AREPO: a moving-mesh code for cosmological hydrodynamical simulations
|
|
|
- Dwain Stanley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AREPO: a moving-mesh code for cosmological hydrodynamical simulations E pur si muove: Galiliean-invariant cosmological hydrodynamical simulations on a moving mesh Springel, 2010 arxiv: Rubens Machado Seminário de Extragaláctica - IAG 27/10/2011
2 and some of its recent results Moving mesh cosmology: numerical techniques and global statistics (Vogelsberger et al, 2011) arxiv: Moving mesh cosmology: the hydrodynamics of galaxy formation (Sijacki et al, 2011) arxiv: Moving mesh cosmology: characteristics of galaxies and haloes (Keres et al, 2011) arxiv:
3 collisionless simulations (only dark matter) N-body problem is well understood there is little doubt about what is required to achieve high accuracy hydrodynamical simulations variety of fundamentally different numerical methods in use most prominent: - Lagrangian (particles) - Eulerian (mesh) both have problems that make them innacurate in certain regimes
4 slide from Springel, 2006
5 slide from Springel, 2006
6 mesh SPH self-gravity needs to be done on a mesh SPH smooths out sharp shocks and contact discontinuities
7 discrete distribution of particles
8 discrete distribution of particles What is the density at any given location? +
9 Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) + kernel interpolation to build continuous fluid quantities from discrete tracer particles
10 Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) + kernel interpolation to build continuous fluid quantities from discrete tracer particles
11 Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR)
12 Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) RAMSES, Teyssier 2010 large dynamical range of cosmological simulations: dense regions require high resolution; low resolution for empty regions
13 AREPO: based on a moving unstructured mesh mesh defined by Voronoi tesselation of a set of discrete points grid-generating points move with the flow inherits main advantages - from SPH: resolution follows density automatically and continuously - from Eulerian codes: finite volume discretization gives accurate treatment of instabilities avoids main problems - from SPH: noise and diffusiveness - from Eulerian: lack of Galilean-invariance
14 Tesselation the careful juxtaposition of shapes in a mosaic pattern no overlaps, no gaps
15 Tesselation the careful juxtaposition of shapes in a mosaic pattern no overlaps, no gaps
16 Delaunay Tesselation triangulation of the plane grid-generating points: vertices of triangles maximizes smallest angle within each circumference: no other points
17 Delaunay Tesselation connecting the centers: centers of circumferences Voronoi Tesselation The centers of the circumcircles around each Delaunay triangle define the vertices of the Voronoi cells.
18 Voronoi Tesselation Voronoi mesh-generating points Delaunay both
19 at each timestep: - calculate a new Voronoi tesselation, based on current coordinates of mesh-generating points - calculate (density, velocity, pressure) in each cell - assign velocities to the mesh-generating points - compute flux across each Voronoi cell - update quantities for this timestep - move mesh-generating points
20 Mesh regularization for computational efficiency, regions of similar gas properties should be represented by cells of comparable size desirable to have cells where center-of-mass is close to its mesh-generating point
21 Mesh regularization Adaptive mesh refinement no longer necessary: The resolution automatically stays where it is needed
22 Self-gravity in cosmological simulations, dark matter structures grow from very small seed perturbations in AMR codes, grid refinement may be placed too late
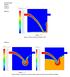
23 Some test problems: Kevin-Helmholtz instability
24 Some test problems: Kevin-Helmholtz instability AREPO moving AREPO fixed ATHENA (in the non-linear regime, KH instability seems to develop faster with AREPO moving mesh)
25 Some test problems: Kevin-Helmholtz instability AREPO fixed = ATHENA Frame of reference velocity: v =1 AREPO fixed = ATHENA AREPO fixed = ATHENA V = 10 with AREPO moving, result is independent of frame-of-reference v = 100
26 Some test problems: isolated disk galaxy
27 Some test problems: galaxy collision initial conditions
28 Some test problems: galaxy collision AMR not well suited for this problem (high resolution regions moving; no Galilean invariance)
29 Some test problems: galaxy collision stars gas AREPO GADGET2
30 Paralelization of the tesselation: Point set is decomposed into disjoint spacial domains, each mapped to a different compute core with its own physical memory... Speed: 2x slower than SPH at same resolution 3-4x slower than Eulerian fixed mesh (polyhedra with more than 6 faces) once self-gravity is included: performance difference less important AREPO reaches good accuracy in test problems at lower resolution than SPH and fixed mesh
31 - first hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy formation using AREPO - comparison with GADGET (same gravity solver, same star formation treatment) - overall distribution of gas temperature and density broadly in agreement - SFR at high z in good agreement global baryon statistics with AREPO: - lower mean temperatures - reduced amount of hot gas - more gas cooling at low z - higher star formation rates in late times
32
33 Gas density
34 Code performance AREPO GADGET
35 - variety of numerical experiments to establish link between simple problems with analytic solutions and systematic effects in cosmological simulations of galaxy formation - With AREPO, gas from infalling substructures is readily depleted and incorporated into the host halo atmosphere, facilitating the formation of an extended central disk. - With GADGET, gaseous subclumps are more coherent, transforming the central disk as they impact it.
