Molecular Distance Geometry and Atomic Orderings
|
|
|
- Janice Tate
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Molecular Distance Geometry and Atomic Orderings Antonio Mucherino IRISA, University of Rennes 1 Workshop Set Computation for Control ENSTA Bretagne, Brest, France December 5 th 2013
2 The Distance Geometry Problem (for molecular conformations) Let G = (V, E, d) be a simple weighted undirected graph, where V the set of vertices of G it is the set of atoms; E the set of edges of G it is the set of known distances; E E the subset of E where distances are exact; d the weights associated to the edges of G the numerical value of each weight corresponds to the known distance; it can be an interval. Definition The DGP. Determine whether there exists a function x : V R K for which, for all edges (u, v) E, x u x v = d(u, v).
3 Sphere intersections and discretization In the 3-dimensional space, the intersection of 2 spheres gives one circle 3 spheres gives two points 2 spheres and 1 spherical shell gives two disjont curves Definition of the spheres / spherical shells: center = vertex w with known position radius = known distance between w and a common vertex (to be placed) Precision of distance information = sphere / spherical shell
4 Importance of orders The definition of an order on the vertices in V allows us to ensure that vertex coordinates are available when needed. Given 1 a simple weighted undirected graph G = (V, E, d) 2 a vertex v V how to identify K vertices w i, with i = 1, 2,..., K, for which???? the coordinates of every w i are available every edge (w i, v) E We refer to w i as a reference vertex for v (w i, v) as a reference distance for v
5 Definition of order Definition An order for V is a sequence r : N V {0} with length r N (for which r i = 0 for all i > r ) such that, for each v V, there is an index i N for which r i = v. and vertex repetitions: they allow for vertex repetitions ( r V ); however, each vertex can be used as a reference only once; simplex inequalities (generally satisfied with probability 1) would not be satisfied if the same vertex were used twice as a reference.
6 Counting the reference vertices Let r be an order for V. Let us consider the following counters. α(r i ): counter of adjacent predecessors of r i ; β(r i ): counter of adjacent successors of r i ; α ex (r i ): counter of adjacent predecessors of r i related to an exact distance. Necessary condition for V to admit a discretization order is that, for any order r on V without repetitions, i {1, 2,..., r }, α(r i ) + β(r i ) K.
7 The ordering problem Definition The interval Vertex Order Problem (idvop). Given a simple weighted undirected graph G = (V, E, d) and a positive integer K, establish whether there exists an order r such that: (a) G C = (V C, E C ) G[{r 1, r 2,...,r K }] is a clique and E C E ; (b) i {K + 1,..., r }, α(r i ) K and α ex (r i ) K 1. Remarks: this problem is NP-complete when K is not fixed no consecutivity assumption: solvable in polynomial time when K is known when dealing with proteins, K = 3
8 0: reorder(g) while (a valid order r is not found yet) do let i = 0; find a K -clique C in G with exact distances; // position C at the beginning of new order for (all vertices v in C) do let i = i + 1; let r i = v; end for // greedy search while (V is not covered) do v = arg max{α(u) j i : r j = u and α ex(u) K 1}; if (α(v) < K ) then break the inner loop: there are no possible for C; end if // adding the vertex to the order let i = i + 1; let r i = v; end while end while return r;
9 An order for the protein backbone This order was automatically obtained by the greedy algorithm; no NMR distances were supposed to be known. In presence of NMR data, the algorithm can be applied again for finding an order that is perfectly tailored to the instance at hand.
10 The Branch & Prune algorithm The Branch & Prune (BP) algorithm is based on the idea of branching over all possible positions for each vertex, and of pruning by using additional distances that are not used in the discretization process (pruning distances). In this tree, it is supposed that all available distances are exact. If not, D sample (exact) distances can be taken from interval distances.
11 Generation of NMR-like instances We consider artificially generated instances that simulate real NMR instances. We consider the molecular graph, describing the chemical structure of the molecule the set of atomic coordinates from the PDB. We compute all distances between pairs of atoms and we add a distance in our instance if this is a distance between - two bonded atoms (exact) - two atoms that are bonded to a common atom (exact) - two atoms belonging to a quadruplet of bonded atoms forming a torsion angle (interval) - two hydrogen atoms whose distance is in the interval [2.5, 5] (interval)
12 NMR-like instances are considered in these, which include protein backbones and side chains. Instance n E D BP calls Time 1niz u6u b jnr pv zec m1a me me dsk All instances were automatically reordered by the greedy algorithm, and the BP algorithm was invoked for finding one solution.
13 The generalized??? The discretization of the curves can lead to the propagation of errors. The number D of sample distances that are taken from each curve plays an inportant role, but it is rather difficult to predict. What if the nodes of the tree do not represent vertex positions, but rather intervals???
14 Work in progress... Can we find orders that help BP in finding solutions? minimize in length the subsequences in the order having no pruning distances minimize the number of vertices that are crossed by the same pruning distance (for proteins) maximize the interval distances that are related to pairs of hydrogen atoms...
15 Other work in progress... make the branching phase of BP adaptive identify clusters of solutions in BP solution sets improve and tailor the parallel versions of BP to interval data (for proteins) exploit energy-based information for pruning purposes (for proteins) use real NMR data and compare our results to what is currently available on the PDB
