FEA of Composites Classical Lamination Theory Example 1
|
|
|
- Clementine Goodwin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
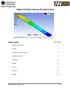
1 FEA of Composites Classical Lamination Theory Example Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Author: Dimitri Soteropoulos Revised by Jacob Wardell Problem Description: A four layer [0/90] s graphite-epoxy composite laminate subjected to an axial load is considered (Figure 1). A finite element model will be constructed using HyperMesh v12.0 where the principal stresses in the respective plies will be analyzed. Figure 1. [0/90] s Laminate [Hyer, 2009] An analytical solution for this example can be found in Stress Analysis of Fiber-Reinforced Composite Materials, Hyer text, pp The given material properties and loading conditions can be seen in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively. Table 1. Graphite-Epoxy Material Properties Table 2. Loading Conditions Material Property Value E GPa E GPa ν G GPa G GPa G GPa Load Value εx 1000 x 10-6 εy 0 γxy REV. 09/03/2014
2 Step 1: Open HyperMesh 1. Open HyperMesh 2. Usually, the User Profiles window ( ) should appear when HyperMesh starts. *If it doesn t appear at start up: From the Preferences menu, select User Profiles. 3. Select OptiStruct: 4. Click OK. 5. Make sure that the Model tab is open on the left side of the window: *If the Model is not selected, left-click on it to make it the current tab REV. 09/03/2014
3 Once the User Profiles window is exited, the HyperMesh interface should look similar to the image below. (Please note that the Model Browser is the area on the left hand side of the Graphics Area, while the Menu Bar is at the top of the window, right below the title bar) Model Browser Graphics Area REV. 09/03/2014
4 Step 2: Create a material 1. Access the Create material window one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose Materials > Create. Right click in the Model browser and click Create > Material. 2. Click the Name: field and enter Graphite-Epoxy 3. Click the square color icon and choose a color (besides gray). 4. Make sure that the Card image: is set to MAT8. 5. Make sure that the box to the left of the text Card edit material on upon is checked. 6. Make sure that the box to the left of the text Close dialog upon creation is checked. *Make sure that the settings are the same as the ones shown below: 7. Click Create REV. 09/03/2014
5 8. The card edit panel for the material will appear (with MAT8 to the left of it). 9. For the value of E1, enter: 155.0e9 *Please note there is no dropdown menu or feature in HyperMesh that sets specific units. All of the dimensions specified in this problem are given in SI units; therefore the respective Young s Modulus ( E ) units should be entered in Pa (Pascals, Newtons per Square Meter: N/m^2). The units chosen for the definition of the material properties should be consistent and dictate what units should be used for the dimensions of the structure. 10. For the value of E2, enter: 12.10e Left-click on the [ NU12 ] in the card edit panel (*It might be gray until it is selected). 12. For the value of [ NU12 ], enter: Enter the values for the corresponding G12,G13, and G23 values as well. *Make sure that the settings are the same as the ones shown below: *These values correspond to the ones given in Table 1: Table 1. Graphite-Epoxy Material Properties Material Property Value E GPa E GPa ν G GPa G GPa G GPa 13. Click the red return button on the bottom-right of the panel below: This will create a material titled Graphite-Epoxy REV. 09/03/2014
6 Step 3: Create a property. 1. Access the Create property window one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose Properties > Create > Properties. Right click in the Model Browser and click Create > Property. 2. Click the Name: field and enter Graphite_Epoxy_prop. 3. To the right of Card image:, select PCOMPP: (*Note: make sure to select PCOMPP, not PCOMP) REV. 09/03/2014
7 4. Click the square color icon and choose a color. 5. Click on the Material tab. 6. Make sure Assign material: is checked. 7. To the right of Name: select Graphite-Epoxy. 8. Make sure that the box to the left of the text Card edit property upon creation is unchecked. 9. Make sure that the box to the left of the text Close dialog upon creation is checked. *Make sure that the settings for the Property tab and Material tab are the same as the ones shown below: 10. Click Create. This will create a property titled Graphite_Epoxy_prop with the assigned material being Graphite-Epoxy REV. 09/03/2014
8 Step 4: Create a component to hold the model s geometry. 1. Access the Create component window one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose Collectors > Create > Components. Right click in the Model Browser and click Create > Component. 2. Click the Name: field and enter Plate. 3. Click the square color icon and choose a color. 4. Click on the Property tab. 5. Make sure that the Assign property: is checked. 6. To the right of Name: make sure that Graphite_Epoxy_prop is selected. 7. Click on the Material tab. 8. Make sure that the Assign material: is checked. 9. To the right of Name: make sure that Graphite_Epoxy is selected REV. 09/03/2014
9 10. Make sure that the box to the left of the text Close dialog upon creation is checked. *Make sure that the settings for the Component, Property, and Material tabs are the same as the ones shown below: 11. Click Create. 12. This will create a new component titled Plate (with Graphite_Epoxy_prop as the assigned Property) *The message Component created should appear in the status bar. (on the bottom-left corner of the screen) *Left-click once anywhere in the Graphics area to dismiss the message in the status bar. *Left click on the + to the left of Component (1) in the Model tab. *The component called Plate is the current component and is bold in the Model Browser REV. 09/03/2014
10 Step 5: Create nodes 1. Create nodes one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose Geometry > Create > Nodes > XYZ Select from the Geom panel: i ) Make sure the Geom panel is selected ii) Click nodes iii) Make sure that the XYZ icon is selected: 2. Enter the X, Y, & Z coordinates of the points listed in Table 1. After entering the X, Y, & Z coordinates for each point, click create to create a node at that point: *Note: a shortcut to create nodes or other geometry items more quickly is to simply click on the mouse wheel button anywhere in the screen, instead of left-clicking on the green create button REV. 09/03/2014
11 Point Once finished, click return. Table 1. Points for Geometry X Coordinate Y Coordinate Z Coordinate *Press F on the keyboard to auto fit the nodes to the screen. They may have been off the current screen view when they were created. Step 6: Display the node numbers. 1. Make sure the view is in the standard XY view by clicking on the XY Top Plane View icon near the top of the HyperMesh window 2. From the menu bar, choose Geometry > Check > Nodes > Numbers. 3. Click on the highlighted nodes button and then click on displayed. 4. Click on the green on button (on the right side). This will display the node numbers: 5. Click return REV. 09/03/2014
12 Step 7: Create straight lines 1. Access the Linear Nodes panel one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose Geometry > Create > Lines > Linear Nodes. Select the Geom panel, click Lines, then select the Linear Nodes icon: (If necessary, click on the small black triangle: to the right of the current line creation icon to select it from a list of options) 2. Make sure that the "Closed line" option is unchecked: 3. With node list selected, click on node 1 (0, 0, 0) and node 2 (1, 0, 0) shown below: 4. Click create. *Note: a shortcut to create lines or other geometry items more quickly is to simply click on the mouse wheel button anywhere in the screen, instead of left-clicking on the green create button. 5. This will create a line going from node 1 to node Repeat this process to create straight lines using the following nodes: 2 & 3 3 & 4 4 & REV. 09/03/2014
13 Once completed, the created lines should look similar to the ones shown in the following image: 7. Click return. Step 8: Create a surface 1. Access the Spline/Filler surface creation panel one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose Geometry > Create > Surfaces > Spline/Filler. Select the Geom panel, click surfaces, then select the Spline/Filler icon: 2. Make sure that the highlighted selector option button on the left is set to lines: *If it is not set to lines, click on the black triangle to the left of the selected option and select lines. 3. Click on the lines highlighted selector option and select displayed. 4. Make sure that the Auto create (free edges only) option is unchecked. 5. Make sure that the Keep tangency option is unchecked. 6. Click create REV. 09/03/2014
