textview("layouts DSL is the only way") { textsize = 45f font = Fonts.MENLO }.lparams { gravity = Gravity.CENTER }
|
|
|
- Janis Poppy Pierce
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 textview("layouts DSL is the only way") { textsize = 45f font = Fonts.MENLO.lparams { gravity = Gravity.CENTER textview("nov 14, 2017")
2
3 XML is <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android=" xmlns:app=" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <android.support.v7.widget.toolbar android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" app:title="hello, I am a Toolbar" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/text" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="hello, I am a TextView" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="hello, I am a Button" /> </LinearLayout> 3
4 XML is verbose <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android=" xmlns:app=" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <android.support.v7.widget.toolbar android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" app:title="hello, I am a Toolbar" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/text" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="hello, I am a TextView" /> <Button android:id="@+id/button" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="hello, I am a Button" /> </LinearLayout> nonsense 4
5 Where s the views, XML View view = layoutinflater.inflate(r.layout.activity_main, null); 5
6 Where s the views, XML View view = layoutinflater.inflate(r.layout.activity_main, null); <TextView android:id="@+id/first_name"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/middle_name"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/last_name"/> too much sense <TextView android:id="@+id/ "/> <TextView android:id="@+id/city"/> 6
7 And then public class MainActivity extends Activity { TextView firstname; TextView middlename; TextView lastname; TextView ; TextView protected void oncreate(bundle savedinstancestate) { super.oncreate(savedinstancestate); setcontentview(r.layout.activity_main); firstname = (TextView) findviewbyid(r.id.first_name); middlename = (TextView) findviewbyid(r.id.middle_name); lastname = (TextView) findviewbyid(r.id.last_name); = (TextView) findviewbyid(r.id. ); city = (TextView) findviewbyid(r.id.city); public void userupdated(user user) { firstname.settext(user.firstname); middlename.settext(user.middlename); lastname.settext(user.lastname); .settext(user. ); city.settext(user.city); 7
8 And then findviewbyid public class MainActivity extends Activity { TextView firstname; TextView middlename; TextView lastname; TextView ; TextView protected void oncreate(bundle savedinstancestate) { super.oncreate(savedinstancestate); setcontentview(r.layout.activity_main); firstname = (TextView) findviewbyid(r.id.first_name); middlename = (TextView) findviewbyid(r.id.middle_name); lastname = (TextView) findviewbyid(r.id.last_name); = (TextView) findviewbyid(r.id. ); city = (TextView) findviewbyid(r.id.city); public void userupdated(user user) { firstname.settext(user.firstname); middlename.settext(user.middlename); lastname.settext(user.lastname); .settext(user. ); city.settext(user.city); boilerplate 8
9 ButterKnife - bit better public class MainActivity extends Activity TextView TextView TextView TextView TextView protected void oncreate(bundle savedinstancestate) { super.oncreate(savedinstancestate); setcontentview(r.layout.activity_main); ButterKnife.bind(this); public void userupdated(user user) { firstname.settext(user.firstname); middlename.settext(user.middlename); lastname.settext(user.lastname); .settext(user. ); city.settext(user.city); 9
10 10
11 Kotlin and Android Extensions - like a magic apply plugin: kotlin-android-extensions import kotlinx.android.synthetic.activity_main.* class MainActivity : Activity() { override fun oncreate(savedinstancestate: Bundle?) { super.oncreate(savedinstancestate) setcontentview(r.layout.activity_main) fun userupdated(user: User) { first_name.text = user.firstname middle_name.text = user.middlename last_name.text = user.lastname .text = user. city.text = user.city 11
12 fun userupdated(user: User) { first_name.text = user.firstname middle_name.text = user.middlename last_name.text = user.lastname .text = user. city.text = user.city state.text = user.state zipcode.text = user.zipcode phone.text = user.phone Your turn, databinding 12
13 android.databindin class MainActivity : Activity() { lateinit var binding: ActivityMainBinding override fun oncreate(savedinstancestate: Bundle?) { super.oncreate(savedinstancestate) binding = DataBindingUtil.setContentView(this, R.layout.activity_main) fun userupdated(user: User) { binding.user = user <layout> <data> <variable name= user" type="com.example.user"/> </data> </layout> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@{user.firstname" /> <TextView android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@{user.lastname" /> 13
14 Wat <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <layout xmlns:android=" <data> <import type="com.example.mystringutils"/> <variable name="user" type="user" /> <variable name="presenter" type="presenter" /> </data> <Button -> presenter.userclicked(user)" View.VISIBLE : View.GONE" /> </layout> 14
15 15
16 Anko Layouts DSL compile "org.jetbrains.anko:anko-sdk25:0.10.2" compile "org.jetbrains.anko:anko-support-v4:0.10.2" compile "org.jetbrains.anko:anko-appcompat-v7:0.10.2" compile "org.jetbrains.anko:anko-recyclerview-v7:0.10.2" compile "org.jetbrains.anko:anko-cardview-v7:0.10.2" compile "org.jetbrains.anko:anko-percent:0.10.2" compile "org.jetbrains.anko:anko-coroutines:0.10.2"... fun Context.scrollView(init: ScrollView.() -> Unit) fun ViewManager.button(init: Button.() -> Unit) button { button.text = "A Button" button.textsize = 14f button.textcolor = Color.BLACK button.setonclicklistener { scrollview { verticallinearlayout { relativelayout { button { text = "A Button".lparams(matchParent, height = dip(300)).lparams(matchparent, wrapcontent).lparams(width = matchparent) framelayout { linearlayout { relativelayout { tablelayout { toolbar { gridlayout { absolutelayout { scrollview {... button { textview { imageview { radiobutton { togglebutton { zoombutton { imagebutton { listview { gridview { searchview { surfaceview { edittext { progressbar { ratingbar { checkbox { seekbar { spinner { switch {... 16
17 android.databinding Anko Layouts DSL <data> <variable name="user" type="user"/> <variable name="presenter" type="presenter"/> </data> <Button View.VISIBLE : View.GONE" android:onclick="@{() -> presenter.userclicked(user)" /> 17
18 android.databinding <data> <variable name="user" type="user"/> <variable name="presenter" type="presenter"/> </data> <Button View.VISIBLE : View.GONE" android:onclick="@{() -> presenter.userclicked(user)" /> Anko Layouts DSL val user: User val presenter: Presenter button { text = user.firstname visibility = if (user.old) View.VISIBLE else View.GONE onclick { presenter.userclicked(user) 18
19 android.databinding <data> <variable name="user" type="user"/> <variable name="presenter" type="presenter"/> </data> <Button View.VISIBLE : View.GONE" android:onclick="@{() -> presenter.userclicked(user)" /> Anko Layouts DSL val user: User val presenter: Presenter button { text = user.firstname visibility = if (user.old) View.VISIBLE else View.GONE onclick { presenter.userclicked(user) <data> <variable name="user" type="user" /> <import type="com.example.mystringutils" /> </data> <Button android:text="@{user.displayname?? user.lastname" android:transitionname='@{"image_" + user.id /> 19
20 android.databinding <data> <variable name="user" type="user"/> <variable name="presenter" type="presenter"/> </data> <Button View.VISIBLE : View.GONE" android:onclick="@{() -> presenter.userclicked(user)" /> <data> <variable name="user" type="user" /> <import type="com.example.mystringutils" /> </data> <Button android:text="@{user.displayname?? user.lastname" android:transitionname='@{"image_" + user.id /> Anko Layouts DSL val user: User val presenter: Presenter button { text = user.firstname visibility = if (user.old) View.VISIBLE else View.GONE onclick { presenter.userclicked(user) import com.example.mystringutils.capitalize val user: User button { text = user.displayname?: user.firstname hint = capitalize(user.lastname) transitionname = "image_${user.id" 20
