Trends in Time Series of Parameters from Ultrasonic Images due to Metabolic Activities of the Human Liver
|
|
|
- Collin May
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Trends in Time Series of Parameters from Ultrasonic Images due to Metabolic Activities of the Human Liver Christian Hansen 1, Ulrich Scheipers 1, Nils Hüttebräuker 1, Michael Gebel 2 and Helmut Ermert 1 1 Institut für Hochfrequenztechnik, Ruhr-Universität Bochum, Bochum, Germany 2 Abteilung für Gastroenterologie, Hepatologie, Endokrinologie, Zentrum für Innere Medizin, Medizinische Hochschule Hannover, Hannover, Germany christian.hansen@ruhr-uni-bochum.de Abstract. Being the biggest inner organ of humans, the liver contributes decisively to metabolism. Hereby, liver activities result from reactions on ingestion and digestion and are assumed to influence the acoustical properties of the liver tissue. In this work we present initial results of the investigation of aforementioned reactions by observing the liver in-vivo with ultrasound during several hours. After extracting various parameters from the recorded radio frequency data sets, time series of these parameters are analysed in order to find relations between a supervised ingestion and changes in the computed time series. 1 Introduction The liver (greek: hepar) is the biggest inner organ of humans performing different metabolic functions. The main tasks of the liver are detoxication of blood, composition, decomposition and modification of metabolites and storage of glycogen. In its function as an exocrine gland the liver also produces biles, which is stored in the gallbladder. The blood supply of the liver is secured from two independent vessel systems. On the one hand the vena porta brings in fresh blood from the gastrointestinal tract (70 % of oxygen supply), on the other hand the arteria hepatica provides a second inflow (30 % of oxygen supply). Up to now, the human liver has been examined concerning different perspectives and questions using all prevalent imaging modalities. Especially diagnostic ultrasound has become popular due to its flexible, non-ionising and inexpensive application. Ultrasonic research has been done on focal and diffuse lesions (i.e. cysts, cancer, cirrhosis etc.) utilizing tissue characterisation, flow analysis, ultrasound contrast agents, elastography and more. Nevertheless, all investigations were focused on spatial considerations and not on inspections of temporal changes in the (healthy or pathological) liver due to metabolic processes. Thus, the analysis of trends in temporal parameter-charts of ultrasonic data is a novel approach to investigate activities of the liver.
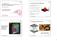
2 The objective of this work is, therefore, the derivation of a relation between a supervised ingestion (activation of the liver) and a change in the corresponding time series computed on parameters that are commonly used in ultrasonic tissue characterization [1]. Such a change in the time series according to a variation in the acoustical properties of the tissue could result from different reasons [2], e.g. an increase of secretion activity, an increase of blood perfusion or changes in pressure due to contraction of the gallbladder. 2 Methods 2.1 Data Acquisition For a period of three hours the livers of four volunteers (normal weight, according to body mass index, BMI) have been scanned using a Siemens Sonoline Antares ultrasound system (probe: curved array C5-2, center frequency: 3.25 MHz, bandwidth: 5.5 MHz, depth: 13 cm, focus: 6 cm, field of view: 70.5, scan lines: 300). In combination with this system we used the Axius Direct Ultrasound Research Interface (URI) to obtain unprocessed, beamformed RF-data with 16 bit resolution and 40 MHz sampling rate. During the aforementioned three-hour-period, one data-frame was acquired and stored every minute. The ultrasound scans were conducted intercostally on the seventh segment of the liver (upper right corner of the liver). This segment turned out to be particularly suitable for tissue characterisation and functional analysis, since only few larger vessels are crossing. This property results in particular homogeneous tissue. In order to spatially stabilise the data acquisition, the ultrasound transducer was fastened on the probands with a custom made belt (Fig. 1 (a)). Furthermore, probands were instructed to exhale completely before each acquisition. Thus, the imaged liver intersection could be maintained throughout the examination. (a) Ultrasound imaging, using a custom made belt to fasten the ultrasound probe. (b) Ultrasound image of the liver. Segmentation into ROIs and combination of ROIs in an AOI. Fig. 1.
3 Each proband was scanned twice, both times in the morning: The first day completely fasting, the other day fasting in the beginning and then after ingestion of a hardboiled egg to stimulate the liver by lipids. 2.2 Parameter Extraction For parameter extraction, parts of an existing system for tissue characterization was used [1,3]. Every data set was subdivided into up to 3000 Regions Of Interest (ROIs). The ROIs consisted of 128 sample points in the transducer axial direction and of 16 scan lines in the lateral direction. Their axial and lateral overlaps were 75 % and 50 %, respectively. Thus, each ROI comprises an area of approximately 5.0 mm 7.0 mm at focal depth (schematic scetch: Fig. 1 (b)). Up to 130 parameters were calculated for each ROI. These parameters can be divided into two larger groups, i.e. spectrum parameters and texture parameters. Spectrum parameters: On the one hand, spectrum parameters were calculated using Fourier transformation after applying a Hamming window to the radio frequency data (RF data) of each ROI. On the other hand, an autoregressive model (AR model) was used to estimate the power spectrum. The order of this model was 15, according to the results achieved by the Akaike information model [4]. For both cases, spectral results of adjacent scan lines were averaged to obtain unbiased estimators. Texture parameters: Both first order and second order texture parameters were computed. Hereby, computations were performed on envelope detected data using Hilbert transform. First order texture parameters consisted of different estimates of echo amplitude evaluating the grey value histograms. Second order parameters (i.e. cooccurrence parameters) incorporate spatial relations between grey scale pixels according to [5,6]. However, those parameters were computed for different distances of the cooccurrance matrix, but only for axial direction to account for the sector geometry of the transducer. For the last step of parameter extraction a particular homogeneous area within the imaged seventh segment of the liver was chosen and called the Area Of Interest (AOI). This AOI comprised an area of approximately 1.6 cm 2.3 cm at focal depth and, therefore, consisted of 105 ROIs. The values of each parameter (one per ROI) were averaged within this AOI. Admittedly, before averaging the values of the ROIs, an elimination of outliers was performed by using the MAD criterion (Median Absolute Deviation). Here, those ROIs of a parameter were neglected whose absolute deviation from their median was greater than six times MAD. The technique of averaging several small, overlapping ROIs and, hence, merging them to one bigger AOI (instead of directly extracting one parameter per AOI) was conducted in order to achieve unbiased estimations. 2.3 Time Series Analysis Stringing all computed values of one parameter together and plotting them over time, one time series per parameter is obtained. Several statistical techniques were carried out for time series analysis [4,7]. However, this analysis was only