14 7. Click on the Shaded Geometry and Surface Edges icon: 8. The created surface should now be visible and look similar to the one in the following image: 9. Click return. This creates a surface bounded by the selected lines REV. 09/03/2014
15 Step 9: Set Meshing Options 1. Access the Meshing Options: From the menu bar, choose Preferences > Meshing Options. 2. For node tol, enter For element size, enter: *Make sure that the settings are the same as the ones shown below: 4. Click return. Step 10: Mesh the Left Side of the Component using 2D AutoMesh 1. Access the 2D AutoMesh panel one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose Mesh > Create > 2D AutoMesh. Press the F12 key on the keyboard. Select the 2D panel and click on the automesh button. 2. Make sure that the yellow selector button is set to surfs *If it is not set to surfs, click on the black triangle ( ) to the left of the yellow button and select surfs. 3. Click on the selector button surfs and select displayed. 4. For element size, enter: To the right of mesh type:, click on the upside-down black triangle ( ) and select quads. 6. Make sure that the settings are set to elems to current comp, first order, and keep connectivity. 7. Make sure that to the right of map:, both size and skew are unchecked. 8. On the bottom left corner of the panel, toggle the setting to be automatic. *Make sure that the settings are the same as the ones shown below: 9. Click mesh. (the green button on the upper right corner of the panel) *The message 400 elements were created should appear in the status bar. (at the bottom-left corner of the screen) REV. 09/03/2014
16 10. The mesh should now look like the one shown below: *If the mesh is not visible, click on the Shaded Elements and Mesh Lines button: 11. Click return. Click return again. Now a quad mesh has been created using the surface, with each element having the size of 0.05 units (making a 20 x 20 square mesh). Step 11: Delete the temporary nodes 1. Access the Temporary Nodes panel one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose Geometry > Delete > Nodes. Select the Geom panel and click on the temp nodes button. 2. Click on the green to clear all button on the right side of the panel. *This deletes all of the temporary nodes. 3. Click return REV. 09/03/2014
17 Step 12: Mask the created geometry 1. Left-click on the geometry icon ( ) to the left of the name of the Plate component in the model browser: The geometry for the Plate component will now be masked. The geometry icon for the Plate component will now appear as the one below: REV. 09/03/2014
18 Step 13: Set the Material Orientation for the elements to match the System XYZ Orientation 1. Select the 1D panel: 2. Click on the systems button: 3. Select the material orientation panel (click on the button on the left side of the panel) 4. Click on the yellow elems button 5. Select all: This selects all of the elements REV. 09/03/2014
19 6. Make sure that the Material orientation method: is set to by system axis : *If necessary, click on the black triangle under Material orientation method: and select by system axis from the options. 7. Make sure that the axis option is set to local 1-axis : *If necessary, click on the black triangle and select local 1-axis from the options. 8. Set the size = to 0.5: 9. Click on the yellow system button: REV. 09/03/2014
20 10. Left-click the global XYZ system on the bottom-left corner of the Graphics Area: *Another way to select the system is to hold down the left mouse button while moving the cursor over the global XYZ system, then releasing the left mouse button. *Once the global XYZ system turns white, this means that it has been selected: 11. Click project: *The material orientation of the selected elements will now be based on the selected system. Select the elements and click review, there should be arrows pointing in the global X direction for all the elements REV. 09/03/2014
21 Step 14: Create Plies 1. Access the Create Ply window one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose Properties > Create > Plies. Right click in the Model browser and click Create > Ply. 2. Click the Name: field and enter Ply1 3. Make sure that the Card image: is set to PLY. 4. Click the square color icon and choose a color (besides gray). 5. Set the Material type: to ORTHOTROPIC. 6. Make sure that the Material: is set to Graphite-Epoxy. 7. For the Thickness, enter: (This will set the thickness to units, which in this case will represent meters, which is equal to 0.150mm) 8. For the Orientation, enter: 0 (This will set the orientation angle of the ply to be 0 degrees) 9. Make sure that the Shape: selector button is set to Element. *If the Shape: selector button is not set to Element, click on the black triangle to the left of the yellow button and select Element from the list: REV. 09/03/2014
22 10. Click twice on the yellow Element selector button: 11. Click on the yellow elems selector button on the left side of the panel: 12. Click on the displayed button: This selects all of the elements that are displayed. 13. Click on the green proceed button on the right side of the panel: REV. 09/03/2014
23 14. Make sure that the box to the left of the text Output results is checked. 15. Make sure that the box to the left of the text Card edit ply on creation is unchecked. 16. Make sure that the box to the left of the text Close dialog upon creation is unchecked. *Make sure that the settings are the same as the ones shown: 17. Click Create. 18. Repeat this process to create three more plies (Ply2, Ply3, and Ply4). (Make sure to select the elements for each ply creation) *All of the plies will have the same settings except for the Orientation angle: i. Ply1 should have an Orientation of 0. ii. Ply2 should have an Orientation of 90. iii. Ply3 should have an Orientation of 90. iv. Ply4 should have an Orientation of Once Ply1, Ply2, Ply3 and Ply4 have been created, close the Create Ply window REV. 09/03/2014
24 Step 15: Create a Ply Laminate 1. Access the Create Laminate window one of the following ways: a. From the menu bar, choose Properties > Create > Laminates. b. Right click in the Model browser and click Create > Laminate. 2. Set the Type: to Ply laminate. 3. Click the Name: field and enter Graphite-Epoxy 4. Make sure that the Card image: is set to STACK. 5. Click the square color icon and choose a color (besides gray). 6. Make sure that the Laminate option: is set to Total. 7. Click on the first blank entry space underneath Name 8. Click on the black triangle to the right of the blank entry space and select Ply1 from the list: REV. 09/03/2014
25 Ply1 is now selected as the first ply in the laminate. 9. Click on the next blank entry space (underneath the now-entered Ply1). 10. Click on the black triangle to the right of the blank entry space and select Ply2 from the list. 11. Repeat this process to include Ply3 and Ply4 as ply layers in the laminate. 12. Make sure that the box to the left of the text Card edit material on creation is unchecked. 13. Make sure that the box to the left of the text Close dialog upon creation is checked. *Make sure that the settings are the same as the ones shown: 14. Click Create. This creates a ply laminate with four layers: Ply1, Ply2, Ply3, and Ply REV. 09/03/2014
26 Step 16: Create a Load Collector 1. Access the Create Load Collector window one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose Collectors > Create > Load Collectors. Right click in the Model Browser and click Create > Load Collector. 2. Click the Name: field and enter SPC. 3. Click the square color icon and choose a color. 4. Set the Card image: to none. 5. Make sure that the Card edit loadcollector upon creation: is unchecked. 6. Make sure that the Close dialog upon creation: is checked REV. 09/03/2014