36 gas density 1014 Mo isolated halo + 10 orbiting subhalos
37
38 AREPO: Moving Mesh Cosmology:
39 "Sator Arepo Tenet Opera Rotas"
Tessellating the Universe: Cosmic Structure Formation on a Moving Mesh
 Tessellating the Universe: Cosmic Structure Formation on a Moving Mesh Volker Springel Introduction: Hydrodynamical simulations in cosmology A finite-volume scheme on a moving mesh Algorithmic aspects
Tessellating the Universe: Cosmic Structure Formation on a Moving Mesh Volker Springel Introduction: Hydrodynamical simulations in cosmology A finite-volume scheme on a moving mesh Algorithmic aspects
Numerical Methods. (Additional Notes from Talks by PFH)
 Numerical Methods (Additional Notes from Talks by PFH) SPH Challenge: POPULAR METHODS FOR HYDRODYNAMICS HAVE PROBLEMS Lucy 77, Gingold & Monaghan 77 Reviews by: Springel 11, Price 12 Smoothed-Particle
Numerical Methods (Additional Notes from Talks by PFH) SPH Challenge: POPULAR METHODS FOR HYDRODYNAMICS HAVE PROBLEMS Lucy 77, Gingold & Monaghan 77 Reviews by: Springel 11, Price 12 Smoothed-Particle
The Swift simulation code
 The Swift simulation code ICC, Durham! : Intro to SPH Bert VandenBroucke: GIZMO Pedro Gonnet: Task-based parallelism Matthieu Schaller: Swift 1 Cosmological hydrodynamical simulations Eagle in Durham 2
The Swift simulation code ICC, Durham! : Intro to SPH Bert VandenBroucke: GIZMO Pedro Gonnet: Task-based parallelism Matthieu Schaller: Swift 1 Cosmological hydrodynamical simulations Eagle in Durham 2
PiTP Summer School 2009
 PiTP Summer School 2009 Plan for my lectures Volker Springel Lecture 1 Basics of collisionless dynamics and the N-body approach Lecture 2 Gravitational solvers suitable for collisionless dynamics, parallelization
PiTP Summer School 2009 Plan for my lectures Volker Springel Lecture 1 Basics of collisionless dynamics and the N-body approach Lecture 2 Gravitational solvers suitable for collisionless dynamics, parallelization
Using GADGET-2 for cosmological simulations - Background -
 Using GADGET-2 for cosmological simulations - Background - 3 Phases of Running a Cosmological Simulation I. Generate Initial Conditions II. Run Simulation Performing a numerical integral III.Analysis Halo
Using GADGET-2 for cosmological simulations - Background - 3 Phases of Running a Cosmological Simulation I. Generate Initial Conditions II. Run Simulation Performing a numerical integral III.Analysis Halo
Lagrangian methods and Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) Computation in Astrophysics Seminar (Spring 2006) L. J. Dursi
 Lagrangian methods and Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) Eulerian Grid Methods The methods covered so far in this course use an Eulerian grid: Prescribed coordinates In `lab frame' Fluid elements flow
Lagrangian methods and Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) Eulerian Grid Methods The methods covered so far in this course use an Eulerian grid: Prescribed coordinates In `lab frame' Fluid elements flow
UCDs for simulations
 UCDs for simulations Laurie D Shaw and Nicholas A Walton June 2004 1 Introduction This is a brief document outlining some of the UCDs that would be required to describe a simulation dataset. It is based
UCDs for simulations Laurie D Shaw and Nicholas A Walton June 2004 1 Introduction This is a brief document outlining some of the UCDs that would be required to describe a simulation dataset. It is based
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.im] 24 Jul 2013
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.im] 24 Jul 2013 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.im] 24 Jul 2013](/thumbs/82/84766851.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 25 July 203 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:305.295v2 [astro-ph.im] 24 Jul 203 Following the flow: tracer particles in astrophysical fluid simulations
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 25 July 203 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:305.295v2 [astro-ph.im] 24 Jul 203 Following the flow: tracer particles in astrophysical fluid simulations
Fault tolerant issues in large scale applications
 Fault tolerant issues in large scale applications Romain Teyssier George Lake, Ben Moore, Joachim Stadel and the other members of the project «Cosmology at the petascale» SPEEDUP 2010 1 Outline Computational
Fault tolerant issues in large scale applications Romain Teyssier George Lake, Ben Moore, Joachim Stadel and the other members of the project «Cosmology at the petascale» SPEEDUP 2010 1 Outline Computational
Adaptive-Mesh-Refinement Hydrodynamic GPU Computation in Astrophysics
 Adaptive-Mesh-Refinement Hydrodynamic GPU Computation in Astrophysics H. Y. Schive ( 薛熙于 ) Graduate Institute of Physics, National Taiwan University Leung Center for Cosmology and Particle Astrophysics
Adaptive-Mesh-Refinement Hydrodynamic GPU Computation in Astrophysics H. Y. Schive ( 薛熙于 ) Graduate Institute of Physics, National Taiwan University Leung Center for Cosmology and Particle Astrophysics
Lecture 2 Unstructured Mesh Generation
 Lecture 2 Unstructured Mesh Generation MIT 16.930 Advanced Topics in Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations Per-Olof Persson (persson@mit.edu) February 13, 2006 1 Mesh Generation Given a
Lecture 2 Unstructured Mesh Generation MIT 16.930 Advanced Topics in Numerical Methods for Partial Differential Equations Per-Olof Persson (persson@mit.edu) February 13, 2006 1 Mesh Generation Given a
C. A. D. Fraga Filho 1,2, D. F. Pezzin 1 & J. T. A. Chacaltana 1. Abstract
 Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XIII 15 A numerical study of heat diffusion using the Lagrangian particle SPH method and the Eulerian Finite-Volume method: analysis of convergence,
Advanced Computational Methods and Experiments in Heat Transfer XIII 15 A numerical study of heat diffusion using the Lagrangian particle SPH method and the Eulerian Finite-Volume method: analysis of convergence,
RAMSES on the GPU: An OpenACC-Based Approach
 RAMSES on the GPU: An OpenACC-Based Approach Claudio Gheller (ETHZ-CSCS) Giacomo Rosilho de Souza (EPFL Lausanne) Romain Teyssier (University of Zurich) Markus Wetzstein (ETHZ-CSCS) PRACE-2IP project EU
RAMSES on the GPU: An OpenACC-Based Approach Claudio Gheller (ETHZ-CSCS) Giacomo Rosilho de Souza (EPFL Lausanne) Romain Teyssier (University of Zurich) Markus Wetzstein (ETHZ-CSCS) PRACE-2IP project EU
Example 13 - Shock Tube
 Example 13 - Shock Tube Summary This famous experiment is interesting for observing the shock-wave propagation. Moreover, this case uses the representation of perfect gas and compares the different formulations:
Example 13 - Shock Tube Summary This famous experiment is interesting for observing the shock-wave propagation. Moreover, this case uses the representation of perfect gas and compares the different formulations:
Particle-based simulations in Astrophysics
 Particle-based simulations in Astrophysics Jun Makino Particle Simulator Research Team, AICS/ Earth-Life Science Institute(ELSI), Tokyo Institute of Technology Feb 28, 2013 3rd AICS International Symposium
Particle-based simulations in Astrophysics Jun Makino Particle Simulator Research Team, AICS/ Earth-Life Science Institute(ELSI), Tokyo Institute of Technology Feb 28, 2013 3rd AICS International Symposium
Computational Eulerian Hydrodynamics and Galilean Invariance
 SLAC-PUB-15677 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 (2009) Printed 16 October 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Computational Eulerian Hydrodynamics and Galilean Invariance Brant E. Robertson, 1,2 Andrey
SLAC-PUB-15677 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 16 (2009) Printed 16 October 2009 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Computational Eulerian Hydrodynamics and Galilean Invariance Brant E. Robertson, 1,2 Andrey
Shape of Things to Come: Next-Gen Physics Deep Dive
 Shape of Things to Come: Next-Gen Physics Deep Dive Jean Pierre Bordes NVIDIA Corporation Free PhysX on CUDA PhysX by NVIDIA since March 2008 PhysX on CUDA available: August 2008 GPU PhysX in Games Physical
