1. Specifications Applicable Conditions Operational Overview of Functions Used Principles of Operation...
|
|
|
- Myron Singleton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 APPLICATION NOTE SH7080 Group Introduction This application note provides information that may be useful in designing software. The note describes how to erase and program the flash memory when the flash reprogram command is received via a UART (Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter) during execution of a user application in the user program mode. In the user program mode, which is one of the three on-board programming modes along with the boot mode and the user boot mode, flash memory can be erased or programmed using any interface. Target Device SH7086 Contents 1. Specifications Applicable Conditions Operational Overview of Functions Used Principles of Operation Description of Software Flowcharts REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 1 of 28
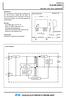
2 1. Specifications SH7080 Group In this sample task, the flash reprogram command is received via a UART while the user application is being executed in the user program mode, and flash memory is erased and programmed. Figure 1 shows the operations of this sample task. SH7080 Group MCU Flash memory Host (PC) Flash erasing/ programming tool and program data RXD1 TXD1 Internal SCI_1 Internal RAM Flash erasing/ programming/ reading program Figure 1 Erasing and Programming Flash Memory in User Boot Mode 2. Applicable Conditions Microcomputer: SH7086 (R5F7086) Operating frequency: Internal clock 80 MHz : Bus clock 40 MHz : Peripheral clock 40 MHz : MTU2 clock 40 MHz : MTU2S clock 80 MHz C Compiler: Renesas Technology V REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 2 of 28
3 3. Operational Overview of Functions Used 3.1 Flash Memory A block diagram of flash memory is shown in figure 2. Block diagram of flash memory Internal address bus Internal data bus (32 bits) FCCS FPCS FECS Module bus FKEY FMATS Control section Memory MAT section FTDAR RAMER User MAT: 512 KB or 256 KB User boot MAT: 12 KB FWE pin Mode pin Operating mode [Legend] FCCS: Flash code control and status register FPCS: Flash program code select register FECS: Flash erasing code select register FKEY: Flash key code register FMATS: Flash MAT select register FTDAR: Flash transfer destination address register RAMER: RAM emulation register Figure 2 Block Diagram of Flash Memory REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 3 of 28
4 The Flash Code Control and Status (FCCS) register consists of the bits for monitoring the FWE pin state, for indicating the error occurrence during execution of flash memory programming or erasing, and the bit for requesting downloading of the internal program. The Flash Program Code Select (FPCS) register is used to select downloading of an internal program related to programming. The Flash Erase Code Select (FECS) register is used to select downloading of an internal program related to erasing. The Flash Key Code (FKEY) register is a software protection register that enables downloading of internal programs, and programming and erasing of flash memory. For these operations, separate key codes are required: one must be written before 1 is written to the SCO bit that enables downloading of an internal program and one must be written before a downloaded programming/erasing program can be executed. The Flash MAT Select (FMATS) register is used to select user MAT or user boot MAT. The Flash Transfer Destination Address Register (FTDAR) is used to specify the address in the internal RAM to which the internal program is to be downloaded. Specify this register before writing 1 to the SCO bit in the FCCS register. The initial register value is H'00, which indicates address H'FFFF9000 in the internal RAM. te: Please see Flash Memory in Section 23 of the SH7080 Group Hardware Manual for details regarding operational specification of each register. REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 4 of 28
5 3.2 Programming/Erasing Interface Parameters SH7080 Group The programming/erasing interface parameters specify the operating frequencies for a downloaded internal program, the user branch destination address, the location for storing program data, the programming destination address, the blocks to be erased, as well as exchanging processing results. The programming/erasing interface parameters are used for the following functions: 1. Download control 2. Initialization before programming or erasing 3. Programming 4. Erasing Table 1 Parameters and Applicable Mode Parameter Name Abbreviation Downloading Initialization Programming Erasing Allocation Download pass/fail result DPFR Ο Internal RAM Flash pass/fail result FPFR* Ο Ο Ο R0 register of the CPU Flash programming/erasing frequency control FPEFEQ Ο R4 register of the CPU Flash user branch address set parameter FUBRA Ο R5 register of the CPU Flash multipurpose address area FMPAR Ο R5 register of the CPU Flash multipurpose data destination area FMPDR Ο R4 register of the CPU Flash erase block select parameter FEBS Ο R4 register of the CPU te: Please see Section 23 Flash Memory of the SH7080 Group Hardware Manual for details regarding operational specification of each register. * For the FPFR parameter, although a processing results of initialization, programming, and erasing operations are returned, the meaning of the bits vary depending on the nature of the processing. Each parameter is readable and writable, and respective initial values are undefined. REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 5 of 28
6 3.3 Specifications of Flash Erasing/Programming SH7080 Group The flash erasing/programming specifications are shown in figure 3. The memory map of the user MAT and internal RAM for this sample task is shown in figure 4. [Internal RAM] [Erasing] User area Address RAMTOP Address FTDAR specification DPFR (Return value: 1 byte) 4 KB x 8 32 KB EB0 to EB7 Download area (size: 3 KB) Erasing program download area Programming program download area System area (15 bytes) FTDAR specification Programming/erasing entry + 16 FTDAR specification Initialization processing entry + 32 Initialization + programming program or initialization + erasing program 64 KB 64 KB 64 KB 64 KB 64 KB EB8 EB9 EB10 EB11 EB12 FTDAR specification KB EB13 User area 64 KB EB14 RAM emulation area 64 KB EB15 User area RAMEND Erase blocks EB1 to EB15 are to be erased. EB0 will not be erased because it contains the communication program. [Programming] Flash memory H' H' H' bytes 128 bytes 128 bytes Data reception (128 bytes) Procedure program Programming control program H'0007FE bytes H'0007FF bytes Data is received from address H' on. Data from address H' on. H'0007FF bytes Figure 3 Flash Erasing/Programming Specifications REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 6 of 28
7 User MAT H' to DF H' to FF H' to FF H' to 0000 FFFF H' to 0007 FFFF H'FFFF 4000 to FFFF 47FF H'FFFF 4800 to FFFF 8FFF H'FFFF 9000 to FFFF 9FFF H'FFFF A000 to FFFF AFFF Vector table User application SCI1 communication program Procedure program storage area Reprogram target area Internal RAM Data area Procedure program execution area Erasing program download area 0000 DPFR (Return value: 1 byte) 0001 to 000F System area (15 bytes) 0010 to 001F Erasing processing entry 0020 to 002F Erasing initialization entry 0030 to 0FFF Erasing initialization + erasing program Programming program download area 0000 DPFR (Return value: 1 byte) 0001 to 000F System area (15 bytes) 0010 to 001F Programming processing entry 0020 to 002F Programming initialization entry 0030 to 0FFF Programming initialization + programming program Figure 4 Memory Map of the User MAT and Internal RAM REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 7 of 28
8 4. Principles of Operation Table 2 Command Specifications Command Command Value Description CMD_GO H 55 Flash erasing/programming request command CMD_READ H AA Flash read request command CMD_ERASE H 77 Flash erasing request command CMD_WRITE H 88 Flash programming request command CMD_WEND H 99 Flash programming end command CMD_OK H 00 OK (normal end response) command CMD_NG H 01 NG (abnormal end response) command CMD_REQUEST H 11 Transmit request command REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 8 of 28
9 The command control sequence in this sample task is shown in figure 5. SH7080 Group Flash erasing/programming tool (UART tool) SH7080 Group MCU Transmit the read data (in 1-byte units) Flash read request command (CMD_READ) Read the flash memory Transmit data equivalent to the specified read request size. Flash erasing/programming request command (CMD_GO) Copy the procedure program to the RAM Execute the procedure program in the RAM Download the erasing program Perform initial setting for erasing Download the programming program CMD_OK Perform initial setting for programming Flash erasing request command (CMD_ERASE) Flash programming request command (CMD_WRITE) Erase the flash memory Receive the programming address and programming size Repeated until there is no more data to be programmed. Transmit request command (CMD_REQUEST) Receive the program data (in 128-byte units) Program the flash memory CMD_OK Confirm the flash programming end command (CMD_WEND) CMD_OK END END Figure 5 Command Control Sequence REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 9 of 28
