What is Java Script? Writing to The HTML Document. What Can JavaScript do? CMPT 165: Java Script
|
|
|
- Jeffery French
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 What is Java Script? CMPT 165: Java Script Tamara Smyth, School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University November 7, 2011 JavaScript was designed to add interactivity to HTML pages JavaScript is a scripting language (a lightweight programming language). It is interpreted and thus does not required preliminary compilation. JavaScript may be embedded directly into HTML pages or in an external file 1 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 2 What Can JavaScript do? Writing to The HTML Document JavaScript provides a tool to program for the web. It s simple syntax makes it suitable for people that are not necessarily programmers. You can use JavaScript to handle events: when something happens (an event), do something else (handle it). Example events can be: a page has finished loading or a user clicks on an HTML element (or form control) JavaScript can: read and write HTML elements change the content of an existing HTML element validate data before it is submitted to a server, saving the server from extra processing. detect the visitor s browser and load another page specifically designed for that browser store and retrieve information on the visitor s computer (create cookies) CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 3 To insert a JavaScript into an HTML page, and have it executed by the browser, write it inside the <script>... tags. Use the type attribute to define the scripting language. This example writes a <p> element with current date information to the HTML document: <h1>my First Web Page</h1> document.write("<p>" + Date() + "</p>"); In general, avoid using document.write() since it will overwrite the entire HTML page. CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 4
2 Changing HTML Element Content Document Object Model The example below writes the current date into an existing <p> element: <h1>my First Web Page</h1> <p id="demo"></p> To manipulate HTML elements JavaScript uses the DOM method getelementbyid(). This method accesses the element with the specified id. The DOM (Document Object Model) allows you to dynamically access and update the content, structure and style of HTML documents. This is done by accessing HTML objects or elements, as well as their styles and attributes. document.getelementbyid("demo").innerhtml=date() If the original HTML paragraph had been <p id="demo">this is a paragraph.</p> the browser would have repaced This is a paragraph with the current date. CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 5 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 6 Where to put JavaScript in the HTML document? JavaScript can be put in the and in the sections of an HTML page. In the above example, the JavaScript was placed in the body and at the bottom of the page to make sure it was not executed before the <p> element is created. JavaScripts in an HTML page will be executed when the page loads. This is not always what we want. Sometimes we want to execute a JavaScript when an event occurs, such as when a user clicks a button. In this case, we can put the script inside a function. Events are normally used in combination with functions: call a function when an event occurs. CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 7 JavaScript in the... This example calls a function when a button is clicked: function displaydate() document.getelementbyid("demo").innerhtml=date(); <h1>my First Web Page</h1> <p id="demo"></p> <button type="button" onclick="displaydate()">display Date</button> It is a common practice to put all functions in the head section, or at the bottom of the page. This way they are all in one place and do not interfere with page content. You can place an unlimited number of scripts in your document, and you can have scripts in both the body and the head section at the same time. CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 8
3 Using an External JavaScript JavaScript Statements JavaScript can also be placed in external files, allowing code to be used on several different web pages. External JavaScript files have the file extension.js. To use an external script, assign the type and src attributes of the <script> tag as follows: <script type="text/javascript" src="xxx.js"> Place the script exactly where you normally would write the script. CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 9 JavaScript is a sequence of statements to be executed by the browser. A JavaScript statement is a command to a browser. The purpose of the command is to tell the browser what to do. Unlike HTML, JavaScript is case sensitive: watch your use of upper and lower case letters when you write JavaScript statements or create/call variables, objects and functions. This JavaScript statement tells the browser to write Hello Dolly to the web page: document.write("hello Dolly"); It is normal (though optional) to add a semicolon at the end of each executable statement. Though it is optional to add a semicolon at the end of a statement (since the browser interprets the end of the line as the end of the statement), using semicolons makes it possible to write multiple statements on one line. CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 10 JavaScript Code JavaScript Blocks JavaScript code (or just JavaScript) is a sequence of JavaScript statements. Each statement is executed by the browser in the sequence they are written. This example will write a heading and two paragraphs to a web page: document.write("<h1>this is a heading</h1>"); document.write("<p>this is a paragraph.</p>"); document.write("<p>this is another paragraph.</p>"); JavaScript statements can be grouped together in blocks. Blocks start with a left curly bracket, and end with a right curly bracket. The purpose of a block is to make the sequence of statements execute together. The above example could have been written as a block of code. document.write("<h1>this is a heading</h1>"); document.write("<p>this is a paragraph.</p>"); document.write("<p>this is another paragraph.</p>"); Though this example is not very useful, it demonstrates the use of a block. Normally a block is used to group statements together in a function or in a condition (where a group of statements should be executed if a condition is met). CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 11 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 12
4 JavaScript Comments JavaScript Variables Comments can be added to explain JavaScript code, or to make the code more readable. Single line comments start with //. Example: // Write a heading document.write("<h1>this is a heading</h1>"); // Write two paragraphs: document.write("<p>this is a paragraph.</p>"); document.write("<p>this is another paragraph.</p>"); They may also be used at the end of a line: document.write("hello"); // Write "Hello" Multi-line comments start with /* and end with */. Example: /* The code below will write one heading and two paragraphs */ document.write("<h1>this is a heading</h1>"); document.write("<p>this is a paragraph.</p>"); document.write("<p>this is another paragraph.</p>"); Consider the algebraic expression: z = x + y. The value z will depend on x and y, that is, all are variables, and the result of the expression z will depend on the values held by x and y. Variables can be used to hold values (e.g. x=5) or expressions (e.g. z=x+y). As with algebra, you can do arithmetic operations with JavaScript variables: y=x-5; z=y+5; A variable name can be short, like x, or a more descriptive, like favoritecolor. Rules for JavaScript variable names: as with anything in JavaScript, variable names are case sensitive (y and Y are two different variables) variable names must begin with a letter or the underscore character CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 13 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 14 can t be a reserved word (a word with another meaning in JS syntax) You can refer to a variable by its name to display or change its value during the execution of a script. Declaring (Creating) JavaScript Variables Creating variables in JavaScript is referred to as declaring variables (akin to declarations in CSS). You declare JavaScript variables with the keyword var var x; var favoritecolor; After the declaration shown above, the variables are empty (they hold no values). It is possible to assign values to the variables when they are declared: var x=5; var favoritecolor="blue"; When you assign a text value to a variable (a string), use quotes around the value. If you redeclare a JavaScript variable, it will not lose its value. CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 15 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 16
5 Local and Global JavaScript Variables Assigning Values to Undeclared JavaScript Variables A variable declared within a JavaScript function can only be accessed within that function. That is, it is local in scope. You can have local variables with the same name in different functions, because their scope is limited to the function in which they are declared. Variables declared outside a function become global and can be accessed anywhere on the web page (including functions). Global variables are destroyed when you close the page. If you declare a variable without using var, the variable always becomes global. If you assign values to variables that have not yet been declared, the variables will automatically be declared as global variables. These statements: x=5; favoritecolor="blue"; will declare the variables x and favoritecolor as global variables (if they don t already exist). CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 17 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 18 JavaScript Operators JavaScript Arithmetic Operators The assignment operator = is used to assign values to JavaScript variables. The arithmetic operator + is used to add values together. For example: y=5; z=2; x=y+z; The value of x, after the execution of the statements above, is 7. Arithmetic operators are used to perform arithmetic between variables and/or values. Given that y=5, the table below explains the arithmetic operators: Operator Description Example + Addition x=y+2 x=7 y=5 - Subtraction x=y-2 x=3 y=5 * Multiplication x=y*2 x=10 y=5 / Division x=y/2 x=2.5 y=5 % Modulus x=y%2 x=1 y=5 ++ Increment x=++y x=6 y=6 x=y++ x=5 y=6 Decrement x= y x=4 y=4 x=y x=5 y=4 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 19 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 20
