Application of spatial classification rules for remotely sensed images
|
|
|
- Adela Nelson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. B Vol. 55, 2014 DOI: /LMR.B pages Application of spatial classification rules for remotely sensed images Giedrius Stabingis, Lijana Stabingienė Department of Mathematics and Statistics, Klaipėda University H. Manto 84, LT Klaipeda gstabingis@gmail.com, lijana.stabingiene@gmail.com Abstract. In this paper the remote sensed image classification example using spacial classification rule with distance (SCRD) is examined. This supervised classification method was first presented in paper [11]. This method is improved version of earlier method PBDF [4, 10, 9], during the classification it incorporates more spatial information. The advantage of this method is its ability to classify data which is corrupted by Gaussian random field and it is typical to remotely sensed images classified in this letter which are corrupted by clouds. Classification accuracy is compared with earlier method and with other commonly used supervised classification methods. Keywords: image classification, spatial classification rules, supervised classification. Introduction The classification of remotely sensed images is widely used in different situations. Lots of methods performs very good in clear situations, but often the remotely sensed images or some parts of them are covered with clouds. In this case these common methods perform errors, because they don t have the information behind the clouds. The methods authors are working with helps in this exact situation, the clouds are modeled according to the training sample information and spatial relation between observation to be classified and the training sample, and this modeled information is used during classification for better decision making. The earlier method [4, 10] was tested in the real situation for classification of the real remotely sensed image covered with clouds in article [9]. Later the more advanced method was created [11] and now in this letter the performance of this method is tested in the same situation. In the paper [9] the remotely sensed image was used from Landast7 satellite. Now, when Landsat8 satellite images are available, the same situation was tested on Landsat8 satellite image which is more corrupted by clouds and the image is larger when the first one. In order to show the complicity of such situation some other common methods are used in the same situation for classification. For the commonly used supervised classification methods the rassclass package from the R system is used. Numerical and visual analysis of discriminant function in the case of isotropic exponential spatial correlation for the nearest neighbor neighborhood system using eight nearest neighbors NN(8) is done. All calculations are done in R system.
2 64 G. Stabingis, L. Stabingienė 1 Method declaration The incorporation of the spatial information into image classification is done by some authors (see e.g., [1, 2]). The statistical supervised classification method (PBDF) [4] was extended by incorporating more influence from the spatial dependency into classification problem and achieving higher accuracy in the paper [11] and this method is named SCRD. The plugin Bayes discriminant function (PBDF) to the classification problem is ( W t (Z 0 ; ˆΨ) = Z 0 (ˆµ0 1t + ˆµ 0 ) 2t) (ˆµ 0 1t ˆµ 0 2t) 2 ˆσ 0t 2 +γ(y), (1) where ˆµ 0 lt = ˆµ l +α 0 (z n X yˆµ), and ˆσ 0t 2 = ˆσ2 R on, γ(y) = ln(π 1 (y)/π 2 (y)). The PBDF classification rule based on the posterior distribution ofy(s 0 ) specified by 1 π 1 (y) = 1+exp { ρ ( )}, n 1 = 0,1,...,n, (2) 1 2n1 n when I 0 = {i: s i N 0 = NN(8), i = 1,...,n} and where ρ is non negative constant called a clustering parameter, and n 1 is the number of locations from N 0 with label equal 1. Here NN(8) is the nearest neighbor scheme with eight nearest neighbors. The new classification rule SCRD is based on the following posterior distribution π 1 (y) = i I 0 δ(y i=1) d(s i,s 0) 1, (3) i I 0 d(s i,s 0) where δ( ) is the 0 1 indicator function and d(, ) denotes the Euclidean distance function between locations. For the case of two classes π 2 = 1 π 1. 2 Methods for comparison In order to verify the reliability of the method and its advantage in this concrete situation, when data is corrupted by spatial noise, the comparison with other commonly used methods is done. These methods are: Support Vector Machines (SVM), Neural Networks (NNet), Random Forests (RF) and Multinomial Logistic Regression (Logit). All these methods belong to the group of supervised classification methods and the classification with these methods is done on the same data and on the same training sample as for the methods proposed in this letter. The advantage of SVMs classifiers is their capabilities to learn from small number of samples [5]. The class (label) of a new sample is determined by a linear combination of the kernel functions evaluated on a certain subset of the examples the support vectors and the input. The coefficients of the combination are obtained as a solution to a convex optimization problem occurring at the learning stage [8]. Neural networks rely on the iterative derivation of weights which effectively define hyper-planes and hyper-regions in the pattern feature space [7]. Although artificial neural network methods are frequently found to give a higher total classification accuracy when compared to other methods, they do not always perform universally well [6].
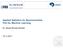
3 Application of spatial classification rules for remotely sensed images 65 (a) (b) Fig. 1. Images used for classification. Random Forests method grows many classification trees and then every tree gives the class label for the observation to be classified. Then the class is assigned according to the most classes given by all trees in the forest [3]. 3 Description of experiment In this letter the experiment with two different remotely sensed images is presented. One image was earlier used in the paper [9]. Here the same image is classified with the new method. This image is obtained by Landsat7 satellite and is from the territory of Lithuania. This image is pixels and is shown in Fig. 1(a). Another image is obtained by the satellite Landsat8 and is also in the territory of Lithuania. The second image is 4 times bigger: pixels. This image is shown in Fig. 1(b). The density of clouds is higher in the second picture so the accuracy of classification must be lower for this image. The original image is naturally corrupted with clouds and such noise is modeled by Gaussian random field (GRF) with zero mean and exponential spatial correlation function given by r(h) = exp{ h 2 /α}. Here α is a spatial correlation range parameter which must be estimated. This parameter is evaluated with function variofit from the geor package in the environment of the R system. The remotely sensed image used for classification is naturally corrupted and then the exact correlation range parameter is unknown. This parameter is estimated according to the training sample points (pixels) using the geor package of the statistical program R. At the same time both classes training sample points are used in order to identify the correlation range parameter. In order to minimize the influence of different classes to the accuracy of the modeling, the means of corresponding classes are subtracted from the training sample points feature values. This way transformed points with their coordinates are then used to calculate empirical semivariogram. It is done with geor packages command variog. The parametric model is then fitted to the empirical semivariogram points using variofit command, which uses least squares method for fitting. After several trials, several different types of models were fitted according to the shape of the empirical semivariogram, it was determined that for this concrete situation best model was of exponential type. The exponential model was best fitted for the both images. The value of the correlation range parameter α = 13 for the first image and α = 68 for the second image were estimated. These numbers were used for classification using SCRD and PBDF methods. Liet. matem. rink. Proc. LMS, Ser. B, 55, 2014,
4 66 G. Stabingis, L. Stabingienė (a) (b) (c) (d) Fig. 2. Classification with Bayes discriminant function results. (a), (c) with SCDR; (b), (d) with PBDF. (a) (b) (c) (d) (e) (f) (g) (h) Fig. 3. Classification results with common supervised classification methods. (a), (e) with Logit. (b), (f) with NNet. (c), (g) with RF. (d), (h) with SVM. Table 1. Classification accuracy. SCRD PBDF Logit NNet RF SVM Image Fig. 1(a) Image Fig. 1(b) Results Visual classification results are shown in Fig. 2 and in Fig. 3. Numerical evaluations of overall accuracy for all methods used in this experiment are provided in Table 1. 5 Conclusions The SCRD method performed better than PBDF, so the incorporation of more spatial information into classification rule helps to get better results. The second image is more corrupted by clouds than the first one and all methods performed worse. If the clouds corrupt image just slightly as in the situation with the first image, other common methods still performs quite well, but if corruption becomes harder, these methods become useless.
