Trigonometry - Activity 9 Tangent ratio: Introduction.
|
|
|
- Brice Watts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name: Class: p 19 Maths Helper Plus Resource Set 2. Copyright 2003 Bruce A. Vaughan, Teachers Choice Software Trigonometry - Activity 9 Tangent ratio: Introduction. Consider this right angled triangle: P q Q p side to angle P side to angle P Side p is to angle P, and side q is to angle P. ( Adjacent means beside ). In right angled triangles, the term is never used to refer to the longest side to the right angle. This is always called the hypotenuse. Only the shorter sides, the legs of the right triangle, can be sides. 1) What side is angle Q? 2) What side is to angle Q? For an angle less than 90º in a right angled triangle, the following ratio: the tangent ratio of the angle. is called For eample, the tangent ratio of angle P above can be found as follows: tangent ratio of P is written as: tan P 3) Complete the following: tan P p q tan Q 4) Start Maths Helper Plus and load the R2 - Tangent ratio 1.mhp document. This document calculates tangent ratios for right triangles. 5) Press the F5 key to display the parameters bo: These edit boes: A, B and C are used to set up the right triangle as follows: vertical leg A C horizontal leg B C multiplier C slider If C 1, then the vertical leg will be A units long, and the horizontal leg will be B units long. If X 1, then the tangent ratio is calculated for angle P. If X 2, then the calculations are based on angle Q. To change a value on the parameters bo: (1) click in the centre of its edit bo, (2) press the backspace key to delete the old value, (3) type the new value and then (4) click the Update button.
2 6) Complete the tangent ratio calculations for the two marked angles in the right angled triangle below: P 5 Q 3 (a) tanp 3 5 (b) tan Q ) Use Maths Helper Plus to check and correct your work. Enter the parameters bo values to create the triangles in question 6: Part (a): A 3, B 5, C 1, X 1 Part (b): A 3, B 5, C 1, X 2 Compare the calculations displayed by the computer with yours and correct any mistakes. Hint: Maths Helper Plus always draws the triangle in the same orientation and with the angles named P and Q. This doesn t matter. The important thing is to enter the and sides correctly. If X 1 on the parameters bo, then A is the side and B is the side. If X 2, then B is the side and A is the side. 8) Calculate the tangent ratios for each of the two marked angles in the triangles below. Show all working, and use Maths Helper Plus to help you check and correct your work. (a) (b) J 6 2 X (b) 12 Y Investigation: 5 K If the size of a triangle is changed, what effect will this have on the tangent ratios? In this activity, you will use Maths Helper Plus to eperiment with right angled triangles while recording some results in a table. You will then be able to answer this question and give a reason for your answer. 9) Set up the parameters bo as follows: A 3, B 4, C 1, X 1 The triangle displayed in Maths Helper Plus now has angle P º, with the side 3, side 4, and the calculated value of tan º ) Change the size of the triangle in small steps, recording the side lengths and tan P values each time. (a) Click on the C edit bo on the parameters bo. (b) Click on the slider button. (On the right-hand side of the parameters bo.) (c) Quickly press and release the keyboard up arrow key to increase the triangle size. (d) Record the and side lengths, and tan P in the table below. angle P side side tan P Repeat these steps until the table is full º ) Does the size of a triangle have any effect on the tangent ratios of its angles? Eplain your answer: 12) To test your findings from question 11 for some other triangles, change the A and C values in the parameters bo to create other tangent ratios, then vary the C value as in 10 above.
3 Name: Class: p 21 Maths Helper Plus Resource Set 2. Copyright 2003 Bruce A. Vaughan, Teachers Choice Software Trigonometry - Activity 10 Tangent ratio: Finding unknown angles in right triangle. The tangent ratio of an angle θ in a right angled triangle is defined as: tan θ The value of tan θ is found to depend only on the size of the angle, θ, so that tan 30º will be the same for all right angled triangles having a 30º angle. You will now create a table of tangent ratios that can be used to find unknown sides and angles in many different triangles. 1) Start Maths Helper Plus and load the R2 - Tangent ratio 2.mhp document. This document calculates tangent ratios for angles in right angled triangles. 2) Press the F5 key to display the parameters bo: Edit boes: A and B are used as follows: angle in degrees side to the angle slider Update button 3) To calculate the tangent ratio for any angle, click on the centre of the edit bo for A on the parameters bo. press backspace to delete the eisting angle. type the new angle. click the Update button. Use Maths Helper Plus to calculate these tangent ratios: (a) tan 15º (b) tan 30º (c) tan 45º (d) tan 60º 4) Creating a table of tangent ratios A table of tangent ratios can be used to find unknown angles and sides in right angled triangles. Use Maths Helper Plus to calculate the tangent ratio for the angles in the table below. Write the values in the table. (In the table, the angle is called A.) Hint: To quickly change the angle on the parameters bo, first click on the A edit bo, backspace and change the number to 5, then click on the slider. Now use the up and down keyboard arrows to change the angle. Aº tan Aº Aº tan Aº Aº tan Aº ) Maths Helper Plus tries to calculate tan 90º, but doesn t really give the true answer. What is the value of tan 90º? [ Hint: When A 90º, how long is the side? ]
4 6) Use the table from question 4 to find the unknown angles below: (a) tan A (b) tan B (c) tan C 1 (d) tan D (e) tan E A B C D E ) Find the unknown angles in the right angled triangles below. Use the two sides given to calculate the tangent ratio for the unknown angle, then use the table of tangent ratios that you created in question 4 to find the angle. (a) (b) (c) A tan A B so A tan B so B C tan C (d) so C D tan D so D (e) E tan E so E
5 Name: Class: p 23 Maths Helper Plus Resource Set 2. Copyright 2003 Bruce A. Vaughan, Teachers Choice Software Trigonometry - Activity 11 Tangent ratio: Finding unknown or sides in right triangles. In this activity you will practice finding unknown sides of right triangles using the tangent ratio, then use Maths Helper Plus to correct your working and answers. The tangent ratio can be used to calculate the length of one of the shorter sides (legs) of a right triangle. To do this you need the tangent ratio for one of the smaller angles, and the length of one leg of the triangle. There are two types of these problems, depending on whether you are finding the or side. Problem type 1: Finding the side. Eample 1: Use the tangent ratio to find the unknown side in this triangle: Solution: tan35 so 10 tan º 10 But tan35º (From a table of tangent ratios, or scientific calculator with a tan button.) so Problem type 2: Finding the side. Eample 2: Use the tangent ratio to find the unknown side in this triangle: Solution: so and tan 40 tan 40 tan 40 40º But tan40º (From a table of tangent ratios, or scientific calculator with a tan button.) so ) Start Maths Helper Plus and load the R2 - Tangent ratio 3.mhp document. This document solves for unknown sides in right triangles using the tan ratio. 2) Press the F5 key to display the parameters bo. (See below.) A, B and C have meanings as shown below: A, one of the two smaller angles of the triangle: The side to angle A : The side to angle A : Only one of the legs of the triangle can be entered at a time. Set the unknown side length to zero. To enter a value, click on an edit bo, backspace to clear the old value, type the new value then click Update. The diagram will always draw the side horizontally, and the side vertically. NOTE: If the diagram becomes too big for your computer screen, press the F10 key to make it smaller. To make the diagram bigger, hold down Shift while you press F10.