10 5. Description of Software 5.1 Description of Modules The modules of this sample task are described in table 3. Table 3 Modules Module Name Label Name File Name Description Main routine main() main.c Initial setting of SCI channel 1 Executes the user application program. Performs flash erasing/programming processing when there is a flash erasing/programming request. SCI channel 1 initial setting routine com_init () sci.c Handles SCIF transmit-fifo-data-empty interrupts. SCI_1 receive data CheckRcv() Checks whether receive data is stored in SCRDR. presence check routine SCI_1 n-byte rcvnbyte() Receives data for the number of bytes specified. reception routine SCI_1 1-byte trs1byte() Writes 1 byte to be output serially. transmission routine Erasing program download and SetupFlashErase() flash.c Downloads the erasing program into the RAM and performs initialization. initialization routine Flash erasing routine FlashErase() Erase the specified erase blocks sequentially starting with the EB0 block. Programming program download and initialization routine Flash programming routine Flash programming main routine Flash reading routine SetupFlashWrite() FlashWrite() FlashMain() FlashRead() Downloads the programming program into the RAM and performs initialization. Writes data to the specified address Checks commands and performs erasing/programming. Reads flash memory starting from the specified address for the specified size. REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 10 of 28
11 5.2 Variables Used The variables used in this sample task are described in table 4. Table 4 Variables Used Variable, Label Name Description Used in unsigned char WriteBuff[128] Program data area FlashMain () unsigned char Erasing program download area SetupFlashErase() flash_erase[2048] unsigned char flash_write[2048] Programming program download area SetupFlashWrite() 5.3 Setting the Registers This section describes the setting of registers used in this sample task. te that the settings shown below are used in the sample task and are not initial values Register for Setting the Clock Pulse Generator (CPG) Frequency Control Register (FRQCR) The Frequency Control Register specifies the division ratio of the operating frequency. Setting value: H'0241 Bit Bit Name Setting Value Function 15 0 Reserved 14 to 12 IFC[2:0] 000 Division ratio of the internal clock (Iφ) frequency 000: x 1, 80 MHz when the input clock is 10 MHz 11 to 9 BFC[2:0] 001 Division ratio of the bus clock (Bφ) frequency 001: x 1/2, 40 MHz when the input clock is 10 MHz 8 to 6 PFC[2:0] 001 Division ratio of the peripheral clock (Pφ) frequency 001: x 1/2, 40 MHz when the input clock is 10 MHz 5 to 3 MIFC[2:0] 000 Division ratio of the MTU2S clock (MIφ) frequency 000: x 1, 80 MHz when the input clock is 10 MHz 2 to 0 MPFC[2:0] 001 Division ratio of the MTU2 clock (MPφ) frequency 001: x 1/2, 40 MHz when the input clock is 10 MHz REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 11 of 28
12 5.3.2 Setting the Power-Down Mode Standby Control Register 3 (STBCR3) This register controls the operation of each module in the power-down mode. Setting value: H'EF Bit Bit Name Setting Value Function 7 MSTP15 1 1: Stops clock supply to I 2 C2 module. 6 MSTP14 1 1: Stops clock supply to the SCIF module. 5 MSTP13 1 1: Stops clock supply to SCI_2 module. 4 MSTP12 0 0: SCI_1 module in operation. 3 MSTP11 1 1: Stops clock supply to SCI_0 module. 2 MSTP10 1 1: Stops clock supply to the SSU module. 1 to 0 11 Reserved SH7080 Group Registers for Setting the Serial Communication Interface-1 (SCI_1) Serial Control Register (SCSCR) This register enables or disables transmit and receive operations and interrupt requests, and selects the clock source for transmit and receive operations. Setting value: H'30 Bit Bit Name Setting Value Function 7 TIE 1 0: Disables transmit-fifo-data-empty interrupt (TXIF) requests. 1: Enables transmit-fifo-data-empty interrupt (TXIF) requests. 6 RIE 0 0: Disables receive-data-full interrupt (RXIF) requests, reception error interrupt (ERIF) requests and break interrupt (BRIF) requests. 5 TE 1 0: Disables transmit operations. 1: Enables transmit operations. 4 RE 0 0: Disables receive operations. 3 REIE 0 0: Disables receive error interrupt (ERIF) requests and break interrupt (BRIF) requests. 2 0 Reserved 1 to 0 CKE[1:0] 00 00: The internal clock/sck pin functions as an input pin (the input signal is ignored). REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 12 of 28
13 Serial Mode Register (SCSMR) This register sets the communication format and selects the clock source of the baud rate generator. Setting value: H'00 Setting Bit Bit Name Value Function 7 C/A 0 0: Asynchronous mode 6 CHR 0 0: 8-bit data 5 PE 0 0: Disables parity bit addition and checking. 4 O/E 0 0: The O/E bit is invalid because PE = 0. 3 STOP 0 0: 1 stop bit 2 0 Reserved 1 to 0 CKS[1:0] 00 00: Pφ clock Bit Rate Register (SCBRR) This register specifies the bit rate for serial transmission and reception. Setting value: 129 Bit Bit Name Setting Value 7 to Function Bit rate for serial transmission/reception Registers for Setting the Pin Function Controller (PFC) Port A I/O register L (PAIORL) This register selects the input directions of the pins in port A. Setting value: H'0010 Bit Bit Name Setting Value Function 15 PA15IOR 0 0: PA15 input 14 PA14IOR 0 0: PA14 input 13 PA13IOR 0 0: PA13 input 12 PA12IOR 0 0: PA12 input 11 PA11IOR 0 0: PA11 input 10 PA10IOR 0 0: PA10 input 9 PA9IOR 0 0: PA9 input 8 PA8IOR 0 0: PA8 input 7 PA7IOR 0 0: PA7 input 6 PA6IOR 0 0: PA6 input 5 PA5IOR 0 0: PA5 input 4 PA4IOR 1 0: PA4 output. TXD1 output pin 3 PA3IOR 0 0: PA3 input. RXD1 input pin 2 PA2IOR 0 0: PA2 input 1 PA1IOR 0 0: PA1 input 0 PA0IOR 0 0: PA0 input REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 13 of 28
14 Port A Control Register L2 (PACRL2) This register selects the functions of multiplexed pins in port A. Setting value: H'0001 Bit Bit Name Setting Value Function 15 0 Reserved 14 to 12 PA7MD[2:0] : PA7 input/output (port) 11 0 Reserved 10 to 8 PA6MD[2:0] : PA6 input/output (port) 7 0 Reserved 6 to 4 PA5MD[2:0] : PA6 input/output (port) 3 0 Reserved 2 to 0 PA4MD[2:0] : TXD1 output (SCI) SH7080 Group Port A Control Register L1 (PACRL1) This register selects the functions of multiplexed pins in port A. Setting value: H'1000 Bit Bit Name Setting Value Function 15 0 Reserved 14 to 12 PA3MD[2:0] : RXD1 input (SCI) 11 0 Reserved 10 to 8 PA2MD[2:0] : PA2 input/output (port) 7 0 Reserved 6 to 4 PA1MD[2-0] : PA1 input/output (port) 3 0 Reserved 2 to 0 PA0MD[2:0] : PA0 input/output (port) REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 14 of 28
15 6. Flowcharts 6.1 Main Routine main( ) Set the Frequency Control Register (FRQCR) Initialize the UART Set the operating frequencies. When the external input clock frequency is 10 MHz: Internal (Iφ) = 80 MHz, bus (Bφ) = 40 MHz, peripheral (Pφ) = 40 MHz, MTU2S (MIφ) = 80 MHz, MTU2 (MPφ) = 40 MHz Initialize SCI channel 1. User application program processing There is no processing in this sample program. Receive data presence check processing Check whether the receive data is stored in SCRDR. Receive data exist? Receive data reading processing Store the receive data in a variable. Command received? Flash erasing/programming request command (Command name: CMD_GO) Flash read request command (Command name: CMD_READ) Flash reading processing Flash erasing/ programming processing After copying the procedure program into the RAM, execute the procedure program in the RAM. REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 15 of 28
16 6.2 SCI Channel 1 Initialization Routine com_init( ) Set the Standby Control Register 3 (STBCR3) Cancel the standby state of SCI_1. Set the Serial Control Register (SCSCR) Clear the RIE, TIE, TEIE, MPIE, TE, and RE bits in SCSCR to 0. Set the Internal clock/sck pin as an input pin. Set the Serial Mode Register (SCSMR) 8-bit data, no parity, and 1 stop bit. Set the Bit Rate Register (SCBRR) Bit rate = 9600 bps at 40 MHz (Pφ) Has a 1-bit period elapsed? Wait for at least a 1-bit period (104 µs). Set Port A I/O Register L (PAIOR) PA4 (TXD1) output pin Set Port A Control Register L2 (PACRL2) TXD1 output Set Port A Control Register L1 (PACRL1) RXD1 input Set the Serial Control Register (SCSCR) Enable receive operation. Enable transmit operation. END REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 16 of 28
17 6.3 SCI_1 Receive Data Presence Check Routine SH7080 Group CheckRcv( ) Read the Serial Status Register (SCSSR) Set the contents of SCSSR in a variable. Reception error? Set the Serial Status Register (SCSSR) Parity error (PER) Framing error (FER) Overrun error (ORER) Clear the ORER, PER and FER flags of SCSSR to 0. Receive data present? If the RDRF flag of SCSSR is 1, received data has been stored in the Receive Data Register (SCRDR). Return the RDRF flag value to the return value. END REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 17 of 28
18 6.4 SCI_1 n-byte Reception Routine rcvnbyte( ) Reading of the number of requested bytes completed? END Read the Serial Status Register (SCSSR) Set the contents of SCSSR in a variable. Reception error? Receive data present? Set the Serial Status Register (SCSSR) Parity error (PER) Framing error(fer) Overrun error(orer) Clear the ORER, PER and FER flags of SCSSR to 0. If RDRF of SCSSR is 1, the received data is stored in the Receive Data Register (SCRDR). Set the receive data in a variable Set the Serial Status Register (SCSSR) Clear the RDRF flag of SCSSR to 0. Decrement the number of requested bytes REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 18 of 28