5 Application of spatial classification rules for remotely sensed images 67 SCRD and PBDF methods performs quite well in both situations, even when image is corrupted quite hard. References [1] P.M. Atkinson. Spatially weighted supervised classification for remote sensing. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinf., 5: , [2] P.M. Atkinson. A geostatistically weighted k-nn classifier for remotely sensed imagery. Geograph. Anal., 42: , [3] L. Breiman. Random forests. Mach. Learn., 45(1):5 32, [4] K. Dučinskas, L. Stabingienė and G. Stabingis. Image classification based on bayes discriminant functions. In Proceedings of the 1th International Conference Spatial Statistics 2011-Mapping Global Change, 7, pp , [5] A.K. Jain, P.W. Duin and J. Mao. Statistical pattern recognition: a review. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 22(1):4 37, [6] I. Kanellopoulos, G.G. Wilkinson and J. Megier. Integration of neural network and statistical image classification for land cover mapping. Geosc. Rem. Sens. Symp., [7] R.P. Lippmann. An introduction to computing with neural nets. IEEE ASSP Mag., 40:4 22, [8] W.W.Y. Ng, A. Dorado, D.S. Yeung, W. Pedrycz and E. Izquierdo. Image classification with the use of radial basis function neural networks and the minimization of the localized generalization error. Patt. Recogn., 40:19 32, [9] L. Stabingienė. Classification of the real remotely sensed image covered with clouds. Liet. matem. rink. Proc. LMS, Ser. A, 53: , [10] L. Stabingienė. Image analysis using Bayes discriminant functions. Doctoral dissertation. Vilnius University, Vilnius, [11] G. Stabingis, K. Dučinskas and L. Stabingienė. Comparison of spatial classification rules with different conditional distributions of class label. Nonl. Anal. Mod. Contr., 19(1): , REZIUMĖ Erdvinių klasifikavimo taisyklių taikymas nuotolinio stebėjimo vaizdams G. Stabingis, L. Stabingienė Šiame straipsnyje pateikiamas erdvinės klasifikavimo taisyklės (SCRD) taikymas nuotolinio stebėjimo vaizdų klasifikavimui. Šis klasifikavimo su mokymu metodas buvo pristatytas straipsnyje [11]. Šis metodas yra patobulinta ankstesnio metodo [4, 10, 9] PBDF versija, klasifikavimo metu dar labiau atsižvelgiant į erdvinės informacijos įtaką. Šio metodo privalumas yra galimybė klasifikuoti duomenis, kurie yra sugadinti Gauso atsitiktiniu lauku, o tai yra būdinga šiame darbe klasifikuojamiems vaizdams iš palydovo, kuriuose tiriama teritorija yra uždengta debesimis. Klasifikavimo tikslumas yra lyginamas su ankstesniu metodu ir kitais plačiai taikomais klasifikavimo su mokymu metodais. Raktiniai žodžiai: vaizdų klasifikaimas, erdvinės klasifikavimo taisyklės, klasifikavimas su mokymu. Liet. matem. rink. Proc. LMS, Ser. B, 55, 2014,
Spatial classification rule with distance in three dimensional space
 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 57, 2016 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2016.15 pages 81 85 Spatial classification rule with distance in three
Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 57, 2016 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2016.15 pages 81 85 Spatial classification rule with distance in three
Contextual High-Resolution Image Classification by Markovian Data Fusion, Adaptive Texture Extraction, and Multiscale Segmentation
 IGARSS-2011 Vancouver, Canada, July 24-29, 29, 2011 Contextual High-Resolution Image Classification by Markovian Data Fusion, Adaptive Texture Extraction, and Multiscale Segmentation Gabriele Moser Sebastiano
IGARSS-2011 Vancouver, Canada, July 24-29, 29, 2011 Contextual High-Resolution Image Classification by Markovian Data Fusion, Adaptive Texture Extraction, and Multiscale Segmentation Gabriele Moser Sebastiano
University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Paper 4F10: Statistical Pattern Processing Handout 11: Non-Parametric Techniques
 University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Paper 4F10: Statistical Pattern Processing Handout 11: Non-Parametric Techniques Mark Gales mjfg@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 2011 11. Non-Parameteric Techniques
University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Paper 4F10: Statistical Pattern Processing Handout 11: Non-Parametric Techniques Mark Gales mjfg@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 2011 11. Non-Parameteric Techniques
Implementation Feasibility of Convex Recursive Deletion Regions Using Multi-Layer Perceptrons
 Implementation Feasibility of Convex Recursive Deletion Regions Using Multi-Layer Perceptrons CHE-CHERN LIN National Kaohsiung Normal University Department of Industrial Technology Education 116 HePing
Implementation Feasibility of Convex Recursive Deletion Regions Using Multi-Layer Perceptrons CHE-CHERN LIN National Kaohsiung Normal University Department of Industrial Technology Education 116 HePing
Neural Networks. CE-725: Statistical Pattern Recognition Sharif University of Technology Spring Soleymani
 Neural Networks CE-725: Statistical Pattern Recognition Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Outline Biological and artificial neural networks Feed-forward neural networks Single layer
Neural Networks CE-725: Statistical Pattern Recognition Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Outline Biological and artificial neural networks Feed-forward neural networks Single layer
ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing
 ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Object Recognition http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/ 2 Outline Knowledge Representation Statistical Pattern Recognition Neural Networks Boosting
ECG782: Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing Object Recognition http://www.ee.unlv.edu/~b1morris/ecg782/ 2 Outline Knowledge Representation Statistical Pattern Recognition Neural Networks Boosting
SUPERVISED LEARNING METHODS. Stanley Liang, PhD Candidate, Lassonde School of Engineering, York University Helix Science Engagement Programs 2018
 SUPERVISED LEARNING METHODS Stanley Liang, PhD Candidate, Lassonde School of Engineering, York University Helix Science Engagement Programs 2018 2 CHOICE OF ML You cannot know which algorithm will work
SUPERVISED LEARNING METHODS Stanley Liang, PhD Candidate, Lassonde School of Engineering, York University Helix Science Engagement Programs 2018 2 CHOICE OF ML You cannot know which algorithm will work
CAMCOS Report Day. December 9 th, 2015 San Jose State University Project Theme: Classification
 CAMCOS Report Day December 9 th, 2015 San Jose State University Project Theme: Classification On Classification: An Empirical Study of Existing Algorithms based on two Kaggle Competitions Team 1 Team 2
CAMCOS Report Day December 9 th, 2015 San Jose State University Project Theme: Classification On Classification: An Empirical Study of Existing Algorithms based on two Kaggle Competitions Team 1 Team 2
On Classification: An Empirical Study of Existing Algorithms Based on Two Kaggle Competitions
 On Classification: An Empirical Study of Existing Algorithms Based on Two Kaggle Competitions CAMCOS Report Day December 9th, 2015 San Jose State University Project Theme: Classification The Kaggle Competition
On Classification: An Empirical Study of Existing Algorithms Based on Two Kaggle Competitions CAMCOS Report Day December 9th, 2015 San Jose State University Project Theme: Classification The Kaggle Competition
Estimating Map Accuracy without a Spatially Representative Training Sample
 Estimating Map Accuracy without a Spatially Representative Training Sample David A. Patterson, Mathematical Sciences, The University of Montana-Missoula Brian M. Steele, Mathematical Sciences, The University
Estimating Map Accuracy without a Spatially Representative Training Sample David A. Patterson, Mathematical Sciences, The University of Montana-Missoula Brian M. Steele, Mathematical Sciences, The University
CS6716 Pattern Recognition
 CS6716 Pattern Recognition Prototype Methods Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia Problem 2b was extended to March 25. Done? PS3 will be out this real soon (tonight) due April 10.