21 android.databinding <data> <variable name="user" type="user"/> <variable name="presenter" type="presenter"/> </data> <Button View.VISIBLE : View.GONE" android:onclick="@{() -> presenter.userclicked(user)" /> <data> <variable name="user" type="user" /> <import type="com.example.mystringutils" /> </data> <Button android:text="@{user.displayname?? user.lastname" android:transitionname='@{"image_" + user.id /> Anko Layouts DSL val user: User val presenter: Presenter button { text = user.firstname visibility = if (user.old) View.VISIBLE else View.GONE onclick { presenter.userclicked(user) import com.example.mystringutils.capitalize val user: User button { text = user.displayname?: user.firstname hint = capitalize(user.lastname) transitionname = bind:loadimage") public static void loadimage(imageview view, String url) { Picasso.with(view.getContext()).load(url).into(view); <ImageView 21
22 android.databinding <data> <variable name="user" type="user"/> <variable name="presenter" type="presenter"/> </data> <Button View.VISIBLE : View.GONE" android:onclick="@{() -> presenter.userclicked(user)" /> <data> <variable name="user" type="user" /> <import type="com.example.mystringutils" /> </data> <Button android:text="@{user.displayname?? user.lastname" android:transitionname='@{"image_" + user.id /> Anko Layouts DSL val user: User val presenter: Presenter button { text = user.firstname visibility = if (user.old) View.VISIBLE else View.GONE onclick { presenter.userclicked(user) import com.example.mystringutils.capitalize val user: User button { text = user.displayname?: user.firstname hint = capitalize(user.lastname) transitionname = bind:loadimage") public static void loadimage(imageview view, String url) { Picasso.with(view.getContext()).load(url).into(view); <ImageView fun ImageView.loadImage(url: String) { Picasso.with(context).load(url).into(this) imageview { loadimage(user.imageurl) 22
23 android.databinding <data> <variable name="user" type="user"/> <variable name="presenter" type="presenter"/> </data> <Button View.VISIBLE : View.GONE" android:onclick="@{() -> presenter.userclicked(user)" /> <data> <variable name="user" type="user" /> <import type="com.example.mystringutils" /> </data> <Button android:text="@{user.displayname?? user.lastname" android:transitionname='@{"image_" + user.id /> Anko Layouts DSL val user: User val presenter: Presenter button { text = user.firstname visibility = if (user.old) View.VISIBLE else View.GONE onclick { presenter.userclicked(user) import com.example.mystringutils.capitalize val user: User button { text = user.displayname?: user.firstname hint = capitalize(user.lastname) transitionname = bind:loadimage") public static void loadimage(imageview view, String url) { Picasso.with(view.getContext()).load(url).into(view); <ImageView fun ImageView.loadImage(url: String) { Picasso.with(context).load(url).into(this) imageview { loadimage(user.imageurl) 23
24 Ok, Anko Layouts, how to use val user: User val presenter: Presenter button { text = user.firstname visibility = if (user.old) View.VISIBLE else View.GONE onclick { presenter.userclicked(user) 24
25 All you need is 25
26 All you need is context 26
27 View Factory typealias ViewFactory = (Context) -> View val buttonfactory: ViewFactory = ::Button val framelayoutfactory: ViewFactory = ::FrameLayout val userprofilefactory: ViewFactory = { context: Context -> with(context) { verticallinearlayout { gravity = Gravity.CENTER textview("foo") { textsize = 20f textcolor = Color.BLUE textview("bar") { textsize = 16f textcolor = Color.RED.lparams { topmargin = dip(10) 27
28 View Factory typealias ViewFactory = (Context) -> View fun viewfactory(factory: Context.() -> View): ViewFactory = { context -> context.factory() val userprofile = viewfactory { verticallinearlayout { gravity = Gravity.CENTER textview("foo") { textsize = 20f textcolor = Color.BLUE textview("bar") { textsize = 16f textcolor = Color.RED.lparams { topmargin = dip(10) 28
29 How to use class MainActivity : Activity() { override fun oncreate(savedinstancestate: Bundle?) { super.oncreate(savedinstancestate) setcontentview(user_profile) fun Activity.setContentView(factory: ViewFactory) = setcontentview(factory(this)) val user_profile = viewfactory { verticallinearlayout { gravity = Gravity.CENTER textview("foo") { textsize = 20f textcolor = Color.BLUE textview("bar") { textsize = 16f textcolor = Color.RED.lparams { topmargin = dip(10) 29
30 Dex count matters Usage Method count Field count val user_profile = viewfactory { 4 1 val user_profile inline get() = viewfactory { 4 0 val user_profile = fun(user: User) = viewfactory { 8 2 fun userprofile() = viewfactory { 4 0 fun userprofile(user: User = User()) = viewfactory {
31 Parameterization val user_profile = fun(user: User) = viewfactory { verticallinearlayout { gravity = Gravity.CENTER textview(user.firstname) { textsize = 20f textcolor = Color.BLUE textview(user.lastname) { textsize = 16f textcolor = Color.RED.lparams { topmargin = dip(10) setcontentview(user_profile(user("foo", "Bar"))) 31
32 Data binding on the spot val user_profile = fun(user: rx.observable<user>) = viewfactory { verticallinearlayout { gravity = Gravity.CENTER textview { user.map(user::firstname).subscribe(::settext) textsize = 20f textcolor = Color.BLUE textview { user.map(user::lastname).subscribe(::settext) textsize = 16f textcolor = Color.RED.lparams { topmargin = dip(10) 32
33 Data binding even simpler val user_profile = fun(user: rx.observable<user>) = viewfactory { verticallinearlayout { gravity = Gravity.CENTER textview(user.map(user::firstname)) { textsize = 20f textcolor = Color.BLUE textview(user.map(user::lastname)) { textsize = 16f textcolor = Color.RED.lparams { topmargin = dip(10) inline fun ViewManager.textView(obsText: Observable<CharSequence>, init: TextView.() -> Unit) = textview { init() obstext.subscribe(::settext) 33
34 Data binding two way import com.jakewharton.rxbinding.* val user_profile = fun(user: rx.observable<user>, saveuser: (User) -> Unit) = viewfactory { verticallinearlayout { gravity = Gravity.CENTER edittext(user.map(user::firstname)) { textsize = 20f textcolor = Color.BLUE textchanges().withlatestfrom(user).map { (name, user) -> user.copy(firstname = name).subscribe(saveuser) edittext(user.map(user::lastname)) { textsize = 16f textcolor = Color.RED textchanges().withlatestfrom(user).map { (name, user) -> user.copy(lastname = name).subscribe(saveuser).lparams { topmargin = dip(10) 34
35 Parameterize them all val screen_main = fun(user: Observable<User>, hisfriends: Observable<List<Friend>>, hisphotos: Observable<List<Photo>>, hiscomments: Observable<List<Comment>>, girlhilikes: Observable<Girl>, answertothequestionoflife: Int) = viewfactory { 35
36 Parameterize them all val screen_main = fun(user: Observable<User>, hisfriends: Observable<List<Friend>>, hisphotos: Observable<List<Photo>>, hiscomments: Observable<List<Comment>>, girlhilikes: Observable<Girl>, answertothequestionoflife: Int) = viewfactory { 36
37 Parameterize them all val screen_main = fun(user: Observable<User>, hisfriends: Observable<List<Friend>>, hisphotos: Observable<List<Photo>>, hiscomments: Observable<List<Comment>>, girlhilikes: Observable<Girl>, answertothequestionoflife: Int) = viewfactory { View Model 37
38 View Model class MainScreenViewModel(source: Source) { val user: Observable<User> = source.getuser() val hisfriends: Observable<List<Friend>> = user.flatmap(source::getfriendsofuser) val hisphotos: Observable<List<Photo>> = user.flatmap(source::getphotosofuser) val hiscomments: Observable<List<Comment>> = source.gethiscomments() val girlhilikes: Observable<Girl> = source.getgirlhilikes() val screen_main = fun(viewmodel: MainScreenViewModel) = viewfactory { verticallinearlayout { addview(user_profile(viewmodel.user)) viewpager { viewmodel.hisphotos.map(::userphotosviewpageradapter).subscribe(::setadapter).lparams(width = matchparent, height = dip(300)) textview { viewmodel.hiscomments.map { "User has ${it.size comments".subscribe(::settext) imageview { viewmodel.girlhilikes.map(girl::avatarurl).subscribe(::loadurl).lparams(dip(150), dip(150)) 38
39 Don t forget about lifecycle import com.jakewharton.rxbinding.* fun <T> Observable<T>.manageLifecycle(view: View) = this.observeon(androidschedulers.mainthread()).delaysubscription(view.attaches()).takeuntil(view.detaches()) s.repeatwhen { view.attaches() val screen_main = fun(viewmodel: MainScreenViewModel) = viewfactory { verticallinearlayout { viewpager { viewmodel.hisphotos.managelifecycle(view = this).map(::userphotosviewpageradapter).subscribe(::setadapter).lparams(width = matchparent, height = dip(300)) textview { viewmodel.hiscomments.managelifecycle(view = this).map { "User has ${it.size comments".subscribe(::settext) 39
40 Lifecycle management is error-prone val screen_main = fun(viewmodel: MainScreenViewModel) = viewfactory { scrollview { verticallinearlayout { viewpager { viewmodel.hisphotos.managelifecycle(view = this).map(::userphotosviewpageradapter).subscribe(::setadapter).lparams(width = matchparent, height = dip(300)) textview { viewmodel.hiscomments.managelifecycle(view = this).map { "User has ${it.size comments".subscribe(::settext) imageview { viewmodel.girlhilikes.map(girl::avatarurl).subscribe(::loadurl).lparams(dip(150), dip(150)) Leak 40