4 performed in time domain, so far. In order to compensate for noise effects and to better detect changes in time series, we smoothed the series by using moving average filters of different window-length, smoothing splines by incorporating a smoothing-parameter of 15 and linear regression models of different orders. Before accomplishing these smoothing techniques, temporal median filtering was conducted using a window-length of five, in order to reduce the contribution of outliers. Furthermore, the time series were analysed in intervals, dividing the series in time segments with respect to their local trends. This division has been conducted by automatically detecting trend reversals [7] and fitting a first order linear regression model within these intervals. 3 Results The analysis of the computed time series showed that a first group of parameters (consisting of both texture and spectral parameters) are not affected by the lipidstimulation. A change or trend reversal can neither be detected in the fasting nor in the non-fasting time series. However, in addition to this first group a second group of parameters (consisting of both types of parameters, too) showed a trend reversal in their non-fasting time series, while the results obtained from the fasting series featured no trend reversal. In figure 2 the median-filtered time series of the normalised second order texture parameter Contrast [5,6] are exemplarily shown for the fasting (a) and the non-fasting (b,c) case of one proband (activation 31 minutes after the start of the examination, BMI = 20.8 kg/m 2 ). In order to smooth the time series, the fasting (a) as well as the non-fasting charts (b) were processed using smoothing splines. Apparently, the fasting series stays stationary, oscillating on a constant level. However, the non-fasting series appears to change its level over time. Performing the detection of trend reversals on the non-fasting series (c), a trend reversal can be found 21 minutes after the ingestion. This delay corresponds to the time of an increase of portal blood circulation after an ingestion and, hence, seems to be also reasonable from a medical point of view. 4 Conclusion The described results encourage for further investigations. Currently, a larger data base is built up by scanning more probands. However, future examinations will be conducted using an ECG trigger (ECG: electrocardiogram) in order to enhance the stabilisation of data acquisition. Investigations have to be made to ensure that computed trends are deterministic (i.e. result form lipid stimulation) and not stochastic. In particular examinations with no activation have to be analysed concerning the observed oscillations. For the next step, parameters will be combined to reduce their large number by applying principal component analysis. Furthermore, future investigations will be conducted not only in the
5 (a) No activation. Medianfiltered series (thin) and smoothing splines (bold). (b) Activation at 31 minutes (vert. line). Medianfiltered series (thin) and smoothing splines (bold). (c) Activation at 31 minutes. Median-filtered series (thin), trend reversals (dashed lines) and first order regression (bold). Fig. 2. Time series of normalised second order texture parameter Contrast. time domain, but also in the frequency domain. Therefore, analysis using jointtime-frequency techniques [8] are considered promising. 5 Acknowledgement This work is an activity of the Ruhr Center of Excellence for Medical Engineering (Kompetenzzentrum Medizintechnik Ruhr, KMR), Bochum. We would like to thank Siemens Medical Solutions for providing us with the Axius Direct Ultrasound Research Interface (URI). References 1. Scheipers, U., Ermert, H., et al: Ultrasonic multifeature tissue characterization for prostate diagnostics. Ultrasound Med Biol 29 (2003) Teichgraeber, U.K.E., Gebel, M., et al: Effect of respiration, exercise, and food intake on hepatic vein circulation. J Ultrasound Med 16 (1997) Scheipers, U., Ermert, H., et al: Ultrasonic tissiue characterization for prostate diagnostics: Spectral parameters vs. texture parameters. Biomed Tech (Berl) 48 (2003) Shumway, R.H., Stoffer, D.S.: Time series analysis and its applications. Springer, New York (2000) 5. Haralick, R.M., et al: Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern C 3 (1973) Valckx, F.M., Thijssen, J.M.: Characterization of echographic image texture by cooccurrance matrix parameters. Ultrasound Med Biol 23 (1997) Schlittgen, R., Streitberg, B.H.J.: Zeitreihenanalyse. 9. edn. (Oldenbourg, München) 8. Qian, S., Chen, D.: Joint time-frequency analysis: Methods and applications. Prentice-Hall, Upper Saddle River (1996)
Texture-Based Detection of Myositis in Ultrasonographies
 Texture-Based Detection of Myositis in Ultrasonographies Tim König 1, Marko Rak 1, Johannes Steffen 1, Grit Neumann 2, Ludwig von Rohden 2, Klaus D. Tönnies 1 1 Institut für Simulation & Graphik, Otto-von-Guericke-Universität
Texture-Based Detection of Myositis in Ultrasonographies Tim König 1, Marko Rak 1, Johannes Steffen 1, Grit Neumann 2, Ludwig von Rohden 2, Klaus D. Tönnies 1 1 Institut für Simulation & Graphik, Otto-von-Guericke-Universität
Towards an Estimation of Acoustic Impedance from Multiple Ultrasound Images
 Towards an Estimation of Acoustic Impedance from Multiple Ultrasound Images Christian Wachinger 1, Ramtin Shams 2, Nassir Navab 1 1 Computer Aided Medical Procedures (CAMP), Technische Universität München
Towards an Estimation of Acoustic Impedance from Multiple Ultrasound Images Christian Wachinger 1, Ramtin Shams 2, Nassir Navab 1 1 Computer Aided Medical Procedures (CAMP), Technische Universität München
Development and validation of a short-lag spatial coherence theory for photoacoustic imaging
 Development and validation of a short-lag spatial coherence theory for photoacoustic imaging Michelle T. Graham 1 and Muyinatu A. Lediju Bell 1,2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Johns
Development and validation of a short-lag spatial coherence theory for photoacoustic imaging Michelle T. Graham 1 and Muyinatu A. Lediju Bell 1,2 1 Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, Johns
Recent Advances in Non-Invasive Thermometry Using Changes in Backscattered Ultrasound
 Recent Advances in Non-Invasive Thermometry Using Changes in Backscattered Ultrasound R. Martin Arthur 1, Jason W. Trobaugh 1, William L. Straube 2 and Eduardo G. Moros 2 1 Electrical & Systems Engineering
Recent Advances in Non-Invasive Thermometry Using Changes in Backscattered Ultrasound R. Martin Arthur 1, Jason W. Trobaugh 1, William L. Straube 2 and Eduardo G. Moros 2 1 Electrical & Systems Engineering
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU)
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Physics Tutorial Physics Tutorial Purpose: Training: Assessments: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Physics Tutorial Physics Tutorial Purpose: Training: Assessments: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for
ESTIMATION OF THE BLOOD VELOCITY SPECTRUM USING A RECURSIVE LATTICE FILTER
 Jørgen Arendt Jensen et al. Paper presented at the IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, San Antonio, Texas, 996: ESTIMATION OF THE BLOOD VELOCITY SPECTRUM USING A RECURSIVE LATTICE FILTER Jørgen Arendt
Jørgen Arendt Jensen et al. Paper presented at the IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium, San Antonio, Texas, 996: ESTIMATION OF THE BLOOD VELOCITY SPECTRUM USING A RECURSIVE LATTICE FILTER Jørgen Arendt
Medical Image Retrieval Performance Comparison using Texture Features
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 9, Issue 9 (January 2014), PP. 30-34 Medical Image Retrieval Performance Comparison
International Journal of Engineering Research and Development e-issn: 2278-067X, p-issn: 2278-800X, www.ijerd.com Volume 9, Issue 9 (January 2014), PP. 30-34 Medical Image Retrieval Performance Comparison
Journal of Visualized Experiments
 Video Article Real-time Monitoring of High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) Ablation of In Vitro Canine Livers Using Harmonic Motion Imaging for Focused Ultrasound (HMIFU) Julien Grondin 1, Thomas Payen
Video Article Real-time Monitoring of High Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) Ablation of In Vitro Canine Livers Using Harmonic Motion Imaging for Focused Ultrasound (HMIFU) Julien Grondin 1, Thomas Payen
A Model-Independent, Multi-Image Approach to MR Inhomogeneity Correction
 Tina Memo No. 2007-003 Published in Proc. MIUA 2007 A Model-Independent, Multi-Image Approach to MR Inhomogeneity Correction P. A. Bromiley and N.A. Thacker Last updated 13 / 4 / 2007 Imaging Science and
Tina Memo No. 2007-003 Published in Proc. MIUA 2007 A Model-Independent, Multi-Image Approach to MR Inhomogeneity Correction P. A. Bromiley and N.A. Thacker Last updated 13 / 4 / 2007 Imaging Science and
Front-line research in Ultrasound CFU research Part 2: Fast Vector Flow Imaging, Pressure Gradients, Super Resolution and Portable Scanners
 Front-line research in Ultrasound CFU research Part 2: Fast Vector Flow Imaging, Pressure Gradients, Super Resolution and Portable Scanners Can measure 3-D flow fast with only 124 transducer elements?
Front-line research in Ultrasound CFU research Part 2: Fast Vector Flow Imaging, Pressure Gradients, Super Resolution and Portable Scanners Can measure 3-D flow fast with only 124 transducer elements?
