GEOMETRY and MEASUREMENT
|
|
|
- Annabelle Randall
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GEOMETRY and MEASUREMENT
2 Table of Contents Let s Stay in Shape!... 1 Line Up!... 2 Get a Good Angle on This One... 3 Measuring Angles...4 Cutting Up... 5 What a Class!... 6 Same As...7 This Works in Any Language!... 8 Mirror Images... 9 Looking in the Mirror It s Customary Metrically Speaking...12 On the Border Using Measures Half the Work...17 Areas of Trapezoids Going Around In Circular Thinking...20 Parts Sectioned Off...21 Diagram Data...22 Block Party Rolling Along...25 Volumes of Prisms...26 Volumes of Cylinders...27 Egyptian or Mexican Design? One Scoop or Two?...29 Using a Model Volumes of Irregular Figures...32 It s a Cover-Up VersaTiles Geometry and Measurement R ISBN Greenview Court Vernon Hills, Illinois hand2mind.com 2009, 1999 by ETA hand2mind. All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording, or otherwise, without prior written permission of the publisher. Developed and printed in the United States of America
3 Let s Stay in Shape! A line is a straight path of points that extends infinitely in opposite directions. A line segment is a part of a line. It has two endpoints and a definite length. A ray is a straight path of points that starts from one endpoint and extends infinitely in one direction. An angle is formed by the meeting of two rays at a vertex. Match the description with its geometric concept. 1 the horizon 3 the top of a classroom chalkboard, from one end to the other 5 the figure formed by a classroom flagpole and the wall on which it is hanging 7 the shape of the pole holding a classroom flag 9 the thing you roll in a typical board game 11 all the points in space that are exactly the same distance from you at this moment 2 a rubber ball sliced in half 4 the shape of a pane of glass in a window of a classroom 6 a beam from a flashlight pointed at the sky 8 the smallest dot that can be drawn on a piece of paper 10 the shape of a typical box of tissues 12 all the points on the floor of a classroom that are exactly the same distance from you at this moment Angle Sphere Hemisphere Ray Cylinder Rectangular prism Line segment Cube Circle Point Rectangle Line Objective: Identify a line, line segment, ray, angle, 2-dimensional shape, and 3-dimensional shape. 1
4 Line Up! Intersecting lines cross each other or, if extended, will cross each other. Perpendicular lines intersect to form a right angle. Parallel lines are lines in the same plane that do not intersect. Use the diagram at the right. Which line(s) are: 1 parallel to line m? 2 perpendicular to line q? 3 parallel to line o? 4 perpendicular to line s? 5 parallel to line m and perpendicular to line s? 6 intersecting, but not perpendicular to line o? 7 parallel to line n? 8 parallel to line p? 9 perpendicular to line o? 10 parallel to line r? 11 intersecting, but not perpendicular to line m? 12 parallel to line q and perpendicular to line n? Lines m, n, q, r Lines m, n Lines o, p Line n Line p Line s Line o Line r Line q Line m Lines o, p, s None 2 Objective: Identify lines as intersecting, perpendicular, or parallel.
5 Get a Good Angle on This One Choose the correct angle to complete the sentence. 1 is a right angle. 2 is a straight angle. 3 is an acute angle. 4 is an obtuse angle. 5 is an acute angle. 6 is an obtuse angle. 7 is a straight angle. 8 is an obtuse angle. 9 is an acute angle. 10 is not an obtuse angle. 11 is not an acute angle. 12 is not an acute angle. WOY WOZ XOZ VOX ROV SOZ WOY SOX TOQ ROU QOV SOU SOQ ROY SOZ ZOX WOZ MOY MOW MOY QOV SOU ROV WOY WOZ MOY VOX SOX UOZ SOU MOV ROU SOQ UOZ TOW WOY SOU MOW ROV UOZ MOV SOQ QOV WOZ MOY SOZ WOY VOX Objective: Identify an angle as acute, right, obtuse, or straight. 3
6 Measuring Angles Find the measure of the angle. 1 2 M Remember! Use the inner scale of a protractor if an angle opens from the right. Use the outer scale if it opens from the left Objective: Measure an angle using a protractor.
