Search Trees - 2. Venkatanatha Sarma Y. Lecture delivered by: Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore. M.S Ramaiah School of Advanced Studies - Bangalore
|
|
|
- Junior Bell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Search Trees - 2 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11
2 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees To discuss in detail the properties and performance of Red- Black Trees and Splay Trees To illustrate the use of balanced trees for Searching To highlight the relative advantages of different balanced trees for Sorting 2
3 Red-Black Trees 3
4 From (2,4) to Red-Black Trees A red-black tree is a representation of a (2,4) tree by means of a binary tree whose nodes are colored red or black In comparison with its associated (2,4) tree, a red-black tree has same logarithmic time performance simpler implementation with a single node type 4
5 Red-Black Trees A red-black tree can also be defined as a binary search tree that satisfies the following properties: Root Property: the root is black External Property: every leaf is black Internal Property: the children of a red node are black Depth Property: all the leaves have the same black depth 5
6 Height of a Red-Black Tree Theorem: A red- black tree storing n entries has height O(log n) Proof: The height of a Red-Black tree is at most twice the height of its associated (2,4) tree, which is O(log n) The search algorithm for a binary search tree is the same as that for a binary search tree By the above theorem, searching in a Red-Black tree takes O(log n) time 6
7 Insertion To perform operation insert(k, o), we execute the insertion algorithm for binary search trees and color red the newly inserted node z unless it is the root We preserve the root, external, and depth properties If the parent v of z is black, we also preserve the internal property and We are done Else (v is red ) we have a double red (i.e., a violation of the internal property), which requires a reorganization of the tree Example where the insertion of 4 causes a double red: 7
8 Remedying a Double Red Consider a double red with child z and parent v, and let w be the sibling of v Case 1: w is black The double red is an incorrect replacement of a 4-node Restructuring: we change the 4- node replacement Case 2: w is red The double red corresponds to an overflow Recoloring: we perform the equivalent of a split 8
9 Restructuring A restructuring remedies a child-parent double red when the parent red node has a black sibling It is equivalent to restoring the correct replacement of a 4-node The internal property is restored and the other properties are preserved 9
10 Restructuring There are four restructuring configurations depending on whether the double red nodes are left or right children 10
11 Re-colouring A recoloring remedies a child-parent double red when the parent red node has a red sibling The parent v and its sibling w become black and the grandparent u becomes red, unless it is the root It is equivalent to performing a split on a 5-node The double red violation may propagate to the grandparent u 11
12 Re-colouring Example 12
13 Algorithm insert(k, o) 1. We search for key k to locate the insertion node z 2. We add the new entry (k, o) at node z and color z red 3. while doublered(z) if isblack(sibling(parent(z) )) z restructure(z) return else { sibling(parent(z) is red } z recolor(z) Analysis of Insertion Recall that a red-black tree has O(log n) height Step 1 takes O(log n) time because we visit O(log n) nodes Step 2 takes O(1) time Step 3 takes O(log n) time because we perform O(log n) recolorings, each taking O(1) time, and at most one restructuring taking O(1) time Thus, an insertion in a redblack tree takes O(log n) time 13
14 Deletion To perform operation remove(k), we first execute the deletion algorithm for binary search trees Let v be the internal node removed, w the external node removed, and r the sibling of w If either v of r was red, we color r black and we are done Else (v and r were both black) we color r double black, which is a violation of the internal property requiring a reorganization of the tree 14
15 Deletion Example Example: deletion of 8 causes a double black: 15
16 Remedying a Double Black The algorithm for remedying a double black node w with sibling y considers three cases Case 1: y is black and has a red child We perform a restructuring, equivalent to a transfer, and we are done Case 2: y is black and its children are both black We perform a recoloring, equivalent to a fusion, which may propagate up the double black violation Case 3: y is red We perform an adjustment, equivalent to choosing a different representation of a 3-node, after which either Case 1 or Case 2 applies Deletion in a red-black tree takes O(log n) time 16
17 Red-Black Tree Reorganization 17
18 Splay Trees 18
19 Splay Trees are Binary Search Trees BST Rules: entries stored only at internal nodes keys stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the key stored at v keys stored at nodes in the right subtree of v are greater than or equal to the key stored at v An inorder traversal will return the keys in order Splay Trees 19
20 Starts the Same as in a BST Search proceeds down the tree to found item or an external node Example: Search for item with key 11 Searching in a Splay Tree 20
21 Searching in a Splay Tree Search for key 8, ends at an internal node. 21
22 Splay Trees Rotations New operation: splay splaying moves a node to the root using rotations right rotation makes the left child x of a node y into y s parent; y becomes the right child of x left rotation makes the right child y of a node x into x s parent; x becomes the left child of y 22
23 Splaying x is a left-left grandchild means x is a left child of its parent, which is itself a left child of its parent p is x s parent; g is p s parent 23
24 Visualizing Splaying 24
25 Let x = (8,N) x is the right child of its parent, which is the left child of the grandparent left-rotate around p, then rightrotate around g Splaying Example 25
26 Splaying Example Now x is the left child of the root. Right-rotate around root 26
