Parallel Techniques. Embarrassingly Parallel Computations. Partitioning and Divide-and-Conquer Strategies. Load Balancing and Termination Detection
|
|
|
- Roderick Hill
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Parallel Techniques Embarrassingly Parallel Computations Partitioning and Divide-and-Conquer Strategies Pipelined Computations Synchronous Computations Asynchronous Computations Load Balancing and Termination Detection 3.1
2 Chapter 3 Embarrassingly Parallel Computations 3.2
3 Embarrassingly Parallel Computations A computation that can obviously be divided into a number of completely independent parts, each of which can be executed by a separate process(or). No communication or very little communication between processes Each process can do its tasks without any interaction with other processes 3.3
4 Practical embarrassingly parallel computation with static process creation and master-slave approach 3.4
5 Practical embarrassingly parallel computation with dynamic process creation and master-slave approach 3.5
6 Embarrassingly Parallel Computation Examples Low level image processing Mandelbrot set Monte Carlo Calculations 3.6
7 Low level image processing Many low level image processing operations only involve local data with very limited if any communication between areas of interest. 3.7
8 Some geometrical operations Shifting Object shifted by x in the x-dimension and y in the y- dimension: x = x + x y = y + y where x and y are the original and x and y are the new coordinates. Scaling Object scaled by a factor S x in x-direction and S y in y- direction: x = xs x y = ys y 3.8
9 Rotation Object rotated through an angle q about the origin of the coordinate system: x = x cosθ + y sinθ y = -x sinθ + y cosθ 3.8
10 Partitioning into regions for individual processes Square region for each process (can also use strips) 3.9
11 Mandelbrot Set Set of points in a complex plane that are quasi-stable (will increase and decrease, but not exceed some limit) when computed by iterating the function where z k +1 is the (k + 1)th iteration of the complex number z = a + bi and c is a complex number giving position of point in the complex plane. The initial value for z is zero. Iterations continued until magnitude of z is greater than 2 or number of iterations reaches arbitrary limit. Magnitude of z is the length of the vector given by 3.10
12 Sequential routine computing value of one point returning number of iterations structure complex { float real; float imag; }; int cal_pixel(complex c) { int count=0, max=256; complex z; float temp, lengthsq; } z.real = 0; z.imag = 0; do { temp = z.real * z.real - z.imag * z.imag + c.real; z.imag = 2 * z.real * z.imag + c.imag; z.real = temp; lengthsq = z.real * z.real + z.imag * z.imag; count++; } while ((lengthsq < 4.0) && (count < max)); return count; 3.11
13 Mandelbrot set 3.12
14 Parallelizing Mandelbrot Set Computation Static Task Assignment Simply divide the region in to fixed number of parts, each computed by a separate processor. Not very successful because different regions require different numbers of iterations and time. Dynamic Task Assignment Have processor request regions after computing previous regions 3.13
15 Dynamic Task Assignment Work Pool/Processor Farms 3.14
16 Monte Carlo Methods Another embarrassingly parallel computation. Monte Carlo methods use of random selections. 3.15
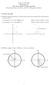
17 Circle formed within a 2 x 2 square. Ratio of area of circle to square given by: Points within square chosen randomly. Score kept of how many points happen to lie within circle. Fraction of points within the circle will be, given a sufficient number of randomly selected samples. 3.16
18 3.17
19 Computing an Integral One quadrant can be described by integral Random pairs of numbers, (xr,yr) generated, each between 0 and 1. Counted as in circle if 3.18
20 Alternative (better) Method Use random values of x to compute f(x) and sum values of f(x): where xr are randomly generated values of x between x 1 and x 2. Monte Carlo method very useful if the function cannot be integrated numerically (maybe having a large number of variables) 3.19
21 Computing the integral Example Sequential Code sum = 0; for (i = 0; i < N; i++) { /* N random samples */ xr = rand_v(x1, x2); /* generate next random value */ sum = sum + xr * xr - 3 * xr; /* compute f(xr) */ } area = (sum / N) * (x2 - x1); Routine randv(x1, x2) returns a pseudorandom number between x1 and x
22 For parallelizing Monte Carlo code, must address best way to generate random numbers in parallel - see textbook 3.21
Embarrassingly Parallel Computations
 Parallel Techniques Embarrassingly Parallel Computations Partitioning and Divide-and-Conquer Strategies Pipelined Computations Synchronous Computations Asynchronous Computations Strategies that achieve
Parallel Techniques Embarrassingly Parallel Computations Partitioning and Divide-and-Conquer Strategies Pipelined Computations Synchronous Computations Asynchronous Computations Strategies that achieve
Parallel Techniques. Embarrassingly Parallel Computations. Partitioning and Divide-and-Conquer Strategies
 slides3-1 Parallel Techniques Embarrassingly Parallel Computations Partitioning and Divide-and-Conquer Strategies Pipelined Computations Synchronous Computations Asynchronous Computations Load Balancing
slides3-1 Parallel Techniques Embarrassingly Parallel Computations Partitioning and Divide-and-Conquer Strategies Pipelined Computations Synchronous Computations Asynchronous Computations Load Balancing
Embarrassingly Parallel Computations
 Embarrassingly Parallel Computations A computation that can be divided into a number of completely independent parts, each of which can be executed by a separate processor. Input data Processes Results
Embarrassingly Parallel Computations A computation that can be divided into a number of completely independent parts, each of which can be executed by a separate processor. Input data Processes Results
Outline: Embarrassingly Parallel Problems
 Outline: Embarrassingly Parallel Problems what they are Mandelbrot Set computation cost considerations static parallelization dynamic parallelizations and its analysis Monte Carlo Methods parallel random
Outline: Embarrassingly Parallel Problems what they are Mandelbrot Set computation cost considerations static parallelization dynamic parallelizations and its analysis Monte Carlo Methods parallel random
Embarrassingly Parallel Computations Creating the Mandelbrot set
 Embarrassingly Parallel Computations Creating the Mandelbrot set Péter Kacsuk Laboratory of Parallel and Distributed Systems MTA SZTAKI Research Institute kacsuk@sztaki.hu www.lpds.sztaki.hu Definition
Embarrassingly Parallel Computations Creating the Mandelbrot set Péter Kacsuk Laboratory of Parallel and Distributed Systems MTA SZTAKI Research Institute kacsuk@sztaki.hu www.lpds.sztaki.hu Definition
Message-Passing Computing Examples
 Message-Passing Computing Examples Problems with a very large degree of parallelism: Image Transformations: Shifting, Rotation, Clipping etc. Mandelbrot Set: Sequential, static assignment, dynamic work
Message-Passing Computing Examples Problems with a very large degree of parallelism: Image Transformations: Shifting, Rotation, Clipping etc. Mandelbrot Set: Sequential, static assignment, dynamic work
Outline: Embarrassingly Parallel Problems. Example#1: Computation of the Mandelbrot Set. Embarrassingly Parallel Problems. The Mandelbrot Set
 Outline: Embarrassingly Parallel Problems Example#1: Computation of the Mandelbrot Set what they are Mandelbrot Set computation cost considerations static parallelization dynamic parallelizations and its
Outline: Embarrassingly Parallel Problems Example#1: Computation of the Mandelbrot Set what they are Mandelbrot Set computation cost considerations static parallelization dynamic parallelizations and its
Algorithms PART I: Embarrassingly Parallel. HPC Fall 2012 Prof. Robert van Engelen
 Algorithms PART I: Embarrassingly Parallel HPC Fall 2012 Prof. Robert van Engelen Overview Ideal parallelism Master-worker paradigm Processor farms Examples Geometrical transformations of images Mandelbrot
Algorithms PART I: Embarrassingly Parallel HPC Fall 2012 Prof. Robert van Engelen Overview Ideal parallelism Master-worker paradigm Processor farms Examples Geometrical transformations of images Mandelbrot
CS 789 Multiprocessor Programming. Optimizing the Sequential Mandelbrot Computation.