6 JavaScript Assignment Operators The + Operator Used on Strings Assignment operators are used to assign values to JavaScript variables. Given that x=10 and y=5, the table below explains the assignment operators: Operator Example Same As Result = x=y x=5 x=5 += x+=y x=x+y x=15 -= x-=y x=x-y x=5 *= x*=y x=x*y x=50 /= x/=y x=x/y x=2 %= x%=y x=x%y x=0 The + operator can also be used to add string variables or text values together. To add two or more string variables together, use the + operator. txt1="what a very"; txt2="nice day"; txt3=txt1 + " "+ txt2; After the execution of the statements above, the variable txt3 contains What a very nice day. Notice the placement of the space between the two strings using the quotes. CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 21 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 22 Adding Strings and Numbers JavaScript Comparison and Logical Operators If you add a number and a string, the result will be a string. Example: x=5+5; //x is an integer, value is 10 x="5"+"5"; //x is a string, value is "55" x=5+"5"; //x is a string, value is "55" Comparison and Logical operators are used to test for true or false. Comparison operators are used in logical statements to determine equality or difference between variables or values. Given that x=5, the table below explains the comparison operators: Operator Description Example(s) == is equal to x==8 is false, x==5 is true === is exactly equal to (value and type) x===5 is true, x=== 5 is false!= is not equal x!=8 is true > is greater than x>8 is false < is less than x<8 is true >= is greater than or equal to x>=8 is false <= is less than or equal to x<=8 is true Comparison operators can be used in conditional statements to compare values and take action depending on the result: if (age<18) document.write("too young"); CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 23 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 24
7 Logical Operators Conditional Operator Logical operators are used to determine the logic between variables or values. Given that x=6 and y=3, the table below explains the logical operators: Operator Description Example && and (x < 10 && y > 1) is true or (x==5 y==5) is false! not!(x==y) is true JavaScript also contains a conditional operator that assigns a value to a variable based on some condition: variablename=(condition)?value1:value2 For example: greeting = (city=="sydney")?"hello from Sydney!":"Hello!"; If the variable city has the value of Sydney, then the variable greeting will be assigned the value Hello from Sydney! else it will be assigned Hello. CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 25 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 26 JavaScript Conditional Statements If Statement Conditional statements are used to perform different actions based on different conditions. In JavaScript we have the following conditional statements: if statement - use this statement to execute some code only if a specified condition is true if...else statement - use this statement to execute some code if the condition is true and another code if the condition is false switch statement - use this statement to select one of many blocks of code to be executed Use the if statement to execute some code only if a specified condition is true. The syntax is: if (condition) code to be executed if condition is true Example: //Write a "Good morning" greeting if //the time is less than 10 var d=new Date(); var time=d.gethours(); if (time<10) document.write("<b>good morning</b>"); CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 27 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 28
8 if...else statement if...else if...else statement Use the if...else statement to execute some code if a condition is true and another code if the condition is not true. The syntax is: if (condition) code to be executed if condition is true else code to be executed if condition is not true For example //If the time is less than 10, you will get a "Good morning" greeting. //Otherwise you will get a "Good day" greeting. var d = new Date(); var time = d.gethours(); if (time < 10) document.write("good morning!"); else document.write("good day!"); Use the if...else if...else statement to select one of several blocks of code to be executed. The syntax is: if (condition1) code to be executed if condition1 is true else if (condition2) code to be executed if condition2 is true else code to be executed if neither condition1 nor condition2 is true For example: var d = new Date() var time = d.gethours() if (time<10) document.write("<b>good morning</b>"); else if (time>=10 && time<16) document.write("<b>good day</b>"); else document.write("<b>hello World!</b>"); CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 29 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 30 JavaScript Switch Statement Switch Example Use the switch statement to select one of many blocks of code to be executed. The syntax is: switch(n) case 1: execute code block 1 break; case 2: execute code block 2 break; default: code to be executed if n is different from case 1 and 2 The variable (or expression) n is valuated once and its value is then compared with the values for each case in the structure. If there is a match, the block of code associated with that case is executed. The word break is used to prevent the code from running into the next case automatically. //You will receive a different greeting based //on what day it is. Note that Sunday=0, //Monday=1, Tuesday=2, etc. var d=new Date(); var theday=d.getday(); switch (theday) case 5: document.write("finally Friday"); break; case 6: document.write("super Saturday"); break; case 0: document.write("sleepy Sunday"); break; default: document.write("i m looking forward to this weekend!"); CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 31 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 32
9 Popup Boxes Alert Box Confirm Box JavaScript has three kind of popup boxes: Alert box, Confirm box, and Prompt box. An Alert Box is often used to make sure information has reached the user. When it pops up, the user will have to click OK to proceed. alert("sometext"); function show_alert() alert("i am an alert box!"); <input type="button" onclick="show_alert()" value="show alert box" /> A confirm box is used if you want the user to verify or accept something. The syntax is: confirm("sometext"); When a confirm box pops up, the user will have to click either OK or Cancel to proceed. If the user clicks OK, the box returns true. If the user clicks Cancel, the box returns false. Example: function show_confirm() var r=confirm("press a button"); if (r==true) alert("you pressed OK!"); else alert("you pressed Cancel!"); <input type="button" onclick="show_confirm()" value="show confirm box" CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 33 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 34 Prompt Box JavaScript Functions A prompt box is used if you want the user to input a value before entering a page. When a prompt box pops up, the user will have to click either OK or Cancel to proceed after entering an input value. If the user clicks OK the box returns the input value. If the user clicks Cancel the box returns null. The syntax is: prompt("sometext","defaultvalue"); Example: function show_prompt() var name=prompt("please enter your name","jane Doe"); if (name!=null && name!="") document.write("hello " + name + "!"); A function is a group of statements that are executed by a call to the function. To keep script from being executed by the browser when it loads a page, you can put it into a function. You may call a function from anywhere within a page (or even from other pages if the function is embedded in an external.js file). Functions can be defined both in the and in the section of a document. To ensure that a function is loaded by the browser before it is called, define it in the section. <input type="button" onclick="show_prompt()" value="show prompt box" /> CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 35 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 36
10 Defining a Function Function Example Use the following syntax to define a function: function functionname(var1,var2,...) some code The word function is a reserved word and used to define your function. The functionname is a word of your choosing, but should be relevant to the task your function will perform. The parameters var1, var2,... are variables or values passed into the function. The and the defines the start and end of the function, much as it did the declaration part of a CSS rule. A function with no parameters must still include (empty) parentheses after the function name. In the following script, the function displaymessage() is executed when the user clicks the input button. function displaymessage() alert("hello World!"); <form> <input type="button" value="click me!" onclick="displaymessage()"> </form> <p>by pressing the button above, a function will be called.</p> CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 37 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 38 The return Statement Java Script Loops The return statement is used to specify the value that is returned from a function. Example: function product(a,b) return a*b; Loops execute a block of code a specified number of times, or while a specified condition is true. In JavaScript, there are two kind of loops: for: loops through a block of code a specified number of times while: loops through a block of code while a specified condition is true var x = 4; var y = 3; document.write("the product of " + x + " and " + CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 39 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 40
11 The For Loop The While Loop The for loop is used when you know how many times the script should run. The syntax is: for (var=startvalue;var<=endvalue;var=var+increment) code to be executed Example: var i; for (i=0;i<=5;i++) document.write("the number is " + i); document.write("<br>"); The while loop loops through a block of code while a specified condition is true. while (variable<=endvalue) code to be executed The <= could be any comparison operator. The example below defines a loop that starts with i=0. The loop will continue to run as long as i is less than, or equal to 5. i will increase by 1 each time the loop runs: var i=0; while (i<=5) document.write("the number is " + i); document.write("<br>"); i++; CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 41 CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 42 The do...while Loop The do...while loop is a variant of the while loop. It will execute the block of code once, and then it will repeat the loop as long as the specified condition is true. do code to be executed while (variable<=endvalue); Example: var i=0; do document.write("the number is " + i); document.write("<br />"); i++; while (i<=5); CMPT 165: Introduction to the Internet and the WWW: Java Script 43
Introduction to JavaScript
 127 Lesson 14 Introduction to JavaScript Aim Objectives : To provide an introduction about JavaScript : To give an idea about, What is JavaScript? How to create a simple JavaScript? More about Java Script
127 Lesson 14 Introduction to JavaScript Aim Objectives : To provide an introduction about JavaScript : To give an idea about, What is JavaScript? How to create a simple JavaScript? More about Java Script
JavaScript Introduction
 JavaScript Introduction JavaScript is the most popular scripting language on the internet, and works in all major browsers, such as Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, and Safari. What is JavaScript?