19 6.5 SCI_1 1-Byte Transmission Routine trs1byte( ) Data programming enabled? Determined by the TDRE flag of SCSSR. Write the transmit data Write 1 byte to SCTDR. Read the Serial Status Register (SCSSR) Clear the TDRE flag of SCSSR to 0. Transmission completed? Determined by the TEND flag of SCSSR. END REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 19 of 28
20 6.6 Flash Programming Main Routine FlashMain( ) Flash write enabled? Error processing (NG command transmission) The FWE signal is not at a high level and the user MAT is not selected. Downloading of erasing program and execution of erasing initialization program Error? Error processing (NG command transmission) Downloading of the erasing program and initialization failed. Preparation for programming/ erasing Downloading of programming program and execution of programming initialization program. Error? Error processing (NG command transmission) Downloading of the programming program and initialization failed. OK command processing Erase command receive processing Receive command is? Command other than the erase command Erase command Error processing (NG command transmission) Erase block receive processing Absence of erase block? Error processing (NG command transmission) Erasing Erasing processing Erasing error? Error processing (NG command transmission) OK command processing 1 REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 20 of 28
21 1 1-byte reception processing Write end command Command is? Command other than the write command Write command Error processing (NG command transmission) Programming start address receive processing Programming size receive processing Programming address or programming size error? Transmit request command transmit processing Error processing (NG command transmission) Determine the receive size Program data receive processing Programming Pad H'FF if less than 128 bytes Flash programming processing Programming error? Error processing (NG command transmission) Update the programming address and programming size Programming of specified size completed? OK command processing OK command processing Wait for a reset. REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 21 of 28
22 6.7 Flash Reading Routine FlashRead( ) Read start address receive processing Read size receive processing Obtain the start address for reading using the rcvnbyte function (SCI_1 n-byte reception). Obtain the size for reading using the rcvnbyte function (SCI_1 n-byte reception). 1-byte transmission of data in flash memory Serial data transmission by the trs1byte function (SCI_1 1-byte transmission), 1 byte at a time from the read start address up to the read size Completed transmission of data in flash memory? END REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 22 of 28
23 6.8 Erasing Program Downloading and initialization Routine SH7080 Group SetupFlashErase( ) Set the Flash Erase Code Select Register (FECS) Select the internal erasing program Set the Flash Transfer Destination Address Register (FTDAR) Download start address: H'FFFF9000 Clear the DPFR parameter value. Set the Flash Key Code Register (FKEY) Enable writing to the SCO bit. Set the Flash Code Control and Status Register (FCCS) After clearing the VBR register, set SCO to 1 and execute downloading. NOP x 4 Set the Flash Key Code Register (FKEY) Clear the FKEY register. Download successful? Set the operating frequency Erasing initialization processing Set the operating frequency to the FPEFEQ parameter value. 80 MHz (80*100) Set the error state (download error) END REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 23 of 28
24 6.9 Flash Erasing Routine FlashErase( ) Set the Flash Key Code Register (FKEY) Enable programming/erasing. Erase block present? Erase block? Erasing processing Erasing error? Increment the erase block number Set the Flash Key Code Register (FKEY) Clear the FKEY register. END REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 24 of 28
25 6.10 Programming Program Download and Initialization Routine SetupFlashWrite() Set the Flash Erase Code Select Register (FECS) Select the internal programming program Set the Flash Transfer Destination Address Register (FTDAR) Download start address: H'FFFFA000 Clear the DPFR parameter value. Set the Flash Key Code Register (FKEY) Enable writing to the SCO bit. Set the Flash Code Control and Status Register (FCCS) After clearing the VBR register, set SCO to 1 and execute downloading. NOP x 4 Set the Flash Key Code Register (FKEY) Clear the FKEY register. Download successful? Set the operating frequency Set the operating frequency to the FPEFEQ parameter value. 80 MHz (80*100) Programming initialization processing Set the error state (download error) END REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 25 of 28
26 6.11 Flash Programming Routine FlashWrite( ) Set the Flash Key Code Register (FKEY) Enabling programming/erasing. Set FMPAR (flash multipurpose address area parameter) Set the start address of the programming destination in the user mat. Set FMPDR (flash multipurpose data destination area parameter) Set the start address of the area that stores the program data. Programming processing Set the Flash Key Code Register (FKEY) Clear the FKEY register. END REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 26 of 28
27 Website and Support Renesas Technology Website Inquiries Revision Record Description Rev. Date Page Summary 1.00 Sep First edition issued REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 27 of 28
28 Keep safety first in your circuit designs! SH7080 Group 1. Renesas Technology Corp. puts the maximum effort into making semiconductor products better and more reliable, but there is always the possibility that trouble may occur with them. Trouble with semiconductors may lead to personal injury, fire or property damage. Remember to give due consideration to safety when making your circuit designs, with appropriate measures such as (i) placement of substitutive, auxiliary circuits, (ii) use of nonflammable material or (iii) prevention against any malfunction or mishap. tes regarding these materials 1. These materials are intended as a reference to assist our customers in the selection of the Renesas Technology Corp. product best suited to the customer's application; they do not convey any license under any intellectual property rights, or any other rights, belonging to Renesas Technology Corp. or a third party. 2. Renesas Technology Corp. assumes no responsibility for any damage, or infringement of any thirdparty's rights, originating in the use of any product data, diagrams, charts, programs, algorithms, or circuit application examples contained in these materials. 3. All information contained in these materials, including product data, diagrams, charts, programs and algorithms represents information on products at the time of publication of these materials, and are subject to change by Renesas Technology Corp. without notice due to product improvements or other reasons. It is therefore recommended that customers contact Renesas Technology Corp. or an authorized Renesas Technology Corp. product distributor for the latest product information before purchasing a product listed herein. The information described here may contain technical inaccuracies or typographical errors. Renesas Technology Corp. assumes no responsibility for any damage, liability, or other loss rising from these inaccuracies or errors. Please also pay attention to information published by Renesas Technology Corp. by various means, including the Renesas Technology Corp. Semiconductor home page ( 4. When using any or all of the information contained in these materials, including product data, diagrams, charts, programs, and algorithms, please be sure to evaluate all information as a total system before making a final decision on the applicability of the information and products. Renesas Technology Corp. assumes no responsibility for any damage, liability or other loss resulting from the information contained herein. 5. Renesas Technology Corp. semiconductors are not designed or manufactured for use in a device or system that is used under circumstances in which human life is potentially at stake. Please contact Renesas Technology Corp. or an authorized Renesas Technology Corp. product distributor when considering the use of a product contained herein for any specific purposes, such as apparatus or systems for transportation, vehicular, medical, aerospace, nuclear, or undersea repeater use. 6. The prior written approval of Renesas Technology Corp. is necessary to reprint or reproduce in whole or in part these materials. 7. If these products or technologies are subject to the Japanese export control restrictions, they must be exported under a license from the Japanese government and cannot be imported into a country other than the approved destination. Any diversion or reexport contrary to the export control laws and regulations of Japan and/or the country of destination is prohibited. 8. Please contact Renesas Technology Corp. for further details on these materials or the products contained therein Renesas Technology Corp., All rights reserved. REJ06B /Rev.1.00 September 2006 Page 28 of 28