Shape of Things to Come: Next-Gen Physics Deep Dive Jean Pierre Bordes NVIDIA Corporation Free PhysX on CUDA PhysX by NVIDIA since March 2008 PhysX on CUDA available: August 2008 GPU PhysX in Games Physical
14 Dec 94. Hydrocode Micro-Model Concept for Multi-Component Flow in Sediments Hans U. Mair
 Hydrocode Micro-Model Concept for Multi-Component Flow in Sediments Hans U. Mair mairh@asme.org Background Hydrocodes are Computational Mechanics tools that simulate the compressible dynamics (i.e., shock
Hydrocode Micro-Model Concept for Multi-Component Flow in Sediments Hans U. Mair mairh@asme.org Background Hydrocodes are Computational Mechanics tools that simulate the compressible dynamics (i.e., shock
Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing. David Eppstein
 Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science (including joint work with Marshall Bern from WADS 01 and SODA 03) Outline
Möbius Transformations in Scientific Computing David Eppstein Univ. of California, Irvine School of Information and Computer Science (including joint work with Marshall Bern from WADS 01 and SODA 03) Outline
Air Movement. Air Movement
 2018 Air Movement In this tutorial you will create an air flow using a supply vent on one side of a room and an open vent on the opposite side. This is a very simple PyroSim/FDS simulation, but illustrates
2018 Air Movement In this tutorial you will create an air flow using a supply vent on one side of a room and an open vent on the opposite side. This is a very simple PyroSim/FDS simulation, but illustrates
Cosmology Simulations with Enzo
 Cosmology Simulations with Enzo John Wise (Georgia Tech) Enzo Workshop 17 Oct 2013 Outline Introduction to unigrid cosmology simulations Introduction to nested grid cosmology simulations Using different
Cosmology Simulations with Enzo John Wise (Georgia Tech) Enzo Workshop 17 Oct 2013 Outline Introduction to unigrid cosmology simulations Introduction to nested grid cosmology simulations Using different
Reducing noise in moving-grid codes with stronglycentroidal Lloyd mesh regularization
 Reducing noise in moving-grid codes with stronglycentroidal Lloyd mesh regularization The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Reducing noise in moving-grid codes with stronglycentroidal Lloyd mesh regularization The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
FINITE ELEMENT MODELING OF THICK PLATE PENETRATIONS IN SMALL CAL MUNITIONS
 FINITE ELEMENT MODELING OF THICK PLATE PENETRATIONS IN SMALL CAL MUNITIONS Raymond Chaplin RDAR-MEM-I Picatinny Arsenal, NJ raymond.c.chaplin@us.army.mil 973-724-8562 Why Finite Element Modeling? Reduced
FINITE ELEMENT MODELING OF THICK PLATE PENETRATIONS IN SMALL CAL MUNITIONS Raymond Chaplin RDAR-MEM-I Picatinny Arsenal, NJ raymond.c.chaplin@us.army.mil 973-724-8562 Why Finite Element Modeling? Reduced
The (fine-grained) phase-space structure of Cold Dark Matter Halos - and its influence on dark matter searches Mak Vogelsberger, Harvard/CfA
 The (fine-grained) phase-space structure of Cold Dark Matter Halos - and its influence on dark matter searches Mak Vogelsberger, Harvard/CfA The content of the Universe Zwicky Evidence Existence: WIMP,
The (fine-grained) phase-space structure of Cold Dark Matter Halos - and its influence on dark matter searches Mak Vogelsberger, Harvard/CfA The content of the Universe Zwicky Evidence Existence: WIMP,
Fluid Simulation. [Thürey 10] [Pfaff 10] [Chentanez 11]
![Fluid Simulation. [Thürey 10] [Pfaff 10] [Chentanez 11] Fluid Simulation. [Thürey 10] [Pfaff 10] [Chentanez 11]](/thumbs/72/66717659.jpg) Fluid Simulation [Thürey 10] [Pfaff 10] [Chentanez 11] 1 Computational Fluid Dynamics 3 Graphics Why don t we just take existing models from CFD for Computer Graphics applications? 4 Graphics Why don t
Fluid Simulation [Thürey 10] [Pfaff 10] [Chentanez 11] 1 Computational Fluid Dynamics 3 Graphics Why don t we just take existing models from CFD for Computer Graphics applications? 4 Graphics Why don t
Adaptive Mesh Refinement
 Aleander Knebe, Universidad Autonoma de Madrid Adaptive Mesh Refinement AMR codes Poisson s equation ΔΦ( ) = 4πGρ( ) Poisson s equation F ( ) = m Φ( ) ΔΦ( ) = 4πGρ( ) particle approach F ( Gm i ) = i m
Aleander Knebe, Universidad Autonoma de Madrid Adaptive Mesh Refinement AMR codes Poisson s equation ΔΦ( ) = 4πGρ( ) Poisson s equation F ( ) = m Φ( ) ΔΦ( ) = 4πGρ( ) particle approach F ( Gm i ) = i m
ALE and AMR Mesh Refinement Techniques for Multi-material Hydrodynamics Problems
 ALE and AMR Mesh Refinement Techniques for Multi-material Hydrodynamics Problems A. J. Barlow, AWE. ICFD Workshop on Mesh Refinement Techniques 7th December 2005 Acknowledgements Thanks to Chris Powell,
ALE and AMR Mesh Refinement Techniques for Multi-material Hydrodynamics Problems A. J. Barlow, AWE. ICFD Workshop on Mesh Refinement Techniques 7th December 2005 Acknowledgements Thanks to Chris Powell,
1 Exercise: Heat equation in 2-D with FE
 1 Exercise: Heat equation in 2-D with FE Reading Hughes (2000, sec. 2.3-2.6 Dabrowski et al. (2008, sec. 1-3, 4.1.1, 4.1.3, 4.2.1 This FE exercise and most of the following ones are based on the MILAMIN
1 Exercise: Heat equation in 2-D with FE Reading Hughes (2000, sec. 2.3-2.6 Dabrowski et al. (2008, sec. 1-3, 4.1.1, 4.1.3, 4.2.1 This FE exercise and most of the following ones are based on the MILAMIN
Realtime Water Simulation on GPU. Nuttapong Chentanez NVIDIA Research
 1 Realtime Water Simulation on GPU Nuttapong Chentanez NVIDIA Research 2 3 Overview Approaches to realtime water simulation Hybrid shallow water solver + particles Hybrid 3D tall cell water solver + particles
1 Realtime Water Simulation on GPU Nuttapong Chentanez NVIDIA Research 2 3 Overview Approaches to realtime water simulation Hybrid shallow water solver + particles Hybrid 3D tall cell water solver + particles
PHYSICALLY BASED ANIMATION
 PHYSICALLY BASED ANIMATION CS148 Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging David Hyde August 2 nd, 2016 WHAT IS PHYSICS? the study of everything? WHAT IS COMPUTATION? the study of everything? OUTLINE
PHYSICALLY BASED ANIMATION CS148 Introduction to Computer Graphics and Imaging David Hyde August 2 nd, 2016 WHAT IS PHYSICS? the study of everything? WHAT IS COMPUTATION? the study of everything? OUTLINE
Acknowledgements. Prof. Dan Negrut Prof. Darryl Thelen Prof. Michael Zinn. SBEL Colleagues: Hammad Mazar, Toby Heyn, Manoj Kumar
 Philipp Hahn Acknowledgements Prof. Dan Negrut Prof. Darryl Thelen Prof. Michael Zinn SBEL Colleagues: Hammad Mazar, Toby Heyn, Manoj Kumar 2 Outline Motivation Lumped Mass Model Model properties Simulation
Philipp Hahn Acknowledgements Prof. Dan Negrut Prof. Darryl Thelen Prof. Michael Zinn SBEL Colleagues: Hammad Mazar, Toby Heyn, Manoj Kumar 2 Outline Motivation Lumped Mass Model Model properties Simulation
Fluid-structure Interaction by the mixed SPH-FE Method with Application to Aircraft Ditching
 Fluid-structure Interaction by the mixed SPH-FE Method with Application to Aircraft Ditching Paul Groenenboom ESI Group Delft, Netherlands Martin Siemann German Aerospace Center (DLR) Stuttgart, Germany
Fluid-structure Interaction by the mixed SPH-FE Method with Application to Aircraft Ditching Paul Groenenboom ESI Group Delft, Netherlands Martin Siemann German Aerospace Center (DLR) Stuttgart, Germany
Tracing the dark matter sheet in phase space
 Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 427, 61 76 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21754.x Tracing the dark matter sheet in phase space Tom Abel, Oliver Hahn and Ralf Kaehler Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 427, 61 76 (2012) doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2012.21754.x Tracing the dark matter sheet in phase space Tom Abel, Oliver Hahn and Ralf Kaehler Kavli Institute for Particle Astrophysics
Recent & Upcoming Features in STAR-CCM+ for Aerospace Applications Deryl Snyder, Ph.D.