6 3) Use the tangent ratio to find the unknown leg in each of the triangles below. For each triangle: Calculate 1. Identify the and legs for the angle given. 2. Obtain the tangent ratio of the angle from a calculator or printed table. 3. Write the tangent ratio rule and substitute the known values. 4. Calculate the answer, showing all working steps. Check 1. Enter the angle and given side into the Maths Helper Plus edit boes. 2. Set the unknown side to zero. Correct 1. Compare your working steps and answers with Maths Helper Plus. 2. Fi your mistakes. 30º (a) (b) 14 19º 8.5 (c) (d) º 42º 9 (e) 5º 10 (f) 48º
7 Name: Class: p 25 Maths Helper Plus Resource Set 2. Copyright 2003 Bruce A. Vaughan, Teachers Choice Software Trigonometry - Activity 12 Tangent ratio: Angles of elevation and depression. Angles of elevation and depression are measured from the horizontal, like this: observer angle of elevation angle of depression horizontal For an object that is higher than the observer, the angle of elevation is measured upwards from the horizontal to the straight line between the observer and the object. For an object that is lower than the observer, the angle of depression is measured downwards from the horizontal to the straight line between the observer and the object. An angle of elevation and depression can help us find an unknown distance. All we need to do is construct a right triangle containing the angle and then use the tan ratio. Case 1 - Angles of elevation Given an angle of elevation and a horizontal or vertical distance between the object and the observer, we can construct a right angled triangle like this: observer angle of elevation horizontal Now we can use the tan ratio to find the unknown horizontal or vertical side. Case 2 - Angles of depression Given an angle of depression and a horizontal or vertical distance between the object and the observer, we can construct a right angled triangle like this: observer A angle of depression horizontal A The angle of depression, A, is the same as the angle in the triangle (near the dog) because the base of the triangle is parallel to the horizontal. Once again, the tan ratio can be used to find the unknown horizontal or vertical side of this triangle.
8 1) Start Maths Helper Plus and load the R2 - Tangent ratio 4.mhp document. This document solves angle of elevation and angle of depression problems. 2) Press the F5 key to display the parameters bo. (See below.) A, B, C and X have meanings as shown: Angle of elevation or depression: Horizontal side ( Set to zero if unknown): Vertical side ( Set to zero if unknown): Set X to: 1 if A is an angle of elevation, or 2 if A is an angle of depression. 3) For each of the word problems below: 1. Draw a labelled diagram of the situation similar to those on the front of this sheet. Include the horizontal line of sight from the observer and a right angled triangle. 2. Use the tangent ratio to calculate the unknown leg of the right triangle. Show all working. 3. Make sure you have answered the original question. Include units if necessary. 4. Use Maths Helper Plus to correct your diagram, working steps and answer. NOTE: If the diagram becomes too big for your computer screen, press the F10 key to make it smaller. To make the diagram bigger, hold down Shift while you press F10. a) A ladder placed on a flat horizontal surface rests against a vertical wall with an angle of elevation of 65º. The foot of the latter is 2 metres from the base of the wall. Find the hight of the point where the ladder touches the wall. To check with Maths Helper Plus, set: A65, B2, C0, X1 b) A hungry cat spies a bird in a tree. The bird is 3.4 metres above the ground, and the angle of elevation to the bird from the cat s point of view is 40º. How far is the cat from the base of the tree? To check with Maths Helper Plus, set: A40, B0, C3.4, X1 c) The common archer fish (Tootes chatareus) is able to squirt a water jet from its mouth with deadly accuracy to shoot down insects crawling on leaves and stems of overhanging vegetation. An archerfish at the surface of the water notices a dragonfly resting on a twig at an angle of elevation º. The dragonfly is eactly above a point on the water that is 30cm from the fish. How high is the dragonfly above the water surface? To check with Maths Helper Plus, set: A, B30, C0, X1 d) A parachutist has an altitude of 320 metres when directly above a high voltage power pole. She spies the landing target and estimates that the angle of depression to the target is 33º. What is the approimate horizontal distance from the power pole to the target? To check with Maths Helper Plus, set: A33, B0, C320, X2 e) A fishing boat is 120 metres away from a point on the water that is directly above a school of large fish. The sonar fish detector on the boat indicates that the angle of depression from the boat to the fish is 55º. How deep are the fish? To check with Maths Helper Plus, set: A55, B120, C0, X2
AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES
 AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Eploring Pythagorean Theorem Using Pythagorean
AW Math 10 UNIT 7 RIGHT ANGLE TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Eploring Pythagorean Theorem Using Pythagorean
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES
 AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
AWM 11 UNIT 4 TRIGONOMETRY OF RIGHT TRIANGLES Assignment Title Work to complete Complete 1 Triangles Labelling Triangles 2 Pythagorean Theorem Exploring Pythagorean Theorem 3 More Pythagorean Theorem Using
Chapter 3: Right Triangle Trigonometry
 10C Name: Chapter 3: Right Triangle Trigonometry 3.1 The Tangent Ratio Outcome : Develop and apply the tangent ratio to solve problems that involve right triangles. Definitions: Adjacent side: the side
10C Name: Chapter 3: Right Triangle Trigonometry 3.1 The Tangent Ratio Outcome : Develop and apply the tangent ratio to solve problems that involve right triangles. Definitions: Adjacent side: the side
Lesson Title 2: Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios
 Part UNIT RIGHT solving TRIANGLE equations TRIGONOMETRY and inequalities Lesson Title : Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios Georgia Performance Standards MMG: Students will define and apply sine,
Part UNIT RIGHT solving TRIANGLE equations TRIGONOMETRY and inequalities Lesson Title : Problem TK Solving with Trigonometric Ratios Georgia Performance Standards MMG: Students will define and apply sine,
Trigonometry Ratios. For each of the right triangles below, the labelled angle is equal to 40. Why then are these triangles similar to each other?
 Name: Trigonometry Ratios A) An Activity with Similar Triangles Date: For each of the right triangles below, the labelled angle is equal to 40. Why then are these triangles similar to each other? Page
Name: Trigonometry Ratios A) An Activity with Similar Triangles Date: For each of the right triangles below, the labelled angle is equal to 40. Why then are these triangles similar to each other? Page
Packet Unit 5 Right Triangles Honors Common Core Math 2 1
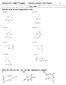 Packet Unit 5 Right Triangles Honors Common Core Math 2 1 Day 1 HW Find the value of each trigonometric ratio. Write the ratios for sinp, cosp, and tanp. Remember to simplify! 9. 10. 11. Packet Unit 5
Packet Unit 5 Right Triangles Honors Common Core Math 2 1 Day 1 HW Find the value of each trigonometric ratio. Write the ratios for sinp, cosp, and tanp. Remember to simplify! 9. 10. 11. Packet Unit 5
Assignment Guide: Chapter 8 Geometry (L3)
 Assignment Guide: Chapter 8 Geometry (L3) (91) 8.1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse Page 495-497 #7-31 odd, 37-47 odd (92) 8.2 Special Right Triangles Page 503-504 #7-12, 15-20, 23-28 (93) 8.2
Assignment Guide: Chapter 8 Geometry (L3) (91) 8.1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse Page 495-497 #7-31 odd, 37-47 odd (92) 8.2 Special Right Triangles Page 503-504 #7-12, 15-20, 23-28 (93) 8.2
Finding Angles and Solving Right Triangles NEW SKILLS: WORKING WITH INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS. Calculate each angle to the nearest degree.