16 Thanks!
The Discretizable Distance Geometry Problem
 Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) The Discretizable Distance Geometry Problem A. Mucherino C. Lavor L. Liberti Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract We introduce the Discretizable
Noname manuscript No. (will be inserted by the editor) The Discretizable Distance Geometry Problem A. Mucherino C. Lavor L. Liberti Received: date / Accepted: date Abstract We introduce the Discretizable
uncorrected proof Recent advances on the interval distance geometry problem Author Proof B Leo Liberti
 DOI 10.1007/s10898-016-0493-6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Recent advances on the interval distance geometry problem Douglas S. Gonçalves 1 Antonio Mucherino 2 Carlile Lavor 3 Leo Liberti 4 Received: 28
DOI 10.1007/s10898-016-0493-6 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Recent advances on the interval distance geometry problem Douglas S. Gonçalves 1 Antonio Mucherino 2 Carlile Lavor 3 Leo Liberti 4 Received: 28
A Parallel Version of the Branch & Prune Algorithm for the Molecular Distance Geometry Problem
 A Parallel Version of the Branch & Prune Algorithm for the Molecular Distance Geometry Problem A. Mucherino C. Lavor L. Liberti E.-G. Talbi INRIA, Lille Nord Europe, France. Emails: antonio.mucherino@inria.fr,
A Parallel Version of the Branch & Prune Algorithm for the Molecular Distance Geometry Problem A. Mucherino C. Lavor L. Liberti E.-G. Talbi INRIA, Lille Nord Europe, France. Emails: antonio.mucherino@inria.fr,
Discretization vertex orders in distance geometry
 Discretization vertex orders in distance geometry Andrea Cassioli 1, Oktay Günlük 2, Carlile Lavor 3, Leo Liberti 2,4 1 MOSEK ApS, Fruebjergvej 3 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark Email:andrea.cassioli@mosek.com
Discretization vertex orders in distance geometry Andrea Cassioli 1, Oktay Günlük 2, Carlile Lavor 3, Leo Liberti 2,4 1 MOSEK ApS, Fruebjergvej 3 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark Email:andrea.cassioli@mosek.com
Notes for Lecture 24
 U.C. Berkeley CS170: Intro to CS Theory Handout N24 Professor Luca Trevisan December 4, 2001 Notes for Lecture 24 1 Some NP-complete Numerical Problems 1.1 Subset Sum The Subset Sum problem is defined
U.C. Berkeley CS170: Intro to CS Theory Handout N24 Professor Luca Trevisan December 4, 2001 Notes for Lecture 24 1 Some NP-complete Numerical Problems 1.1 Subset Sum The Subset Sum problem is defined
Chordal graphs MPRI
 Chordal graphs MPRI 2017 2018 Michel Habib habib@irif.fr http://www.irif.fr/~habib Sophie Germain, septembre 2017 Schedule Chordal graphs Representation of chordal graphs LBFS and chordal graphs More structural
Chordal graphs MPRI 2017 2018 Michel Habib habib@irif.fr http://www.irif.fr/~habib Sophie Germain, septembre 2017 Schedule Chordal graphs Representation of chordal graphs LBFS and chordal graphs More structural
A Parallel Implementation of a Higher-order Self Consistent Mean Field. Effectively solving the protein repacking problem is a key step to successful
 Karl Gutwin May 15, 2005 18.336 A Parallel Implementation of a Higher-order Self Consistent Mean Field Effectively solving the protein repacking problem is a key step to successful protein design. Put
Karl Gutwin May 15, 2005 18.336 A Parallel Implementation of a Higher-order Self Consistent Mean Field Effectively solving the protein repacking problem is a key step to successful protein design. Put
Introduction to Hermes
 Introduction to Hermes Version 2.0 November 2017 Hermes v1.9 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Visualising and Editing the MLL1 fusion protein... 2 Opening Files in Hermes... 3 Setting Style Preferences...
Introduction to Hermes Version 2.0 November 2017 Hermes v1.9 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Visualising and Editing the MLL1 fusion protein... 2 Opening Files in Hermes... 3 Setting Style Preferences...
Computational Geometry
 Casting a polyhedron CAD/CAM systems CAD/CAM systems allow you to design objects and test how they can be constructed Many objects are constructed used a mold Casting Casting A general question: Given
Casting a polyhedron CAD/CAM systems CAD/CAM systems allow you to design objects and test how they can be constructed Many objects are constructed used a mold Casting Casting A general question: Given
A FILTERING TECHNIQUE FOR FRAGMENT ASSEMBLY- BASED PROTEINS LOOP MODELING WITH CONSTRAINTS
 A FILTERING TECHNIQUE FOR FRAGMENT ASSEMBLY- BASED PROTEINS LOOP MODELING WITH CONSTRAINTS F. Campeotto 1,2 A. Dal Palù 3 A. Dovier 2 F. Fioretto 1 E. Pontelli 1 1. Dept. Computer Science, NMSU 2. Dept.
A FILTERING TECHNIQUE FOR FRAGMENT ASSEMBLY- BASED PROTEINS LOOP MODELING WITH CONSTRAINTS F. Campeotto 1,2 A. Dal Palù 3 A. Dovier 2 F. Fioretto 1 E. Pontelli 1 1. Dept. Computer Science, NMSU 2. Dept.
Testing Bipartiteness of Geometric Intersection Graphs David Eppstein
 Testing Bipartiteness of Geometric Intersection Graphs David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science Intersection Graphs Given arrangement of geometric objects,
Testing Bipartiteness of Geometric Intersection Graphs David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science Intersection Graphs Given arrangement of geometric objects,
Archbold Area Schools Math Curriculum Map
 Math 8 August - May Mathematical Processes Formulate a problem or mathematical model in response to a specific need or situation, determine information required to solve the problem, choose method for
Math 8 August - May Mathematical Processes Formulate a problem or mathematical model in response to a specific need or situation, determine information required to solve the problem, choose method for
Practice Final Exam 2: Solutions
 lgorithm Design Techniques Practice Final Exam 2: Solutions 1. The Simplex lgorithm. (a) Take the LP max x 1 + 2x 2 s.t. 2x 1 + x 2 3 x 1 x 2 2 x 1, x 2 0 and write it in dictionary form. Pivot: add x
lgorithm Design Techniques Practice Final Exam 2: Solutions 1. The Simplex lgorithm. (a) Take the LP max x 1 + 2x 2 s.t. 2x 1 + x 2 3 x 1 x 2 2 x 1, x 2 0 and write it in dictionary form. Pivot: add x
The Maximum Clique Problem
 November, 2012 Motivation How to put as much left-over stuff as possible in a tasty meal before everything will go off? Motivation Find the largest collection of food where everything goes together! Here,
November, 2012 Motivation How to put as much left-over stuff as possible in a tasty meal before everything will go off? Motivation Find the largest collection of food where everything goes together! Here,
The k-center problem Approximation Algorithms 2009 Petros Potikas
 Approximation Algorithms 2009 Petros Potikas 1 Definition: Let G=(V,E) be a complete undirected graph with edge costs satisfying the triangle inequality and k be an integer, 0 < k V. For any S V and vertex
Approximation Algorithms 2009 Petros Potikas 1 Definition: Let G=(V,E) be a complete undirected graph with edge costs satisfying the triangle inequality and k be an integer, 0 < k V. For any S V and vertex
Comparisons between an Exact and a Meta-Heuristic Algorithm for the Molecular Distance Geometry Problem
 Comparisons between an Exact and a Meta-Heuristic Algorithm for the Molecular Distance Geometry Problem Antonio Mucherino Leo Liberti LIX, École Polytechnique, Palaiseau, France {mucherino,liberti}@ lix.polytechnique.fr
Comparisons between an Exact and a Meta-Heuristic Algorithm for the Molecular Distance Geometry Problem Antonio Mucherino Leo Liberti LIX, École Polytechnique, Palaiseau, France {mucherino,liberti}@ lix.polytechnique.fr
CS 372: Computational Geometry Lecture 10 Linear Programming in Fixed Dimension
 CS 372: Computational Geometry Lecture 10 Linear Programming in Fixed Dimension Antoine Vigneron King Abdullah University of Science and Technology November 7, 2012 Antoine Vigneron (KAUST) CS 372 Lecture
CS 372: Computational Geometry Lecture 10 Linear Programming in Fixed Dimension Antoine Vigneron King Abdullah University of Science and Technology November 7, 2012 Antoine Vigneron (KAUST) CS 372 Lecture
Decision Problems. Observation: Many polynomial algorithms. Questions: Can we solve all problems in polynomial time? Answer: No, absolutely not.