41 View Model Lifecycle Proxy interface ViewModel class ViewModelProxy: ViewModel val obs1: Observable<Int> val obs2: Observable<User> override val obs1 get() = super.obs1.managelifecycle(view) override val obs2 get() = super.obs2.managelifecycle(view) 41
42 Lifecycle Proxy Implemenation interface MyViewModel { val answer get() = Observable.just(42) class Impl : MyViewModel class MyViewModelLifecycleProxy(val view: View): MyViewModel by MyViewModel.Impl() { override val answer: Observable<Int> get() = super.answer.observeon(androidschedulers.mainthread()).delaysubscription(view.attaches()).takeuntil(view.detaches()).repeatwhen { view.attaches() 42
43 Lifecycle Proxy Implemenation interface MyViewModel { val answer get() = Observable.just(42) class Impl : MyViewModel class MyViewModelLifecycleProxy(val view: View): MyViewModel by MyViewModel.Impl() { override val answer: Observable<Int> get() = super.answer.observeon(androidschedulers.mainthread()).delaysubscription(view.attaches()).takeuntil(view.detaches()).repeatwhen { view.attaches() 43
44 Java Dynamic Proxy The class java.lang.reflect.proxy allows you to implement interfaces dynamically by handling method calls in an InvocationHandler. It is considered part of Java's reflection facility, has nothing to do with bytecode generation. 44
45 For example Retrofit public interface GitHubService Call<List<Repo>> listrepos(@path("user") String user); GitHubService service = retrofit.create(githubservice.class); Call<List<Repo>> repos = service.listrepos("octocat"); public <T> Retrofit.create(final Class<T> service) { return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(service.getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{service, new InvocationHandler() public Object invoke(object proxy, Method Object[] args) throws Throwable { ServiceMethod<Object, Object> servicemethod = (ServiceMethod<Object, Object>) loadservicemethod(method); OkHttpCall<Object> okhttpcall = new OkHttpCall<>(serviceMethod, args); return servicemethod.calladapter.adapt(okhttpcall); ); 45
46 View Model Dynamic Lifecycle Proxy interface ViewModelMarker fun <VM : ViewModelMarker> dynamiclifecycleproxy(viewmodel: VM, vminterface: Class<*>, view: Observable<View>): VM { val handler = InvocationHandler { proxy, method, args -> if (method.returntype == rx.observable::class.java) { (method.invoke(viewmodel, args) as Observable<*>).observeOn(AndroidSchedulers.mainThread()).delaySubscription(view.flatMap(View::attaches)).takeUntil(view.flatMap(View::detaches)).repeatWhen { view.flatmap(view::attaches) else { method.invoke(viewmodel, args) return Proxy.newProxyInstance( classloader = vminterface.classloader, interfaces = arrayof(vminterface), invocationhandler = handler ) as VM 46
47 How to use interface MainScreenViewModel : ViewModelMarker { val username get() = Observable.just("Foobar") class Impl: MainScreenViewModel fun usage(context: Context) { 1) val viewmodel = MainScreenViewModel.Impl() 2) val viewbus = PublishSubject.create<View>() 3) val viewmodelproxy = createlifecycleproxy( viewmodel, MainScreenViewModel::class.java, viewbus) 4) val mainscreenviewfactory = screen_main(viewmodelproxy) val mainscreenview = mainscreenviewfactory(context) 5) viewbus.onnext(mainscreenview) val screen_main = fun(viewmodel: MainScreenViewModel) = viewfactory { framelayout { textview(viewmodel.username) 47
48 Let s simplify typealias ViewFactory = (Context) -> View 48
49 Let s simplify typealias ViewFactory = (Context) -> View typealias ViewWithModelFactory<VM> = (Context, VM) -> View 49
50 Let s simplify typealias ViewFactory = (Context) -> View typealias ViewWithModelFactory<VM> = (Context, VM) -> View fun viewfactory(factory: Context.() -> View) : ViewFactory = { ctx -> ctx.factory() 50
51 Let s simplify typealias ViewFactory = (Context) -> View typealias ViewWithModelFactory<VM> = (Context, VM) -> View fun viewfactory(factory: Context.() -> View) : ViewFactory = { ctx -> ctx.factory() fun <VM : ViewModelMarker> viewwithmodelfactory(factory: Context.(VM) -> View) : ViewWithModelFactory<VM> = { ctx, vm -> ctx.factory(vm) 51
52 Let s simplify typealias ViewFactory = (Context) -> View typealias ViewWithModelFactory<VM> = (Context, VM) -> View fun viewfactory(factory: Context.() -> View) : ViewFactory = { ctx -> ctx.factory() fun <VM : ViewModelMarker> viewwithmodelfactory(factory: Context.(VM) -> View) : ViewWithModelFactory<VM> = { ctx, vm -> ctx.factory(vm) fun <VM : ViewModelMarker> ViewWithModelFactory<VM>.bind(vmFactory: () -> VM) : ViewFactory = { ctx ->... createlifecycleproxy... 52
53 Let s simplify typealias ViewFactory = (Context) -> View typealias ViewWithModelFactory<VM> = (Context, VM) -> View fun viewfactory(factory: Context.() -> View) : ViewFactory = { ctx -> ctx.factory() fun <VM : ViewModelMarker> viewwithmodelfactory(factory: Context.(VM) -> View) : ViewWithModelFactory<VM> = { ctx, vm -> ctx.factory(vm) fun <VM : ViewModelMarker> ViewWithModelFactory<VM>.bind(vmFactory: () -> VM) : ViewFactory = { ctx ->... createlifecycleproxy... setcontentview(screen_main.bind(mainscreenviewmodel::impl)) val screen_main = viewwithmodelfactory<mainscreenviewmodel> { framelayout { textview(it.username) it?? 53
54 Context With View Model class ContextWithViewModel<VM : ViewModelMarker>( val viewmodel: VM, context: Context ) : ContextWrapper(context) 54
55 Let s simplify typealias ViewFactory = (Context) -> View typealias ViewWithModelFactory<VM> = (ContextWithViewModel<VM>) -> View 55
56 Let s simplify typealias ViewFactory = (Context) -> View typealias ViewWithModelFactory<VM> = (ContextWithViewModel<VM>) -> View fun viewfactory(factory: Context.() -> View) : ViewFactory = { ctx -> ctx.factory() fun <VM : ViewModelMarker> viewwithmodelfactory(fct: ContextWithViewModel<VM>.() -> View) : ViewWithModelFactory<VM> = { ctx -> ctx.fct() 56
57 Let s simplify typealias ViewFactory = (Context) -> View typealias ViewWithModelFactory<VM> = (ContextWithViewModel<VM>) -> View fun viewfactory(factory: Context.() -> View) : ViewFactory = { ctx -> ctx.factory() fun <VM : ViewModelMarker> viewwithmodelfactory(fct: ContextWithViewModel<VM>.() -> View) : ViewWithModelFactory<VM> = { ctx -> ctx.fct() fun <VM : ViewModelMarker> ViewWithModelFactory<VM>.bind(vmFactory: () -> VM) : ViewFactory = { ctx ->... createlifecycleproxy... setcontentview(screen_main.bind(mainscreenviewmodel::impl)) val screen_main = viewwithmodelfactory<mainscreenviewmodel> { framelayout { textview(viewmodel.username) 57
58 An example data class Listing( val id: String, val make: String?, val model: String?, val price: Int?,... ) interface ListingViewModel : ViewModelMarker { val listing: Observable<Listing> fun bookmark() { id.take(1).subscribe(logic::bookmarklisting) fun smstoseller(message: String) {... fun calltoseller() {... fun report(reason: String) {... class Impl(override val listing: Observable<Listing>) : ListingViewModel companion object { fun byid(listingid: String) = Impl(Logic.getListingById(listingId)) val ListingViewModel.id val ListingViewModel.make val ListingViewModel.model val ListingViewModel.price get() = listing.map(listing::id) get() = listing.map(listing::make) get() = listing.map(listing::model) get() = listing.map(listing::price) 58
59 viewwithmodel<listingviewmodel>... val listing_recommended_grid_item = viewwithmodel<listingviewmodel> { val listing_discovery_feed_item = viewwithmodel<listingviewmodel> { val listing_horizontal_view = viewwithmodel<listingviewmodel> { val listing_profile_screen = viewwithmodel<listingviewmodel> { 37 matches in 5 files thousands of lines of DSL several ID for testing purpose several ID for view state saving 0 lines of lifecycle management 59
60 Dynamic Proxy Performance Nexus 5X (mid 2015) Android Just proxy instantiation Methods in interface First (ms) Subsequent (ms) Method invocation Without any modification With rx.observable modification Calls Time (ms) Calls Time (ms)
61 Ok, Layouts DSL Benefits: DSL is imperative, but declarative, but imperative 61
62 Ok, Layouts DSL Benefits: DSL is imperative, but declarative, but imperative - Control-flow: if, when, for, while 62
63 Ok, Layouts DSL Benefits: DSL is imperative, but declarative, but imperative - Control-flow: if, when, for, while - Async programming: Promise, RxJava, Coroutines 63
64 Ok, Layouts DSL Benefits: DSL is imperative, but declarative, but imperative - Control-flow: if, when, for, while - Async programming: Promise, RxJava, Coroutines - - ALL THE POWER OF KOTLIN in your layouts 64