JavaScript Introduction JavaScript is the most popular scripting language on the internet, and works in all major browsers, such as Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, and Safari. What is JavaScript?
<form>. input elements. </form>
 CS 183 4/8/2010 A form is an area that can contain form elements. Form elements are elements that allow the user to enter information (like text fields, text area fields, drop-down menus, radio buttons,
CS 183 4/8/2010 A form is an area that can contain form elements. Form elements are elements that allow the user to enter information (like text fields, text area fields, drop-down menus, radio buttons,
JavaScript s role on the Web
 Chris Panayiotou JavaScript s role on the Web JavaScript Programming Language Developed by Netscape for use in Navigator Web Browsers Purpose make web pages (documents) more dynamic and interactive Change
Chris Panayiotou JavaScript s role on the Web JavaScript Programming Language Developed by Netscape for use in Navigator Web Browsers Purpose make web pages (documents) more dynamic and interactive Change
Just add an HTML comment tag <!-- before the first JavaScript statement, and an end-of comment tag --> after the last JavaScript statement, like this:
 JavaScript Basic JavaScript How To and Where To JavaScript Statements and Comments JavaScript Variables JavaScript Operators JavaScript Comparisons JavaScript If Else JavaScript Loops JavaScript Flow Control
JavaScript Basic JavaScript How To and Where To JavaScript Statements and Comments JavaScript Variables JavaScript Operators JavaScript Comparisons JavaScript If Else JavaScript Loops JavaScript Flow Control
JavaScript Introduction
 JavaScript Introduction What is JavaScript? JavaScript was designed to add interactivity to HTML pages JavaScript is usually embedded directly into HTML pages JavaScript is an interpreted language (means
JavaScript Introduction What is JavaScript? JavaScript was designed to add interactivity to HTML pages JavaScript is usually embedded directly into HTML pages JavaScript is an interpreted language (means
The first sample. What is JavaScript?
 Java Script Introduction JavaScript is the most popular scripting language on the internet, and works in all major browsers, such as Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, and Safari. In this lecture
Java Script Introduction JavaScript is the most popular scripting language on the internet, and works in all major browsers, such as Internet Explorer, Firefox, Chrome, Opera, and Safari. In this lecture
CGS 3066: Spring 2015 JavaScript Reference
 CGS 3066: Spring 2015 JavaScript Reference Can also be used as a study guide. Only covers topics discussed in class. 1 Introduction JavaScript is a scripting language produced by Netscape for use within
CGS 3066: Spring 2015 JavaScript Reference Can also be used as a study guide. Only covers topics discussed in class. 1 Introduction JavaScript is a scripting language produced by Netscape for use within
Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University. Computer Sciences Department
 Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University 1 And use http://www.w3schools.com/ JavaScript Objectives Introduction to JavaScript Objects Data Variables Operators Types Functions Events 4 Why Study JavaScript?
Princess Nourah bint Abdulrahman University 1 And use http://www.w3schools.com/ JavaScript Objectives Introduction to JavaScript Objects Data Variables Operators Types Functions Events 4 Why Study JavaScript?
Session 16. JavaScript Part 1. Reading
 Session 16 JavaScript Part 1 1 Reading Reading Wikipedia en.wikipedia.org/wiki/javascript / p W3C www.w3.org/tr/rec-html40/interact/scripts.html Web Developers Notes www.webdevelopersnotes.com/tutorials/javascript/
Session 16 JavaScript Part 1 1 Reading Reading Wikipedia en.wikipedia.org/wiki/javascript / p W3C www.w3.org/tr/rec-html40/interact/scripts.html Web Developers Notes www.webdevelopersnotes.com/tutorials/javascript/
Session 6. JavaScript Part 1. Reading
 Session 6 JavaScript Part 1 Reading Reading Wikipedia en.wikipedia.org/wiki/javascript Web Developers Notes www.webdevelopersnotes.com/tutorials/javascript/ JavaScript Debugging www.w3schools.com/js/js_debugging.asp
Session 6 JavaScript Part 1 Reading Reading Wikipedia en.wikipedia.org/wiki/javascript Web Developers Notes www.webdevelopersnotes.com/tutorials/javascript/ JavaScript Debugging www.w3schools.com/js/js_debugging.asp
CITS1231 Web Technologies. JavaScript
 CITS1231 Web Technologies JavaScript Contents Introduction to JavaScript Variables Operators Conditional Statements Program Loops Popup Boxes Functions 2 User Interaction User interaction requires web
CITS1231 Web Technologies JavaScript Contents Introduction to JavaScript Variables Operators Conditional Statements Program Loops Popup Boxes Functions 2 User Interaction User interaction requires web
Manju Muralidharan Priya. CS4PM Web Aesthetics and Development WEEK 11
 CS4PM Web Aesthetics and Development WEEK 11 Objective: Understand basics of JScript Outline: a. Basics of JScript Reading: Refer to w3schools websites and use the TRY IT YOURSELF editor and play with
CS4PM Web Aesthetics and Development WEEK 11 Objective: Understand basics of JScript Outline: a. Basics of JScript Reading: Refer to w3schools websites and use the TRY IT YOURSELF editor and play with
CISC 1600 Lecture 2.4 Introduction to JavaScript
 CISC 1600 Lecture 2.4 Introduction to JavaScript Topics: Javascript overview The DOM Variables and objects Selection and Repetition Functions A simple animation What is JavaScript? JavaScript is not Java
CISC 1600 Lecture 2.4 Introduction to JavaScript Topics: Javascript overview The DOM Variables and objects Selection and Repetition Functions A simple animation What is JavaScript? JavaScript is not Java
Outline. Introduction to JavaScript Resources What is JavaScript? JavaScript in web pages
 JavaScript CMPT 281 Outline Introduction to JavaScript Resources What is JavaScript? JavaScript in web pages Announcements Layout with tables Assignment 3 JavaScript Resources Resources Why JavaScript?
JavaScript CMPT 281 Outline Introduction to JavaScript Resources What is JavaScript? JavaScript in web pages Announcements Layout with tables Assignment 3 JavaScript Resources Resources Why JavaScript?
