Title Description Participants Textbook
|
|
|
- Erica Dickerson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Podcast Ch24c Title: Breadth First Search Description: Breadth first search algorithm; bfs() method; an example Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert and Tobie Williams (students) Textbook: Data Structures for Java; William H. Ford and William R. Topp
2 Graph Traversal Algorithms In general, graphs do not have a vertex, like a root, that initiates unique paths to each of the vertices. From any starting vertex in a graph, it might not be possible to search all of the vertices. In addition, a graph could have a cycle that results in multiple visits to a vertex.
3 Graph Traversal Algorithms The breadth-first search visits vertices in the order of their path length from a starting vertex. It may not visit every vertex of the graph The depth-first search traverses all the vertices of a graph by making a series of recursive calls that follow paths through the graph. Graph algorithms discern the state of a vertex during the algorithm by using the colors WHITE, GRAY, and BLACK.
4 Breadth-First Search Algorithm
5 Breadth-First Search Algorithm Color all vertices of the sample graph WHITE and push the starting vertex (A) onto the queue visitqueue. Pop A from the queue, color it BLACK, and insert it into visitlist, which is the list of visited vertices. Push all WHITE neighbors onto the queue.
6 Breadth-First Search Algorithm Pop B from the queue and place it in visitlist with color BLACK. The only adjacent vertex for B is D, which is still colored WHITE. Color D GRAY and add it to the queue
7 Breadth-First Search Algorithm Pop C and place it in visitlist. The adjacent vertex G is GRAY. No new vertices enter the queue.
8 Breadth-First Search Algorithm Pop vertex G from the queue and place it in visitlist. G has no adjacent vertices, so pop D from the queue. The neighbors, E and F, enter the queue.
9 Breadth-First Search Algorithm Continue in this fashion until the queue is empty.
10 Implementing Breadth-First Search The color attribute of a vertex. public enum VertexColor { WHITE, GRAY, BLACK } class DiGraph<T> (color methods) void colorwhite() Set the color in each vertex to WHITE. VertexColor getcolor(t v) Returns the color of vertex v. If v is not a graph vertex, throws IllegalArgumentException. ds.util VertexColor setcolor(t v, VertexColor c) Sets the color of vertex v and returns the previous color. If v is not a graph vertex, throws IllegalArgumentException.
11 bfs() // perform the breadth-first traversal // from svertex and return the list // of visited vertices public static <T> LinkedList<T> bfs( DiGraph<T> g, T svertex) { // queue stores adjacent vertices; list // stores visited vertices LinkedQueue<T> visitqueue = new LinkedQueue<T>(); LinkedList<T> visitlist = new LinkedList<T>(); // set and iterator retrieve and scan // neighbors of a vertex Set<T> edgeset; Iterator<T> edgeiter; T currvertex = null, neighborvertex = null;
12 bfs() (continued) // check that starting vertex is valid if (!g.containsvertex(svertex)) throw new IllegalArgumentException( "bfs(): starting vertex not in the graph"); // color all vertices WHITE g.colorwhite(); // initialize queue with starting vertex visitqueue.push(svertex); while (!visitqueue.isempty()) { // remove a vertex from the queue, color // it black, and add to the list of // visited vertices currvertex = visitqueue.pop(); g.setcolor(currvertex,vertexcolor.black); visitlist.add(currvertex);
13 } bfs() (continued) // obtain set of neighbors for current vertex edgeset = g.getneighbors(currvertex); // sequence through the neighbors and look // for vertices that have not been visited edgeiter = edgeset.iterator(); while (edgeiter.hasnext()){ neighborvertex = edgeiter.next(); if (g.getcolor(neighborvertex) == VertexColor.WHITE) { // color unvisited vertex GRAY and // push it onto queue g.setcolor(neighborvertex,vertexcolor.gray); visitqueue.push(neighborvertex); } } } return visitlist;
14 Running Time of Breadth-First Search The running time for the breadth-first search is O(V + E), where V is the number of vertices and E is the number of edges.