27 Tree might not be more balanced e.g. splay (40,X) Before, the depth of the shallowest leaf is 3 and the deepest is 7 After, the depth of shallowest leaf is 1 and deepest is 8 Result of Splaying 27
28 Splay Tree Re-Definition We now define a Splay Tree in terms of Splaying A Splay Tree is a binary search tree where a node is splayed after it is accessed (for a search or update) deepest internal node accessed is splayed splaying costs O(h), where h is height of the tree which is still O(n) worst-case O(h) rotations, each of which is O(1) 28
29 Splay Trees and Ordered Dictionaries Which nodes are splayed after each operation? method splay node find(k) if key found, use that node if key not found, use parent of ending external node insert(k,v) use the new node containing the entry inserted remove(k ) use the parent of the internal node that was actually removed from the tree (the parent of the node that the removed item was swapped with) 29
30 Amortized Analysis of Splay Trees Running time of each operation is proportional to time for splaying. Define rank(v) as the logarithm (base 2) of the number of nodes in subtree rooted at v. Costs: zig = 1, zig-zig = 2, zig-zag = 2. Thus, cost for playing a node at depth d = d. Imagine that we store rank(v) cost at each node v of the splay tree (just for the sake of analysis). 30
31 Cost Per zig Doing a zig at x costs at most rank (x) - rank(x): cost = rank (x) + rank (y) - rank(y) - rank(x) < rank (x) - rank(x). 31
32 Cost Per zig-zig and zig-zag Doing a zig- zig or zig- zag at x costs at most 3(rank (x) - rank(x))
33 Cost of Splaying Cost of splaying a node x at depth d of a tree rooted at r: at most 3(rank(r) - rank(x)) - d + 2 Proof: Splaying x takes d/2 splaying substeps 33
34 Performance of Splay Trees Recall: rank of a node is logarithm of its size. Thus, amortized cost of any splay operation is O(log n). In fact, the analysis goes through for any reasonable definition of rank(x). This implies that splay trees can actually adapt to perform searches on frequently requested items much faster than O(log n) in some cases. 34
35 Summary Red-Black Trees is (2,4) tree implemented as a binary tree Red-Black Trees are easy to implement and give the same O (log n) performance Splay Trees are special binary search trees where the key at a node dominates keys of all the left descendents and is dominated by the keys of all the right descendents This imposed order can be used by an inorder traversal to search keys in order To maintain this order, splaying is performed after each access operation The amortised cost of any Splay Trees operation is O (log n) 35
Splay Trees Goodrich, Tamassia, Dickerson. Splay Trees 1
 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: entries stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored
Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: entries stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored
Splay Trees. Splay Trees 1
 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
Search Trees - 1 Venkatanatha Sarma Y
 Search Trees - 1 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Search Trees - 1 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Splay Trees 3/20/14. Splay Trees. Splay Trees are Binary Search Trees. note that two keys of equal value may be wellseparated (7,T) (1,Q) (1,C) (5,H)
 Spla Trees 3/20/14 Presentation for use with the tetbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, b M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wile, 2014 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 2013
Spla Trees 3/20/14 Presentation for use with the tetbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, b M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wile, 2014 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 2013
Red-Black Trees. 2/24/2006 Red-Black Trees 1
 Red-Black Trees 3 8 //00 Red-Black Trees 1 Outline and Reading From (,) trees to red-black trees ( 10.5) Red-black tree ( 10.5.1) Definition Height Insertion restructuring recoloring Deletion restructuring
Red-Black Trees 3 8 //00 Red-Black Trees 1 Outline and Reading From (,) trees to red-black trees ( 10.5) Red-black tree ( 10.5.1) Definition Height Insertion restructuring recoloring Deletion restructuring
Data Structure: Search Trees 2. Instructor: Prof. Young-guk Ha Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering
 Data Structure: Search Trees 2 2017 Instructor: Prof. Young-guk Ha Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Search Trees Tree data structures that can be used to implement a dictionary, especially an ordered
Data Structure: Search Trees 2 2017 Instructor: Prof. Young-guk Ha Dept. of Computer Science & Engineering Search Trees Tree data structures that can be used to implement a dictionary, especially an ordered
(2,4) Trees. 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2/22/2006 (2,4) Trees 1 Outline and Reading Multi-way search tree ( 10.4.1) Definition Search (2,4) tree ( 10.4.2) Definition Search Insertion Deletion Comparison of dictionary
Red-Black Trees Goodrich, Tamassia. Red-Black Trees 1
 Red-Black Trees 3 8 00 Goodrich, Tamassia Red-Black Trees 1 From (,) to Red-Black Trees A red-black tree is a representation of a (,) tree by means of a binary tree hose nodes are colored red or black
Red-Black Trees 3 8 00 Goodrich, Tamassia Red-Black Trees 1 From (,) to Red-Black Trees A red-black tree is a representation of a (,) tree by means of a binary tree hose nodes are colored red or black
Ch04 Balanced Search Trees
 Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
Presentation for use with the textbook Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 05 Ch0 Balanced Search Trees v 3 8 z Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries,
From (2,4) to Red-Black Trees
 Red-Black Trees 3/0/1 Presentation for use ith the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Jaa, th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldasser, Wiley, 01 Red-Black Trees 3 8 01 Goodrich,