CSC Web Programming. Introduction to JavaScript
 CSC 242 - Web Programming Introduction to JavaScript JavaScript JavaScript is a client-side scripting language the code is executed by the web browser JavaScript is an embedded language it relies on its
CSC 242 - Web Programming Introduction to JavaScript JavaScript JavaScript is a client-side scripting language the code is executed by the web browser JavaScript is an embedded language it relies on its
A.A. 2008/09. Why introduce JavaScript. G. Cecchetti Internet Software Technologies
 Internet t Software Technologies JavaScript part one IMCNE A.A. 2008/09 Gabriele Cecchetti Why introduce JavaScript To add dynamicity and interactivity to HTML pages 2 What s a script It s a little interpreted
Internet t Software Technologies JavaScript part one IMCNE A.A. 2008/09 Gabriele Cecchetti Why introduce JavaScript To add dynamicity and interactivity to HTML pages 2 What s a script It s a little interpreted
Javascript. UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS AMHERST CMPSCI 120 Fall 2010
 Lecture 14 Javascript Announcements Project #2 New website Exam#2 No. Class Date Subject and Handout(s) 17 11/4/10 Examination Review Practice Exam PDF 18 11/9/10 Search, Safety, Security Slides PDF UMass
Lecture 14 Javascript Announcements Project #2 New website Exam#2 No. Class Date Subject and Handout(s) 17 11/4/10 Examination Review Practice Exam PDF 18 11/9/10 Search, Safety, Security Slides PDF UMass
Web Programming/Scripting: JavaScript
 CS 312 Internet Concepts Web Programming/Scripting: JavaScript Dr. Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Old Dominion University mweigle@cs.odu.edu http://www.cs.odu.edu/~mweigle/cs312-f11/ 1 Outline!
CS 312 Internet Concepts Web Programming/Scripting: JavaScript Dr. Michele Weigle Department of Computer Science Old Dominion University mweigle@cs.odu.edu http://www.cs.odu.edu/~mweigle/cs312-f11/ 1 Outline!
Javascript. UNIVERSITY OF MASSACHUSETTS AMHERST CMPSCI 120 Fall 2010
 Lecture 15 Javascript Announcements Project #1 Graded VG, G= doing well, OK = did the minimum, OK - = some issues, do better on P#2 Homework #6 posted, due 11/5 Get JavaScript by Example Most examples
Lecture 15 Javascript Announcements Project #1 Graded VG, G= doing well, OK = did the minimum, OK - = some issues, do better on P#2 Homework #6 posted, due 11/5 Get JavaScript by Example Most examples
What is PHP? [1] Figure 1 [1]
![What is PHP? [1] Figure 1 [1] What is PHP? [1] Figure 1 [1]](/thumbs/80/82156183.jpg) PHP What is PHP? [1] PHP is an acronym for "PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor" PHP is a widely-used, open source scripting language PHP scripts are executed on the server PHP is free to download and use Figure
PHP What is PHP? [1] PHP is an acronym for "PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor" PHP is a widely-used, open source scripting language PHP scripts are executed on the server PHP is free to download and use Figure
Syllabus - July to Sept
 Class IX Sub: Computer Syllabus - July to Sept What is www: The World Wide Web (www, W3) is an information space where documents and other web resources are identified by URIs, interlinked by hypertext
Class IX Sub: Computer Syllabus - July to Sept What is www: The World Wide Web (www, W3) is an information space where documents and other web resources are identified by URIs, interlinked by hypertext
Q1. What is JavaScript?
 Q1. What is JavaScript? JavaScript was designed to add interactivity to HTML pages JavaScript is a scripting language A scripting language is a lightweight programming language JavaScript is usually embedded
Q1. What is JavaScript? JavaScript was designed to add interactivity to HTML pages JavaScript is a scripting language A scripting language is a lightweight programming language JavaScript is usually embedded
Programing for Digital Media EE1707. Lecture 3 JavaScript By: A. Mousavi and P. Broomhead SERG, School of Engineering Design, Brunel University, UK
 Programing for Digital Media EE1707 Lecture 3 JavaScript By: A. Mousavi and P. Broomhead SERG, School of Engineering Design, Brunel University, UK 1 JavaScript Syntax Cont. 1. Conditional statements 2.
Programing for Digital Media EE1707 Lecture 3 JavaScript By: A. Mousavi and P. Broomhead SERG, School of Engineering Design, Brunel University, UK 1 JavaScript Syntax Cont. 1. Conditional statements 2.
CHAPTER 6 JAVASCRIPT PART 1
 CHAPTER 6 JAVASCRIPT PART 1 1 OVERVIEW OF JAVASCRIPT JavaScript is an implementation of the ECMAScript language standard and is typically used to enable programmatic access to computational objects within
CHAPTER 6 JAVASCRIPT PART 1 1 OVERVIEW OF JAVASCRIPT JavaScript is an implementation of the ECMAScript language standard and is typically used to enable programmatic access to computational objects within
Learning JavaScript. A C P K Siriwardhana, BSc, MSc
 Learning JavaScript A C P K Siriwardhana, BSc, MSc Condition Statements If statements loop statements switch statement IF THEN ELSE If something is true, take a specified action. If false, take some other
Learning JavaScript A C P K Siriwardhana, BSc, MSc Condition Statements If statements loop statements switch statement IF THEN ELSE If something is true, take a specified action. If false, take some other
Note: Java and JavaScript are two completely different languages in both concept and design!
 Java Script: JavaScript was designed to add interactivity to HTML pages JavaScript is a scripting language A scripting language is a lightweight programming language JavaScript is usually embedded directly
Java Script: JavaScript was designed to add interactivity to HTML pages JavaScript is a scripting language A scripting language is a lightweight programming language JavaScript is usually embedded directly
JavaScript Introduction
 JavaScript Introduction JavaScript: Writing Into HTML Output document.write("this is a heading"); document.write("this is a paragraph"); JavaScript: Reacting to Events
JavaScript Introduction JavaScript: Writing Into HTML Output document.write("this is a heading"); document.write("this is a paragraph"); JavaScript: Reacting to Events
JavaScript CS 4640 Programming Languages for Web Applications
 JavaScript CS 4640 Programming Languages for Web Applications 1 How HTML, CSS, and JS Fit Together {css} javascript() Content layer The HTML gives the page structure and adds semantics Presentation
JavaScript CS 4640 Programming Languages for Web Applications 1 How HTML, CSS, and JS Fit Together {css} javascript() Content layer The HTML gives the page structure and adds semantics Presentation
Lecture 14. Introduction to JavaScript. Mr. Mubashir Ali Lecturer (Dept. of Computer Science)
 Lecture 14 Introduction to JavaScript Mr. Mubashir Ali Lecturer (Dept. of dr.mubashirali1@gmail.com 1 Outline What is JavaScript? Embedding JavaScript with HTML JavaScript conventions Variables in JavaScript
Lecture 14 Introduction to JavaScript Mr. Mubashir Ali Lecturer (Dept. of dr.mubashirali1@gmail.com 1 Outline What is JavaScript? Embedding JavaScript with HTML JavaScript conventions Variables in JavaScript
Unit 20 - Client Side Customisation of Web Pages. Week 4 Lesson 5 Fundamentals of Scripting
 Unit 20 - Client Side Customisation of Web Pages Week 4 Lesson 5 Fundamentals of Scripting The story so far... three methods of writing CSS: In-line Embedded }These are sometimes called External } block
Unit 20 - Client Side Customisation of Web Pages Week 4 Lesson 5 Fundamentals of Scripting The story so far... three methods of writing CSS: In-line Embedded }These are sometimes called External } block
JavaScript CS 4640 Programming Languages for Web Applications
 JavaScript CS 4640 Programming Languages for Web Applications 1 How HTML, CSS, and JS Fit Together {css} javascript() Content layer The HTML gives the page structure and adds semantics Presentation
JavaScript CS 4640 Programming Languages for Web Applications 1 How HTML, CSS, and JS Fit Together {css} javascript() Content layer The HTML gives the page structure and adds semantics Presentation
JavaScript is described in detail in many books on the subject, and there is excellent tutorial material at
 JavaScript (last updated April 15, 2013: LSS) JavaScript is a scripting language, specifically for use on web pages. It runs within the browser (that is to say, it is a client- side scripting language),
JavaScript (last updated April 15, 2013: LSS) JavaScript is a scripting language, specifically for use on web pages. It runs within the browser (that is to say, it is a client- side scripting language),
Chapter 3 - Simple JavaScript - Programming Basics. Lesson 1 - JavaScript: What is it and what does it look like?