 Recent & Upcoming Features in STAR-CCM+ for Aerospace Applications Deryl Snyder, Ph.D. Outline Introduction Aerospace Applications Summary New Capabilities for Aerospace Continuity Convergence Accelerator
Recent & Upcoming Features in STAR-CCM+ for Aerospace Applications Deryl Snyder, Ph.D. Outline Introduction Aerospace Applications Summary New Capabilities for Aerospace Continuity Convergence Accelerator
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 4 Apr 2012
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 4 Apr 2012 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 4 Apr 2012](/thumbs/75/71678094.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 5 April 2012 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Subsonic turbulence in smoothed particle hydrodynamics and moving-mesh simulations Andreas Bauer 1 and Volker
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 5 April 2012 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) Subsonic turbulence in smoothed particle hydrodynamics and moving-mesh simulations Andreas Bauer 1 and Volker
Solidification using Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics
 Solidification using Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Master Thesis CA-3817512 Game and Media Technology Utrecht University, The Netherlands Supervisors: dr. ir. J.Egges dr. N.G. Pronost July, 2014 - 2
Solidification using Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics Master Thesis CA-3817512 Game and Media Technology Utrecht University, The Netherlands Supervisors: dr. ir. J.Egges dr. N.G. Pronost July, 2014 - 2
2.7 Cloth Animation. Jacobs University Visualization and Computer Graphics Lab : Advanced Graphics - Chapter 2 123
 2.7 Cloth Animation 320491: Advanced Graphics - Chapter 2 123 Example: Cloth draping Image Michael Kass 320491: Advanced Graphics - Chapter 2 124 Cloth using mass-spring model Network of masses and springs
2.7 Cloth Animation 320491: Advanced Graphics - Chapter 2 123 Example: Cloth draping Image Michael Kass 320491: Advanced Graphics - Chapter 2 124 Cloth using mass-spring model Network of masses and springs
Module 4: Fluid Dynamics Lecture 9: Lagrangian and Eulerian approaches; Euler's acceleration formula. Fluid Dynamics: description of fluid-motion
 Fluid Dynamics: description of fluid-motion Lagrangian approach Eulerian approach (a field approach) file:///d /Web%20Course/Dr.%20Nishith%20Verma/local%20server/fluid_mechanics/lecture9/9_1.htm[5/9/2012
Fluid Dynamics: description of fluid-motion Lagrangian approach Eulerian approach (a field approach) file:///d /Web%20Course/Dr.%20Nishith%20Verma/local%20server/fluid_mechanics/lecture9/9_1.htm[5/9/2012
High performance computing and numerical modeling
 High performance computing and numerical modeling Volker Springel Plan for my lectures Lecture 1: Collisional and collisionless N-body dynamics Lecture 2: Gravitational force calculation Lecture 3: Basic
High performance computing and numerical modeling Volker Springel Plan for my lectures Lecture 1: Collisional and collisionless N-body dynamics Lecture 2: Gravitational force calculation Lecture 3: Basic
CGT 581 G Fluids. Overview. Some terms. Some terms
 CGT 581 G Fluids Bedřich Beneš, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Technology Overview Some terms Incompressible Navier-Stokes Boundary conditions Lagrange vs. Euler Eulerian approaches
CGT 581 G Fluids Bedřich Beneš, Ph.D. Purdue University Department of Computer Graphics Technology Overview Some terms Incompressible Navier-Stokes Boundary conditions Lagrange vs. Euler Eulerian approaches
GPU-Based Visualization of AMR and N-Body Dark Matter Simulation Data. Ralf Kähler (KIPAC/SLAC)
 GPU-Based Visualization of AMR and N-Body Dark Matter Simulation Data Ralf Kähler (KIPAC/SLAC) HiPACC-Meeting 03/21/2014 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Rasterization COMPUTER GRAPHICS Assumption (for now): Input object(s)
GPU-Based Visualization of AMR and N-Body Dark Matter Simulation Data Ralf Kähler (KIPAC/SLAC) HiPACC-Meeting 03/21/2014 COMPUTER GRAPHICS Rasterization COMPUTER GRAPHICS Assumption (for now): Input object(s)
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 16: Voronoi Diagrams and Tries. The Lecture Contains: Voronoi diagrams. Tries. Index structures
 The Lecture Contains: Voronoi diagrams Tries Delaunay triangulation Algorithms Extensions Index structures 1-dimensional index structures Memory-based index structures Disk-based index structures Classification
The Lecture Contains: Voronoi diagrams Tries Delaunay triangulation Algorithms Extensions Index structures 1-dimensional index structures Memory-based index structures Disk-based index structures Classification
Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics. D. Murrin
 Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics D. Murrin Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat transfer, mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena
Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics D. Murrin Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat transfer, mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena
Directions: 1) Delete this text box 2) Insert desired picture here
 Directions: 1) Delete this text box 2) Insert desired picture here Multi-Disciplinary Applications using Overset Grid Technology in STAR-CCM+ CD-adapco Dmitry Pinaev, Frank Schäfer, Eberhard Schreck Outline
Directions: 1) Delete this text box 2) Insert desired picture here Multi-Disciplinary Applications using Overset Grid Technology in STAR-CCM+ CD-adapco Dmitry Pinaev, Frank Schäfer, Eberhard Schreck Outline
SPH: Why and what for?