Red-Black Trees 3/0/1 Presentation for use ith the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Jaa, th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldasser, Wiley, 01 Red-Black Trees 3 8 01 Goodrich,
Red-Black Trees. Based on materials by Dennis Frey, Yun Peng, Jian Chen, and Daniel Hood
 Red-Black Trees Based on materials by Dennis Frey, Yun Peng, Jian Chen, and Daniel Hood Quick Review of Binary Search Trees n Given a node n... q All elements of n s left subtree are less than n.data q
Red-Black Trees Based on materials by Dennis Frey, Yun Peng, Jian Chen, and Daniel Hood Quick Review of Binary Search Trees n Given a node n... q All elements of n s left subtree are less than n.data q
Search Trees. COMPSCI 355 Fall 2016
 Search Trees COMPSCI 355 Fall 2016 2-4 Trees Search Trees AVL trees Red-Black trees Splay trees Multiway Search Trees (2, 4) Trees External Search Trees (optimized for reading and writing large blocks)
Search Trees COMPSCI 355 Fall 2016 2-4 Trees Search Trees AVL trees Red-Black trees Splay trees Multiway Search Trees (2, 4) Trees External Search Trees (optimized for reading and writing large blocks)
(2,4) Trees Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d -1 key-element
CS350: Data Structures Red-Black Trees
 Red-Black Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Red-Black Tree An alternative to AVL trees Insertion can be done in a bottom-up or
Red-Black Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Red-Black Tree An alternative to AVL trees Insertion can be done in a bottom-up or
13.4 Deletion in red-black trees
 Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to insertion. Apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees. Apply node color changes and left/right rotations to fix the violations of RBT tree properties.
Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to insertion. Apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees. Apply node color changes and left/right rotations to fix the violations of RBT tree properties.
Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees. Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler
 Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Multiway Seach Tree: a new type of search trees: for ordered d dictionary
Lecture 11: Multiway and (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline Multiway Seach Tree: a new type of search trees: for ordered d dictionary
Algorithms. Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees
 Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Self-Balancing Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Self-Balancing Search Trees Chapter 11 Chapter Objectives To understand the impact that balance has on the performance of binary search trees To learn about the AVL tree for storing and maintaining a binary
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees
 Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Chapter 22 Splay Trees
 Chapter 22 Splay Trees Introduction Splay trees support all the operations of binary trees. But they do not guarantee Ο(log N) worst-case performance. Instead, its bounds are amortized, meaning that although
Chapter 22 Splay Trees Introduction Splay trees support all the operations of binary trees. But they do not guarantee Ο(log N) worst-case performance. Instead, its bounds are amortized, meaning that although
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS. Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap Summary of the previous lecture TREE is hierarchical (non linear) data structure Binary trees Definitions Full tree,
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap Summary of the previous lecture TREE is hierarchical (non linear) data structure Binary trees Definitions Full tree,
Analysis of Algorithms
 Analysis of Algorithms Trees-I Prof. Muhammad Saeed Tree Representation.. Analysis Of Algorithms 2 .. Tree Representation Analysis Of Algorithms 3 Nomenclature Nodes (13) Size (13) Degree of a node Depth
Analysis of Algorithms Trees-I Prof. Muhammad Saeed Tree Representation.. Analysis Of Algorithms 2 .. Tree Representation Analysis Of Algorithms 3 Nomenclature Nodes (13) Size (13) Degree of a node Depth
13.4 Deletion in red-black trees
 The operation of Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to the operation of Insertion on the tree. That is, apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees to delete a node z; apply node color changes
The operation of Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to the operation of Insertion on the tree. That is, apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees to delete a node z; apply node color changes
CIS265/ Trees Red-Black Trees. Some of the following material is from:
 CIS265/506 2-3-4 Trees Red-Black Trees Some of the following material is from: Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp ISBN 0-13-047724-9 Chapter 27 Balanced Search Trees Bret Ford 2005,
CIS265/506 2-3-4 Trees Red-Black Trees Some of the following material is from: Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp ISBN 0-13-047724-9 Chapter 27 Balanced Search Trees Bret Ford 2005,
Heaps and Priority Queues
 Heaps and Priority Queues Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce Priority Queue ADT To discuss and illustrate Priority Queues for sorting
Heaps and Priority Queues Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce Priority Queue ADT To discuss and illustrate Priority Queues for sorting
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees
 Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Algorithms. AVL Tree
 Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Multiway Search Trees. Multiway-Search Trees (cont d)
 Multiway Search Trees Each internal node v of a multi-way search tree T has at least two children contains d-1 items, where d is the number of children of v an item is of the form (k i,x i ) for 1 i d-1,
Multiway Search Trees Each internal node v of a multi-way search tree T has at least two children contains d-1 items, where d is the number of children of v an item is of the form (k i,x i ) for 1 i d-1,
CMPS 2200 Fall 2017 Red-black trees Carola Wenk