 Chapter 3 - Simple JavaScript - Programming Basics Lesson 1 - JavaScript: What is it and what does it look like? PP presentation JavaScript.ppt. Lab 3.1. Lesson 2 - JavaScript Comments, document.write(),
Chapter 3 - Simple JavaScript - Programming Basics Lesson 1 - JavaScript: What is it and what does it look like? PP presentation JavaScript.ppt. Lab 3.1. Lesson 2 - JavaScript Comments, document.write(),
Working with JavaScript
 Working with JavaScript Creating a Programmable Web Page for North Pole Novelties 1 Objectives Introducing JavaScript Inserting JavaScript into a Web Page File Writing Output to the Web Page 2 Objectives
Working with JavaScript Creating a Programmable Web Page for North Pole Novelties 1 Objectives Introducing JavaScript Inserting JavaScript into a Web Page File Writing Output to the Web Page 2 Objectives
CSC 337. JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Rick Mercer
 CSC 337 JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Rick Mercer Why JSON over XML? JSON was built to know JS JSON JavaScript Object Notation Data-interchange format Lightweight Replacement for XML It's just a string
CSC 337 JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) Rick Mercer Why JSON over XML? JSON was built to know JS JSON JavaScript Object Notation Data-interchange format Lightweight Replacement for XML It's just a string
Produced by. App Development & Modeling. BSc in Applied Computing. Eamonn de Leastar
 App Development & Modeling BSc in Applied Computing Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie http://elearning.wit.ie
App Development & Modeling BSc in Applied Computing Produced by Eamonn de Leastar (edeleastar@wit.ie) Department of Computing, Maths & Physics Waterford Institute of Technology http://www.wit.ie http://elearning.wit.ie
COMS 469: Interactive Media II
 COMS 469: Interactive Media II Agenda Review Data Types & Variables Decisions, Loops, and Functions Review gunkelweb.com/coms469 Review Basic Terminology Computer Languages Interpreted vs. Compiled Client
COMS 469: Interactive Media II Agenda Review Data Types & Variables Decisions, Loops, and Functions Review gunkelweb.com/coms469 Review Basic Terminology Computer Languages Interpreted vs. Compiled Client
CSS The web browser uses its own resources, and eases the burden on the server. It has fewer features than server side scripting.
 What is JavaScript? HTML and CSS concentrate on a static rendering of a page; things do not change on the page over time, or because of events. To do these things, we use scripting languages, which allow
What is JavaScript? HTML and CSS concentrate on a static rendering of a page; things do not change on the page over time, or because of events. To do these things, we use scripting languages, which allow
JavaScript By: A. Mousavi & P. Broomhead SERG, School of Engineering Design, Brunel University, UK
 Programming for Digital Media EE1707 JavaScript By: A. Mousavi & P. Broomhead SERG, School of Engineering Design, Brunel University, UK 1 References and Sources 1. Javascript & JQuery: interactive front-end
Programming for Digital Media EE1707 JavaScript By: A. Mousavi & P. Broomhead SERG, School of Engineering Design, Brunel University, UK 1 References and Sources 1. Javascript & JQuery: interactive front-end
introjs.notebook March 02, 2014
 1 document.write() uses the write method to write on the document. It writes the literal Hello World! which is enclosed in quotes since it is a literal and then enclosed in the () of the write method.
1 document.write() uses the write method to write on the document. It writes the literal Hello World! which is enclosed in quotes since it is a literal and then enclosed in the () of the write method.
PIC 40A. Lecture 10: JS: Wrapper objects, Input and Output, Control structures, random numbers. Copyright 2011 Jukka Virtanen UCLA 1 04/24/17
 PIC 40A Lecture 10: JS: Wrapper objects, Input and Output, Control structures, random numbers 04/24/17 Copyright 2011 Jukka Virtanen UCLA 1 Objects in JS In C++ we have classes, in JS we have OBJECTS.
PIC 40A Lecture 10: JS: Wrapper objects, Input and Output, Control structures, random numbers 04/24/17 Copyright 2011 Jukka Virtanen UCLA 1 Objects in JS In C++ we have classes, in JS we have OBJECTS.
<script type="text/javascript"> script commands </script>
 JavaScript Java vs. JavaScript JavaScript is a subset of Java JavaScript is simpler and less powerful than Java JavaScript programs can be embedded within HTML files; Java code must be separate Java code
JavaScript Java vs. JavaScript JavaScript is a subset of Java JavaScript is simpler and less powerful than Java JavaScript programs can be embedded within HTML files; Java code must be separate Java code
By the end of this section of the practical, the students should be able to:
 By the end of this section of the practical, the students should be able to: Write JavaScript to generate HTML Create simple scripts which include input and output statements, arithmetic, relational and
By the end of this section of the practical, the students should be able to: Write JavaScript to generate HTML Create simple scripts which include input and output statements, arithmetic, relational and
SEEM4570 System Design and Implementation Lecture 03 JavaScript
 SEEM4570 System Design and Implementation Lecture 03 JavaScript JavaScript (JS)! Developed by Netscape! A cross platform script language! Mainly used in web environment! Run programs on browsers (HTML
SEEM4570 System Design and Implementation Lecture 03 JavaScript JavaScript (JS)! Developed by Netscape! A cross platform script language! Mainly used in web environment! Run programs on browsers (HTML
Exercise 1: Basic HTML and JavaScript
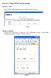 Exercise 1: Basic HTML and JavaScript Question 1: Table Create HTML markup that produces the table as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 Question 2: Spacing Spacing can be added using CellSpacing and CellPadding
Exercise 1: Basic HTML and JavaScript Question 1: Table Create HTML markup that produces the table as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 Question 2: Spacing Spacing can be added using CellSpacing and CellPadding
c122mar413.notebook March 06, 2013
 These are the programs I am going to cover today. 1 2 Javascript is embedded in HTML. The document.write() will write the literal Hello World! to the web page document. Then the alert() puts out a pop
These are the programs I am going to cover today. 1 2 Javascript is embedded in HTML. The document.write() will write the literal Hello World! to the web page document. Then the alert() puts out a pop
Web Programming and Design. MPT Junior Cycle Tutor: Tamara Demonstrators: Aaron, Marion, Hugh
 Web Programming and Design MPT Junior Cycle Tutor: Tamara Demonstrators: Aaron, Marion, Hugh Plan for the next 5 weeks: Introduction to HTML tags, creating our template file Introduction to CSS and style
Web Programming and Design MPT Junior Cycle Tutor: Tamara Demonstrators: Aaron, Marion, Hugh Plan for the next 5 weeks: Introduction to HTML tags, creating our template file Introduction to CSS and style