7 Cutting Up Use the diagram to answer the question. m E = 124 m G = 124 What is the measure of the angle? 1 C 2 F 3 I What is the sum of the measures of the angles? 4 H and J 5 M and C 6 E and K 7 P and H 8 G and N 9 What is the difference between the measures of K and D? 10 What is the difference between the measures of P and A? 11 What is the sum of the measures of C, H, I, and N? 12 What is the sum of the measures of H, E, and Q? Objective: Identify the relationships between angles formed when parallel lines are cut by a transversal. 5
8 What a Class! Find the figure that best fits the description. 1 a triangle with no sides congruent and one obtuse angle 2 a triangle with a right angle and two congruent sides 3 a quadrilateral with opposite sides congruent, consecutive sides different lengths, and all right angles 4 a quadrilateral with all sides congruent and no right angles 5 a triangle with no angles equal to or greater than 90 and no congruent sides 6 a quadrilateral with 4 congruent sides and all right angles 7 a quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and congruent and with consecutive sides different lengths 8 a triangle with a right angle and no congruent sides 9 a quadrilateral with exactly one pair of parallel sides 10 a quadrilateral with no pairs of parallel sides 11 a triangle with all sides congruent 12 a triangle with no angles equal to or greater than 90 and one pair of congruent sides Figure ABC is a right scalene triangle. Figure DEFG is a parallelogram, a rectangle, a rhombus, and a square. 6 Objective: Classify triangles and quadrilaterals.
9 Same As Use the given information for each pair of congruent figures to find the correct answer. ABC DEF AB corresponds to DE. BC corresponds to EF. Trapezoid LMNP Trapezoid QRST MN is parallel to LP. MN corresponds to RS. NP corresponds to ST. 1 Which side corresponds to AC? 2 Which angle corresponds to DFE? 3 Which angle corresponds to FDE? 4 Which side is parallel to RS? 5 Which side corresponds to ML? 6 Which angle corresponds to MNP? 7 Which angle corresponds to PLM? 8 Which angle corresponds to NML? Quadrilateral UVWX Quadrilateral PQRS VUX is a right angle. UV corresponds to PQ. WX corresponds to RS. VW corresponds to QR. 9 Which angle in quadrilateral PQRS is a right angle? 10 Which angle corresponds to VWX? 11 Which angle corresponds to UVW? 12 Which side corresponds to XU? means is congruent to. RST ACB TQR QRS CAB QPS SP SRQ QT DF RQ PQR Objective: Identify a figure as being congruent to a given figure. 7
10 This Works in Any Language! Remember! Apply the translation to each coordinate of the original figure. Find the coordinates of the missing vertex of the translation image. Original Figure Translation Rule Translation Image 1 (2, 5), (7, 5), (7, 10) (+ 2, + 4) (4, 9), (9, 9), 2 (1, 0), (8, 0), (1, 12) (+ 5, + 1) (6, 1), (13, 1), 3 (7, 11), (11, 12), (14, 19) (+ 8, + 3) (15, 14), (19, 15), 4 ( 2, 0), ( 4, 1), ( 6, 5) (+ 7, + 8) (5, 8), (3, 7), 5 ( 3, 5), ( 8, 9), ( 2, 12) (+ 6, + 2) (3, 7), ( 2, 11), 6 (5, 8), (1, 9), (6, 6) (+ 8, 2) (13, 10), (9, 11), 7 (10, 6), (9, 15), (7, 5) ( 4, 6) (6, 12),, (3, 11) 8 ( 12, 8), ( 1, 9), ( 4, 3) ( 4, 8) ( 16, 16),, ( 8, 11) 9 (4, 2), ( 3, 2), (0, 0) (+ 5, 2) (9, 4), (2, 0), 10 ( 6, 1), ( 6, 5), ( 2, 5), ( 2, 1) (+ 4, 1) ( 2, 0), ( 2, 4), (2, 4), 11 (7, 8), (1, 1), (5, 9), (4, 7) ( 3, 5) (4, 13), ( 2, 4), (2, 4), 12 (8, 0), (4, 4), (0, 8) ( 9, + 6) ( 1, 6),, ( 9, 14) (9, 14) (1, 3) ( 5, 10) ( 5, 17) (5, 2) (22, 22) (2, 0) (5, 21) (6, 13) (14, 8) (1, 2) (4, 14) 8 Objective: Identify the translation of a figure in a coordinate plane.