65 Ok, Layouts DSL Benefits: DSL is imperative, but declarative, but imperative - Control-flow: if, when, for, while - Async programming: Promise, RxJava, Coroutines - - ALL THE POWER OF KOTLIN in your layouts Easy to use 65
66 Ok, Layouts DSL Benefits: DSL is imperative, but declarative, but imperative - Control-flow: if, when, for, while - Async programming: Promise, RxJava, Coroutines - - ALL THE POWER OF KOTLIN in your layouts Easy to use A bit faster at runtime than XML 66
67 Ok, Layouts DSL Benefits: DSL is imperative, but declarative, but imperative - Control-flow: if, when, for, while - Async programming: Promise, RxJava, Coroutines - - ALL THE POWER OF KOTLIN in your layouts Easy to use A bit faster at runtime than XML Drawbacks: Tooling is not so good yet - No preview - No drag-n-drop layout development - No layout qualifiers: layout-xlarge-land, layout-sw720dp 67
68 Ok, Layouts DSL Benefits: DSL is imperative, but declarative, but imperative - Control-flow: if, when, for, while - Async programming: Promise, RxJava, Coroutines - - ALL THE POWER OF KOTLIN in your layouts Easy to use A bit faster at runtime than XML Drawbacks: Tooling is not so good yet - No preview - No drag-n-drop layout development - No layout qualifiers: layout-xlarge-land, layout-sw720dp DSL is code - More time to compile - More DEX methods 68
69 Ok, Layouts DSL Benefits: DSL is imperative, but declarative, but imperative - Control-flow: if, when, for, while - Async programming: Promise, RxJava, Coroutines - - ALL THE POWER OF KOTLIN in your layouts Easy to use A bit faster at runtime than XML Drawbacks: Tooling is not so good yet - No preview - No drag-n-drop layout development - No layout qualifiers: layout-xlarge-land, layout-sw720dp DSL is code - More time to compile - More DEX methods Yet another hipster thing 69
70 Contact: Code: bit.ly/dsl-the-only-way textview( Q&A ) { textsize = 100f font = Fonts.HELVETICA.lparams { gravity = Gravity.CENTER WANTED Kotlin Android Developer instamotor.com/careers 70
Overview. What are layouts Creating and using layouts Common layouts and examples Layout parameters Types of views Event listeners
 Layouts and Views http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html http://developer.android.com/reference/android/view/view.html Repo: https://github.com/karlmorris/viewsandlayouts Overview
Layouts and Views http://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html http://developer.android.com/reference/android/view/view.html Repo: https://github.com/karlmorris/viewsandlayouts Overview
Programming with Android: Introduction. Layouts. Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Università di Bologna
 Programming with Android: Introduction Layouts Luca Bedogni Marco Di Felice Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Università di Bologna Views: outline Main difference between a Drawable and
Programming with Android: Introduction Layouts Luca Bedogni Marco Di Felice Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Università di Bologna Views: outline Main difference between a Drawable and
Android App Development. Mr. Michaud ICE Programs Georgia Institute of Technology
 Android App Development Mr. Michaud ICE Programs Georgia Institute of Technology Android Operating System Created by Android, Inc. Bought by Google in 2005. First Android Device released in 2008 Based
Android App Development Mr. Michaud ICE Programs Georgia Institute of Technology Android Operating System Created by Android, Inc. Bought by Google in 2005. First Android Device released in 2008 Based
Intents. Your first app assignment
 Intents Your first app assignment We will make this. Decidedly lackluster. Java Code Java Code XML XML Preview XML Java Code Java Code XML Buttons that work
Intents Your first app assignment We will make this. Decidedly lackluster. Java Code Java Code XML XML Preview XML Java Code Java Code XML Buttons that work
ARCHETYPE MODERN ANDROID ARCHITECTURE STEPAN GONCHAROV / DENIS NEKLIUDOV
 ARCHETYPE MODERN ANDROID ARCHITECTURE STEPAN GONCHAROV / DENIS NEKLIUDOV 90seconds.tv 14000+ VIDEOS 1200+ BRANDS 92+ COUNTRIES data class RegisterViewModelStateImpl( override val email: ObservableString
ARCHETYPE MODERN ANDROID ARCHITECTURE STEPAN GONCHAROV / DENIS NEKLIUDOV 90seconds.tv 14000+ VIDEOS 1200+ BRANDS 92+ COUNTRIES data class RegisterViewModelStateImpl( override val email: ObservableString
Diving into Android. By Jeroen Tietema. Jeroen Tietema,
 Diving into Android By Jeroen Tietema Jeroen Tietema, 2015 1 Requirements 4 Android SDK 1 4 Android Studio (or your IDE / editor of choice) 4 Emulator (Genymotion) or a real device. 1 See https://developer.android.com
Diving into Android By Jeroen Tietema Jeroen Tietema, 2015 1 Requirements 4 Android SDK 1 4 Android Studio (or your IDE / editor of choice) 4 Emulator (Genymotion) or a real device. 1 See https://developer.android.com
ANDROID USER INTERFACE
 1 ANDROID USER INTERFACE Views FUNDAMENTAL UI DESIGN Visual interface element (controls or widgets) ViewGroup Contains multiple widgets. Layouts inherit the ViewGroup class Activities Screen being displayed
1 ANDROID USER INTERFACE Views FUNDAMENTAL UI DESIGN Visual interface element (controls or widgets) ViewGroup Contains multiple widgets. Layouts inherit the ViewGroup class Activities Screen being displayed
Hello World. Lesson 1. Android Developer Fundamentals. Android Developer Fundamentals. Layouts, and. NonCommercial
 Hello World Lesson 1 This work is licensed This under work a Creative is is licensed Commons under a a Attribution-NonCommercial Creative 4.0 Commons International Attribution- License 1 NonCommercial
Hello World Lesson 1 This work is licensed This under work a Creative is is licensed Commons under a a Attribution-NonCommercial Creative 4.0 Commons International Attribution- License 1 NonCommercial
Data binding. in a Kotlin world. Lisa
 Data binding in a Kotlin world Lisa Wray Data binding in a Kotlin world Lisa Wray Data binding in a Kotlin world Lisa Wray Less code is better code 1. Quick tour of The Best Parts of data binding 2. Kotlin
Data binding in a Kotlin world Lisa Wray Data binding in a Kotlin world Lisa Wray Data binding in a Kotlin world Lisa Wray Less code is better code 1. Quick tour of The Best Parts of data binding 2. Kotlin
Kotlin for Android developers
 ROME - APRIL 13/14 2018 Kotlin for Android developers Victor Kropp, JetBrains @kropp Kotlin on JVM + Android JS In development: Kotlin/Native ios/macos/windows/linux Links Kotlin https://kotlinlang.org
ROME - APRIL 13/14 2018 Kotlin for Android developers Victor Kropp, JetBrains @kropp Kotlin on JVM + Android JS In development: Kotlin/Native ios/macos/windows/linux Links Kotlin https://kotlinlang.org
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING Application Tip: Managing Screen Orientation
 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 Application Tip: Managing Screen Orientation ORIENTATIONS Portrait Landscape Reverse portrait Reverse landscape ON REVERSE PORTRAIT Android: all four orientations are
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 Application Tip: Managing Screen Orientation ORIENTATIONS Portrait Landscape Reverse portrait Reverse landscape ON REVERSE PORTRAIT Android: all four orientations are
Android Apps Development for Mobile and Tablet Device (Level I) Lesson 2
 Workshop 1. Compare different layout by using Change Layout button (Page 1 5) Relative Layout Linear Layout (Horizontal) Linear Layout (Vertical) Frame Layout 2. Revision on basic programming skill - control
Workshop 1. Compare different layout by using Change Layout button (Page 1 5) Relative Layout Linear Layout (Horizontal) Linear Layout (Vertical) Frame Layout 2. Revision on basic programming skill - control
Arrays of Buttons. Inside Android
 Arrays of Buttons Inside Android The Complete Code Listing. Be careful about cutting and pasting.
Arrays of Buttons Inside Android The Complete Code Listing. Be careful about cutting and pasting.
MAD ASSIGNMENT NO 2. Submitted by: Rehan Asghar BSSE AUGUST 25, SUBMITTED TO: SIR WAQAS ASGHAR Superior CS&IT Dept.
 MAD ASSIGNMENT NO 2 Submitted by: Rehan Asghar BSSE 7 15126 AUGUST 25, 2017 SUBMITTED TO: SIR WAQAS ASGHAR Superior CS&IT Dept. Android Widgets There are given a lot of android widgets with simplified
MAD ASSIGNMENT NO 2 Submitted by: Rehan Asghar BSSE 7 15126 AUGUST 25, 2017 SUBMITTED TO: SIR WAQAS ASGHAR Superior CS&IT Dept. Android Widgets There are given a lot of android widgets with simplified
CS371m - Mobile Computing. User Interface Basics
 CS371m - Mobile Computing User Interface Basics Clicker Question Have you ever implemented a Graphical User Interface (GUI) as part of a program? A. Yes, in another class. B. Yes, at a job or internship.
