Lecture Overview. Readings. Recall: Binary Search Trees (BSTs) The importance of being balanced. AVL trees. Balance Insert. Other balanced trees
|
|
|
- Nelson Riley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 alanced inar Search Trees Lecture Overview The importance of being balanced VL trees Definition alance Insert Other balanced trees Data structures in general Readings LRS hapter. and. (but different approach: red-blac trees) Recall: inar Search Trees (STs) rooted binar tree each node has e left pointer right pointer parent pointer See Fig Figure : Heights of nodes in a ST
2 Figure : ST propert ST propert (see Fig. ). height of node = length ( edges) of longest downward path to a leaf (see LRS.5 for details). The Importance of eing alanced: STs support insert, min, delete, ran, etc. in O(h) time, where h = height of tree (= height of root). h is between lg(n) and n: Fig. ). vs. Perfectl alanced Path Figure : alancing STs balanced ST maintains h = O(lg n) all operations run in O(lg n) time.
3 Lecture 4 alanced inar Search Trees Spring 008 VL Trees: Definition VL trees are self-balancing binar search trees. These trees are named after their two inventors G.M. del son-vel sii and E.M. Landis n VL tree is one that requires heights of left and right children of ever node to differ b at most ±. This is illustrated in Fig. 4) - Figure 4: VL Tree oncept In order to implement an VL tree, follow two critical steps: Treat nil tree as height. Each node stores its height. This is inherentl a DT STRUTURE UGMENTTION procedure, similar to augmenting subtree size. lternativel, one can just store difference in heights. good animation applet for VL trees is available at this lin. To compare inar Search Trees and VL balancing of trees use code provided here. Original Russian article: delson-velsii, G.; E. M. Landis (96). n algorithm for the organization of information. Proceedings of the USSR cadem of Sciences 46: 666. (English translation b Mron J. Ricci in Soviet Math. Dolad, :596, 96.)
4 Lecture 4 alanced inar Search Trees Spring 008 alance: The balance is the worst when ever node differs b. Let N h = min ( nodes). N h = N h + N h + lternativel: > N h N h > h/ = h < lg h N h > F n (n th Fibonacci number) In fact,n h = F n+ (simple induction) h F h = 5 (rounded to nearest integer) + 5 where =.68 = mah log (n).440 lg(n) (golden ratio) VL Insert:. insert as in simple ST. wor our wa up tree, restoring VL propert (and updating heights as ou go). Each Step: suppose is lowest node violating VL assume is right-heav (left case smmetric) if s right child is right-heav or balanced: follow steps in Fig. 5 else follow steps in Fig. 6 then continue up to s grandparent, greatgrandparent... 4
5 Lecture 4 alanced inar Search Trees Spring Left-Rotate() z + Left-Rotate() + - Figure 5: VL Insert alancing + Right-Rotate(z) - z + Left-Rotate() z D or - D - - or - Figure 6: VL Insert alancing 5
6 Lecture 4 alanced inar Search Trees Spring 008 Eample: n eample implementation of the VL Insert process is illustrated in Fig. 7 Insert() 4 = 9: left-left case Done 4 6 Insert(55) =: left-right case 4 Done Figure 7: Illustration of VL Tree Insert Process omment. In general, process ma need several rotations before an Insert is completed. omment. Delete(-min) harder but possible. 6
7 Lecture 4 alanced inar Search Trees Spring 008 alanced Search Trees: There are man balanced search trees. VL Trees del son-velsii and Landis 96 -Trees/--4 Trees aer and Mcreight 97 (see LRS 8) [α] Trees Nievergelt and Reingold 97 Red-blac Trees LRS hapter Spla-Trees Sleator and Tarjan 985 Sip Lists Pugh 989 Scapegoat Trees Galperin and Rivest 99 Treaps Seidel and ragon 996 Note. Sip Lists and Treaps use random numbers to mae decisions fast with high probabilit. Note. Spla Trees and Scapegoat Trees are amortized : adding up costs for several operations = fast on average. 7
8 Lecture 4 alanced inar Search Trees Spring 008 Spla Trees Upon access (search or insert), move node to root b sequence of rotations and/or doublerotations (just lie VL trees). Height can be linear but still O(lg n) per operation on average (amortized) Note: We will see more on amortization in a couple of lectures. Optimalit For STs, cannot do better than O(lg n) per search in worst case. In some cases, can do better e.g. in-order traversal taes Θ(n) time for n elements. put more frequent items near root onjecture: Spla trees are O(best ST) for ever access pattern. With fancier trics, can achieve O(lg lg u) performance for integers u [Van Ernde oas; see or 6.85 (dvanced Data Structures)] ig Picture: bstract Data Tpe(DT): interface spec. e.g. Priorit Queue: Q = new-empt-queue() Q.insert() = Q.deletemin() vs. Data Structure (DS): algorithm for each op. There are man possible DSs for one DT. One eample that we will discuss much later in the course is the heap priorit queue. 8
AVL Trees. Version of September 6, AVL Trees Version of September 6, / 22
 VL Trees Version of September 6, 6 VL Trees Version of September 6, 6 / inary Search Trees x 8 4 4 < x > x 7 9 3 inary-search-tree property For every node x ll eys in its left subtree are smaller than
VL Trees Version of September 6, 6 VL Trees Version of September 6, 6 / inary Search Trees x 8 4 4 < x > x 7 9 3 inary-search-tree property For every node x ll eys in its left subtree are smaller than
Advanced Tree Structures
 Data Structure hapter 13 dvanced Tree Structures Dr. Patrick han School of omputer Science and Engineering South hina Universit of Technolog utline VL Tree (h 13..1) Interval Heap ST Recall, inar Search
Data Structure hapter 13 dvanced Tree Structures Dr. Patrick han School of omputer Science and Engineering South hina Universit of Technolog utline VL Tree (h 13..1) Interval Heap ST Recall, inar Search
Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
AVL Trees. Reading: 9.2
 AVL Trees Reading: 9.2 Balance Factor of a Node The difference in height of its two subtrees (h R -h L ) Balanced Node if -1 BF 1 Unbalanced Node if BF 1 h L h R Balance Factor of a Binar Tree Corresponds