 324 MathWorks 10 Workbook 7.5 Finding Angles and Solving Right Triangles NEW SKILLS: WORKING WITH INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS The trigonometric ratios discussed in this chapter are unaffected by the size
324 MathWorks 10 Workbook 7.5 Finding Angles and Solving Right Triangles NEW SKILLS: WORKING WITH INVERSE TRIGONOMETRIC RATIOS The trigonometric ratios discussed in this chapter are unaffected by the size
Chapter 7 - Trigonometry
 Chapter 7 Notes Lessons 7.1 7.5 Geometry 1 Chapter 7 - Trigonometry Table of Contents (you can click on the links to go directly to the lesson you want). Lesson Pages 7.1 and 7.2 - Trigonometry asics Pages
Chapter 7 Notes Lessons 7.1 7.5 Geometry 1 Chapter 7 - Trigonometry Table of Contents (you can click on the links to go directly to the lesson you want). Lesson Pages 7.1 and 7.2 - Trigonometry asics Pages
Trigonometry is concerned with the connection between the sides and angles in any right angled triangle.
 Trigonometry Obj: I can to use trigonometry to find unknown sides and unknown angles in a triangle. Trigonometry is concerned with the connection between the sides and angles in any right angled triangle.
Trigonometry Obj: I can to use trigonometry to find unknown sides and unknown angles in a triangle. Trigonometry is concerned with the connection between the sides and angles in any right angled triangle.
Angles of a Triangle. Activity: Show proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle add up to Finding the third angle of a triangle
 Angles of a Triangle Activity: Show proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle add up to 180 0 Finding the third angle of a triangle Pythagorean Theorem Is defined as the square of the length of the
Angles of a Triangle Activity: Show proof that the sum of the angles of a triangle add up to 180 0 Finding the third angle of a triangle Pythagorean Theorem Is defined as the square of the length of the
2.1 The Tangent Ratio
 2.1 The Tangent Ratio C 2.1 Concept: 14, 15 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 1 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 2 Online Video
2.1 The Tangent Ratio C 2.1 Concept: 14, 15 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 1 PreAP FPCM 10 (Ms. Carignan) Outcome FP10.4 Trigonometry Chapter 2 Page 2 Online Video
Chapter 7. Right Triangles and Trigonometry
 hapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry 7.1 pply the Pythagorean Theorem 7.2 Use the onverse of the Pythagorean Theorem 7.3 Use Similar Right Triangles 7.4 Special Right Triangles 7.5 pply the Tangent
hapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry 7.1 pply the Pythagorean Theorem 7.2 Use the onverse of the Pythagorean Theorem 7.3 Use Similar Right Triangles 7.4 Special Right Triangles 7.5 pply the Tangent
Trigonometry Practise 2 - Mrs. Maharaj
 Trigonometry Practise 2 - Mrs. Maharaj Question 1 Question 2 Use a calculator to evaluate cos 82 correct to three decimal places. cos 82 = (to 3 decimal places) Complete the working to find the value of
Trigonometry Practise 2 - Mrs. Maharaj Question 1 Question 2 Use a calculator to evaluate cos 82 correct to three decimal places. cos 82 = (to 3 decimal places) Complete the working to find the value of
Unit 1 Trigonometry. Topics and Assignments. General Outcome: Develop spatial sense and proportional reasoning. Specific Outcomes:
 1 Unit 1 Trigonometry General Outcome: Develop spatial sense and proportional reasoning. Specific Outcomes: 1.1 Develop and apply the primary trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) to solve problems
1 Unit 1 Trigonometry General Outcome: Develop spatial sense and proportional reasoning. Specific Outcomes: 1.1 Develop and apply the primary trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) to solve problems
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 3. Primary Trigonometric Ratios
 Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 3 Suggested Time: 75 minutes Primary Trigonometric Ratios What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will use trigonometry (sin, cos, tan) to measure
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 3 Suggested Time: 75 minutes Primary Trigonometric Ratios What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will use trigonometry (sin, cos, tan) to measure
Cumulative Review: SOHCAHTOA and Angles of Elevation and Depression
 Cumulative Review: SOHCAHTOA and Angles of Elevation and Depression Part 1: Model Problems The purpose of this worksheet is to provide students the opportunity to review the following topics in right triangle
Cumulative Review: SOHCAHTOA and Angles of Elevation and Depression Part 1: Model Problems The purpose of this worksheet is to provide students the opportunity to review the following topics in right triangle
Name: Block: What I can do for this unit:
 Unit 8: Trigonometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 8-1 I can use and understand triangle similarity and the Pythagorean
Unit 8: Trigonometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 10 Common Name: Block: What I can do for this unit: After Practice After Review How I Did 8-1 I can use and understand triangle similarity and the Pythagorean
SOH CAH TOA Worksheet Name. Find the following ratios using the given right triangles
 Name: Algebra II Period: 9.1 Introduction to Trig 12.1 Worksheet Name GETTIN' TRIGGY WIT IT SOH CAH TOA Find the following ratios using the given right triangles. 1. 2. Sin A = Sin B = Sin A = Sin B =
Name: Algebra II Period: 9.1 Introduction to Trig 12.1 Worksheet Name GETTIN' TRIGGY WIT IT SOH CAH TOA Find the following ratios using the given right triangles. 1. 2. Sin A = Sin B = Sin A = Sin B =
DAY 1 - Pythagorean Theorem
 1 U n i t 6 10P Date: Name: DAY 1 - Pythagorean Theorem 1. 2. 3. 1 2 U n i t 6 10P Date: Name: 4. 5. 6. 7. 2 3 U n i t 6 10P Date: Name: IF there s time Investigation: Complete the table below using the
1 U n i t 6 10P Date: Name: DAY 1 - Pythagorean Theorem 1. 2. 3. 1 2 U n i t 6 10P Date: Name: 4. 5. 6. 7. 2 3 U n i t 6 10P Date: Name: IF there s time Investigation: Complete the table below using the
hypotenuse adjacent leg Preliminary Information: SOH CAH TOA is an acronym to represent the following three 28 m 28 m opposite leg 13 m
 On Twitter: twitter.com/engagingmath On FaceBook: www.mathworksheetsgo.com/facebook I. odel Problems II. Practice Problems III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer ey Web Resources Using the inverse sine, cosine,
On Twitter: twitter.com/engagingmath On FaceBook: www.mathworksheetsgo.com/facebook I. odel Problems II. Practice Problems III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer ey Web Resources Using the inverse sine, cosine,
Review of Sine, Cosine, and Tangent for Right Triangle
 Review of Sine, Cosine, and Tangent for Right Triangle In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C.