 CMPS 2200 Fall 2017 Red-black trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with changes by Carola Wenk 9/13/17 CMPS 2200 Intro. to Algorithms 1 Dynamic Set A dynamic set, or dictionary, is a
CMPS 2200 Fall 2017 Red-black trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with changes by Carola Wenk 9/13/17 CMPS 2200 Intro. to Algorithms 1 Dynamic Set A dynamic set, or dictionary, is a
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Searching Red-Black and Other Dynamically BalancedTrees PLSD210 Searching - Re-visited Binary tree O(log n) if it stays balanced Simple binary tree good for static collections
Data Structures and Algorithms Searching Red-Black and Other Dynamically BalancedTrees PLSD210 Searching - Re-visited Binary tree O(log n) if it stays balanced Simple binary tree good for static collections
Uses for Trees About Trees Binary Trees. Trees. Seth Long. January 31, 2010
 Uses for About Binary January 31, 2010 Uses for About Binary Uses for Uses for About Basic Idea Implementing Binary Example: Expression Binary Search Uses for Uses for About Binary Uses for Storage Binary
Uses for About Binary January 31, 2010 Uses for About Binary Uses for Uses for About Basic Idea Implementing Binary Example: Expression Binary Search Uses for Uses for About Binary Uses for Storage Binary
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming. Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2
 CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2 Last Time Binary search trees (Ch 14) The locate method Further Implementation 2 Today s Outline Binary search trees
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2 Last Time Binary search trees (Ch 14) The locate method Further Implementation 2 Today s Outline Binary search trees
Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS )
 Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu October 08, 2014 1 Outline of Today s Class 2 Traversals Querying Insertion and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 3 Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu October 08, 2014 1 Outline of Today s Class 2 Traversals Querying Insertion and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 3 Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Multi-way Search Trees. (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 25
 Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
Multi-way Search Trees (Multi-way Search Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 25 Multi-way Search Trees Each internal node of a multi-way search tree T: has at least two children contains
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms. Trees IV. Lecture 21. Prof.
 ECE 22 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece22/ Trees IV Lecture 2 Prof. Eric Polizzi Summary previous lectures Implementations BST 5 5 7 null 8 null null 7 null
ECE 22 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece22/ Trees IV Lecture 2 Prof. Eric Polizzi Summary previous lectures Implementations BST 5 5 7 null 8 null null 7 null
ICS 691: Advanced Data Structures Spring Lecture 3
 ICS 691: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2016 Prof. Nodari Sitchinava Lecture 3 Scribe: Ben Karsin 1 Overview In the last lecture we started looking at self-adjusting data structures, specifically, move-to-front
ICS 691: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2016 Prof. Nodari Sitchinava Lecture 3 Scribe: Ben Karsin 1 Overview In the last lecture we started looking at self-adjusting data structures, specifically, move-to-front
A red-black tree is a balanced binary search tree with the following properties:
 Binary search trees work best when they are balanced or the path length from root to any leaf is within some bounds. The red-black tree algorithm is a method for balancing trees. The name derives from
Binary search trees work best when they are balanced or the path length from root to any leaf is within some bounds. The red-black tree algorithm is a method for balancing trees. The name derives from
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Splay Trees. (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 27
 Splay Trees (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 27 Basic Idea Invented by Sleator and Tarjan (1985) Blind rebalancing no height info kept! Worst-case time per operation is O(n)
Splay Trees (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 27 Basic Idea Invented by Sleator and Tarjan (1985) Blind rebalancing no height info kept! Worst-case time per operation is O(n)
CSE 326: Data Structures Splay Trees. James Fogarty Autumn 2007 Lecture 10
 CSE 32: Data Structures Splay Trees James Fogarty Autumn 2007 Lecture 10 AVL Trees Revisited Balance condition: Left and right subtrees of every node have heights differing by at most 1 Strong enough :
CSE 32: Data Structures Splay Trees James Fogarty Autumn 2007 Lecture 10 AVL Trees Revisited Balance condition: Left and right subtrees of every node have heights differing by at most 1 Strong enough :
Final Exam. EECS 2011 Prof. J. Elder - 1 -
 Final Exam Ø Wed Apr 11 2pm 5pm Aviva Tennis Centre Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps and hash tables, binary search, loop
Final Exam Ø Wed Apr 11 2pm 5pm Aviva Tennis Centre Ø Closed Book Ø Format similar to midterm Ø Will cover whole course, with emphasis on material after midterm (maps and hash tables, binary search, loop
(2,4) Trees Goodrich, Tamassia. (2,4) Trees 1
 (2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree ( 9.4.1) A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d 1 key-element items
(2,4) Trees 9 2 5 7 10 14 (2,4) Trees 1 Multi-Way Search Tree ( 9.4.1) A multi-way search tree is an ordered tree such that Each internal node has at least two children and stores d 1 key-element items
Introduction. for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit times closer to O(log N) binary search tree
 Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 13: Index structure. The Lecture Contains: Index structure. Binary search tree (BST) B-tree. B+-tree.