1. Specifications Operational Overview of Functions Used Principles of Operation Description of Software...
 APPLICATION NOTE SH7080 Group Introduction This application note describes the serial data transmission function that uses the transmit-fifo-data-empty interrupt source of the SCIF (Serial Communication
APPLICATION NOTE SH7080 Group Introduction This application note describes the serial data transmission function that uses the transmit-fifo-data-empty interrupt source of the SCIF (Serial Communication
1. Specifications Functions Used Operation Software Flowcharts Program Listing... 13
 APPLICATION NOTE SH7145F Summary The SH7144 series is a single-chip microprocessor based on the SH-2 RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) CPU core and integrating a number of peripheral functions. This
APPLICATION NOTE SH7145F Summary The SH7144 series is a single-chip microprocessor based on the SH-2 RISC (Reduced Instruction Set Computer) CPU core and integrating a number of peripheral functions. This
SCIF Asynchronous Serial Data Transfer Function Using the DTC. 1. Specifications Operational Overview of Functions Used...
 Introduction APPLICATION NOTE This application note describes data transmission and reception that uses the internal SCIF (Serial Communication Interface with FIFO) for asynchronous serial transfer and
Introduction APPLICATION NOTE This application note describes data transmission and reception that uses the internal SCIF (Serial Communication Interface with FIFO) for asynchronous serial transfer and
H8SX Family APPLICATION NOTE. Vector Table Address Switching. Introduction. Target Devices. Contents
 APPLICATION NOTE H8SX Family Introduction This application note describes how to change the vector table address. Target Devices H8SX family Contents 1. Overview... 2 2. Applicable Conditions... 2 3. Configuration...
APPLICATION NOTE H8SX Family Introduction This application note describes how to change the vector table address. Target Devices H8SX family Contents 1. Overview... 2 2. Applicable Conditions... 2 3. Configuration...
SH7080/SH7146/SH7125/SH7200 Series
 APPLICATION NOTE SH78/SH746/SH75/SH7 Series Introduction This application note discusses synchronous operation of the MTU and MTUS timers, Target Device Microcomputer: SH785 (R5F785) Operating frequency:
APPLICATION NOTE SH78/SH746/SH75/SH7 Series Introduction This application note discusses synchronous operation of the MTU and MTUS timers, Target Device Microcomputer: SH785 (R5F785) Operating frequency:
Interrupt Level Setting and Modification by Interrupt Controller
 Controller Introduction APPLICATION NOTE Interrupts of different levels are generated by specifying interrupt levels via the interrupt controller (INTC) of the SH7145F. Target Device SH7145F Contents 1.
Controller Introduction APPLICATION NOTE Interrupts of different levels are generated by specifying interrupt levels via the interrupt controller (INTC) of the SH7145F. Target Device SH7145F Contents 1.
Multi-Bit Shift of 32-Bit Data (Arithmetic Right Shift)
 SH7 Series APPLICATION NOTE Label: Functions Used: SHARN SHLR2 Instruction SHLR8 Instruction SHLR16 Instruction Contents 1. Function... 2 2. Arguments... 2 3. Internal Register Changes and Flag Changes...
SH7 Series APPLICATION NOTE Label: Functions Used: SHARN SHLR2 Instruction SHLR8 Instruction SHLR16 Instruction Contents 1. Function... 2 2. Arguments... 2 3. Internal Register Changes and Flag Changes...
This function allows the user to erase any Flash block within the MCU including the near area memory (below address 0xFFFF).
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62P, M16C/26 1.0 Abstract A simple Application Program Interface (API) has been created to allow programmers of the M16C/62P (M30626FHP) and M16C/26 (M30262F8) to easily integrate
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62P, M16C/26 1.0 Abstract A simple Application Program Interface (API) has been created to allow programmers of the M16C/62P (M30626FHP) and M16C/26 (M30262F8) to easily integrate
In repeat transfer mode of DMAC, choose functions from those listed in Table 1. Operations of the checked items are described below.
 APPLICATION NOTE 1. Abstract In repeat transfer mode of DMAC, choose functions from those listed in Table 1. Operations of the checked items are described below. Table 1. Choosed Functions Item Transfer
APPLICATION NOTE 1. Abstract In repeat transfer mode of DMAC, choose functions from those listed in Table 1. Operations of the checked items are described below. Table 1. Choosed Functions Item Transfer
M16C/60 Series and M16C/20 Series
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/60 Series and M16C/20 Series General-purpose Program for Converting from Uppercase Alphabet to Lowercase Alphabet 1. Abstract This program converts an uppercase English alphabet in
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/60 Series and M16C/20 Series General-purpose Program for Converting from Uppercase Alphabet to Lowercase Alphabet 1. Abstract This program converts an uppercase English alphabet in
SH7144/45 Group APPLICATION NOTE. 2-Phase Encoder Count. 1. Specifications
 APPLICATION NOTE SH7144/45 Group 1. Specifications Two external clocks are input to channel 1 (ch1), and a counter is incremented or decremented according to the phase difference of the pulses, as shown
APPLICATION NOTE SH7144/45 Group 1. Specifications Two external clocks are input to channel 1 (ch1), and a counter is incremented or decremented according to the phase difference of the pulses, as shown
M16C/62 APPLICATION NOTE. Programming the M16C/62 in Flash Parallel Mode. 1.0 Abstract. 2.0 Introduction. 3.0 Setting Up the PGM1000 Programmer
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 1.0 Abstract The following article describes using the ATC (Advanced Transdata) PGM1000 programmer to parallel program the flash memory of the M16C/62 series of microcontrollers.
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 1.0 Abstract The following article describes using the ATC (Advanced Transdata) PGM1000 programmer to parallel program the flash memory of the M16C/62 series of microcontrollers.
M16C R8C FoUSB/UART Debugger. User Manual REJ10J
 REJ10J1725-0100 M16C R8C FoUSB/UART Debugger User Manual Renesas Microcomputer Development Environment System R8C Family R8C/2x Series Notes on Connecting R8C/2A, R8C/2B, R8C/2C, R8C/2D Rev.1.00 Issued
REJ10J1725-0100 M16C R8C FoUSB/UART Debugger User Manual Renesas Microcomputer Development Environment System R8C Family R8C/2x Series Notes on Connecting R8C/2A, R8C/2B, R8C/2C, R8C/2D Rev.1.00 Issued
RTE/L Return from Exception Handling with Data Restoration
 APPLICATION NOTE Introduction Shows an example of C compiler use of the RTE/L instruction Contents 1 Specifications 2 2 Functions Used 2 3 Principles of Operation 2 4 Development Environment 3 5 Description
APPLICATION NOTE Introduction Shows an example of C compiler use of the RTE/L instruction Contents 1 Specifications 2 2 Functions Used 2 3 Principles of Operation 2 4 Development Environment 3 5 Description
1. Specifications Conditions for Application Description of Modules Used Description of Operation... 7
 APPLICATION NOTE H8SX Family Introduction Relative phases of the two-phase pulse signal input from the two external clock pins are detected by the 6-bit timer pulse unit (TPU). Whether the timer counter
APPLICATION NOTE H8SX Family Introduction Relative phases of the two-phase pulse signal input from the two external clock pins are detected by the 6-bit timer pulse unit (TPU). Whether the timer counter
This document describes how to set up and use the timer RA in timer mode on the R8C/25 Group device.