AVL Trees Reading: 9.2 Balance Factor of a Node The difference in height of its two subtrees (h R -h L ) Balanced Node if -1 BF 1 Unbalanced Node if BF 1 h L h R Balance Factor of a Binar Tree Corresponds
CS 380 ALGORITHM DESIGN AND ANALYSIS
 CS 380 ALGORITHM DESIGN AND ANALYSIS Lecture 12: Red-Black Trees Text Reference: Chapters 12, 13 Binary Search Trees (BST): Review Each node in tree T is a object x Contains attributes: Data Pointers to
CS 380 ALGORITHM DESIGN AND ANALYSIS Lecture 12: Red-Black Trees Text Reference: Chapters 12, 13 Binary Search Trees (BST): Review Each node in tree T is a object x Contains attributes: Data Pointers to
Splay Trees. Splay Trees 1
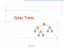 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
CSC 263 Lecture 4. September 13, 2006
 S 263 Lecture 4 September 13, 2006 7 ugmenting Red-lack Trees 7.1 Introduction Suppose that ou are asked to implement an DT that is the same as a dictionar but has one additional operation: operation:
S 263 Lecture 4 September 13, 2006 7 ugmenting Red-lack Trees 7.1 Introduction Suppose that ou are asked to implement an DT that is the same as a dictionar but has one additional operation: operation:
Splay Trees Goodrich, Tamassia, Dickerson. Splay Trees 1
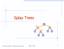 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: entries stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored
Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: entries stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored
Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS )
 Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu October 08, 2014 1 Outline of Today s Class 2 Traversals Querying Insertion and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 3 Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu October 08, 2014 1 Outline of Today s Class 2 Traversals Querying Insertion and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 3 Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Search Trees. Undirected graph Directed graph Tree Binary search tree
 Search Trees Undirected graph Directed graph Tree Binary search tree 1 Binary Search Tree Binary search key property: Let x be a node in a binary search tree. If y is a node in the left subtree of x, then
Search Trees Undirected graph Directed graph Tree Binary search tree 1 Binary Search Tree Binary search key property: Let x be a node in a binary search tree. If y is a node in the left subtree of x, then
Binary Heaps in Dynamic Arrays
 Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland We have already learned that the binary heap serves as an efficient implementation of a priority queue. Our previous discussion was based on pointers (for getting
Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland We have already learned that the binary heap serves as an efficient implementation of a priority queue. Our previous discussion was based on pointers (for getting
Splay Trees 3/20/14. Splay Trees. Splay Trees are Binary Search Trees. note that two keys of equal value may be wellseparated (7,T) (1,Q) (1,C) (5,H)
 Spla Trees 3/20/14 Presentation for use with the tetbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, b M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wile, 2014 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 2013
Spla Trees 3/20/14 Presentation for use with the tetbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, b M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wile, 2014 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 2013
Comparisons. Θ(n 2 ) Θ(n) Sorting Revisited. So far we talked about two algorithms to sort an array of numbers. What is the advantage of merge sort?
 So far we have studied: Comparisons Insertion Sort Merge Sort Worst case Θ(n 2 ) Θ(nlgn) Best case Θ(n) Θ(nlgn) Sorting Revisited So far we talked about two algorithms to sort an array of numbers What
So far we have studied: Comparisons Insertion Sort Merge Sort Worst case Θ(n 2 ) Θ(nlgn) Best case Θ(n) Θ(nlgn) Sorting Revisited So far we talked about two algorithms to sort an array of numbers What
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS. Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap Summary of the previous lecture TREE is hierarchical (non linear) data structure Binary trees Definitions Full tree,
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS Hierarchical data structures: AVL tree, Bayer tree, Heap Summary of the previous lecture TREE is hierarchical (non linear) data structure Binary trees Definitions Full tree,
Comparisons. Heaps. Heaps. Heaps. Sorting Revisited. Heaps. So far we talked about two algorithms to sort an array of numbers
 So far we have studied: Comparisons Tree is completely filled on all levels except possibly the lowest, which is filled from the left up to a point Insertion Sort Merge Sort Worst case Θ(n ) Θ(nlgn) Best
So far we have studied: Comparisons Tree is completely filled on all levels except possibly the lowest, which is filled from the left up to a point Insertion Sort Merge Sort Worst case Θ(n ) Θ(nlgn) Best
B Tree. Also, every non leaf node must have at least two successors and all leaf nodes must be at the same level.
 B Tree If there is just one item in the node, then the B Tree is organised as a binar search tree: all items in the left sub tree must be less than the item in the node, and all items in the right sub
B Tree If there is just one item in the node, then the B Tree is organised as a binar search tree: all items in the left sub tree must be less than the item in the node, and all items in the right sub
CPSC 223 Algorithms & Data Abstract Structures
 PS 223 lgorithms & ata bstract Structures Lecture 17: Self-alancing inary Search Trees * Material adapted from. arrano, K. Yerion, and K. ant Today Quiz alanced inary Search Trees (STs) Quick review of
PS 223 lgorithms & ata bstract Structures Lecture 17: Self-alancing inary Search Trees * Material adapted from. arrano, K. Yerion, and K. ant Today Quiz alanced inary Search Trees (STs) Quick review of
Binary search trees. Binary search trees are data structures based on binary trees that support operations on dynamic sets.