 CS 789 Multiprocessor Programming Optimizing the Sequential Mandelbrot Computation. School of Computer Science Howard Hughes College of Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas (c) Matt Pedersen, 2010
CS 789 Multiprocessor Programming Optimizing the Sequential Mandelbrot Computation. School of Computer Science Howard Hughes College of Engineering University of Nevada, Las Vegas (c) Matt Pedersen, 2010
Message Passing Interface (MPI)
 What the course is: An introduction to parallel systems and their implementation using MPI A presentation of all the basic functions and types you are likely to need in MPI A collection of examples What
What the course is: An introduction to parallel systems and their implementation using MPI A presentation of all the basic functions and types you are likely to need in MPI A collection of examples What
Common Parallel Programming Paradigms
 Parallel Program Models Last Time» Message Passing Model» Message Passing Interface (MPI) Standard» Examples Today» Embarrassingly Parallel» Master-Worer Reminders/Announcements» Homewor #3 is due Wednesday,
Parallel Program Models Last Time» Message Passing Model» Message Passing Interface (MPI) Standard» Examples Today» Embarrassingly Parallel» Master-Worer Reminders/Announcements» Homewor #3 is due Wednesday,
Pipelined Computations
 Pipelined Computations In the pipeline technique, the problem is divided into a series of tasks that have to be completed one after the other. In fact, this is the basis of sequential programming. Each
Pipelined Computations In the pipeline technique, the problem is divided into a series of tasks that have to be completed one after the other. In fact, this is the basis of sequential programming. Each
ICS 161 Algorithms Winter 1998 Final Exam. 1: out of 15. 2: out of 15. 3: out of 20. 4: out of 15. 5: out of 20. 6: out of 15.
 ICS 161 Algorithms Winter 1998 Final Exam Name: ID: 1: out of 15 2: out of 15 3: out of 20 4: out of 15 5: out of 20 6: out of 15 total: out of 100 1. Solve the following recurrences. (Just give the solutions;
ICS 161 Algorithms Winter 1998 Final Exam Name: ID: 1: out of 15 2: out of 15 3: out of 20 4: out of 15 5: out of 20 6: out of 15 total: out of 100 1. Solve the following recurrences. (Just give the solutions;
Tareador: understanding and predicting the potential of task decomposition strategies
 Tareador: understanding and predicting the potential of task decomposition strategies Vladimir Subotic PATC14: Barcelona 14.10.2014. Tareador environment Task decomposition Our first approach to teach
Tareador: understanding and predicting the potential of task decomposition strategies Vladimir Subotic PATC14: Barcelona 14.10.2014. Tareador environment Task decomposition Our first approach to teach
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates
 COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
COMP30019 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
Lesson 27: Angles in Standard Position
 Lesson 27: Angles in Standard Position PreCalculus - Santowski PreCalculus - Santowski 1 QUIZ Draw the following angles in standard position 50 130 230 320 770-50 2 radians PreCalculus - Santowski 2 Fast
Lesson 27: Angles in Standard Position PreCalculus - Santowski PreCalculus - Santowski 1 QUIZ Draw the following angles in standard position 50 130 230 320 770-50 2 radians PreCalculus - Santowski 2 Fast
Parallelism in Software
 Parallelism in Software Minsoo Ryu Department of Computer Science and Engineering 2 1 Parallelism in Software 2 Creating a Multicore Program 3 Multicore Design Patterns 4 Q & A 2 3 Types of Parallelism
Parallelism in Software Minsoo Ryu Department of Computer Science and Engineering 2 1 Parallelism in Software 2 Creating a Multicore Program 3 Multicore Design Patterns 4 Q & A 2 3 Types of Parallelism
High Performance Computing Lecture 41. Matthew Jacob Indian Institute of Science
 High Performance Computing Lecture 41 Matthew Jacob Indian Institute of Science Example: MPI Pi Calculating Program /Each process initializes, determines the communicator size and its own rank MPI_Init
High Performance Computing Lecture 41 Matthew Jacob Indian Institute of Science Example: MPI Pi Calculating Program /Each process initializes, determines the communicator size and its own rank MPI_Init
TABLE 2: Mathematics College Readiness Standards for Score Range 13 15
 TABLE 2: Mathematics College Readiness Standards for Score Range 13 15 Perform one-operation computation with whole numbers and decimals Solve problems in one or two steps using whole numbers Perform common
TABLE 2: Mathematics College Readiness Standards for Score Range 13 15 Perform one-operation computation with whole numbers and decimals Solve problems in one or two steps using whole numbers Perform common
Math 12 Final Review Quiz 3
 Math 12 Final Review Quiz 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement answers the question. 1. What is the measure of the reference angle f an angle of in standard position?