 APPLICATION NOTE R8C/25 Group 1. Abstract This document describes how to set up and use the timer RA in timer mode on the R8C/25 Group device. 2. Introduction The application example described in this
APPLICATION NOTE R8C/25 Group 1. Abstract This document describes how to set up and use the timer RA in timer mode on the R8C/25 Group device. 2. Introduction The application example described in this
M16C/62 Group APPLICATION NOTE. Signed 32 Bit Multiplication Library. 1. Abstract. 2. Introduction
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 Group 1. Abstract This application note describes an operational library of the multiplicant (signed 32 bit) X the multiplication (signed 32 bit) = the product (signed 64 bit )
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 Group 1. Abstract This application note describes an operational library of the multiplicant (signed 32 bit) X the multiplication (signed 32 bit) = the product (signed 64 bit )
Example of Setting the SCIF for Clocked Synchronous Serial Communication (Full-Duplex Communication)
 APPLICATION NOTE Example of Setting the SCIF for Clocked Synchronous Serial Communication (Full-Duplex Communication) Introduction This application note presents an example of configuring the serial communication
APPLICATION NOTE Example of Setting the SCIF for Clocked Synchronous Serial Communication (Full-Duplex Communication) Introduction This application note presents an example of configuring the serial communication
This application note describes the time measurement function of Timer S with the gate function.
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/28, 29 Group Time Measuerment Function of Time S with Gate Function 1. Abstract This application note describes the time measurement function of Timer S with the gate function. 2.
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/28, 29 Group Time Measuerment Function of Time S with Gate Function 1. Abstract This application note describes the time measurement function of Timer S with the gate function. 2.
M16C/62 APPLICATION NOTE. Using the M16C/62 DMAC in Forward Source Mode. 1.0 Abstract. 2.0 Introduction
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 1.0 Abstract The following article introduces and shows an example of how to use the DMAC function of the M16C/62 with a forward counting source address and fixed destination address.
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 1.0 Abstract The following article introduces and shows an example of how to use the DMAC function of the M16C/62 with a forward counting source address and fixed destination address.
Single Power Supply F-ZTAT On-Board Programming
 Single Power Supply F-ZTAT On-Board Programming Renesas F-ZTAT Microcomputer Rev.2.00 Revision Date: Dec 13, 2004 Keep safety first in your circuit designs! 1. Renesas Technology Corp. puts the maximum
Single Power Supply F-ZTAT On-Board Programming Renesas F-ZTAT Microcomputer Rev.2.00 Revision Date: Dec 13, 2004 Keep safety first in your circuit designs! 1. Renesas Technology Corp. puts the maximum
M16C R8C FoUSB/UART Debugger. User s Manual REJ10J
 REJ10J1217-0100 M16C R8C FoUSB/UART Debugger User s Manual RENESAS MICROCOMPUTER Development Environment System M16C Family R8C/Tiny Series Precautions on Connecting R8C/20, R8C/21, R8C/22, R8C/23 Rev.1.00
REJ10J1217-0100 M16C R8C FoUSB/UART Debugger User s Manual RENESAS MICROCOMPUTER Development Environment System M16C Family R8C/Tiny Series Precautions on Connecting R8C/20, R8C/21, R8C/22, R8C/23 Rev.1.00
M16C/26 APPLICATION NOTE. Using the DMAC with a Forward Source. 1.0 Abstract. 2.0 Introduction
 APPLICATION NOTE 1.0 Abstract The following article introduces and shows an example of how to use the DMAC function of the with a forward counting source address and fixed destination address. 2.0 Introduction
APPLICATION NOTE 1.0 Abstract The following article introduces and shows an example of how to use the DMAC function of the with a forward counting source address and fixed destination address. 2.0 Introduction
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
M16C/62 APPLICATION NOTE. Using the M16C/62 CRC. 1.0 Abstract. 2.0 Introduction. 3.0 A Lesson in CRC and the CCITT Polynomial
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 1.0 Abstract The register sets of the M16C/62 devices contain a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) calculating peripheral. This gives the user the ability to quickly calculate a CRC
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 1.0 Abstract The register sets of the M16C/62 devices contain a Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) calculating peripheral. This gives the user the ability to quickly calculate a CRC
32176 Group APPLICATION NOTE. Application of the CAN Module (Remote Frame Transmission) 1. Overview. 2. Introduction
 32176 Group 1. Overview APPLICATION NOTE The sample task described in this document uses the 32176 Group microcomputer s on-chip CAN (Controller Area Network) module. 2. Introduction The sample task described
32176 Group 1. Overview APPLICATION NOTE The sample task described in this document uses the 32176 Group microcomputer s on-chip CAN (Controller Area Network) module. 2. Introduction The sample task described
This document describes how to set up and use the timer RB in programmable one-shot generation mode on the R8C/25 Group device.
 APPLICATION NOTE R8C/25 Group 1. Abstract This document describes how to set up and use the timer RB in programmable one-shot generation mode on the R8C/25 Group device. 2. Introduction The application
APPLICATION NOTE R8C/25 Group 1. Abstract This document describes how to set up and use the timer RB in programmable one-shot generation mode on the R8C/25 Group device. 2. Introduction The application
M16C APPLICATION NOTE. Target Setup for the In-Circuit Debugger. 1.0 Abstract. 2.0 Introduction
 APPLICATION NOTE MC.0 Abstract The ICD (In-Circuit Debugger), or USB-Monitor, is a low cost, compact interface that has two functions for Renesas MC Flash microcontrollers: ) an in-circuit debugger tool
APPLICATION NOTE MC.0 Abstract The ICD (In-Circuit Debugger), or USB-Monitor, is a low cost, compact interface that has two functions for Renesas MC Flash microcontrollers: ) an in-circuit debugger tool
The following article describes how to use the M16C/62 timers A s as square wave generators (Pulse Output Mode).
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 1.0 Abstract The following article describes how to use the M16C/62 timers A s as square wave generators (Pulse Output Mode). 2.0 Introduction The M16C/62 is a 16-bit MCU, based
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 1.0 Abstract The following article describes how to use the M16C/62 timers A s as square wave generators (Pulse Output Mode). 2.0 Introduction The M16C/62 is a 16-bit MCU, based
M16C APPLICATION NOTE. Firmware Requirements for In-Circuit Debugger. 1.0 Abstract. 2.0 Introduction
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C 1.0 Abstract The USB-Monitor is a low cost, compact interface that has two functions for Renesas M16C Flash microcontrollers 1) an in-circuit debugger tool with KD30 Debugger, and
APPLICATION NOTE M16C 1.0 Abstract The USB-Monitor is a low cost, compact interface that has two functions for Renesas M16C Flash microcontrollers 1) an in-circuit debugger tool with KD30 Debugger, and
M32C/84 Group APPLICATION NOTE. Operation of Key-Input Interrupt. 1. Abstract. 2. Introduction
 APPLICATION NOTE M32C/84 Group 1. Abstract The following is an operation of key-input interrupt. Figure 1 shows an example of a circuit that uses the key-input interrupt, Figure 2 shows an example of operation
APPLICATION NOTE M32C/84 Group 1. Abstract The following is an operation of key-input interrupt. Figure 1 shows an example of a circuit that uses the key-input interrupt, Figure 2 shows an example of operation
M16C/26 APPLICATION NOTE. Measuring Computation Time of a Function Call. 1.0 Abstract. 2.0 Introduction. 3.0 Number of Function Call Returns
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/26 1.0 Abstract The following article discusses a technique for measuring computation time spent during a function call, which can be in C or Assembly, from a main C program for the
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/26 1.0 Abstract The following article discusses a technique for measuring computation time spent during a function call, which can be in C or Assembly, from a main C program for the
Renesas LIN Overview. White paper REU05B Introduction
 White paper Introduction LIN is a communication and distributed processing bus system. It is characterized by low cost hardware and a relatively low data transmission speed and number of bus nodes. Only
White paper Introduction LIN is a communication and distributed processing bus system. It is characterized by low cost hardware and a relatively low data transmission speed and number of bus nodes. Only
M16C/26 APPLICATION NOTE. Using Timer B in Pulse Period/Width Measurement Mode. 1.0 Abstract. 2.0 Introduction
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/26 1.0 Abstract Measuring the frequency (1/period) or the pulse width of an input signal is useful in applications such as tachometers, DC motor control, power usage calculations,
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/26 1.0 Abstract Measuring the frequency (1/period) or the pulse width of an input signal is useful in applications such as tachometers, DC motor control, power usage calculations,
M16C/Tiny Series APPLICATION NOTE. Operation of Timer A. (2-Phase Pulse Signal Process in Event Counter Mode, Multiply-by-4 Mode) 1.