Web Application Development (WAD) V th Sem BBAITM(Unit-1) By: Binit Patel
 Web Application Development (WAD) V th Sem BBAITM(Unit-1) By: Binit Patel Introduction: PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) was invented by Rasmus Lerdorf in 1994. First it was known as Personal Home Page. Later
Web Application Development (WAD) V th Sem BBAITM(Unit-1) By: Binit Patel Introduction: PHP (Hypertext Preprocessor) was invented by Rasmus Lerdorf in 1994. First it was known as Personal Home Page. Later
JAVASCRIPT. sarojpandey.com.np/iroz. JavaScript
 JAVASCRIPT 1 Introduction JAVASCRIPT is a compact, object-based scripting language for developing client Internet applications. was designed to add interactivity to HTML pages. is a scripting language
JAVASCRIPT 1 Introduction JAVASCRIPT is a compact, object-based scripting language for developing client Internet applications. was designed to add interactivity to HTML pages. is a scripting language
CSCE 120: Learning To Code
 CSCE 120: Learning To Code Manipulating Data I Introduction This module is designed to get you started working with data by understanding and using variables and data types in JavaScript. It will also
CSCE 120: Learning To Code Manipulating Data I Introduction This module is designed to get you started working with data by understanding and using variables and data types in JavaScript. It will also
INFS 2150 Introduction to Web Development and e-commerce Technology. Programming with JavaScript
 INFS 2150 Introduction to Web Development and e-commerce Technology Programming with JavaScript 1 Objectives JavaScript client-side programming Example of a JavaScript program The element
INFS 2150 Introduction to Web Development and e-commerce Technology Programming with JavaScript 1 Objectives JavaScript client-side programming Example of a JavaScript program The element
Objectives. Introduction to JavaScript. Introduction to JavaScript INFS Peter Y. Wu, RMU 1
 Objectives INFS 2150 Introduction to Web Development and e-commerce Technology Programming with JavaScript JavaScript client-side programming Example of a JavaScript program The element
Objectives INFS 2150 Introduction to Web Development and e-commerce Technology Programming with JavaScript JavaScript client-side programming Example of a JavaScript program The element
Lecture 8: JavaScript
 Lecture 8: JavaScript JavaScript introduction Examples Languages syntax and semantics Delegation vs. inheritance CS 242, Fall 2011, Lecture 8 1 What is JavaScript? JavaScript is a scripting language heavily
Lecture 8: JavaScript JavaScript introduction Examples Languages syntax and semantics Delegation vs. inheritance CS 242, Fall 2011, Lecture 8 1 What is JavaScript? JavaScript is a scripting language heavily
5. JavaScript Basics
 CHAPTER 5: JavaScript Basics 88 5. JavaScript Basics 5.1 An Introduction to JavaScript A Programming language for creating active user interface on Web pages JavaScript script is added in an HTML page,
CHAPTER 5: JavaScript Basics 88 5. JavaScript Basics 5.1 An Introduction to JavaScript A Programming language for creating active user interface on Web pages JavaScript script is added in an HTML page,
HTML 5 and CSS 3, Illustrated Complete. Unit L: Programming Web Pages with JavaScript
 HTML 5 and CSS 3, Illustrated Complete Unit L: Programming Web Pages with JavaScript Objectives Explore the Document Object Model Add content using a script Trigger a script using an event handler Create
HTML 5 and CSS 3, Illustrated Complete Unit L: Programming Web Pages with JavaScript Objectives Explore the Document Object Model Add content using a script Trigger a script using an event handler Create
Place User-Defined Functions in the HEAD Section
 JavaScript Functions Notes (Modified from: w3schools.com) A function is a block of code that will be executed when "someone" calls it. In JavaScript, we can define our own functions, called user-defined
JavaScript Functions Notes (Modified from: w3schools.com) A function is a block of code that will be executed when "someone" calls it. In JavaScript, we can define our own functions, called user-defined
Objectives. Chapter 2: Basic Elements of C++ Introduction. Objectives (cont d.) A C++ Program (cont d.) A C++ Program
 Objectives Chapter 2: Basic Elements of C++ In this chapter, you will: Become familiar with functions, special symbols, and identifiers in C++ Explore simple data types Discover how a program evaluates
Objectives Chapter 2: Basic Elements of C++ In this chapter, you will: Become familiar with functions, special symbols, and identifiers in C++ Explore simple data types Discover how a program evaluates
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of C++
 Chapter 2: Basic Elements of C++ Objectives In this chapter, you will: Become familiar with functions, special symbols, and identifiers in C++ Explore simple data types Discover how a program evaluates
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of C++ Objectives In this chapter, you will: Become familiar with functions, special symbols, and identifiers in C++ Explore simple data types Discover how a program evaluates
Programming language components
 Programming language components syntax: grammar rules for defining legal statements what's grammatically legal? how are things built up from smaller things? semantics: what things mean what do they compute?
Programming language components syntax: grammar rules for defining legal statements what's grammatically legal? how are things built up from smaller things? semantics: what things mean what do they compute?
COMS W3101: SCRIPTING LANGUAGES: JAVASCRIPT (FALL 2017)
 COMS W3101: SCRIPTING LANGUAGES: JAVASCRIPT (FALL 2017) RAMANA ISUKAPALLI RAMANA@CS.COLUMBIA.EDU 1 LECTURE-1 Course overview See http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~ramana Overview of HTML Formatting, headings,
COMS W3101: SCRIPTING LANGUAGES: JAVASCRIPT (FALL 2017) RAMANA ISUKAPALLI RAMANA@CS.COLUMBIA.EDU 1 LECTURE-1 Course overview See http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~ramana Overview of HTML Formatting, headings,
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of C++ Objectives. Objectives (cont d.) A C++ Program. Introduction
 Chapter 2: Basic Elements of C++ C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Fifth Edition 1 Objectives In this chapter, you will: Become familiar with functions, special symbols, and identifiers
Chapter 2: Basic Elements of C++ C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program Design, Fifth Edition 1 Objectives In this chapter, you will: Become familiar with functions, special symbols, and identifiers
CSC Software I: Utilities and Internals. Programming in Python
 CSC 271 - Software I: Utilities and Internals Lecture #8 An Introduction to Python Programming in Python Python is a general purpose interpreted language. There are two main versions of Python; Python
CSC 271 - Software I: Utilities and Internals Lecture #8 An Introduction to Python Programming in Python Python is a general purpose interpreted language. There are two main versions of Python; Python
Then there are methods ; each method describes an action that can be done to (or with) the object.