 SPH: Why and what for? 4 th SPHERIC training day David Le Touzé, Fluid Mechanics Laboratory, Ecole Centrale de Nantes / CNRS SPH What for and why? How it works? Why not for everything? Duality of SPH SPH
SPH: Why and what for? 4 th SPHERIC training day David Le Touzé, Fluid Mechanics Laboratory, Ecole Centrale de Nantes / CNRS SPH What for and why? How it works? Why not for everything? Duality of SPH SPH
Challenges and recent progress in developing numerical methods for multi-material ALE Hydrocodes
 Challenges and recent progress in developing numerical methods for multi-material ALE Hydrocodes ICFD 25 year Anniversary Conference 15-16 th September 2008 Oxford University Andrew Barlow AWE Introduction
Challenges and recent progress in developing numerical methods for multi-material ALE Hydrocodes ICFD 25 year Anniversary Conference 15-16 th September 2008 Oxford University Andrew Barlow AWE Introduction
1.6 Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH)
 26 Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics 1.6 Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) 1.6.1 The SPH method In the SPH method, the state of a system is represented by a set of particles, which possess individual
26 Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics 1.6 Smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) 1.6.1 The SPH method In the SPH method, the state of a system is represented by a set of particles, which possess individual
Tiling Three-Dimensional Space with Simplices. Shankar Krishnan AT&T Labs - Research
 Tiling Three-Dimensional Space with Simplices Shankar Krishnan AT&T Labs - Research What is a Tiling? Partition of an infinite space into pieces having a finite number of distinct shapes usually Euclidean
Tiling Three-Dimensional Space with Simplices Shankar Krishnan AT&T Labs - Research What is a Tiling? Partition of an infinite space into pieces having a finite number of distinct shapes usually Euclidean
Methods of Computational Astrophysics. Galaxy Simulation
 : Galaxy Simulation Department of Physics & Astronomy Outline N-body Methods The Problem Direct N-body Barnes-Hut Particle-Mesh Time Integration 1 N-body Methods The Problem Direct N-body Barnes-Hut Particle-Mesh
: Galaxy Simulation Department of Physics & Astronomy Outline N-body Methods The Problem Direct N-body Barnes-Hut Particle-Mesh Time Integration 1 N-body Methods The Problem Direct N-body Barnes-Hut Particle-Mesh
Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation
 Last Time? Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation Pop Worksheet! Teams of 2. Hand in to Jeramey after we discuss. Sketch the first few frames of a 2D explicit Euler mass-spring simulation for a 2x3 cloth network
Last Time? Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation Pop Worksheet! Teams of 2. Hand in to Jeramey after we discuss. Sketch the first few frames of a 2D explicit Euler mass-spring simulation for a 2x3 cloth network
Visualization Challenges for Large Scale Astrophysical Simulation Data. Ultrascale Visualization Workshop
 Visualization Challenges for Large Scale Astrophysical Simulation Data Ralf Kähler (KIPAC/SLAC) Tom Abel (KIPAC/Stanford) Marcelo Alvarez (CITA) Oliver Hahn (Stanford) Hans-Christian Hege (ZIB) Ji-hoon
Visualization Challenges for Large Scale Astrophysical Simulation Data Ralf Kähler (KIPAC/SLAC) Tom Abel (KIPAC/Stanford) Marcelo Alvarez (CITA) Oliver Hahn (Stanford) Hans-Christian Hege (ZIB) Ji-hoon
Support for Multi physics in Chrono
 Support for Multi physics in Chrono The Story Ahead Overview of multi physics strategy in Chrono Summary of handling rigid/flexible body dynamics using Lagrangian approach Summary of handling fluid, and
Support for Multi physics in Chrono The Story Ahead Overview of multi physics strategy in Chrono Summary of handling rigid/flexible body dynamics using Lagrangian approach Summary of handling fluid, and
NUMERICAL VISCOSITY. Convergent Science White Paper. COPYRIGHT 2017 CONVERGENT SCIENCE. All rights reserved.
 Convergent Science White Paper COPYRIGHT 2017 CONVERGENT SCIENCE. All rights reserved. This document contains information that is proprietary to Convergent Science. Public dissemination of this document
Convergent Science White Paper COPYRIGHT 2017 CONVERGENT SCIENCE. All rights reserved. This document contains information that is proprietary to Convergent Science. Public dissemination of this document
Enzo-P / Cello. Scalable Adaptive Mesh Refinement for Astrophysics and Cosmology. San Diego Supercomputer Center. Department of Physics and Astronomy
 Enzo-P / Cello Scalable Adaptive Mesh Refinement for Astrophysics and Cosmology James Bordner 1 Michael L. Norman 1 Brian O Shea 2 1 University of California, San Diego San Diego Supercomputer Center 2
Enzo-P / Cello Scalable Adaptive Mesh Refinement for Astrophysics and Cosmology James Bordner 1 Michael L. Norman 1 Brian O Shea 2 1 University of California, San Diego San Diego Supercomputer Center 2
arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 18 Mar 2016
![arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 18 Mar 2016 arxiv: v1 [physics.comp-ph] 18 Mar 2016](/thumbs/72/66524675.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 23 March 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:1603.06753v1 [physics.comp-ph] 18 Mar 2016 Grid Noise in Moving Mesh Codes: Fixing The Volume Inconsistency
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 000 000 (0000) Printed 23 March 2016 (MN LATEX style file v2.2) arxiv:1603.06753v1 [physics.comp-ph] 18 Mar 2016 Grid Noise in Moving Mesh Codes: Fixing The Volume Inconsistency
Validation of an Unstructured Overset Mesh Method for CFD Analysis of Store Separation D. Snyder presented by R. Fitzsimmons
 Validation of an Unstructured Overset Mesh Method for CFD Analysis of Store Separation D. Snyder presented by R. Fitzsimmons Stores Separation Introduction Flight Test Expensive, high-risk, sometimes catastrophic
Validation of an Unstructured Overset Mesh Method for CFD Analysis of Store Separation D. Snyder presented by R. Fitzsimmons Stores Separation Introduction Flight Test Expensive, high-risk, sometimes catastrophic
Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics Mech 122 D. Fabris, K. Lynch, D. Rich
 Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics Mech 122 D. Fabris, K. Lynch, D. Rich 1 Computational Fluid dynamics Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the analysis of systems involving fluid flow, heat
Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics Mech 122 D. Fabris, K. Lynch, D. Rich 1 Computational Fluid dynamics Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the analysis of systems involving fluid flow, heat