 COMP3600/6466 Algorithms 2018 Lecture 12 1 Binary search trees Reading: Cormen et al, Sections 12.1 to 12.3 Binary search trees are data structures based on binary trees that support operations on dynamic
COMP3600/6466 Algorithms 2018 Lecture 12 1 Binary search trees Reading: Cormen et al, Sections 12.1 to 12.3 Binary search trees are data structures based on binary trees that support operations on dynamic
A red-black tree is a balanced binary search tree with the following properties:
 Binary search trees work best when they are balanced or the path length from root to any leaf is within some bounds. The red-black tree algorithm is a method for balancing trees. The name derives from
Binary search trees work best when they are balanced or the path length from root to any leaf is within some bounds. The red-black tree algorithm is a method for balancing trees. The name derives from
Section 4 SOLUTION: AVL Trees & B-Trees
 Section 4 SOLUTION: AVL Trees & B-Trees 1. What 3 properties must an AVL tree have? a. Be a binary tree b. Have Binary Search Tree ordering property (left children < parent, right children > parent) c.
Section 4 SOLUTION: AVL Trees & B-Trees 1. What 3 properties must an AVL tree have? a. Be a binary tree b. Have Binary Search Tree ordering property (left children < parent, right children > parent) c.
Sorted Arrays. Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min
 Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Balanced search trees
 Balanced search trees Ordinary binary search trees have expected height Θ(log n) if items are inserted and deleted in random order, but for other orders the height can be Θ(n). This is undesirable, since
Balanced search trees Ordinary binary search trees have expected height Θ(log n) if items are inserted and deleted in random order, but for other orders the height can be Θ(n). This is undesirable, since
CPSC 223 Algorithms & Data Abstract Structures
 PS 223 lgorithms & Data bstract Structures Lecture 18: VL Trees (cont.) Today In-place mergesort Midterm overview VL Trees (cont.) [h 12: pp. 681-686] Heapsort exercise 1 Midterm Overview Midterm There
PS 223 lgorithms & Data bstract Structures Lecture 18: VL Trees (cont.) Today In-place mergesort Midterm overview VL Trees (cont.) [h 12: pp. 681-686] Heapsort exercise 1 Midterm Overview Midterm There
Properties of red-black trees
 Red-Black Trees Introduction We have seen that a binary search tree is a useful tool. I.e., if its height is h, then we can implement any basic operation on it in O(h) units of time. The problem: given
Red-Black Trees Introduction We have seen that a binary search tree is a useful tool. I.e., if its height is h, then we can implement any basic operation on it in O(h) units of time. The problem: given
Red-Black Trees. Based on materials by Dennis Frey, Yun Peng, Jian Chen, and Daniel Hood
 Red-Black Trees Based on materials by Dennis Frey, Yun Peng, Jian Chen, and Daniel Hood Quick Review of Binary Search Trees n Given a node n... q All elements of n s left subtree are less than n.data q
Red-Black Trees Based on materials by Dennis Frey, Yun Peng, Jian Chen, and Daniel Hood Quick Review of Binary Search Trees n Given a node n... q All elements of n s left subtree are less than n.data q
Lecture: Analysis of Algorithms (CS )
 Lecture: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu Fall 2017 1 Binary Search Trees Traversals, Querying, Insertion, and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 2 Example: Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Lecture: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu Fall 2017 1 Binary Search Trees Traversals, Querying, Insertion, and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 2 Example: Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Binary Trees. Binary Search Trees
 Binar Trees A binar tree is a rooted tree where ever node has at most two children. When a node has onl one child, we still distinguish whether this is the left child or the right child of the parent.
Binar Trees A binar tree is a rooted tree where ever node has at most two children. When a node has onl one child, we still distinguish whether this is the left child or the right child of the parent.