A Robust Meshing and Calibration Approach for Sensorless Freehand 3D Ultrasound
 A Robust Meshing and Calibration Approach for Sensorless Freehand 3D Ultrasound Hassan Rivaz a,emadboctor a, and Gabor Fichtinger a,b,c Department of a Computer Science, b Mechanical Engineering, c Radiology,
A Robust Meshing and Calibration Approach for Sensorless Freehand 3D Ultrasound Hassan Rivaz a,emadboctor a, and Gabor Fichtinger a,b,c Department of a Computer Science, b Mechanical Engineering, c Radiology,
High Resolution Phased Array Imaging using the Total Focusing Method
 19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 High Resolution Phased Array Imaging using the Total Focusing Method Wolfram A. Karl DEUTSCH 1, Werner ROYE 1, Helge RAST 1, Philippe BENOIST 2 1
19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 High Resolution Phased Array Imaging using the Total Focusing Method Wolfram A. Karl DEUTSCH 1, Werner ROYE 1, Helge RAST 1, Philippe BENOIST 2 1
Efficient Image Compression of Medical Images Using the Wavelet Transform and Fuzzy c-means Clustering on Regions of Interest.
 Efficient Image Compression of Medical Images Using the Wavelet Transform and Fuzzy c-means Clustering on Regions of Interest. D.A. Karras, S.A. Karkanis and D. E. Maroulis University of Piraeus, Dept.
Efficient Image Compression of Medical Images Using the Wavelet Transform and Fuzzy c-means Clustering on Regions of Interest. D.A. Karras, S.A. Karkanis and D. E. Maroulis University of Piraeus, Dept.
Fast 3D Mean Shift Filter for CT Images
 Fast 3D Mean Shift Filter for CT Images Gustavo Fernández Domínguez, Horst Bischof, and Reinhard Beichel Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision, Graz University of Technology Inffeldgasse 16/2, A-8010,
Fast 3D Mean Shift Filter for CT Images Gustavo Fernández Domínguez, Horst Bischof, and Reinhard Beichel Institute for Computer Graphics and Vision, Graz University of Technology Inffeldgasse 16/2, A-8010,
Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks
 Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks Du-Yih Tsai, Masaru Sekiya and Yongbum Lee Department of Radiological Technology, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of
Computer-Aided Diagnosis in Abdominal and Cardiac Radiology Using Neural Networks Du-Yih Tsai, Masaru Sekiya and Yongbum Lee Department of Radiological Technology, School of Health Sciences, Faculty of
Prostate Tissue Texture Feature Extraction for Suspicious Regions Identification on TRUS Images
 Prostate Tissue Texture Feature Extraction for Suspicious Regions Identification on TRUS Images S.S. Mohamed, J. Li, M.M.A. Salama and G. Freeman In this work, two different approaches are proposed for
Prostate Tissue Texture Feature Extraction for Suspicious Regions Identification on TRUS Images S.S. Mohamed, J. Li, M.M.A. Salama and G. Freeman In this work, two different approaches are proposed for
ADVANCED ULTRASOUND WAVEFORM ANALYSIS PACKAGE FOR MANUFACTURING AND IN-SERVICE USE R. A Smith, QinetiQ Ltd, Farnborough, GU14 0LX, UK.
 ADVANCED ULTRASOUND WAVEFORM ANALYSIS PACKAGE FOR MANUFACTURING AND IN-SERVICE USE R. A Smith, QinetiQ Ltd, Farnborough, GU14 0LX, UK. Abstract: Users of ultrasonic NDT are fundamentally limited by the
ADVANCED ULTRASOUND WAVEFORM ANALYSIS PACKAGE FOR MANUFACTURING AND IN-SERVICE USE R. A Smith, QinetiQ Ltd, Farnborough, GU14 0LX, UK. Abstract: Users of ultrasonic NDT are fundamentally limited by the
Edge-Preserving Denoising for Segmentation in CT-Images
 Edge-Preserving Denoising for Segmentation in CT-Images Eva Eibenberger, Anja Borsdorf, Andreas Wimmer, Joachim Hornegger Lehrstuhl für Mustererkennung, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg
Edge-Preserving Denoising for Segmentation in CT-Images Eva Eibenberger, Anja Borsdorf, Andreas Wimmer, Joachim Hornegger Lehrstuhl für Mustererkennung, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität Erlangen-Nürnberg
CHAPTER 2 TEXTURE CLASSIFICATION METHODS GRAY LEVEL CO-OCCURRENCE MATRIX AND TEXTURE UNIT
 CHAPTER 2 TEXTURE CLASSIFICATION METHODS GRAY LEVEL CO-OCCURRENCE MATRIX AND TEXTURE UNIT 2.1 BRIEF OUTLINE The classification of digital imagery is to extract useful thematic information which is one
CHAPTER 2 TEXTURE CLASSIFICATION METHODS GRAY LEVEL CO-OCCURRENCE MATRIX AND TEXTURE UNIT 2.1 BRIEF OUTLINE The classification of digital imagery is to extract useful thematic information which is one
연구용유방초음파질관리 원광대학병원김혜원
 연구용유방초음파질관리 원광대학병원김혜원 Why US QC? Quality control (QC) testing of ultrasound scanners is important to verify the proper and consistent operation of these devices. main goal ; quality improvement Guidelines
연구용유방초음파질관리 원광대학병원김혜원 Why US QC? Quality control (QC) testing of ultrasound scanners is important to verify the proper and consistent operation of these devices. main goal ; quality improvement Guidelines
Respiratory Motion Compensation for C-arm CT Liver Imaging
 Respiratory Motion Compensation for C-arm CT Liver Imaging Aline Sindel 1, Marco Bögel 1,2, Andreas Maier 1,2, Rebecca Fahrig 3, Joachim Hornegger 1,2, Arnd Dörfler 4 1 Pattern Recognition Lab, FAU Erlangen-Nürnberg
Respiratory Motion Compensation for C-arm CT Liver Imaging Aline Sindel 1, Marco Bögel 1,2, Andreas Maier 1,2, Rebecca Fahrig 3, Joachim Hornegger 1,2, Arnd Dörfler 4 1 Pattern Recognition Lab, FAU Erlangen-Nürnberg
IDENTIFYING GEOMETRICAL OBJECTS USING IMAGE ANALYSIS
 IDENTIFYING GEOMETRICAL OBJECTS USING IMAGE ANALYSIS Fathi M. O. Hamed and Salma F. Elkofhaifee Department of Statistics Faculty of Science University of Benghazi Benghazi Libya felramly@gmail.com and
IDENTIFYING GEOMETRICAL OBJECTS USING IMAGE ANALYSIS Fathi M. O. Hamed and Salma F. Elkofhaifee Department of Statistics Faculty of Science University of Benghazi Benghazi Libya felramly@gmail.com and
Computer Aided Diagnosis Based on Medical Image Processing and Artificial Intelligence Methods
 International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 3, Number 9 (2013), pp. 887-892 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Computer
International Journal of Information and Computation Technology. ISSN 0974-2239 Volume 3, Number 9 (2013), pp. 887-892 International Research Publications House http://www. irphouse.com /ijict.htm Computer
Automated segmentation methods for liver analysis in oncology applications
 University of Szeged Department of Image Processing and Computer Graphics Automated segmentation methods for liver analysis in oncology applications Ph. D. Thesis László Ruskó Thesis Advisor Dr. Antal
University of Szeged Department of Image Processing and Computer Graphics Automated segmentation methods for liver analysis in oncology applications Ph. D. Thesis László Ruskó Thesis Advisor Dr. Antal
Fiber Selection from Diffusion Tensor Data based on Boolean Operators