CS371m - Mobile Computing User Interface Basics Clicker Question Have you ever implemented a Graphical User Interface (GUI) as part of a program? A. Yes, in another class. B. Yes, at a job or internship.
Chapter 5 Flashing Neon FrameLayout
 5.1 Case Overview This case mainly introduced the usages of FrameLayout; we can use FrameLayout to realize the effect, the superposition of multiple widgets. This example is combined with Timer and Handler
5.1 Case Overview This case mainly introduced the usages of FrameLayout; we can use FrameLayout to realize the effect, the superposition of multiple widgets. This example is combined with Timer and Handler
ANDROID PROGRAMS DAY 3
 ANDROID PROGRAMS DAY 3 //Android project to navigate from first page to second page using Intent Step 1: Create a new project Step 2: Enter necessary details while creating project. Step 3: Drag and drop
ANDROID PROGRAMS DAY 3 //Android project to navigate from first page to second page using Intent Step 1: Create a new project Step 2: Enter necessary details while creating project. Step 3: Drag and drop
Android HelloWorld - Example. Tushar B. Kute,
 Android HelloWorld - Example Tushar B. Kute, http://tusharkute.com Anatomy of Android Application Anatomy of Android Application Java This contains the.java source files for your project. By default, it
Android HelloWorld - Example Tushar B. Kute, http://tusharkute.com Anatomy of Android Application Anatomy of Android Application Java This contains the.java source files for your project. By default, it
User Interface Development. CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion Course Coordinator: Dr.
 User Interface Development CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Outline UI Support in Android Fragments 2 UI Support in the Android
User Interface Development CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Outline UI Support in Android Fragments 2 UI Support in the Android
KAI KOENIG ANKO THE ULTIMATE NINJA OF KOTLIN LIBRARIES?
 KAI KOENIG (@AGENTK) ANKO THE ULTIMATE NINJA OF KOTLIN LIBRARIES? AGENDA What are Kotlin and Anko? Anko-related idioms and language concepts Anko DSL The hidden parts of Anko Anko VS The Rest Final thoughts
KAI KOENIG (@AGENTK) ANKO THE ULTIMATE NINJA OF KOTLIN LIBRARIES? AGENDA What are Kotlin and Anko? Anko-related idioms and language concepts Anko DSL The hidden parts of Anko Anko VS The Rest Final thoughts
Chapter 8 Positioning with Layouts
 Introduction to Android Application Development, Android Essentials, Fifth Edition Chapter 8 Positioning with Layouts Chapter 8 Overview Create user interfaces in Android by defining resource files or
Introduction to Android Application Development, Android Essentials, Fifth Edition Chapter 8 Positioning with Layouts Chapter 8 Overview Create user interfaces in Android by defining resource files or
CS 528 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2a: Introduction to Android Programming. Emmanuel Agu
 CS 528 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2a: Introduction to Android Programming Emmanuel Agu Editting in Android Studio Recall: Editting Android Can edit apps in: Text View: edit XML directly Design
CS 528 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2a: Introduction to Android Programming Emmanuel Agu Editting in Android Studio Recall: Editting Android Can edit apps in: Text View: edit XML directly Design
Mobile Programming Lecture 2. Layouts, Widgets, Toasts, and Event Handling
 Mobile Programming Lecture 2 Layouts, Widgets, Toasts, and Event Handling Lecture 1 Review How to edit XML files in Android Studio? What holds all elements (Views) that appear to the user in an Activity?
Mobile Programming Lecture 2 Layouts, Widgets, Toasts, and Event Handling Lecture 1 Review How to edit XML files in Android Studio? What holds all elements (Views) that appear to the user in an Activity?
Fragments. Lecture 11
 Fragments Lecture 11 Situational layouts Your app can use different layouts in different situations Different device type (tablet vs. phone vs. watch) Different screen size Different orientation (portrait
Fragments Lecture 11 Situational layouts Your app can use different layouts in different situations Different device type (tablet vs. phone vs. watch) Different screen size Different orientation (portrait
GUI Widget. Lecture6
 GUI Widget Lecture6 AnalogClock/Digital Clock Button CheckBox DatePicker EditText Gallery ImageView/Button MapView ProgressBar RadioButton Spinner TextView TimePicker WebView Android Widgets Designing
GUI Widget Lecture6 AnalogClock/Digital Clock Button CheckBox DatePicker EditText Gallery ImageView/Button MapView ProgressBar RadioButton Spinner TextView TimePicker WebView Android Widgets Designing
Programming with Android: Layouts, Widgets and Events. Dipartimento di Scienze dell Informazione Università di Bologna
 Programming with Android: Layouts, Widgets and Events Luca Bedogni Marco Di Felice Dipartimento di Scienze dell Informazione Università di Bologna Outline Components of an Activity ViewGroup: definition
Programming with Android: Layouts, Widgets and Events Luca Bedogni Marco Di Felice Dipartimento di Scienze dell Informazione Università di Bologna Outline Components of an Activity ViewGroup: definition
MC Android Programming
 MC1921 - Android Programming Duration: 5 days Course Price: $3,395 Course Description Android is an open source platform for mobile computing. Applications are developed using familiar Java and Eclipse
MC1921 - Android Programming Duration: 5 days Course Price: $3,395 Course Description Android is an open source platform for mobile computing. Applications are developed using familiar Java and Eclipse
Applied Cognitive Computing Fall 2016 Android Application + IBM Bluemix (Cloudant NoSQL DB)
 Applied Cognitive Computing Fall 2016 Android Application + IBM Bluemix (Cloudant NoSQL DB) In this exercise, we will create a simple Android application that uses IBM Bluemix Cloudant NoSQL DB. The application
Applied Cognitive Computing Fall 2016 Android Application + IBM Bluemix (Cloudant NoSQL DB) In this exercise, we will create a simple Android application that uses IBM Bluemix Cloudant NoSQL DB. The application
South Africa
 South Africa 2013 Lecture 6: Layouts, Menus, Views http://aiti.mit.edu Create an Android Virtual Device Click the AVD Icon: Window -> AVD Manager -> New Name & start the virtual device (this may take a
South Africa 2013 Lecture 6: Layouts, Menus, Views http://aiti.mit.edu Create an Android Virtual Device Click the AVD Icon: Window -> AVD Manager -> New Name & start the virtual device (this may take a
05. RecyclerView and Styles
 05. RecyclerView and Styles 08.03.2018 1 Agenda Intents Creating Lists with RecyclerView Creating Cards with CardView Application Bar Menu Styles and Themes 2 Intents 3 What is Intent? An Intent is an
05. RecyclerView and Styles 08.03.2018 1 Agenda Intents Creating Lists with RecyclerView Creating Cards with CardView Application Bar Menu Styles and Themes 2 Intents 3 What is Intent? An Intent is an
Programming with Android: Introduction. Layouts. Luca Bedogni. Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Università di Bologna
 Programming with Android: Introduction Layouts Luca Bedogni Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Uniersità di Bologna Views: outline Main difference between a Drawable and a View is reaction
Programming with Android: Introduction Layouts Luca Bedogni Dipartimento di Informatica: Scienza e Ingegneria Uniersità di Bologna Views: outline Main difference between a Drawable and a View is reaction
CS 528 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2a: Android UI Design in XML + Examples. Emmanuel Agu
 CS 528 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2a: Android UI Design in XML + Examples Emmanuel Agu Android UI Design in XML Recall: Files Hello World Android Project XML file used to design Android UI
CS 528 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2a: Android UI Design in XML + Examples Emmanuel Agu Android UI Design in XML Recall: Files Hello World Android Project XML file used to design Android UI
Mobile Application Development Lab [] Simple Android Application for Native Calculator. To develop a Simple Android Application for Native Calculator.