 The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
Heaps. 2/13/2006 Heaps 1
 Heaps /13/00 Heaps 1 Outline and Reading What is a heap ( 8.3.1) Height of a heap ( 8.3.) Insertion ( 8.3.3) Removal ( 8.3.3) Heap-sort ( 8.3.) Arraylist-based implementation ( 8.3.) Bottom-up construction
Heaps /13/00 Heaps 1 Outline and Reading What is a heap ( 8.3.1) Height of a heap ( 8.3.) Insertion ( 8.3.3) Removal ( 8.3.3) Heap-sort ( 8.3.) Arraylist-based implementation ( 8.3.) Bottom-up construction
Balanced Binary Search Trees. Victor Gao
 Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Properties of red-black trees
 Red-Black Trees Introduction We have seen that a binary search tree is a useful tool. I.e., if its height is h, then we can implement any basic operation on it in O(h) units of time. The problem: given
Red-Black Trees Introduction We have seen that a binary search tree is a useful tool. I.e., if its height is h, then we can implement any basic operation on it in O(h) units of time. The problem: given
Binary Search Trees. Analysis of Algorithms
 Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Binary Search Trees Analysis of Algorithms Binary Search Trees A BST is a binary tree in symmetric order 31 Each node has a key and every node s key is: 19 23 25 35 38 40 larger than all keys in its left
Trees. Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler
 Lecture 12: BT Trees Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline B-tree Special case of multiway search trees used when data must be stored on the disk, i.e. too large
Lecture 12: BT Trees Courtesy to Goodrich, Tamassia and Olga Veksler Instructor: Yuzhen Xie Outline B-tree Special case of multiway search trees used when data must be stored on the disk, i.e. too large
Dictionaries. 2/17/2006 Dictionaries 1
 Dictionaries < 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 /17/006 Dictionaries 1 Outline and Reading Dictionary ADT ( 9.3) Log file ( 9.3.1) Binary search ( 9.3.3) Lookup table ( 9.3.3) Binary search tree ( 10.1) Search ( 10.1.1)
Dictionaries < 6 > 1 4 = 8 9 /17/006 Dictionaries 1 Outline and Reading Dictionary ADT ( 9.3) Log file ( 9.3.1) Binary search ( 9.3.3) Lookup table ( 9.3.3) Binary search tree ( 10.1) Search ( 10.1.1)
CMPS 2200 Fall 2015 Red-black trees Carola Wenk
 CMPS 2200 Fall 2015 Red-black trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with changes by Carola Wenk 9/9/15 CMPS 2200 Intro. to Algorithms 1 ADT Dictionary / Dynamic Set Abstract data type
CMPS 2200 Fall 2015 Red-black trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with changes by Carola Wenk 9/9/15 CMPS 2200 Intro. to Algorithms 1 ADT Dictionary / Dynamic Set Abstract data type
8.1. Optimal Binary Search Trees:
 DATA STRUCTERS WITH C 10CS35 UNIT 8 : EFFICIENT BINARY SEARCH TREES 8.1. Optimal Binary Search Trees: An optimal binary search tree is a binary search tree for which the nodes are arranged on levels such
DATA STRUCTERS WITH C 10CS35 UNIT 8 : EFFICIENT BINARY SEARCH TREES 8.1. Optimal Binary Search Trees: An optimal binary search tree is a binary search tree for which the nodes are arranged on levels such
Heaps Goodrich, Tamassia. Heaps 1
 Heaps Heaps 1 Recall Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insert(k, x) inserts an entry with key k
Heaps Heaps 1 Recall Priority Queue ADT A priority queue stores a collection of entries Each entry is a pair (key, value) Main methods of the Priority Queue ADT insert(k, x) inserts an entry with key k
Red-black trees (19.5), B-trees (19.8), trees
 Red-black trees (19.5), B-trees (19.8), 2-3-4 trees Red-black trees A red-black tree is a balanced BST It has a more complicated invariant than an AVL tree: Each node is coloured red or black A red node
Red-black trees (19.5), B-trees (19.8), 2-3-4 trees Red-black trees A red-black tree is a balanced BST It has a more complicated invariant than an AVL tree: Each node is coloured red or black A red node
COMP171. AVL-Trees (Part 1)
 COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
COMP11 AVL-Trees (Part 1) AVL Trees / Slide 2 Data, a set of elements Data structure, a structured set of elements, linear, tree, graph, Linear: a sequence of elements, array, linked lists Tree: nested