 Decision Problems Observation: Many polynomial algorithms. Questions: Can we solve all problems in polynomial time? Answer: No, absolutely not. Definition: The class of problems that can be solved by polynomial-time
Decision Problems Observation: Many polynomial algorithms. Questions: Can we solve all problems in polynomial time? Answer: No, absolutely not. Definition: The class of problems that can be solved by polynomial-time
Chordal Graphs: Theory and Algorithms
 Chordal Graphs: Theory and Algorithms 1 Chordal graphs Chordal graph : Every cycle of four or more vertices has a chord in it, i.e. there is an edge between two non consecutive vertices of the cycle. Also
Chordal Graphs: Theory and Algorithms 1 Chordal graphs Chordal graph : Every cycle of four or more vertices has a chord in it, i.e. there is an edge between two non consecutive vertices of the cycle. Also
Computing optimal total vertex covers for trees
 Computing optimal total vertex covers for trees Pak Ching Li Department of Computer Science University of Manitoba Winnipeg, Manitoba Canada R3T 2N2 Abstract. Let G = (V, E) be a simple, undirected, connected
Computing optimal total vertex covers for trees Pak Ching Li Department of Computer Science University of Manitoba Winnipeg, Manitoba Canada R3T 2N2 Abstract. Let G = (V, E) be a simple, undirected, connected
COMP 355 Advanced Algorithms Approximation Algorithms: VC and TSP Chapter 11 (KT) Section (CLRS)
 COMP 355 Advanced Algorithms Approximation Algorithms: VC and TSP Chapter 11 (KT) Section 35.1-35.2(CLRS) 1 Coping with NP-Completeness Brute-force search: This is usually only a viable option for small
COMP 355 Advanced Algorithms Approximation Algorithms: VC and TSP Chapter 11 (KT) Section 35.1-35.2(CLRS) 1 Coping with NP-Completeness Brute-force search: This is usually only a viable option for small
Approximation Algorithms for Geometric Intersection Graphs
 Approximation Algorithms for Geometric Intersection Graphs Subhas C. Nandy (nandysc@isical.ac.in) Advanced Computing and Microelectronics Unit Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata 700108, India. Outline
Approximation Algorithms for Geometric Intersection Graphs Subhas C. Nandy (nandysc@isical.ac.in) Advanced Computing and Microelectronics Unit Indian Statistical Institute Kolkata 700108, India. Outline
Prentice Hall Mathematics: Course Correlated to: The Pennsylvania Math Assessment Anchors and Eligible Content (Grade 8)
 M8.A Numbers and Operations M8.A.1 Demonstrate an understanding of numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers and number systems. M8.A.1.1 Represent numbers in equivalent forms.
M8.A Numbers and Operations M8.A.1 Demonstrate an understanding of numbers, ways of representing numbers, relationships among numbers and number systems. M8.A.1.1 Represent numbers in equivalent forms.
Version 1.0 November2016 Hermes V1.8.2
 Hermes in a Nutshell Version 1.0 November2016 Hermes V1.8.2 Table of Contents Hermes in a Nutshell... 1 Introduction... 2 Example 1. Visualizing and Editing the MLL1 fusion protein... 3 Setting Your Display...
Hermes in a Nutshell Version 1.0 November2016 Hermes V1.8.2 Table of Contents Hermes in a Nutshell... 1 Introduction... 2 Example 1. Visualizing and Editing the MLL1 fusion protein... 3 Setting Your Display...
Complexity Results on Graphs with Few Cliques
 Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical Computer Science DMTCS vol. 9, 2007, 127 136 Complexity Results on Graphs with Few Cliques Bill Rosgen 1 and Lorna Stewart 2 1 Institute for Quantum Computing and School
Discrete Mathematics and Theoretical Computer Science DMTCS vol. 9, 2007, 127 136 Complexity Results on Graphs with Few Cliques Bill Rosgen 1 and Lorna Stewart 2 1 Institute for Quantum Computing and School
Fast algorithms for max independent set
 Fast algorithms for max independent set N. Bourgeois 1 B. Escoffier 1 V. Th. Paschos 1 J.M.M. van Rooij 2 1 LAMSADE, CNRS and Université Paris-Dauphine, France {bourgeois,escoffier,paschos}@lamsade.dauphine.fr
Fast algorithms for max independent set N. Bourgeois 1 B. Escoffier 1 V. Th. Paschos 1 J.M.M. van Rooij 2 1 LAMSADE, CNRS and Université Paris-Dauphine, France {bourgeois,escoffier,paschos}@lamsade.dauphine.fr
Molecular Surface Representation
 Molecular Surface Representation Applications to docking 1 Motivation Studies of protein folding (Lee and Richards). Prediction of biomolecular recognition. Detection of drug binding cavities. Molecular
Molecular Surface Representation Applications to docking 1 Motivation Studies of protein folding (Lee and Richards). Prediction of biomolecular recognition. Detection of drug binding cavities. Molecular
6 Randomized rounding of semidefinite programs
 6 Randomized rounding of semidefinite programs We now turn to a new tool which gives substantially improved performance guarantees for some problems We now show how nonlinear programming relaxations can
6 Randomized rounding of semidefinite programs We now turn to a new tool which gives substantially improved performance guarantees for some problems We now show how nonlinear programming relaxations can
Faster parameterized algorithms for Minimum Fill-In
 Faster parameterized algorithms for Minimum Fill-In Hans L. Bodlaender Pinar Heggernes Yngve Villanger Technical Report UU-CS-2008-042 December 2008 Department of Information and Computing Sciences Utrecht
Faster parameterized algorithms for Minimum Fill-In Hans L. Bodlaender Pinar Heggernes Yngve Villanger Technical Report UU-CS-2008-042 December 2008 Department of Information and Computing Sciences Utrecht
On the Min-Max 2-Cluster Editing Problem
 JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING 29, 1109-1120 (2013) On the Min-Max 2-Cluster Editing Problem LI-HSUAN CHEN 1, MAW-SHANG CHANG 2, CHUN-CHIEH WANG 1 AND BANG YE WU 1,* 1 Department of Computer
JOURNAL OF INFORMATION SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING 29, 1109-1120 (2013) On the Min-Max 2-Cluster Editing Problem LI-HSUAN CHEN 1, MAW-SHANG CHANG 2, CHUN-CHIEH WANG 1 AND BANG YE WU 1,* 1 Department of Computer