IMPROVED WALL BOUNDARY CONDITIONS WITH IMPLICITLY DEFINED WALLS FOR PARTICLE BASED FLUID SIMULATION
 6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 1115 June 2018, Glasgow, UK IMPROVED WALL BOUNDARY CONDITIONS WITH IMPLICITLY
6th European Conference on Computational Mechanics (ECCM 6) 7th European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics (ECFD 7) 1115 June 2018, Glasgow, UK IMPROVED WALL BOUNDARY CONDITIONS WITH IMPLICITLY
Sliding and multi-fluid velocities in Staggered Mesh Eulerian and MMALE codes
 Sliding and multi-fluid velocities in Staggered Mesh Eulerian and MMALE codes Gabi Luttwak 1 1 Rafael, P.O. Box 2250, Haifa 31021, Israel The Velocity in Eulerian and MMALE Codes Most Eulerian and MMALE
Sliding and multi-fluid velocities in Staggered Mesh Eulerian and MMALE codes Gabi Luttwak 1 1 Rafael, P.O. Box 2250, Haifa 31021, Israel The Velocity in Eulerian and MMALE Codes Most Eulerian and MMALE
Gadget in yt. christopher erick moody
 Gadget in yt First of all, hello, and thank you for giving me the opp to speak My name is chris moody and I m a grad student here at uc santa cruz and I ve been working with Joel for the last year and
Gadget in yt First of all, hello, and thank you for giving me the opp to speak My name is chris moody and I m a grad student here at uc santa cruz and I ve been working with Joel for the last year and
Fluent User Services Center
 Solver Settings 5-1 Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring Stability Accelerating Convergence Accuracy Grid Independence Adaption Appendix: Background Finite Volume
Solver Settings 5-1 Using the Solver Setting Solver Parameters Convergence Definition Monitoring Stability Accelerating Convergence Accuracy Grid Independence Adaption Appendix: Background Finite Volume
Topics in Computer Animation
 Topics in Computer Animation Animation Techniques Artist Driven animation The artist draws some frames (keyframing) Usually in 2D The computer generates intermediate frames using interpolation The old
Topics in Computer Animation Animation Techniques Artist Driven animation The artist draws some frames (keyframing) Usually in 2D The computer generates intermediate frames using interpolation The old
An Object-Oriented Serial and Parallel DSMC Simulation Package
 An Object-Oriented Serial and Parallel DSMC Simulation Package Hongli Liu and Chunpei Cai Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, New Mexico, 88, USA
An Object-Oriented Serial and Parallel DSMC Simulation Package Hongli Liu and Chunpei Cai Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, New Mexico State University, Las Cruces, New Mexico, 88, USA
arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Nov 2016
![arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Nov 2016 arxiv: v1 [astro-ph.ga] 8 Nov 2016](/thumbs/72/66524642.jpg) Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 9 (2016) Printed 10 November 2016 (MN LATE style file v2.2) Integer Lattice Dynamics for Vlasov-Poisson Philip Mocz 1 and Sauro Succi 2,3 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for
Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 000, 1 9 (2016) Printed 10 November 2016 (MN LATE style file v2.2) Integer Lattice Dynamics for Vlasov-Poisson Philip Mocz 1 and Sauro Succi 2,3 1 Harvard-Smithsonian Center for
The ICON project: Design and performance of an unstructured grid approach for a global triangular grid model
 The ICON project: Design and performance of an unstructured grid approach for a global triangular grid model Luis Kornblueh, Luca Bonaventura, and Peter Sanders,... ICON : ICOsahedral, Nonhdyrostatic model
The ICON project: Design and performance of an unstructured grid approach for a global triangular grid model Luis Kornblueh, Luca Bonaventura, and Peter Sanders,... ICON : ICOsahedral, Nonhdyrostatic model
Overview of Traditional Surface Tracking Methods
 Liquid Simulation With Mesh-Based Surface Tracking Overview of Traditional Surface Tracking Methods Matthias Müller Introduction Research lead of NVIDIA PhysX team PhysX GPU acc. Game physics engine www.nvidia.com\physx
Liquid Simulation With Mesh-Based Surface Tracking Overview of Traditional Surface Tracking Methods Matthias Müller Introduction Research lead of NVIDIA PhysX team PhysX GPU acc. Game physics engine www.nvidia.com\physx
Finite Volume Discretization on Irregular Voronoi Grids
 Finite Volume Discretization on Irregular Voronoi Grids C.Huettig 1, W. Moore 1 1 Hampton University / National Institute of Aerospace Folie 1 The earth and its terrestrial neighbors NASA Colin Rose, Dorling
Finite Volume Discretization on Irregular Voronoi Grids C.Huettig 1, W. Moore 1 1 Hampton University / National Institute of Aerospace Folie 1 The earth and its terrestrial neighbors NASA Colin Rose, Dorling
Michela Mapelli. N-body techniques for astrophysics: Lecture 6 GAS
 Michela Mapelli N-body techniques for astrophysics: Lecture 6 GAS PhD School in Astrophysics, University of Padova November 19-30, 2018 OUTLINE of this lecture: 1 Equations of gas 2 Mesh codes/ Adaptive
Michela Mapelli N-body techniques for astrophysics: Lecture 6 GAS PhD School in Astrophysics, University of Padova November 19-30, 2018 OUTLINE of this lecture: 1 Equations of gas 2 Mesh codes/ Adaptive
Particle-based Fluid Simulation
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Particle-based Fluid Simulation Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Application (with Pixar) 10 million fluid + 4 million rigid particles,
Simulation in Computer Graphics Particle-based Fluid Simulation Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Application (with Pixar) 10 million fluid + 4 million rigid particles,
J. Vira, M. Sofiev SILAM winter school, February 2013, FMI
 Numerical aspects of the advection-diffusion equation J. Vira, M. Sofiev SILAM winter school, February 2013, FMI Outline Intro Some common requirements for numerical transport schemes Lagrangian approach
Numerical aspects of the advection-diffusion equation J. Vira, M. Sofiev SILAM winter school, February 2013, FMI Outline Intro Some common requirements for numerical transport schemes Lagrangian approach
GAMER : a GPU-accelerated Adaptive-MEsh-Refinement Code for Astrophysics GPU 與自適性網格於天文模擬之應用與效能
 GAMER : a GPU-accelerated Adaptive-MEsh-Refinement Code for Astrophysics GPU 與自適性網格於天文模擬之應用與效能 Hsi-Yu Schive ( 薛熙于 ), Tzihong Chiueh ( 闕志鴻 ), Yu-Chih Tsai ( 蔡御之 ), Ui-Han Zhang ( 張瑋瀚 ) Graduate Institute
GAMER : a GPU-accelerated Adaptive-MEsh-Refinement Code for Astrophysics GPU 與自適性網格於天文模擬之應用與效能 Hsi-Yu Schive ( 薛熙于 ), Tzihong Chiueh ( 闕志鴻 ), Yu-Chih Tsai ( 蔡御之 ), Ui-Han Zhang ( 張瑋瀚 ) Graduate Institute
Erosion modeling to improve asset life prediction