 APPLICATION NOTE 1. Abstract In processing 2-phase pulse signals in event counter mode, choose functions from those listed in Table 1. Operations of the selected items are described below. Figure 1 shows
APPLICATION NOTE 1. Abstract In processing 2-phase pulse signals in event counter mode, choose functions from those listed in Table 1. Operations of the selected items are described below. Figure 1 shows
APPLICATION NOTE R8C, M16C, M32C
 APPLICATION NOTE R8C, M16C, M32C 1. Abstract Since the internal flash of a Renesas R8C/M16C/M32C microcontroller can be erased and programmed in-circuit, an application has been created in order to eliminate
APPLICATION NOTE R8C, M16C, M32C 1. Abstract Since the internal flash of a Renesas R8C/M16C/M32C microcontroller can be erased and programmed in-circuit, an application has been created in order to eliminate
M16C/26 APPLICATION NOTE. Using the M16C/26 Timer in Event Counter Mode. 1.0 Abstract. 2.0 Introduction
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/26 1.0 Abstract Event counters are useful in automated packaging lines, tachometers, and mechanical equipment monitoring. The event counters on the M16C/26 can be configured to interrupt
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/26 1.0 Abstract Event counters are useful in automated packaging lines, tachometers, and mechanical equipment monitoring. The event counters on the M16C/26 can be configured to interrupt
M32C/84 Group APPLICATION NOTE. Operation of timer A (2-phase pulse signal process in event counter mode, normal mode selected) 1.
 APPLICATION NOTE Operation of timer A (2-phase pulse signal process in event counter mode, normal mode selected) 1. Abstract In processing 2-phase pulse signals in event counter mode, choose functions
APPLICATION NOTE Operation of timer A (2-phase pulse signal process in event counter mode, normal mode selected) 1. Abstract In processing 2-phase pulse signals in event counter mode, choose functions
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
Asynchronous Transfer of Data with Appended CRC Codes via an SCI Interface
 Introduction APPLICATION NOTE The SCI module and CRC calculator applied in the asynchronous transfer of four-byte data blocks. In transmission, a two-byte CRC is appended to every byte of transmitted data.
Introduction APPLICATION NOTE The SCI module and CRC calculator applied in the asynchronous transfer of four-byte data blocks. In transmission, a two-byte CRC is appended to every byte of transmitted data.
The following article introduces and shows an example of how to set up and use the watchdog timer on the M16C/26 microcontroller (MCU).
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/26 1.0 Abstract The following article introduces and shows an example of how to set up and use the watchdog timer on the M16C/26 microcontroller (MCU). 2.0 Introduction The Renesas
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/26 1.0 Abstract The following article introduces and shows an example of how to set up and use the watchdog timer on the M16C/26 microcontroller (MCU). 2.0 Introduction The Renesas
Data Transfer between On-chip RAM Areas with DMAC (Burst Mode) 1. Introduction Description of Sample Application... 3
 Introduction APPLICATION NOTE This application note describes the operation of the DMAC, and is intended for reference to help in the design of user software. Target Device SH7211 Contents 1. Introduction...
Introduction APPLICATION NOTE This application note describes the operation of the DMAC, and is intended for reference to help in the design of user software. Target Device SH7211 Contents 1. Introduction...
Silicon Epitaxial Planar Zener Diode for Stabilized Power Supply. Type No. Mark Package Code HZS Series Type No. MHD B 7
 Silicon Epitaxial Planar Zener Diode for Stabilized Power Supply Features REJ3G184-3Z (Previous: ADE-28-12B) Rev.3. Mar.11.24 Low leakage, low zener impedance and maximum power dissipation of 4 mw are
Silicon Epitaxial Planar Zener Diode for Stabilized Power Supply Features REJ3G184-3Z (Previous: ADE-28-12B) Rev.3. Mar.11.24 Low leakage, low zener impedance and maximum power dissipation of 4 mw are
Regarding the change of names mentioned in the document, such as Hitachi Electric and Hitachi XX, to Renesas Technology Corp.
 To all our customers Regarding the change of names mentioned in the document, such as Hitachi Electric and Hitachi XX, to Renesas Technology Corp. The semiconductor operations of Mitsubishi Electric and
To all our customers Regarding the change of names mentioned in the document, such as Hitachi Electric and Hitachi XX, to Renesas Technology Corp. The semiconductor operations of Mitsubishi Electric and
M16C/62 APPLICATION NOTE. Using the Expanded Memory Mode with the M16C/ Abstract. 2.0 Introduction. 3.0 Memory Expansion Mode
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 1.0 Abstract The following article introduces and shows an example of how to access external memory using the expanded memory mode of the M16C/62 series of microcontrollers. 2.0
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 1.0 Abstract The following article introduces and shows an example of how to access external memory using the expanded memory mode of the M16C/62 series of microcontrollers. 2.0
F-ZTAT Microcomputer On-Board Programming
 F-ZTAT Microcomputer On-Board Programming Renesas F-ZTAT Microcomputer Rev.2.00 Revision Date: Dec 13, 2004 Keep safety first in your circuit designs! 1. Renesas Technology Corp. puts the maximum effort
F-ZTAT Microcomputer On-Board Programming Renesas F-ZTAT Microcomputer Rev.2.00 Revision Date: Dec 13, 2004 Keep safety first in your circuit designs! 1. Renesas Technology Corp. puts the maximum effort
1. Specification Applicable conditions Description of Modules Used Principles of Operation... 8
 Using the DMAC to Drive Continuous SCI Transmission Introduction APPLICATION NOTE Asynchronous transfer is used to transmit 128 bytes of data. Using the DMAC to handle the transfer (transmission) of data
Using the DMAC to Drive Continuous SCI Transmission Introduction APPLICATION NOTE Asynchronous transfer is used to transmit 128 bytes of data. Using the DMAC to handle the transfer (transmission) of data
M32C/84, 85, 86, 87, 88 Group
 Version 1. Abstract APPLICATION NOTE The document describes how to reduce power consumption in the flash memory version and shows an application example. 2. Introduction The application example described
Version 1. Abstract APPLICATION NOTE The document describes how to reduce power consumption in the flash memory version and shows an application example. 2. Introduction The application example described
M16C/26 APPLICATION NOTE. Implementing Real Time Clock and WAIT Mode. 1.0 Abstract. 2.0 Introduction. 3.0 Real-Time Clock Setup and Implementation
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/26 1.0 Abstract The following article describes the implementation of a low-power, real time clock using the sub-clock circuit with a 32.768 khz crystal and Wait mode of the M16C/26
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/26 1.0 Abstract The following article describes the implementation of a low-power, real time clock using the sub-clock circuit with a 32.768 khz crystal and Wait mode of the M16C/26
Regarding the change of names mentioned in the document, such as Hitachi Electric and Hitachi XX, to Renesas Technology Corp.
 To all our customers Regarding the change of names mentioned in the document, such as Hitachi Electric and Hitachi XX, to Renesas Technology Corp. The semiconductor operations of Mitsubishi Electric and
To all our customers Regarding the change of names mentioned in the document, such as Hitachi Electric and Hitachi XX, to Renesas Technology Corp. The semiconductor operations of Mitsubishi Electric and
VLA HYBRID IC ISOLATED TYPE DC-DC CONVERTER DESCRIPTION OUTLINE DRAWING FEATURES APPLICATIONS BLOCK DIAGRAM. +Vo +V IN.
