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 Elementray Programming / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 Elementray Programming / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch.](/thumbs/88/115141835.jpg) 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 41 / 68 Example Given the radius
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Elementray Programming" 4 5 } 6 7 / References 8 [1] Ch. 2 in YDL 9 [2] Ch. 2 and 3 in Sharan 10 [3] Ch. 2 in HS 11 / Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 41 / 68 Example Given the radius
Practice Midterm 1. Problem Points Score TOTAL 50
 CS 120 Software Design I Spring 2019 Practice Midterm 1 University of Wisconsin - La Crosse February 25 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages including the
CS 120 Software Design I Spring 2019 Practice Midterm 1 University of Wisconsin - La Crosse February 25 NAME: Do not turn the page until instructed to do so. This booklet contains 10 pages including the
false, import, new 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
false, import, new 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
Full file at
 Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.1 Introduction ( none ) Section 2.2 First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler
Chapter 2 Introduction to Java Applications Section 2.1 Introduction ( none ) Section 2.2 First Program in Java: Printing a Line of Text 2.2 Q1: End-of-line comments that should be ignored by the compiler
CS & IT Conversions. Magnitude 10,000 1,
 CS & IT Conversions There are several number systems that you will use when working with computers. These include decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal. Knowing how to convert between these number systems
CS & IT Conversions There are several number systems that you will use when working with computers. These include decimal, binary, octal, and hexadecimal. Knowing how to convert between these number systems
FINAL QUIZ. Marlene Galea
 FINAL QUIZ Marlene Galea Give 2 possible disadvantages of computerising a system Give 2 possible disadvantages of computerising a system - Dependency : users may grow increasingly dependent on the computerised
FINAL QUIZ Marlene Galea Give 2 possible disadvantages of computerising a system Give 2 possible disadvantages of computerising a system - Dependency : users may grow increasingly dependent on the computerised
University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science. Computer Science 1015F ~ 2007
 Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2007 Final Examination Question Max
Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2007 Final Examination Question Max
University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ June Exam
 Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2009 June Exam Question Max Internal
Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2009 June Exam Question Max Internal
Exam 1. CSC 121 Spring Lecturer: Howard Rosenthal. March 1, 2017
 Exam 1. CSC 121 Spring 2017 Lecturer: Howard Rosenthal March 1, 2017 Your Name: Key 1. Fill in the following table for the 8 primitive data types. Spell the types exactly correctly. (16 points total) Data
Exam 1. CSC 121 Spring 2017 Lecturer: Howard Rosenthal March 1, 2017 Your Name: Key 1. Fill in the following table for the 8 primitive data types. Spell the types exactly correctly. (16 points total) Data
6. Under which of the following categories is a laptop computer classified? (1) Microcomputer (2) Minicomputer (3) Mainframe (4) Supercomputer
 General Certificate of Education (Ord.Level) Examination 2007 Information & Communication Technology I One hour Note: Answer all questions. In each of the questions 1 to 40 pick one of the alternatives
General Certificate of Education (Ord.Level) Examination 2007 Information & Communication Technology I One hour Note: Answer all questions. In each of the questions 1 to 40 pick one of the alternatives
Department of Computer Science Purdue University, West Lafayette
 Department of Computer Science Purdue University, West Lafayette Fall 2011: CS 180 Problem Solving and OO Programming Exam 1 Solutions Q 1 Answer the questions below assuming that binary integers are represented
Department of Computer Science Purdue University, West Lafayette Fall 2011: CS 180 Problem Solving and OO Programming Exam 1 Solutions Q 1 Answer the questions below assuming that binary integers are represented
CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ C++ Basics
 CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ C++ Basics Integers Basic Types Can be short, long, or just plain int C++ does not define the size of them other than short
CS2141 Software Development using C/C++ C++ Basics Integers Basic Types Can be short, long, or just plain int C++ does not define the size of them other than short
Programming: Java. Chapter Objectives. Chapter Objectives (continued) Program Design Including Data Structures. Chapter 7: User-Defined Methods
 Chapter 7: User-Defined Methods Java Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures Chapter Objectives Understand how methods are used in Java programming Learn about standard (predefined) methods
Chapter 7: User-Defined Methods Java Programming: Program Design Including Data Structures Chapter Objectives Understand how methods are used in Java programming Learn about standard (predefined) methods
Pace University. Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1
 Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
Pace University Fundamental Concepts of CS121 1 Dr. Lixin Tao http://csis.pace.edu/~lixin Computer Science Department Pace University October 12, 2005 This document complements my tutorial Introduction
Software Practice 1 Basic Grammar
 Software Practice 1 Basic Grammar Basic Syntax Data Type Loop Control Making Decision Prof. Joonwon Lee T.A. Jaehyun Song Jongseok Kim (42) T.A. Sujin Oh Junseong Lee (43) 1 2 Java Program //package details
Software Practice 1 Basic Grammar Basic Syntax Data Type Loop Control Making Decision Prof. Joonwon Lee T.A. Jaehyun Song Jongseok Kim (42) T.A. Sujin Oh Junseong Lee (43) 1 2 Java Program //package details
Give one example where you might wish to use a three dimensional array
 CS 110: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE SAMPLE TEST 3 TIME ALLOWED: 60 MINUTES Student s Name: MAXIMUM MARK 100 NOTE: Unless otherwise stated, the questions are with reference to the Java Programming
CS 110: INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTER SCIENCE SAMPLE TEST 3 TIME ALLOWED: 60 MINUTES Student s Name: MAXIMUM MARK 100 NOTE: Unless otherwise stated, the questions are with reference to the Java Programming
CEN 414 Java Programming
 CEN 414 Java Programming Instructor: H. Esin ÜNAL SPRING 2017 Slides are modified from original slides of Y. Daniel Liang WEEK 2 ELEMENTARY PROGRAMMING 2 Computing the Area of a Circle public class ComputeArea
CEN 414 Java Programming Instructor: H. Esin ÜNAL SPRING 2017 Slides are modified from original slides of Y. Daniel Liang WEEK 2 ELEMENTARY PROGRAMMING 2 Computing the Area of a Circle public class ComputeArea
Programming with Java
 Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
Programming with Java Data Types & Input Statement Lecture 04 First stage Software Engineering Dep. Saman M. Omer 2017-2018 Objectives q By the end of this lecture you should be able to : ü Know rules
Date: Dr. Essam Halim
 Assignment (1) Date: 11-2-2013 Dr. Essam Halim Part 1: Chapter 2 Elementary Programming 1 Suppose a Scanner object is created as follows: Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); What method do you use
Assignment (1) Date: 11-2-2013 Dr. Essam Halim Part 1: Chapter 2 Elementary Programming 1 Suppose a Scanner object is created as follows: Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in); What method do you use
Cambridge Ordinary Level 2210 Computer Science November 2016 Principal Examiner Report for Teachers
 COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper 2210/12 Paper 1 Key messages If a candidate writes the answer to a question on an additional page they must indicate very clearly to the Examiner where the revised answer can be
COMPUTER SCIENCE Paper 2210/12 Paper 1 Key messages If a candidate writes the answer to a question on an additional page they must indicate very clearly to the Examiner where the revised answer can be
Full file at
 Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Java Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, 3 rd Edition 2-1 Chapter 2 Basic Elements of Java At a Glance Instructor s Manual Table of Contents Overview Objectives s Quick Quizzes Class
Motivating Examples (1.1) Selections. Motivating Examples (1.2) Learning Outcomes. EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018
 Motivating Examples (1.1) Selections EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG 1 import java.util.scanner; 2 public class ComputeArea { 3 public static void main(string[] args)