Overview of Presentation. Heapsort. Heap Properties. What is Heap? Building a Heap. Two Basic Procedure on Heap
 Heapsort Submitted by : Hardik Parikh(hjp0608) Soujanya Soni (sxs3298) Overview of Presentation Heap Definition. Adding a Node. Removing a Node. Array Implementation. Analysis What is Heap? A Heap is a
Heapsort Submitted by : Hardik Parikh(hjp0608) Soujanya Soni (sxs3298) Overview of Presentation Heap Definition. Adding a Node. Removing a Node. Array Implementation. Analysis What is Heap? A Heap is a
Quiz 1 Solutions. (a) f(n) = n g(n) = log n Circle all that apply: f = O(g) f = Θ(g) f = Ω(g)
 Introduction to Algorithms March 11, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Spring 2009 Professors Sivan Toledo and Alan Edelman Quiz 1 Solutions Problem 1. Quiz 1 Solutions Asymptotic orders
Introduction to Algorithms March 11, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Spring 2009 Professors Sivan Toledo and Alan Edelman Quiz 1 Solutions Problem 1. Quiz 1 Solutions Asymptotic orders
CSE2331/5331. Topic 6: Binary Search Tree. Data structure Operations CSE 2331/5331
 CSE2331/5331 Topic 6: Binary Search Tree Data structure Operations Set Operations Maximum Extract-Max Insert Increase-key We can use priority queue (implemented by heap) Search Delete Successor Predecessor
CSE2331/5331 Topic 6: Binary Search Tree Data structure Operations Set Operations Maximum Extract-Max Insert Increase-key We can use priority queue (implemented by heap) Search Delete Successor Predecessor
Algorithms. AVL Tree
 Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees
 Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2015) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction Binar search trees are an ecellent data structure to implement associative arras, maps,
Lecture 16 Notes AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2015) Frank Pfenning 1 Introduction Binar search trees are an ecellent data structure to implement associative arras, maps,
CS Transform-and-Conquer
 CS483-11 Transform-and-Conquer Instructor: Fei Li Room 443 ST II Office hours: Tue. & Thur. 1:30pm - 2:30pm or by appointments lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS483 http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ lifei/teaching/cs483_fall07/
CS483-11 Transform-and-Conquer Instructor: Fei Li Room 443 ST II Office hours: Tue. & Thur. 1:30pm - 2:30pm or by appointments lifei@cs.gmu.edu with subject: CS483 http://www.cs.gmu.edu/ lifei/teaching/cs483_fall07/
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees
 Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Trees. Prof. Dr. Debora Weber-Wulff
 Trees Prof. Dr. Debora Weber-Wulff Flickr, _marmota, 2007 Major Sources Michell Waite & Robert Lafore, Data Structures & Algorithms in Java Michael T. Goodrich and Roberto Tamassia Data Structures and
Trees Prof. Dr. Debora Weber-Wulff Flickr, _marmota, 2007 Major Sources Michell Waite & Robert Lafore, Data Structures & Algorithms in Java Michael T. Goodrich and Roberto Tamassia Data Structures and
Splay Trees. (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 27
 Splay Trees (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 27 Basic Idea Invented by Sleator and Tarjan (1985) Blind rebalancing no height info kept! Worst-case time per operation is O(n)
Splay Trees (Splay Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2017 1 / 27 Basic Idea Invented by Sleator and Tarjan (1985) Blind rebalancing no height info kept! Worst-case time per operation is O(n)
Outline. Definition. 2 Height-Balance. 3 Searches. 4 Rotations. 5 Insertion. 6 Deletions. 7 Reference. 1 Every node is either red or black.
 Outline 1 Definition Computer Science 331 Red-Black rees Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lectures #20-22 2 Height-Balance 3 Searches 4 Rotations 5 s: Main Case 6 Partial
Outline 1 Definition Computer Science 331 Red-Black rees Mike Jacobson Department of Computer Science University of Calgary Lectures #20-22 2 Height-Balance 3 Searches 4 Rotations 5 s: Main Case 6 Partial
CISC 235: Topic 4. Balanced Binary Search Trees
 CISC 235: Topic 4 Balanced Binary Search Trees Outline Rationale and definitions Rotations AVL Trees, Red-Black, and AA-Trees Algorithms for searching, insertion, and deletion Analysis of complexity CISC
CISC 235: Topic 4 Balanced Binary Search Trees Outline Rationale and definitions Rotations AVL Trees, Red-Black, and AA-Trees Algorithms for searching, insertion, and deletion Analysis of complexity CISC
Lecture 5: Sorting Part A
 Lecture 5: Sorting Part A Heapsort Running time O(n lg n), like merge sort Sorts in place (as insertion sort), only constant number of array elements are stored outside the input array at any time Combines
Lecture 5: Sorting Part A Heapsort Running time O(n lg n), like merge sort Sorts in place (as insertion sort), only constant number of array elements are stored outside the input array at any time Combines
Lecture Notes on AVL Trees
 Lecture Notes on AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 19 March 28, 2013 1 Introduction Binar search trees are an ecellent data structure to implement associative
Lecture Notes on AVL Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation Frank Pfenning Lecture 19 March 28, 2013 1 Introduction Binar search trees are an ecellent data structure to implement associative
Trees. Eric McCreath
 Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Trees Eric McCreath 2 Overview In this lecture we will explore: general trees, binary trees, binary search trees, and AVL and B-Trees. 3 Trees Trees are recursive data structures. They are useful for:
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees
 Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
Dynamic Access Binary Search Trees 1 * are self-adjusting binary search trees in which the shape of the tree is changed based upon the accesses performed upon the elements. When an element of a splay tree
How much space does this routine use in the worst case for a given n? public static void use_space(int n) { int b; int [] A;
![How much space does this routine use in the worst case for a given n? public static void use_space(int n) { int b; int [] A; How much space does this routine use in the worst case for a given n? public static void use_space(int n) { int b; int [] A;](/thumbs/82/85312801.jpg) How much space does this routine use in the worst case for a given n? public static void use_space(int n) { int b; int [] A; } if (n
How much space does this routine use in the worst case for a given n? public static void use_space(int n) { int b; int [] A; } if (n
13.4 Deletion in red-black trees
 The operation of Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to the operation of Insertion on the tree. That is, apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees to delete a node z; apply node color changes
The operation of Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to the operation of Insertion on the tree. That is, apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees to delete a node z; apply node color changes
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 13: Index structure. The Lecture Contains: Index structure. Binary search tree (BST) B-tree. B+-tree.
 The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
ECE 242 Data Structures and Algorithms. Trees IV. Lecture 21. Prof.