arxiv: v1 [q-bio.qm] 2 May 2012
![arxiv: v1 [q-bio.qm] 2 May 2012 arxiv: v1 [q-bio.qm] 2 May 2012](/thumbs/89/99983235.jpg) Euclidean distance geometry and applications Leo Liberti Carlile Lavor Nelson Maculan Antonio Mucherino arxiv:1205.0349v1 [q-bio.qm] 2 May 2012 May 3, 2012 Abstract Euclidean distance geometry is the study
Euclidean distance geometry and applications Leo Liberti Carlile Lavor Nelson Maculan Antonio Mucherino arxiv:1205.0349v1 [q-bio.qm] 2 May 2012 May 3, 2012 Abstract Euclidean distance geometry is the study
Estrada Index. Bo Zhou. Augest 5, Department of Mathematics, South China Normal University
 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Results for 3. References Bo Zhou Department of Mathematics, South China Normal University Augest 5, 2010 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Results for 3. References Outline 1. Introduction
Outline 1. Introduction 2. Results for 3. References Bo Zhou Department of Mathematics, South China Normal University Augest 5, 2010 Outline 1. Introduction 2. Results for 3. References Outline 1. Introduction
Solutions to Exercise 4 Algebraic Curve, Surface Splines IV: Molecular Models
 Solutions to Exercise 4 Algebraic Curve, Surface Splines IV: Molecular Models CS384R, CAM 395T, BME 385J: Fall 2007 Question 1. Describe the LEG (Labelled Embedded Graph) atomic representations as per
Solutions to Exercise 4 Algebraic Curve, Surface Splines IV: Molecular Models CS384R, CAM 395T, BME 385J: Fall 2007 Question 1. Describe the LEG (Labelled Embedded Graph) atomic representations as per
Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder]
![Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder] Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder]](/thumbs/93/111713975.jpg) Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder] Preliminaries Recall: Given a smooth function f:r R, the function
Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder] Preliminaries Recall: Given a smooth function f:r R, the function
Protein Flexibility Predictions
 Protein Flexibility Predictions Using Graph Theory by D.J. Jacobs, A.J. Rader et. al. from the Michigan State University Talk by Jan Christoph, 19th January 2007 Outline 1. Introduction / Motivation 2.
Protein Flexibility Predictions Using Graph Theory by D.J. Jacobs, A.J. Rader et. al. from the Michigan State University Talk by Jan Christoph, 19th January 2007 Outline 1. Introduction / Motivation 2.
CSC Linear Programming and Combinatorial Optimization Lecture 12: Semidefinite Programming(SDP) Relaxation
 CSC411 - Linear Programming and Combinatorial Optimization Lecture 1: Semidefinite Programming(SDP) Relaxation Notes taken by Xinwei Gui May 1, 007 Summary: This lecture introduces the semidefinite programming(sdp)
CSC411 - Linear Programming and Combinatorial Optimization Lecture 1: Semidefinite Programming(SDP) Relaxation Notes taken by Xinwei Gui May 1, 007 Summary: This lecture introduces the semidefinite programming(sdp)
NOTE ON MINIMALLY k-connected GRAPHS
 NOTE ON MINIMALLY k-connected GRAPHS R. Rama a, Suresh Badarla a a Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Technology, Chennai, India ABSTRACT A k-tree is either a complete graph on (k+1) vertices
NOTE ON MINIMALLY k-connected GRAPHS R. Rama a, Suresh Badarla a a Department of Mathematics, Indian Institute of Technology, Chennai, India ABSTRACT A k-tree is either a complete graph on (k+1) vertices
Energy Minimization -Non-Derivative Methods -First Derivative Methods. Background Image Courtesy: 3dciencia.com visual life sciences
 Energy Minimization -Non-Derivative Methods -First Derivative Methods Background Image Courtesy: 3dciencia.com visual life sciences Introduction Contents Criteria to start minimization Energy Minimization
Energy Minimization -Non-Derivative Methods -First Derivative Methods Background Image Courtesy: 3dciencia.com visual life sciences Introduction Contents Criteria to start minimization Energy Minimization
2 hours THE UNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER. 23 May :45 11:45
 2 hours MAT20902 TE UNIVERSITY OF MANCESTER DISCRETE MATEMATICS 23 May 2018 9:45 11:45 Answer ALL TREE questions in Section A (30 marks in total). Answer TWO of the TREE questions in Section B (50 marks
2 hours MAT20902 TE UNIVERSITY OF MANCESTER DISCRETE MATEMATICS 23 May 2018 9:45 11:45 Answer ALL TREE questions in Section A (30 marks in total). Answer TWO of the TREE questions in Section B (50 marks
A Performance Analysis on Maximal Common Subgraph Algorithms
 A Performance Analysis on Maximal Common Subgraph Algorithms Ruud Welling University of Twente P.O. Box 217, 7500AE Enschede The Netherlands r.h.a.welling@student.utwente.nl ABSTRACT Graphs can be used
A Performance Analysis on Maximal Common Subgraph Algorithms Ruud Welling University of Twente P.O. Box 217, 7500AE Enschede The Netherlands r.h.a.welling@student.utwente.nl ABSTRACT Graphs can be used
Introduction to Approximation Algorithms
 Introduction to Approximation Algorithms Dr. Gautam K. Das Departmet of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati, India gkd@iitg.ernet.in February 19, 2016 Outline of the lecture Background
Introduction to Approximation Algorithms Dr. Gautam K. Das Departmet of Mathematics Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati, India gkd@iitg.ernet.in February 19, 2016 Outline of the lecture Background
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 8: GRAPHICAL MODELS
 PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 8: GRAPHICAL MODELS Bayesian Networks Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) Bayesian Networks General Factorization Bayesian Curve Fitting (1) Polynomial Bayesian
PATTERN RECOGNITION AND MACHINE LEARNING CHAPTER 8: GRAPHICAL MODELS Bayesian Networks Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) Bayesian Networks General Factorization Bayesian Curve Fitting (1) Polynomial Bayesian
3 No-Wait Job Shops with Variable Processing Times