AVL Trees (10.2) AVL Trees
 AVL Trees (0.) CSE 0 Winter 0 8 February 0 AVL Trees AVL trees are balanced. An AVL Tree is a binary search tree such that for every internal node v of T, the heights of the children of v can differ by
AVL Trees (0.) CSE 0 Winter 0 8 February 0 AVL Trees AVL trees are balanced. An AVL Tree is a binary search tree such that for every internal node v of T, the heights of the children of v can differ by
Chapter. Binary Search Trees. Contents
 Chapter 4 Balanced Binary Search Trees U.S. Navy Blue Angels, performing their delta formation during the Blues on the Bay Air Show at Marine Corps Base Hawaii in 2007. U.S. government photo by Petty Officer
Chapter 4 Balanced Binary Search Trees U.S. Navy Blue Angels, performing their delta formation during the Blues on the Bay Air Show at Marine Corps Base Hawaii in 2007. U.S. government photo by Petty Officer
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
Chapter 12 Advanced Data Structures
 Chapter 12 Advanced Data Structures 2 Red-Black Trees add the attribute of (red or black) to links/nodes red-black trees used in C++ Standard Template Library (STL) Java to implement maps (or, as in Python)
Chapter 12 Advanced Data Structures 2 Red-Black Trees add the attribute of (red or black) to links/nodes red-black trees used in C++ Standard Template Library (STL) Java to implement maps (or, as in Python)
Augmenting Data Structures
 Augmenting Data Structures [Not in G &T Text. In CLRS chapter 14.] An AVL tree by itself is not very useful. To support more useful queries we need more structure. General Definition: An augmented data
Augmenting Data Structures [Not in G &T Text. In CLRS chapter 14.] An AVL tree by itself is not very useful. To support more useful queries we need more structure. General Definition: An augmented data
Chapter 2: Basic Data Structures
 Chapter 2: Basic Data Structures Basic Data Structures Stacks Queues Vectors, Linked Lists Trees (Including Balanced Trees) Priority Queues and Heaps Dictionaries and Hash Tables Spring 2014 CS 315 2 Two
Chapter 2: Basic Data Structures Basic Data Structures Stacks Queues Vectors, Linked Lists Trees (Including Balanced Trees) Priority Queues and Heaps Dictionaries and Hash Tables Spring 2014 CS 315 2 Two
CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES. 3 8 z 4
 CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES v 6 3 8 z 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
CHAPTER 10 AVL TREES v 6 3 8 z 4 ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY
9/29/2016. Chapter 4 Trees. Introduction. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology
 Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
Balanced search trees. DS 2017/2018
 Balanced search trees. DS 2017/2018 Red-black trees Symmetric binary B-tree, Rudolf Bayer, 1972. The balancing is maintained by using a coloring of the nodes. The red-black trees are binary search trees
Balanced search trees. DS 2017/2018 Red-black trees Symmetric binary B-tree, Rudolf Bayer, 1972. The balancing is maintained by using a coloring of the nodes. The red-black trees are binary search trees
Lecture: Analysis of Algorithms (CS )
 Lecture: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu Fall 2017 1 Binary Search Trees Traversals, Querying, Insertion, and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 2 Example: Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Lecture: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu Fall 2017 1 Binary Search Trees Traversals, Querying, Insertion, and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 2 Example: Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Multi-Way Search Trees
 Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
CS 3343 Fall 2007 Red-black trees Carola Wenk
 CS 3343 Fall 2007 Red-black trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with small changes by Carola Wenk CS 334 Analysis of Algorithms 1 Search Trees A binary search tree is a binary tree.
CS 3343 Fall 2007 Red-black trees Carola Wenk Slides courtesy of Charles Leiserson with small changes by Carola Wenk CS 334 Analysis of Algorithms 1 Search Trees A binary search tree is a binary tree.