 Fiber Selection from Diffusion Tensor Data based on Boolean Operators D. Merhof 1, G. Greiner 2, M. Buchfelder 3, C. Nimsky 4 1 Visual Computing, University of Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany 2 Computer Graphics
Fiber Selection from Diffusion Tensor Data based on Boolean Operators D. Merhof 1, G. Greiner 2, M. Buchfelder 3, C. Nimsky 4 1 Visual Computing, University of Konstanz, Konstanz, Germany 2 Computer Graphics
ECE 176 Digital Image Processing Handout #14 Pamela Cosman 4/29/05 TEXTURE ANALYSIS
 ECE 176 Digital Image Processing Handout #14 Pamela Cosman 4/29/ TEXTURE ANALYSIS Texture analysis is covered very briefly in Gonzalez and Woods, pages 66 671. This handout is intended to supplement that
ECE 176 Digital Image Processing Handout #14 Pamela Cosman 4/29/ TEXTURE ANALYSIS Texture analysis is covered very briefly in Gonzalez and Woods, pages 66 671. This handout is intended to supplement that
Advanced Image Reconstruction Methods for Photoacoustic Tomography
 Advanced Image Reconstruction Methods for Photoacoustic Tomography Mark A. Anastasio, Kun Wang, and Robert Schoonover Department of Biomedical Engineering Washington University in St. Louis 1 Outline Photoacoustic/thermoacoustic
Advanced Image Reconstruction Methods for Photoacoustic Tomography Mark A. Anastasio, Kun Wang, and Robert Schoonover Department of Biomedical Engineering Washington University in St. Louis 1 Outline Photoacoustic/thermoacoustic
Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images
 16 Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images 3.1 MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) MRI is a technique of measuring physical structure within the human anatomy. Our proposed research focuses
16 Chapter 3 Set Redundancy in Magnetic Resonance Brain Images 3.1 MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) MRI is a technique of measuring physical structure within the human anatomy. Our proposed research focuses
CHAPTER 6 DETECTION OF MASS USING NOVEL SEGMENTATION, GLCM AND NEURAL NETWORKS
 130 CHAPTER 6 DETECTION OF MASS USING NOVEL SEGMENTATION, GLCM AND NEURAL NETWORKS A mass is defined as a space-occupying lesion seen in more than one projection and it is described by its shapes and margin
130 CHAPTER 6 DETECTION OF MASS USING NOVEL SEGMENTATION, GLCM AND NEURAL NETWORKS A mass is defined as a space-occupying lesion seen in more than one projection and it is described by its shapes and margin
GE Healthcare. Agile Ultrasound. The Next Revolution in Ultrasound Imaging
 Agile Ultrasound The Next Revolution in Ultrasound Imaging Abstract Diagnostic use of ultrasound has greatly expanded over the past couple of decades because it offers many advantages as an imaging modality.
Agile Ultrasound The Next Revolution in Ultrasound Imaging Abstract Diagnostic use of ultrasound has greatly expanded over the past couple of decades because it offers many advantages as an imaging modality.
Refined Measurement of Digital Image Texture Loss Peter D. Burns Burns Digital Imaging Fairport, NY USA
 Copyright 3 SPIE Refined Measurement of Digital Image Texture Loss Peter D. Burns Burns Digital Imaging Fairport, NY USA ABSTRACT Image texture is the term given to the information-bearing fluctuations
Copyright 3 SPIE Refined Measurement of Digital Image Texture Loss Peter D. Burns Burns Digital Imaging Fairport, NY USA ABSTRACT Image texture is the term given to the information-bearing fluctuations
TEXTURE BASED APPROACH FOR BUILDING THE IMAGISTIC MODEL OF HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA. Pharmacy, Cluj-Napoca
 TEXTURE BASED APPROACH FOR BUILDING THE IMAGISTIC MODEL OF HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA Delia Mitrea, Sergiu Nedevschi, Paulina Mitrea, Monica Lupsor 2, Radu Badea 2 Computer-Science Department, Technical
TEXTURE BASED APPROACH FOR BUILDING THE IMAGISTIC MODEL OF HEPATOCELLULAR CARCINOMA Delia Mitrea, Sergiu Nedevschi, Paulina Mitrea, Monica Lupsor 2, Radu Badea 2 Computer-Science Department, Technical
Tracked Ultrasound Elastography (TrUE)
 Tracked Ultrasound Elastography (TrUE) Pezhman Foroughi, Hassan Rivaz, Ioana N. Fleming, Gregory D. Hager, and Emad M. Boctor,2 Dept. of Computer Science, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA 2
Tracked Ultrasound Elastography (TrUE) Pezhman Foroughi, Hassan Rivaz, Ioana N. Fleming, Gregory D. Hager, and Emad M. Boctor,2 Dept. of Computer Science, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA 2
3-D Compounding of B-Scan Ultrasound Images
 3-D Compounding of B-Scan Ultrasound Images Jochen F. Krücker, Charles R. Meyer, Theresa A. Tuthill, Gerald L. LeCarpentier, J. Brian Fowlkes, Paul L. Carson University of Michigan, Dept. of Radiology,
3-D Compounding of B-Scan Ultrasound Images Jochen F. Krücker, Charles R. Meyer, Theresa A. Tuthill, Gerald L. LeCarpentier, J. Brian Fowlkes, Paul L. Carson University of Michigan, Dept. of Radiology,
A Workflow Optimized Software Platform for Multimodal Neurosurgical Planning and Monitoring
 A Workflow Optimized Software Platform for Multimodal Neurosurgical Planning and Monitoring Eine Workflow Optimierte Software Umgebung für Multimodale Neurochirurgische Planung und Verlaufskontrolle A
A Workflow Optimized Software Platform for Multimodal Neurosurgical Planning and Monitoring Eine Workflow Optimierte Software Umgebung für Multimodale Neurochirurgische Planung und Verlaufskontrolle A
SAFT-Reconstruction in ultrasonic immersion technique using phased array transducers
 SAFT-Reconstruction in ultrasonic immersion technique using phased array transducers J. Kitze, J. Prager, R. Boehm, U. Völz, H.-J. Montag Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing Berlin, Division
SAFT-Reconstruction in ultrasonic immersion technique using phased array transducers J. Kitze, J. Prager, R. Boehm, U. Völz, H.-J. Montag Federal Institute for Materials Research and Testing Berlin, Division
Nuclear Associates and
 Nuclear Associates 84-317 and 84-317-7000 Multipurpose Tissue/Cyst Ultrasound Phantoms Users Manual February 2005 Manual No. 84-317-1 Rev. 2 2004, 2005 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserved. Printed in
Nuclear Associates 84-317 and 84-317-7000 Multipurpose Tissue/Cyst Ultrasound Phantoms Users Manual February 2005 Manual No. 84-317-1 Rev. 2 2004, 2005 Fluke Corporation, All rights reserved. Printed in
Image Processing and Analysis
 Image Processing and Analysis 3 stages: Image Restoration - correcting errors and distortion. Warping and correcting systematic distortion related to viewing geometry Correcting "drop outs", striping and
Image Processing and Analysis 3 stages: Image Restoration - correcting errors and distortion. Warping and correcting systematic distortion related to viewing geometry Correcting "drop outs", striping and
HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu HST.583 Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Data Acquisition and Analysis Fall 2008 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms.