27 *Make sure that the settings are the same as the ones shown below: 15. Click Create. This creates a load collector to contain the constraints. Step 17: Apply Constraints 1. Access the constraints panel one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose BCs > Create > Constraints Select the Analysis panel, then click constraints. 2. Make sure that the option button on the left side is set to create. 3. Make sure that all of the settings are the same as the ones shown below: 4. Click on the yellow nodes selector button. 5. Left-click in a blank region of the Graphics Area. 6. Make sure the view is in the standard XY view by clicking on the XY Top Plane View icon near the top of the HyperMesh window 7. Hold down the Shift key on the keyboard, move the mouse cursor close to one of the corners of the component in the Graphics Area, and hold down the left mouse button, dragging the cursor to draw a selection rectangle that encloses the nodes on the left and right edges of the mesh. (Each individual node can also be individually selected by left-clicking on each one) REV. 09/03/2014
28 8. The selected nodes should be the ones shown below: 9. Click create. 10. The resulting constraints should look similar to the ones shown below: 11. This creates constraints, restricting all 6 degrees of freedom (dof s), on all of the selected nodes. Next, ensure dof 2, dof 4 and dof 6 are the only ones checked and select the nodes on the top and bottom of the plate (see image below). Click create REV. 09/03/2014
29 12. This creates constraints, restricting all 6 degrees of freedom (dof s), on all of the selected nodes. Next, ensure dof 2, dof 4 and dof 6 are the only ones checked and select the nodes on the top and bottom of the plate (see image below). Click create. 13. Do not click Return. Stay in this panel for the subsequent step. Step 18: Apply a Displacement via Constraints *An extensional strain of 1000 x 10-6 will be applied to the model in the form of an x direction displacement. 1. Click on the yellow nodes selector button. 2. Left-click in a blank region of the Graphics Area. 3. Select all of the nodes on the right edge of the mesh: Hold down the Shift key on the keyboard, move the mouse cursor close to one of the corners of the component in the Graphics Area, and hold down the left mouse button, dragging the cursor to draw a selection rectangle that encloses the nodes on the right edge of the mesh. (Each individual node can also be individually selected by left-clicking on each one). 4. Click create. 5. Click return REV. 09/03/2014
30 *This creates constraints on (dof1) the right side that will cause a displacement of in the x direction Step 19: Create a Load Step 1. Access the constraints panel one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose Setup > Create > LoadSteps Select the Analysis panel, then click loadsteps. 2. For name =, enter: Stretch. 3. Set the type: to linear static. 4. Make sure that SPC is checked. 5. Click on the = to the right of SPC, and select SPC. 6. Make sure that all of the settings are the same as the ones shown below: 7. Click create. 8. Click return. Step 20: Autocolor the Plies (OPTIONAL STEP) 1. Left click on the + to the left of Ply (4) in the Model tab: 2. Left-click on Ply1: REV. 09/03/2014
31 3. Holding down the Shift key on the keyboard, left-click on Ply4. Now all four plies should be selected. Right-click on one of the square color icons to the right of the names of the plies: 4. Click on Autocolor : 5. Click anywhere in the Model Browser. Now all four plies automatically have different colors: REV. 09/03/2014
32 Step 21: Visualize the Plies (OPTIONAL STEP) 1. Click on the small black triangle to the right of the Element Color Mode setting: 2. Switch the Element Color Mode to By Prop : 3. Click on the small black triangle to the right of the Element Representation setting icon ( ): REV. 09/03/2014
33 4. Click on 3D Element Representation : The elements in the Graphics Area now will have a three-dimensional representation 5. Click on the small black triangle to the right of the Layer Representation setting icon ( ): 6. Click on Composite Layers with Fiber Direction : The composite layers, each with its own fiber direction, will now be visible in the Graphics Area. 7. From the Preferences menu, select Graphics REV. 09/03/2014
34 8. On the Graphics panel, set the value of the ply visualization thickness factor to 100 : *This will cause each ply in the Graphics Area to be displayed with a thickness of 1000 times the actual thickness. 9. Click return. Step 22: View the Model (OPTIONAL STEP) 1. To ROTATE the model: Hold down the Ctrl key on the keyboard, point the cursor anywhere in the Graphics Area, hold down the left mouse button and drag it any direction. 2. To ZOOM IN and ZOOM OUT: Hold down the Ctrl key on the keyboard, point the cursor anywhere in the Graphics Area, and scroll the mouse scroll wheel to zoom in or out. 3. To FIT the entire model in the Graphics Area: Press F on the keyboard. 2. To MASK or UNMASK the mesh for each ply separately: Left-click on the mesh icon ( ) to the left of the name of one of the plies in the model browser to toggle it on or off: 4. To TRANSLATE the model: Hold down the Ctrl key on the keyboard, point the cursor anywhere in the Graphics Area, hold down the right mouse button and drag it any direction REV. 09/03/2014
35 Step 23: Global Output Requests 1. Access the Control Cards panel by clicking Setup > Create > Control Cards 2. Click Next on the panel to source to the page that has GLOBAL_OUTPUT_REQUESTS 3. Click GLOBAL_OUTPUT_REQUESTS and check CSTRAIN and CSTRESS. Set the Type and Options the same as the image below. Step 24: Launch the OptiStruct job. 1. Choose the Analysis page and select the OptiStruct panel. 2. Click save as. A Save file browser window pops up 3. Select the directory where you would like to write the model file and enter the file name, plate.fem, in the File name: field. The.fem file name extension is the suggested extension for OptiStruct input decks. 4. Click Save. Note the name and location of the plate.fem file now displays in the input file: field. 5. Set the memory toggle, located in the center of the panel, to memory default. 6. Set the run options toggle, located on the left side of the panel, to analysis. 7. Set the export options: toggle, underneath the run options switch, to all. *Make sure that the settings are the same as the ones shown below: 8. Click OptiStruct REV. 09/03/2014
36 This exports the input file and launches the job. If the job is successful, new results files can be seen in the directory where the model file was written. The "plate.out" file is a good place to look for error messages that will help to debug the input deck if any errors are present. The default files written to your directory are: plate.html plate.out plate.res plate.stat plate.h3d HTML report of the analysis, giving a summary of the problem formulation and the analysis results. ASCII output file containing specific information on the file set up, the set up of your optimization problem, estimate for the amount of RAM and disk space required for the run, information for each optimization iteration, and compute time information. Review this file for warnings and errors. HyperMesh binary results file. Summary of analysis process, providing CPU information for each step during analysis process. HyperView binary result file. The pop-up window should display ANALYSIS COMPLETED in the upper left text box and ==== Job completed ==== in the lower text box REV. 09/03/2014
37 Step 25: Post-process the OptiStruct job 1. Open HyperView one of the following ways: In the HyperWorks Solver View pop-up window, click on the Results button (to the left of View and the Close button) at the bottom-right corner of window. Close the pop-up window. On the OptiStruct panel, click on the green HyperView button. HyperView will open and automatically load the H3D file from the OptiStruct job for post-processing. Step 26: View the results in HyperView 1. Make sure the view is in the standard XY view by clicking on the XY Top Plane View icon near the top of the HyperMesh window (right under the pull-down menus): 2. Click on the Contour button: The Contour panel now appears REV. 09/03/2014
38 3. Click on the highlighted yellow Components button, then select All. 4. Under Result type: select Composite Stresses (s). 5. Select Normal X Stress from the second drop-down menu. 6. Select Ply 1 under the Layers option. 7. Make sure that the Contour panel settings are the same as the settings in the image below: 8. Click Apply 9. Change the Layers option to Ply 2, 3, or 4 to view the results in each individual ply. You must click Apply each time. Step 27: Query Results 1. Query results by clicking Results > Query. Change the selector to elements and click on an element near the center of the plate. Conclusion 1. Save the HyperView session one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose File > Save > Session. Just below the menu bar, click on the Save Session button: 2. Close HyperView: File > Exit. 3. Save the HyperMesh file one of the following ways: From the menu bar, choose File > Save. Just below the menu bar, click on the Save Model button: 4. Close HyperMesh: File > Exit. This completes the Composite Finite Element Project Tutorial REV. 09/03/2014