Math 12 Final Review Quiz 3 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement answers the question. 1. What is the measure of the reference angle f an angle of in standard position?
Random Numbers Random Walk
 Random Numbers Random Walk Computational Physics Random Numbers Random Walk Outline Random Systems Random Numbers Monte Carlo Integration Example Random Walk Exercise 7 Introduction Random Systems Deterministic
Random Numbers Random Walk Computational Physics Random Numbers Random Walk Outline Random Systems Random Numbers Monte Carlo Integration Example Random Walk Exercise 7 Introduction Random Systems Deterministic
Contents. Preface. About the Authors BASIC TECHNIQUES CHAPTER 1 PARALLEL COMPUTERS. l. 1 The Demand for Computational Speed 3
 Preface About the Authors PARTI BASIC TECHNIQUES CHAPTER 1 PARALLEL COMPUTERS l. 1 The Demand for Computational Speed 3 1.2 Potential for Increased Computational Speed 6 Speedup Factor 6 What Is the Maximum
Preface About the Authors PARTI BASIC TECHNIQUES CHAPTER 1 PARALLEL COMPUTERS l. 1 The Demand for Computational Speed 3 1.2 Potential for Increased Computational Speed 6 Speedup Factor 6 What Is the Maximum
Trigonometry Summer Assignment
 Name: Trigonometry Summer Assignment Due Date: The beginning of class on September 8, 017. The purpose of this assignment is to have you practice the mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Trigonometry.
Name: Trigonometry Summer Assignment Due Date: The beginning of class on September 8, 017. The purpose of this assignment is to have you practice the mathematical skills necessary to be successful in Trigonometry.
Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates
 433-324 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
433-324 Graphics and Interaction Transformation geometry and homogeneous coordinates Department of Computer Science and Software Engineering The Lecture outline Introduction Vectors and matrices Translation
Outline. CSC 447: Parallel Programming for Multi- Core and Cluster Systems
 CSC 447: Parallel Programming for Multi- Core and Cluster Systems Performance Analysis Instructor: Haidar M. Harmanani Spring 2018 Outline Performance scalability Analytical performance measures Amdahl
CSC 447: Parallel Programming for Multi- Core and Cluster Systems Performance Analysis Instructor: Haidar M. Harmanani Spring 2018 Outline Performance scalability Analytical performance measures Amdahl
Prentice Hall Algebra Correlated to: ACT College Readiness Standards for Mathematics
 Score Range 1 12 Students who score in the 1 12 range are most likely beginning to develop the knowledge and skills assessed in the other score ranges. Score Range 13-15 Perform one-operation computation
Score Range 1 12 Students who score in the 1 12 range are most likely beginning to develop the knowledge and skills assessed in the other score ranges. Score Range 13-15 Perform one-operation computation
Patterns for! Parallel Programming II!
 Lecture 4! Patterns for! Parallel Programming II! John Cavazos! Dept of Computer & Information Sciences! University of Delaware! www.cis.udel.edu/~cavazos/cisc879! Task Decomposition Also known as functional
Lecture 4! Patterns for! Parallel Programming II! John Cavazos! Dept of Computer & Information Sciences! University of Delaware! www.cis.udel.edu/~cavazos/cisc879! Task Decomposition Also known as functional
Applications of MPI I
 Applications of MPI I N-Dimensional Integration Using Monte Carlo Techniques Gürsan ÇOBAN 4.06.202 Outline Numerical Integration Techniques Monte Carlo Techniques for Numerical Integration Some MPI Examples
Applications of MPI I N-Dimensional Integration Using Monte Carlo Techniques Gürsan ÇOBAN 4.06.202 Outline Numerical Integration Techniques Monte Carlo Techniques for Numerical Integration Some MPI Examples
DD2429 Computational Photography :00-19:00
 . Examination: DD2429 Computational Photography 202-0-8 4:00-9:00 Each problem gives max 5 points. In order to pass you need about 0-5 points. You are allowed to use the lecture notes and standard list
. Examination: DD2429 Computational Photography 202-0-8 4:00-9:00 Each problem gives max 5 points. In order to pass you need about 0-5 points. You are allowed to use the lecture notes and standard list
Preliminaries: Size Measures and Shape Coordinates
 2 Preliminaries: Size Measures and Shape Coordinates 2.1 Configuration Space Definition 2.1 The configuration is the set of landmarks on a particular object. The configuration matrix X is the k m matrix
2 Preliminaries: Size Measures and Shape Coordinates 2.1 Configuration Space Definition 2.1 The configuration is the set of landmarks on a particular object. The configuration matrix X is the k m matrix
Lesson 5.6: Angles in Standard Position
 Lesson 5.6: Angles in Standard Position IM3 - Santowski IM3 - Santowski 1 Fast Five Opening Exercises! Use your TI 84 calculator:! Evaluate sin(50 ) " illustrate with a diagram! Evaluate sin(130 ) " Q
Lesson 5.6: Angles in Standard Position IM3 - Santowski IM3 - Santowski 1 Fast Five Opening Exercises! Use your TI 84 calculator:! Evaluate sin(50 ) " illustrate with a diagram! Evaluate sin(130 ) " Q
Random and Parallel Algorithms a journey from Monte Carlo to Las Vegas
 Random and Parallel Algorithms a journey from Monte Carlo to Las Vegas Google Maps couldn t help! Bogdán Zaválnij Institute of Mathematics and Informatics University of Pecs Ljubljana, 2014 Bogdán Zaválnij
Random and Parallel Algorithms a journey from Monte Carlo to Las Vegas Google Maps couldn t help! Bogdán Zaválnij Institute of Mathematics and Informatics University of Pecs Ljubljana, 2014 Bogdán Zaválnij
Computational Methods. Randomness and Monte Carlo Methods
 Computational Methods Randomness and Monte Carlo Methods Manfred Huber 2010 1 Randomness and Monte Carlo Methods Introducing randomness in an algorithm can lead to improved efficiencies Random sampling
Computational Methods Randomness and Monte Carlo Methods Manfred Huber 2010 1 Randomness and Monte Carlo Methods Introducing randomness in an algorithm can lead to improved efficiencies Random sampling
1. Practice the use of the C ++ repetition constructs of for, while, and do-while. 2. Use computer-generated random numbers.