11 Mirror Images Find the missing coordinates of the image after it is reflected over the y-axis. Original Figure Reflection ( 4, 8), ( 5, 10), ( 4, 12) (4, 8), (5, 10), 1 ( 2, 5), ( 2, 9), ( 5, 9), ( 5, 5) (2, 5), (2, 9), (5, 9), 2 ( 2, 5), ( 2, 9), ( 5, 9), ( 5, 5) (2, 5), (2, 9), (5, 9), 3 ( 4, 8), ( 5, 10), ( 4, 12) (4, 8), (5, 10), 4 (4, 8), (4, 12), (5, 10) ( 4, 8), 5, ( 5, 10) (2, 5), (2, 9), (5, 9), (5, 5) ( 2, 5), ( 2, 9), ( 5, 9), 6 Look for a pattern in the numbers. Find the missing coordinates of the image after it is reflected over the x-axis. Original Figure Reflection (3, 8), (4, 12), (9, 5) (3, 8), (4, 12), 7 ( 5, 10), ( 6, 14), ( 3, 14), ( 2, 10) ( 5, 10), ( 6, 14), ( 3, 14), 8 ( 5 10), ( 6, 14), ( 3, 14), ( 2, 10) ( 5, 10), ( 6, 14), ( 3, 14), 9 ( 3, 8), ( 9, 5), ( 4, 12) ( 3, 8), 10, ( 4, 12) ( 3, 8), ( 4, 12), ( 9, 5) ( 3, 8), ( 4, 12), 11 (5, 10), (6, 14), (3, 14), (2, 10) (5, 10), (6, 14), (3, 14), 12 ( 2, 10) (2, 10) ( 9, 5) ( 4, 12) ( 9, 5) (9, 5) (5, 5) ( 5, 5) ( 2, 10) (5, 5) (4, 12) (4, 12) Objective: Identify the reflection of a figure in a coordinate plane. 9
12 Looking in the Mirror A line of symmetry divides a figure into two halves that are mirror images of each other. line of symmetry Find the number of lines of symmetry for the figure Find the figure that matches the description. 7 a figure with 6 lines of symmetry 8 a triangle with no lines of symmetry 9 a plane figure with an infinite number of lines of symmetry 10 a quadrilateral with one line of symmetry 11 a quadrilateral with 2 lines of symmetry 12 a triangle with one line of symmetry Remember! You can test your solutions with a mirror. Rhombus Scalene triangle Isosceles right triangle Circle 3 Isosceles trapezoid Regular hexagon Objective: Identify the line(s) of symmetry for a given figure.
13 It s Customary 1 ft = 12 in. 1 c = 8 fl oz 1 lb = 16 oz 1 yd = 3 ft 1 pt = 2 c = 16 fl oz 1 T = 2,000 lb 1 mi = 5,280 ft 1 qt = 4 c = 32 fl oz 1 mi = 1,760 yd 1 gal = 4 qt Find the equivalent measure. 1 4 ft 2 1 yd 2 ft 3 3 c 4 2 lb 5 oz 5 1 qt 3 c 6 2 yd 1 ft mi 8 2 mi 9 1 gal yd 11 4 qt 2 c in. 2,640 ft 48 in. 56 fl oz 16 c 8 ft 60 in. 37 oz 2,550 ft 24 fl oz 18 c 84 in. 3,520 yd Find the equivalent measure in oz 3 72 oz fl oz 5 40 ft in. 7 2,360 yd 8 6,000 ft fl oz qt ft in. 4 lb 8 oz 6 gal 125 fl oz 5 yd 20 in. 1 mi 720 ft 3 qt 4 fl oz 4 ft 11 in. 28 yd 2 ft 13 yd 1 ft 20 yd 30 in. 2 lb 6 oz 7 gal 3 qt 1 mi 600 yd Objective: Convert units of length, capacity, and weight in the customary system. 11
14 Metrically Speaking 1 cm = 10 mm 1 L = 1,000 ml 1 g = 1,000 mg 1 m = 100 cm = 1,000 mm 1 kg = 1,000 g 1 km = 1,000 m Find the equivalent measure cm 5 35 kg g 2 3,500 ml 6 35,000 mm ml g L 11 3,500 g mm km cm m 3,500 m L 0.35 m 35,000 g 3.5 kg 3.5 L 35 m 3.5 m 350 ml kg 0.35 kg Find the equivalent measure kg L 9 83,500 cm m ml kg cm 7 8,350 cm kg kg 8 10,500 ml L 7,500 g 75 g 10.5 L 105 ml km 83.5 mm 83.5 m 750 g L 835 cm 1,050 ml 75,000 g 12 Objective: Convert units of length, capacity, and mass in the metric system.