 When the browser loads a page, it stores it in an electronic form that programmers can then access through something known as an interface. The interface is a little like a predefined set of questions
When the browser loads a page, it stores it in an electronic form that programmers can then access through something known as an interface. The interface is a little like a predefined set of questions
CS1046 Lab 4. Timing: This lab should take you 85 to 130 minutes. Objectives: By the end of this lab you should be able to:
 CS1046 Lab 4 Timing: This lab should take you 85 to 130 minutes. Objectives: By the end of this lab you should be able to: Define the terms: function, calling and user-defined function and predefined function
CS1046 Lab 4 Timing: This lab should take you 85 to 130 minutes. Objectives: By the end of this lab you should be able to: Define the terms: function, calling and user-defined function and predefined function
Mobile Site Development
 Mobile Site Development HTML Basics What is HTML? Editors Elements Block Elements Attributes Make a new line using HTML Headers & Paragraphs Creating hyperlinks Using images Text Formatting Inline styling
Mobile Site Development HTML Basics What is HTML? Editors Elements Block Elements Attributes Make a new line using HTML Headers & Paragraphs Creating hyperlinks Using images Text Formatting Inline styling
JavaScript Basics. The Big Picture
 JavaScript Basics At this point, you should have reached a certain comfort level with typing and running JavaScript code assuming, of course, that someone has already written it for you This handout aims
JavaScript Basics At this point, you should have reached a certain comfort level with typing and running JavaScript code assuming, of course, that someone has already written it for you This handout aims
Chapter 17. Fundamental Concepts Expressed in JavaScript
 Chapter 17 Fundamental Concepts Expressed in JavaScript Learning Objectives Tell the difference between name, value, and variable List three basic data types and the rules for specifying them in a program
Chapter 17 Fundamental Concepts Expressed in JavaScript Learning Objectives Tell the difference between name, value, and variable List three basic data types and the rules for specifying them in a program
Operators. Java operators are classified into three categories:
 Operators Operators are symbols that perform arithmetic and logical operations on operands and provide a meaningful result. Operands are data values (variables or constants) which are involved in operations.
Operators Operators are symbols that perform arithmetic and logical operations on operands and provide a meaningful result. Operands are data values (variables or constants) which are involved in operations.
JQuery and Javascript
 JQuery and Javascript Javascript - a programming language to perform calculations/ manipulate HTML and CSS/ make a web page interactive JQuery - a javascript framework to help manipulate HTML and CSS JQuery
JQuery and Javascript Javascript - a programming language to perform calculations/ manipulate HTML and CSS/ make a web page interactive JQuery - a javascript framework to help manipulate HTML and CSS JQuery
Chapter 9: Simple JavaScript
 Chapter 9: Simple JavaScript Learning Outcomes: Identify the benefits and uses of JavaScript Identify the key components of the JavaScript language, including selection, iteration, variables, functions
Chapter 9: Simple JavaScript Learning Outcomes: Identify the benefits and uses of JavaScript Identify the key components of the JavaScript language, including selection, iteration, variables, functions
Controlled Assessment Task. Question 1 - Describe how this HTML code produces the form displayed in the browser.
 Controlled Assessment Task Question 1 - Describe how this HTML code produces the form displayed in the browser. The form s code is displayed in the tags; this creates the object which is the visible
Controlled Assessment Task Question 1 - Describe how this HTML code produces the form displayed in the browser. The form s code is displayed in the tags; this creates the object which is the visible
Intro to Programming. Unit 7. What is Programming? What is Programming? Intro to Programming
 Intro to Programming Unit 7 Intro to Programming 1 What is Programming? 1. Programming Languages 2. Markup vs. Programming 1. Introduction 2. Print Statement 3. Strings 4. Types and Values 5. Math Externals
Intro to Programming Unit 7 Intro to Programming 1 What is Programming? 1. Programming Languages 2. Markup vs. Programming 1. Introduction 2. Print Statement 3. Strings 4. Types and Values 5. Math Externals
Chapter 2: Functions and Control Structures
 Chapter 2: Functions and Control Structures TRUE/FALSE 1. A function definition contains the lines of code that make up a function. T PTS: 1 REF: 75 2. Functions are placed within parentheses that follow
Chapter 2: Functions and Control Structures TRUE/FALSE 1. A function definition contains the lines of code that make up a function. T PTS: 1 REF: 75 2. Functions are placed within parentheses that follow
Lecture 2. The variable 'x' can store integers, characters, string, float, boolean.
 In this lecture we will learn 1 Arrays 2 Expressions and Operators 3 Functions 4 If-else construct 5 Switch Construct 6 loop constructs For While do-while Lecture 2 More about data types As I told in my
In this lecture we will learn 1 Arrays 2 Expressions and Operators 3 Functions 4 If-else construct 5 Switch Construct 6 loop constructs For While do-while Lecture 2 More about data types As I told in my
Object-Oriented Programming
 Object-Oriented Programming Java Syntax Program Structure Variables and basic data types. Industry standard naming conventions. Java syntax and coding conventions If Then Else Case statements Looping (for,
Object-Oriented Programming Java Syntax Program Structure Variables and basic data types. Industry standard naming conventions. Java syntax and coding conventions If Then Else Case statements Looping (for,
Client-Side Web Technologies. JavaScript Part I
 Client-Side Web Technologies JavaScript Part I JavaScript First appeared in 1996 in Netscape Navigator Main purpose was to handle input validation that was currently being done server-side Now a powerful
Client-Side Web Technologies JavaScript Part I JavaScript First appeared in 1996 in Netscape Navigator Main purpose was to handle input validation that was currently being done server-side Now a powerful
Web Development & Design Foundations with HTML5
 1 Web Development & Design Foundations with HTML5 CHAPTER 14 A BRIEF LOOK AT JAVASCRIPT Copyright Terry Felke-Morris 2 Learning Outcomes In this chapter, you will learn how to: Describe common uses of
1 Web Development & Design Foundations with HTML5 CHAPTER 14 A BRIEF LOOK AT JAVASCRIPT Copyright Terry Felke-Morris 2 Learning Outcomes In this chapter, you will learn how to: Describe common uses of
CMPT 100 : INTRODUCTION TO
 CMPT 100 : INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING TUTORIAL #5 : JAVASCRIPT 2 GUESSING GAME 1 By Wendy Sharpe BEFORE WE GET STARTED... If you have not been to the first tutorial introduction JavaScript then you must
CMPT 100 : INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTING TUTORIAL #5 : JAVASCRIPT 2 GUESSING GAME 1 By Wendy Sharpe BEFORE WE GET STARTED... If you have not been to the first tutorial introduction JavaScript then you must
Let's Look Back. We talked about how to create a form in HTML. Forms are one way to interact with users
 Introduction to PHP Let's Look Back We talked about how to create a form in HTML Forms are one way to interact with users Users can enter information into forms which can be used by you (programmer) We
Introduction to PHP Let's Look Back We talked about how to create a form in HTML Forms are one way to interact with users Users can enter information into forms which can be used by you (programmer) We
Loops/Confirm Tutorial:
 Loops/Confirm Tutorial: What you ve learned so far: 3 ways to call a function how to write a function how to send values into parameters in a function How to create an array (of pictures, of sentences,
Loops/Confirm Tutorial: What you ve learned so far: 3 ways to call a function how to write a function how to send values into parameters in a function How to create an array (of pictures, of sentences,
1. Cascading Style Sheet and JavaScript
 1. Cascading Style Sheet and JavaScript Cascading Style Sheet or CSS allows you to specify styles for visual element of the website. Styles specify the appearance of particular page element on the screen.
1. Cascading Style Sheet and JavaScript Cascading Style Sheet or CSS allows you to specify styles for visual element of the website. Styles specify the appearance of particular page element on the screen.