15 Breadth-First Search Example // create g; declare startvertex and visitlist DiGraph<String> g = DiGraph.readGraph("bfsgraph.dat"); String startvertex; List<String> visitlist;... // call bfs() with arguments g and startvertx visitlist = DiGraphs.bfs(g, startvertex); // output the visitlist System.out.println("BFS visitlist from " + startvertex + ": " + visitlist);
16 Breadth-First Search Example (concluded) Output: Run 1: (startvertex = "A") BFS visitlist from A: [A, G, B, C, D, E, F] Run 2: (startvertex = "D") BFS visitlist from D: [D, E, F, G] Run 3: (startvertex = "E") BFS visitlist from E: [E]
Title Description Participants Textbook
 Podcast Ch24d Title: Depth First Search and Acyclic Graphs Description: Depth-first visit; dfsvisit() method; dfs() method; acyclic graphs; Program 24.2 Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert
Podcast Ch24d Title: Depth First Search and Acyclic Graphs Description: Depth-first visit; dfsvisit() method; dfs() method; acyclic graphs; Program 24.2 Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert
Title Description Participants Textbook
 Podcast Ch18d Title: Binary Search Tree Iterator Description: Additional operations first and last; the BST iterator Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert and Tobie Williams (students) Textbook:
Podcast Ch18d Title: Binary Search Tree Iterator Description: Additional operations first and last; the BST iterator Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert and Tobie Williams (students) Textbook:
LECTURE 17 GRAPH TRAVERSALS
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 17 GRAPH TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD STRATEGIES Traversals of graphs are also called searches We can use either breadth-first
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 17 GRAPH TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD STRATEGIES Traversals of graphs are also called searches We can use either breadth-first
Title Description Participants Textbook
 Podcast Ch17b Title: Iterative Tree Traversal Description: Iterative tree traversal; the InorderIterator Class; program 17.2 Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert and Tobie Williams (students)
Podcast Ch17b Title: Iterative Tree Traversal Description: Iterative tree traversal; the InorderIterator Class; program 17.2 Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert and Tobie Williams (students)
Title Description Participants Textbook
 Podcast Ch18c Title: BST delete operation Description: Deleting a leaf; deleting a node with one nonnull child; deleting a node with two nonnull children Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert
Podcast Ch18c Title: BST delete operation Description: Deleting a leaf; deleting a node with one nonnull child; deleting a node with two nonnull children Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert
CISC 3150 Sample Final Exam
 CISC 3150 Sample Final Exam Question 1: Trace the program and give the output for parts (a) through (d). #include using namespace std; class basecl public: basecl(): databcl(5) void output()
CISC 3150 Sample Final Exam Question 1: Trace the program and give the output for parts (a) through (d). #include using namespace std; class basecl public: basecl(): databcl(5) void output()
Title Description Participants Textbook
 Podcast Ch24b Title: Graphs and Digraphs Description: The Graph Interface; the Digraph class; Program 24.1 Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert and Tobie Williams (students) Textbook: Data
Podcast Ch24b Title: Graphs and Digraphs Description: The Graph Interface; the Digraph class; Program 24.1 Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert and Tobie Williams (students) Textbook: Data
Title Description Participants Textbook
 Podcast Ch21c Title: Hash Table Implementation Description: Overview of implementation; load factors; add() method; rehash() method; remove() method Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert
Podcast Ch21c Title: Hash Table Implementation Description: Overview of implementation; load factors; add() method; rehash() method; remove() method Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert
Breadth First Search. cse2011 section 13.3 of textbook
 Breadth irst Search cse section. of textbook Graph raversal (.) Application example Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph, find all paths from s to the other vertices. wo common graph
Breadth irst Search cse section. of textbook Graph raversal (.) Application example Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph, find all paths from s to the other vertices. wo common graph
Title Description Participants Textbook
 Podcast Ch23c Title: Binary Files Description: Overview of binary files; DataInputStream; DataOutputStream; Program 23.1; file compression Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert and Tobie
Podcast Ch23c Title: Binary Files Description: Overview of binary files; DataInputStream; DataOutputStream; Program 23.1; file compression Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert and Tobie
Title Description Participants Textbook
 Podcast Ch16f Title: Binary Tree Algorithms Description: Computing height; copying tree; displaying tree Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert and Tobie Williams (students) Textbook: Data
Podcast Ch16f Title: Binary Tree Algorithms Description: Computing height; copying tree; displaying tree Participants: Barry Kurtz (instructor); John Helfert and Tobie Williams (students) Textbook: Data
LECTURE 11 TREE TRAVERSALS
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 11 TREE TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD BACKGROUND All the objects stored in an array or linked list can be accessed sequentially
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 11 TREE TRAVERSALS IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD BACKGROUND All the objects stored in an array or linked list can be accessed sequentially
Breadth First Search. Graph Traversal. CSE 2011 Winter Application examples. Two common graph traversal algorithms
 Breadth irst Search CSE Winter Graph raversal Application examples Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph ind all paths from s to the other vertices wo common graph traversal algorithms
Breadth irst Search CSE Winter Graph raversal Application examples Given a graph representation and a vertex s in the graph ind all paths from s to the other vertices wo common graph traversal algorithms
csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals
 csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals Graph traversal (BFS and DFS) G can be undirected or directed We think about coloring each vertex WHITE before we start GRAY after we visit a vertex but before
csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals Graph traversal (BFS and DFS) G can be undirected or directed We think about coloring each vertex WHITE before we start GRAY after we visit a vertex but before
Algorithms and Theory of Computation. Lecture 3: Graph Algorithms
 Algorithms and Theory of Computation Lecture 3: Graph Algorithms Xiaohui Bei MAS 714 August 20, 2018 Nanyang Technological University MAS 714 August 20, 2018 1 / 18 Connectivity In a undirected graph G
Algorithms and Theory of Computation Lecture 3: Graph Algorithms Xiaohui Bei MAS 714 August 20, 2018 Nanyang Technological University MAS 714 August 20, 2018 1 / 18 Connectivity In a undirected graph G
Scribes: Romil Verma, Juliana Cook (2015), Virginia Williams, Date: May 1, 2017 and Seth Hildick-Smith (2016), G. Valiant (2017), M.