CS6716 Pattern Recognition Prototype Methods Aaron Bobick School of Interactive Computing Administrivia Problem 2b was extended to March 25. Done? PS3 will be out this real soon (tonight) due April 10.
University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Paper 4F10: Statistical Pattern Processing Handout 11: Non-Parametric Techniques.
 . Non-Parameteric Techniques University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Paper 4F: Statistical Pattern Processing Handout : Non-Parametric Techniques Mark Gales mjfg@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 23 Introduction
. Non-Parameteric Techniques University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Paper 4F: Statistical Pattern Processing Handout : Non-Parametric Techniques Mark Gales mjfg@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 23 Introduction
Random Forest A. Fornaser
 Random Forest A. Fornaser alberto.fornaser@unitn.it Sources Lecture 15: decision trees, information theory and random forests, Dr. Richard E. Turner Trees and Random Forests, Adele Cutler, Utah State University
Random Forest A. Fornaser alberto.fornaser@unitn.it Sources Lecture 15: decision trees, information theory and random forests, Dr. Richard E. Turner Trees and Random Forests, Adele Cutler, Utah State University
University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Paper 4F10: Statistical Pattern Processing Handout 11: Non-Parametric Techniques
 University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Paper 4F10: Statistical Pattern Processing Handout 11: Non-Parametric Techniques Mark Gales mjfg@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 2015 11. Non-Parameteric Techniques
University of Cambridge Engineering Part IIB Paper 4F10: Statistical Pattern Processing Handout 11: Non-Parametric Techniques Mark Gales mjfg@eng.cam.ac.uk Michaelmas 2015 11. Non-Parameteric Techniques
Supplementary material: Strengthening the Effectiveness of Pedestrian Detection with Spatially Pooled Features
 Supplementary material: Strengthening the Effectiveness of Pedestrian Detection with Spatially Pooled Features Sakrapee Paisitkriangkrai, Chunhua Shen, Anton van den Hengel The University of Adelaide,
Supplementary material: Strengthening the Effectiveness of Pedestrian Detection with Spatially Pooled Features Sakrapee Paisitkriangkrai, Chunhua Shen, Anton van den Hengel The University of Adelaide,
SIMULATION OF ARTIFICIAL SYSTEMS BEHAVIOR IN PARAMETRIC EIGHT-DIMENSIONAL SPACE
 78 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Informatics and Information Technology SIMULATION OF ARTIFICIAL SYSTEMS BEHAVIOR IN PARAMETRIC EIGHT-DIMENSIONAL SPACE D. Ulbikiene, J. Ulbikas, K.
78 Proceedings of the 4 th International Conference on Informatics and Information Technology SIMULATION OF ARTIFICIAL SYSTEMS BEHAVIOR IN PARAMETRIC EIGHT-DIMENSIONAL SPACE D. Ulbikiene, J. Ulbikas, K.
GENDER CLASSIFICATION USING SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES
 GENDER CLASSIFICATION USING SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Ashwin Swaminathan ashwins@umd.edu ENEE633: Statistical and Neural Pattern Recognition Instructor : Prof. Rama Chellappa Project 2, Part (a) 1. INTRODUCTION
GENDER CLASSIFICATION USING SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINES Ashwin Swaminathan ashwins@umd.edu ENEE633: Statistical and Neural Pattern Recognition Instructor : Prof. Rama Chellappa Project 2, Part (a) 1. INTRODUCTION
Temporal Modeling and Missing Data Estimation for MODIS Vegetation data
 Temporal Modeling and Missing Data Estimation for MODIS Vegetation data Rie Honda 1 Introduction The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) is the primary instrument on board NASA s Earth
Temporal Modeling and Missing Data Estimation for MODIS Vegetation data Rie Honda 1 Introduction The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) is the primary instrument on board NASA s Earth
Machine Learning Lecture 3
 Machine Learning Lecture 3 Probability Density Estimation II 19.10.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Announcements Exam dates We re in the process
Machine Learning Lecture 3 Probability Density Estimation II 19.10.2017 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Announcements Exam dates We re in the process
Extension of training set using mean shift procedure for aerospace images classification
 Extension of training set using mean shift procedure for aerospace images classification Yuriy N. Sinyavskiy 1,*, Pavel V. Melnikov 1, and Igor A. Pestunov 1 1 Institute of Computational Technologies of
Extension of training set using mean shift procedure for aerospace images classification Yuriy N. Sinyavskiy 1,*, Pavel V. Melnikov 1, and Igor A. Pestunov 1 1 Institute of Computational Technologies of
COSC160: Detection and Classification. Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor
 COSC160: Detection and Classification Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Problem I. Strategies II. Features for training III. Using spatial information? IV. Reducing dimensionality
COSC160: Detection and Classification Jeremy Bolton, PhD Assistant Teaching Professor Outline I. Problem I. Strategies II. Features for training III. Using spatial information? IV. Reducing dimensionality
Applied Statistics for Neuroscientists Part IIa: Machine Learning
 Applied Statistics for Neuroscientists Part IIa: Machine Learning Dr. Seyed-Ahmad Ahmadi 04.04.2017 16.11.2017 Outline Machine Learning Difference between statistics and machine learning Modeling the problem
Applied Statistics for Neuroscientists Part IIa: Machine Learning Dr. Seyed-Ahmad Ahmadi 04.04.2017 16.11.2017 Outline Machine Learning Difference between statistics and machine learning Modeling the problem
On the security of RSA textbook signature scheme on Paillier ciphertext
 Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 57, 2016 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2016.16 pages 86 90 On the security of RSA textbook signature scheme
Lietuvos matematikos rinkinys ISSN 0132-2818 Proc. of the Lithuanian Mathematical Society, Ser. A Vol. 57, 2016 DOI: 10.15388/LMR.A.2016.16 pages 86 90 On the security of RSA textbook signature scheme
Non-Parametric Modeling