39 REV. 09/03/2014
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v12.0, OptiStruct, HyperView This tutorial
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v12.0, OptiStruct, HyperView This tutorial
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos, Sanjay Nainani Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v2017.2, OptiStruct,
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Michael Schraiber, Dimitri Soteropoulos, Sanjay Nainani Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop v2017.2, OptiStruct,
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PROPPED CANTILEVER BEAM
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PROPPED CANTILEVER BEAM Problem Description: Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Venkat Putcha, Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop 12.0, OptiStruct,
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PROPPED CANTILEVER BEAM Problem Description: Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Venkat Putcha, Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: HyperMesh Desktop 12.0, OptiStruct,
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PROPPED CANTILEVER BEAM
 FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PROPPED CANTILEVER BEAM Problem Description: Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Venkat Putcha, Dimitri Soteropoulos, Sanjay Nainani Programs Utilized: HyperMesh
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PROPPED CANTILEVER BEAM Problem Description: Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Venkat Putcha, Dimitri Soteropoulos, Sanjay Nainani Programs Utilized: HyperMesh
Exercise 9a - Analysis Setup and Loading
 Exercise 9a - Analysis Setup and Loading This exercise will focus on setting up a model for analysis. At the end of this exercise, you will run an analysis in OptiStruct. While this exercise is focused
Exercise 9a - Analysis Setup and Loading This exercise will focus on setting up a model for analysis. At the end of this exercise, you will run an analysis in OptiStruct. While this exercise is focused
FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS
 Problem Description: FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: Abaqus/CAE 6.11-2 This tutorial explains how to build
Problem Description: FINITE ELEMENT ANALYSIS OF A PLANAR TRUSS Instructor: Professor James Sherwood Revised: Dimitri Soteropoulos Programs Utilized: Abaqus/CAE 6.11-2 This tutorial explains how to build
RD-1070: Analysis of an Axi-symmetric Structure using RADIOSS
 RADIOSS, MotionSolve, and OptiStruct RD-1070: Analysis of an Axi-symmetric Structure using RADIOSS In this tutorial, you will learn the method of modeling an axi- symmetry problem in RADIOSS. The figure
RADIOSS, MotionSolve, and OptiStruct RD-1070: Analysis of an Axi-symmetric Structure using RADIOSS In this tutorial, you will learn the method of modeling an axi- symmetry problem in RADIOSS. The figure
Exercise 1a: Interacting With HyperMesh
 Exercise 1a: Interacting With HyperMesh This exercise will cover many of the basic concepts that are central to many of the features in HyperMesh. By the end of this exercise you should be familiar with
Exercise 1a: Interacting With HyperMesh This exercise will cover many of the basic concepts that are central to many of the features in HyperMesh. By the end of this exercise you should be familiar with
Defining ABAQUS Contacts for 3-D Models in HyperMesh - HM-4320
 Defining ABAQUS Contacts for 3-D Models in HyperMesh - HM-4320 For this tutorial it is recommended that you complete the introductory tutorial, Getting Started with HyperMesh - HM-1000. This tutorial explains
Defining ABAQUS Contacts for 3-D Models in HyperMesh - HM-4320 For this tutorial it is recommended that you complete the introductory tutorial, Getting Started with HyperMesh - HM-1000. This tutorial explains
Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu.
 4. MEMBRANE MODEL 1.1. Preprocessing with surface elements Start New Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu. Create a
4. MEMBRANE MODEL 1.1. Preprocessing with surface elements Start New Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu. Create a
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Getting Started with Abaqus: Interactive Edition Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you
Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam
 Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Problem Specification Finite Element Course ANSYS Mechanical Tutorial Tutorial 3 Cantilever Beam Consider the beam in the figure below. It is clamped on the left side and has a point force of 8kN acting
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10
 Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Torsional-lateral buckling large displacement analysis with a simple beam using Abaqus 6.10 This document contains an Abaqus tutorial for performing a buckling analysis using the finite element program
Obtaining Meshable Surfaces
 Chapter 2 Obtaining Meshable Surfaces Exercise 2a: Importing and Repairing CAD Geometry Overview of Exercise Strategy: Import CAD geometry and organize your model using the Assembly Hierarchy. Evaluate
Chapter 2 Obtaining Meshable Surfaces Exercise 2a: Importing and Repairing CAD Geometry Overview of Exercise Strategy: Import CAD geometry and organize your model using the Assembly Hierarchy. Evaluate
Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu.
 1. BEAM MODEL Start New Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu. Create a new model with the New Icon. In the dialogue
1. BEAM MODEL Start New Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu. Create a new model with the New Icon. In the dialogue
ME 442. Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1
 ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
ME 442 Overview Marc/Mentat-2011 Tutorial-1 The purpose of this tutorial is to introduce the new user to the MSC/MARC/MENTAT finite element program. It should take about one hour to complete. The MARC/MENTAT
Case Study 1: Piezoelectric Rectangular Plate
 Case Study 1: Piezoelectric Rectangular Plate PROBLEM - 3D Rectangular Plate, k31 Mode, PZT4, 40mm x 6mm x 1mm GOAL Evaluate the operation of a piezoelectric rectangular plate having electrodes in the
Case Study 1: Piezoelectric Rectangular Plate PROBLEM - 3D Rectangular Plate, k31 Mode, PZT4, 40mm x 6mm x 1mm GOAL Evaluate the operation of a piezoelectric rectangular plate having electrodes in the
ME 475 FEA of a Composite Panel
 ME 475 FEA of a Composite Panel Objectives: To determine the deflection and stress state of a composite panel subjected to asymmetric loading. Introduction: Composite laminates are composed of thin layers
ME 475 FEA of a Composite Panel Objectives: To determine the deflection and stress state of a composite panel subjected to asymmetric loading. Introduction: Composite laminates are composed of thin layers
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description
 Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
Tutorial 1: Welded Frame - Problem Description Introduction In this first tutorial, we will analyse a simple frame: firstly as a welded frame, and secondly as a pin jointed truss. In each case, we will
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Stepped Shaft in Axial Tension Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Contents: Problem Specification 3 Learning Goals 4 Pre-Analysis & Start Up 5 Calculation
Modal Analysis of a Steel Frame
 Modal Analysis of a Steel Frame Name: Sushanth Kumareshwar Panchaxrimath Department: Mechanical Engineering Course: Powertrain NVH of Electrified Vehicles Date: 11/26/2016 SUMMARY A dynamic modal analysis
Modal Analysis of a Steel Frame Name: Sushanth Kumareshwar Panchaxrimath Department: Mechanical Engineering Course: Powertrain NVH of Electrified Vehicles Date: 11/26/2016 SUMMARY A dynamic modal analysis
v Annotation Tools GMS 10.4 Tutorial Use scale bars, North arrows, floating images, text boxes, lines, arrows, circles/ovals, and rectangles.