 Lecture 9 Graphs Scribes: Romil Verma, Juliana Cook (2015), Virginia Williams, Date: May 1, 2017 and Seth Hildick-Smith (2016), G. Valiant (2017), M. Wootters (2017) 1 Graphs A graph is a set of vertices
Lecture 9 Graphs Scribes: Romil Verma, Juliana Cook (2015), Virginia Williams, Date: May 1, 2017 and Seth Hildick-Smith (2016), G. Valiant (2017), M. Wootters (2017) 1 Graphs A graph is a set of vertices
Outlines: Graphs Part-2
 Elementary Graph Algorithms PART-2 1 Outlines: Graphs Part-2 Graph Search Methods Breadth-First Search (BFS): BFS Algorithm BFS Example BFS Time Complexity Output of BFS: Shortest Path Breath-First Tree
Elementary Graph Algorithms PART-2 1 Outlines: Graphs Part-2 Graph Search Methods Breadth-First Search (BFS): BFS Algorithm BFS Example BFS Time Complexity Output of BFS: Shortest Path Breath-First Tree
The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value
 The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value 1 Possible implementations Sorted linear implementations o Appropriate if
The ADT priority queue Orders its items by a priority value The first item removed is the one having the highest priority value 1 Possible implementations Sorted linear implementations o Appropriate if
implementing the breadth-first search algorithm implementing the depth-first search algorithm
 Graph Traversals 1 Graph Traversals representing graphs adjacency matrices and adjacency lists 2 Implementing the Breadth-First and Depth-First Search Algorithms implementing the breadth-first search algorithm
Graph Traversals 1 Graph Traversals representing graphs adjacency matrices and adjacency lists 2 Implementing the Breadth-First and Depth-First Search Algorithms implementing the breadth-first search algorithm
Chapter 14. Graphs Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1
 Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
I want an Oompa-Loompa! screamed Veruca. Roald Dahl, Charlie and the Chocolate Factory
 Greedy and Basic Graph Algorithms CS 421 - Algorithms Spring 2019 Apr 5, 2019 Name: Collaborators: I want an Oompa-Loompa! screamed Veruca. Roald Dahl, Charlie and the Chocolate Factory This problem set
Greedy and Basic Graph Algorithms CS 421 - Algorithms Spring 2019 Apr 5, 2019 Name: Collaborators: I want an Oompa-Loompa! screamed Veruca. Roald Dahl, Charlie and the Chocolate Factory This problem set
Graph: representation and traversal
 Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Trees : Part 1. Section 4.1. Theory and Terminology. A Tree? A Tree? Theory and Terminology. Theory and Terminology
 Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
Trees : Part Section. () (2) Preorder, Postorder and Levelorder Traversals Definition: A tree is a connected graph with no cycles Consequences: Between any two vertices, there is exactly one unique path
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 13 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Depth First Search (DFS) Shortest path Shortest weight path (Dijkstra's
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 13 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Depth First Search (DFS) Shortest path Shortest weight path (Dijkstra's
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
Figure 1. A breadth-first traversal.
 4.3 Tree Traversals Stepping, or iterating, through the entries of a linearly ordered list has only two obvious orders: from front to back or from back to front. There is no obvious traversal of a general
4.3 Tree Traversals Stepping, or iterating, through the entries of a linearly ordered list has only two obvious orders: from front to back or from back to front. There is no obvious traversal of a general
Chapter 5. Decrease-and-Conquer. Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Decrease-and-Conquer Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Decrease-and-Conquer 1. Reduce problem instance to smaller instance of the same problem 2. Solve smaller instance
Chapter 5 Decrease-and-Conquer Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Decrease-and-Conquer 1. Reduce problem instance to smaller instance of the same problem 2. Solve smaller instance
22.1 Representations of graphs
 22.1 Representations of graphs There are two standard ways to represent a (directed or undirected) graph G = (V,E), where V is the set of vertices (or nodes) and E is the set of edges (or links). Adjacency
22.1 Representations of graphs There are two standard ways to represent a (directed or undirected) graph G = (V,E), where V is the set of vertices (or nodes) and E is the set of edges (or links). Adjacency
Trees. Arash Rafiey. 20 October, 2015
 20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
20 October, 2015 Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called a tree if G is connected and contains no cycle. Definition Let G = (V, E) be a loop-free undirected graph. G is called
csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals
 csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals 1 Depth-first search (DFS) G can be directed or undirected DFS(v) mark v visited for all adjacent edges (v,w) of v do if w is not visited parent(w) = v (v,w)