 Non-Parametric Modeling CE-725: Statistical Pattern Recognition Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Outline Introduction Non-Parametric Density Estimation Parzen Windows Kn-Nearest Neighbor
Non-Parametric Modeling CE-725: Statistical Pattern Recognition Sharif University of Technology Spring 2013 Soleymani Outline Introduction Non-Parametric Density Estimation Parzen Windows Kn-Nearest Neighbor
5 Learning hypothesis classes (16 points)
 5 Learning hypothesis classes (16 points) Consider a classification problem with two real valued inputs. For each of the following algorithms, specify all of the separators below that it could have generated
5 Learning hypothesis classes (16 points) Consider a classification problem with two real valued inputs. For each of the following algorithms, specify all of the separators below that it could have generated
Robotics Programming Laboratory
 Chair of Software Engineering Robotics Programming Laboratory Bertrand Meyer Jiwon Shin Lecture 8: Robot Perception Perception http://pascallin.ecs.soton.ac.uk/challenges/voc/databases.html#caltech car
Chair of Software Engineering Robotics Programming Laboratory Bertrand Meyer Jiwon Shin Lecture 8: Robot Perception Perception http://pascallin.ecs.soton.ac.uk/challenges/voc/databases.html#caltech car
Generative and discriminative classification techniques
 Generative and discriminative classification techniques Machine Learning and Category Representation 013-014 Jakob Verbeek, December 13+0, 013 Course website: http://lear.inrialpes.fr/~verbeek/mlcr.13.14
Generative and discriminative classification techniques Machine Learning and Category Representation 013-014 Jakob Verbeek, December 13+0, 013 Course website: http://lear.inrialpes.fr/~verbeek/mlcr.13.14
Fuzzy Entropy based feature selection for classification of hyperspectral data
 Fuzzy Entropy based feature selection for classification of hyperspectral data Mahesh Pal Department of Civil Engineering NIT Kurukshetra, 136119 mpce_pal@yahoo.co.uk Abstract: This paper proposes to use
Fuzzy Entropy based feature selection for classification of hyperspectral data Mahesh Pal Department of Civil Engineering NIT Kurukshetra, 136119 mpce_pal@yahoo.co.uk Abstract: This paper proposes to use
CLASSIFICATION WITH RADIAL BASIS AND PROBABILISTIC NEURAL NETWORKS
 CLASSIFICATION WITH RADIAL BASIS AND PROBABILISTIC NEURAL NETWORKS CHAPTER 4 CLASSIFICATION WITH RADIAL BASIS AND PROBABILISTIC NEURAL NETWORKS 4.1 Introduction Optical character recognition is one of
CLASSIFICATION WITH RADIAL BASIS AND PROBABILISTIC NEURAL NETWORKS CHAPTER 4 CLASSIFICATION WITH RADIAL BASIS AND PROBABILISTIC NEURAL NETWORKS 4.1 Introduction Optical character recognition is one of
Bagging for One-Class Learning
 Bagging for One-Class Learning David Kamm December 13, 2008 1 Introduction Consider the following outlier detection problem: suppose you are given an unlabeled data set and make the assumptions that one
Bagging for One-Class Learning David Kamm December 13, 2008 1 Introduction Consider the following outlier detection problem: suppose you are given an unlabeled data set and make the assumptions that one
A STUDY OF SOME DATA MINING CLASSIFICATION TECHNIQUES
 A STUDY OF SOME DATA MINING CLASSIFICATION TECHNIQUES Narsaiah Putta Assistant professor Department of CSE, VASAVI College of Engineering, Hyderabad, Telangana, India Abstract Abstract An Classification
A STUDY OF SOME DATA MINING CLASSIFICATION TECHNIQUES Narsaiah Putta Assistant professor Department of CSE, VASAVI College of Engineering, Hyderabad, Telangana, India Abstract Abstract An Classification
CIS 520, Machine Learning, Fall 2015: Assignment 7 Due: Mon, Nov 16, :59pm, PDF to Canvas [100 points]
![CIS 520, Machine Learning, Fall 2015: Assignment 7 Due: Mon, Nov 16, :59pm, PDF to Canvas [100 points] CIS 520, Machine Learning, Fall 2015: Assignment 7 Due: Mon, Nov 16, :59pm, PDF to Canvas [100 points]](/thumbs/89/100746783.jpg) CIS 520, Machine Learning, Fall 2015: Assignment 7 Due: Mon, Nov 16, 2015. 11:59pm, PDF to Canvas [100 points] Instructions. Please write up your responses to the following problems clearly and concisely.
CIS 520, Machine Learning, Fall 2015: Assignment 7 Due: Mon, Nov 16, 2015. 11:59pm, PDF to Canvas [100 points] Instructions. Please write up your responses to the following problems clearly and concisely.
Shape Context Matching For Efficient OCR
 Matching For Efficient OCR May 14, 2012 Matching For Efficient OCR Table of contents 1 Motivation Background 2 What is a? Matching s Simliarity Measure 3 Matching s via Pyramid Matching Matching For Efficient
Matching For Efficient OCR May 14, 2012 Matching For Efficient OCR Table of contents 1 Motivation Background 2 What is a? Matching s Simliarity Measure 3 Matching s via Pyramid Matching Matching For Efficient
International Journal of Scientific Research & Engineering Trends Volume 4, Issue 6, Nov-Dec-2018, ISSN (Online): X
 Analysis about Classification Techniques on Categorical Data in Data Mining Assistant Professor P. Meena Department of Computer Science Adhiyaman Arts and Science College for Women Uthangarai, Krishnagiri,
Analysis about Classification Techniques on Categorical Data in Data Mining Assistant Professor P. Meena Department of Computer Science Adhiyaman Arts and Science College for Women Uthangarai, Krishnagiri,
Adaptive Wavelet Image Denoising Based on the Entropy of Homogenus Regions
 International Journal of Electrical and Electronic Science 206; 3(4): 9-25 http://www.aascit.org/journal/ijees ISSN: 2375-2998 Adaptive Wavelet Image Denoising Based on the Entropy of Homogenus Regions
International Journal of Electrical and Electronic Science 206; 3(4): 9-25 http://www.aascit.org/journal/ijees ISSN: 2375-2998 Adaptive Wavelet Image Denoising Based on the Entropy of Homogenus Regions
Keyword Extraction by KNN considering Similarity among Features
 64 Int'l Conf. on Advances in Big Data Analytics ABDA'15 Keyword Extraction by KNN considering Similarity among Features Taeho Jo Department of Computer and Information Engineering, Inha University, Incheon,
64 Int'l Conf. on Advances in Big Data Analytics ABDA'15 Keyword Extraction by KNN considering Similarity among Features Taeho Jo Department of Computer and Information Engineering, Inha University, Incheon,
Equation to LaTeX. Abhinav Rastogi, Sevy Harris. I. Introduction. Segmentation.