![Mobile Application Development Lab [] Simple Android Application for Native Calculator. To develop a Simple Android Application for Native Calculator. Mobile Application Development Lab [] Simple Android Application for Native Calculator. To develop a Simple Android Application for Native Calculator.](/thumbs/96/129287620.jpg) Simple Android Application for Native Calculator Aim: To develop a Simple Android Application for Native Calculator. Procedure: Creating a New project: Open Android Stdio and then click on File -> New
Simple Android Application for Native Calculator Aim: To develop a Simple Android Application for Native Calculator. Procedure: Creating a New project: Open Android Stdio and then click on File -> New
Android Application Development
 Android Application Development Octav Chipara What is Android A free, open source mobile platform A Linux-based, multiprocess, multithreaded OS Android is not a device or a product It s not even limited
Android Application Development Octav Chipara What is Android A free, open source mobile platform A Linux-based, multiprocess, multithreaded OS Android is not a device or a product It s not even limited
CSE 660 Lab 3 Khoi Pham Thanh Ho April 19 th, 2015
 CSE 660 Lab 3 Khoi Pham Thanh Ho April 19 th, 2015 Comment and Evaluation: This lab introduces us about Android SDK and how to write a program for Android platform. The calculator is pretty easy, everything
CSE 660 Lab 3 Khoi Pham Thanh Ho April 19 th, 2015 Comment and Evaluation: This lab introduces us about Android SDK and how to write a program for Android platform. The calculator is pretty easy, everything
Android Programming (5 Days)
 www.peaklearningllc.com Android Programming (5 Days) Course Description Android is an open source platform for mobile computing. Applications are developed using familiar Java and Eclipse tools. This Android
www.peaklearningllc.com Android Programming (5 Days) Course Description Android is an open source platform for mobile computing. Applications are developed using familiar Java and Eclipse tools. This Android
Dynamically Create Admob Banner and Interstitial Ads
 Dynamically Create Admob Banner and Interstitial Ads activity_main.xml file 0 0 0
Dynamically Create Admob Banner and Interstitial Ads activity_main.xml file 0 0 0
Android UI Development
 Android UI Development Android UI Studio Widget Layout Android UI 1 Building Applications A typical application will include: Activities - MainActivity as your entry point - Possibly other activities (corresponding
Android UI Development Android UI Studio Widget Layout Android UI 1 Building Applications A typical application will include: Activities - MainActivity as your entry point - Possibly other activities (corresponding
Computer Science E-76 Building Mobile Applications
 Computer Science E-76 Building Mobile Applications Lecture 3: [Android] The SDK, Activities, and Views February 13, 2012 Dan Armendariz danallan@mit.edu 1 http://developer.android.com Android SDK and NDK
Computer Science E-76 Building Mobile Applications Lecture 3: [Android] The SDK, Activities, and Views February 13, 2012 Dan Armendariz danallan@mit.edu 1 http://developer.android.com Android SDK and NDK
TextView Control. EditText Control. TextView Attributes. android:id - This is the ID which uniquely identifies the control.
 A TextView displays text to the user. TextView Attributes TextView Control android:id - This is the ID which uniquely identifies the control. android:capitalize - If set, specifies that this TextView has
A TextView displays text to the user. TextView Attributes TextView Control android:id - This is the ID which uniquely identifies the control. android:capitalize - If set, specifies that this TextView has
CS 4518 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2: Introduction to Android Programming. Emmanuel Agu
 CS 4518 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2: Introduction to Android Programming Emmanuel Agu Android Apps: Big Picture UI Design using XML UI design code (XML) separate from the program (Java) Why?
CS 4518 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2: Introduction to Android Programming Emmanuel Agu Android Apps: Big Picture UI Design using XML UI design code (XML) separate from the program (Java) Why?
Android Layout Types
 Android Layout Types Android Linear Layout Android LinearLayout is a view group that aligns all children in either vertically or horizontally. android:divider - This is drawable to use as a vertical divider
Android Layout Types Android Linear Layout Android LinearLayout is a view group that aligns all children in either vertically or horizontally. android:divider - This is drawable to use as a vertical divider
Embedded Systems Programming - PA8001
 Embedded Systems Programming - PA8001 http://goo.gl/ydeczu Lecture 9 Mohammad Mousavi m.r.mousavi@hh.se Center for Research on Embedded Systems School of Information Science, Computer and Electrical Engineering
Embedded Systems Programming - PA8001 http://goo.gl/ydeczu Lecture 9 Mohammad Mousavi m.r.mousavi@hh.se Center for Research on Embedded Systems School of Information Science, Computer and Electrical Engineering
DSL. ~ dsl_slides * about::contacts(me)
 DSL ~ dsl_slides * about::contacts(me) Aliaksandr Salnikau (Александр Сальников) Company: EPAM Position: Lead Software Engineer Primary skill: Android Contacts: email: aliaksandr_salnikau@epam.com skype:
DSL ~ dsl_slides * about::contacts(me) Aliaksandr Salnikau (Александр Сальников) Company: EPAM Position: Lead Software Engineer Primary skill: Android Contacts: email: aliaksandr_salnikau@epam.com skype:
Let s take a display of HTC Desire smartphone as an example. Screen size = 3.7 inches, resolution = 800x480 pixels.
 Screens To begin with, here is some theory about screens. A screen has such physical properties as size and resolution. Screen size - a distance between two opposite corners of the screens, usually measured
Screens To begin with, here is some theory about screens. A screen has such physical properties as size and resolution. Screen size - a distance between two opposite corners of the screens, usually measured
ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE AND TABLET DEVICE (LEVEL I)
 ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE AND TABLET DEVICE (LEVEL I) Lecture 3: Android Life Cycle and Permission Android Lifecycle An activity begins its lifecycle when entering the oncreate() state If not
ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE AND TABLET DEVICE (LEVEL I) Lecture 3: Android Life Cycle and Permission Android Lifecycle An activity begins its lifecycle when entering the oncreate() state If not
Screen Slides. The Android Studio wizard adds a TextView to the fragment1.xml layout file and the necessary code to Fragment1.java.
 Screen Slides References https://developer.android.com/training/animation/screen-slide.html https://developer.android.com/guide/components/fragments.html Overview A fragment can be defined by a class and
Screen Slides References https://developer.android.com/training/animation/screen-slide.html https://developer.android.com/guide/components/fragments.html Overview A fragment can be defined by a class and
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing: Android Programming (part 3)
 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing: Android Programming (part 3) Master studies, Winter 2015/2016 Dr Veljko Pejović Veljko.Pejovic@fri.uni-lj.si Based on Programming Handheld Systems, Adam Porter, University
Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing: Android Programming (part 3) Master studies, Winter 2015/2016 Dr Veljko Pejović Veljko.Pejovic@fri.uni-lj.si Based on Programming Handheld Systems, Adam Porter, University
Android Application Model I
 Android Application Model I CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath Reading: Big Nerd Ranch Guide, Chapters 3, 5 (Activities);
Android Application Model I CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath Reading: Big Nerd Ranch Guide, Chapters 3, 5 (Activities);
Android Application Model I. CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr.
 Android Application Model I CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Framework Support (e.g. Android) 2 Framework Capabilities
Android Application Model I CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Instructor: Adam C. Champion, Ph.D. Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath 1 Framework Support (e.g. Android) 2 Framework Capabilities
Upon completion of the second part of the lab the students will have:
 ETSN05, Fall 2017, Version 2.0 Software Development of Large Systems Lab 2 1. INTRODUCTION The goal of lab 2 is to introduce students to the basics of Android development and help them to create a starting
ETSN05, Fall 2017, Version 2.0 Software Development of Large Systems Lab 2 1. INTRODUCTION The goal of lab 2 is to introduce students to the basics of Android development and help them to create a starting
Produced by. Mobile Application Development. Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science. Eamonn de Leastar
 Mobile Application Development Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology
Mobile Application Development Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology
ELET4133: Embedded Systems. Topic 15 Sensors
 ELET4133: Embedded Systems Topic 15 Sensors Agenda What is a sensor? Different types of sensors Detecting sensors Example application of the accelerometer 2 What is a sensor? Piece of hardware that collects
ELET4133: Embedded Systems Topic 15 Sensors Agenda What is a sensor? Different types of sensors Detecting sensors Example application of the accelerometer 2 What is a sensor? Piece of hardware that collects
EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces. More About Layouts. Scott MacKenzie. York University. Overview (Review)
 EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces More About Layouts Scott MacKenzie York University Overview (Review) A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget
EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces More About Layouts Scott MacKenzie York University Overview (Review) A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget
Mobila applikationer och trådlösa nät, HI1033, HT2013
 Mobila applikationer och trådlösa nät, HI1033, HT2013 Today: - User Interface basics - View components - Event driven applications and callbacks - Menu and Context Menu - ListView and Adapters - Android
Mobila applikationer och trådlösa nät, HI1033, HT2013 Today: - User Interface basics - View components - Event driven applications and callbacks - Menu and Context Menu - ListView and Adapters - Android
M.A.D ASSIGNMENT # 2 REHAN ASGHAR BSSE 15126
 M.A.D ASSIGNMENT # 2 REHAN ASGHAR BSSE 15126 Submitted to: Sir Waqas Asghar MAY 23, 2017 SUBMITTED BY: REHAN ASGHAR Intent in Android What are Intent? An Intent is a messaging object you can use to request
M.A.D ASSIGNMENT # 2 REHAN ASGHAR BSSE 15126 Submitted to: Sir Waqas Asghar MAY 23, 2017 SUBMITTED BY: REHAN ASGHAR Intent in Android What are Intent? An Intent is a messaging object you can use to request
CS378 -Mobile Computing. User Interface Basics
 CS378 -Mobile Computing User Interface Basics User Interface Elements View Control ViewGroup Layout Widget (Compound Control) Many pre built Views Button, CheckBox, RadioButton TextView, EditText, ListView
CS378 -Mobile Computing User Interface Basics User Interface Elements View Control ViewGroup Layout Widget (Compound Control) Many pre built Views Button, CheckBox, RadioButton TextView, EditText, ListView
Android CardView Tutorial
 Android CardView Tutorial by Kapil - Wednesday, April 13, 2016 http://www.androidtutorialpoint.com/material-design/android-cardview-tutorial/ YouTube Video We have already discussed about RecyclerView
Android CardView Tutorial by Kapil - Wednesday, April 13, 2016 http://www.androidtutorialpoint.com/material-design/android-cardview-tutorial/ YouTube Video We have already discussed about RecyclerView
Android UI: Overview
 1 Android UI: Overview An Activity is the front end component and it can contain screens. Android screens are composed of components or screen containers and components within the containers Screen containers
1 Android UI: Overview An Activity is the front end component and it can contain screens. Android screens are composed of components or screen containers and components within the containers Screen containers
Beginning Android 4 Application Development
 Beginning Android 4 Application Development Lee, Wei-Meng ISBN-13: 9781118199541 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION xxi CHAPTER 1: GETTING STARTED WITH ANDROID PROGRAMMING 1 What Is Android? 2 Android Versions
Beginning Android 4 Application Development Lee, Wei-Meng ISBN-13: 9781118199541 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION xxi CHAPTER 1: GETTING STARTED WITH ANDROID PROGRAMMING 1 What Is Android? 2 Android Versions
Mobile Application Development Android
 Mobile Application Development Android Lecture 2 MTAT.03.262 Satish Srirama satish.srirama@ut.ee Android Lecture 1 -recap What is Android How to develop Android applications Run & debug the applications
Mobile Application Development Android Lecture 2 MTAT.03.262 Satish Srirama satish.srirama@ut.ee Android Lecture 1 -recap What is Android How to develop Android applications Run & debug the applications
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING UI Specification: Approaches
 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 UI Specification: Approaches UIS: APPROACHES Programmatic approach: UI elements are created inside the application code Declarative approach: UI elements are listed
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 UI Specification: Approaches UIS: APPROACHES Programmatic approach: UI elements are created inside the application code Declarative approach: UI elements are listed
Adaptation of materials: dr Tomasz Xięski. Based on presentations made available by Victor Matos, Cleveland State University.