csci 210: Data Structures Graph Traversals 1 Depth-first search (DFS) G can be directed or undirected DFS(v) mark v visited for all adjacent edges (v,w) of v do if w is not visited parent(w) = v (v,w)
 UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
UNIT IV -NON-LINEAR DATA STRUCTURES 4.1 Trees TREE: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that there is a specially designated node called the Root, and zero or more non empty sub trees T1,
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1
 CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
CS24 Week 8 Lecture 1 Kyle Dewey Overview Tree terminology Tree traversals Implementation (if time) Terminology Node The most basic component of a tree - the squares Edge The connections between nodes
CS 161 Lecture 11 BFS, Dijkstra s algorithm Jessica Su (some parts copied from CLRS) 1 Review
 1 Review 1 Something I did not emphasize enough last time is that during the execution of depth-firstsearch, we construct depth-first-search trees. One graph may have multiple depth-firstsearch trees,
1 Review 1 Something I did not emphasize enough last time is that during the execution of depth-firstsearch, we construct depth-first-search trees. One graph may have multiple depth-firstsearch trees,
CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms. Lecture 24 Fall 2017
 CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 24 Fall 2017 ANALYSIS OF DIJKSTRA S ALGORITHM CSC 172, Fall 2017 Implementation and analysis The initialization requires Q( V ) memory and run time We iterate
CSC 172 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture 24 Fall 2017 ANALYSIS OF DIJKSTRA S ALGORITHM CSC 172, Fall 2017 Implementation and analysis The initialization requires Q( V ) memory and run time We iterate
CISC 3130 Data Structures Spring 2018
 CISC 3130 Data Structures Spring 2018 Instructor: Ari Mermelstein Email address for questions: mermelstein AT sci DOT brooklyn DOT cuny DOT edu Email address for homework submissions: mermelstein DOT homework
CISC 3130 Data Structures Spring 2018 Instructor: Ari Mermelstein Email address for questions: mermelstein AT sci DOT brooklyn DOT cuny DOT edu Email address for homework submissions: mermelstein DOT homework
TIE Graph algorithms
 TIE-20106 239 11 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
TIE-20106 239 11 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
CS 1114: Implementing Search. Last time. ! Graph traversal. ! Two types of todo lists: ! Prof. Graeme Bailey.
 CS 1114: Implementing Search! Prof. Graeme Bailey http://cs1114.cs.cornell.edu (notes modified from Noah Snavely, Spring 2009) Last time! Graph traversal 1 1 2 10 9 2 3 6 3 5 6 8 5 4 7 9 4 7 8 10! Two
CS 1114: Implementing Search! Prof. Graeme Bailey http://cs1114.cs.cornell.edu (notes modified from Noah Snavely, Spring 2009) Last time! Graph traversal 1 1 2 10 9 2 3 6 3 5 6 8 5 4 7 9 4 7 8 10! Two
Definition Example Solution
 Section 11.4 Spanning Trees Definition: Let G be a simple graph. A spanning tree of G is a subgraph of G that is a tree containing every vertex of G. Example: Find the spanning tree of this simple graph:
Section 11.4 Spanning Trees Definition: Let G be a simple graph. A spanning tree of G is a subgraph of G that is a tree containing every vertex of G. Example: Find the spanning tree of this simple graph:
Graph Traversals BFS & DFS 1 CS S-16
 CS-8S- BFS & DFS -: Visit every vertex, in an order defined by the topololgy of the graph. Two major traversals: Depth First Search Breadth First Search -: Depth First Search Starting from a specific node
CS-8S- BFS & DFS -: Visit every vertex, in an order defined by the topololgy of the graph. Two major traversals: Depth First Search Breadth First Search -: Depth First Search Starting from a specific node
CSCI-142 Exam 2 Review November 2, 2018 Presented by the RIT Computer Science Community
 CSCI-142 Exam 2 Review November 2, 2018 Presented by the RIT Computer Science Community http://csc.cs.rit.edu 1. Suppose we are talking about the depth-first search (DFS) algorithm. Nodes are added to
CSCI-142 Exam 2 Review November 2, 2018 Presented by the RIT Computer Science Community http://csc.cs.rit.edu 1. Suppose we are talking about the depth-first search (DFS) algorithm. Nodes are added to
TIE Graph algorithms
 TIE-20106 1 1 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
TIE-20106 1 1 Graph algorithms This chapter discusses the data structure that is a collection of points (called nodes or vertices) and connections between them (called edges or arcs) a graph. The common
Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms
 Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms Pierre Flener Lars-enrik Eriksson (version of 2013-02-10) Different kinds of graphs List Tree A B C A B C Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) D A B C D E Directed Graph (Digraph)
Topic 12: Elementary Graph Algorithms Pierre Flener Lars-enrik Eriksson (version of 2013-02-10) Different kinds of graphs List Tree A B C A B C Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) D A B C D E Directed Graph (Digraph)
Mystery Algorithm! ALGORITHM MYSTERY( G = (V,E), start_v ) mark all vertices in V as unvisited mystery( start_v )