 1 Purpose This lab illustrates the use of looping structures by introducing a class of programming problems called numerical algorithms. 1. Practice the use of the C ++ repetition constructs of for, while,
1 Purpose This lab illustrates the use of looping structures by introducing a class of programming problems called numerical algorithms. 1. Practice the use of the C ++ repetition constructs of for, while,
Unit 2: Trigonometry. This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses.
 Unit 2: Trigonometry This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses. Pythagorean Theorem Recall that, for any right angled triangle, the square
Unit 2: Trigonometry This lesson is not covered in your workbook. It is a review of trigonometry topics from previous courses. Pythagorean Theorem Recall that, for any right angled triangle, the square
Computer Vision. Coordinates. Prof. Flávio Cardeal DECOM / CEFET- MG.
 Computer Vision Coordinates Prof. Flávio Cardeal DECOM / CEFET- MG cardeal@decom.cefetmg.br Abstract This lecture discusses world coordinates and homogeneous coordinates, as well as provides an overview
Computer Vision Coordinates Prof. Flávio Cardeal DECOM / CEFET- MG cardeal@decom.cefetmg.br Abstract This lecture discusses world coordinates and homogeneous coordinates, as well as provides an overview
CSE 421 Closest Pair of Points, Master Theorem, Integer Multiplication
 CSE 421 Closest Pair of Points, Master Theorem, Integer Multiplication Shayan Oveis Gharan 1 Finding the Closest Pair of Points Closest Pair of Points (non geometric) Given n points and arbitrary distances
CSE 421 Closest Pair of Points, Master Theorem, Integer Multiplication Shayan Oveis Gharan 1 Finding the Closest Pair of Points Closest Pair of Points (non geometric) Given n points and arbitrary distances
Ganado Unified School District Pre-Calculus 11 th /12 th Grade
 Ganado Unified School District Pre-Calculus 11 th /12 th Grade PACING Guide SY 2016-2017 Timeline & Resources Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to highlight
Ganado Unified School District Pre-Calculus 11 th /12 th Grade PACING Guide SY 2016-2017 Timeline & Resources Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to highlight
Today s class. Viewing transformation Menus Mandelbrot set and pixel drawing. Informationsteknologi
 Today s class Viewing transformation Menus Mandelbrot set and pixel drawing Monday, November 2, 27 Computer Graphics - Class 7 The world & the window World coordinates describe the coordinate system used
Today s class Viewing transformation Menus Mandelbrot set and pixel drawing Monday, November 2, 27 Computer Graphics - Class 7 The world & the window World coordinates describe the coordinate system used
The MPI Message-passing Standard Lab Time Hands-on. SPD Course Massimo Coppola
 The MPI Message-passing Standard Lab Time Hands-on SPD Course 2016-2017 Massimo Coppola Remember! Simplest programs do not need much beyond Send and Recv, still... Each process lives in a separate memory
The MPI Message-passing Standard Lab Time Hands-on SPD Course 2016-2017 Massimo Coppola Remember! Simplest programs do not need much beyond Send and Recv, still... Each process lives in a separate memory
Ganado Unified School District #20 (Pre-Calculus 11th/12th Grade)
 Ganado Unified School District #20 (Pre-Calculus 11th/12th Grade) PACING Guide SY 2018-2019 Timeline & Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity
Ganado Unified School District #20 (Pre-Calculus 11th/12th Grade) PACING Guide SY 2018-2019 Timeline & Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity
Ganado Unified School District Trigonometry/Pre-Calculus 12 th Grade
 Ganado Unified School District Trigonometry/Pre-Calculus 12 th Grade PACING Guide SY 2014-2015 Timeline & Resources Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to
Ganado Unified School District Trigonometry/Pre-Calculus 12 th Grade PACING Guide SY 2014-2015 Timeline & Resources Quarter 1 AZ College and Career Readiness Standard HS.A-CED.4. Rearrange formulas to
MA 154 PRACTICE QUESTIONS FOR THE FINAL 11/ The angles with measures listed are all coterminal except: 5π B. A. 4
 . If θ is in the second quadrant and sinθ =.6, find cosθ..7.... The angles with measures listed are all coterminal except: E. 6. The radian measure of an angle of is: 7. Use a calculator to find the sec
. If θ is in the second quadrant and sinθ =.6, find cosθ..7.... The angles with measures listed are all coterminal except: E. 6. The radian measure of an angle of is: 7. Use a calculator to find the sec
Review of Trigonometry
 Worksheet 8 Properties of Trigonometric Functions Section Review of Trigonometry This section reviews some of the material covered in Worksheets 8, and The reader should be familiar with the trig ratios,
Worksheet 8 Properties of Trigonometric Functions Section Review of Trigonometry This section reviews some of the material covered in Worksheets 8, and The reader should be familiar with the trig ratios,
Patterns for! Parallel Programming!
 Lecture 4! Patterns for! Parallel Programming! John Cavazos! Dept of Computer & Information Sciences! University of Delaware!! www.cis.udel.edu/~cavazos/cisc879! Lecture Overview Writing a Parallel Program
Lecture 4! Patterns for! Parallel Programming! John Cavazos! Dept of Computer & Information Sciences! University of Delaware!! www.cis.udel.edu/~cavazos/cisc879! Lecture Overview Writing a Parallel Program
PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES
 10 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS & POLAR COORDINATES A coordinate system represents a point in the plane by an ordered pair of numbers called coordinates. PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS
10 PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS AND POLAR COORDINATES PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS & POLAR COORDINATES A coordinate system represents a point in the plane by an ordered pair of numbers called coordinates. PARAMETRIC EQUATIONS
Workloads Programmierung Paralleler und Verteilter Systeme (PPV)
 Workloads Programmierung Paralleler und Verteilter Systeme (PPV) Sommer 2015 Frank Feinbube, M.Sc., Felix Eberhardt, M.Sc., Prof. Dr. Andreas Polze Workloads 2 Hardware / software execution environment
Workloads Programmierung Paralleler und Verteilter Systeme (PPV) Sommer 2015 Frank Feinbube, M.Sc., Felix Eberhardt, M.Sc., Prof. Dr. Andreas Polze Workloads 2 Hardware / software execution environment
Math 26: Fall (part 1) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pythagorean Identity)
 Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Math : Fall 0 0. (part ) The Unit Circle: Cosine and Sine (Evaluating Cosine and Sine, and The Pthagorean Identit) Cosine and Sine Angle θ standard position, P denotes point where the terminal side of
Content. Coordinate systems Orthographic projection. (Engineering Drawings)
 Projection Views Content Coordinate systems Orthographic projection (Engineering Drawings) Graphical Coordinator Systems A coordinate system is needed to input, store and display model geometry and graphics.