FAULT DETECTION AND ISOLATION USING SPECTRAL ANALYSIS. Eugen Iancu
 FAULT DETECTION AND ISOLATION USING SPECTRAL ANALYSIS Eugen Iancu Automation and Mechatronics Department University of Craiova Eugen.Iancu@automation.ucv.ro Abstract: In this work, spectral signal analyses
FAULT DETECTION AND ISOLATION USING SPECTRAL ANALYSIS Eugen Iancu Automation and Mechatronics Department University of Craiova Eugen.Iancu@automation.ucv.ro Abstract: In this work, spectral signal analyses
A method and algorithm for Tomographic Imaging of highly porous specimen using Low Frequency Acoustic/Ultrasonic signals
 More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=15210 A method and algorithm for Tomographic Imaging of highly porous specimen using Low Frequency Acoustic/Ultrasonic signals Subodh P S 1,a, Reghunathan
More Info at Open Access Database www.ndt.net/?id=15210 A method and algorithm for Tomographic Imaging of highly porous specimen using Low Frequency Acoustic/Ultrasonic signals Subodh P S 1,a, Reghunathan
HIGH-PERFORMANCE TOMOGRAPHIC IMAGING AND APPLICATIONS
 HIGH-PERFORMANCE TOMOGRAPHIC IMAGING AND APPLICATIONS Hua Lee and Yuan-Fang Wang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Santa Barbara ABSTRACT Tomographic imaging systems
HIGH-PERFORMANCE TOMOGRAPHIC IMAGING AND APPLICATIONS Hua Lee and Yuan-Fang Wang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California, Santa Barbara ABSTRACT Tomographic imaging systems
Model-Based Segmentation of Impression Marks
 Model-Based Segmentation of Impression Marks Christoph Brein Institut für Mess- und Regelungstechnik, Universität Karlsruhe (TH), D-76128 Karlsruhe, Germany ABSTRACT Impression marks are commonly found
Model-Based Segmentation of Impression Marks Christoph Brein Institut für Mess- und Regelungstechnik, Universität Karlsruhe (TH), D-76128 Karlsruhe, Germany ABSTRACT Impression marks are commonly found
Wavelet-based Texture Classification of Tissues in Computed Tomography
 Wavelet-based Texture Classification of Tissues in Computed Tomography Lindsay Semler, Lucia Dettori, Jacob Furst Intelligent Multimedia Processing Laboratory School of Computer Science, Telecommunications,
Wavelet-based Texture Classification of Tissues in Computed Tomography Lindsay Semler, Lucia Dettori, Jacob Furst Intelligent Multimedia Processing Laboratory School of Computer Science, Telecommunications,
LOGIQ. V2 Ultrasound. Part of LOGIQ Vision Series. Imagination at work LOGIQ is a trademark of General Electric Company.
 TM LOGIQ V2 Ultrasound Part of LOGIQ Vision Series Imagination at work The brilliance of color. The simplicity of GE. Now you can add the advanced capabilities of color Doppler to patient care with the
TM LOGIQ V2 Ultrasound Part of LOGIQ Vision Series Imagination at work The brilliance of color. The simplicity of GE. Now you can add the advanced capabilities of color Doppler to patient care with the
Adaptive Focusing Technology for the Inspection of Variable Geometry. Composite Material
 More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=22711 Adaptive Focusing Technology for the Inspection of Variable Geometry Composite Material Etienne GRONDIN 1 1 Olympus Scientific Solutions Americas,
More info about this article: http://www.ndt.net/?id=22711 Adaptive Focusing Technology for the Inspection of Variable Geometry Composite Material Etienne GRONDIN 1 1 Olympus Scientific Solutions Americas,
Drywall state detection in image data for automatic indoor progress monitoring C. Kropp, C. Koch and M. König
 Drywall state detection in image data for automatic indoor progress monitoring C. Kropp, C. Koch and M. König Chair for Computing in Engineering, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Ruhr-Universität
Drywall state detection in image data for automatic indoor progress monitoring C. Kropp, C. Koch and M. König Chair for Computing in Engineering, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, Ruhr-Universität
Time-Frequency Method Based Activation Detection in Functional MRI Time-Series
 Time-Frequency Method Based Activation Detection in Functional MRI Time-Series Arun Kumar 1,2 and Jagath C. Rajapakse 1,3 1 School of Computing, NTU, Singapore 2 School of EEE,Singapore Polytechnic, Singapore
Time-Frequency Method Based Activation Detection in Functional MRI Time-Series Arun Kumar 1,2 and Jagath C. Rajapakse 1,3 1 School of Computing, NTU, Singapore 2 School of EEE,Singapore Polytechnic, Singapore
A Systematic Analysis System for CT Liver Image Classification and Image Segmentation by Local Entropy Method
 A Systematic Analysis System for CT Liver Image Classification and Image Segmentation by Local Entropy Method A.Anuja Merlyn 1, A.Anuba Merlyn 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
A Systematic Analysis System for CT Liver Image Classification and Image Segmentation by Local Entropy Method A.Anuja Merlyn 1, A.Anuba Merlyn 2 1 PG Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering,
A COMPARISON OF WAVELET-BASED AND RIDGELET- BASED TEXTURE CLASSIFICATION OF TISSUES IN COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY
 A COMPARISON OF WAVELET-BASED AND RIDGELET- BASED TEXTURE CLASSIFICATION OF TISSUES IN COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Lindsay Semler Lucia Dettori Intelligent Multimedia Processing Laboratory School of Computer Scienve,
A COMPARISON OF WAVELET-BASED AND RIDGELET- BASED TEXTURE CLASSIFICATION OF TISSUES IN COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Lindsay Semler Lucia Dettori Intelligent Multimedia Processing Laboratory School of Computer Scienve,
Measurement of Residual Thickness in Case of Corrosion Close to the Welds with an Adaptive Total Focusing Method
 19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 Measurement of Residual Thickness in Case of Corrosion Close to the Welds with an Adaptive Total Focusing Method Olivier ROY 1, hilippe BENOIST 1,
19 th World Conference on Non-Destructive Testing 2016 Measurement of Residual Thickness in Case of Corrosion Close to the Welds with an Adaptive Total Focusing Method Olivier ROY 1, hilippe BENOIST 1,
Image Optimisation. -How to Get the Most out of your Echo Machine. Katarina Winkler, Biomedicinsk analytiker, Barnhjärtcentrum i Lund
 Image Optimisation -How to Get the Most out of your Echo Machine analytiker, Barnhjärtcentrum i Lund Image Optimisation Helpful tips to improve the 2D-Image and Doppler registrations. Common adjustments
Image Optimisation -How to Get the Most out of your Echo Machine analytiker, Barnhjärtcentrum i Lund Image Optimisation Helpful tips to improve the 2D-Image and Doppler registrations. Common adjustments
High-speed volumetric ultrasound has a unique ability
 IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, vol. 61, no. 7, July 2014 1113 Short-Lag Spatial Coherence Imaging on Matrix Arrays, Part II: Phantom and In Vivo Experiments Marko
IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, vol. 61, no. 7, July 2014 1113 Short-Lag Spatial Coherence Imaging on Matrix Arrays, Part II: Phantom and In Vivo Experiments Marko
Resona 7. New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation. Premium Ultrasound System
 Resona 7 Premium Ultrasound System New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation With over 20 years of experience, Mindray hosts a wide range of ultrasound imaging solutions including cart-based and portable systems.
Resona 7 Premium Ultrasound System New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation With over 20 years of experience, Mindray hosts a wide range of ultrasound imaging solutions including cart-based and portable systems.