 Mystery Algorithm! 0 2 ALGORITHM MYSTERY( G = (V,E), start_v ) mark all vertices in V as unvisited mystery( start_v ) 3 1 4 7 6 5 mystery( v ) mark vertex v as visited PRINT v for each vertex w adjacent
Mystery Algorithm! 0 2 ALGORITHM MYSTERY( G = (V,E), start_v ) mark all vertices in V as unvisited mystery( start_v ) 3 1 4 7 6 5 mystery( v ) mark vertex v as visited PRINT v for each vertex w adjacent
Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 dvanced ata Structures and lgorithms ssociate Professor r. Raed Ibraheem amed University of uman evelopment, College of Science and Technology Computer Science epartment 2015 2016 epartment of Computer
dvanced ata Structures and lgorithms ssociate Professor r. Raed Ibraheem amed University of uman evelopment, College of Science and Technology Computer Science epartment 2015 2016 epartment of Computer
COSC 2007 Data Structures II Final Exam. Part 1: multiple choice (1 mark each, total 30 marks, circle the correct answer)
 COSC 2007 Data Structures II Final Exam Thursday, April 13 th, 2006 This is a closed book and closed notes exam. There are total 3 parts. Please answer the questions in the provided space and use back
COSC 2007 Data Structures II Final Exam Thursday, April 13 th, 2006 This is a closed book and closed notes exam. There are total 3 parts. Please answer the questions in the provided space and use back
CSE 100: GRAPH SEARCH
 CSE 100: GRAPH SEARCH Announcements PA3 released Checkpoint due Tuesday, May 5 @10:00pm Final submission due Thursday, May 14 @10:00PM Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! I
CSE 100: GRAPH SEARCH Announcements PA3 released Checkpoint due Tuesday, May 5 @10:00pm Final submission due Thursday, May 14 @10:00PM Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! Start early! I
Chapter 28 Graphs and Applications. Objectives
 Chapter 28 Graphs and Applications CS2: Data Structures and Algorithms Colorado State University Original slides by Daniel Liang Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Wim Bohm, and Russ Wakefield 1 Objectives
Chapter 28 Graphs and Applications CS2: Data Structures and Algorithms Colorado State University Original slides by Daniel Liang Modified slides by Chris Wilcox, Wim Bohm, and Russ Wakefield 1 Objectives
Graph Algorithms. Chapter 22. CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms 1
 Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Graph Algorithms Chapter 22 CPTR 430 Algorithms Graph Algorithms Why Study Graph Algorithms? Mathematical graphs seem to be relatively specialized and abstract Why spend so much time and effort on algorithms
Graphs Chapter 24. Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013
 Graphs Chapter 24 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Graphs: Directed and undirected graphs Weighted graphs (networks) Common graph algorithms Wk12.5 Slide 2 3 Graphs
Graphs Chapter 24 Instructor: Scott Kristjanson CMPT 125/125 SFU Burnaby, Fall 2013 2 Scope Graphs: Directed and undirected graphs Weighted graphs (networks) Common graph algorithms Wk12.5 Slide 2 3 Graphs
Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs. CMSC 420: Lecture 3
 Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs CMSC 420: Lecture 3 Mini-Review Abstract Data Types: List Stack Queue Deque Dictionary Set Implementations: Linked Lists Circularly linked lists Doubly linked lists XOR
Multidimensional Arrays & Graphs CMSC 420: Lecture 3 Mini-Review Abstract Data Types: List Stack Queue Deque Dictionary Set Implementations: Linked Lists Circularly linked lists Doubly linked lists XOR
2. True or false: even though BFS and DFS have the same space complexity, they do not always have the same worst case asymptotic time complexity.
 1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
1. T F: Consider a directed graph G = (V, E) and a vertex s V. Suppose that for all v V, there exists a directed path in G from s to v. Suppose that a DFS is run on G, starting from s. Then, true or false:
Figure 1: A directed graph.
 1 Graphs A graph is a data structure that expresses relationships between objects. The objects are called nodes and the relationships are called edges. For example, social networks can be represented as
1 Graphs A graph is a data structure that expresses relationships between objects. The objects are called nodes and the relationships are called edges. For example, social networks can be represented as
lecture27: Graph Traversals
 lecture27: Largely based on slides by Cinda Heeren CS 225 UIUC 25th July, 2013 Announcements mp7.1 extra credit due tomorrow night (7/26) Code challenge tomorrow night (7/26) at 6pm in 0224 lab hash due
lecture27: Largely based on slides by Cinda Heeren CS 225 UIUC 25th July, 2013 Announcements mp7.1 extra credit due tomorrow night (7/26) Code challenge tomorrow night (7/26) at 6pm in 0224 lab hash due
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
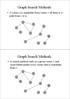 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms
 (Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
(Re)Introduction to Graphs and Some Algorithms Graph Terminology (I) A graph is defined by a set of vertices V and a set of edges E. The edge set must work over the defined vertices in the vertex set.