 Creating dialogs Adaptation of materials: dr Tomasz Xięski. Based on presentations made available by Victor Matos, Cleveland State University. Portions of this page are reproduced from work created and
Creating dialogs Adaptation of materials: dr Tomasz Xięski. Based on presentations made available by Victor Matos, Cleveland State University. Portions of this page are reproduced from work created and
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING Application Tip: Saving State
 EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 Application Tip: Saving State THE PROBLEM How to save the state (of a UI, for instance) so that it survives even when the application is closed/killed The state should
EMBEDDED SYSTEMS PROGRAMMING 2016-17 Application Tip: Saving State THE PROBLEM How to save the state (of a UI, for instance) so that it survives even when the application is closed/killed The state should
CS 528 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2: Intro to Android Programming Emmanuel Agu
 CS 528 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2: Intro to Android Programming Emmanuel Agu Students: Please Introduce Yourselves! Name Status: grad/undergrad, year Relevant background: e.g. coal miner
CS 528 Mobile and Ubiquitous Computing Lecture 2: Intro to Android Programming Emmanuel Agu Students: Please Introduce Yourselves! Name Status: grad/undergrad, year Relevant background: e.g. coal miner
Introductory Android Development
 Introductory Android Development 152-163 Notes Quick Links & Text References Introduction Pages Layout Concepts Pages Layout Types Pages 35 37 XML Overview Pages Common Attributes Layout Height & Width
Introductory Android Development 152-163 Notes Quick Links & Text References Introduction Pages Layout Concepts Pages Layout Types Pages 35 37 XML Overview Pages Common Attributes Layout Height & Width
Android Application Development. By : Shibaji Debnath
 Android Application Development By : Shibaji Debnath About Me I have over 10 years experience in IT Industry. I have started my career as Java Software Developer. I worked in various multinational company.
Android Application Development By : Shibaji Debnath About Me I have over 10 years experience in IT Industry. I have started my career as Java Software Developer. I worked in various multinational company.
android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_margintop="30dp"> <Button android:text="button2"
 Parametrų keitimas veikiančioje aplikacijoje Let s create a project: Project name: P0181_DynamicLayout3 Build Target: Android 2.3.3 Application name: DynamicLayout3 Package name: ru.startandroid.develop.dynamiclayout3
Parametrų keitimas veikiančioje aplikacijoje Let s create a project: Project name: P0181_DynamicLayout3 Build Target: Android 2.3.3 Application name: DynamicLayout3 Package name: ru.startandroid.develop.dynamiclayout3
Android Programs Day 5
 Android Programs Day 5 //Android Program to demonstrate the working of Options Menu. 1. Create a New Project. 2. Write the necessary codes in the MainActivity.java to create OptionMenu. 3. Add the oncreateoptionsmenu()
Android Programs Day 5 //Android Program to demonstrate the working of Options Menu. 1. Create a New Project. 2. Write the necessary codes in the MainActivity.java to create OptionMenu. 3. Add the oncreateoptionsmenu()
External Services. CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath Instructor: Adam C. Champion
 External Services CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath Instructor: Adam C. Champion 1 External Services Viewing websites Location- and map-based functionality
External Services CSE 5236: Mobile Application Development Course Coordinator: Dr. Rajiv Ramnath Instructor: Adam C. Champion 1 External Services Viewing websites Location- and map-based functionality
EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces. More About Layouts. Scott MacKenzie. York University
 EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces More About Layouts Scott MacKenzie York University Overview (Review) A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget
EECS 4443 Mobile User Interfaces More About Layouts Scott MacKenzie York University Overview (Review) A layout defines the visual structure for a user interface, such as the UI for an activity or app widget
Graphical User Interfaces
 Graphical User Interfaces Some suggestions Avoid displaying too many things Well-known anti-patterns Display useful content on your start screen Use action bars to provide consistent navigation Keep your
Graphical User Interfaces Some suggestions Avoid displaying too many things Well-known anti-patterns Display useful content on your start screen Use action bars to provide consistent navigation Keep your
ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE AND TABLET DEVICE (LEVEL I)
 ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE AND TABLET DEVICE (LEVEL I) Lecture 3: Android Life Cycle and Permission Entire Lifetime An activity begins its lifecycle when entering the oncreate() state If not interrupted
ANDROID APPS DEVELOPMENT FOR MOBILE AND TABLET DEVICE (LEVEL I) Lecture 3: Android Life Cycle and Permission Entire Lifetime An activity begins its lifecycle when entering the oncreate() state If not interrupted
android-espresso #androidespresso
 android-espresso #androidespresso Table of Contents About 1 Chapter 1: Getting started with android-espresso 2 Remarks 2 Examples 2 Espresso setup instructions 2 Checking an Options Menu items (using Spoon
android-espresso #androidespresso Table of Contents About 1 Chapter 1: Getting started with android-espresso 2 Remarks 2 Examples 2 Espresso setup instructions 2 Checking an Options Menu items (using Spoon
Mobile Computing Practice # 2c Android Applications - Interface
 Mobile Computing Practice # 2c Android Applications - Interface One more step in the restaurants application. 1. Design an alternative layout for showing up in landscape mode. Our current layout is not
Mobile Computing Practice # 2c Android Applications - Interface One more step in the restaurants application. 1. Design an alternative layout for showing up in landscape mode. Our current layout is not
PENGEMBANGAN APLIKASI PERANGKAT BERGERAK (MOBILE)
 PENGEMBANGAN APLIKASI PERANGKAT BERGERAK (MOBILE) Network Connection Web Service K Candra Brata andra.course@gmail.com Mobille App Lab 2015-2016 Network Connection http://developer.android.com/training/basics/network-ops/connecting.html
PENGEMBANGAN APLIKASI PERANGKAT BERGERAK (MOBILE) Network Connection Web Service K Candra Brata andra.course@gmail.com Mobille App Lab 2015-2016 Network Connection http://developer.android.com/training/basics/network-ops/connecting.html
Java & Android. Java Fundamentals. Madis Pink 2016 Tartu
 Java & Android Java Fundamentals Madis Pink 2016 Tartu 1 Agenda» Brief background intro to Android» Android app basics:» Activities & Intents» Resources» GUI» Tools 2 Android» A Linux-based Operating System»
Java & Android Java Fundamentals Madis Pink 2016 Tartu 1 Agenda» Brief background intro to Android» Android app basics:» Activities & Intents» Resources» GUI» Tools 2 Android» A Linux-based Operating System»
TextView. A label is called a TextView. TextViews are typically used to display a caption TextViews are not editable, therefore they take no input
 1 UI Components 2 UI Components 3 A label is called a TextView. TextView TextViews are typically used to display a caption TextViews are not editable, therefore they take no input - - - - - - -
1 UI Components 2 UI Components 3 A label is called a TextView. TextView TextViews are typically used to display a caption TextViews are not editable, therefore they take no input - - - - - - -
When programming in groups of people, it s essential to version the code. One of the most popular versioning tools is git. Some benefits of git are:
 ETSN05, Fall 2017, Version 1.0 Software Development of Large Systems Lab 2 preparations Read through this document carefully. In order to pass lab 2, you will need to understand the topics presented in
ETSN05, Fall 2017, Version 1.0 Software Development of Large Systems Lab 2 preparations Read through this document carefully. In order to pass lab 2, you will need to understand the topics presented in
Fragment Example Create the following files and test the application on emulator or device.