Computed tomography - outline
 Computed tomography - outline Computed Tomography Systems Jørgen Arendt Jensen and Mikael Jensen (DTU Nutech) October 6, 216 Center for Fast Ultrasound Imaging, Build 349 Department of Electrical Engineering
Computed tomography - outline Computed Tomography Systems Jørgen Arendt Jensen and Mikael Jensen (DTU Nutech) October 6, 216 Center for Fast Ultrasound Imaging, Build 349 Department of Electrical Engineering
Application of Tatian s Method to Slanted-Edge MTF Measurement
 Application of s Method to Slanted-Edge MTF Measurement Peter D. Burns Eastman Kodak Company, Rochester, NY USA 465-95 ABSTRACT The 33 method for the measurement of the spatial frequency response () of
Application of s Method to Slanted-Edge MTF Measurement Peter D. Burns Eastman Kodak Company, Rochester, NY USA 465-95 ABSTRACT The 33 method for the measurement of the spatial frequency response () of
ChristoHouston Energy Inc. (CHE INC.) Pipeline Anomaly Analysis By Liquid Green Technologies Corporation
 ChristoHouston Energy Inc. () Pipeline Anomaly Analysis By Liquid Green Technologies Corporation CHE INC. Overview: Review of Scope of Work Wall thickness analysis - Pipeline and sectional statistics Feature
ChristoHouston Energy Inc. () Pipeline Anomaly Analysis By Liquid Green Technologies Corporation CHE INC. Overview: Review of Scope of Work Wall thickness analysis - Pipeline and sectional statistics Feature
3D Guide Wire Navigation from Single Plane Fluoroscopic Images in Abdominal Catheterizations
 3D Guide Wire Navigation from Single Plane Fluoroscopic Images in Abdominal Catheterizations Martin Groher 2, Frederik Bender 1, Ali Khamene 3, Wolfgang Wein 3, Tim Hauke Heibel 2, Nassir Navab 2 1 Siemens
3D Guide Wire Navigation from Single Plane Fluoroscopic Images in Abdominal Catheterizations Martin Groher 2, Frederik Bender 1, Ali Khamene 3, Wolfgang Wein 3, Tim Hauke Heibel 2, Nassir Navab 2 1 Siemens
Slide 1. Technical Aspects of Quality Control in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Slide 2. Annual Compliance Testing. of MRI Systems.
 Slide 1 Technical Aspects of Quality Control in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Slide 2 Compliance Testing of MRI Systems, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI Slide 3 Compliance Testing
Slide 1 Technical Aspects of Quality Control in Magnetic Resonance Imaging Slide 2 Compliance Testing of MRI Systems, Ph.D. Department of Radiology Henry Ford Hospital, Detroit, MI Slide 3 Compliance Testing
International Journal of the Korean Society of Precision Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, June 2000.
 International Journal of the Korean Society of Precision Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, June 2000. Jae-Yeol Kim *, Gyu-Jae Cho * and Chang-Hyun Kim ** * School of Mechanical Engineering, Chosun University,
International Journal of the Korean Society of Precision Engineering, Vol. 1, No. 1, June 2000. Jae-Yeol Kim *, Gyu-Jae Cho * and Chang-Hyun Kim ** * School of Mechanical Engineering, Chosun University,
University of Lübeck, Medical Laser Center Lübeck GmbH Optical Coherence Tomography
 University of Lübeck, Medical Laser Center Lübeck GmbH Optical Coherence Tomography. Theory Dr. Gereon Hüttmann / 009 What is OCT? ( for the MD ) Lichtquelle Probe Detektor Display OCT is Ultrasound with
University of Lübeck, Medical Laser Center Lübeck GmbH Optical Coherence Tomography. Theory Dr. Gereon Hüttmann / 009 What is OCT? ( for the MD ) Lichtquelle Probe Detektor Display OCT is Ultrasound with
John R. Mandeville Senior Consultant NDICS, Norwich, CT Jesse A. Skramstad President - NDT Solutions Inc., New Richmond, WI
 Enhanced Defect Detection on Aircraft Structures Automatic Flaw Classification Software (AFCS) John R. Mandeville Senior Consultant NDICS, Norwich, CT Jesse A. Skramstad President - NDT Solutions Inc.,
Enhanced Defect Detection on Aircraft Structures Automatic Flaw Classification Software (AFCS) John R. Mandeville Senior Consultant NDICS, Norwich, CT Jesse A. Skramstad President - NDT Solutions Inc.,
Interactive segmentation of vascular structures in CT images for liver surgery planning
 Interactive segmentation of vascular structures in CT images for liver surgery planning L. Wang¹, C. Hansen¹, S.Zidowitz¹, H. K. Hahn¹ ¹ Fraunhofer MEVIS, Institute for Medical Image Computing, Bremen,
Interactive segmentation of vascular structures in CT images for liver surgery planning L. Wang¹, C. Hansen¹, S.Zidowitz¹, H. K. Hahn¹ ¹ Fraunhofer MEVIS, Institute for Medical Image Computing, Bremen,
Chapter 5. Track Geometry Data Analysis
 Chapter Track Geometry Data Analysis This chapter explains how and why the data collected for the track geometry was manipulated. The results of these studies in the time and frequency domain are addressed.
Chapter Track Geometry Data Analysis This chapter explains how and why the data collected for the track geometry was manipulated. The results of these studies in the time and frequency domain are addressed.
k-nearest Neighbor Eiji Uchino, Kazuhiro Tokunaga, Hiroki Tanaka, Noriaki Suetake
 IVUS-Based Coronary Plaque Tissue Characterization Using Weighted Multiple k-nearest Neighbor Eiji Uchino, Kazuhiro Tokunaga, Hiroki Tanaka, Noriaki Suetake Abstract In this paper, we propose an extended
IVUS-Based Coronary Plaque Tissue Characterization Using Weighted Multiple k-nearest Neighbor Eiji Uchino, Kazuhiro Tokunaga, Hiroki Tanaka, Noriaki Suetake Abstract In this paper, we propose an extended
Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
1 CS 9 Final Project Classification of Subject Motion for Improved Reconstruction of Dynamic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Feiyu Chen Department of Electrical Engineering ABSTRACT Subject motion is a significant
Bone registration with 3D CT and ultrasound data sets
 International Congress Series 1256 (2003) 426 432 Bone registration with 3D CT and ultrasound data sets B. Brendel a, *,1, S. Winter b,1, A. Rick c,1, M. Stockheim d,1, H. Ermert a,1 a Institute of High
International Congress Series 1256 (2003) 426 432 Bone registration with 3D CT and ultrasound data sets B. Brendel a, *,1, S. Winter b,1, A. Rick c,1, M. Stockheim d,1, H. Ermert a,1 a Institute of High
Clinical Importance. Aortic Stenosis. Aortic Regurgitation. Ultrasound vs. MRI. Carotid Artery Stenosis
 Clinical Importance Rapid cardiovascular flow quantitation using sliceselective Fourier velocity encoding with spiral readouts Valve disease affects 10% of patients with heart disease in the U.S. Most
Clinical Importance Rapid cardiovascular flow quantitation using sliceselective Fourier velocity encoding with spiral readouts Valve disease affects 10% of patients with heart disease in the U.S. Most
Trajectory-based Deformation Correction in Ultrasound Images
 Trajectory-based Deformation Correction in Ultrasound Images The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
Trajectory-based Deformation Correction in Ultrasound Images The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation As Published
Segmenting 2D Ultrasound Images using Seeded Region Growing
 University of British Columbia Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EECE 544 Medical Imaging Term Project Segmenting 2D Ultrasound Images using Seeded Region Growing David Boen #43589050 April
University of British Columbia Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering EECE 544 Medical Imaging Term Project Segmenting 2D Ultrasound Images using Seeded Region Growing David Boen #43589050 April
Depth-Layer-Based Patient Motion Compensation for the Overlay of 3D Volumes onto X-Ray Sequences
 Depth-Layer-Based Patient Motion Compensation for the Overlay of 3D Volumes onto X-Ray Sequences Jian Wang 1,2, Anja Borsdorf 2, Joachim Hornegger 1,3 1 Pattern Recognition Lab, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität
Depth-Layer-Based Patient Motion Compensation for the Overlay of 3D Volumes onto X-Ray Sequences Jian Wang 1,2, Anja Borsdorf 2, Joachim Hornegger 1,3 1 Pattern Recognition Lab, Friedrich-Alexander-Universität
ULTRASONIC INSPECT ABILITY MODELS FOR JET ENGINE FORGINGS
 ULTRASONIC INSPECT ABILITY MODELS FOR JET ENGINE FORGINGS INTRODUCTION T. A. Gray Center for Nondestructive Evaluation Iowa State University Ames, IA 50011 Ultrasonic inspections of axially symmetric forgings,
ULTRASONIC INSPECT ABILITY MODELS FOR JET ENGINE FORGINGS INTRODUCTION T. A. Gray Center for Nondestructive Evaluation Iowa State University Ames, IA 50011 Ultrasonic inspections of axially symmetric forgings,
VEVO 1100 Sole Source Specifications
 VEVO 1100 Sole Source Specifications Table of Contents 1.SYSTEM... 2 1-1 Licensing for the User... 2 1-2 Safety... 2 1-3 Portability... 2 2.TRANSDUCERS... 2 2-1 MicroScan transducers... 2 3. IMAGING STATION...