 3 No-Wait Job Shops with Variable Processing Times In this chapter we assume that, on top of the classical no-wait job shop setting, we are given a set of processing times for each operation. We may select
3 No-Wait Job Shops with Variable Processing Times In this chapter we assume that, on top of the classical no-wait job shop setting, we are given a set of processing times for each operation. We may select
1 Unweighted Set Cover
 Comp 60: Advanced Algorithms Tufts University, Spring 018 Prof. Lenore Cowen Scribe: Yuelin Liu Lecture 7: Approximation Algorithms: Set Cover and Max Cut 1 Unweighted Set Cover 1.1 Formulations There
Comp 60: Advanced Algorithms Tufts University, Spring 018 Prof. Lenore Cowen Scribe: Yuelin Liu Lecture 7: Approximation Algorithms: Set Cover and Max Cut 1 Unweighted Set Cover 1.1 Formulations There
arxiv: v1 [cs.dm] 10 Sep 2018
![arxiv: v1 [cs.dm] 10 Sep 2018 arxiv: v1 [cs.dm] 10 Sep 2018](/thumbs/87/95825148.jpg) Minimum Eccentric Connectivity Index for Graphs with Fixed Order and Fixed Number of Pending Vertices Gauvain Devillez 1, Alain Hertz 2, Hadrien Mélot 1, Pierre Hauweele 1 1 Computer Science Department
Minimum Eccentric Connectivity Index for Graphs with Fixed Order and Fixed Number of Pending Vertices Gauvain Devillez 1, Alain Hertz 2, Hadrien Mélot 1, Pierre Hauweele 1 1 Computer Science Department
The ILP approach to the layered graph drawing. Ago Kuusik
 The ILP approach to the layered graph drawing Ago Kuusik Veskisilla Teooriapäevad 1-3.10.2004 1 Outline Introduction Hierarchical drawing & Sugiyama algorithm Linear Programming (LP) and Integer Linear
The ILP approach to the layered graph drawing Ago Kuusik Veskisilla Teooriapäevad 1-3.10.2004 1 Outline Introduction Hierarchical drawing & Sugiyama algorithm Linear Programming (LP) and Integer Linear
Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Bayesian Networks Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) Bayesian Networks General Factorization Curve Fitting Re-visited Maximum Likelihood Determine by minimizing sum-of-squares
Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Bayesian Networks Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) Bayesian Networks General Factorization Curve Fitting Re-visited Maximum Likelihood Determine by minimizing sum-of-squares
UML CS Algorithms Qualifying Exam Spring, 2004 ALGORITHMS QUALIFYING EXAM
 NAME: This exam is open: - books - notes and closed: - neighbors - calculators ALGORITHMS QUALIFYING EXAM The upper bound on exam time is 3 hours. Please put all your work on the exam paper. (Partial credit
NAME: This exam is open: - books - notes and closed: - neighbors - calculators ALGORITHMS QUALIFYING EXAM The upper bound on exam time is 3 hours. Please put all your work on the exam paper. (Partial credit
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 4. Probabilistic Graphical Models Directed Models
 Prof. Daniel Cremers 4. Probabilistic Graphical Models Directed Models The Bayes Filter (Rep.) (Bayes) (Markov) (Tot. prob.) (Markov) (Markov) 2 Graphical Representation (Rep.) We can describe the overall
Prof. Daniel Cremers 4. Probabilistic Graphical Models Directed Models The Bayes Filter (Rep.) (Bayes) (Markov) (Tot. prob.) (Markov) (Markov) 2 Graphical Representation (Rep.) We can describe the overall
How many colors are needed to color a map?
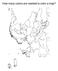 How many colors are needed to color a map? Is 4 always enough? Two relevant concepts How many colors do we need to color a map so neighboring countries get different colors? Simplifying assumption (not
How many colors are needed to color a map? Is 4 always enough? Two relevant concepts How many colors do we need to color a map so neighboring countries get different colors? Simplifying assumption (not
Braid groups and Curvature Talk 2: The Pieces
 Braid groups and Curvature Talk 2: The Pieces Jon McCammond UC Santa Barbara Regensburg, Germany Sept 2017 Rotations in Regensburg Subsets, Subdisks and Rotations Recall: for each A [n] of size k > 1 with
Braid groups and Curvature Talk 2: The Pieces Jon McCammond UC Santa Barbara Regensburg, Germany Sept 2017 Rotations in Regensburg Subsets, Subdisks and Rotations Recall: for each A [n] of size k > 1 with
Homology Modeling Professional for HyperChem Release Notes
 Homology Modeling Professional for HyperChem Release Notes This document lists additional information about Homology Modeling Professional for HyperChem. Current Revision Revision H1 (Version 8.1.1) Current
Homology Modeling Professional for HyperChem Release Notes This document lists additional information about Homology Modeling Professional for HyperChem. Current Revision Revision H1 (Version 8.1.1) Current
Preferred directions for resolving the non-uniqueness of Delaunay triangulations
 Preferred directions for resolving the non-uniqueness of Delaunay triangulations Christopher Dyken and Michael S. Floater Abstract: This note proposes a simple rule to determine a unique triangulation
Preferred directions for resolving the non-uniqueness of Delaunay triangulations Christopher Dyken and Michael S. Floater Abstract: This note proposes a simple rule to determine a unique triangulation
Molecular Shapes and Surfaces *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m11616 1 Molecular Shapes and Surfaces * Lydia E. Kavraki This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 1.0 Topics in this Module
OpenStax-CNX module: m11616 1 Molecular Shapes and Surfaces * Lydia E. Kavraki This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 1.0 Topics in this Module
Polynomial-Time Approximation Algorithms
 6.854 Advanced Algorithms Lecture 20: 10/27/2006 Lecturer: David Karger Scribes: Matt Doherty, John Nham, Sergiy Sidenko, David Schultz Polynomial-Time Approximation Algorithms NP-hard problems are a vast
6.854 Advanced Algorithms Lecture 20: 10/27/2006 Lecturer: David Karger Scribes: Matt Doherty, John Nham, Sergiy Sidenko, David Schultz Polynomial-Time Approximation Algorithms NP-hard problems are a vast
Unit 8: Coping with NP-Completeness. Complexity classes Reducibility and NP-completeness proofs Coping with NP-complete problems. Y.-W.