15 On the Border Find the perimeter square ABCD: AB = 38 in. 6 square GHIJ: GH = 138 cm 7 regular hexagon BCDEFG: BC = 1 ft 3 in. 8 rectangle QRST: QR = 159 cm, RS = 49 cm 9 parallelogram WXYZ: XY= 2 ft 7 in., YZ = 1 ft 8 in. 10 regular pentagon GHIJK: JK = 1,350 mm 11 rectangle MNPQ: MN = 4 ft 7 in., MQ = 19 in. 12 rhombus JKLM: LM = 105 cm Remember! To convert from inches (a small unit) to feet (a larger unit), divide by m 4.16 m 12 ft 8 in. 12 ft 4 in. 7 ft 6 in m 5.52 m 6 m 6 ft 7 in. 8 ft 6 in. 4.1 m 6 ft 8 in. Objective: Find the perimeter of a 2-dimensional figure. 13
16 Using Measures Find the perimeter of the triangle rounded to the nearest whole number. Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of c. Find the perimeter of the triangle. So, the perimeter of the triangle is about 14 ft. c 2 = a 2 + b 2 c 2 = (3 ft) 2 + (5 ft) 2 c 2 = 9 ft ft 2 c = c = 5.8 ft, or 6 ft rounded to the nearest whole number. P = a + b + c P = 3 ft + 5 ft + 6 ft P = 14 ft Find the perimeter of the section rounded to the nearest foot. 1 section M 2 section N 3 section O 4 section P 5 section Q 6 section R 14
17 Remember! You may have to divide the sections into smaller parts to find the area of the whole section. Find the area in square feet of the section. 7 section M 8 section N 9 section O 10 section P 11 section Q 12 section R 87,200 1,160 90,000 1, ,000 1,340 72,000 1,605 1,280 62,400 1, ,000 Objective: Solve a problem involving measures by using data from a diagram. 15
18 It s a Cover-Up Find the area of the parallelogram. Use the formula for the area of a parallelogram. Area = base height (A = b h). So, the area of the parallelogram is 336 in. 2 base = 23 in. + 5 in. = 28 in. A = b h = 28 in. 12 in = 336 in. 2 Find the area of the parallelogram or rectangle parallelogram: b = 1 ft 8 in., h = 15 in. 6 parallelogram: b = 0.9 m, h = 25 cm 7 rectangle: b = 0.75 ft, h = 1 ft 10 in. 8 parallelogram: b = 1.2 m, h = 19 cm 9 parallelogram: b = 1.5 ft, h = 21 in. 10 rectangle: b = 24 in., h = 2.5 ft 11 parallelogram: b = 45 cm, h = 16 cm 12 rectangle: b = 1.4 m, h = 0.4 m Remember! The height of a parallelogram is always perpendicular to the base. 812 cm in cm in in. 2 5,600 cm in in cm in. 2 2,280 cm 2 2,250 cm 2 16 Objective: Find the area of a rectangle or a parallelogram.
19 Half the Work Find the area of the triangle. Determine the lengths of the base and height. b = 7 cm + 34 cm = 41 cm h = 24 cm Use the formula for the area of a triangle: Area = 1 2 base height A = 1 2 bh So, the area of the triangle is 492 cm 2. A = 1 2 bh = cm 24 cm = 492 cm 2 Find the area of the triangle cm 12 cm 13 cm 5 cm 5 NBA 6 BCN 7 AJF 8 DEF 9 HFI 10 ANC 11 FLM 12 AKM 24 cm 2 20 cm cm 2 78 cm cm 2 22 cm cm cm 2 90 cm cm cm cm 2 Objective: Find the area of a triangle. 17
20 Areas of Trapezoids You can think of a trapezoid as half a parallelogram. b 2 b 1 = base 1, b 2 = base 2, h = height Since the area of the parallelogram is (b 1 + b 2 )h, the area of the trapezoid is (b 1 + b 2 )h 2 b 1 b 2 Find the area of the trapezoid b 1 = 14 in., b 2 = 1 ft 5 in., h = 4 in. 9 b 1 = 26 cm, b 2 = 0.4 m, h = 12 cm 11 b 1 = 130 mm, b 2 = 18 cm, h = 8 cm 8 b 1 = 12.5 in., b 2 = 20.5 in., h = 0.5 ft 10 b 1 = 0.25 ft, b 2 = 8 in., h = 5 in. 12 b 1 = 3 ft, b 2 = 1 ft, h = 10 in. 240 in in in in cm cm 2 80 cm 2 99 in in cm in cm 2 18 Objective: Find the area of a trapezoid.