 v. 10.4 GMS 10.4 Tutorial Use scale bars, North arrows, floating images, text boxes, lines, arrows, circles/ovals, and rectangles. Objectives GMS includes a number of annotation tools that can be used
v. 10.4 GMS 10.4 Tutorial Use scale bars, North arrows, floating images, text boxes, lines, arrows, circles/ovals, and rectangles. Objectives GMS includes a number of annotation tools that can be used
Abaqus CAE Tutorial 1: 2D Plane Truss
 ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 1: 2D Plane Truss Lab TA: Xiaotong Huo EN 3029B xh0381@mun.ca Download link for Abaqus student edition: http://academy.3ds.com/software/simulia/abaqus-student-edition/
ENGI 7706/7934: Finite Element Analysis Abaqus CAE Tutorial 1: 2D Plane Truss Lab TA: Xiaotong Huo EN 3029B xh0381@mun.ca Download link for Abaqus student edition: http://academy.3ds.com/software/simulia/abaqus-student-edition/
Exercise 12a - Post Processing for Stress/Strain Analysis
 Exercise 12a - Post Processing for Stress/Strain Analysis This tutorial will walk through some of the most basic features of HyperView. Note: The model results used for this tutorial had an unrealistic,
Exercise 12a - Post Processing for Stress/Strain Analysis This tutorial will walk through some of the most basic features of HyperView. Note: The model results used for this tutorial had an unrealistic,
ANSYS Workbench Guide
 ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
ANSYS Workbench Guide Introduction This document serves as a step-by-step guide for conducting a Finite Element Analysis (FEA) using ANSYS Workbench. It will cover the use of the simulation package through
Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE
 Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
Appendix B: Creating and Analyzing a Simple Model in Abaqus/CAE The following section is a basic tutorial for the experienced Abaqus user. It leads you through the Abaqus/CAE modeling process by visiting
Free-Shape Optimization of a 3-D Bracket using the Free-shape Method
 Free-Shape Optimization of a 3-D Bracket using the Free-shape Method In this exercise, shape optimization on a solid bracket model will be performed using the Free- Shape optimization method. The objective
Free-Shape Optimization of a 3-D Bracket using the Free-shape Method In this exercise, shape optimization on a solid bracket model will be performed using the Free- Shape optimization method. The objective
Pre-Lab Excel Problem
 Pre-Lab Excel Problem Read and follow the instructions carefully! Below you are given a problem which you are to solve using Excel. If you have not used the Excel spreadsheet a limited tutorial is given
Pre-Lab Excel Problem Read and follow the instructions carefully! Below you are given a problem which you are to solve using Excel. If you have not used the Excel spreadsheet a limited tutorial is given
XnView 1.9. a ZOOMERS guide. Introduction...2 Browser Mode... 5 Image View Mode...15 Printing Image Editing...28 Configuration...
 XnView 1.9 a ZOOMERS guide Introduction...2 Browser Mode... 5 Image View Mode...15 Printing... 22 Image Editing...28 Configuration... 36 Written by Chorlton Workshop for hsbp Introduction This is a guide
XnView 1.9 a ZOOMERS guide Introduction...2 Browser Mode... 5 Image View Mode...15 Printing... 22 Image Editing...28 Configuration... 36 Written by Chorlton Workshop for hsbp Introduction This is a guide
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies
 Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models
 Exercise A Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models Beam and Brick Elements Objective: Geometry: Determine the stress distribution in the spur gears when a moment of 93.75 in-lb is
Exercise A Spur Gears Static Stress Analysis with Linear Material Models Beam and Brick Elements Objective: Geometry: Determine the stress distribution in the spur gears when a moment of 93.75 in-lb is
XnView Image Viewer. a ZOOMERS guide
 XnView Image Viewer a ZOOMERS guide Introduction...2 Browser Mode... 5 Image View Mode...14 Printing... 22 Image Editing...26 Configuration... 34 Note that this guide is for XnView version 1.8. The current
XnView Image Viewer a ZOOMERS guide Introduction...2 Browser Mode... 5 Image View Mode...14 Printing... 22 Image Editing...26 Configuration... 34 Note that this guide is for XnView version 1.8. The current
Exercise 1a: Topology Optimization of a Control Arm
 Exercise 1a: Topology Optimization of a Control Arm The purpose of this exercise is to determine the basic minimum information required to run a topology optimization exercise. The control arm can be considered
Exercise 1a: Topology Optimization of a Control Arm The purpose of this exercise is to determine the basic minimum information required to run a topology optimization exercise. The control arm can be considered
Composite Bike Frame Optimization (Updated to , by Premanand Suryavanshi)
 Composite Bike Frame Optimization (Updated to 2017.2, by Premanand Suryavanshi) In this tutorial, you learn the steps required to perform a ply orientation optimization for a composite structure. The figure
Composite Bike Frame Optimization (Updated to 2017.2, by Premanand Suryavanshi) In this tutorial, you learn the steps required to perform a ply orientation optimization for a composite structure. The figure
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis
 Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis
 Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Exercise 2: Bike Frame Analysis This exercise will analyze a new, innovative mountain bike frame design under structural loads. The objective is to determine the maximum stresses in the frame due to the
Introduction To Finite Element Analysis
 Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Creating a Part In this part of the tutorial we will introduce you to some basic modelling concepts. If you are already familiar with modelling in Pro Engineer you will find this section very easy. Before
Basic Modeling 1 Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006
 Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents Contents 3 1 5 1.1 Start Tekla Structures 6 1.2 Create a New Model BasicModel1 7 1.3 Create Grids 10 1.4
Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents Contents 3 1 5 1.1 Start Tekla Structures 6 1.2 Create a New Model BasicModel1 7 1.3 Create Grids 10 1.4
2D Tutorial. Project Description: Running VisualAnalysis: Setting Up the Project:
 2D Tutorial Project Description: This project has been set-up to demonstrate the basic features of VisualAnalysis. You will model and analyze the following two-dimensional frame with a curved glue-laminated
2D Tutorial Project Description: This project has been set-up to demonstrate the basic features of VisualAnalysis. You will model and analyze the following two-dimensional frame with a curved glue-laminated
BioIRC solutions. CFDVasc manual
 BioIRC solutions CFDVasc manual Main window of application is consisted from two parts: toolbar - which consist set of button for accessing variety of present functionalities image area area in which is
BioIRC solutions CFDVasc manual Main window of application is consisted from two parts: toolbar - which consist set of button for accessing variety of present functionalities image area area in which is
Installation Guide. Beginners guide to structural analysis
 Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
Installation Guide To install Abaqus, students at the School of Civil Engineering, Sohngaardsholmsvej 57, should log on to \\studserver, whereas the staff at the Department of Civil Engineering should
Exercise 2b: Applying Entity Attributes, Masking, and Creating Groups
 Exercise 2b: Applying Entity Attributes, Masking, and Creating Groups This exercise uses the model file, truck.key and the corresponding d3plot file as the results file. Step 1: Turning components on and
Exercise 2b: Applying Entity Attributes, Masking, and Creating Groups This exercise uses the model file, truck.key and the corresponding d3plot file as the results file. Step 1: Turning components on and
Exercise 1: Axle Structural Static Analysis
 Exercise 1: Axle Structural Static Analysis The purpose of this exercise is to cover the basic functionality of the Mechanical Toolbar (MTB) in the context of performing an actual analysis. Details of
Exercise 1: Axle Structural Static Analysis The purpose of this exercise is to cover the basic functionality of the Mechanical Toolbar (MTB) in the context of performing an actual analysis. Details of
Exercise Guide. Published: August MecSoft Corpotation
 VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
VisualCAD Exercise Guide Published: August 2018 MecSoft Corpotation Copyright 1998-2018 VisualCAD 2018 Exercise Guide by Mecsoft Corporation User Notes: Contents 2 Table of Contents About this Guide 4
Simulation of fiber reinforced composites using NX 8.5 under the example of a 3- point-bending beam
 R Simulation of fiber reinforced composites using NX 8.5 under the example of a 3- point-bending beam Ralph Kussmaul Zurich, 08-October-2015 IMES-ST/2015-10-08 Simulation of fiber reinforced composites
R Simulation of fiber reinforced composites using NX 8.5 under the example of a 3- point-bending beam Ralph Kussmaul Zurich, 08-October-2015 IMES-ST/2015-10-08 Simulation of fiber reinforced composites
Tutorial 2: Particles convected with the flow along a curved pipe.