Review of Sine, Cosine, and Tangent for Right Triangle In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are labeled with capital letters. The right angle is usually labeled C.
Ch 8: Right Triangles and Trigonometry 8-1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse 8-2 Special Right Triangles 8-3 The Tangent Ratio
 Ch 8: Right Triangles and Trigonometry 8-1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse 8- Special Right Triangles 8-3 The Tangent Ratio 8-1: The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse Focused Learning Target:
Ch 8: Right Triangles and Trigonometry 8-1 The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse 8- Special Right Triangles 8-3 The Tangent Ratio 8-1: The Pythagorean Theorem and Its Converse Focused Learning Target:
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 2. Ratios of Sides of Right-Angle Triangles
 Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 2 Ratios of Sides of Right-Angle s Suggested Time: 75 minutes What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will learn through investigation, the relationship
Student Instruction Sheet: Unit 4, Lesson 2 Ratios of Sides of Right-Angle s Suggested Time: 75 minutes What s important in this lesson: In this lesson, you will learn through investigation, the relationship
2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the.
 2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Key Ideas: The three angles in a triangle sum to. Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the. In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are
2.0 Trigonometry Review Date: Key Ideas: The three angles in a triangle sum to. Pythagorean Theorem: where c is always the. In trigonometry problems, all vertices (corners or angles) of the triangle are
MBF 3C. Foundations for College Mathematics Grade 11 College Mitchell District High School. Unit 1 Trigonometry 9 Video Lessons
 MBF 3C Foundations for College Mathematics Grade 11 College Mitchell District High School Unit 1 Trigonometry 9 Video Lessons Allow no more than 15 class days for this unit This includes time for review
MBF 3C Foundations for College Mathematics Grade 11 College Mitchell District High School Unit 1 Trigonometry 9 Video Lessons Allow no more than 15 class days for this unit This includes time for review
Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form.
 Pythagorean Theorem word problems Solve each of the following. Please draw a picture and use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve. Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form. 1.
Pythagorean Theorem word problems Solve each of the following. Please draw a picture and use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve. Be sure to label all answers and leave answers in exact simplified form. 1.
14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio.
 14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio. Using the space below, draw at least right triangles, each of which has one
14.1 Similar Triangles and the Tangent Ratio Per Date Trigonometric Ratios Investigate the relationship of the tangent ratio. Using the space below, draw at least right triangles, each of which has one
Year 10 Term 2 Homework
 Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 2 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 9 Year 10 Term 2 Week 9 Homework 1 9.1 Trigonometry with right Triangles........................... 1 9.1.1
Yimin Math Centre Year 10 Term 2 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 9 Year 10 Term 2 Week 9 Homework 1 9.1 Trigonometry with right Triangles........................... 1 9.1.1
Solving Right Triangles. How do you solve right triangles?
 Solving Right Triangles How do you solve right triangles? The Trigonometric Functions we will be looking at SINE COSINE TANGENT The Trigonometric Functions SINE COSINE TANGENT SINE Pronounced sign TANGENT
Solving Right Triangles How do you solve right triangles? The Trigonometric Functions we will be looking at SINE COSINE TANGENT The Trigonometric Functions SINE COSINE TANGENT SINE Pronounced sign TANGENT
SM 2. Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or
 SM 2 Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or. It doesn t matter which leg is a and which leg is b. The hypotenuse is the side across from the right angle. To find the length
SM 2 Date: Section: Objective: The Pythagorean Theorem: In a triangle, or. It doesn t matter which leg is a and which leg is b. The hypotenuse is the side across from the right angle. To find the length
These are the type of problems that you will be working on in class. These problems are from Lesson 7.
 Pre-Class Problems 10 for Wednesda, October 10 These are the tpe of problems that ou will be working on in class. These problems are from Lesson 7. Solution to Problems on the Pre-Eam. You can go to the
Pre-Class Problems 10 for Wednesda, October 10 These are the tpe of problems that ou will be working on in class. These problems are from Lesson 7. Solution to Problems on the Pre-Eam. You can go to the
10-1. Three Trigonometric Functions. Vocabulary. Lesson
 Chapter 10 Lesson 10-1 Three Trigonometric Functions BIG IDEA The sine, cosine, and tangent of an acute angle are each a ratio of particular sides of a right triangle with that acute angle. Vocabulary
Chapter 10 Lesson 10-1 Three Trigonometric Functions BIG IDEA The sine, cosine, and tangent of an acute angle are each a ratio of particular sides of a right triangle with that acute angle. Vocabulary
Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231
 1 Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231 What is Trigonometry? 2 It is defined as the study of triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides.
1 Lesson 10.1 TRIG RATIOS AND COMPLEMENTARY ANGLES PAGE 231 What is Trigonometry? 2 It is defined as the study of triangles and the relationships between their sides and the angles between these sides.
The Crooked Foundation The Bird House. 100ft. Inter-Island Journey. East Fence. 150ft. South Fence
 13.1 - Opening Per Date It is another beautiful day on the Big Island, and Grandma is out and about planning her net set of projects. First she wants to build a bird house for her new team of homing pigeons.
13.1 - Opening Per Date It is another beautiful day on the Big Island, and Grandma is out and about planning her net set of projects. First she wants to build a bird house for her new team of homing pigeons.