Projection Views Content Coordinate systems Orthographic projection (Engineering Drawings) Graphical Coordinator Systems A coordinate system is needed to input, store and display model geometry and graphics.
SNAP Centre Workshop. Introduction to Trigonometry
 SNAP Centre Workshop Introduction to Trigonometry 62 Right Triangle Review A right triangle is any triangle that contains a 90 degree angle. There are six pieces of information we can know about a given
SNAP Centre Workshop Introduction to Trigonometry 62 Right Triangle Review A right triangle is any triangle that contains a 90 degree angle. There are six pieces of information we can know about a given
Trigonometry Curriculum Guide Scranton School District Scranton, PA
 Trigonometry Scranton School District Scranton, PA Trigonometry Prerequisite: Algebra II, Geometry, Algebra I Intended Audience: This course is designed for the student who has successfully completed Algebra
Trigonometry Scranton School District Scranton, PA Trigonometry Prerequisite: Algebra II, Geometry, Algebra I Intended Audience: This course is designed for the student who has successfully completed Algebra
FRAQCEL USER GUIDE
 FRAQCEL 2.7.1 USER GUIDE Author: Kevin Orloske Email Address: orloske.1@osu.edu Overview: This document provides user instructions for Fraqcel (pronounced frack-cell). Fraqcel is an open source fractal
FRAQCEL 2.7.1 USER GUIDE Author: Kevin Orloske Email Address: orloske.1@osu.edu Overview: This document provides user instructions for Fraqcel (pronounced frack-cell). Fraqcel is an open source fractal
Embarrassingly Parallel Computations
 Embarrassingly Parallel Computations Embarrassingly Parallel Computations A computation that can be divided into completely independent parts, each of which can be executed on a separate process(or) is
Embarrassingly Parallel Computations Embarrassingly Parallel Computations A computation that can be divided into completely independent parts, each of which can be executed on a separate process(or) is
Written test, 25 problems / 90 minutes
 Sponsored by: UGA Math Department and UGA Math Club Written test, 5 problems / 90 minutes November 8, 04 Instructions. At the top of the left of side of your scan-tron answer sheet, fill in your last name,
Sponsored by: UGA Math Department and UGA Math Club Written test, 5 problems / 90 minutes November 8, 04 Instructions. At the top of the left of side of your scan-tron answer sheet, fill in your last name,
Parallel Monte Carlo Sampling Scheme for Sphere and Hemisphere
 Parallel Monte Carlo Sampling Scheme for Sphere and Hemisphere I.T. Dimov 1,A.A.Penzov 2, and S.S. Stoilova 3 1 Institute for Parallel Processing, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Acad. G. Bonchev Str., bl.
Parallel Monte Carlo Sampling Scheme for Sphere and Hemisphere I.T. Dimov 1,A.A.Penzov 2, and S.S. Stoilova 3 1 Institute for Parallel Processing, Bulgarian Academy of Sciences Acad. G. Bonchev Str., bl.
Math 231E, Lecture 34. Polar Coordinates and Polar Parametric Equations
 Math 231E, Lecture 34. Polar Coordinates and Polar Parametric Equations 1 Definition of polar coordinates Let us first recall the definition of Cartesian coordinates: to each point in the plane we can
Math 231E, Lecture 34. Polar Coordinates and Polar Parametric Equations 1 Definition of polar coordinates Let us first recall the definition of Cartesian coordinates: to each point in the plane we can
7 Parallel Programming and Parallel Algorithms
 7 Parallel Programming and Parallel Algorithms 7.1 INTRODUCTION Algorithms in which operations must be executed step by step are called serial or sequential algorithms. Algorithms in which several operations
7 Parallel Programming and Parallel Algorithms 7.1 INTRODUCTION Algorithms in which operations must be executed step by step are called serial or sequential algorithms. Algorithms in which several operations
ITCS 4145/5145 Assignment 1 Using the Seeds Pattern Programming Framework Workpool Pattern
 Seeds Framework ITCS 4145/5145 Assignment 1 Using the Seeds Pattern Programming Framework Workpool Pattern Author: B. Wilkinson and C. Ferner. Modification date: Jan 28, 2014 The purpose of this assignment
Seeds Framework ITCS 4145/5145 Assignment 1 Using the Seeds Pattern Programming Framework Workpool Pattern Author: B. Wilkinson and C. Ferner. Modification date: Jan 28, 2014 The purpose of this assignment
Convex Hulls in Three Dimensions. Polyhedra
 Convex Hulls in Three Dimensions Polyhedra Polyhedron 1.A polyhedron is the generalization of a 2- D polygon to 3-D A finite number of flat polygonal faces The boundary or surface of a polyhedron - Zero-dimensional
Convex Hulls in Three Dimensions Polyhedra Polyhedron 1.A polyhedron is the generalization of a 2- D polygon to 3-D A finite number of flat polygonal faces The boundary or surface of a polyhedron - Zero-dimensional
Rational Numbers: Graphing: The Coordinate Plane
 Rational Numbers: Graphing: The Coordinate Plane A special kind of plane used in mathematics is the coordinate plane, sometimes called the Cartesian plane after its inventor, René Descartes. It is one
Rational Numbers: Graphing: The Coordinate Plane A special kind of plane used in mathematics is the coordinate plane, sometimes called the Cartesian plane after its inventor, René Descartes. It is one
Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder]
![Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder] Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder]](/thumbs/93/111713975.jpg) Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder] Preliminaries Recall: Given a smooth function f:r R, the function
Differential Geometry: Circle Patterns (Part 1) [Discrete Conformal Mappinngs via Circle Patterns. Kharevych, Springborn and Schröder] Preliminaries Recall: Given a smooth function f:r R, the function
PreCalculus Unit 1: Unit Circle Trig Quiz Review (Day 9)
 PreCalculus Unit 1: Unit Circle Trig Quiz Review (Day 9) Name Date Directions: You may NOT use Right Triangle Trigonometry for any of these problems! Use your unit circle knowledge to solve these problems.