VEVO 1100 Sole Source Specifications Table of Contents 1.SYSTEM... 2 1-1 Licensing for the User... 2 1-2 Safety... 2 1-3 Portability... 2 2.TRANSDUCERS... 2 2-1 MicroScan transducers... 2 3. IMAGING STATION...
New Technology Allows Multiple Image Contrasts in a Single Scan
 These images were acquired with an investigational device. PD T2 T2 FLAIR T1 MAP T1 FLAIR PSIR T1 New Technology Allows Multiple Image Contrasts in a Single Scan MR exams can be time consuming. A typical
These images were acquired with an investigational device. PD T2 T2 FLAIR T1 MAP T1 FLAIR PSIR T1 New Technology Allows Multiple Image Contrasts in a Single Scan MR exams can be time consuming. A typical
NDT OF SPECIMEN OF COMPLEX GEOMETRY USING ULTRASONIC ADAPTIVE
 NDT OF SPECIMEN OF COMPLEX GEOMETRY USING ULTRASONIC ADAPTIVE TECHNIQUES - THE F.A.U.S.T. SYSTEM INTRODUCTION O. Roy, S. Mahaut, M. Serre Commissariat a I'Energie Atomique CEAlCEREM, CE Saclay France Phased
NDT OF SPECIMEN OF COMPLEX GEOMETRY USING ULTRASONIC ADAPTIVE TECHNIQUES - THE F.A.U.S.T. SYSTEM INTRODUCTION O. Roy, S. Mahaut, M. Serre Commissariat a I'Energie Atomique CEAlCEREM, CE Saclay France Phased
MONITORING THE REPEATABILITY AND REPRODUCIBILTY OF A NATURAL GAS CALIBRATION FACILITY
 MONITORING THE REPEATABILITY AND REPRODUCIBILTY OF A NATURAL GAS CALIBRATION FACILITY T.M. Kegel and W.R. Johansen Colorado Engineering Experiment Station, Inc. (CEESI) 54043 WCR 37, Nunn, CO, 80648 USA
MONITORING THE REPEATABILITY AND REPRODUCIBILTY OF A NATURAL GAS CALIBRATION FACILITY T.M. Kegel and W.R. Johansen Colorado Engineering Experiment Station, Inc. (CEESI) 54043 WCR 37, Nunn, CO, 80648 USA
Tutorial BOLD Module
 m a k i n g f u n c t i o n a l M R I e a s y n o r d i c B r a i n E x Tutorial BOLD Module Please note that this tutorial is for the latest released nordicbrainex. If you are using an older version please
m a k i n g f u n c t i o n a l M R I e a s y n o r d i c B r a i n E x Tutorial BOLD Module Please note that this tutorial is for the latest released nordicbrainex. If you are using an older version please
Introducing Robotics Vision System to a Manufacturing Robotics Course
 Paper ID #16241 Introducing Robotics Vision System to a Manufacturing Robotics Course Dr. Yuqiu You, Ohio University c American Society for Engineering Education, 2016 Introducing Robotics Vision System
Paper ID #16241 Introducing Robotics Vision System to a Manufacturing Robotics Course Dr. Yuqiu You, Ohio University c American Society for Engineering Education, 2016 Introducing Robotics Vision System
A Non-Linear Image Registration Scheme for Real-Time Liver Ultrasound Tracking using Normalized Gradient Fields
 A Non-Linear Image Registration Scheme for Real-Time Liver Ultrasound Tracking using Normalized Gradient Fields Lars König, Till Kipshagen and Jan Rühaak Fraunhofer MEVIS Project Group Image Registration,
A Non-Linear Image Registration Scheme for Real-Time Liver Ultrasound Tracking using Normalized Gradient Fields Lars König, Till Kipshagen and Jan Rühaak Fraunhofer MEVIS Project Group Image Registration,
Supplementary Figure 1. Decoding results broken down for different ROIs
 Supplementary Figure 1 Decoding results broken down for different ROIs Decoding results for areas V1, V2, V3, and V1 V3 combined. (a) Decoded and presented orientations are strongly correlated in areas
Supplementary Figure 1 Decoding results broken down for different ROIs Decoding results for areas V1, V2, V3, and V1 V3 combined. (a) Decoded and presented orientations are strongly correlated in areas
BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging
 1 Lucas Parra, CCNY BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging Lecture 4 Computed Tomography Lucas C. Parra, parra@ccny.cuny.edu some slides inspired by lecture notes of Andreas H. Hilscher at Columbia University.
1 Lucas Parra, CCNY BME I5000: Biomedical Imaging Lecture 4 Computed Tomography Lucas C. Parra, parra@ccny.cuny.edu some slides inspired by lecture notes of Andreas H. Hilscher at Columbia University.
ULTRASONIC TESTING AND FLAW CHARACTERIZATION. Alex KARPELSON Kinectrics Inc., Toronto, Canada
 ULTRASONIC TESTING AND FLAW CHARACTERIZATION Alex KARPELSON Kinectrics Inc., Toronto, Canada 1. Introduction Ultrasonic Testing (UT) is a commonly used inspection method. Various techniques are employed
ULTRASONIC TESTING AND FLAW CHARACTERIZATION Alex KARPELSON Kinectrics Inc., Toronto, Canada 1. Introduction Ultrasonic Testing (UT) is a commonly used inspection method. Various techniques are employed
APPLICATION OF DATA FUSION THEORY AND SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE TO X-RAY CASTINGS INSPECTION
 APPLICATION OF DATA FUSION THEORY AND SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE TO X-RAY CASTINGS INSPECTION Ahmad Osman 1*, Valérie Kaftandjian 2, Ulf Hassler 1 1 Fraunhofer Development Center X-ray Technologies, A Cooperative
APPLICATION OF DATA FUSION THEORY AND SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE TO X-RAY CASTINGS INSPECTION Ahmad Osman 1*, Valérie Kaftandjian 2, Ulf Hassler 1 1 Fraunhofer Development Center X-ray Technologies, A Cooperative
Resona 7. Premium Ultrasound System. New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation
 Resona 7 Premium Ultrasound System New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation Since the company was founded, Mindray is continuously exploring new ways to improve diagnostic
Resona 7 Premium Ultrasound System New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation New Waves in Ultrasound Innovation Since the company was founded, Mindray is continuously exploring new ways to improve diagnostic
Phase Insensitive Homomorphic Image Processing for Speckle Reduction
 ULTRASONIC IMAGING 18, 122 139 (1996) ARTICLE NO. 0007 Phase Insensitive Homomorphic Image Processing for Speckle Reduction YAN CHEN, SHIRA L. BROSCHAT, AND PATRICK J. FLYNN School of Electrical Engineering
ULTRASONIC IMAGING 18, 122 139 (1996) ARTICLE NO. 0007 Phase Insensitive Homomorphic Image Processing for Speckle Reduction YAN CHEN, SHIRA L. BROSCHAT, AND PATRICK J. FLYNN School of Electrical Engineering
IMAGE SEGMENTATION. Václav Hlaváč
 IMAGE SEGMENTATION Václav Hlaváč Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Department of Cybernetics Center for Machine Perception http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/ hlavac, hlavac@fel.cvut.cz
IMAGE SEGMENTATION Václav Hlaváč Czech Technical University in Prague Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Department of Cybernetics Center for Machine Perception http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/ hlavac, hlavac@fel.cvut.cz
S. J. Wormley, B. P. Newberry, M. S. Hughes D. K. Hsu, and D. O. Thompson Center for NDE Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 50011