 ECE 22 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece22/ Trees IV Lecture 2 Prof. Eric Polizzi Summary previous lectures Implementations BST 5 5 7 null 8 null null 7 null
ECE 22 Data Structures and Algorithms http://www.ecs.umass.edu/~polizzi/teaching/ece22/ Trees IV Lecture 2 Prof. Eric Polizzi Summary previous lectures Implementations BST 5 5 7 null 8 null null 7 null
Lesson 21: AVL Trees. Rotation
 The time required to perform operations on a binary search tree is proportional to the length of the path from root to leaf. This isn t bad in a well-balanced tree. But nothing prevents a tree from becoming
The time required to perform operations on a binary search tree is proportional to the length of the path from root to leaf. This isn t bad in a well-balanced tree. But nothing prevents a tree from becoming
Partha Sarathi Manal
 MA 515: Introduction to Algorithms & MA353 : Design and Analysis of Algorithms [3-0-0-6] Lecture 11 http://www.iitg.ernet.in/psm/indexing_ma353/y09/index.html Partha Sarathi Manal psm@iitg.ernet.in Dept.
MA 515: Introduction to Algorithms & MA353 : Design and Analysis of Algorithms [3-0-0-6] Lecture 11 http://www.iitg.ernet.in/psm/indexing_ma353/y09/index.html Partha Sarathi Manal psm@iitg.ernet.in Dept.
Balanced Binary Search Trees
 Balanced Binary Search Trees In the previous section we looked at building a binary search tree. As we learned, the performance of the binary search tree can degrade to O(n) for operations like getand
Balanced Binary Search Trees In the previous section we looked at building a binary search tree. As we learned, the performance of the binary search tree can degrade to O(n) for operations like getand
Data Structure. Chapter 10 Search Structures (Part II)
 Data Structure Chapter 1 Search Structures (Part II) Instructor: ngela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 29 Spring Outline VL trees Introduction
Data Structure Chapter 1 Search Structures (Part II) Instructor: ngela Chih-Wei Tang Department of Communication Engineering National Central University Jhongli, Taiwan 29 Spring Outline VL trees Introduction
CS711008Z Algorithm Design and Analysis
 CS700Z Algorithm Design and Analysis Lecture 7 Binary heap, binomial heap, and Fibonacci heap Dongbo Bu Institute of Computing Technology Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China 1 / Outline Introduction
CS700Z Algorithm Design and Analysis Lecture 7 Binary heap, binomial heap, and Fibonacci heap Dongbo Bu Institute of Computing Technology Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China 1 / Outline Introduction
Algorithms. Red-Black Trees
 Algorithms Red-Black Trees Red-Black Trees Balanced binary search trees guarantee an O(log n) running time Red-black-tree Binary search tree with an additional attribute for its nodes: color which can
Algorithms Red-Black Trees Red-Black Trees Balanced binary search trees guarantee an O(log n) running time Red-black-tree Binary search tree with an additional attribute for its nodes: color which can
CS711008Z Algorithm Design and Analysis
 CS711008Z Algorithm Design and Analysis Lecture 7. Binary heap, binomial heap, and Fibonacci heap Dongbo Bu Institute of Computing Technology Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China 1 / 108 Outline
CS711008Z Algorithm Design and Analysis Lecture 7. Binary heap, binomial heap, and Fibonacci heap Dongbo Bu Institute of Computing Technology Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China 1 / 108 Outline
CSE 548: Analysis of Algorithms. Lectures 14 & 15 ( Dijkstra s SSSP & Fibonacci Heaps )
 CSE 548: Analysis of Algorithms Lectures 14 & 15 ( Dijkstra s SSSP & Fibonacci Heaps ) Rezaul A. Chowdhury Department of Computer Science SUNY Stony Brook Fall 2012 Fibonacci Heaps ( Fredman & Tarjan,
CSE 548: Analysis of Algorithms Lectures 14 & 15 ( Dijkstra s SSSP & Fibonacci Heaps ) Rezaul A. Chowdhury Department of Computer Science SUNY Stony Brook Fall 2012 Fibonacci Heaps ( Fredman & Tarjan,
Red-Black-Trees and Heaps in Timestamp-Adjusting Sweepline Based Algorithms
 Department of Informatics, University of Zürich Vertiefungsarbeit Red-Black-Trees and Heaps in Timestamp-Adjusting Sweepline Based Algorithms Mirko Richter Matrikelnummer: 12-917-175 Email: mirko.richter@uzh.ch
Department of Informatics, University of Zürich Vertiefungsarbeit Red-Black-Trees and Heaps in Timestamp-Adjusting Sweepline Based Algorithms Mirko Richter Matrikelnummer: 12-917-175 Email: mirko.richter@uzh.ch