 Equation to LaTeX Abhinav Rastogi, Sevy Harris {arastogi,sharris5}@stanford.edu I. Introduction Copying equations from a pdf file to a LaTeX document can be time consuming because there is no easy way
Equation to LaTeX Abhinav Rastogi, Sevy Harris {arastogi,sharris5}@stanford.edu I. Introduction Copying equations from a pdf file to a LaTeX document can be time consuming because there is no easy way
CS 179 Lecture 16. Logistic Regression & Parallel SGD
 CS 179 Lecture 16 Logistic Regression & Parallel SGD 1 Outline logistic regression (stochastic) gradient descent parallelizing SGD for neural nets (with emphasis on Google s distributed neural net implementation)
CS 179 Lecture 16 Logistic Regression & Parallel SGD 1 Outline logistic regression (stochastic) gradient descent parallelizing SGD for neural nets (with emphasis on Google s distributed neural net implementation)
Machine Learning. Supervised Learning. Manfred Huber
 Machine Learning Supervised Learning Manfred Huber 2015 1 Supervised Learning Supervised learning is learning where the training data contains the target output of the learning system. Training data D
Machine Learning Supervised Learning Manfred Huber 2015 1 Supervised Learning Supervised learning is learning where the training data contains the target output of the learning system. Training data D
HANDWRITTEN GURMUKHI CHARACTER RECOGNITION USING WAVELET TRANSFORMS
 International Journal of Electronics, Communication & Instrumentation Engineering Research and Development (IJECIERD) ISSN 2249-684X Vol.2, Issue 3 Sep 2012 27-37 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd., HANDWRITTEN GURMUKHI
International Journal of Electronics, Communication & Instrumentation Engineering Research and Development (IJECIERD) ISSN 2249-684X Vol.2, Issue 3 Sep 2012 27-37 TJPRC Pvt. Ltd., HANDWRITTEN GURMUKHI
Basis Functions. Volker Tresp Summer 2017
 Basis Functions Volker Tresp Summer 2017 1 Nonlinear Mappings and Nonlinear Classifiers Regression: Linearity is often a good assumption when many inputs influence the output Some natural laws are (approximately)
Basis Functions Volker Tresp Summer 2017 1 Nonlinear Mappings and Nonlinear Classifiers Regression: Linearity is often a good assumption when many inputs influence the output Some natural laws are (approximately)
Sequential Nonlinear Mapping versus Simultaneous One
 INFORMATICA, 2002, Vol. 13, No. 3, 333 344 333 2002 Institute of Mathematics and Informatics, Vilnius Sequential Nonlinear Mapping versus Simultaneous One Algirdas Mykolas MONTVILAS Institute of Mathematics
INFORMATICA, 2002, Vol. 13, No. 3, 333 344 333 2002 Institute of Mathematics and Informatics, Vilnius Sequential Nonlinear Mapping versus Simultaneous One Algirdas Mykolas MONTVILAS Institute of Mathematics
Remote Sensed Image Classification based on Spatial and Spectral Features using SVM
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Remote Sensed Image Classification based on Spatial and Spectral Features using SVM Mary Jasmine. E PG Scholar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University College
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Remote Sensed Image Classification based on Spatial and Spectral Features using SVM Mary Jasmine. E PG Scholar Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University College
A review of data complexity measures and their applicability to pattern classification problems. J. M. Sotoca, J. S. Sánchez, R. A.
 A review of data complexity measures and their applicability to pattern classification problems J. M. Sotoca, J. S. Sánchez, R. A. Mollineda Dept. Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics Universitat Jaume I
A review of data complexity measures and their applicability to pattern classification problems J. M. Sotoca, J. S. Sánchez, R. A. Mollineda Dept. Llenguatges i Sistemes Informàtics Universitat Jaume I
Facial Expression Recognition using Principal Component Analysis with Singular Value Decomposition
 ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 1, Issue 6, November 2013 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsms.com Facial
ISSN: 2321-7782 (Online) Volume 1, Issue 6, November 2013 International Journal of Advance Research in Computer Science and Management Studies Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsms.com Facial
arxiv: v2 [cs.lg] 11 Sep 2015
![arxiv: v2 [cs.lg] 11 Sep 2015 arxiv: v2 [cs.lg] 11 Sep 2015](/thumbs/75/72864154.jpg) A DEEP analysis of the META-DES framework for dynamic selection of ensemble of classifiers Rafael M. O. Cruz a,, Robert Sabourin a, George D. C. Cavalcanti b a LIVIA, École de Technologie Supérieure, University
A DEEP analysis of the META-DES framework for dynamic selection of ensemble of classifiers Rafael M. O. Cruz a,, Robert Sabourin a, George D. C. Cavalcanti b a LIVIA, École de Technologie Supérieure, University
Machine Learning Lecture 3
 Course Outline Machine Learning Lecture 3 Fundamentals (2 weeks) Bayes Decision Theory Probability Density Estimation Probability Density Estimation II 26.04.206 Discriminative Approaches (5 weeks) Linear
Course Outline Machine Learning Lecture 3 Fundamentals (2 weeks) Bayes Decision Theory Probability Density Estimation Probability Density Estimation II 26.04.206 Discriminative Approaches (5 weeks) Linear
Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering 1 PG Student, JSPM s Imperial College of Engineering and Research, Pune (M.H.
 Volume 5, Issue 4, 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Introduction to Probabilistic
Volume 5, Issue 4, 2015 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Introduction to Probabilistic
Machine Learning / Jan 27, 2010
 Revisiting Logistic Regression & Naïve Bayes Aarti Singh Machine Learning 10-701/15-781 Jan 27, 2010 Generative and Discriminative Classifiers Training classifiers involves learning a mapping f: X -> Y,
Revisiting Logistic Regression & Naïve Bayes Aarti Singh Machine Learning 10-701/15-781 Jan 27, 2010 Generative and Discriminative Classifiers Training classifiers involves learning a mapping f: X -> Y,
Instance-based Learning CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology. M. Soleymani Fall 2015
 Instance-based Learning CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2015 Outline Non-parametric approach Unsupervised: Non-parametric density estimation Parzen Windows K-Nearest
Instance-based Learning CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology M. Soleymani Fall 2015 Outline Non-parametric approach Unsupervised: Non-parametric density estimation Parzen Windows K-Nearest
Introduction to Pattern Recognition Part II. Selim Aksoy Bilkent University Department of Computer Engineering
 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Part II Selim Aksoy Bilkent University Department of Computer Engineering saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr RETINA Pattern Recognition Tutorial, Summer 2005 Overview Statistical
Introduction to Pattern Recognition Part II Selim Aksoy Bilkent University Department of Computer Engineering saksoy@cs.bilkent.edu.tr RETINA Pattern Recognition Tutorial, Summer 2005 Overview Statistical
Evaluation of texture features for image segmentation
 RIT Scholar Works Articles 9-14-2001 Evaluation of texture features for image segmentation Navid Serrano Jiebo Luo Andreas Savakis Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarworks.rit.edu/article