 Tutorial 2: Particles convected with the flow along a curved pipe. Part 1: Creating an elbow In part 1 of this tutorial, you will create a model of a 90 elbow featuring a long horizontal inlet and a short
Tutorial 2: Particles convected with the flow along a curved pipe. Part 1: Creating an elbow In part 1 of this tutorial, you will create a model of a 90 elbow featuring a long horizontal inlet and a short
PLAY VIDEO. Fences can be any shape from a simple rectangle to a multisided polygon, even a circle.
 Chapter Eight Groups PLAY VIDEO INTRODUCTION There will be times when you need to perform the same operation on several elements. Although this can be done by repeating the operation for each individual
Chapter Eight Groups PLAY VIDEO INTRODUCTION There will be times when you need to perform the same operation on several elements. Although this can be done by repeating the operation for each individual
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND
 1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY
 1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
1 FOUNDATION IN OVERCONSOLIDATED CLAY In this chapter a first application of PLAXIS 3D is considered, namely the settlement of a foundation in clay. This is the first step in becoming familiar with the
TUTORIAL 03: RHINO DRAWING & ORGANIZATIONAL AIDS. By Jeremy L Roh, Professor of Digital Methods I UNC Charlotte s School of Architecture
 TUTORIAL 03: RHINO DRAWING & ORGANIZATIONAL AIDS By Jeremy L Roh, Professor of Digital Methods I UNC Charlotte s School of Architecture Modeling in 3D requires the use of various drawing and organizational
TUTORIAL 03: RHINO DRAWING & ORGANIZATIONAL AIDS By Jeremy L Roh, Professor of Digital Methods I UNC Charlotte s School of Architecture Modeling in 3D requires the use of various drawing and organizational
Quick Guide for Photoshop CC Basics April 2016 Training:
 Photoshop CC Basics Creating a New File 1. Click File > New 2. Keep Default Photoshop Size selected in the Preset drop-down list. 3. Click OK. Showing Rulers 1. On the Menu bar, click View. 2. Click Rulers.
Photoshop CC Basics Creating a New File 1. Click File > New 2. Keep Default Photoshop Size selected in the Preset drop-down list. 3. Click OK. Showing Rulers 1. On the Menu bar, click View. 2. Click Rulers.
v Introduction to WMS WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Prerequisite Tutorials None Required Components Data Map
 s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
s v. 11.0 WMS 11.0 Tutorial Become familiar with the WMS interface Objectives Import files into WMS and change modules and display options to become familiar with the WMS interface. Prerequisite Tutorials
Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran
 Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
Appendix B Finite Element Analysis Using NEi Nastran B.1 INTRODUCTION NEi Nastran is engineering analysis and simulation software developed by Noran Engineering, Inc. NEi Nastran is a general purpose finite
How to Launch an Online Course for the first time
 How to Launch an Online Course for the first time This tutorial walks you through the steps to find, view and launch online courses that you have purchased using Council Connect. Important information
How to Launch an Online Course for the first time This tutorial walks you through the steps to find, view and launch online courses that you have purchased using Council Connect. Important information
Abaqus 6.9SE Handout
 MANE 4240/ CIVL 4240: Introduction to Finite Elements Abaqus 6.9SE Handout Professor Suvranu De Department of Mechanical, Aerospace and Nuclear Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Table of Contents
MANE 4240/ CIVL 4240: Introduction to Finite Elements Abaqus 6.9SE Handout Professor Suvranu De Department of Mechanical, Aerospace and Nuclear Engineering Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute Table of Contents
Optimizing ImmuNet. In this chapter: Optimizing Browser Performance Running Reports with Adobe Acrobat Reader Efficient Screen Navigation
 Optimizing ImmuNet In this chapter: Optimizing Browser Performance Running Reports with Adobe Acrobat Reader Efficient Screen Navigation Optimizing Browser Performance Unless instructed to do otherwise,
Optimizing ImmuNet In this chapter: Optimizing Browser Performance Running Reports with Adobe Acrobat Reader Efficient Screen Navigation Optimizing Browser Performance Unless instructed to do otherwise,
Optimizing GRITS. In this chapter:
 Optimizing GRITS In this chapter: Creating Favorites and Shortcuts Optimizing Browser Performance Running Reports with Acrobat Reader Efficient Screen Navigation Creating Favorites and Shortcuts To access
Optimizing GRITS In this chapter: Creating Favorites and Shortcuts Optimizing Browser Performance Running Reports with Acrobat Reader Efficient Screen Navigation Creating Favorites and Shortcuts To access
Multiframe Windows Version 16. User Manual
 Multiframe Windows Version 16 User Manual Bentley Systems, Incorporated 2013 License & Copyright Multiframe Program & User Manual 2013 Bentley Systems, Incorporated iii Table of Contents License & Copyright...
Multiframe Windows Version 16 User Manual Bentley Systems, Incorporated 2013 License & Copyright Multiframe Program & User Manual 2013 Bentley Systems, Incorporated iii Table of Contents License & Copyright...
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide
 Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
Autodesk Fusion 360 Training: The Future of Making Things Attendee Guide Abstract After completing this workshop, you will have a basic understanding of editing 3D models using Autodesk Fusion 360 TM to
MSC/PATRAN LAMINATE MODELER COURSE PAT 325 Workbook
 MSC/PATRAN LAMINATE MODELER COURSE PAT 325 Workbook P3*V8.0*Z*Z*Z*SM-PAT325-WBK - 1 - - 2 - Table of Contents Page 1 Composite Model of Loaded Flat Plate 2 Failure Criteria for Flat Plate 3 Making Plies
MSC/PATRAN LAMINATE MODELER COURSE PAT 325 Workbook P3*V8.0*Z*Z*Z*SM-PAT325-WBK - 1 - - 2 - Table of Contents Page 1 Composite Model of Loaded Flat Plate 2 Failure Criteria for Flat Plate 3 Making Plies
Two Dimensional Truss
 Two Dimensional Truss Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple 2D Truss problem. This is the first of four introductory ANSYS tutorials. Problem Description Determine the
Two Dimensional Truss Introduction This tutorial was created using ANSYS 7.0 to solve a simple 2D Truss problem. This is the first of four introductory ANSYS tutorials. Problem Description Determine the
Ancient Cell Phone Tracing an Object and Drawing with Layers
 Ancient Cell Phone Tracing an Object and Drawing with Layers 1) Open Corel Draw. Create a blank 8.5 x 11 Document. 2) Go to the Import option and browse to the Graphics 1 > Lessons folder 3) Find the Cell
Ancient Cell Phone Tracing an Object and Drawing with Layers 1) Open Corel Draw. Create a blank 8.5 x 11 Document. 2) Go to the Import option and browse to the Graphics 1 > Lessons folder 3) Find the Cell
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam
 Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
Module 1.7W: Point Loading of a 3D Cantilever Beam Table of Contents Page Number Problem Description 2 Theory 2 Workbench Analysis System 4 Engineering Data 5 Geometry 6 Model 11 Setup 13 Solution 14 Results
DMU Engineering Analysis Review
 Page 1 DMU Engineering Analysis Review Preface Using This Guide Where to Find More Information Conventions What's New? Getting Started Inserting a CATAnalysis Document Using DMU Space Analysis From CATAnalysis
Page 1 DMU Engineering Analysis Review Preface Using This Guide Where to Find More Information Conventions What's New? Getting Started Inserting a CATAnalysis Document Using DMU Space Analysis From CATAnalysis
Guide to WB Annotations