9.1 Use Trigonometry with Right Triangles
 9.1 Use Trigonometry with Right Triangles Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing lengths in right triangles. Find trigonometric ratios using right triangles. Use trigonometric ratios to find angle
9.1 Use Trigonometry with Right Triangles Use the Pythagorean Theorem to find missing lengths in right triangles. Find trigonometric ratios using right triangles. Use trigonometric ratios to find angle
Historical Note Trigonometry Ratios via Similarity
 Section 12-6 Trigonometry Ratios via Similarity 1 12-6 Trigonometry Ratios via Similarity h 40 190 ft of elevation Figure 12-83 Measurements of buildings, structures, and some other objects are frequently
Section 12-6 Trigonometry Ratios via Similarity 1 12-6 Trigonometry Ratios via Similarity h 40 190 ft of elevation Figure 12-83 Measurements of buildings, structures, and some other objects are frequently
CK-12 Geometry: Inverse Trigonometric Ratios
 CK-12 Geometry: Inverse Trigonometric Ratios Learning Objectives Use the inverse trigonometric ratios to find an angle in a right triangle. Solve a right triangle. Apply inverse trigonometric ratios to
CK-12 Geometry: Inverse Trigonometric Ratios Learning Objectives Use the inverse trigonometric ratios to find an angle in a right triangle. Solve a right triangle. Apply inverse trigonometric ratios to
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS through 7.1.5
 SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 7.1. through 7.1.5 Students have used the equation = m + b throughout this course to graph lines and describe patterns. When the equation is written in -form, the m is the
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 7.1. through 7.1.5 Students have used the equation = m + b throughout this course to graph lines and describe patterns. When the equation is written in -form, the m is the
Introduction to Trigonometry
 NAME COMMON CORE GEOMETRY- Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry DATE PAGE TOPIC HOMEWORK 1/22 2-4 Lesson 1 : Incredibly Useful Ratios Homework Worksheet 1/23 5-6 LESSON 2: Using Trigonometry to find missing
NAME COMMON CORE GEOMETRY- Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry DATE PAGE TOPIC HOMEWORK 1/22 2-4 Lesson 1 : Incredibly Useful Ratios Homework Worksheet 1/23 5-6 LESSON 2: Using Trigonometry to find missing
I. Model Problems II. Practice III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer Key. Sine, Cosine Tangent
 On Twitter: twitter.com/engagingmath On FaceBook: www.mathworksheetsgo.com/facebook I. Model Problems II. Practice III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer Key Web Resources Sine, Cosine Tangent www.mathwarehouse.com/trigonometry/sine-cosine-tangent.html
On Twitter: twitter.com/engagingmath On FaceBook: www.mathworksheetsgo.com/facebook I. Model Problems II. Practice III. Challenge Problems IV. Answer Key Web Resources Sine, Cosine Tangent www.mathwarehouse.com/trigonometry/sine-cosine-tangent.html
Geometry. Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry. Name Period
 Geometry Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry Name Period 1 Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW
Geometry Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry Name Period 1 Chapter 7 Right Triangles and Trigonometry ***In order to get full credit for your assignments they must me done on time and you must SHOW
Unit 6: Triangle Geometry
 Unit 6: Triangle Geometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 9 Principles Name: lock: What I can do for this unit: fter Practice fter Review How I id 6-1 I can recognize similar triangles using the ngle Test,
Unit 6: Triangle Geometry Student Tracking Sheet Math 9 Principles Name: lock: What I can do for this unit: fter Practice fter Review How I id 6-1 I can recognize similar triangles using the ngle Test,
UNIT 9 - RIGHT TRIANGLES AND TRIG FUNCTIONS
 UNIT 9 - RIGHT TRIANGLES AND TRIG FUNCTIONS Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem Objectives: SWBAT use the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems. SWBAT use side lengths to classify triangles
UNIT 9 - RIGHT TRIANGLES AND TRIG FUNCTIONS Converse of the Pythagorean Theorem Objectives: SWBAT use the converse of the Pythagorean Theorem to solve problems. SWBAT use side lengths to classify triangles
5.5 Right Triangles. 1. For an acute angle A in right triangle ABC, the trigonometric functions are as follow:
 5.5 Right Triangles 1. For an acute angle A in right triangle ABC, the trigonometric functions are as follow: sin A = side opposite hypotenuse cos A = side adjacent hypotenuse B tan A = side opposite side
5.5 Right Triangles 1. For an acute angle A in right triangle ABC, the trigonometric functions are as follow: sin A = side opposite hypotenuse cos A = side adjacent hypotenuse B tan A = side opposite side
C if U can Shape and space
 C if U can Shape and space Name How will this booklet help you to move from a D to a C grade? The topic of shape and space is split into five units angles, transformations, the circle, area and volume
C if U can Shape and space Name How will this booklet help you to move from a D to a C grade? The topic of shape and space is split into five units angles, transformations, the circle, area and volume
Solving Right Triangles. LEARN ABOUT the Math
 7.5 Solving Right Triangles GOL Use primary trigonometric ratios to calculate side lengths and angle measures in right triangles. LERN OUT the Math farmers co-operative wants to buy and install a grain
7.5 Solving Right Triangles GOL Use primary trigonometric ratios to calculate side lengths and angle measures in right triangles. LERN OUT the Math farmers co-operative wants to buy and install a grain
G.8 Right Triangles STUDY GUIDE
 G.8 Right Triangles STUDY GUIDE Name Date Block Chapter 7 Right Triangles Review and Study Guide Things to Know (use your notes, homework, quizzes, textbook as well as flashcards at quizlet.com (http://quizlet.com/4216735/geometry-chapter-7-right-triangles-flashcardsflash-cards/)).
G.8 Right Triangles STUDY GUIDE Name Date Block Chapter 7 Right Triangles Review and Study Guide Things to Know (use your notes, homework, quizzes, textbook as well as flashcards at quizlet.com (http://quizlet.com/4216735/geometry-chapter-7-right-triangles-flashcardsflash-cards/)).
Assignment. Pg. 567 #16-33, even pg 577 # 1-17 odd, 32-37
 Assignment Intro to Ch. 8 8.1 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Da 1 8. Da Review Quiz 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Etra Practice 8.5 8.5 In-class project 8.6 Da 1 8.6 Da Ch. 8 review Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet
Assignment Intro to Ch. 8 8.1 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Da 1 8. Da Review Quiz 8. Da 1 8. Da 8. Etra Practice 8.5 8.5 In-class project 8.6 Da 1 8.6 Da Ch. 8 review Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet Worksheet
UNIT 4 MODULE 2: Geometry and Trigonometry
 Year 12 Further Mathematics UNIT 4 MODULE 2: Geometry and Trigonometry CHAPTER 8 - TRIGONOMETRY This module covers the application of geometric and trigonometric knowledge and techniques to various two-
Year 12 Further Mathematics UNIT 4 MODULE 2: Geometry and Trigonometry CHAPTER 8 - TRIGONOMETRY This module covers the application of geometric and trigonometric knowledge and techniques to various two-
Acute Angles and Right Triangles. Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 2 Acute Angles and Right Triangles Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 2.5 Further Applications of Right Triangles Historical Background Bearing Further Applications Copyright 2017, 2013,
2 Acute Angles and Right Triangles Copyright 2017, 2013, 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. 1 2.5 Further Applications of Right Triangles Historical Background Bearing Further Applications Copyright 2017, 2013,
Eamination Question 1: alculate the angle marked. Give your answer correct to one decimal place. 12 m 15m Eamination Question 2: 20 m Work out the siz
 Revision Topic 18: Trigonometry Trigonometry connects the length of sides and angles in right-angled triangles. Some important terms In a right-angled triangle, the side opposite the right angle is called
Revision Topic 18: Trigonometry Trigonometry connects the length of sides and angles in right-angled triangles. Some important terms In a right-angled triangle, the side opposite the right angle is called
Transformations in the Plane - Activity 1 Reflections in axes and an oblique line.