RIT Scholar Works Articles 9-14-2001 Evaluation of texture features for image segmentation Navid Serrano Jiebo Luo Andreas Savakis Follow this and additional works at: http://scholarworks.rit.edu/article
Bayes Risk. Classifiers for Recognition Reading: Chapter 22 (skip 22.3) Discriminative vs Generative Models. Loss functions in classifiers
 Classifiers for Recognition Reading: Chapter 22 (skip 22.3) Examine each window of an image Classify object class within each window based on a training set images Example: A Classification Problem Categorize
Classifiers for Recognition Reading: Chapter 22 (skip 22.3) Examine each window of an image Classify object class within each window based on a training set images Example: A Classification Problem Categorize
Classification of Printed Chinese Characters by Using Neural Network
 Classification of Printed Chinese Characters by Using Neural Network ATTAULLAH KHAWAJA Ph.D. Student, Department of Electronics engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, 100081 Beijing, P.R.CHINA ABDUL
Classification of Printed Chinese Characters by Using Neural Network ATTAULLAH KHAWAJA Ph.D. Student, Department of Electronics engineering, Beijing Institute of Technology, 100081 Beijing, P.R.CHINA ABDUL
Introduction to object recognition. Slides adapted from Fei-Fei Li, Rob Fergus, Antonio Torralba, and others
 Introduction to object recognition Slides adapted from Fei-Fei Li, Rob Fergus, Antonio Torralba, and others Overview Basic recognition tasks A statistical learning approach Traditional or shallow recognition
Introduction to object recognition Slides adapted from Fei-Fei Li, Rob Fergus, Antonio Torralba, and others Overview Basic recognition tasks A statistical learning approach Traditional or shallow recognition
Figure (5) Kohonen Self-Organized Map
 2- KOHONEN SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS (SOM) - The self-organizing neural networks assume a topological structure among the cluster units. - There are m cluster units, arranged in a one- or two-dimensional array;
2- KOHONEN SELF-ORGANIZING MAPS (SOM) - The self-organizing neural networks assume a topological structure among the cluster units. - There are m cluster units, arranged in a one- or two-dimensional array;
Moving Object Segmentation Method Based on Motion Information Classification by X-means and Spatial Region Segmentation
 IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.13 No.11, November 2013 1 Moving Object Segmentation Method Based on Motion Information Classification by X-means and Spatial
IJCSNS International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security, VOL.13 No.11, November 2013 1 Moving Object Segmentation Method Based on Motion Information Classification by X-means and Spatial
Texture recognition of medical images with the ICM method
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 525 (2004) 387 391 Texture recognition of medical images with the ICM method Jason M. Kinser*, Guisong Wang George Mason University, Institute for
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 525 (2004) 387 391 Texture recognition of medical images with the ICM method Jason M. Kinser*, Guisong Wang George Mason University, Institute for
Multiview Pedestrian Detection Based on Online Support Vector Machine Using Convex Hull
 Multiview Pedestrian Detection Based on Online Support Vector Machine Using Convex Hull Revathi M K 1, Ramya K P 2, Sona G 3 1, 2, 3 Information Technology, Anna University, Dr.Sivanthi Aditanar College
Multiview Pedestrian Detection Based on Online Support Vector Machine Using Convex Hull Revathi M K 1, Ramya K P 2, Sona G 3 1, 2, 3 Information Technology, Anna University, Dr.Sivanthi Aditanar College
Feature scaling in support vector data description
 Feature scaling in support vector data description P. Juszczak, D.M.J. Tax, R.P.W. Duin Pattern Recognition Group, Department of Applied Physics, Faculty of Applied Sciences, Delft University of Technology,
Feature scaling in support vector data description P. Juszczak, D.M.J. Tax, R.P.W. Duin Pattern Recognition Group, Department of Applied Physics, Faculty of Applied Sciences, Delft University of Technology,
Spatial Information Based Image Classification Using Support Vector Machine
 Spatial Information Based Image Classification Using Support Vector Machine P.Jeevitha, Dr. P. Ganesh Kumar PG Scholar, Dept of IT, Regional Centre of Anna University, Coimbatore, India. Assistant Professor,
Spatial Information Based Image Classification Using Support Vector Machine P.Jeevitha, Dr. P. Ganesh Kumar PG Scholar, Dept of IT, Regional Centre of Anna University, Coimbatore, India. Assistant Professor,
Toward Part-based Document Image Decoding
 2012 10th IAPR International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems Toward Part-based Document Image Decoding Wang Song, Seiichi Uchida Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan wangsong@human.ait.kyushu-u.ac.jp,
2012 10th IAPR International Workshop on Document Analysis Systems Toward Part-based Document Image Decoding Wang Song, Seiichi Uchida Kyushu University, Fukuoka, Japan wangsong@human.ait.kyushu-u.ac.jp,
Classifiers for Recognition Reading: Chapter 22 (skip 22.3)
 Classifiers for Recognition Reading: Chapter 22 (skip 22.3) Examine each window of an image Classify object class within each window based on a training set images Slide credits for this chapter: Frank
Classifiers for Recognition Reading: Chapter 22 (skip 22.3) Examine each window of an image Classify object class within each window based on a training set images Slide credits for this chapter: Frank
Applying Supervised Learning
 Applying Supervised Learning When to Consider Supervised Learning A supervised learning algorithm takes a known set of input data (the training set) and known responses to the data (output), and trains
Applying Supervised Learning When to Consider Supervised Learning A supervised learning algorithm takes a known set of input data (the training set) and known responses to the data (output), and trains
Pattern recognition methods for electronic tongue systems. Patrycja Ciosek
 Pattern recognition methods for electronic tongue systems 1 Electronic tongue A SYSTEM FOR AUTOMATIC ANALYSIS AND CLASSIFICATION (RECOGNITION) OF LIQUID SAMPLES AN ARRAY OF CHEMICAL SENSORS PATTERN RECOGNITION
Pattern recognition methods for electronic tongue systems 1 Electronic tongue A SYSTEM FOR AUTOMATIC ANALYSIS AND CLASSIFICATION (RECOGNITION) OF LIQUID SAMPLES AN ARRAY OF CHEMICAL SENSORS PATTERN RECOGNITION
Adaptive Metric Nearest Neighbor Classification
 Adaptive Metric Nearest Neighbor Classification Carlotta Domeniconi Jing Peng Dimitrios Gunopulos Computer Science Department Computer Science Department Computer Science Department University of California
Adaptive Metric Nearest Neighbor Classification Carlotta Domeniconi Jing Peng Dimitrios Gunopulos Computer Science Department Computer Science Department Computer Science Department University of California
An Introduction to Machine Learning
 TRIPODS Summer Boorcamp: Topology and Machine Learning August 6, 2018 General Set-up Introduction Set-up and Goal Suppose we have X 1,X 2,...,X n data samples. Can we predict properites about any given
TRIPODS Summer Boorcamp: Topology and Machine Learning August 6, 2018 General Set-up Introduction Set-up and Goal Suppose we have X 1,X 2,...,X n data samples. Can we predict properites about any given
Correlation Based Feature Selection with Irrelevant Feature Removal