 Guide to WB Annotations 04 May 2016 Annotations are a powerful new feature added to Workbench v1.2.0 (Released May 2016) for placing text and symbols within wb_view tabs and windows. They enable generation
Guide to WB Annotations 04 May 2016 Annotations are a powerful new feature added to Workbench v1.2.0 (Released May 2016) for placing text and symbols within wb_view tabs and windows. They enable generation
Tutorial #3 LSDyna: Pop Can Crushing Analysis By C. Daley
 Engineering 9093 Ice Class Ship Structures Tutorial #3 LSDyna: Pop Can Crushing Analysis By C. Daley Overview For a general introduction of LSDyna see Tut #1. Unlike most finite element programs LSDyna
Engineering 9093 Ice Class Ship Structures Tutorial #3 LSDyna: Pop Can Crushing Analysis By C. Daley Overview For a general introduction of LSDyna see Tut #1. Unlike most finite element programs LSDyna
Assembly Design: A Hands-On Experience
 Mark Thompson Sr. Application Engineer Assembly Design: A Hands-On Experience Solid Edge University 2014 May 12-14, Atlanta, GA, USA SOLID EDGE UNIVERSITY 2014 Re-imagine What s Possible #SEU14 Agenda
Mark Thompson Sr. Application Engineer Assembly Design: A Hands-On Experience Solid Edge University 2014 May 12-14, Atlanta, GA, USA SOLID EDGE UNIVERSITY 2014 Re-imagine What s Possible #SEU14 Agenda
Quick Tips to Using I-DEAS. Learn about:
 Learn about: Quick Tips to Using I-DEAS I-DEAS Tutorials: Fundamental Skills windows mouse buttons applications and tasks menus icons part modeling viewing selecting data management using the online tutorials
Learn about: Quick Tips to Using I-DEAS I-DEAS Tutorials: Fundamental Skills windows mouse buttons applications and tasks menus icons part modeling viewing selecting data management using the online tutorials
Linear Buckling Analysis of a Plate
 Workshop 9 Linear Buckling Analysis of a Plate Objectives Create a geometric representation of a plate. Apply a compression load to two apposite sides of the plate. Run a linear buckling analysis. 9-1
Workshop 9 Linear Buckling Analysis of a Plate Objectives Create a geometric representation of a plate. Apply a compression load to two apposite sides of the plate. Run a linear buckling analysis. 9-1
Exercise 2a: Load, Animate and Review a Model
 Exercise 2a: Load, Animate and Review a Model This exercise uses the file bumper_deck.key and the corresponding d3plot. Step 1: Load the solver input and result files, bumper_deck.key and d3plot. 1. From
Exercise 2a: Load, Animate and Review a Model This exercise uses the file bumper_deck.key and the corresponding d3plot. Step 1: Load the solver input and result files, bumper_deck.key and d3plot. 1. From
User Interface Guide
 User Interface Guide 1 Contents Overview... 3 Tabmenu... 4 Design modes... 4 Tool groups... 5 Design function groups... 5 Main menu... 6 Toolbars... 7 Drawing area... 9 Status bar... 11 Coordinate box...
User Interface Guide 1 Contents Overview... 3 Tabmenu... 4 Design modes... 4 Tool groups... 5 Design function groups... 5 Main menu... 6 Toolbars... 7 Drawing area... 9 Status bar... 11 Coordinate box...
GUIDE TO View3D. Introduction to View3D
 View3D Guide Introduction to View3D... 1 Starting Hampson-Russell Software... 2 Starting View3D... 4 A Brief Summary of the View3D Process... 8 Loading the Seismic and Horizon Data... 8 Viewing the Data...
View3D Guide Introduction to View3D... 1 Starting Hampson-Russell Software... 2 Starting View3D... 4 A Brief Summary of the View3D Process... 8 Loading the Seismic and Horizon Data... 8 Viewing the Data...
Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals
 1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
Parametric Modeling with UGS NX 4
 Parametric Modeling with UGS NX 4 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling
Parametric Modeling with UGS NX 4 Randy H. Shih Oregon Institute of Technology SDC PUBLICATIONS Schroff Development Corporation www.schroff.com www.schroff-europe.com 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling
Module 1B: Parallel-Line Flat Pattern Development of Sheet- Metal Folded Model Wrapping the 3D Space of A Truncated Right Prism
 Inventor (5) Module 1B: 1B- 1 Module 1B: Parallel-Line Flat Pattern Development of Sheet- Metal Folded Model Wrapping the 3D Space of A Truncated Right Prism In this Module, we will learn how to create
Inventor (5) Module 1B: 1B- 1 Module 1B: Parallel-Line Flat Pattern Development of Sheet- Metal Folded Model Wrapping the 3D Space of A Truncated Right Prism In this Module, we will learn how to create
Recipes4Success. Draw and Animate a Rocket Ship. Frames 5 - Drawing Tools
 Recipes4Success You can use the drawing tools and path animation tools in Frames to create illustrated cartoons. In this Recipe, you will draw and animate a rocket ship. 2012. All Rights Reserved. This
Recipes4Success You can use the drawing tools and path animation tools in Frames to create illustrated cartoons. In this Recipe, you will draw and animate a rocket ship. 2012. All Rights Reserved. This
SAPPHIRE Viewer: The Collaboration Tool
 SAPPHIRE Viewer: The Collaboration Tool MiTek SAPPHIRE Viewer is a scaled down version of SAPPHIRE Structure that allows users to open, view, comment on, and print Structure files. This free application
SAPPHIRE Viewer: The Collaboration Tool MiTek SAPPHIRE Viewer is a scaled down version of SAPPHIRE Structure that allows users to open, view, comment on, and print Structure files. This free application
TexGraf4 GRAPHICS PROGRAM FOR UTEXAS4. Stephen G. Wright. May Shinoak Software Austin, Texas
 TexGraf4 GRAPHICS PROGRAM FOR UTEXAS4 By Stephen G. Wright May 1999 Shinoak Software Austin, Texas Copyright 1999, 2007 by Stephen G. Wright - All Rights Reserved i TABLE OF CONTENTS Page LIST OF TABLES...v
TexGraf4 GRAPHICS PROGRAM FOR UTEXAS4 By Stephen G. Wright May 1999 Shinoak Software Austin, Texas Copyright 1999, 2007 by Stephen G. Wright - All Rights Reserved i TABLE OF CONTENTS Page LIST OF TABLES...v
Press the Plus + key to zoom in. Press the Minus - key to zoom out. Scroll the mouse wheel away from you to zoom in; towards you to zoom out.
 Navigate Around the Map Interactive maps provide many choices for displaying information, searching for more details, and moving around the map. Most navigation uses the mouse, but at times you may also
Navigate Around the Map Interactive maps provide many choices for displaying information, searching for more details, and moving around the map. Most navigation uses the mouse, but at times you may also
Exercise 1. 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method
 Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method Contents Learn how to... 1 Given... 2 Questions... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 2 A. Preprocessor (Setting up the Model)... 3 A.1
Exercise 1 3-Point Bending Using the GUI and the Bottom-up-Method Contents Learn how to... 1 Given... 2 Questions... 2 Taking advantage of symmetries... 2 A. Preprocessor (Setting up the Model)... 3 A.1
SimLab 14.3 Release Notes
 SimLab 14.3 Release Notes Highlights SimLab 14.0 introduced new graphical user interface and since then this has evolved continuously in subsequent versions. In addition, many new core features have been
SimLab 14.3 Release Notes Highlights SimLab 14.0 introduced new graphical user interface and since then this has evolved continuously in subsequent versions. In addition, many new core features have been
for ArcSketch Version 1.1 ArcSketch is a sample extension to ArcGIS. It works with ArcGIS 9.1
 ArcSketch User Guide for ArcSketch Version 1.1 ArcSketch is a sample extension to ArcGIS. It works with ArcGIS 9.1 ArcSketch allows the user to quickly create, or sketch, features in ArcMap using easy-to-use
ArcSketch User Guide for ArcSketch Version 1.1 ArcSketch is a sample extension to ArcGIS. It works with ArcGIS 9.1 ArcSketch allows the user to quickly create, or sketch, features in ArcMap using easy-to-use
The original image. Let s get started! The final result.