 Fragment Example Create the following files and test the application on emulator or device. File: AndroidManifest.xml
Fragment Example Create the following files and test the application on emulator or device. File: AndroidManifest.xml
Mobile Software Development for Android - I397
 1 Mobile Software Development for Android - I397 IT COLLEGE, ANDRES KÄVER, 2015-2016 EMAIL: AKAVER@ITCOLLEGE.EE WEB: HTTP://ENOS.ITCOLLEGE.EE/~AKAVER/2015-2016/DISTANCE/ANDROID SKYPE: AKAVER Timetable
1 Mobile Software Development for Android - I397 IT COLLEGE, ANDRES KÄVER, 2015-2016 EMAIL: AKAVER@ITCOLLEGE.EE WEB: HTTP://ENOS.ITCOLLEGE.EE/~AKAVER/2015-2016/DISTANCE/ANDROID SKYPE: AKAVER Timetable
Produced by. Mobile Application Development. Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science. Eamonn de Leastar
 Mobile Application Development Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology
Mobile Application Development Higher Diploma in Science in Computer Science Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology
Vienos veiklos būsena. Theory
 Vienos veiklos būsena Theory While application is running, we create new Activities and close old ones, hide the application and open it again and so on, and Activity can process all these events. It is
Vienos veiklos būsena Theory While application is running, we create new Activities and close old ones, hide the application and open it again and so on, and Activity can process all these events. It is
Agenda. Overview of Xamarin and Xamarin.Android Xamarin.Android fundamentals Creating a detail screen
 Gill Cleeren Agenda Overview of Xamarin and Xamarin.Android Xamarin.Android fundamentals Creating a detail screen Lists and navigation Navigating from master to detail Optimizing the application Preparing
Gill Cleeren Agenda Overview of Xamarin and Xamarin.Android Xamarin.Android fundamentals Creating a detail screen Lists and navigation Navigating from master to detail Optimizing the application Preparing
Adapter.
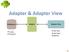 1 Adapter An Adapter object acts as a bridge between an AdapterView and the underlying data for that view The Adapter provides access to the data items The Adapter is also responsible for making a View
1 Adapter An Adapter object acts as a bridge between an AdapterView and the underlying data for that view The Adapter provides access to the data items The Adapter is also responsible for making a View
Lecture 14. Android Application Development
 Lecture 14 Android Application Development Notification Instructor Muhammad Owais muhammad.owais@riphah.edu.pk Cell: 03215500223 Notifications Used to notify user for events Three general forms of Notifications
Lecture 14 Android Application Development Notification Instructor Muhammad Owais muhammad.owais@riphah.edu.pk Cell: 03215500223 Notifications Used to notify user for events Three general forms of Notifications
Create new Android project in Android Studio Add Button and TextView to layout Learn how to use buttons to call methods. Modify strings.
 Hello World Lab Objectives: Create new Android project in Android Studio Add Button and TextView to layout Learn how to use buttons to call methods. Modify strings.xml What to Turn in: The lab evaluation
Hello World Lab Objectives: Create new Android project in Android Studio Add Button and TextView to layout Learn how to use buttons to call methods. Modify strings.xml What to Turn in: The lab evaluation
Topics of Discussion
 Reference CPET 565 Mobile Computing Systems CPET/ITC 499 Mobile Computing Fragments, ActionBar and Menus Part 3 of 5 Android Programming Concepts, by Trish Cornez and Richard Cornez, pubslihed by Jones
Reference CPET 565 Mobile Computing Systems CPET/ITC 499 Mobile Computing Fragments, ActionBar and Menus Part 3 of 5 Android Programming Concepts, by Trish Cornez and Richard Cornez, pubslihed by Jones
 Statistics http://www.statista.com/topics/840/smartphones/ http://www.statista.com/topics/876/android/ http://www.statista.com/statistics/271774/share-of-android-platforms-on-mobile-devices-with-android-os/
Statistics http://www.statista.com/topics/840/smartphones/ http://www.statista.com/topics/876/android/ http://www.statista.com/statistics/271774/share-of-android-platforms-on-mobile-devices-with-android-os/
Starting Another Activity Preferences
 Starting Another Activity Preferences Android Application Development Training Xorsat Pvt. Ltd www.xorsat.net fb.com/xorsat.education Outline Starting Another Activity Respond to the Button Create the
Starting Another Activity Preferences Android Application Development Training Xorsat Pvt. Ltd www.xorsat.net fb.com/xorsat.education Outline Starting Another Activity Respond to the Button Create the
TPCT s College of Engineering, Osmanabad. Laboratory Manual SDL-II. Mobile Application Development (Android) For. Third Year Students (CSE)
 TPCT s College of Engineering, Osmanabad Laboratory Manual SDL-II Mobile Application Development (Android) For Third Year Students (CSE) Manual Prepared by Prof. Sujata A. Gaikwad Author COE, Osmanabad
TPCT s College of Engineering, Osmanabad Laboratory Manual SDL-II Mobile Application Development (Android) For Third Year Students (CSE) Manual Prepared by Prof. Sujata A. Gaikwad Author COE, Osmanabad
Basic GUI elements - exercises
 Basic GUI elements - exercises https://developer.android.com/studio/index.html LIVE DEMO Please create a simple application, which will be used to calculate the area of basic geometric figures. To add
Basic GUI elements - exercises https://developer.android.com/studio/index.html LIVE DEMO Please create a simple application, which will be used to calculate the area of basic geometric figures. To add
Android DP SDK Integration Guide
 Android DP SDK Integration Guide Requirements Minimum Android Version : Android 4.1 'Jelly Bean' (API level 16) instant Run Removal. (Preferences -> Instant Run -> Unlock to Enable Instant Run) Step 1.
Android DP SDK Integration Guide Requirements Minimum Android Version : Android 4.1 'Jelly Bean' (API level 16) instant Run Removal. (Preferences -> Instant Run -> Unlock to Enable Instant Run) Step 1.
ListView Containers. Resources. Creating a ListView
 ListView Containers Resources https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/layout/listview.html https://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/listview.html Creating a ListView A ListView is a
ListView Containers Resources https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/layout/listview.html https://developer.android.com/reference/android/widget/listview.html Creating a ListView A ListView is a
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.internet"/>
 Chapter 11 Playing Video 11.1 Introduction We have discussed how to play audio in Chapter 9 using the class MediaPlayer. This class can also play video clips. In fact, the Android multimedia framework
Chapter 11 Playing Video 11.1 Introduction We have discussed how to play audio in Chapter 9 using the class MediaPlayer. This class can also play video clips. In fact, the Android multimedia framework
Creating a Custom ListView
 Creating a Custom ListView References https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html#adapterviews Overview The ListView in the previous tutorial creates a TextView object for each
Creating a Custom ListView References https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/ui/declaring-layout.html#adapterviews Overview The ListView in the previous tutorial creates a TextView object for each
Mobile Computing Fragments
 Fragments APM@FEUP 1 Fragments (1) Activities are used to define a full screen interface and its functionality That s right for small screen devices (smartphones) In bigger devices we can have more interface
Fragments APM@FEUP 1 Fragments (1) Activities are used to define a full screen interface and its functionality That s right for small screen devices (smartphones) In bigger devices we can have more interface
Open Lecture Mobile Programming. Intro to Material Design
 Open Lecture Mobile Programming Intro to Material Design Agenda Introduction to Material Design Applying a Material Theme Toolbar/Action Bar Navigation Drawer RecyclerView CardView Support Design Widgets/Tools
Open Lecture Mobile Programming Intro to Material Design Agenda Introduction to Material Design Applying a Material Theme Toolbar/Action Bar Navigation Drawer RecyclerView CardView Support Design Widgets/Tools
Tablets have larger displays than phones do They can support multiple UI panes / user behaviors at the same time
 Tablets have larger displays than phones do They can support multiple UI panes / user behaviors at the same time The 1 activity 1 thing the user can do heuristic may not make sense for larger devices Application
Tablets have larger displays than phones do They can support multiple UI panes / user behaviors at the same time The 1 activity 1 thing the user can do heuristic may not make sense for larger devices Application
Getting Started. Dr. Miguel A. Labrador Department of Computer Science & Engineering
 Getting Started Dr. Miguel A. Labrador Department of Computer Science & Engineering labrador@csee.usf.edu http://www.csee.usf.edu/~labrador 1 Goals Setting up your development environment Android Framework
Getting Started Dr. Miguel A. Labrador Department of Computer Science & Engineering labrador@csee.usf.edu http://www.csee.usf.edu/~labrador 1 Goals Setting up your development environment Android Framework