9. Which situation is true regarding a cascading cut that produces c trees for a Fibonacci heap?
 1 1 Name Test 1 - Closed Book Student ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each 1. During which operation on a leftist heap may subtree swaps be needed? A. DECREASE-KEY
1 1 Name Test 1 - Closed Book Student ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each 1. During which operation on a leftist heap may subtree swaps be needed? A. DECREASE-KEY
Balanced Search Trees. CS 3110 Fall 2010
 Balanced Search Trees CS 3110 Fall 2010 Some Search Structures Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Balanced Search Trees CS 3110 Fall 2010 Some Search Structures Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Lecture 5: Scheduling and Binary Search Trees
 Lecture 5: Scheduling and Binary Search Trees Lecture Overview Runway reservation system Definition How to solve with lists Binary Search Trees Readings Operations CLRS Chapter 10, 12.1-3 Runway Reservation
Lecture 5: Scheduling and Binary Search Trees Lecture Overview Runway reservation system Definition How to solve with lists Binary Search Trees Readings Operations CLRS Chapter 10, 12.1-3 Runway Reservation
A data structure and associated algorithms, NOT GARBAGE COLLECTION
 CS4 Lecture Notes /30/0 Heaps, Heapsort, Priority Queues Sorting problem so far: Heap: Insertion Sort: In Place, O( n ) worst case Merge Sort : Not in place, O( n lg n) worst case Quicksort : In place,
CS4 Lecture Notes /30/0 Heaps, Heapsort, Priority Queues Sorting problem so far: Heap: Insertion Sort: In Place, O( n ) worst case Merge Sort : Not in place, O( n lg n) worst case Quicksort : In place,
Recall from Last Time: AVL Trees
 CSE 326 Lecture 8: Getting to now AVL Trees Today s Topics: Balanced Search Trees AVL Trees and Rotations Splay trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Recall from Last Time: AVL Trees AVL trees are height-balanced
CSE 326 Lecture 8: Getting to now AVL Trees Today s Topics: Balanced Search Trees AVL Trees and Rotations Splay trees Covered in Chapter 4 of the text Recall from Last Time: AVL Trees AVL trees are height-balanced
Binary search trees 3. Binary search trees. Binary search trees 2. Reading: Cormen et al, Sections 12.1 to 12.3
 Binary search trees Reading: Cormen et al, Sections 12.1 to 12.3 Binary search trees 3 Binary search trees are data structures based on binary trees that support operations on dynamic sets. Each element
Binary search trees Reading: Cormen et al, Sections 12.1 to 12.3 Binary search trees 3 Binary search trees are data structures based on binary trees that support operations on dynamic sets. Each element
BM267 - Introduction to Data Structures
 BM267 - Introduction to Data Structures 9. Heapsort Ankara University Computer Engineering Department Bulent Tugrul BLM 267 1 (Binary) Heap Structure The heap data structure is an array organized as a
BM267 - Introduction to Data Structures 9. Heapsort Ankara University Computer Engineering Department Bulent Tugrul BLM 267 1 (Binary) Heap Structure The heap data structure is an array organized as a
Sorting and Searching
 Sorting and Searching Lecture 2: Priority Queues, Heaps, and Heapsort Lecture 2: Priority Queues, Heaps, and Heapsort Sorting and Searching 1 / 24 Priority Queue: Motivating Example 3 jobs have been submitted
Sorting and Searching Lecture 2: Priority Queues, Heaps, and Heapsort Lecture 2: Priority Queues, Heaps, and Heapsort Sorting and Searching 1 / 24 Priority Queue: Motivating Example 3 jobs have been submitted
/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Priority Queues / Heaps Date: 9/27/17
 01.433/33 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Priority Queues / Heaps Date: 9/2/1.1 Introduction In this lecture we ll talk about a useful abstraction, priority queues, which are
01.433/33 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Priority Queues / Heaps Date: 9/2/1.1 Introduction In this lecture we ll talk about a useful abstraction, priority queues, which are
LECTURE 18 AVL TREES
 DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 18 AVL TREES IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD PROTOTYPICAL EXAMPLES These two examples demonstrate how we can correct for imbalances: starting
DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS LECTURE 18 AVL TREES IMRAN IHSAN ASSISTANT PROFESSOR AIR UNIVERSITY, ISLAMABAD PROTOTYPICAL EXAMPLES These two examples demonstrate how we can correct for imbalances: starting
Note that this is a rep invariant! The type system doesn t enforce this but you need it to be true. Should use repok to check in debug version.
 Announcements: Prelim tonight! 7:30-9:00 in Thurston 203/205 o Handed back in section tomorrow o If you have a conflict you can take the exam at 5:45 but can t leave early. Please email me so we have a
Announcements: Prelim tonight! 7:30-9:00 in Thurston 203/205 o Handed back in section tomorrow o If you have a conflict you can take the exam at 5:45 but can t leave early. Please email me so we have a
On the power of structural violations in priority queues
 On the power of structural violations in priority queues Jyrki Katajainen (University of Copenhagen) Joint work with Amr Elmasry (Alexandria University) and Claus Jensen (University of Copenhagen) These
On the power of structural violations in priority queues Jyrki Katajainen (University of Copenhagen) Joint work with Amr Elmasry (Alexandria University) and Claus Jensen (University of Copenhagen) These
Trees (Part 1, Theoretical) CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures University of Texas at Arlington
 Trees (Part 1, Theoretical) CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures University of Texas at Arlington 1 Trees Trees are a natural data structure for representing specific data. Family trees. Organizational
Trees (Part 1, Theoretical) CSE 2320 Algorithms and Data Structures University of Texas at Arlington 1 Trees Trees are a natural data structure for representing specific data. Family trees. Organizational
Heaps. Heapsort. [Reading: CLRS 6] Laura Toma, csci2000, Bowdoin College
![Heaps. Heapsort. [Reading: CLRS 6] Laura Toma, csci2000, Bowdoin College Heaps. Heapsort. [Reading: CLRS 6] Laura Toma, csci2000, Bowdoin College](/thumbs/71/65822704.jpg) Heaps. Heapsort. [Reading: CLRS 6] Laura Toma, csci000, Bowdoin College So far we have discussed tools necessary for analysis of algorithms (growth, summations and recurrences) and we have seen a couple
Heaps. Heapsort. [Reading: CLRS 6] Laura Toma, csci000, Bowdoin College So far we have discussed tools necessary for analysis of algorithms (growth, summations and recurrences) and we have seen a couple
Heaps and Priority Queues
 Heaps and Priority Queues (A Data Structure Intermezzo) Frits Vaandrager Heapsort Running time is O(n lg n) Sorts in place Introduces an algorithm design technique» Create data structure (heap) to manage