 Name: Class: p 5 Maths Helper Plus Resource Set. Copyright 00 Bruce A. Vaughan, Teachers Choice Software Transformations in the Plane - Activity Reflections in axes and an oblique line. ) On the diagram
Name: Class: p 5 Maths Helper Plus Resource Set. Copyright 00 Bruce A. Vaughan, Teachers Choice Software Transformations in the Plane - Activity Reflections in axes and an oblique line. ) On the diagram
DAY 1 - GEOMETRY FLASHBACK
 DAY 1 - GEOMETRY FLASHBACK Sine Opposite Hypotenuse Cosine Adjacent Hypotenuse sin θ = opp. hyp. cos θ = adj. hyp. tan θ = opp. adj. Tangent Opposite Adjacent a 2 + b 2 = c 2 csc θ = hyp. opp. sec θ =
DAY 1 - GEOMETRY FLASHBACK Sine Opposite Hypotenuse Cosine Adjacent Hypotenuse sin θ = opp. hyp. cos θ = adj. hyp. tan θ = opp. adj. Tangent Opposite Adjacent a 2 + b 2 = c 2 csc θ = hyp. opp. sec θ =
4Trigonometry of Right Triangles
 197 Chapter 4Trigonometr of Right Triangles Surveors use theodolites to measure angles in the field. These angles can be used to solve problems involving trigonometric ratios. Solving for Angles, Lengths,
197 Chapter 4Trigonometr of Right Triangles Surveors use theodolites to measure angles in the field. These angles can be used to solve problems involving trigonometric ratios. Solving for Angles, Lengths,
UNIT 2 RIGHT TRIANGLE TRIGONOMETRY Lesson 1: Exploring Trigonometric Ratios Instruction
 Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: measuring angles with a protractor understanding how to label angles and sides in triangles converting fractions into decimals
Prerequisite Skills This lesson requires the use of the following skills: measuring angles with a protractor understanding how to label angles and sides in triangles converting fractions into decimals
Math 21 Home. Book 9: Triangles. Name:
 Math 21 Home Book 9: Triangles Name: Start Date: Completion Date: Year Overview: Earning and Spending Money Home Travel and Transportation Recreation and Wellness 1. Budget 2. Personal Banking 3. Interest
Math 21 Home Book 9: Triangles Name: Start Date: Completion Date: Year Overview: Earning and Spending Money Home Travel and Transportation Recreation and Wellness 1. Budget 2. Personal Banking 3. Interest
2.7 Solving Problems Involving More than One Right Triangle
 2.7 Solving roblems Involving ore than One Right Triangle OCUS Use trigonometric ratios to solve problems that involve more than one right triangle. When a problem involves more than one right triangle,
2.7 Solving roblems Involving ore than One Right Triangle OCUS Use trigonometric ratios to solve problems that involve more than one right triangle. When a problem involves more than one right triangle,
Coordinates - Activity 1 Plotting whole number ordered pairs.
 Name: Class: p 3 Maths Helper Plus Resource Set 1. Copyright 2002 Bruce A. Vaughan, Teachers Choice Software Coordinates - Activity 1 Plotting whole number ordered pairs. 1) Start Maths Helper Plus and
Name: Class: p 3 Maths Helper Plus Resource Set 1. Copyright 2002 Bruce A. Vaughan, Teachers Choice Software Coordinates - Activity 1 Plotting whole number ordered pairs. 1) Start Maths Helper Plus and
Name Class Date. Investigating a Ratio in a Right Triangle
 Name lass Date Trigonometric Ratios Going Deeper Essential question: How do you find the tangent, sine, and cosine ratios for acute angles in a right triangle? In this chapter, you will be working etensively
Name lass Date Trigonometric Ratios Going Deeper Essential question: How do you find the tangent, sine, and cosine ratios for acute angles in a right triangle? In this chapter, you will be working etensively
The Tangent Ratio K L M N O P Q
 9.4 The Tangent Ratio Essential Question How is a right triangle used to find the tangent of an acute angle? Is there a unique right triangle that must be used? et be a right triangle with acute. The tangent
9.4 The Tangent Ratio Essential Question How is a right triangle used to find the tangent of an acute angle? Is there a unique right triangle that must be used? et be a right triangle with acute. The tangent
Lesson 26 - Review of Right Triangle Trigonometry
 Lesson 26 - Review of Right Triangle Trigonometry PreCalculus Santowski PreCalculus - Santowski 1 (A) Review of Right Triangle Trig Trigonometry is the study and solution of Triangles. Solving a triangle
Lesson 26 - Review of Right Triangle Trigonometry PreCalculus Santowski PreCalculus - Santowski 1 (A) Review of Right Triangle Trig Trigonometry is the study and solution of Triangles. Solving a triangle
Pythagoras Theorem. Recall. Pythagoras theorem gives the relationship between the lengths of side in right angled triangles.
 Pythagoras Theorem Recall Pythagoras theorem gives the relationship between the lengths of side in right angled triangles. It is generally conveyed as follows: The square of the hypotenuse is equal to
Pythagoras Theorem Recall Pythagoras theorem gives the relationship between the lengths of side in right angled triangles. It is generally conveyed as follows: The square of the hypotenuse is equal to
Accel. Geometry - Concepts Similar Figures, Right Triangles, Trigonometry
 Accel. Geometry - Concepts 16-19 Similar Figures, Right Triangles, Trigonometry Concept 16 Ratios and Proportions (Section 7.1) Ratio: Proportion: Cross-Products Property If a b = c, then. d Properties
Accel. Geometry - Concepts 16-19 Similar Figures, Right Triangles, Trigonometry Concept 16 Ratios and Proportions (Section 7.1) Ratio: Proportion: Cross-Products Property If a b = c, then. d Properties
7.4. The Sine and Cosine Ratios. Investigate. Tools
 7.4 The Sine and osine Ratios We depend on ships and aircraft to transport goods and people all over the world. If you were the captain of a ship or the pilot of an airplane, how could you make sure that
7.4 The Sine and osine Ratios We depend on ships and aircraft to transport goods and people all over the world. If you were the captain of a ship or the pilot of an airplane, how could you make sure that
Practice For use with pages
 9.1 For use with pages 453 457 Find the square roots of the number. 1. 36. 361 3. 79 4. 1089 5. 4900 6. 10,000 Approimate the square root to the nearest integer. 7. 39 8. 85 9. 105 10. 136 11. 17.4 1.
9.1 For use with pages 453 457 Find the square roots of the number. 1. 36. 361 3. 79 4. 1089 5. 4900 6. 10,000 Approimate the square root to the nearest integer. 7. 39 8. 85 9. 105 10. 136 11. 17.4 1.
Math-2 Lesson 8-7: Unit 5 Review (Part -2)
 Math- Lesson 8-7: Unit 5 Review (Part -) Trigonometric Functions sin cos A A SOH-CAH-TOA Some old horse caught another horse taking oats away. opposite ( length ) o sin A hypotenuse ( length ) h SOH adjacent
Math- Lesson 8-7: Unit 5 Review (Part -) Trigonometric Functions sin cos A A SOH-CAH-TOA Some old horse caught another horse taking oats away. opposite ( length ) o sin A hypotenuse ( length ) h SOH adjacent
This simple one is based on looking at various sized right angled triangles with angles 37 (36á9 ), 53 (53á1 ) and 90.