PreCalculus Unit 1: Unit Circle Trig Quiz Review (Day 9) Name Date Directions: You may NOT use Right Triangle Trigonometry for any of these problems! Use your unit circle knowledge to solve these problems.
1.6 Applying Trig Functions to Angles of Rotation
 wwwck1org Chapter 1 Right Triangles and an Introduction to Trigonometry 16 Applying Trig Functions to Angles of Rotation Learning Objectives Find the values of the six trigonometric functions for angles
wwwck1org Chapter 1 Right Triangles and an Introduction to Trigonometry 16 Applying Trig Functions to Angles of Rotation Learning Objectives Find the values of the six trigonometric functions for angles
Section 2.3: Monte Carlo Simulation
 Section 2.3: Monte Carlo Simulation Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course c 2006 Pearson Ed., Inc. 0-13-142917-5 Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course Section 2.3: Monte Carlo Simulation 1/1 Section
Section 2.3: Monte Carlo Simulation Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course c 2006 Pearson Ed., Inc. 0-13-142917-5 Discrete-Event Simulation: A First Course Section 2.3: Monte Carlo Simulation 1/1 Section
CHAPTER 5 Pipelined Computations
 CHAPTER 5 Pipelined Computations In the pipeline technique, the problem is divided into a series of tasks that have to be completed one after the other. In fact, this is the basis of sequential programming.
CHAPTER 5 Pipelined Computations In the pipeline technique, the problem is divided into a series of tasks that have to be completed one after the other. In fact, this is the basis of sequential programming.
Vector Addition. Qty Item Part Number 1 Force Table ME-9447B 1 Mass and Hanger Set ME Carpenter s level 1 String
 rev 05/2018 Vector Addition Equipment List Qty Item Part Number 1 Force Table ME-9447B 1 Mass and Hanger Set ME-8979 1 Carpenter s level 1 String Purpose The purpose of this lab is for the student to gain
rev 05/2018 Vector Addition Equipment List Qty Item Part Number 1 Force Table ME-9447B 1 Mass and Hanger Set ME-8979 1 Carpenter s level 1 String Purpose The purpose of this lab is for the student to gain
SENIOR HIGH MATH LEAGUE April 24, 2001 SECTION I: ONE POINT EACH
 GROUP V OPEN DIVISION TEST A Unless otherwise stated give exact answers. 1. Find the quotient when 8x 3 +1 is divided by 2 x + 1. 2. Given f ( x) = 5x 2b while g (x) = 4bx. If f (g(1)) = 36, what is g
GROUP V OPEN DIVISION TEST A Unless otherwise stated give exact answers. 1. Find the quotient when 8x 3 +1 is divided by 2 x + 1. 2. Given f ( x) = 5x 2b while g (x) = 4bx. If f (g(1)) = 36, what is g
CSAP Achievement Levels Mathematics Grade 7 March, 2006
 Advanced Performance Level 4 (Score range: 614 to 860) Students apply equivalent representations of decimals, factions, percents; apply congruency to multiple polygons, use fractional parts of geometric
Advanced Performance Level 4 (Score range: 614 to 860) Students apply equivalent representations of decimals, factions, percents; apply congruency to multiple polygons, use fractional parts of geometric
A Short Introduction to OpenMP. Mark Bull, EPCC, University of Edinburgh
 A Short Introduction to OpenMP Mark Bull, EPCC, University of Edinburgh Overview Shared memory systems Basic Concepts in Threaded Programming Basics of OpenMP Parallel regions Parallel loops 2 Shared memory
A Short Introduction to OpenMP Mark Bull, EPCC, University of Edinburgh Overview Shared memory systems Basic Concepts in Threaded Programming Basics of OpenMP Parallel regions Parallel loops 2 Shared memory
SENIOR HIGH MATH LEAGUE April 24, GROUP IV Emphasis on TRIGONOMETRY
 SENIOR HIGH MATH LEAGUE TEST A Write all radical expressions in simplified form and unless otherwise stated give exact answers. 1. Give the exact value for each of the following where the angle is given
SENIOR HIGH MATH LEAGUE TEST A Write all radical expressions in simplified form and unless otherwise stated give exact answers. 1. Give the exact value for each of the following where the angle is given
Number Sense and Operations Curriculum Framework Learning Standard
 Grade 5 Expectations in Mathematics Learning Standards from the MA Mathematics Curriculum Framework for the end of Grade 6 are numbered and printed in bold. The Franklin Public School System s grade level
Grade 5 Expectations in Mathematics Learning Standards from the MA Mathematics Curriculum Framework for the end of Grade 6 are numbered and printed in bold. The Franklin Public School System s grade level
Acknowledgments. Amdahl s Law. Contents. Programming with MPI Parallel programming. 1 speedup = (1 P )+ P N. Type to enter text
 Acknowledgments Programming with MPI Parallel ming Jan Thorbecke Type to enter text This course is partly based on the MPI courses developed by Rolf Rabenseifner at the High-Performance Computing-Center
Acknowledgments Programming with MPI Parallel ming Jan Thorbecke Type to enter text This course is partly based on the MPI courses developed by Rolf Rabenseifner at the High-Performance Computing-Center
Parallel Computing. Parallel Algorithm Design
 Parallel Computing Parallel Algorithm Design Task/Channel Model Parallel computation = set of tasks Task Program Local memory Collection of I/O ports Tasks interact by sending messages through channels
Parallel Computing Parallel Algorithm Design Task/Channel Model Parallel computation = set of tasks Task Program Local memory Collection of I/O ports Tasks interact by sending messages through channels
SECTION 4.5: GRAPHS OF SINE AND COSINE FUNCTIONS
 SECTION 4.5: GRAPHS OF SINE AND COSINE FUNCTIONS 4.33 PART A : GRAPH f ( θ ) = sinθ Note: We will use θ and f ( θ) for now, because we would like to reserve x and y for discussions regarding the Unit Circle.