 : Coping with NP-Completeness Course contents: Complexity classes Reducibility and NP-completeness proofs Coping with NP-complete problems Reading: Chapter 34 Chapter 35.1, 35.2 Y.-W. Chang 1 Complexity
: Coping with NP-Completeness Course contents: Complexity classes Reducibility and NP-completeness proofs Coping with NP-complete problems Reading: Chapter 34 Chapter 35.1, 35.2 Y.-W. Chang 1 Complexity
CSE 548: Analysis of Algorithms. Lecture 13 ( Approximation Algorithms )
 CSE 548: Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 13 ( Approximation Algorithms ) Rezaul A. Chowdhury Department of Computer Science SUNY Stony Brook Fall 2017 Approximation Ratio Consider an optimization problem
CSE 548: Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 13 ( Approximation Algorithms ) Rezaul A. Chowdhury Department of Computer Science SUNY Stony Brook Fall 2017 Approximation Ratio Consider an optimization problem
Data mining, 4 cu Lecture 8:
 582364 Data mining, 4 cu Lecture 8: Graph mining Spring 2010 Lecturer: Juho Rousu Teaching assistant: Taru Itäpelto Frequent Subgraph Mining Extend association rule mining to finding frequent subgraphs
582364 Data mining, 4 cu Lecture 8: Graph mining Spring 2010 Lecturer: Juho Rousu Teaching assistant: Taru Itäpelto Frequent Subgraph Mining Extend association rule mining to finding frequent subgraphs
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Input: undirected graph G=(V,E), c: E R + Goal: find a tour (Hamiltonian cycle) of minimum cost
 Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Input: undirected graph G=(V,E), c: E R + Goal: find a tour (Hamiltonian cycle) of minimum cost Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Input: undirected graph G=(V,E), c: E R
Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Input: undirected graph G=(V,E), c: E R + Goal: find a tour (Hamiltonian cycle) of minimum cost Traveling Salesman Problem (TSP) Input: undirected graph G=(V,E), c: E R
COMP Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
 COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Approximation Algorithms CLRS 35.1-35.5 University of Manitoba COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures 1 / 30 Approaching
COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Approximation Algorithms CLRS 35.1-35.5 University of Manitoba COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures 1 / 30 Approaching
Science Olympiad Protein Modeling Event Guide to Scoring Zinc Finger Motif
 Science Olympiad Protein Modeling Event Guide to Scoring Zinc Finger Motif Once you have folded the zinc finger motif (chain C, residues 4-31 of 1ZAA.pdb), use this guide in conjunction with the rubric
Science Olympiad Protein Modeling Event Guide to Scoring Zinc Finger Motif Once you have folded the zinc finger motif (chain C, residues 4-31 of 1ZAA.pdb), use this guide in conjunction with the rubric
9 About Intersection Graphs
 9 About Intersection Graphs Since this lecture we focus on selected detailed topics in Graph theory that are close to your teacher s heart... The first selected topic is that of intersection graphs, i.e.
9 About Intersection Graphs Since this lecture we focus on selected detailed topics in Graph theory that are close to your teacher s heart... The first selected topic is that of intersection graphs, i.e.
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning
 STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 5 Inference
STA 4273H: Statistical Machine Learning Russ Salakhutdinov Department of Statistics! rsalakhu@utstat.toronto.edu! http://www.utstat.utoronto.ca/~rsalakhu/ Sidney Smith Hall, Room 6002 Lecture 5 Inference
Solutions for the Exam 6 January 2014
 Mastermath and LNMB Course: Discrete Optimization Solutions for the Exam 6 January 2014 Utrecht University, Educatorium, 13:30 16:30 The examination lasts 3 hours. Grading will be done before January 20,
Mastermath and LNMB Course: Discrete Optimization Solutions for the Exam 6 January 2014 Utrecht University, Educatorium, 13:30 16:30 The examination lasts 3 hours. Grading will be done before January 20,
Stanford University CS261: Optimization Handout 1 Luca Trevisan January 4, 2011
 Stanford University CS261: Optimization Handout 1 Luca Trevisan January 4, 2011 Lecture 1 In which we describe what this course is about and give two simple examples of approximation algorithms 1 Overview
Stanford University CS261: Optimization Handout 1 Luca Trevisan January 4, 2011 Lecture 1 In which we describe what this course is about and give two simple examples of approximation algorithms 1 Overview
Tutorial 3 Comparing Biological Shapes Patrice Koehl and Joel Hass
 Tutorial 3 Comparing Biological Shapes Patrice Koehl and Joel Hass University of California, Davis, USA http://www.cs.ucdavis.edu/~koehl/ims2017/ What is a shape? A shape is a 2-manifold with a Riemannian
Tutorial 3 Comparing Biological Shapes Patrice Koehl and Joel Hass University of California, Davis, USA http://www.cs.ucdavis.edu/~koehl/ims2017/ What is a shape? A shape is a 2-manifold with a Riemannian
Coloring. Radhika Gupta. Problem 1. What is the chromatic number of the arc graph of a polygonal disc of N sides?
 Coloring Radhika Gupta 1 Coloring of A N Let A N be the arc graph of a polygonal disc with N sides, N > 4 Problem 1 What is the chromatic number of the arc graph of a polygonal disc of N sides? Or we would
Coloring Radhika Gupta 1 Coloring of A N Let A N be the arc graph of a polygonal disc with N sides, N > 4 Problem 1 What is the chromatic number of the arc graph of a polygonal disc of N sides? Or we would
KINARI-Lib A library for Combinatorial Rigidity analysis and applications
 KINARI-Lib A library for Combinatorial Rigidity analysis and applications Naomi Fox Filip Jagodzinski Ileana Streinu Linkage Lab http://linkage.cs.umass.edu Department of Computer Science Smith College
KINARI-Lib A library for Combinatorial Rigidity analysis and applications Naomi Fox Filip Jagodzinski Ileana Streinu Linkage Lab http://linkage.cs.umass.edu Department of Computer Science Smith College
Antibandwidth of Hamming graphs
 Antibandwidth of Hamming graphs Štefan Dobrev Rastislav Královič Dana Pardubská Ľubomír Török Imrich Vrťo Workshop on Discrete Mathematics Vienna, November 19-22, 2008 Antibandwidth problem Consists of
Antibandwidth of Hamming graphs Štefan Dobrev Rastislav Královič Dana Pardubská Ľubomír Török Imrich Vrťo Workshop on Discrete Mathematics Vienna, November 19-22, 2008 Antibandwidth problem Consists of
Optimal Linear Arrangement of Interval Graphs
 /5 Optimal Linear Arrangement of Interval Graphs Johanne Cohen Fedor Fomin Pinar Heggernes Dieter Kratsch Gregory Kucherov 4 LORIA/CNRS, Nancy, France. Department of Informatics, University of Bergen,
/5 Optimal Linear Arrangement of Interval Graphs Johanne Cohen Fedor Fomin Pinar Heggernes Dieter Kratsch Gregory Kucherov 4 LORIA/CNRS, Nancy, France. Department of Informatics, University of Bergen,
Lecture outline. Graph coloring Examples Applications Algorithms