 TRIGONOMETRY IN A RIGHT ANGLED TRIANGLE There are various ways of introducing Trigonometry, including the use of computers, videos and graphics calculators. This simple one is based on looking at various
TRIGONOMETRY IN A RIGHT ANGLED TRIANGLE There are various ways of introducing Trigonometry, including the use of computers, videos and graphics calculators. This simple one is based on looking at various
Investigating a Ratio in a Right Triangle. Leg opposite. Leg adjacent to A
 Name lass ate 13.1 Tangent atio Essential uestion: How do you find the tangent ratio for an acute angle? esource Locker Explore Investigating a atio in a ight Triangle In a given a right triangle,, with
Name lass ate 13.1 Tangent atio Essential uestion: How do you find the tangent ratio for an acute angle? esource Locker Explore Investigating a atio in a ight Triangle In a given a right triangle,, with
Review Journal 7 Page 57
 Student Checklist Unit 1 - Trigonometry 1 1A Prerequisites: I can use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve a missing side of a right triangle. Note p. 2 1B Prerequisites: I can convert within the imperial
Student Checklist Unit 1 - Trigonometry 1 1A Prerequisites: I can use the Pythagorean Theorem to solve a missing side of a right triangle. Note p. 2 1B Prerequisites: I can convert within the imperial
Name: Pythagorean Theorem February 3, 2014
 1. John leaves school to go home. He walks 6 blocks North and then 8 blocks west. How far is John from the school? 5. A 26 foot long ladder is leaning up against a house with its base 10 feet away from
1. John leaves school to go home. He walks 6 blocks North and then 8 blocks west. How far is John from the school? 5. A 26 foot long ladder is leaning up against a house with its base 10 feet away from
Mathematics Placement Assessment
 Mathematics Placement Assessment Courage, Humility, and Largeness of Heart Oldfields School Thank you for taking the time to complete this form accurately prior to returning this mathematics placement
Mathematics Placement Assessment Courage, Humility, and Largeness of Heart Oldfields School Thank you for taking the time to complete this form accurately prior to returning this mathematics placement
Geometry- Unit 6 Notes. Simplifying Radicals
 Geometry- Unit 6 Notes Name: Review: Evaluate the following WITHOUT a calculator. a) 2 2 b) 3 2 c) 4 2 d) 5 2 e) 6 2 f) 7 2 g) 8 2 h) 9 2 i) 10 2 j) 2 2 k) ( 2) 2 l) 2 0 Simplifying Radicals n r Example
Geometry- Unit 6 Notes Name: Review: Evaluate the following WITHOUT a calculator. a) 2 2 b) 3 2 c) 4 2 d) 5 2 e) 6 2 f) 7 2 g) 8 2 h) 9 2 i) 10 2 j) 2 2 k) ( 2) 2 l) 2 0 Simplifying Radicals n r Example
Assignment. Framing a Picture Similar and Congruent Polygons
 Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Framing a Picture Similar and Congruent Polygons Determine whether each pair of polygons is similar. If necessary, write the similarity statement. Determine
Assignment Assignment for Lesson.1 Name Date Framing a Picture Similar and Congruent Polygons Determine whether each pair of polygons is similar. If necessary, write the similarity statement. Determine
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry. TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator is required for this course.
 Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios
Summer Review for Students Entering Pre-Calculus with Trigonometry 1. Using Function Notation and Identifying Domain and Range 2. Multiplying Polynomials and Solving Quadratics 3. Solving with Trig Ratios
UNIT 5 TRIGONOMETRY Lesson 5.4: Calculating Sine, Cosine, and Tangent. Instruction. Guided Practice 5.4. Example 1
 Lesson : Calculating Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Guided Practice Example 1 Leo is building a concrete pathway 150 feet long across a rectangular courtyard, as shown in the following figure. What is the length
Lesson : Calculating Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Guided Practice Example 1 Leo is building a concrete pathway 150 feet long across a rectangular courtyard, as shown in the following figure. What is the length
Name Class Date. Essential question: How do you find the tangent, sine, and cosine ratios for acute angles in a right triangle?
 Name lass Date 8-2 Trigonometric Ratios Going Deeper Essential question: How do you find the tangent, sine, and cosine ratios for acute angles in a right triangle? In this chapter, you will be working
Name lass Date 8-2 Trigonometric Ratios Going Deeper Essential question: How do you find the tangent, sine, and cosine ratios for acute angles in a right triangle? In this chapter, you will be working
7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse
 7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse Remember what we know about a right triangle: In a right triangle, the square of the length of the is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths
7.1/7.2 Apply the Pythagorean Theorem and its Converse Remember what we know about a right triangle: In a right triangle, the square of the length of the is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths
Semester 2 Review Problems will be sectioned by chapters. The chapters will be in the order by which we covered them.
 Semester 2 Review Problems will be sectioned by chapters. The chapters will be in the order by which we covered them. Chapter 9 and 10: Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios 1. The hypotenuse of a right
Semester 2 Review Problems will be sectioned by chapters. The chapters will be in the order by which we covered them. Chapter 9 and 10: Right Triangles and Trigonometric Ratios 1. The hypotenuse of a right
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson 7.1
 Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Tangent Ratio Tangent Ratio, Cotangent Ratio, and Inverse Tangent Vocabulary Match each description to its corresponding term for triangle EFG. F
Skills Practice Skills Practice for Lesson.1 Name Date Tangent Ratio Tangent Ratio, Cotangent Ratio, and Inverse Tangent Vocabulary Match each description to its corresponding term for triangle EFG. F
MEP Practice Book ES4. b 4 2
 4 Trigonometr MEP Practice ook ES4 4.4 Sine, osine and Tangent 1. For each of the following triangles, all dimensions are in cm. Find the tangent ratio of the shaded angle. c b 4 f 4 1 k 5. Find each of
4 Trigonometr MEP Practice ook ES4 4.4 Sine, osine and Tangent 1. For each of the following triangles, all dimensions are in cm. Find the tangent ratio of the shaded angle. c b 4 f 4 1 k 5. Find each of
Three Angle Measure. Introduction to Trigonometry. LESSON 9.1 Assignment
 LESSON.1 Assignment Name Date Three Angle Measure Introduction to Trigonometry 1. Analyze triangle A and triangle DEF. Use /A and /D as the reference angles. E 7.0 cm 10.5 cm A 35 10.0 cm D 35 15.0 cm
LESSON.1 Assignment Name Date Three Angle Measure Introduction to Trigonometry 1. Analyze triangle A and triangle DEF. Use /A and /D as the reference angles. E 7.0 cm 10.5 cm A 35 10.0 cm D 35 15.0 cm
Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall Nov.4/5 The Pythagorean Theorem
 1 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall 2014 - Nov.4/5 The Pythagorean Theorem Introduction A right triangle is any triangle
1 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 7/8 Math Circles Fall 2014 - Nov.4/5 The Pythagorean Theorem Introduction A right triangle is any triangle
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS through 2.1.4
 SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 2.1.2 through 2.1.4 Students used the equation = m + b to graph lines and describe patterns in previous courses. Lesson 2.1.1 is a review. When the equation of a line is written
SLOPE A MEASURE OF STEEPNESS 2.1.2 through 2.1.4 Students used the equation = m + b to graph lines and describe patterns in previous courses. Lesson 2.1.1 is a review. When the equation of a line is written
Date. Refraction. What do you think is happening in the above photo and why? Key words Reflection Reflected Ray Incident Ray Normal Refraction Convex
 Refraction Date Key words Reflection Reflected Ray Incident Ray Normal Refraction Convex What do you think is happening in the above photo and why? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o08jgkut7e8 Refraction
Refraction Date Key words Reflection Reflected Ray Incident Ray Normal Refraction Convex What do you think is happening in the above photo and why? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=o08jgkut7e8 Refraction
Parallel Lines Investigation
 Year 9 - The Maths Knowledge Autumn 1 (x, y) Along the corridor, up the stairs (3,1) x = 3 Gradient (-5,-2) (0,0) y-intercept Vertical lines are always x = y = 6 Horizontal lines are always y = Parallel
Year 9 - The Maths Knowledge Autumn 1 (x, y) Along the corridor, up the stairs (3,1) x = 3 Gradient (-5,-2) (0,0) y-intercept Vertical lines are always x = y = 6 Horizontal lines are always y = Parallel