SECTION 4.5: GRAPHS OF SINE AND COSINE FUNCTIONS 4.33 PART A : GRAPH f ( θ ) = sinθ Note: We will use θ and f ( θ) for now, because we would like to reserve x and y for discussions regarding the Unit Circle.
Homework Project #1. Math 365
 Homework Project # Math 365 For this homework, you are asked to write several files to disk using the function write file. For example, to save an array v to the file mysoln.out, use the command write_file(v,
Homework Project # Math 365 For this homework, you are asked to write several files to disk using the function write file. For example, to save an array v to the file mysoln.out, use the command write_file(v,
Introduction to Parallel Programming
 Introduction to Parallel Programming David Lifka lifka@cac.cornell.edu May 23, 2011 5/23/2011 www.cac.cornell.edu 1 y What is Parallel Programming? Using more than one processor or computer to complete
Introduction to Parallel Programming David Lifka lifka@cac.cornell.edu May 23, 2011 5/23/2011 www.cac.cornell.edu 1 y What is Parallel Programming? Using more than one processor or computer to complete
EXPLORE MATHEMATICS TEST
 EXPLORE MATHEMATICS TEST Table 4: The College Readiness The describe what students who score in the specified score ranges are likely to know and to be able to do. The help teachers identify ways of enhancing
EXPLORE MATHEMATICS TEST Table 4: The College Readiness The describe what students who score in the specified score ranges are likely to know and to be able to do. The help teachers identify ways of enhancing
As stated earlier, the declaration
 The int data type As stated earlier, the declaration int a; is an instruction to the compiler to reserve a certain amount of memory to hold the values of the variable a. How much memory? Two bytes (usually,
The int data type As stated earlier, the declaration int a; is an instruction to the compiler to reserve a certain amount of memory to hold the values of the variable a. How much memory? Two bytes (usually,
Interactive Math Glossary Terms and Definitions
 Terms and Definitions Absolute Value the magnitude of a number, or the distance from 0 on a real number line Addend any number or quantity being added addend + addend = sum Additive Property of Area the
Terms and Definitions Absolute Value the magnitude of a number, or the distance from 0 on a real number line Addend any number or quantity being added addend + addend = sum Additive Property of Area the
Scope and Sequence for the New Jersey Core Curriculum Content Standards
 Scope and Sequence for the New Jersey Core Curriculum Content Standards The following chart provides an overview of where within Prentice Hall Course 3 Mathematics each of the Cumulative Progress Indicators
Scope and Sequence for the New Jersey Core Curriculum Content Standards The following chart provides an overview of where within Prentice Hall Course 3 Mathematics each of the Cumulative Progress Indicators
Numerical Algorithms
 Chapter 10 Slide 464 Numerical Algorithms Slide 465 Numerical Algorithms In textbook do: Matrix multiplication Solving a system of linear equations Slide 466 Matrices A Review An n m matrix Column a 0,0
Chapter 10 Slide 464 Numerical Algorithms Slide 465 Numerical Algorithms In textbook do: Matrix multiplication Solving a system of linear equations Slide 466 Matrices A Review An n m matrix Column a 0,0
AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas
 AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas This document covers all the specific areas of the AQA GCSE Further Maths course, your job is to review all the topic areas, answering the questions if you feel you need
AQA GCSE Further Maths Topic Areas This document covers all the specific areas of the AQA GCSE Further Maths course, your job is to review all the topic areas, answering the questions if you feel you need
Big Orange Bramble. August 09, 2016
 Big Orange Bramble August 09, 2016 Overview HPL SPH PiBrot Numeric Integration Parallel Pi Monte Carlo FDS DANNA HPL High Performance Linpack is a benchmark for clusters Created here at the University
Big Orange Bramble August 09, 2016 Overview HPL SPH PiBrot Numeric Integration Parallel Pi Monte Carlo FDS DANNA HPL High Performance Linpack is a benchmark for clusters Created here at the University
EE/CSCI 451 Midterm 1
 EE/CSCI 451 Midterm 1 Spring 2018 Instructor: Xuehai Qian Friday: 02/26/2018 Problem # Topic Points Score 1 Definitions 20 2 Memory System Performance 10 3 Cache Performance 10 4 Shared Memory Programming
EE/CSCI 451 Midterm 1 Spring 2018 Instructor: Xuehai Qian Friday: 02/26/2018 Problem # Topic Points Score 1 Definitions 20 2 Memory System Performance 10 3 Cache Performance 10 4 Shared Memory Programming
Introduction to High Performance Computing
 Introduction to High Performance Computing Gregory G. Howes Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Iowa Iowa High Performance Computing Summer School University of Iowa Iowa City, Iowa 25-26
Introduction to High Performance Computing Gregory G. Howes Department of Physics and Astronomy University of Iowa Iowa High Performance Computing Summer School University of Iowa Iowa City, Iowa 25-26
Monte Carlo Integration and Random Numbers
 Monte Carlo Integration and Random Numbers Higher dimensional integration u Simpson rule with M evaluations in u one dimension the error is order M -4! u d dimensions the error is order M -4/d u In general
Monte Carlo Integration and Random Numbers Higher dimensional integration u Simpson rule with M evaluations in u one dimension the error is order M -4! u d dimensions the error is order M -4/d u In general
Monte Carlo Method on Parallel Computing. Jongsoon Kim
 Monte Carlo Method on Parallel Computing Jongsoon Kim Introduction Monte Carlo methods Utilize random numbers to perform a statistical simulation of a physical problem Extremely time-consuming Inherently
Monte Carlo Method on Parallel Computing Jongsoon Kim Introduction Monte Carlo methods Utilize random numbers to perform a statistical simulation of a physical problem Extremely time-consuming Inherently
CSAP Achievement Levels Mathematics Grade 6 March, 2006
 Advanced Performance Level 4 (Score range: 589 to 830) Students demonstrate equivalency among fractions decimals, and percents; apply number sense; solve real-world problems using geometric and numeric
Advanced Performance Level 4 (Score range: 589 to 830) Students demonstrate equivalency among fractions decimals, and percents; apply number sense; solve real-world problems using geometric and numeric
Algebra II Trigonometric Functions
 Slide 1 / 162 Slide 2 / 162 Algebra II Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 162 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
Slide 1 / 162 Slide 2 / 162 Algebra II Trigonometric Functions 2015-12-17 www.njctl.org Slide 3 / 162 Trig Functions click on the topic to go to that section Radians & Degrees & Co-terminal angles Arc