Motivating Examples (1.1) Selections EECS1022: Programming for Mobile Computing Winter 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG 1 import java.util.scanner; 2 public class ComputeArea { 3 public static void main(string[] args)
Data Types. 1 You cannot change the type of the variable after declaration. Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 52 / 87
 Data Types Java is a strongly-typed 1 programming language. Every variable has a type. Also, every (mathematical) expression has a type. There are two categories of data types: primitive data types, and
Data Types Java is a strongly-typed 1 programming language. Every variable has a type. Also, every (mathematical) expression has a type. There are two categories of data types: primitive data types, and
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming. February 29, 2012 Midterm
 CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
CIS 110 Introduction To Computer Programming February 29, 2012 Midterm Name: Recitation # (e.g. 201): Pennkey (e.g. bjbrown): My signature below certifies that I have complied with the University of Pennsylvania
IT 1003 Introduction to Programming (New)
 [All Rights Reserved] SLIATE SRI LANKA INSTITUTE OF ADVANCED TECHNOLOGICAL EDUCATION (Established in the Ministry of Higher Education, vide in Act No. 29 of 1995) Instructions for Candidates: Answer five
[All Rights Reserved] SLIATE SRI LANKA INSTITUTE OF ADVANCED TECHNOLOGICAL EDUCATION (Established in the Ministry of Higher Education, vide in Act No. 29 of 1995) Instructions for Candidates: Answer five
COMP 202 Java in one week
 CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator COMP 202 Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
CONTENTS: Basics of Programming Variables and Assignment Data Types: int, float, (string) Example: Implementing a calculator COMP 202 Java in one week The Java Programming Language A programming language
CSE 201 JAVA PROGRAMMING I. Copyright 2016 by Smart Coding School
 CSE 201 JAVA PROGRAMMING I Primitive Data Type Primitive Data Type 8-bit signed Two s complement Integer -128 ~ 127 Primitive Data Type 16-bit signed Two s complement Integer -32768 ~ 32767 Primitive Data
CSE 201 JAVA PROGRAMMING I Primitive Data Type Primitive Data Type 8-bit signed Two s complement Integer -128 ~ 127 Primitive Data Type 16-bit signed Two s complement Integer -32768 ~ 32767 Primitive Data
What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements
 Week 4 - Friday What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements History of computers Hardware Software development Basic Java syntax Output with System.out.print() Mechanical Calculation
Week 4 - Friday What did we talk about last time? Examples switch statements History of computers Hardware Software development Basic Java syntax Output with System.out.print() Mechanical Calculation
Introduction to Computer Science II (CSI 1101)
 Introduction to Computer Science II (CSI 1101) Professor: M. Turcotte February 2002, duration: 75 minutes Identification Student name: last name: Section: Student number: initials: Signature: Instructions
Introduction to Computer Science II (CSI 1101) Professor: M. Turcotte February 2002, duration: 75 minutes Identification Student name: last name: Section: Student number: initials: Signature: Instructions
a) Answer all questions. b) Write your answers in the space provided. c) Show all calculations where applicable.
 Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2008 January Exam Question Max Internal
Name: Please fill in your Student Number and Name. Student Number : Student Number: University of Cape Town ~ Department of Computer Science Computer Science 1015F ~ 2008 January Exam Question Max Internal
false, import, new 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4
 1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
1 class Lecture2 { 2 3 "Data types, Variables, and Operators" 4 5 } 6 7 // Keywords: 8 byte, short, int, long, char, float, double, boolean, true, false, import, new Zheng-Liang Lu Java Programming 44
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method. Elementary Programming. Learning Outcomes. Development Process
 Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
Entry Point of Execution: the main Method Elementary Programming EECS1021: Object Oriented Programming: from Sensors to Actuators Winter 2019 CHEN-WEI WANG For now, all your programming exercises will
Review Chapters 1 to 4. Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013