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 4, April 2014,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 4, April 2014,
Artificial Intelligence. Programming Styles
 Artificial Intelligence Intro to Machine Learning Programming Styles Standard CS: Explicitly program computer to do something Early AI: Derive a problem description (state) and use general algorithms to
Artificial Intelligence Intro to Machine Learning Programming Styles Standard CS: Explicitly program computer to do something Early AI: Derive a problem description (state) and use general algorithms to
A NEW APPROACH TO OBJECT RECOGNITION ON HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGE *
 A NEW APPROACH TO OBJECT RECOGNITION ON HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGE Qiming QIN,Yinhuan YUAN, Rongjian LU Peking University, P.R China,100871 Institute of Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System
A NEW APPROACH TO OBJECT RECOGNITION ON HIGH RESOLUTION SATELLITE IMAGE Qiming QIN,Yinhuan YUAN, Rongjian LU Peking University, P.R China,100871 Institute of Remote Sensing and Geographic Information System
The Boundary Graph Supervised Learning Algorithm for Regression and Classification
 The Boundary Graph Supervised Learning Algorithm for Regression and Classification! Jonathan Yedidia! Disney Research!! Outline Motivation Illustration using a toy classification problem Some simple refinements
The Boundary Graph Supervised Learning Algorithm for Regression and Classification! Jonathan Yedidia! Disney Research!! Outline Motivation Illustration using a toy classification problem Some simple refinements
Open Access Research on the Prediction Model of Material Cost Based on Data Mining
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 1062 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2015, 9, 1062-1066 Open Access Research on the Prediction Model of Material Cost Based on Data Mining
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.ae 1062 The Open Mechanical Engineering Journal, 2015, 9, 1062-1066 Open Access Research on the Prediction Model of Material Cost Based on Data Mining
Detection of Rooftop Regions in Rural Areas Using Support Vector Machine
 549 Detection of Rooftop Regions in Rural Areas Using Support Vector Machine Liya Joseph 1, Laya Devadas 2 1 (M Tech Scholar, Department of Computer Science, College of Engineering Munnar, Kerala) 2 (Associate
549 Detection of Rooftop Regions in Rural Areas Using Support Vector Machine Liya Joseph 1, Laya Devadas 2 1 (M Tech Scholar, Department of Computer Science, College of Engineering Munnar, Kerala) 2 (Associate
CSE 252B: Computer Vision II
 CSE 252B: Computer Vision II Lecturer: Serge Belongie Scribes: Jeremy Pollock and Neil Alldrin LECTURE 14 Robust Feature Matching 14.1. Introduction Last lecture we learned how to find interest points
CSE 252B: Computer Vision II Lecturer: Serge Belongie Scribes: Jeremy Pollock and Neil Alldrin LECTURE 14 Robust Feature Matching 14.1. Introduction Last lecture we learned how to find interest points
A MAXIMUM NOISE FRACTION TRANSFORM BASED ON A SENSOR NOISE MODEL FOR HYPERSPECTRAL DATA. Naoto Yokoya 1 and Akira Iwasaki 2
 A MAXIMUM NOISE FRACTION TRANSFORM BASED ON A SENSOR NOISE MODEL FOR HYPERSPECTRAL DATA Naoto Yokoya 1 and Akira Iwasaki 1 Graduate Student, Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, The University of
A MAXIMUM NOISE FRACTION TRANSFORM BASED ON A SENSOR NOISE MODEL FOR HYPERSPECTRAL DATA Naoto Yokoya 1 and Akira Iwasaki 1 Graduate Student, Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, The University of
A FRAMEWORK FOR ANALYZING TEXTURE DESCRIPTORS
 A FRAMEWORK FOR ANALYZING TEXTURE DESCRIPTORS Timo Ahonen and Matti Pietikäinen Machine Vision Group, University of Oulu, PL 4500, FI-90014 Oulun yliopisto, Finland tahonen@ee.oulu.fi, mkp@ee.oulu.fi Keywords:
A FRAMEWORK FOR ANALYZING TEXTURE DESCRIPTORS Timo Ahonen and Matti Pietikäinen Machine Vision Group, University of Oulu, PL 4500, FI-90014 Oulun yliopisto, Finland tahonen@ee.oulu.fi, mkp@ee.oulu.fi Keywords:
Naïve Bayes for text classification
 Road Map Basic concepts Decision tree induction Evaluation of classifiers Rule induction Classification using association rules Naïve Bayesian classification Naïve Bayes for text classification Support
Road Map Basic concepts Decision tree induction Evaluation of classifiers Rule induction Classification using association rules Naïve Bayesian classification Naïve Bayes for text classification Support
Patch-Based Image Classification Using Image Epitomes
 Patch-Based Image Classification Using Image Epitomes David Andrzejewski CS 766 - Final Project December 19, 2005 Abstract Automatic image classification has many practical applications, including photo
Patch-Based Image Classification Using Image Epitomes David Andrzejewski CS 766 - Final Project December 19, 2005 Abstract Automatic image classification has many practical applications, including photo
Case-Based Reasoning. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall Nearest-Neighbor Classification. Parametric / Non-parametric.
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley 1 1 Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Fall 2008 Lecture 25: Kernels and Clustering 12/2/2008 Dan Klein UC Berkeley 1 1 Case-Based Reasoning Similarity for classification Case-based reasoning Predict an instance
10-701/15-781, Fall 2006, Final
 -7/-78, Fall 6, Final Dec, :pm-8:pm There are 9 questions in this exam ( pages including this cover sheet). If you need more room to work out your answer to a question, use the back of the page and clearly
-7/-78, Fall 6, Final Dec, :pm-8:pm There are 9 questions in this exam ( pages including this cover sheet). If you need more room to work out your answer to a question, use the back of the page and clearly
A Review on Image InpaintingTechniques and Its analysis Indraja Mali 1, Saumya Saxena 2,Padmaja Desai 3,Ajay Gite 4
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS A Review on Image InpaintingTechniques and Its analysis Indraja Mali 1, Saumya Saxena 2,Padmaja Desai 3,Ajay Gite 4 1,2,3,4 (Computer Science, Savitribai Phule Pune University,Pune)
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS A Review on Image InpaintingTechniques and Its analysis Indraja Mali 1, Saumya Saxena 2,Padmaja Desai 3,Ajay Gite 4 1,2,3,4 (Computer Science, Savitribai Phule Pune University,Pune)
Dynamic skin detection in color images for sign language recognition
 Dynamic skin detection in color images for sign language recognition Michal Kawulok Institute of Computer Science, Silesian University of Technology, Akademicka 16, 44-100 Gliwice, Poland michal.kawulok@polsl.pl
Dynamic skin detection in color images for sign language recognition Michal Kawulok Institute of Computer Science, Silesian University of Technology, Akademicka 16, 44-100 Gliwice, Poland michal.kawulok@polsl.pl
Segmentation of Images
 Segmentation of Images SEGMENTATION If an image has been preprocessed appropriately to remove noise and artifacts, segmentation is often the key step in interpreting the image. Image segmentation is a
Segmentation of Images SEGMENTATION If an image has been preprocessed appropriately to remove noise and artifacts, segmentation is often the key step in interpreting the image. Image segmentation is a
Contribution to Multicriterial Classification of Spatial Data
 Magyar Kutatók 8. Nemzetközi Szimpóziuma 8 th International Symposium of Hungarian Researchers on Computational Intelligence and Informatics Contribution to Multicriterial Classification of Spatial Data