 Erosion modeling to improve asset life prediction Erosion caused by solid particles in process flows impacting on the surfaces of downhole equipment or pipe walls is a common cause of damage and wear in
Erosion modeling to improve asset life prediction Erosion caused by solid particles in process flows impacting on the surfaces of downhole equipment or pipe walls is a common cause of damage and wear in
Smoke Simulation using Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) Shruti Jain MSc Computer Animation and Visual Eects Bournemouth University
 Smoke Simulation using Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) Shruti Jain MSc Computer Animation and Visual Eects Bournemouth University 21st November 2014 1 Abstract This report is based on the implementation
Smoke Simulation using Smoothed Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH) Shruti Jain MSc Computer Animation and Visual Eects Bournemouth University 21st November 2014 1 Abstract This report is based on the implementation
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING
 CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
Adaptive Mesh Astrophysical Fluid Simulations on GPU. San Jose 10/2/2009 Peng Wang, NVIDIA
 Adaptive Mesh Astrophysical Fluid Simulations on GPU San Jose 10/2/2009 Peng Wang, NVIDIA Overview Astrophysical motivation & the Enzo code Finite volume method and adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) CUDA
Adaptive Mesh Astrophysical Fluid Simulations on GPU San Jose 10/2/2009 Peng Wang, NVIDIA Overview Astrophysical motivation & the Enzo code Finite volume method and adaptive mesh refinement (AMR) CUDA
Solver Basics. Introductory FLUENT Training ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary
 Solver Basics Introductory FLUENT Training 2006 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 2006 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 3-2 Solver Execution The menus are arranged such that the order of operation is generally
Solver Basics Introductory FLUENT Training 2006 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 2006 ANSYS, Inc. All rights reserved. 3-2 Solver Execution The menus are arranged such that the order of operation is generally
Figure 2: Water Into Kerosene, Volume Fraction (Left) And Total Density Of Mixture (Right)
 Jared Bottlinger MAE598 Project 3 11/16/17 Task 1 a) Figure 1: Volume Fraction Of Water At 0.4s Task 1 b) Figure 2: Water Into Kerosene, Volume Fraction (Left) And Total Density Of Mixture (Right) Task
Jared Bottlinger MAE598 Project 3 11/16/17 Task 1 a) Figure 1: Volume Fraction Of Water At 0.4s Task 1 b) Figure 2: Water Into Kerosene, Volume Fraction (Left) And Total Density Of Mixture (Right) Task
FLUID FLOW TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION USING POLYGINAL ELEMENTS: STABILITY AND COMPUTATIONAL IMPLEMENTATION IN PolyTop
 FLUID FLOW TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION USING POLYGINAL ELEMENTS: STABILITY AND COMPUTATIONAL IMPLEMENTATION IN PolyTop Anderson Pereira (Tecgraf/PUC-Rio) Cameron Talischi (UIUC) - Ivan Menezes (PUC-Rio) - Glaucio
FLUID FLOW TOPOLOGY OPTIMIZATION USING POLYGINAL ELEMENTS: STABILITY AND COMPUTATIONAL IMPLEMENTATION IN PolyTop Anderson Pereira (Tecgraf/PUC-Rio) Cameron Talischi (UIUC) - Ivan Menezes (PUC-Rio) - Glaucio
Metafor FE Software. 2. Operator split. 4. Rezoning methods 5. Contact with friction
 ALE simulations ua sus using Metafor eao 1. Introduction 2. Operator split 3. Convection schemes 4. Rezoning methods 5. Contact with friction 1 Introduction EULERIAN FORMALISM Undistorted mesh Ideal for
ALE simulations ua sus using Metafor eao 1. Introduction 2. Operator split 3. Convection schemes 4. Rezoning methods 5. Contact with friction 1 Introduction EULERIAN FORMALISM Undistorted mesh Ideal for
Simulation in Computer Graphics. Introduction. Matthias Teschner. Computer Science Department University of Freiburg
 Simulation in Computer Graphics Introduction Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Contact Matthias Teschner Computer Graphics University of Freiburg Georges-Koehler-Allee
Simulation in Computer Graphics Introduction Matthias Teschner Computer Science Department University of Freiburg Contact Matthias Teschner Computer Graphics University of Freiburg Georges-Koehler-Allee
NVIDIA. Interacting with Particle Simulation in Maya using CUDA & Maximus. Wil Braithwaite NVIDIA Applied Engineering Digital Film
 NVIDIA Interacting with Particle Simulation in Maya using CUDA & Maximus Wil Braithwaite NVIDIA Applied Engineering Digital Film Some particle milestones FX Rendering Physics 1982 - First CG particle FX
NVIDIA Interacting with Particle Simulation in Maya using CUDA & Maximus Wil Braithwaite NVIDIA Applied Engineering Digital Film Some particle milestones FX Rendering Physics 1982 - First CG particle FX
Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation
 Last Time? Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation Optional Reading for Last Time: Spring-Mass Systems Numerical Integration (Euler, Midpoint, Runge-Kutta) Modeling string, hair, & cloth HW2: Cloth & Fluid Simulation
Last Time? Navier-Stokes & Flow Simulation Optional Reading for Last Time: Spring-Mass Systems Numerical Integration (Euler, Midpoint, Runge-Kutta) Modeling string, hair, & cloth HW2: Cloth & Fluid Simulation
Coupled Simulation of Flow and Body Motion Using Overset Grids. Eberhard Schreck & Milovan Perić
 Coupled Simulation of Flow and Body Motion Using Overset Grids Eberhard Schreck & Milovan Perić Contents Dynamic Fluid-Body Interaction (DFBI) model in STAR-CCM+ Overset grids method in STAR-CCM+ Advantages
Coupled Simulation of Flow and Body Motion Using Overset Grids Eberhard Schreck & Milovan Perić Contents Dynamic Fluid-Body Interaction (DFBI) model in STAR-CCM+ Overset grids method in STAR-CCM+ Advantages
Lattice Boltzmann with CUDA
 Lattice Boltzmann with CUDA Lan Shi, Li Yi & Liyuan Zhang Hauptseminar: Multicore Architectures and Programming Page 1 Outline Overview of LBM An usage of LBM Algorithm Implementation in CUDA and Optimization
Lattice Boltzmann with CUDA Lan Shi, Li Yi & Liyuan Zhang Hauptseminar: Multicore Architectures and Programming Page 1 Outline Overview of LBM An usage of LBM Algorithm Implementation in CUDA and Optimization
Computational Fluid Dynamic Hydraulic Characterization: G3 Cube vs. Dolos Armour Unit. IS le Roux, WJS van der Merwe & CL de Wet
 Computational Fluid Dynamic Hydraulic Characterization: G3 Cube vs. Dolos Armour Unit IS le Roux, WJS van der Merwe & CL de Wet Presentation Outline Scope. Assumptions and boundary values. Numerical mesh.
Computational Fluid Dynamic Hydraulic Characterization: G3 Cube vs. Dolos Armour Unit IS le Roux, WJS van der Merwe & CL de Wet Presentation Outline Scope. Assumptions and boundary values. Numerical mesh.