Stacks API and finding the convex hull. CS Spring 2017
 Stacks API and finding the convex hull CS 146 - Spring 2017 Today Collision detection Convex hull Graham scan algorithm DFS traversal The stack API push() pop()
Stacks API and finding the convex hull CS 146 - Spring 2017 Today Collision detection Convex hull Graham scan algorithm DFS traversal The stack API push() pop()
CSCI-140 Midterm Review October 10, 2015 Presented by the RIT Computer Science Community
 CSCI-140 Midterm Review October 10, 2015 Presented by the RIT Computer Science Community http://csc.cs.rit.edu 1. In each of the following situations, would it be better to use array-backed storage or
CSCI-140 Midterm Review October 10, 2015 Presented by the RIT Computer Science Community http://csc.cs.rit.edu 1. In each of the following situations, would it be better to use array-backed storage or
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms CS5-5S-6 Graph Traversals BFS & DFS David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 6-: Graph Traversals Visit every vertex, in an order defined by
Data Structures and Algorithms CS5-5S-6 Graph Traversals BFS & DFS David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 6-: Graph Traversals Visit every vertex, in an order defined by
Sample Solutions to Homework #4
 National Taiwan University Handout #25 Department of Electrical Engineering January 02, 207 Algorithms, Fall 206 TA: Zhi-Wen Lin and Yen-Chun Liu Sample Solutions to Homework #4. (0) (a) Both of the answers
National Taiwan University Handout #25 Department of Electrical Engineering January 02, 207 Algorithms, Fall 206 TA: Zhi-Wen Lin and Yen-Chun Liu Sample Solutions to Homework #4. (0) (a) Both of the answers
Lecture 24 Notes Search in Graphs
 Lecture 24 Notes Search in Graphs 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning, André Platzer, Rob Simmons, Penny Anderson 1 Introduction In this lecture, we will discuss the
Lecture 24 Notes Search in Graphs 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Spring 2016) Frank Pfenning, André Platzer, Rob Simmons, Penny Anderson 1 Introduction In this lecture, we will discuss the
Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS
 Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Directed and Undirected Graphs I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Directed and Undirected Graphs I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms. Brute-Force Approach
 CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
Solutions to Midterm 2 - Monday, July 11th, 2009
 Solutions to Midterm - Monday, July 11th, 009 CPSC30, Summer009. Instructor: Dr. Lior Malka. (liorma@cs.ubc.ca) 1. Dynamic programming. Let A be a set of n integers A 1,..., A n such that 1 A i n for each
Solutions to Midterm - Monday, July 11th, 009 CPSC30, Summer009. Instructor: Dr. Lior Malka. (liorma@cs.ubc.ca) 1. Dynamic programming. Let A be a set of n integers A 1,..., A n such that 1 A i n for each
tree nonlinear Examples
 The Tree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree example 10-2
The Tree ADT Objectives Define trees as data structures Define the terms associated with trees Discuss tree traversal algorithms Discuss a binary tree implementation Examine a binary tree example 10-2
Homework 2. Sample Solution. Due Date: Thursday, May 31, 11:59 pm
 Homework Sample Solution Due Date: Thursday, May 31, 11:59 pm Directions: Your solutions should be typed and submitted as a single pdf on Gradescope by the due date. L A TEX is preferred but not required.
Homework Sample Solution Due Date: Thursday, May 31, 11:59 pm Directions: Your solutions should be typed and submitted as a single pdf on Gradescope by the due date. L A TEX is preferred but not required.
Module 6: Binary Trees
 Module : Binary Trees Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 327 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Tree All the data structures we have seen
Module : Binary Trees Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 327 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Tree All the data structures we have seen
I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of. I Formally: G =(V, E), where V is a set and E V V.
 Directed and Undirected Graphs Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
Directed and Undirected Graphs Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
CS350: Data Structures Dijkstra s Shortest Path Alg.