 DESCRIPTION The is a DC-DC converter. Its output power is 1.5W and the input is isolated from the output. The over-current protection circuit is built-in and it is the best for on-board power supplies,
DESCRIPTION The is a DC-DC converter. Its output power is 1.5W and the input is isolated from the output. The over-current protection circuit is built-in and it is the best for on-board power supplies,
M16C/26 APPLICATION NOTE. Interfacing with 1-Wire Devices. 1.0 Abstract. 2.0 Introduction Wire Interface. 3.1 Hardware
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/26 1.0 Abstract The following article introduces and shows an example of how to interface Renesas 16-bit microcontrollers (MCU) to a 1-wire device. A demo program developed for the
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/26 1.0 Abstract The following article introduces and shows an example of how to interface Renesas 16-bit microcontrollers (MCU) to a 1-wire device. A demo program developed for the
M32C/84, 85, 86, 87, 88 Group
 APPLICATION NOTE 1. Abstract The direct memory access controller (DMAC) function allows data to be transferred without using the CPU. DMAC transfers one data (8-bit or 16-bit) from a source address to
APPLICATION NOTE 1. Abstract The direct memory access controller (DMAC) function allows data to be transferred without using the CPU. DMAC transfers one data (8-bit or 16-bit) from a source address to
Regarding the change of names mentioned in the document, such as Hitachi Electric and Hitachi XX, to Renesas Technology Corp.
 To all our customers Regarding the change of names mentioned in the document, such as Hitachi Electric and Hitachi XX, to Renesas Technology Corp. The semiconductor operations of Mitsubishi Electric and
To all our customers Regarding the change of names mentioned in the document, such as Hitachi Electric and Hitachi XX, to Renesas Technology Corp. The semiconductor operations of Mitsubishi Electric and
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
This document describes a program for timer RA in pulse period measurement mode.
 APPLICATION NOTE R8C/25 Group. Abstract This document describes a program for timer RA in pulse period measurement mode. 2. Introduction The application example described in this document applies to the
APPLICATION NOTE R8C/25 Group. Abstract This document describes a program for timer RA in pulse period measurement mode. 2. Introduction The application example described in this document applies to the
VLA A HYBRID IC ISOLATED TYPE DC-DC CONVERTER DESCRIPTION FEATURES BLOCK DIAGRAM
 DESCRIPTION The is an isolated DC-DC converter designed to control the industrial equipment. It can input the DC400~850V directly and convert to low voltage. Total output power is 150W. FEATURES Input
DESCRIPTION The is an isolated DC-DC converter designed to control the industrial equipment. It can input the DC400~850V directly and convert to low voltage. Total output power is 150W. FEATURES Input
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
1. Specification Applicable Conditions Description of Modules Used Principles of Operation... 9
 APPLICATION NOTE H8SX Family Introduction The H8SX/1638F microcomputer has a deep software standby mode as one of its low-power states. This application note gives an example of employment of the deep
APPLICATION NOTE H8SX Family Introduction The H8SX/1638F microcomputer has a deep software standby mode as one of its low-power states. This application note gives an example of employment of the deep
This document describes a program for timer RF in pulse width measurement mode.
 R8C/25 Group. Abstract This document describes a program for timer RF in pulse width measurement mode. 2. Introduction The application example described in this document applies to the following MCU and
R8C/25 Group. Abstract This document describes a program for timer RF in pulse width measurement mode. 2. Introduction The application example described in this document applies to the following MCU and
Application Note [AN-006] Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Construction Methods
![Application Note [AN-006] Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Construction Methods Application Note [AN-006] Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) Construction Methods](/thumbs/77/75189326.jpg) Application Note [AN-006] Liquid Crystal Display () Construction Methods Introduction In a module the driver electronics, which control the voltage applied to each pixel need to be connected to the cell.
Application Note [AN-006] Liquid Crystal Display () Construction Methods Introduction In a module the driver electronics, which control the voltage applied to each pixel need to be connected to the cell.
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
Operation of Timer A (2-phase pulse signal process in event counter mode, multiply-by-4 processing operation)
 APPLICATION NOTE in event counter mode, multiply-by-4 processing operation) 1. Abstract In processing 2-phase pulse signals in event counter mode, choose functions from those listed in Table 1. Operations
APPLICATION NOTE in event counter mode, multiply-by-4 processing operation) 1. Abstract In processing 2-phase pulse signals in event counter mode, choose functions from those listed in Table 1. Operations
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April st, 2, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took over
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April st, 2, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took over
M37544 StarterKit. User s Manual REJ10J Z. RENESAS SINGLE-CHIP MICROCOMPUTER 740 Family 740 Series. Rev.1.00 Revision Date : Nov 26, 2004
 REJ10J0822-0100Z M37544 StarterKit User s Manual RENESAS SINGLE-CHIP MICROCOMPUTER 740 Family 740 Series Rev.1.00 Revision Date : Nov 26, 2004 Renesas Soluctions Corp. www.renesas.com Keep safety first
REJ10J0822-0100Z M37544 StarterKit User s Manual RENESAS SINGLE-CHIP MICROCOMPUTER 740 Family 740 Series Rev.1.00 Revision Date : Nov 26, 2004 Renesas Soluctions Corp. www.renesas.com Keep safety first
In timer mode, choose functions from those listed in Table 1. Operations of the circled items are described below.
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/64 Group 1. Abstract In timer mode, choose functions from those listed in Table 1. Operations of the circled items are described below. 2. Introduction This application note is applied
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/64 Group 1. Abstract In timer mode, choose functions from those listed in Table 1. Operations of the circled items are described below. 2. Introduction This application note is applied
M3H Group(2) Application Note Asynchronous Serial Communication Circuit (UART-C)
 M3H Group(2) Asynchronous Serial Communication Circuit (UART-C) Outlines This application note is a erence material for developing products using the asynchronous serial communication circuit (UART) function
M3H Group(2) Asynchronous Serial Communication Circuit (UART-C) Outlines This application note is a erence material for developing products using the asynchronous serial communication circuit (UART) function
RL78 Family. User s Manual. Flash Self-Programming Library Type Bit Single-Chip Microcontrollers. Rev.1.04 Dec 2016.
 User s Manual 表紙 RL78 Family 16 16-Bit Single-Chip Microcontrollers Flash Self-Programming Library Type01 Japanese Release ZIP file name : JP_R_FSL_RL78_T01_Vx.xx_x_E All information contained in these
User s Manual 表紙 RL78 Family 16 16-Bit Single-Chip Microcontrollers Flash Self-Programming Library Type01 Japanese Release ZIP file name : JP_R_FSL_RL78_T01_Vx.xx_x_E All information contained in these
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
A 24-hour clock (which is updated at 1-minute intervals) is created by using the 32K timer.
 APPLICATION TE H8SX Family (Updated at -Minute Intervals) Introduction A 24-hour clock (which is updated at -minute intervals) is created by using the 32K timer. Target Device H8SX/668R Preface Although
APPLICATION TE H8SX Family (Updated at -Minute Intervals) Introduction A 24-hour clock (which is updated at -minute intervals) is created by using the 32K timer. Target Device H8SX/668R Preface Although
1. Specification Applicable Conditions Description of Functions Used Principles of Operation... 5
 APPLICATION NOTE Introduction This application note describes the usage of the I 2 C bus interface 2 (IIC2) module in the multi-master mode. Target Device H8SX/1663 Contents 1. Specification... 2 2. Applicable
APPLICATION NOTE Introduction This application note describes the usage of the I 2 C bus interface 2 (IIC2) module in the multi-master mode. Target Device H8SX/1663 Contents 1. Specification... 2 2. Applicable
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
M16C/62 APPLICATION NOTE. Using the M16C/62 Power Saving Modes. 1.0 Abstract. 2.0 Introduction. 3.0 Power Conservation: Introduction
 APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 1.0 Abstract This article discusses the various power saving modes of the M16C device. A short program is provided that can be run on the MSV3062 development board. Using an Amp
APPLICATION NOTE M16C/62 1.0 Abstract This article discusses the various power saving modes of the M16C device. A short program is provided that can be run on the MSV3062 development board. Using an Amp
OUTLINE DRAWING. ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS (Tc=25 C UNLESS OTHERWISE NOTED)
 DESCRIPTION is a MOS FET type transistor designed for VHF/UHF RF driver device. OUTLINE DRAWING FEATURES 1.High Power Gain and High Efficiency Pout>1.0W, Gp=15dB, Drain Effi. =70%typ @ f=527mhz, V DS =7.2V,
DESCRIPTION is a MOS FET type transistor designed for VHF/UHF RF driver device. OUTLINE DRAWING FEATURES 1.High Power Gain and High Efficiency Pout>1.0W, Gp=15dB, Drain Effi. =70%typ @ f=527mhz, V DS =7.2V,
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
MN101EF69D. 8-bit Single-chip Communication LSI. Overview
 8-bit Single-chip Communication LSI Overview The MN101EF69D is single chip communication LSI with the BPSK communication facility. By the BPSK communication facility, many (up to 32) MN101EF69Ds share
8-bit Single-chip Communication LSI Overview The MN101EF69D is single chip communication LSI with the BPSK communication facility. By the BPSK communication facility, many (up to 32) MN101EF69Ds share
Regarding the change of names mentioned in the document, such as Hitachi Electric and Hitachi XX, to Renesas Technology Corp.