Heaps and Priority Queues (A Data Structure Intermezzo) Frits Vaandrager Heapsort Running time is O(n lg n) Sorts in place Introduces an algorithm design technique» Create data structure (heap) to manage
Search Trees - 2. Venkatanatha Sarma Y. Lecture delivered by: Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore. M.S Ramaiah School of Advanced Studies - Bangalore
 Search Trees - 2 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Search Trees - 2 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming. Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2
 CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2 Last Time Binary search trees (Ch 14) The locate method Further Implementation 2 Today s Outline Binary search trees
CSCI 136 Data Structures & Advanced Programming Lecture 25 Fall 2018 Instructor: B 2 Last Time Binary search trees (Ch 14) The locate method Further Implementation 2 Today s Outline Binary search trees
Augmenting Data Structures
 Augmenting Data Structures [Not in G &T Text. In CLRS chapter 14.] An AVL tree by itself is not very useful. To support more useful queries we need more structure. General Definition: An augmented data
Augmenting Data Structures [Not in G &T Text. In CLRS chapter 14.] An AVL tree by itself is not very useful. To support more useful queries we need more structure. General Definition: An augmented data
CS350: Data Structures AVL Trees
 S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
S35: Data Structures VL Trees James Moscola Department of Engineering & omputer Science York ollege of Pennsylvania S35: Data Structures James Moscola Balanced Search Trees Binary search trees are not
Lecture 13: AVL Trees and Binary Heaps
 Data Structures Brett Bernstein Lecture 13: AVL Trees and Binary Heaps Review Exercises 1. ( ) Interview question: Given an array show how to shue it randomly so that any possible reordering is equally
Data Structures Brett Bernstein Lecture 13: AVL Trees and Binary Heaps Review Exercises 1. ( ) Interview question: Given an array show how to shue it randomly so that any possible reordering is equally
Computational Optimization ISE 407. Lecture 16. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
quiz heapsort intuition overview Is an algorithm with a worst-case time complexity in O(n) data structures and algorithms lecture 3
 quiz data structures and algorithms 2018 09 10 lecture 3 Is an algorithm with a worst-case time complexity in O(n) always faster than an algorithm with a worst-case time complexity in O(n 2 )? intuition
quiz data structures and algorithms 2018 09 10 lecture 3 Is an algorithm with a worst-case time complexity in O(n) always faster than an algorithm with a worst-case time complexity in O(n 2 )? intuition
Balanced Binary Search Trees. Victor Gao
 Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
Balanced Binary Search Trees Victor Gao OUTLINE Binary Heap Revisited BST Revisited Balanced Binary Search Trees Rotation Treap Splay Tree BINARY HEAP: REVIEW A binary heap is a complete binary tree such
3137 Data Structures and Algorithms in C++
 3137 Data Structures and Algorithms in C++ Lecture 4 July 17 2006 Shlomo Hershkop 1 Announcements please make sure to keep up with the course, it is sometimes fast paced for extra office hours, please
3137 Data Structures and Algorithms in C++ Lecture 4 July 17 2006 Shlomo Hershkop 1 Announcements please make sure to keep up with the course, it is sometimes fast paced for extra office hours, please
Sorting and Searching
 Sorting and Searching Lecture 2: Priority Queues, Heaps, and Heapsort Lecture 2: Priority Queues, Heaps, and Heapsort Sorting and Searching 1 / 24 Priority Queue: Motivating Example 3 jobs have been submitted
Sorting and Searching Lecture 2: Priority Queues, Heaps, and Heapsort Lecture 2: Priority Queues, Heaps, and Heapsort Sorting and Searching 1 / 24 Priority Queue: Motivating Example 3 jobs have been submitted
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Binary Search Tree - Best Time All BST operations are O(d), where d is tree depth minimum d is d = ëlog for a binary tree
CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Binary Search Tree - Best Time All BST operations are O(d), where d is tree depth minimum d is d = ëlog for a binary tree
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Balanced search trees Balanced search tree: A search-tree data structure for which a height of O(lg n) is guaranteed when
CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Balanced search trees Balanced search tree: A search-tree data structure for which a height of O(lg n) is guaranteed when
Properties of a heap (represented by an array A)
 Chapter 6. HeapSort Sorting Problem Input: A sequence of n numbers < a1, a2,..., an > Output: A permutation (reordering) of the input sequence such that ' ' ' < a a a > 1 2... n HeapSort O(n lg n) worst
Chapter 6. HeapSort Sorting Problem Input: A sequence of n numbers < a1, a2,..., an > Output: A permutation (reordering) of the input sequence such that ' ' ' < a a a > 1 2... n HeapSort O(n lg n) worst
The Heap Data Structure
 The Heap Data Structure Def: A heap is a nearly complete binary tree with the following two properties: Structural property: all levels are full, except possibly the last one, which is filled from left
The Heap Data Structure Def: A heap is a nearly complete binary tree with the following two properties: Structural property: all levels are full, except possibly the last one, which is filled from left
9/29/2016. Chapter 4 Trees. Introduction. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology
 Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
Introduction Chapter 4 Trees for large input, even linear access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit average running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 2 Terminology recursive
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 12: Heaps and Priority Queues MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 Heaps and Priority Queues 2 Priority Queues Heaps Priority Queue 3 QueueADT Objects are added and
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 12: Heaps and Priority Queues MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 Heaps and Priority Queues 2 Priority Queues Heaps Priority Queue 3 QueueADT Objects are added and
ICS 691: Advanced Data Structures Spring Lecture 3
 ICS 691: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2016 Prof. Nodari Sitchinava Lecture 3 Scribe: Ben Karsin 1 Overview In the last lecture we started looking at self-adjusting data structures, specifically, move-to-front
ICS 691: Advanced Data Structures Spring 2016 Prof. Nodari Sitchinava Lecture 3 Scribe: Ben Karsin 1 Overview In the last lecture we started looking at self-adjusting data structures, specifically, move-to-front
13.4 Deletion in red-black trees
 Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to insertion. Apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees. Apply node color changes and left/right rotations to fix the violations of RBT tree properties.
Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to insertion. Apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees. Apply node color changes and left/right rotations to fix the violations of RBT tree properties.
Algorithm Theory, Winter Term 2015/16 Problem Set 5 - Sample Solution
 Albert-Ludwigs-Universität, Inst. für Informatik Prof. Dr. Fabian Kuhn M. Ahmadi, O. Saukh, A. R. Molla November, 20 Algorithm Theory, Winter Term 20/6 Problem Set - Sample Solution Exercise : Amortized
Albert-Ludwigs-Universität, Inst. für Informatik Prof. Dr. Fabian Kuhn M. Ahmadi, O. Saukh, A. R. Molla November, 20 Algorithm Theory, Winter Term 20/6 Problem Set - Sample Solution Exercise : Amortized
Inf 2B: AVL Trees. Lecture 5 of ADS thread. Kyriakos Kalorkoti. School of Informatics University of Edinburgh
 Inf 2B: AVL Trees Lecture 5 of ADS thread Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Dictionaries A Dictionary stores key element pairs, called items. Several elements might have
Inf 2B: AVL Trees Lecture 5 of ADS thread Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Dictionaries A Dictionary stores key element pairs, called items. Several elements might have
Level-Balanced B-Trees
 Gerth Stølting rodal RICS University of Aarhus Pankaj K. Agarwal Lars Arge Jeffrey S. Vitter Center for Geometric Computing Duke University January 1999 1 -Trees ayer, McCreight 1972 Level 2 Level 1 Leaves
Gerth Stølting rodal RICS University of Aarhus Pankaj K. Agarwal Lars Arge Jeffrey S. Vitter Center for Geometric Computing Duke University January 1999 1 -Trees ayer, McCreight 1972 Level 2 Level 1 Leaves
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Priority Queues Outline Priority Queues 1 Priority Queues Jumping the Queue Priority Queues In normal queue, the mode of selection is first in,
Data Structures and Algorithms Spring 2017-2018 Outline 1 Priority Queues Outline Priority Queues 1 Priority Queues Jumping the Queue Priority Queues In normal queue, the mode of selection is first in,
Some Search Structures. Balanced Search Trees. Binary Search Trees. A Binary Search Tree. Review Binary Search Trees
 Some Search Structures Balanced Search Trees Lecture 8 CS Fall Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Some Search Structures Balanced Search Trees Lecture 8 CS Fall Sorted Arrays Advantages Search in O(log n) time (binary search) Disadvantages Need to know size in advance Insertion, deletion O(n) need
Advanced Algorithms. Class Notes for Thursday, September 18, 2014 Bernard Moret
 Advanced Algorithms Class Notes for Thursday, September 18, 2014 Bernard Moret 1 Amortized Analysis (cont d) 1.1 Side note: regarding meldable heaps When we saw how to meld two leftist trees, we did not
Advanced Algorithms Class Notes for Thursday, September 18, 2014 Bernard Moret 1 Amortized Analysis (cont d) 1.1 Side note: regarding meldable heaps When we saw how to meld two leftist trees, we did not
Introduction. for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit times closer to O(log N) binary search tree
 Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
Chapter 4 Trees 2 Introduction for large input, even access time may be prohibitive we need data structures that exhibit running times closer to O(log N) binary search tree 3 Terminology recursive definition
In a non-ideal situation, we can allow the binary tree to grow to twice the height of the perfect tree (2 lg n) and periodically balance it
 Balanced Trees bst algorithms can degenerate to worst case performance, which is bad because the worst case is likely to occur in practice, with ordered files, for example We will like to keep our trees
Balanced Trees bst algorithms can degenerate to worst case performance, which is bad because the worst case is likely to occur in practice, with ordered files, for example We will like to keep our trees
Introduction to Algorithms March 11, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Spring 2009 Professors Sivan Toledo and Alan Edelman Quiz 1
 Introduction to Algorithms March 11, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Spring 2009 Professors Sivan Toledo and Alan Edelman Quiz 1 Quiz 1 Do not open this quiz booklet until directed to
Introduction to Algorithms March 11, 2009 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.006 Spring 2009 Professors Sivan Toledo and Alan Edelman Quiz 1 Quiz 1 Do not open this quiz booklet until directed to
Trees. Q: Why study trees? A: Many advance ADTs are implemented using tree-based data structures.
 Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Trees Q: Why study trees? : Many advance DTs are implemented using tree-based data structures. Recursive Definition of (Rooted) Tree: Let T be a set with n 0 elements. (i) If n = 0, T is an empty tree,
Graduate Algorithms CS F-07 Red/Black Trees
 Graduate Algorithms CS673-2016F-07 Red/lack Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 07-0: inary Search Trees inary Trees For each node n, (value stored at node n)
Graduate Algorithms CS673-2016F-07 Red/lack Trees David Galles Department of Computer Science University of San Francisco 07-0: inary Search Trees inary Trees For each node n, (value stored at node n)
10/23/2013. AVL Trees. Height of an AVL Tree. Height of an AVL Tree. AVL Trees
 // AVL Trees AVL Trees An AVL tree is a binary search tree with a balance condition. AVL is named for its inventors: Adel son-vel skii and Landis AVL tree approximates the ideal tree (completely balanced
// AVL Trees AVL Trees An AVL tree is a binary search tree with a balance condition. AVL is named for its inventors: Adel son-vel skii and Landis AVL tree approximates the ideal tree (completely balanced