Verification and Validation in CFD and Heat Transfer: ANSYS Practice and the New ASME Standard
 Verification and Validation in CFD and Heat Transfer: ANSYS Practice and the New ASME Standard Dimitri P. Tselepidakis & Lewis Collins ASME 2012 Verification and Validation Symposium May 3 rd, 2012 1 Outline
Verification and Validation in CFD and Heat Transfer: ANSYS Practice and the New ASME Standard Dimitri P. Tselepidakis & Lewis Collins ASME 2012 Verification and Validation Symposium May 3 rd, 2012 1 Outline
Preliminary Spray Cooling Simulations Using a Full-Cone Water Spray
 39th Dayton-Cincinnati Aerospace Sciences Symposium Preliminary Spray Cooling Simulations Using a Full-Cone Water Spray Murat Dinc Prof. Donald D. Gray (advisor), Prof. John M. Kuhlman, Nicholas L. Hillen,
39th Dayton-Cincinnati Aerospace Sciences Symposium Preliminary Spray Cooling Simulations Using a Full-Cone Water Spray Murat Dinc Prof. Donald D. Gray (advisor), Prof. John M. Kuhlman, Nicholas L. Hillen,
Technical Report TR
 Technical Report TR-2015-09 Boundary condition enforcing methods for smoothed particle hydrodynamics Arman Pazouki 1, Baofang Song 2, Dan Negrut 1 1 University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, 53706-1572,
Technical Report TR-2015-09 Boundary condition enforcing methods for smoothed particle hydrodynamics Arman Pazouki 1, Baofang Song 2, Dan Negrut 1 1 University of Wisconsin-Madison, Madison, WI, 53706-1572,
Interactive Fluid Simulation using Augmented Reality Interface
 Interactive Fluid Simulation using Augmented Reality Interface Makoto Fuisawa 1, Hirokazu Kato 1 1 Graduate School of Information Science, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, 8916-5 Takayama, Ikoma,
Interactive Fluid Simulation using Augmented Reality Interface Makoto Fuisawa 1, Hirokazu Kato 1 1 Graduate School of Information Science, Nara Institute of Science and Technology, 8916-5 Takayama, Ikoma,
A brief description of the particle finite element method (PFEM2). Extensions to free surface
 A brief description of the particle finite element method (PFEM2). Extensions to free surface flows. Juan M. Gimenez, L.M. González, CIMEC Universidad Nacional del Litoral (UNL) Santa Fe, Argentina Universidad
A brief description of the particle finite element method (PFEM2). Extensions to free surface flows. Juan M. Gimenez, L.M. González, CIMEC Universidad Nacional del Litoral (UNL) Santa Fe, Argentina Universidad
DisPerSE: robust structure identification in 2D and 3D
 DisPerSE: robust structure identification in 2D and 3D Thierry Sousbie arxiv:1302.6221v1 [astro-ph.co] 25 Feb 2013 Abstract We present the DIScrete PERsistent Structures Extractor (DisPerSE), an open source
DisPerSE: robust structure identification in 2D and 3D Thierry Sousbie arxiv:1302.6221v1 [astro-ph.co] 25 Feb 2013 Abstract We present the DIScrete PERsistent Structures Extractor (DisPerSE), an open source
CFD Simulation of a dry Scroll Vacuum Pump including Leakage Flows
 CFD Simulation of a dry Scroll Vacuum Pump including Leakage Flows Jan Hesse, Rainer Andres CFX Berlin Software GmbH, Berlin, Germany 1 Introduction Numerical simulation results of a dry scroll vacuum
CFD Simulation of a dry Scroll Vacuum Pump including Leakage Flows Jan Hesse, Rainer Andres CFX Berlin Software GmbH, Berlin, Germany 1 Introduction Numerical simulation results of a dry scroll vacuum
Ocean Simulations using MPAS-Ocean
 Ocean Simulations using MPAS-Ocean Mark Petersen and the MPAS-Ocean development team Los Alamos National Laboratory U N C L A S S I F I E D Slide 1 Progress on MPAS-Ocean in 2010 MPAS-Ocean is a functioning
Ocean Simulations using MPAS-Ocean Mark Petersen and the MPAS-Ocean development team Los Alamos National Laboratory U N C L A S S I F I E D Slide 1 Progress on MPAS-Ocean in 2010 MPAS-Ocean is a functioning
Development of a Computational Framework for Block-Based AMR Simulations
 Procedia Computer Science Volume 29, 2014, Pages 2351 2359 ICCS 2014. 14th International Conference on Computational Science Development of a Computational Framework for Block-Based AMR Simulations Hideyuki
Procedia Computer Science Volume 29, 2014, Pages 2351 2359 ICCS 2014. 14th International Conference on Computational Science Development of a Computational Framework for Block-Based AMR Simulations Hideyuki
VoroCrust: Simultaneous Surface Reconstruction and Volume Meshing with Voronoi cells
 VoroCrust: Simultaneous Surface Reconstruction and Volume Meshing with Voronoi cells Scott A. Mitchell (speaker), joint work with Ahmed H. Mahmoud, Ahmad A. Rushdi, Scott A. Mitchell, Ahmad Abdelkader
VoroCrust: Simultaneous Surface Reconstruction and Volume Meshing with Voronoi cells Scott A. Mitchell (speaker), joint work with Ahmed H. Mahmoud, Ahmad A. Rushdi, Scott A. Mitchell, Ahmad Abdelkader
Part I: Theoretical Background and Integration-Based Methods
 Large Vector Field Visualization: Theory and Practice Part I: Theoretical Background and Integration-Based Methods Christoph Garth Overview Foundations Time-Varying Vector Fields Numerical Integration
Large Vector Field Visualization: Theory and Practice Part I: Theoretical Background and Integration-Based Methods Christoph Garth Overview Foundations Time-Varying Vector Fields Numerical Integration
arxiv: v2 [physics.comp-ph] 3 Sep 2014
![arxiv: v2 [physics.comp-ph] 3 Sep 2014 arxiv: v2 [physics.comp-ph] 3 Sep 2014](/thumbs/81/83613372.jpg) Diffusion-Based Coarse Graining in Hybrid Continuum Discrete Solvers: Applications in CFD DEM arxiv:1409.0022v2 [physics.comp-ph] 3 Sep 2014 Rui Sun, Heng Xiao Department of Aerospace and Ocean Engineering,
Diffusion-Based Coarse Graining in Hybrid Continuum Discrete Solvers: Applications in CFD DEM arxiv:1409.0022v2 [physics.comp-ph] 3 Sep 2014 Rui Sun, Heng Xiao Department of Aerospace and Ocean Engineering,
arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 22 Jul 2010
![arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 22 Jul 2010 arxiv: v2 [astro-ph.co] 22 Jul 2010](/thumbs/93/112837104.jpg) Merging and fragmentation in the Burgers dynamics Francis Bernardeau and Patrick Valageas Institut de Physique Théorique, CEA/DSM/IPhT, Unité de recherche associée au CNRS, CEA/Saclay, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette
Merging and fragmentation in the Burgers dynamics Francis Bernardeau and Patrick Valageas Institut de Physique Théorique, CEA/DSM/IPhT, Unité de recherche associée au CNRS, CEA/Saclay, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette
Constraint fluids in Sprinkle. Dennis Gustafsson Mediocre
 Constraint fluids in Sprinkle Dennis Gustafsson Mediocre Sprinkle. Sequel. Put out fires. Makeshift firetruck. Distant moon of Saturn. Fluid sim used at the core. Not only to put out fires -> move obstacles,
Constraint fluids in Sprinkle Dennis Gustafsson Mediocre Sprinkle. Sequel. Put out fires. Makeshift firetruck. Distant moon of Saturn. Fluid sim used at the core. Not only to put out fires -> move obstacles,
Numerical Methods for PDEs. SSC Workgroup Meetings Juan J. Alonso October 8, SSC Working Group Meetings, JJA 1
 Numerical Methods for PDEs SSC Workgroup Meetings Juan J. Alonso October 8, 2001 SSC Working Group Meetings, JJA 1 Overview These notes are meant to be an overview of the various memory access patterns
Numerical Methods for PDEs SSC Workgroup Meetings Juan J. Alonso October 8, 2001 SSC Working Group Meetings, JJA 1 Overview These notes are meant to be an overview of the various memory access patterns