 Lecture outline Graph coloring Examples Applications Algorithms Graph coloring Adjacent nodes must have different colors. How many colors do we need? Graph coloring Neighbors must have different colors
Lecture outline Graph coloring Examples Applications Algorithms Graph coloring Adjacent nodes must have different colors. How many colors do we need? Graph coloring Neighbors must have different colors
Grundy chromatic number of the complement of bipartite graphs
 Grundy chromatic number of the complement of bipartite graphs Manouchehr Zaker Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences P. O. BOX 45195-159 Zanjan, Iran E-mail: mzaker@iasbs.ac.ir Abstract A Grundy
Grundy chromatic number of the complement of bipartite graphs Manouchehr Zaker Institute for Advanced Studies in Basic Sciences P. O. BOX 45195-159 Zanjan, Iran E-mail: mzaker@iasbs.ac.ir Abstract A Grundy
Decision and approximation complexity for identifying codes and locating-dominating sets in restricted graph classes
 Decision and approximation complexity for identifying codes and locating-dominating sets in restricted graph classes Florent Foucaud a,b,c a Department of Mathematics, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg
Decision and approximation complexity for identifying codes and locating-dominating sets in restricted graph classes Florent Foucaud a,b,c a Department of Mathematics, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg
Chapter 8 DOMINATING SETS
 Chapter 8 DOMINATING SETS Distributed Computing Group Mobile Computing Summer 2004 Overview Motivation Dominating Set Connected Dominating Set The Greedy Algorithm The Tree Growing Algorithm The Marking
Chapter 8 DOMINATING SETS Distributed Computing Group Mobile Computing Summer 2004 Overview Motivation Dominating Set Connected Dominating Set The Greedy Algorithm The Tree Growing Algorithm The Marking
Localization of Sensor Networks Using Sweeps
 Localization of Sensor Networks Using Sweeps J. Fang Dept. of Electrical Engineering Yale University jia.fang@yale.edu M. Cao Dept. of Electrical Engineering Yale University m.cao@yale.edu A. S. Morse
Localization of Sensor Networks Using Sweeps J. Fang Dept. of Electrical Engineering Yale University jia.fang@yale.edu M. Cao Dept. of Electrical Engineering Yale University m.cao@yale.edu A. S. Morse
END-TERM EXAMINATION
 (Please Write your Exam Roll No. immediately) Exam. Roll No... END-TERM EXAMINATION Paper Code : MCA-205 DECEMBER 2006 Subject: Design and analysis of algorithm Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 60 Note: Attempt
(Please Write your Exam Roll No. immediately) Exam. Roll No... END-TERM EXAMINATION Paper Code : MCA-205 DECEMBER 2006 Subject: Design and analysis of algorithm Time: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 60 Note: Attempt
CS 580: Algorithm Design and Analysis. Jeremiah Blocki Purdue University Spring 2018
 CS 580: Algorithm Design and Analysis Jeremiah Blocki Purdue University Spring 2018 Chapter 11 Approximation Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright @ 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
CS 580: Algorithm Design and Analysis Jeremiah Blocki Purdue University Spring 2018 Chapter 11 Approximation Algorithms Slides by Kevin Wayne. Copyright @ 2005 Pearson-Addison Wesley. All rights reserved.
Part 3 - Changing Colors and Display Formats
 Part 3 - Changing Colors and Display Formats http://cbm.msoe.edu/newwebsite/learntomodel Introduction One of the most powerful features of Jmol is the ability to completely customize how your structure
Part 3 - Changing Colors and Display Formats http://cbm.msoe.edu/newwebsite/learntomodel Introduction One of the most powerful features of Jmol is the ability to completely customize how your structure
The External Network Problem
 The External Network Problem Jan van den Heuvel and Matthew Johnson CDAM Research Report LSE-CDAM-2004-15 December 2004 Abstract The connectivity of a communications network can often be enhanced if the
The External Network Problem Jan van den Heuvel and Matthew Johnson CDAM Research Report LSE-CDAM-2004-15 December 2004 Abstract The connectivity of a communications network can often be enhanced if the
Maximum Clique on Disks
 Maximum Clique on Disks Édouard Bonnet joint work with Panos Giannopoulos, Eun Jung Kim, Paweł Rzążewski, and Florian Sikora Middlesex University, London Séminaire équipe Optimisation Combinatoire, G-SCOP,
Maximum Clique on Disks Édouard Bonnet joint work with Panos Giannopoulos, Eun Jung Kim, Paweł Rzążewski, and Florian Sikora Middlesex University, London Séminaire équipe Optimisation Combinatoire, G-SCOP,
γ 2 γ 3 γ 1 R 2 (b) a bounded Yin set (a) an unbounded Yin set
 γ 1 γ 3 γ γ 3 γ γ 1 R (a) an unbounded Yin set (b) a bounded Yin set Fig..1: Jordan curve representation of a connected Yin set M R. A shaded region represents M and the dashed curves its boundary M that
γ 1 γ 3 γ γ 3 γ γ 1 R (a) an unbounded Yin set (b) a bounded Yin set Fig..1: Jordan curve representation of a connected Yin set M R. A shaded region represents M and the dashed curves its boundary M that
Alpha-Beta Community
 Alpha-Beta Community Supasorn Suwajanakorn March 15, 2010 Supasorn Suwajanakorn () Alpha-Beta Community March 15, 2010 1 / 19 Definition from Nina s paper Definition 1. Given a graph G = (V, E), where
Alpha-Beta Community Supasorn Suwajanakorn March 15, 2010 Supasorn Suwajanakorn () Alpha-Beta Community March 15, 2010 1 / 19 Definition from Nina s paper Definition 1. Given a graph G = (V, E), where
Graph Theory. Probabilistic Graphical Models. L. Enrique Sucar, INAOE. Definitions. Types of Graphs. Trajectories and Circuits.
 Theory Probabilistic ical Models L. Enrique Sucar, INAOE and (INAOE) 1 / 32 Outline and 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 and 9 (INAOE) 2 / 32 A graph provides a compact way to represent binary relations between a set of
Theory Probabilistic ical Models L. Enrique Sucar, INAOE and (INAOE) 1 / 32 Outline and 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 and 9 (INAOE) 2 / 32 A graph provides a compact way to represent binary relations between a set of
Chapter 8 DOMINATING SETS
 Distributed Computing Group Chapter 8 DOMINATING SETS Mobile Computing Summer 2004 Overview Motivation Dominating Set Connected Dominating Set The Greedy Algorithm The Tree Growing Algorithm The Marking
Distributed Computing Group Chapter 8 DOMINATING SETS Mobile Computing Summer 2004 Overview Motivation Dominating Set Connected Dominating Set The Greedy Algorithm The Tree Growing Algorithm The Marking
Conformations of Proteins on Lattice Models. Jiangbo Miao Natalie Kantz
 Conformations of Proteins on Lattice Models Jiangbo Miao Natalie Kantz Lattice Model The lattice model offers a discrete space that limits the infinite number of protein conformations to the lattice space.
Conformations of Proteins on Lattice Models Jiangbo Miao Natalie Kantz Lattice Model The lattice model offers a discrete space that limits the infinite number of protein conformations to the lattice space.