 Dijkstra s Shortest Path Alg. James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Shortest Path Algorithms Several different shortest path algorithms exist
Dijkstra s Shortest Path Alg. James Moscola Department of Engineering & Computer Science York College of Pennsylvania James Moscola Shortest Path Algorithms Several different shortest path algorithms exist
CIS265/ Trees Red-Black Trees. Some of the following material is from:
 CIS265/506 2-3-4 Trees Red-Black Trees Some of the following material is from: Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp ISBN 0-13-047724-9 Chapter 27 Balanced Search Trees Bret Ford 2005,
CIS265/506 2-3-4 Trees Red-Black Trees Some of the following material is from: Data Structures for Java William H. Ford William R. Topp ISBN 0-13-047724-9 Chapter 27 Balanced Search Trees Bret Ford 2005,
Fundamental Algorithms
 Fundamental Algorithms Chapter 8: Graphs Jan Křetínský Winter 2017/18 Chapter 8: Graphs, Winter 2017/18 1 Graphs Definition (Graph) A graph G = (V, E) consists of a set V of vertices (nodes) and a set
Fundamental Algorithms Chapter 8: Graphs Jan Křetínský Winter 2017/18 Chapter 8: Graphs, Winter 2017/18 1 Graphs Definition (Graph) A graph G = (V, E) consists of a set V of vertices (nodes) and a set
Graphs. CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington
 Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
Graphs CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures Alexandra Stefan and Vassilis Athitsos University of Texas at Arlington 1 Representation Adjacency matrix??adjacency lists?? Review Graphs (from CSE 2315)
CS302 - Data Structures using C++
 CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
CS61BL. Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting
 CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
Graph Representation
 Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
חומר עזר לבחינה מבוא למדעי המחשב
 שיטות במחלקה Object // Indicates whether some other object is "equal to" // this one. boolean equals(object other) // Returns a string representation of the object. String tostring() // Returns the length
שיטות במחלקה Object // Indicates whether some other object is "equal to" // this one. boolean equals(object other) // Returns a string representation of the object. String tostring() // Returns the length
To list all vertices connected to a vertex u in graph G we can use the following loop:
 Using nextdjacent() To list all vertices connected to a vertex u in graph we can use the following loop: for (int v=.nextdjacent(u,-1); v>=0; v=.nextdjacent(u,v)) { System.out.print(v); djacency Lists
Using nextdjacent() To list all vertices connected to a vertex u in graph we can use the following loop: for (int v=.nextdjacent(u,-1); v>=0; v=.nextdjacent(u,v)) { System.out.print(v); djacency Lists
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs
 CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
Tutorial. Question There are no forward edges. 4. For each back edge u, v, we have 0 d[v] d[u].
![Tutorial. Question There are no forward edges. 4. For each back edge u, v, we have 0 d[v] d[u]. Tutorial. Question There are no forward edges. 4. For each back edge u, v, we have 0 d[v] d[u].](/thumbs/88/114871846.jpg) Tutorial Question 1 A depth-first forest classifies the edges of a graph into tree, back, forward, and cross edges. A breadth-first tree can also be used to classify the edges reachable from the source
Tutorial Question 1 A depth-first forest classifies the edges of a graph into tree, back, forward, and cross edges. A breadth-first tree can also be used to classify the edges reachable from the source
Graphs: Graph Data Structure:
 Graphs: A graph is a pictorial representation of a set of objects where some pairs of objects are connected by links. The interconnected objects are represented by points termed as vertices, and the links
Graphs: A graph is a pictorial representation of a set of objects where some pairs of objects are connected by links. The interconnected objects are represented by points termed as vertices, and the links
This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science.
 Lecture 9 Graphs This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science. You need to be familiar with the design and use of basic data structures such as Lists, Stacks,
Lecture 9 Graphs This course is intended for 3rd and/or 4th year undergraduate majors in Computer Science. You need to be familiar with the design and use of basic data structures such as Lists, Stacks,
Graphs and Algorithms
 Graphs and Algorithms Graphs are a mathematical concept readily adapted into computer programming. Graphs are not just data structures, that is, they are not solutions to simple data storage problems.
Graphs and Algorithms Graphs are a mathematical concept readily adapted into computer programming. Graphs are not just data structures, that is, they are not solutions to simple data storage problems.
Chapter 9 STACK, QUEUE
 Chapter 9 STACK, QUEUE 1 LIFO: Last In, First Out. Stacks Restricted form of list: Insert and remove only at front of list. Notation: Insert: PUSH Remove: POP The accessible element is called TOP. Stack
Chapter 9 STACK, QUEUE 1 LIFO: Last In, First Out. Stacks Restricted form of list: Insert and remove only at front of list. Notation: Insert: PUSH Remove: POP The accessible element is called TOP. Stack
( ) ( ) C. " 1 n. ( ) $ f n. ( ) B. " log( n! ) ( ) and that you already know ( ) ( ) " % g( n) ( ) " #&
 CSE 0 Name Test Summer 008 Last 4 Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time for the following code is in which set? for (i=0; i
CSE 0 Name Test Summer 008 Last 4 Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time for the following code is in which set? for (i=0; i
 CS6301 Programming and Data Structures II Unit -5 REPRESENTATION OF GRAPHS Graph and its representations Graph is a data structure that consists of following two components: 1. A finite set of vertices
CS6301 Programming and Data Structures II Unit -5 REPRESENTATION OF GRAPHS Graph and its representations Graph is a data structure that consists of following two components: 1. A finite set of vertices
Data Structure Advanced
 Data Structure Advanced 1. Is it possible to find a loop in a Linked list? a. Possilbe at O(n) b. Not possible c. Possible at O(n^2) only d. Depends on the position of loop Solution: a. Possible at O(n)
Data Structure Advanced 1. Is it possible to find a loop in a Linked list? a. Possilbe at O(n) b. Not possible c. Possible at O(n^2) only d. Depends on the position of loop Solution: a. Possible at O(n)
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12. Questions? Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first Search. (Introduce permutation and subset generation)
 MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
Graphs - II. Announcements. Where did I leave that book? Where did I leave that book? Where did I leave that book? CS 2110, Fall 2016
 Graphs - II CS, Fall Announcements A will be available tonight or tomorrow. Gries lunch canceled today Gries office hours today from to only Q. Why do programmers confuse Halloween and Christmas? Answer.