Heaps 2. Recall Priority Queue ADT. Heaps 3/19/14
 Heaps 3// Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 Heaps Heaps Recall Priority Queue ADT
Heaps 3// Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 Heaps Heaps Recall Priority Queue ADT
Section 1: True / False (1 point each, 15 pts total)
 Section : True / False ( point each, pts total) Circle the word TRUE or the word FALSE. If neither is circled, both are circled, or it impossible to tell which is circled, your answer will be considered
Section : True / False ( point each, pts total) Circle the word TRUE or the word FALSE. If neither is circled, both are circled, or it impossible to tell which is circled, your answer will be considered
Multi-Way Search Trees
 Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
Multi-Way Search Trees Manolis Koubarakis 1 Multi-Way Search Trees Multi-way trees are trees such that each internal node can have many children. Let us assume that the entries we store in a search tree
COMP Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
 COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Lecture 9 - Jan. 22, 2018 CLRS 12.2, 12.3, 13.2, read problem 13-3 University of Manitoba COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Lecture 9 - Jan. 22, 2018 CLRS 12.2, 12.3, 13.2, read problem 13-3 University of Manitoba COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
COSC160: Data Structures Balanced Trees. Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor
 COSC160: Data Structures Balanced Trees Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Balanced Trees I. AVL Trees I. Balance Constraint II. Examples III. Searching IV. Insertions V. Removals
COSC160: Data Structures Balanced Trees Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Balanced Trees I. AVL Trees I. Balance Constraint II. Examples III. Searching IV. Insertions V. Removals
Search Trees (Ch. 9) > = Binary Search Trees 1
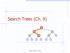 Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
Search Trees (Ch. 9) < 6 > = 1 4 8 9 Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionaries Keys are assumed to come from a total order. New operations: closestbefore(k) closestafter(k) Binary Search Trees Binary
Advanced Set Representation Methods
 Advanced Set Representation Methods AVL trees. 2-3(-4) Trees. Union-Find Set ADT DSA - lecture 4 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1 Advanced Set Representation. AVL Trees Problem with BSTs: worst case operation
Advanced Set Representation Methods AVL trees. 2-3(-4) Trees. Union-Find Set ADT DSA - lecture 4 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1 Advanced Set Representation. AVL Trees Problem with BSTs: worst case operation
Advanced Algorithms. Class Notes for Thursday, September 18, 2014 Bernard Moret
 Advanced Algorithms Class Notes for Thursday, September 18, 2014 Bernard Moret 1 Amortized Analysis (cont d) 1.1 Side note: regarding meldable heaps When we saw how to meld two leftist trees, we did not
Advanced Algorithms Class Notes for Thursday, September 18, 2014 Bernard Moret 1 Amortized Analysis (cont d) 1.1 Side note: regarding meldable heaps When we saw how to meld two leftist trees, we did not
2-3 Tree. Outline B-TREE. catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } ADD SLIDES ON DISJOINT SETS
 Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Red-Black-Trees and Heaps in Timestamp-Adjusting Sweepline Based Algorithms
 Department of Informatics, University of Zürich Vertiefungsarbeit Red-Black-Trees and Heaps in Timestamp-Adjusting Sweepline Based Algorithms Mirko Richter Matrikelnummer: 12-917-175 Email: mirko.richter@uzh.ch
Department of Informatics, University of Zürich Vertiefungsarbeit Red-Black-Trees and Heaps in Timestamp-Adjusting Sweepline Based Algorithms Mirko Richter Matrikelnummer: 12-917-175 Email: mirko.richter@uzh.ch
Binary Search Trees > = 2014 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser. Binary Search Trees 1
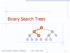 Binary Search Trees < > = Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionary (Map) ADT get (k): record with key k put (k,data): add record (k,data) remove (k): delete record with key k smallest(): record with smallest
Binary Search Trees < > = Binary Search Trees 1 Ordered Dictionary (Map) ADT get (k): record with key k put (k,data): add record (k,data) remove (k): delete record with key k smallest(): record with smallest
Self Adjusting Data Structures
 Self Adjusting Data Structures Pedro Ribeiro DCC/FCUP 2014/2015 Pedro Ribeiro (DCC/FCUP) Self Adjusting Data Structures 2014/2015 1 / 31 What are self adjusting data structures? Data structures that can
Self Adjusting Data Structures Pedro Ribeiro DCC/FCUP 2014/2015 Pedro Ribeiro (DCC/FCUP) Self Adjusting Data Structures 2014/2015 1 / 31 What are self adjusting data structures? Data structures that can
Search Trees. Undirected graph Directed graph Tree Binary search tree
 Search Trees Undirected graph Directed graph Tree Binary search tree 1 Binary Search Tree Binary search key property: Let x be a node in a binary search tree. If y is a node in the left subtree of x, then
Search Trees Undirected graph Directed graph Tree Binary search tree 1 Binary Search Tree Binary search key property: Let x be a node in a binary search tree. If y is a node in the left subtree of x, then
Sorted Arrays. Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min
 Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Outline. Definition. 2 Height-Balance. 3 Searches. 4 Rotations. 5 Insertion. 6 Deletions. 7 Reference. 1 Every node is either red or black.