 To all our customers Regarding the change of names mentioned in the document, such as Hitachi Electric and Hitachi XX, to Renesas Technology Corp. The semiconductor operations of Mitsubishi Electric and
To all our customers Regarding the change of names mentioned in the document, such as Hitachi Electric and Hitachi XX, to Renesas Technology Corp. The semiconductor operations of Mitsubishi Electric and
M3H Group(1) Application Note. I 2 C Interface (I2C-B) MASTER/SLAVE
 M3H Group(1) I 2 C Interface (I2C-B) MASTER/SLAVE Outlines This application note is a reference material for developing products using the Master/Slave function in I2C interface (I2C) functions of M3H
M3H Group(1) I 2 C Interface (I2C-B) MASTER/SLAVE Outlines This application note is a reference material for developing products using the Master/Slave function in I2C interface (I2C) functions of M3H
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
MN101E50 Series. 8-bit Single-chip Microcontroller
 8-bit Single-chip Microcontroller Overview The MN101E series of 8-bit single-chip microcomputers (the memory expansion version of MN101C series) incorporate multiple types of peripheral functions. This
8-bit Single-chip Microcontroller Overview The MN101E series of 8-bit single-chip microcomputers (the memory expansion version of MN101C series) incorporate multiple types of peripheral functions. This
Flash Self-programming Library
 16 Flash Self-programming Library Type T01, European Release 16 Bit Single-chip Microcontroller RL78 Series Installer: RENESAS_FSL_RL78_T01E_Vx.xxx All information contained in these materials, including
16 Flash Self-programming Library Type T01, European Release 16 Bit Single-chip Microcontroller RL78 Series Installer: RENESAS_FSL_RL78_T01E_Vx.xxx All information contained in these materials, including
Data Flash Reprogramming Using Background Operation (BGO) 1. Introduction Description of Functions Used... 4
 Introduction APPLICATION NOTE R01AN0290EJ0220 Rev.2.20 This application note describes the use of background operation (BGO) on the SH7216. BGO allows the CPU to perform other operations while the on-chip
Introduction APPLICATION NOTE R01AN0290EJ0220 Rev.2.20 This application note describes the use of background operation (BGO) on the SH7216. BGO allows the CPU to perform other operations while the on-chip
( 2 / 26 ) * TR4943, R4945 and R4945A are trademarks of Advantest Corporation.
 PCA4738F-42A PCA4738S-42A PCA4738F-64A PCA4738L-64A PCA4738S-64A PCA4738H-80A PCA4738G-80A PCA4738F-80A PCA4738L-80A PCA4738H-100A PCA4738G-100A PCA4738F-100A PCA4738L-100A PCA4738L-160A PCA4738F-176A
PCA4738F-42A PCA4738S-42A PCA4738F-64A PCA4738L-64A PCA4738S-64A PCA4738H-80A PCA4738G-80A PCA4738F-80A PCA4738L-80A PCA4738H-100A PCA4738G-100A PCA4738F-100A PCA4738L-100A PCA4738L-160A PCA4738F-176A
SPI Overview and Operation
 White Paper Abstract Communications between semiconductor devices is very common. Many different protocols are already defined in addition to the infinite ways to communicate with a proprietary protocol.
White Paper Abstract Communications between semiconductor devices is very common. Many different protocols are already defined in addition to the infinite ways to communicate with a proprietary protocol.
M3H Group(1) Application Note I 2 C Interface (I2C-B)
 M3H Group(1) I 2 C Interface (I2C-B) Outlines This application note is a erence material for developing products using I2C interface (I2C) functions of M3H Group(1). This document helps the user check
M3H Group(1) I 2 C Interface (I2C-B) Outlines This application note is a erence material for developing products using I2C interface (I2C) functions of M3H Group(1). This document helps the user check
Date: Jul. 26, 2016 RENESAS TECHNICAL UPDATE TOYOSU FORESIA, , Toyosu, Koto-ku, Tokyo , Japan Renesas Electronics Corporation
 Date: Jul. 26, 2016 RENESAS TECHNICAL UPDATE TOYOSU FORESIA, 3-2-24, Toyosu, Koto-ku, Tokyo 135-0061, Japan Renesas Electronics Corporation Product Category MPU/MCU Document No. TN-SY*-A008A/E Rev. 1.00
Date: Jul. 26, 2016 RENESAS TECHNICAL UPDATE TOYOSU FORESIA, 3-2-24, Toyosu, Koto-ku, Tokyo 135-0061, Japan Renesas Electronics Corporation Product Category MPU/MCU Document No. TN-SY*-A008A/E Rev. 1.00
S1C17 Family EEPROM Emulation Library Manual
 S1C17 Family EEPROM Emulation Library Manual Rev.1.1 Evaluation board/kit and Development tool important notice 1. This evaluation board/kit or development tool is designed for use for engineering evaluation,
S1C17 Family EEPROM Emulation Library Manual Rev.1.1 Evaluation board/kit and Development tool important notice 1. This evaluation board/kit or development tool is designed for use for engineering evaluation,
Date: Jul. 26, 2016 RENESAS TECHNICAL UPDATE TOYOSU FORESIA, , Toyosu, Koto-ku, Tokyo , Japan Renesas Electronics Corporation
 Date: Jul. 26, 2016 RENESAS TECHNICAL UPDATE TOYOSU FORESIA, 3-2-24, Toyosu, Koto-ku, Tokyo 135-0061, Japan Renesas Electronics Corporation Product Category MPU/MCU Document No. TN-SY*-A007A/E Rev. 1.00
Date: Jul. 26, 2016 RENESAS TECHNICAL UPDATE TOYOSU FORESIA, 3-2-24, Toyosu, Koto-ku, Tokyo 135-0061, Japan Renesas Electronics Corporation Product Category MPU/MCU Document No. TN-SY*-A007A/E Rev. 1.00
HCS12 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Block Guide V02.06
 DOCUMENT NUMBER S12SCIV2/D HCS12 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Block Guide V02.06 Original Release Date: June 4, 1999 Revised: Oct 10, 2001 Motorola, Inc. Motorola reserves the right to make changes
DOCUMENT NUMBER S12SCIV2/D HCS12 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Block Guide V02.06 Original Release Date: June 4, 1999 Revised: Oct 10, 2001 Motorola, Inc. Motorola reserves the right to make changes
A B C D E F 0480 FE B F5 3B FC F3 E 1A 1D 2A 2D 3A 3D 4A 4D 5A 5D 6A 6D 7A 7D
 What's on the 9S12 bus as it executes a program The 9S12 Serial Communications Interface 9S12 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Block Guide V02.05 Huang, Sections 9.2-9.6 Consider a 9S12 executing
What's on the 9S12 bus as it executes a program The 9S12 Serial Communications Interface 9S12 Serial Communications Interface (SCI) Block Guide V02.05 Huang, Sections 9.2-9.6 Consider a 9S12 executing
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April st, 2, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took over
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April st, 2, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took over
AN Entering ISP mode from user code. Document information. ARM ISP, bootloader
 Rev. 03 13 September 2006 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content ARM ISP, bootloader Entering ISP mode is normally done by sampling a pin during reset. This application note
Rev. 03 13 September 2006 Application note Document information Info Keywords Abstract Content ARM ISP, bootloader Entering ISP mode is normally done by sampling a pin during reset. This application note
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documts On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Resas Technology Corporation, and Resas Electronics Corporation took over all
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documts On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Resas Technology Corporation, and Resas Electronics Corporation took over all
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 21, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took over
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 21, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took over
Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents
 To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
To our customers, Old Company Name in Catalogs and Other Documents On April 1 st, 2010, NEC Electronics Corporation merged with Renesas Technology Corporation, and Renesas Electronics Corporation took