Graphs - II CS, Fall Announcements A will be available tonight or tomorrow. Gries lunch canceled today Gries office hours today from to only Q. Why do programmers confuse Halloween and Christmas? Answer.
Graphs. Graph G = (V, E) Types of graphs E = O( V 2 ) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V)
 Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
Graph Algorithms Graphs Graph G = (V, E) V = set of vertices E = set of edges (V V) Types of graphs Undirected: edge (u, v) = (v, u); for all v, (v, v) E (No self loops.) Directed: (u, v) is edge from
Lecture 24 Search in Graphs
 Lecture 24 Search in Graphs 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning, André Platzer, Rob Simmons, Penny Anderson, Iliano Cervesato In this lecture, we will discuss the question
Lecture 24 Search in Graphs 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning, André Platzer, Rob Simmons, Penny Anderson, Iliano Cervesato In this lecture, we will discuss the question
Unweighted Graphs & Algorithms
 Unweighted Graphs & Algorithms Zachary Friggstad Programming Club Meeting References Chapter 4: Graph (Section 4.2) Chapter 22: Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Features: vertices/nodes/dots and edges/links/lines
Unweighted Graphs & Algorithms Zachary Friggstad Programming Club Meeting References Chapter 4: Graph (Section 4.2) Chapter 22: Elementary Graph Algorithms Graphs Features: vertices/nodes/dots and edges/links/lines
Linear Structures. Linear Structure. Implementations. Array details. List details. Operations 4/18/2013
 Linear Structure Linear Structures Chapter 4 CPTR 318 Every non-empty linear structure has A unique element called first A unique element called last Every element except last has a unique successor Every
Linear Structure Linear Structures Chapter 4 CPTR 318 Every non-empty linear structure has A unique element called first A unique element called last Every element except last has a unique successor Every
FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- MARCH, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours
 TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) (Maximum marks: 100) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- MARCH, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours PART
TED (10)-3071 Reg. No.. (REVISION-2010) (Maximum marks: 100) Signature. FORTH SEMESTER DIPLOMA EXAMINATION IN ENGINEERING/ TECHNOLIGY- MARCH, 2012 DATA STRUCTURE (Common to CT and IF) [Time: 3 hours PART
CS Elementary Graph Algorithms
 CS43-09 Elementary Graph Algorithms Outline Representation of Graphs Instructor: Fei Li Room 443 ST II Office hours: Tue. & Thur. 1:30pm - 2:30pm or by appointments lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS43
CS43-09 Elementary Graph Algorithms Outline Representation of Graphs Instructor: Fei Li Room 443 ST II Office hours: Tue. & Thur. 1:30pm - 2:30pm or by appointments lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS43
CS Elementary Graph Algorithms
 CS483-09 Elementary Graph Algorithms Instructor: Fei Li Room 443 ST II Office hours: Tue. & Thur. 1:30pm - 2:30pm or by appointments lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS483 http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ lifei/teaching/cs483_fall07/
CS483-09 Elementary Graph Algorithms Instructor: Fei Li Room 443 ST II Office hours: Tue. & Thur. 1:30pm - 2:30pm or by appointments lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS483 http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ lifei/teaching/cs483_fall07/
9/26/2018 Data Structure & Algorithm. Assignment04: 3 parts Quiz: recursion, insertionsort, trees Basic concept: Linked-List Priority queues Heaps
 9/26/2018 Data Structure & Algorithm Assignment04: 3 parts Quiz: recursion, insertionsort, trees Basic concept: Linked-List Priority queues Heaps 1 Quiz 10 points (as stated in the first class meeting)
9/26/2018 Data Structure & Algorithm Assignment04: 3 parts Quiz: recursion, insertionsort, trees Basic concept: Linked-List Priority queues Heaps 1 Quiz 10 points (as stated in the first class meeting)
Homework Assignment #3 Graph
 CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of MCA
 INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : 30/3/15 Max Marks : 50 Name of faculty : Sabeeha Sultana Subject & Code : ADA(13MCA41) Answer any five full question: 1.Illustrate Mergesort for the dataset 8,3,2,9,7,1,5,4.
INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : 30/3/15 Max Marks : 50 Name of faculty : Sabeeha Sultana Subject & Code : ADA(13MCA41) Answer any five full question: 1.Illustrate Mergesort for the dataset 8,3,2,9,7,1,5,4.
Draw the resulting binary search tree. Be sure to show intermediate steps for partial credit (in case your final tree is incorrect).
 Problem 1. Binary Search Trees (36 points) a) (12 points) Assume that the following numbers are inserted into an (initially empty) binary search tree in the order shown below (from left to right): 42 36
Problem 1. Binary Search Trees (36 points) a) (12 points) Assume that the following numbers are inserted into an (initially empty) binary search tree in the order shown below (from left to right): 42 36