Ray shooting from convex ranges
 Discrete Applied Mathematics 108 (2001) 259 267 Ray shooting from convex ranges Evangelos Kranakis a, Danny Krizanc b, Anil Maheshwari a;, Jorg-Rudiger Sack a, Jorge Urrutia c a School of Computer Science,
Discrete Applied Mathematics 108 (2001) 259 267 Ray shooting from convex ranges Evangelos Kranakis a, Danny Krizanc b, Anil Maheshwari a;, Jorg-Rudiger Sack a, Jorge Urrutia c a School of Computer Science,
The complement of PATH is in NL
 340 The complement of PATH is in NL Let c be the number of nodes in graph G that are reachable from s We assume that c is provided as an input to M Given G, s, t, and c the machine M operates as follows:
340 The complement of PATH is in NL Let c be the number of nodes in graph G that are reachable from s We assume that c is provided as an input to M Given G, s, t, and c the machine M operates as follows:
Computer Vision Group Prof. Daniel Cremers. 4. Probabilistic Graphical Models Directed Models
 Prof. Daniel Cremers 4. Probabilistic Graphical Models Directed Models The Bayes Filter (Rep.) (Bayes) (Markov) (Tot. prob.) (Markov) (Markov) 2 Graphical Representation (Rep.) We can describe the overall
Prof. Daniel Cremers 4. Probabilistic Graphical Models Directed Models The Bayes Filter (Rep.) (Bayes) (Markov) (Tot. prob.) (Markov) (Markov) 2 Graphical Representation (Rep.) We can describe the overall
Introduction to Algorithms
 Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401J Lecture 24 Prof. Piotr Indyk Dealing with Hard Problems What to do if: Divide and conquer Dynamic programming Greedy Linear Programming/Network Flows does not
Introduction to Algorithms 6.046J/18.401J Lecture 24 Prof. Piotr Indyk Dealing with Hard Problems What to do if: Divide and conquer Dynamic programming Greedy Linear Programming/Network Flows does not
Greencastle-Antrim School District Planned Course Board Approved: March 2010
 Greencastle-Antrim School District Planned Course Board Approved: March 2010 Course Title: Pre-Algebra Grade Levels: 7 and 8 Course materials: Textbooks,, Teacher-Generated Materials, Computer Programs
Greencastle-Antrim School District Planned Course Board Approved: March 2010 Course Title: Pre-Algebra Grade Levels: 7 and 8 Course materials: Textbooks,, Teacher-Generated Materials, Computer Programs
Example of a Demonstration that a Problem is NP-Complete by reduction from CNF-SAT
 20170926 CNF-SAT: CNF-SAT is a problem in NP, defined as follows: Let E be a Boolean expression with m clauses and n literals (literals = variables, possibly negated), in which - each clause contains only
20170926 CNF-SAT: CNF-SAT is a problem in NP, defined as follows: Let E be a Boolean expression with m clauses and n literals (literals = variables, possibly negated), in which - each clause contains only
Simplicial Complexes of Networks and Their Statistical Properties
 Simplicial Complexes of Networks and Their Statistical Properties Slobodan Maletić, Milan Rajković*, and Danijela Vasiljević Institute of Nuclear Sciences Vinča, elgrade, Serbia *milanr@vin.bg.ac.yu bstract.
Simplicial Complexes of Networks and Their Statistical Properties Slobodan Maletić, Milan Rajković*, and Danijela Vasiljević Institute of Nuclear Sciences Vinča, elgrade, Serbia *milanr@vin.bg.ac.yu bstract.
Predicting Protein Folding Paths. S.Will, , Fall 2011
 Predicting Protein Folding Paths Protein Folding by Robotics Probabilistic Roadmap Planning (PRM): Thomas, Song, Amato. Protein folding by motion planning. Phys. Biol., 2005 Aims Find good quality folding
Predicting Protein Folding Paths Protein Folding by Robotics Probabilistic Roadmap Planning (PRM): Thomas, Song, Amato. Protein folding by motion planning. Phys. Biol., 2005 Aims Find good quality folding
Maximum Clique Problem. Team Bushido bit.ly/parallel-computing-fall-2014
 Maximum Clique Problem Team Bushido bit.ly/parallel-computing-fall-2014 Agenda Problem summary Research Paper 1 Research Paper 2 Research Paper 3 Software Design Demo of Sequential Program Summary Of the
Maximum Clique Problem Team Bushido bit.ly/parallel-computing-fall-2014 Agenda Problem summary Research Paper 1 Research Paper 2 Research Paper 3 Software Design Demo of Sequential Program Summary Of the
Best known solution time is Ω(V!) Check every permutation of vertices to see if there is a graph edge between adjacent vertices
 Hard Problems Euler-Tour Problem Undirected graph G=(V,E) An Euler Tour is a path where every edge appears exactly once. The Euler-Tour Problem: does graph G have an Euler Path? Answerable in O(E) time.
Hard Problems Euler-Tour Problem Undirected graph G=(V,E) An Euler Tour is a path where every edge appears exactly once. The Euler-Tour Problem: does graph G have an Euler Path? Answerable in O(E) time.
Some Open Problems in Graph Theory and Computational Geometry
 Some Open Problems in Graph Theory and Computational Geometry David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine Dept. of Information and Computer Science ICS 269, January 25, 2002 Two Models of Algorithms Research
Some Open Problems in Graph Theory and Computational Geometry David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine Dept. of Information and Computer Science ICS 269, January 25, 2002 Two Models of Algorithms Research
And Now From a New Angle Special Angles and Postulates LEARNING GOALS
 And Now From a New Angle Special Angles and Postulates LEARNING GOALS KEY TERMS. In this lesson, you will: Calculate the complement and supplement of an angle. Classify adjacent angles, linear pairs, and
And Now From a New Angle Special Angles and Postulates LEARNING GOALS KEY TERMS. In this lesson, you will: Calculate the complement and supplement of an angle. Classify adjacent angles, linear pairs, and
Flattening Fixed-Angle Chains Is Strongly NP-Hard
 Flattening Fixed-Angle Chains Is Strongly NP-Hard Erik D. Demaine and Sarah Eisenstat MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, 32 Vassar St., Cambridge, MA 02139, USA {edemaine,seisenst}@mit.edu
Flattening Fixed-Angle Chains Is Strongly NP-Hard Erik D. Demaine and Sarah Eisenstat MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, 32 Vassar St., Cambridge, MA 02139, USA {edemaine,seisenst}@mit.edu
This theorem concerned a spherical gradient index in which the refractive density of a medium
 APPENDIX Theorem 461 This theorem concerned a spherical gradient index in which the refractive density of a medium varied with a given power, q, of the distance, x, from a point, P. Young was more interested
APPENDIX Theorem 461 This theorem concerned a spherical gradient index in which the refractive density of a medium varied with a given power, q, of the distance, x, from a point, P. Young was more interested
Linear Programming. Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015
 Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Linear Programming 2015 Goodrich and Tamassia 1 Formulating the Problem q The function
Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Linear Programming 2015 Goodrich and Tamassia 1 Formulating the Problem q The function