 Outline 1 Definition Computer Science 331 Red-Black rees Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lectures #20-22 2 Height-Balance 3 Searches 4 Rotations 5 s: Main Case 6 Partial
Outline 1 Definition Computer Science 331 Red-Black rees Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lectures #20-22 2 Height-Balance 3 Searches 4 Rotations 5 s: Main Case 6 Partial
COMP Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
 COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Lecture 9 - Jan. 22, 2018 CLRS 12.2, 12.3, 13.2, read problem 13-3 University of Manitoba 1 / 12 Binary Search Trees (review) Structure
COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Lecture 9 - Jan. 22, 2018 CLRS 12.2, 12.3, 13.2, read problem 13-3 University of Manitoba 1 / 12 Binary Search Trees (review) Structure
B-Trees and External Memory
 Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 and External Memory 1 1 (2, 4) Trees: Generalization of BSTs Each internal node
Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 and External Memory 1 1 (2, 4) Trees: Generalization of BSTs Each internal node
AVL Trees. (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 17
 AVL Trees (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 17 Balanced Binary Tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time
AVL Trees (AVL Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 17 Balanced Binary Tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time
B-Trees and External Memory
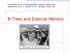 Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 B-Trees and External Memory 1 (2, 4) Trees: Generalization of BSTs Each internal
Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 B-Trees and External Memory 1 (2, 4) Trees: Generalization of BSTs Each internal
Trees. Eric McCreath
 Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
B Tree. Also, every non leaf node must have at least two successors and all leaf nodes must be at the same level.
 B Tree If there is just one item in the node, then the B Tree is organised as a binar search tree: all items in the left sub tree must be less than the item in the node, and all items in the right sub
B Tree If there is just one item in the node, then the B Tree is organised as a binar search tree: all items in the left sub tree must be less than the item in the node, and all items in the right sub
12 July, Red-Black Trees. Red-Black Trees
 1 BST work well if the data is inserted into the tree in random order. They work much slower if the data is inserted in already sorted order. When the values to be inserted are already ordered, a binary
1 BST work well if the data is inserted into the tree in random order. They work much slower if the data is inserted in already sorted order. When the values to be inserted are already ordered, a binary
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Balanced search trees Balanced search tree: A search-tree data structure for which a height of O(lg n) is guaranteed when
CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Balanced search trees Balanced search tree: A search-tree data structure for which a height of O(lg n) is guaranteed when
Note that this is a rep invariant! The type system doesn t enforce this but you need it to be true. Should use repok to check in debug version.
 Announcements: Prelim tonight! 7:30-9:00 in Thurston 203/205 o Handed back in section tomorrow o If you have a conflict you can take the exam at 5:45 but can t leave early. Please email me so we have a
Announcements: Prelim tonight! 7:30-9:00 in Thurston 203/205 o Handed back in section tomorrow o If you have a conflict you can take the exam at 5:45 but can t leave early. Please email me so we have a
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Binary Search Tree - Best Time All BST operations are O(d), where d is tree depth minimum d is d = ëlog for a binary tree
CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Binary Search Tree - Best Time All BST operations are O(d), where d is tree depth minimum d is d = ëlog for a binary tree
AVL Tree Definition. An example of an AVL tree where the heights are shown next to the nodes. Adelson-Velsky and Landis
 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 0 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser
Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wiley, 0 AVL Trees v 6 3 8 z 0 Goodrich, Tamassia, Goldwasser
Lec 17 April 8. Topics: binary Trees expression trees. (Chapter 5 of text)
 Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
Lec 17 April 8 Topics: binary Trees expression trees Binary Search Trees (Chapter 5 of text) Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Heap can t support search in O(log N) time. (takes O(N)
HEAPS: IMPLEMENTING EFFICIENT PRIORITY QUEUES
 HEAPS: IMPLEMENTING EFFICIENT PRIORITY QUEUES 2 5 6 9 7 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H., Wiley, 2014
HEAPS: IMPLEMENTING EFFICIENT PRIORITY QUEUES 2 5 6 9 7 Presentation for use with the textbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, by M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H., Wiley, 2014
Balanced search trees
 Balanced search trees Ordinary binary search trees have expected height Θ(log n) if items are inserted and deleted in random order, but for other orders the height can be Θ(n). This is undesirable, since
Balanced search trees Ordinary binary search trees have expected height Θ(log n) if items are inserted and deleted in random order, but for other orders the height can be Θ(n). This is undesirable, since
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees
 Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
Trees 2: Linked Representation, Tree Traversal, and Binary Search Trees Linked representation of binary tree Again, as with linked list, entire tree can be represented with a single pointer -- in this
Level-Balanced B-Trees
 Gerth Stølting rodal RICS University of Aarhus Pankaj K. Agarwal Lars Arge Jeffrey S. Vitter Center for Geometric Computing Duke University January 1999 1 -Trees ayer, McCreight 1972 Level 2 Level 1 Leaves
Gerth Stølting rodal RICS University of Aarhus Pankaj K. Agarwal Lars Arge Jeffrey S. Vitter Center for Geometric Computing Duke University January 1999 1 -Trees ayer, McCreight 1972 Level 2 Level 1 Leaves