Magyar Kutatók 8. Nemzetközi Szimpóziuma 8 th International Symposium of Hungarian Researchers on Computational Intelligence and Informatics Contribution to Multicriterial Classification of Spatial Data
A Combined Method for On-Line Signature Verification
 BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 14, No 2 Sofia 2014 Print ISSN: 1311-9702; Online ISSN: 1314-4081 DOI: 10.2478/cait-2014-0022 A Combined Method for On-Line
BULGARIAN ACADEMY OF SCIENCES CYBERNETICS AND INFORMATION TECHNOLOGIES Volume 14, No 2 Sofia 2014 Print ISSN: 1311-9702; Online ISSN: 1314-4081 DOI: 10.2478/cait-2014-0022 A Combined Method for On-Line
Machine Learning Lecture 3
 Many slides adapted from B. Schiele Machine Learning Lecture 3 Probability Density Estimation II 26.04.2016 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course
Many slides adapted from B. Schiele Machine Learning Lecture 3 Probability Density Estimation II 26.04.2016 Bastian Leibe RWTH Aachen http://www.vision.rwth-aachen.de leibe@vision.rwth-aachen.de Course
Last week. Multi-Frame Structure from Motion: Multi-View Stereo. Unknown camera viewpoints
 Last week Multi-Frame Structure from Motion: Multi-View Stereo Unknown camera viewpoints Last week PCA Today Recognition Today Recognition Recognition problems What is it? Object detection Who is it? Recognizing
Last week Multi-Frame Structure from Motion: Multi-View Stereo Unknown camera viewpoints Last week PCA Today Recognition Today Recognition Recognition problems What is it? Object detection Who is it? Recognizing
Radial Basis Function Neural Network Classifier
 Recognition of Unconstrained Handwritten Numerals by a Radial Basis Function Neural Network Classifier Hwang, Young-Sup and Bang, Sung-Yang Department of Computer Science & Engineering Pohang University
Recognition of Unconstrained Handwritten Numerals by a Radial Basis Function Neural Network Classifier Hwang, Young-Sup and Bang, Sung-Yang Department of Computer Science & Engineering Pohang University
Sketchable Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Object Detection
 Sketchable Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Object Detection No Author Given No Institute Given Abstract. In this paper we investigate a new representation approach for visual object recognition. The
Sketchable Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Object Detection No Author Given No Institute Given Abstract. In this paper we investigate a new representation approach for visual object recognition. The
Binarization of Color Character Strings in Scene Images Using K-means Clustering and Support Vector Machines
 2011 International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition Binarization of Color Character Strings in Scene Images Using K-means Clustering and Support Vector Machines Toru Wakahara Kohei Kita
2011 International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition Binarization of Color Character Strings in Scene Images Using K-means Clustering and Support Vector Machines Toru Wakahara Kohei Kita
Generative and discriminative classification techniques
 Generative and discriminative classification techniques Machine Learning and Category Representation 2014-2015 Jakob Verbeek, November 28, 2014 Course website: http://lear.inrialpes.fr/~verbeek/mlcr.14.15
Generative and discriminative classification techniques Machine Learning and Category Representation 2014-2015 Jakob Verbeek, November 28, 2014 Course website: http://lear.inrialpes.fr/~verbeek/mlcr.14.15
Hybrid Model with Super Resolution and Decision Boundary Feature Extraction and Rule based Classification of High Resolution Data
 Hybrid Model with Super Resolution and Decision Boundary Feature Extraction and Rule based Classification of High Resolution Data Navjeet Kaur M.Tech Research Scholar Sri Guru Granth Sahib World University
Hybrid Model with Super Resolution and Decision Boundary Feature Extraction and Rule based Classification of High Resolution Data Navjeet Kaur M.Tech Research Scholar Sri Guru Granth Sahib World University
Encoding Words into String Vectors for Word Categorization
 Int'l Conf. Artificial Intelligence ICAI'16 271 Encoding Words into String Vectors for Word Categorization Taeho Jo Department of Computer and Information Communication Engineering, Hongik University,
Int'l Conf. Artificial Intelligence ICAI'16 271 Encoding Words into String Vectors for Word Categorization Taeho Jo Department of Computer and Information Communication Engineering, Hongik University,
STUDY PAPER ON CLASSIFICATION TECHIQUE IN DATA MINING
 Journal of Analysis and Computation (JAC) (An International Peer Reviewed Journal), www.ijaconline.com, ISSN 0973-2861 International Conference on Emerging Trends in IOT & Machine Learning, 2018 STUDY
Journal of Analysis and Computation (JAC) (An International Peer Reviewed Journal), www.ijaconline.com, ISSN 0973-2861 International Conference on Emerging Trends in IOT & Machine Learning, 2018 STUDY
Machine Learning. Topic 5: Linear Discriminants. Bryan Pardo, EECS 349 Machine Learning, 2013
 Machine Learning Topic 5: Linear Discriminants Bryan Pardo, EECS 349 Machine Learning, 2013 Thanks to Mark Cartwright for his extensive contributions to these slides Thanks to Alpaydin, Bishop, and Duda/Hart/Stork
Machine Learning Topic 5: Linear Discriminants Bryan Pardo, EECS 349 Machine Learning, 2013 Thanks to Mark Cartwright for his extensive contributions to these slides Thanks to Alpaydin, Bishop, and Duda/Hart/Stork
Network Traffic Measurements and Analysis
 DEIB - Politecnico di Milano Fall, 2017 Sources Hastie, Tibshirani, Friedman: The Elements of Statistical Learning James, Witten, Hastie, Tibshirani: An Introduction to Statistical Learning Andrew Ng:
DEIB - Politecnico di Milano Fall, 2017 Sources Hastie, Tibshirani, Friedman: The Elements of Statistical Learning James, Witten, Hastie, Tibshirani: An Introduction to Statistical Learning Andrew Ng:
Traffic Signs Recognition using HP and HOG Descriptors Combined to MLP and SVM Classifiers
 Traffic Signs Recognition using HP and HOG Descriptors Combined to MLP and SVM Classifiers A. Salhi, B. Minaoui, M. Fakir, H. Chakib, H. Grimech Faculty of science and Technology Sultan Moulay Slimane
Traffic Signs Recognition using HP and HOG Descriptors Combined to MLP and SVM Classifiers A. Salhi, B. Minaoui, M. Fakir, H. Chakib, H. Grimech Faculty of science and Technology Sultan Moulay Slimane
HUMAN S FACIAL PARTS EXTRACTION TO RECOGNIZE FACIAL EXPRESSION
 HUMAN S FACIAL PARTS EXTRACTION TO RECOGNIZE FACIAL EXPRESSION Dipankar Das Department of Information and Communication Engineering, University of Rajshahi, Rajshahi-6205, Bangladesh ABSTRACT Real-time
HUMAN S FACIAL PARTS EXTRACTION TO RECOGNIZE FACIAL EXPRESSION Dipankar Das Department of Information and Communication Engineering, University of Rajshahi, Rajshahi-6205, Bangladesh ABSTRACT Real-time
Practice EXAM: SPRING 2012 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE
 Practice EXAM: SPRING 0 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE The exam is closed book. You are allowed four pages of double sided cheat sheets. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets.
Practice EXAM: SPRING 0 CS 6375 INSTRUCTOR: VIBHAV GOGATE The exam is closed book. You are allowed four pages of double sided cheat sheets. Answer the questions in the spaces provided on the question sheets.