4. Describe the correlation shown by the scatter plot. 8. Find the distance between the lines with the equations and.
 Integrated Math III Summer Review Packet DUE THE FIRST DAY OF SCHOOL The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous mathematics courses that are essential to your success
Integrated Math III Summer Review Packet DUE THE FIRST DAY OF SCHOOL The problems in this packet are designed to help you review topics from previous mathematics courses that are essential to your success
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 3 - Foundations 7. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: Class: Date: Chapter 3 - Foundations 7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the value of tan 59, to four decimal places. a.
Name: Class: Date: Chapter 3 - Foundations 7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Determine the value of tan 59, to four decimal places. a.
Packet Unit 5 Trigonometry Honors Math 2 17
 Packet Unit 5 Trigonometry Honors Math 2 17 Homework Day 12 Part 1 Cumulative Review of this unit Show ALL work for the following problems! Use separate paper, if needed. 1) If AC = 34, AB = 16, find sin
Packet Unit 5 Trigonometry Honors Math 2 17 Homework Day 12 Part 1 Cumulative Review of this unit Show ALL work for the following problems! Use separate paper, if needed. 1) If AC = 34, AB = 16, find sin
Preparing for AS Level Further Mathematics
 Preparing for AS Level Further Mathematics Algebraic skills are incredibly important in the study of further mathematics at AS and A level. You should therefore make sure you are confident with all of
Preparing for AS Level Further Mathematics Algebraic skills are incredibly important in the study of further mathematics at AS and A level. You should therefore make sure you are confident with all of
Chapter 2: Trigonometry
 What You Will Learn hapter 2: Trigonometry In a right triangle, The ratio of any two sides remains constant even if the triangle is enlarged or reduced. You can use the ratio of the lengths of two sides
What You Will Learn hapter 2: Trigonometry In a right triangle, The ratio of any two sides remains constant even if the triangle is enlarged or reduced. You can use the ratio of the lengths of two sides
Chapter 8 Diagnostic Test
 Chapter 8 Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 422 455 1. Determine the measures of the indicated angles in each diagram. b) 2. Determine the value of each trigonometric ratio to four decimal places. sin
Chapter 8 Diagnostic Test STUDENT BOOK PAGES 422 455 1. Determine the measures of the indicated angles in each diagram. b) 2. Determine the value of each trigonometric ratio to four decimal places. sin
Inequalities in Triangles Geometry 5-5
 Inequalities in Triangles Geometry 5-5 Name: ate: Period: Theorem 5-10 Theorem 5-11 If two sides of a triangle are not If two angles of a triangle are not congruent, then the larger angle congruent, then
Inequalities in Triangles Geometry 5-5 Name: ate: Period: Theorem 5-10 Theorem 5-11 If two sides of a triangle are not If two angles of a triangle are not congruent, then the larger angle congruent, then
Exercise 1. Exercise 2. MAT 012 SS218 Worksheet 9 Sections Name: Consider the triangle drawn below. C. c a. A b
 Consider the triangle drawn below. C Exercise 1 c a A b B 1. Suppose a = 5 and b = 12. Find c, and then find sin( A), cos( A), tan( A), sec( A), csc( A), and cot( A). 2. Now suppose a = 10 and b = 24.
Consider the triangle drawn below. C Exercise 1 c a A b B 1. Suppose a = 5 and b = 12. Find c, and then find sin( A), cos( A), tan( A), sec( A), csc( A), and cot( A). 2. Now suppose a = 10 and b = 24.
Following are the solutions for the Shop Math Quiz found in the September issue of Tooling & Production magazine s Shop Talk with Steve Rose.
 RTSI Quiz Solutions Following are the solutions for the Shop Math Quiz found in the September issue of Tooling & Production magazine s Shop Talk with Steve Rose. 1. What is the decimal equivalent of 27/40?
RTSI Quiz Solutions Following are the solutions for the Shop Math Quiz found in the September issue of Tooling & Production magazine s Shop Talk with Steve Rose. 1. What is the decimal equivalent of 27/40?
RIGHT TRIANGLES. Dates, assignments, and quizzes subject to change without advance notice. Monday Tuesday Block Day Friday
 Name: Period RIGHT TRIANGLES I can define, identify and illustrate the following terms: Square root radicals Rationalize Pythagorean Theorem Special Right Triangles Sine Cosine Tangent θ (Theta) Angle
Name: Period RIGHT TRIANGLES I can define, identify and illustrate the following terms: Square root radicals Rationalize Pythagorean Theorem Special Right Triangles Sine Cosine Tangent θ (Theta) Angle
Distance in Coordinate Geometry
 Page 1 of 6 L E S S O N 9.5 We talk too much; we should talk less and draw more. Distance in Coordinate Geometry Viki is standing on the corner of Seventh Street and 8th Avenue, and her brother Scott is
Page 1 of 6 L E S S O N 9.5 We talk too much; we should talk less and draw more. Distance in Coordinate Geometry Viki is standing on the corner of Seventh Street and 8th Avenue, and her brother Scott is
5.6 More Than Right. A Develop Understanding Task
 MODELING WITH GEOMETRY 5.6 5.6 More Than Right A Develop Understanding Task We can use right triangle trigonometry and the Pythagorean theorem to solve for missing sides and angles in a right triangle.
MODELING WITH GEOMETRY 5.6 5.6 More Than Right A Develop Understanding Task We can use right triangle trigonometry and the Pythagorean theorem to solve for missing sides and angles in a right triangle.
Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry
 Lesson 1: Incredibly Useful Ratios Opening Exercise Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry Use right triangle ΔABC to answer 1 3. 1. Name the side of the triangle opposite A in two different ways. 2. Name
Lesson 1: Incredibly Useful Ratios Opening Exercise Unit 6 Introduction to Trigonometry Use right triangle ΔABC to answer 1 3. 1. Name the side of the triangle opposite A in two different ways. 2. Name
Math 1201 Chapter 2 Review
 ath 1201 hapter 2 Review ultiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. etermine tan and tan. 8 10 a. tan = 1.25; tan = 0.8 c. tan = 0.8; tan = 1.25 b.
ath 1201 hapter 2 Review ultiple hoice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. etermine tan and tan. 8 10 a. tan = 1.25; tan = 0.8 c. tan = 0.8; tan = 1.25 b.