JavaScript Syntax. Web Authoring and Design. Benjamin Kenwright
 JavaScript Syntax Web Authoring and Design Benjamin Kenwright Milestone Dates Demonstrate Coursework 1 Friday (15 th December) 10 Minutes Each Coursework 2 (Group Project) Website (XMAS) Javascript Game
JavaScript Syntax Web Authoring and Design Benjamin Kenwright Milestone Dates Demonstrate Coursework 1 Friday (15 th December) 10 Minutes Each Coursework 2 (Group Project) Website (XMAS) Javascript Game
HTML5 and CSS3 More JavaScript Page 1
 HTML5 and CSS3 More JavaScript Page 1 1 HTML5 and CSS3 MORE JAVASCRIPT 3 4 6 7 9 The Math Object The Math object lets the programmer perform built-in mathematical tasks Includes several mathematical methods
HTML5 and CSS3 More JavaScript Page 1 1 HTML5 and CSS3 MORE JAVASCRIPT 3 4 6 7 9 The Math Object The Math object lets the programmer perform built-in mathematical tasks Includes several mathematical methods
CMPT 125: Lecture 3 Data and Expressions
 CMPT 125: Lecture 3 Data and Expressions Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 1 Character Strings A character string is an object in Java,
CMPT 125: Lecture 3 Data and Expressions Tamara Smyth, tamaras@cs.sfu.ca School of Computing Science, Simon Fraser University January 3, 2009 1 Character Strings A character string is an object in Java,
Overview: Programming Concepts. Programming Concepts. Names, Values, And Variables
 Chapter 18: Get With the Program: Fundamental Concepts Expressed in JavaScript Fluency with Information Technology Third Edition by Lawrence Snyder Overview: Programming Concepts Programming: Act of formulating
Chapter 18: Get With the Program: Fundamental Concepts Expressed in JavaScript Fluency with Information Technology Third Edition by Lawrence Snyder Overview: Programming Concepts Programming: Act of formulating
Overview: Programming Concepts. Programming Concepts. Chapter 18: Get With the Program: Fundamental Concepts Expressed in JavaScript
 Chapter 18: Get With the Program: Fundamental Concepts Expressed in JavaScript Fluency with Information Technology Third Edition by Lawrence Snyder Overview: Programming Concepts Programming: Act of formulating
Chapter 18: Get With the Program: Fundamental Concepts Expressed in JavaScript Fluency with Information Technology Third Edition by Lawrence Snyder Overview: Programming Concepts Programming: Act of formulating
3 The Building Blocks: Data Types, Literals, and Variables
 chapter 3 The Building Blocks: Data Types, Literals, and Variables 3.1 Data Types A program can do many things, including calculations, sorting names, preparing phone lists, displaying images, validating
chapter 3 The Building Blocks: Data Types, Literals, and Variables 3.1 Data Types A program can do many things, including calculations, sorting names, preparing phone lists, displaying images, validating
For loops and Window Objects:
 For loops and Window Objects: So far we ve been dealing with the document object. The document object has many properties all elements within the html document are part of the document object. Thus we
For loops and Window Objects: So far we ve been dealing with the document object. The document object has many properties all elements within the html document are part of the document object. Thus we
(Refer Slide Time: 01:40)
 Internet Technology Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No #25 Javascript Part I Today will be talking about a language
Internet Technology Prof. Indranil Sengupta Department of Computer Science and Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture No #25 Javascript Part I Today will be talking about a language
JavaScript code is inserted between tags, just like normal HTML tags:
 Introduction to JavaScript In this lesson we will provide a brief introduction to JavaScript. We won t go into a ton of detail. There are a number of good JavaScript tutorials on the web. What is JavaScript?
Introduction to JavaScript In this lesson we will provide a brief introduction to JavaScript. We won t go into a ton of detail. There are a number of good JavaScript tutorials on the web. What is JavaScript?
Tutorial 10: Programming with JavaScript
 Tutorial 10: Programming with JavaScript College of Computing & Information Technology King Abdulaziz University CPCS-665 Internet Technology Objectives Learn the history of JavaScript Create a script
Tutorial 10: Programming with JavaScript College of Computing & Information Technology King Abdulaziz University CPCS-665 Internet Technology Objectives Learn the history of JavaScript Create a script
Full file at C How to Program, 6/e Multiple Choice Test Bank
 2.1 Introduction 2.2 A Simple Program: Printing a Line of Text 2.1 Lines beginning with let the computer know that the rest of the line is a comment. (a) /* (b) ** (c) REM (d)
2.1 Introduction 2.2 A Simple Program: Printing a Line of Text 2.1 Lines beginning with let the computer know that the rest of the line is a comment. (a) /* (b) ** (c) REM (d)
JavaScript: The Basics
 JavaScript: The Basics CISC 282 October 4, 2017 JavaScript A programming language "Lightweight" and versatile Not universally respected Appreciated in the web domain Adds programmatic functionality to
JavaScript: The Basics CISC 282 October 4, 2017 JavaScript A programming language "Lightweight" and versatile Not universally respected Appreciated in the web domain Adds programmatic functionality to
Enhancing Web Pages with JavaScript
 Enhancing Web Pages with JavaScript Introduction In this Tour we will cover: o The basic concepts of programming o How those concepts are translated into JavaScript o How JavaScript can be used to enhance
Enhancing Web Pages with JavaScript Introduction In this Tour we will cover: o The basic concepts of programming o How those concepts are translated into JavaScript o How JavaScript can be used to enhance
Manju Muralidharan Priya. CS4PM Web Aesthetics and Development WEEK 12
 CS4PM Web Aesthetics and Development WEEK 12 Objective: 1. Understand the basic operations in JavaScript 2. Understand and Prepare a 3 page Website (Homework for Week 15) 3. Finish Quiz 2 Outline: a. Basics
CS4PM Web Aesthetics and Development WEEK 12 Objective: 1. Understand the basic operations in JavaScript 2. Understand and Prepare a 3 page Website (Homework for Week 15) 3. Finish Quiz 2 Outline: a. Basics
Elementary Computing CSC 100. M. Cheng, Computer Science
 Elementary Computing CSC 100 1 Basic Programming Concepts A computer is a kind of universal machine. By using different software, a computer can do different things. A program is a sequence of instructions
Elementary Computing CSC 100 1 Basic Programming Concepts A computer is a kind of universal machine. By using different software, a computer can do different things. A program is a sequence of instructions
A Balanced Introduction to Computer Science, 3/E David Reed, Creighton University 2011 Pearson Prentice Hall ISBN
 A Balanced Introduction to Computer Science, 3/E David Reed, Creighton University 2011 Pearson Prentice Hall ISBN 978-0-13-216675-1 Chapter 5 JavaScript and User Interaction 1 Text Boxes HTML event handlers
A Balanced Introduction to Computer Science, 3/E David Reed, Creighton University 2011 Pearson Prentice Hall ISBN 978-0-13-216675-1 Chapter 5 JavaScript and User Interaction 1 Text Boxes HTML event handlers
C++ Basic Elements of COMPUTER PROGRAMMING. Special symbols include: Word symbols. Objectives. Programming. Symbols. Symbols.
 EEE-117 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING Basic Elements of C++ Objectives General Questions Become familiar with the basic components of a C++ program functions, special symbols, and identifiers Data types Arithmetic
EEE-117 COMPUTER PROGRAMMING Basic Elements of C++ Objectives General Questions Become familiar with the basic components of a C++ program functions, special symbols, and identifiers Data types Arithmetic
c) Comments do not cause any machine language object code to be generated. d) Lengthy comments can cause poor execution-time performance.
 2.1 Introduction (No questions.) 2.2 A Simple Program: Printing a Line of Text 2.1 Which of the following must every C program have? (a) main (b) #include (c) /* (d) 2.2 Every statement in C
2.1 Introduction (No questions.) 2.2 A Simple Program: Printing a Line of Text 2.1 Which of the following must every C program have? (a) main (b) #include (c) /* (d) 2.2 Every statement in C