 APPLICATION OF GAUSS-HERMITE BEAM MODEL TO THE DESIGN OF ULTRASONIC PROBES S. J. Wormley, B. P. Newberry, M. S. Hughes D. K. Hsu, and D. O. Thompson Center for NDE Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 50011
APPLICATION OF GAUSS-HERMITE BEAM MODEL TO THE DESIGN OF ULTRASONIC PROBES S. J. Wormley, B. P. Newberry, M. S. Hughes D. K. Hsu, and D. O. Thompson Center for NDE Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 50011
ULTRASONIC IMAGE RESTORATION BY PSEUDO THREE-DIMENSIONAL POWER SPECTRUM EQUALIZATION
 ULTRASONIC IMAGE RESTORATION BY PSEUDO THREE-DIMENSIONAL POWER SPECTRUM EQUALIZATION Prasanna Karpur and Brian G. Frock University of Dayton Research Institute 300 College Park Avenue Dayton, OH 45469-0001
ULTRASONIC IMAGE RESTORATION BY PSEUDO THREE-DIMENSIONAL POWER SPECTRUM EQUALIZATION Prasanna Karpur and Brian G. Frock University of Dayton Research Institute 300 College Park Avenue Dayton, OH 45469-0001
Generation of Triangle Meshes from Time-of-Flight Data for Surface Registration
 Generation of Triangle Meshes from Time-of-Flight Data for Surface Registration Thomas Kilgus, Thiago R. dos Santos, Alexander Seitel, Kwong Yung, Alfred M. Franz, Anja Groch, Ivo Wolf, Hans-Peter Meinzer,
Generation of Triangle Meshes from Time-of-Flight Data for Surface Registration Thomas Kilgus, Thiago R. dos Santos, Alexander Seitel, Kwong Yung, Alfred M. Franz, Anja Groch, Ivo Wolf, Hans-Peter Meinzer,
High Resolution Phased Array Imaging using the Total Focusing Method
 High Resolution Phased Array Imaging using the Total Focusing Method S. Kierspel, Wolfram A. Karl Deutsch, Helge Rast, Philippe Benoist 1, Venkat A 2 KARL DEUTSCH Pruef- und Messgeraetebau GmbH + Co KG
High Resolution Phased Array Imaging using the Total Focusing Method S. Kierspel, Wolfram A. Karl Deutsch, Helge Rast, Philippe Benoist 1, Venkat A 2 KARL DEUTSCH Pruef- und Messgeraetebau GmbH + Co KG
COMPLEX CONTOUR ULTRASONIC SCANNING SYSTEM APPLICATION AND TRAINING
 COMPLEX CONTOUR ULTRASONIC SCANNING SYSTEM APPLICATION AND TRAINING SJ. Wormley and H. Zhang Center for Nondestructive Evaluation Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 50011-3042 INTRODUCTION It was anticipated
COMPLEX CONTOUR ULTRASONIC SCANNING SYSTEM APPLICATION AND TRAINING SJ. Wormley and H. Zhang Center for Nondestructive Evaluation Iowa State University Ames, Iowa 50011-3042 INTRODUCTION It was anticipated
Automatic Extraction of quasi-synchronous Views from Rotational Angiographic Sequence without ECG-Data
 Automatic Extraction of quasi-synchronous Views from Rotational Angiographic Sequence without ECG-Data Sahla Bouattour and Dietrich Paulus Institute of Computational Visualistics, University of Koblenz-Landau,
Automatic Extraction of quasi-synchronous Views from Rotational Angiographic Sequence without ECG-Data Sahla Bouattour and Dietrich Paulus Institute of Computational Visualistics, University of Koblenz-Landau,
Beyond Performance and Value
 Putting the back in ultrasound Beyond Performance and Value Esaote s new ultra-performance MyLab 9 exp ultrasound system is designed to support a full range of shared service diagnostic imaging environments.
Putting the back in ultrasound Beyond Performance and Value Esaote s new ultra-performance MyLab 9 exp ultrasound system is designed to support a full range of shared service diagnostic imaging environments.
Quick reference guide. MyLab50
 Quick reference guide MyLab50 Quick reference guide MyLab50 Introduction This Quick Guide describes only the basic operating procedures for the diagnostic ultrasound MyLab50 Family, named in the following
Quick reference guide MyLab50 Quick reference guide MyLab50 Introduction This Quick Guide describes only the basic operating procedures for the diagnostic ultrasound MyLab50 Family, named in the following
PMOD Features dedicated to Oncology Research
 While brain research using dynamic data has always been a main target of PMOD s developments, many scientists working with static oncology data have also found ways to leverage PMOD s unique functionality.
While brain research using dynamic data has always been a main target of PMOD s developments, many scientists working with static oncology data have also found ways to leverage PMOD s unique functionality.
Evaluation of texture features for image segmentation
 RIT Scholar Works Articles 9-14-2001 Evaluation of texture features for image segmentation Navid Serrano Jiebo Luo Andreas Savakis Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarworks.rit.edu/article
RIT Scholar Works Articles 9-14-2001 Evaluation of texture features for image segmentation Navid Serrano Jiebo Luo Andreas Savakis Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarworks.rit.edu/article
DUAL energy X-ray radiography [1] can be used to separate
![DUAL energy X-ray radiography [1] can be used to separate DUAL energy X-ray radiography [1] can be used to separate](/thumbs/91/106229592.jpg) IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 53, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2006 133 A Scatter Correction Using Thickness Iteration in Dual-Energy Radiography S. K. Ahn, G. Cho, and H. Jeon Abstract In dual-energy
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON NUCLEAR SCIENCE, VOL. 53, NO. 1, FEBRUARY 2006 133 A Scatter Correction Using Thickness Iteration in Dual-Energy Radiography S. K. Ahn, G. Cho, and H. Jeon Abstract In dual-energy
A fast breast nonlinear elastography reconstruction technique using the Veronda-Westman model
 A fast breast nonlinear elastography reconstruction technique using the Veronda-Westman model Mohammadhosein Amooshahi a and Abbas Samani abc a Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University
A fast breast nonlinear elastography reconstruction technique using the Veronda-Westman model Mohammadhosein Amooshahi a and Abbas Samani abc a Department of Electrical & Computer Engineering, University
Experimentation on the use of Chromaticity Features, Local Binary Pattern and Discrete Cosine Transform in Colour Texture Analysis
 Experimentation on the use of Chromaticity Features, Local Binary Pattern and Discrete Cosine Transform in Colour Texture Analysis N.Padmapriya, Ovidiu Ghita, and Paul.F.Whelan Vision Systems Laboratory,
Experimentation on the use of Chromaticity Features, Local Binary Pattern and Discrete Cosine Transform in Colour Texture Analysis N.Padmapriya, Ovidiu Ghita, and Paul.F.Whelan Vision Systems Laboratory,
SYSTEM LINEARITY LAB MANUAL: 2 Modifications for P551 Fall 2013 Medical Physics Laboratory
 SYSTEM LINEARITY LAB MANUAL: 2 Modifications for P551 Fall 2013 Medical Physics Laboratory Introduction In this lab exercise, you will investigate the linearity of the DeskCAT scanner by making measurements
SYSTEM LINEARITY LAB MANUAL: 2 Modifications for P551 Fall 2013 Medical Physics Laboratory Introduction In this lab exercise, you will investigate the linearity of the DeskCAT scanner by making measurements