2013 Four-by-Four Competition Thursday, January 31st, Round Four-by-Four Competition Thursday, January 31st, 2013.
 Round 1 Round 1 1. What is the sum of the terms of an infinite geometric sequence with first term 2016 and common ratio? 2. In how many distinguishable ways can five extra copies of your sided house key
Round 1 Round 1 1. What is the sum of the terms of an infinite geometric sequence with first term 2016 and common ratio? 2. In how many distinguishable ways can five extra copies of your sided house key
Communicating Process Architectures in Light of Parallel Design Patterns and Skeletons
 Communicating Process Architectures in Light of Parallel Design Patterns and Skeletons Dr Kevin Chalmers School of Computing Edinburgh Napier University Edinburgh k.chalmers@napier.ac.uk Overview ˆ I started
Communicating Process Architectures in Light of Parallel Design Patterns and Skeletons Dr Kevin Chalmers School of Computing Edinburgh Napier University Edinburgh k.chalmers@napier.ac.uk Overview ˆ I started
Year Term Week Chapter Ref Lesson 18.1 Cubic and reciprocal functions. 18 Graphs 2. (Algebra) 18.4 Gradients and areas under graphs
 Year Term Week Chapter Ref Lesson 18.1 Cubic and reciprocal functions Year 3 Autumn Term 1-2 3-4 18 Graphs 2 (Algebra) 18.2 Exponential and trigonometric functions 18.3 Real-life graphs 18.4 Gradients
Year Term Week Chapter Ref Lesson 18.1 Cubic and reciprocal functions Year 3 Autumn Term 1-2 3-4 18 Graphs 2 (Algebra) 18.2 Exponential and trigonometric functions 18.3 Real-life graphs 18.4 Gradients
A NON-TRIGONOMETRIC, PSEUDO AREA PRESERVING, POLYLINE SMOOTHING ALGORITHM
 A NON-TRIGONOMETRIC, PSEUDO AREA PRESERVING, POLYLINE SMOOTHING ALGORITHM Wayne Brown and Leemon Baird Department of Computer Science The United States Air Force Academy 2354 Fairchild Dr., Suite 6G- USAF
A NON-TRIGONOMETRIC, PSEUDO AREA PRESERVING, POLYLINE SMOOTHING ALGORITHM Wayne Brown and Leemon Baird Department of Computer Science The United States Air Force Academy 2354 Fairchild Dr., Suite 6G- USAF
Parallel Algorithm Design. CS595, Fall 2010
 Parallel Algorithm Design CS595, Fall 2010 1 Programming Models The programming model o determines the basic concepts of the parallel implementation and o abstracts from the hardware as well as from the
Parallel Algorithm Design CS595, Fall 2010 1 Programming Models The programming model o determines the basic concepts of the parallel implementation and o abstracts from the hardware as well as from the
Scan Algorithm Effects on Parallelism and Memory Conflicts
 Scan Algorithm Effects on Parallelism and Memory Conflicts 11 Parallel Prefix Sum (Scan) Definition: The all-prefix-sums operation takes a binary associative operator with identity I, and an array of n
Scan Algorithm Effects on Parallelism and Memory Conflicts 11 Parallel Prefix Sum (Scan) Definition: The all-prefix-sums operation takes a binary associative operator with identity I, and an array of n
Philipp Slusallek Karol Myszkowski. Realistic Image Synthesis SS18 Instant Global Illumination
 Realistic Image Synthesis - Instant Global Illumination - Karol Myszkowski Overview of MC GI methods General idea Generate samples from lights and camera Connect them and transport illumination along paths
Realistic Image Synthesis - Instant Global Illumination - Karol Myszkowski Overview of MC GI methods General idea Generate samples from lights and camera Connect them and transport illumination along paths
Parallel Programming Patterns
 Parallel Programming Patterns Moreno Marzolla Dip. di Informatica Scienza e Ingegneria (DISI) Università di Bologna http://www.moreno.marzolla.name/ Copyright 2013, 2017, 2018 Moreno Marzolla, Università
Parallel Programming Patterns Moreno Marzolla Dip. di Informatica Scienza e Ingegneria (DISI) Università di Bologna http://www.moreno.marzolla.name/ Copyright 2013, 2017, 2018 Moreno Marzolla, Università
Hiram High School Accelerated Pre-Calculus Summer Assignment
 Hiram High School Accelerated Pre-Calculus Summer Assignment This is a fast-paced, college-preparatory course that will prepare you to be successful in college math and in AP Calculus. This is a rigorous
Hiram High School Accelerated Pre-Calculus Summer Assignment This is a fast-paced, college-preparatory course that will prepare you to be successful in college math and in AP Calculus. This is a rigorous
Double Integrals over Polar Coordinate
 1. 15.4 DOUBLE INTEGRALS OVER POLAR COORDINATE 1 15.4 Double Integrals over Polar Coordinate 1. Polar Coordinates. The polar coordinates (r, θ) of a point are related to the rectangular coordinates (x,y)
1. 15.4 DOUBLE INTEGRALS OVER POLAR COORDINATE 1 15.4 Double Integrals over Polar Coordinate 1. Polar Coordinates. The polar coordinates (r, θ) of a point are related to the rectangular coordinates (x,y)
Mathematics Placement Assessment
 Mathematics Placement Assessment Courage, Humility, and Largeness of Heart Oldfields School Thank you for taking the time to complete this form accurately prior to returning this mathematics placement
Mathematics Placement Assessment Courage, Humility, and Largeness of Heart Oldfields School Thank you for taking the time to complete this form accurately prior to returning this mathematics placement