 Review Chapters 1 to 4 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 Introduction to Java Chapters 1 and 2 The Java Language Section 1.1 Data & Expressions Sections 2.1 2.5 Instructor:
Review Chapters 1 to 4 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 Introduction to Java Chapters 1 and 2 The Java Language Section 1.1 Data & Expressions Sections 2.1 2.5 Instructor:
Representation of Non Negative Integers
 Representation of Non Negative Integers In each of one s complement and two s complement arithmetic, no special steps are required to represent a non negative integer. All conversions to the complement
Representation of Non Negative Integers In each of one s complement and two s complement arithmetic, no special steps are required to represent a non negative integer. All conversions to the complement
2.8. Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators
 Page 1 of 6 [Page 56] 2.8. Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators A condition is an expression that can be either true or false. This section introduces a simple version of Java's if statement
Page 1 of 6 [Page 56] 2.8. Decision Making: Equality and Relational Operators A condition is an expression that can be either true or false. This section introduces a simple version of Java's if statement
CSCI 1226 Sample Midterm Exam
 CSCI 1226 Test #1 February 2017 General Instructions CSCI 1226 Sample Midterm Exam (A bit long since it combines parts of three earlier tests) Read and follow all directions carefully. Name: Student #:
CSCI 1226 Test #1 February 2017 General Instructions CSCI 1226 Sample Midterm Exam (A bit long since it combines parts of three earlier tests) Read and follow all directions carefully. Name: Student #:
Midterm Exam. CSCI 2132: Software Development. March 4, Marks. Question 1 (10) Question 2 (10) Question 3 (10) Question 4 (10) Question 5 (5)
 Banner number: Name: Midterm Exam CSCI 2132: Software Development March 4, 2019 Marks Question 1 (10) Question 2 (10) Question 3 (10) Question 4 (10) Question 5 (5) Question 6 (5) Total (50) Instructions:
Banner number: Name: Midterm Exam CSCI 2132: Software Development March 4, 2019 Marks Question 1 (10) Question 2 (10) Question 3 (10) Question 4 (10) Question 5 (5) Question 6 (5) Total (50) Instructions:
University of Cape Town Department of Computer Science. Computer Science CSC115F. June 2003/2004 Supplementary Exam
 University of Cape Town Department of Computer Science Computer Science CSC115F June 2003/2004 Supplementary Exam Answer all questions. All questions that refer to elements of programming make reference
University of Cape Town Department of Computer Science Computer Science CSC115F June 2003/2004 Supplementary Exam Answer all questions. All questions that refer to elements of programming make reference
St. Catherine s High School
 St. Catherine s High School Annual June 2015 Class: Senior 4 Subject: Computer Studies Total: Duration: 2 hrs Final Total: /100 MAKE SURE TO CHECK THAT YOU ARE GIVEN FIVE PRINTED PAGES Calculators may
St. Catherine s High School Annual June 2015 Class: Senior 4 Subject: Computer Studies Total: Duration: 2 hrs Final Total: /100 MAKE SURE TO CHECK THAT YOU ARE GIVEN FIVE PRINTED PAGES Calculators may
Computational Expression
 Computational Expression Variables, Primitive Data Types, Expressions Janyl Jumadinova 28-30 January, 2019 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 28-30 January, 2019 1 / 17 Variables Variable is a name
Computational Expression Variables, Primitive Data Types, Expressions Janyl Jumadinova 28-30 January, 2019 Janyl Jumadinova Computational Expression 28-30 January, 2019 1 / 17 Variables Variable is a name
Section 003 Fall CS 170 Exam 1. Name (print): Instructions:
 CS 170 Exam 1 Section 003 Fall 2012 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
CS 170 Exam 1 Section 003 Fall 2012 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
Primitive Data, Variables, and Expressions; Simple Conditional Execution
 Unit 2, Part 1 Primitive Data, Variables, and Expressions; Simple Conditional Execution Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Overview of the Programming Process Analysis/Specification
Unit 2, Part 1 Primitive Data, Variables, and Expressions; Simple Conditional Execution Computer Science S-111 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Overview of the Programming Process Analysis/Specification
Choose 3 of the 1 st 4 questions (#'s 1 through 4) to complete. Each question is worth 12 points.