 Vertical Photo Panels Effect In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create the illusion that a single photo is being displayed as a series of vertical panels. It may look complicated, but as we
Vertical Photo Panels Effect In this Photoshop tutorial, we ll learn how to create the illusion that a single photo is being displayed as a series of vertical panels. It may look complicated, but as we
Analysis Steps 1. Start Abaqus and choose to create a new model database
 Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
Source: Online tutorials for ABAQUS Problem Description The two dimensional bridge structure, which consists of steel T sections (b=0.25, h=0.25, I=0.125, t f =t w =0.05), is simply supported at its lower
Mn/DOT MnCMAT Crash Analysis Application Help
 Mn/DOT MnCMAT Crash Analysis Application Contents Login... 5 User Login Dialog... 5 Login... 5 Request Access Dialog... 5 Forgotten Password Dialog... 6 Create/Open Project... 7 Create/Open Project Dialog...
Mn/DOT MnCMAT Crash Analysis Application Contents Login... 5 User Login Dialog... 5 Login... 5 Request Access Dialog... 5 Forgotten Password Dialog... 6 Create/Open Project... 7 Create/Open Project Dialog...
RAPIDMAP Geocortex HTML5 Viewer Manual
 RAPIDMAP Geocortex HTML5 Viewer Manual This site was developed using the evolving HTML5 web standard and should work in most modern browsers including IE, Safari, Chrome and Firefox. Even though it was
RAPIDMAP Geocortex HTML5 Viewer Manual This site was developed using the evolving HTML5 web standard and should work in most modern browsers including IE, Safari, Chrome and Firefox. Even though it was
Roof Designer USER S GUIDE
 Roof Designer USER S GUIDE Roof Designer-1 Roof Designer-2 Roof Designer The Roof Designer makes it easy to define and place custom roofs in your project. You can start the Roof Designer independently,
Roof Designer USER S GUIDE Roof Designer-1 Roof Designer-2 Roof Designer The Roof Designer makes it easy to define and place custom roofs in your project. You can start the Roof Designer independently,
Exporting distribution lists from Thunderbird to Outlook
 Exporting distribution lists from Thunderbird to Outlook PLEASE NOTE: Do not export the lists under Distribution Lists in your Thunderbird Address Book as these will no longer be maintained on the new
Exporting distribution lists from Thunderbird to Outlook PLEASE NOTE: Do not export the lists under Distribution Lists in your Thunderbird Address Book as these will no longer be maintained on the new
Introduction And Overview ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
 Introduction And Overview 2006 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary The ANSYS Workbench represents more than a general purpose engineering tool. It provides a highly integrated engineering
Introduction And Overview 2006 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary The ANSYS Workbench represents more than a general purpose engineering tool. It provides a highly integrated engineering
First Animated Model Yellow Submarine
 Course: 3D Design Title: First Animated Model Yellow Submarine Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig (May 2012) First Animated Model Yellow Submarine Most of you are perhaps too young
Course: 3D Design Title: First Animated Model Yellow Submarine Blender: Version 2.6X Level: Beginning Author; Neal Hirsig (May 2012) First Animated Model Yellow Submarine Most of you are perhaps too young
Introducing Gupta Report Builder
 Business Reporting Chapter 1 Introducing Gupta Report Builder You can use Report Builder to design reports. This chapter describes: Our approach to building reports. Some of the reports you can build.
Business Reporting Chapter 1 Introducing Gupta Report Builder You can use Report Builder to design reports. This chapter describes: Our approach to building reports. Some of the reports you can build.
Lesson 1: Creating T- Spline Forms. In Samples section of your Data Panel, browse to: Fusion 101 Training > 03 Sculpt > 03_Sculpting_Introduction.
 3.1: Sculpting Sculpting in Fusion 360 allows for the intuitive freeform creation of organic solid bodies and surfaces by leveraging the T- Splines technology. In the Sculpt Workspace, you can rapidly
3.1: Sculpting Sculpting in Fusion 360 allows for the intuitive freeform creation of organic solid bodies and surfaces by leveraging the T- Splines technology. In the Sculpt Workspace, you can rapidly
Exercise 5a - Remeshing and Modifying an Orphaned Mesh
 Exercise 5a - Remeshing and Modifying an Orphaned Mesh In this exercise, you will rework an orphan mesh using the Automesh panel, Imprint panel, and some of the utilities in the Geom/Mesh page of the Utility
Exercise 5a - Remeshing and Modifying an Orphaned Mesh In this exercise, you will rework an orphan mesh using the Automesh panel, Imprint panel, and some of the utilities in the Geom/Mesh page of the Utility
Tutorial- Tetrahedral-meshing of a Steering Wheel
 Tutorial- Tetrahedral-meshing of a Steering Wheel (Written by Moritz Günther, Student at Altair) Updated to 2017.2 by Premanand Suryavanshi 1. Click on file open steering_wheel_tetra.hm. Now your model
Tutorial- Tetrahedral-meshing of a Steering Wheel (Written by Moritz Günther, Student at Altair) Updated to 2017.2 by Premanand Suryavanshi 1. Click on file open steering_wheel_tetra.hm. Now your model
Creating a Text Frame. Create a Table and Type Text. Pointer Tool Text Tool Table Tool Word Art Tool
 Pointer Tool Text Tool Table Tool Word Art Tool Picture Tool Clipart Tool Creating a Text Frame Select the Text Tool with the Pointer Tool. Position the mouse pointer where you want one corner of the text
Pointer Tool Text Tool Table Tool Word Art Tool Picture Tool Clipart Tool Creating a Text Frame Select the Text Tool with the Pointer Tool. Position the mouse pointer where you want one corner of the text
SolidWorks Intro Part 1b
 SolidWorks Intro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part We ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select File New Templates IPSpart If the SolidWorks
SolidWorks Intro Part 1b Dave Touretzky and Susan Finger 1. Create a new part We ll create a CAD model of the 2 ½ D key fob below to make on the laser cutter. Select File New Templates IPSpart If the SolidWorks
Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals
 2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded Solid Models Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Procedure Create 2-D Sketches Understand the "Shape before Size" Approach Use
2-1 Chapter 2 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Extruded Solid Models Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Procedure Create 2-D Sketches Understand the "Shape before Size" Approach Use
Tutorial 10: Composite impact using multi-layered shell elements
 Tutorial 10 Impact of a Composite Disc using Multilayered Shell Elements Problem description Outline Analysis type(s): Element type(s): Materials law(s): Model options: Key results: Prepared by: Date:
Tutorial 10 Impact of a Composite Disc using Multilayered Shell Elements Problem description Outline Analysis type(s): Element type(s): Materials law(s): Model options: Key results: Prepared by: Date:
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Thermal Stresses in a Bar
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Thermal Stresses in a Bar Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Pre-Analysis Start-Up Geometry Draw Geometry Create
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Thermal Stresses in a Bar Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi, ANSYS Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Pre-Analysis Start-Up Geometry Draw Geometry Create
Quick Start Guide. ARIS Architect. Version 9.8 Service Release 2
 ARIS Architect Version 9.8 Service Release 2 October 2015 This document applies to ARIS Version 9.8 and to all subsequent releases. Specifications contained herein are subject to change and these changes
ARIS Architect Version 9.8 Service Release 2 October 2015 This document applies to ARIS Version 9.8 and to all subsequent releases. Specifications contained herein are subject to change and these changes