 Choose 3 of the 1 st 4 questions (#'s 1 through 4) to complete. Each question is worth 12 points. Use the remaining question as extra credit (worth 1/2 of the points earned). Specify which question is
Choose 3 of the 1 st 4 questions (#'s 1 through 4) to complete. Each question is worth 12 points. Use the remaining question as extra credit (worth 1/2 of the points earned). Specify which question is
POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN LIBRARY AUTOMATION AND NETWORKING (PGDLAN)
 No. of Printed Pages : 6 MLI-007 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN LIBRARY AUTOMATION AND NETWKING (PGDLAN) 00942 Term-End Examination June, 2017 MLI-007 : PROGRAMMING Time 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 (Weightage
No. of Printed Pages : 6 MLI-007 POST GRADUATE DIPLOMA IN LIBRARY AUTOMATION AND NETWKING (PGDLAN) 00942 Term-End Examination June, 2017 MLI-007 : PROGRAMMING Time 2 hours Maximum Marks : 50 (Weightage
Software Practice 1 - Basic Grammar Basic Syntax Data Type Loop Control Making Decision
 Software Practice 1 - Basic Grammar Basic Syntax Data Type Loop Control Making Decision Prof. Hwansoo Han T.A. Minseop Jeong T.A. Wonseok Choi 1 Java Program //package details public class ClassName {
Software Practice 1 - Basic Grammar Basic Syntax Data Type Loop Control Making Decision Prof. Hwansoo Han T.A. Minseop Jeong T.A. Wonseok Choi 1 Java Program //package details public class ClassName {
data_type variable_name = value; Here value is optional because in java, you can declare the variable first and then later assign the value to it.
 Introduction to JAVA JAVA is a programming language which is used in Android App Development. It is class based and object oriented programming whose syntax is influenced by C++. The primary goals of JAVA
Introduction to JAVA JAVA is a programming language which is used in Android App Development. It is class based and object oriented programming whose syntax is influenced by C++. The primary goals of JAVA
Introduction to Java Applications
 2 Introduction to Java Applications OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn: To write simple Java applications. To use input and output statements. Java s primitive types. Basic memory concepts. To use
2 Introduction to Java Applications OBJECTIVES In this chapter you will learn: To write simple Java applications. To use input and output statements. Java s primitive types. Basic memory concepts. To use
1. [3 pts] What is your section number, the period your discussion meets, and the name of your discussion leader?
![1. [3 pts] What is your section number, the period your discussion meets, and the name of your discussion leader? 1. [3 pts] What is your section number, the period your discussion meets, and the name of your discussion leader?](/thumbs/82/85726241.jpg) CIS 3022 Prog for CIS Majors I October 4, 2007 Exam I Print Your Name Your Section # Total Score Your work is to be done individually. The exam is worth 104 points (four points of extra credit are available
CIS 3022 Prog for CIS Majors I October 4, 2007 Exam I Print Your Name Your Section # Total Score Your work is to be done individually. The exam is worth 104 points (four points of extra credit are available
LAB 1 Binary Numbers/ Introduction to C. Rajesh Rajamani. ME 4231 Department of Mechanical Engineering University Of Minnesota
 LAB 1 Binary Numbers/ Introduction to C Rajesh Rajamani ME 431 Department of Mechanical Engineering University Of Minnesota OVERVIEW What is feedback control? Binary and Hexadecimal Numbers Working with
LAB 1 Binary Numbers/ Introduction to C Rajesh Rajamani ME 431 Department of Mechanical Engineering University Of Minnesota OVERVIEW What is feedback control? Binary and Hexadecimal Numbers Working with
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal
 Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Selec%on and Decision Structures in Java: If Statements and Switch Statements CSC 121 Spring 2016 Howard Rosenthal Lesson Goals Understand Control Structures Understand how to control the flow of a program
Connecting with Computer Science, 2e. Chapter 15 Programming II
 Connecting with Computer Science, 2e Chapter 15 Programming II Objectives In this chapter you will: Gain an understanding of the basics of high-level programming languages, using Java and C++ as examples
Connecting with Computer Science, 2e Chapter 15 Programming II Objectives In this chapter you will: Gain an understanding of the basics of high-level programming languages, using Java and C++ as examples
BCS THE CHARTERED INSTITUTE FOR IT. BCS HIGHER EDUCATION QUALIFICATIONS BCS Level 4 Certificate in IT SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT
 BCS THE CHARTERED INSTITUTE FOR IT BCS HIGHER EDUCATION QUALIFICATIONS BCS Level 4 Certificate in IT SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT Wednesday 25th March 2015 - Afternoon Time: TWO hours Section A and Section B each
BCS THE CHARTERED INSTITUTE FOR IT BCS HIGHER EDUCATION QUALIFICATIONS BCS Level 4 Certificate in IT SOFTWARE DEVELOPMENT Wednesday 25th March 2015 - Afternoon Time: TWO hours Section A and Section B each
Digital Arithmetic. Digital Arithmetic: Operations and Circuits Dr. Farahmand
 Digital Arithmetic Digital Arithmetic: Operations and Circuits Dr. Farahmand Binary Arithmetic Digital circuits are frequently used for arithmetic operations Fundamental arithmetic operations on binary
Digital Arithmetic Digital Arithmetic: Operations and Circuits Dr. Farahmand Binary Arithmetic Digital circuits are frequently used for arithmetic operations Fundamental arithmetic operations on binary
Question: Total Points: Score:
 CS 170 Exam 1 Section 001 Fall 2014 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
CS 170 Exam 1 Section 001 Fall 2014 Name (print): Instructions: Keep your eyes on your own paper and do your best to prevent anyone else from seeing your work. Do NOT communicate with anyone other than
Decimal & Binary Representation Systems. Decimal & Binary Representation Systems
 Decimal & Binary Representation Systems Decimal & binary are positional representation systems each position has a value: d*base i for example: 321 10 = 3*10 2 + 2*10 1 + 1*10 0 for example: 101000001
Decimal & Binary Representation Systems Decimal & binary are positional representation systems each position has a value: d*base i for example: 321 10 = 3*10 2 + 2*10 1 + 1*10 0 for example: 101000001
Java is an objet-oriented programming language providing features that support
 Java Essentials CSCI 136: Spring 2018 Handout 2 February 2 Language Basics Java is an objet-oriented programming language providing features that support Data abstraction Code reuse Modular development
Java Essentials CSCI 136: Spring 2018 Handout 2 February 2 Language Basics Java is an objet-oriented programming language providing features that support Data abstraction Code reuse Modular development
UNIT 7A Data Representation: Numbers and Text. Digital Data
 UNIT 7A Data Representation: Numbers and Text 1 Digital Data 10010101011110101010110101001110 What does this binary sequence represent? It could be: an integer a floating point number text encoded with
UNIT 7A Data Representation: Numbers and Text 1 Digital Data 10010101011110101010110101001110 What does this binary sequence represent? It could be: an integer a floating point number text encoded with
Groups of two-state devices are used to represent data in a computer. In general, we say the states are either: high/low, on/off, 1/0,...
 Chapter 9 Computer Arithmetic Reading: Section 9.1 on pp. 290-296 Computer Representation of Data Groups of two-state devices are used to represent data in a computer. In general, we say the states are
Chapter 9 Computer Arithmetic Reading: Section 9.1 on pp. 290-296 Computer Representation of Data Groups of two-state devices are used to represent data in a computer. In general, we say the states are
Fall 2017 CISC124 9/16/2017
 CISC124 Labs start this week in JEFF 155: Meet your TA. Check out the course web site, if you have not already done so. Watch lecture videos if you need to review anything we have already done. Problems
CISC124 Labs start this week in JEFF 155: Meet your TA. Check out the course web site, if you have not already done so. Watch lecture videos if you need to review anything we have already done. Problems
Number Systems (2.1.1)
 Number Systems (2.1.1) Concept of a register. Operations of register, Complementation, Ranges, Left and right shifts, Addition of two binary number, Numerical overflow, 2 s complement representation, Binary
Number Systems (2.1.1) Concept of a register. Operations of register, Complementation, Ranges, Left and right shifts, Addition of two binary number, Numerical overflow, 2 s complement representation, Binary
Java Classes: Math, Integer A C S L E C T U R E 8
 Java Classes: Math, Integer A C S - 1903 L E C T U R E 8 Math class Math class is a utility class You cannot create an instance of Math All references to constants and methods will use the prefix Math.
Java Classes: Math, Integer A C S - 1903 L E C T U R E 8 Math class Math class is a utility class You cannot create an instance of Math All references to constants and methods will use the prefix Math.
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ
 AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
AP Computer Science Unit 1. Writing Programs Using BlueJ 1. Open up BlueJ. Click on the Project menu and select New Project. You should see the window on the right. Navigate to wherever you plan to save