21 Going Around In... Find the circumference of the circle rounded to the nearest tenth. Use π Use the formula for the circumference of a circle: Circumference = 2 π radius C = 2πr C = 2πr or = 2 π 17 cm Circumference = π diameter cm C = πd So, the circumference rounded to the nearest tenth is cm. Find the circumference of the circle rounded to the nearest tenth. Use π cm 5 r = 390 mm 6 r = 1 ft 4 in. 7 d = 0.7 m 8 r = 33 cm 9 d = 46 in. 10 d = 2 ft 10 in. 11 r = 430 mm 12 d = 1 2 ft cm in in in in cm cm in in cm cm cm Objective: Find the circumference of a circle. 19
22 Circular Thinking Find the area rounded to the nearest tenth. Use π Use the formula for the area of a circle: A = πr 2 Area = π radius radius cm 7 cm A = πr cm 2 So, the area is approximately cm 2. Find the area rounded to the nearest tenth. Use π d = 2 ft 2 in. 8 r = 150 mm 9 d = 1.5 ft 10 d = 0.6 m 11 r = 22.8 cm 12 d = ft in cm 2 1,133.5 cm 2 1,632.3 cm in. 2 2,826 cm cm in cm in in cm 2 20 Objective: Find the area of a circle.
23 Parts Sectioned Off Find the area of the section rounded to the nearest whole number. Use π Find the area as if the entire figure is completed. A = πr (10 cm) cm 2 Divide the missing parts. Area of quarter circle = 1 4 πr (3.14) (10 cm) cm 2 79 cm 2 So, the area of the section is approximately 79 cm 2. Find the area of the section(s) rounded to the nearest whole number. Use π N 3 N, O, and P 5 O, M, and S 7 N, P, R, and T 9 N, M, and T 11 N, O, P, Q, R, S, and T 2 N and O 4 M 6 M and Q 8 O, M, S, and Q 10 P, Q, and R 12 O and S 1,554 cm 2 3,323 cm 2 1,960 cm cm 2 2,268 cm 2 1,190 cm 2 2,977 cm 2 3,416 cm 2 2,091 cm 2 1,035 cm 2 1,017 cm 2 3,285 cm 2 Objective: Find the area of an irregular figure by combining the areas of its parts. 21
24 Diagram Data The diagram shows how one square mile of property is divided. Each section is called a parcel. Find the area in square feet. 1 parcel II 2 a parcel made up of I and IV 3 a parcel made up of VIII, IX, and X 4 a parcel made up of XIII, XIV, and XV 5 a parcel made up of VII, XII, XIII, and XIV 6 a parcel made up of V, VIII, X, and XI Remember! 1 mi = 5,280 ft 1 acre = 43,560 ft 2 22
25 Which parcels have an area of: 7 193,600 yd 2? 8 96,800 yd 2? 9 48,400 yd 2? 10 How many square yards are there in one acre? How many acres are there in a parcel made up of the following sections? 11 I and IV 12 IV, V, and VIII 3,484,800 IV, V, VI VIII, IX, X, 2,613,600 XIV, XV 4,356,000 VII XI, XII, XIII, XVI 4,840 1,742,400 3,920, ,227, Objective: Solve a problem by using data from a diagram. 23
26 Block Party Find the surface area of the rectangular prism. Each edge is 1 in. Look at the figure from above. You see 4 in. 2 Therefore, the bottom must be 4 in. 2 Look at the figure from the front. You see 8 in. 2 Therefore, the back must be 8 in. 2 Look at the figure from the right. You see 2 in. 2 Therefore, the left must be 2 in. 2 So, the surface area of the figure is 28 in. 2 Find the surface area of the cube or rectangular prism. Area of top and bottom: 2 4 in. 2 = 8 in. 2 Area of front and back: 2 8 in. 2 = 16 in. 2 Area of right and left: 2 2 in. 2 = 4 in. 2 Total area: 28 in cm 1 cm 1 cm 1 cm 1 cm 1 cm 1 cm 1 cm 5 cube: 1 cm on each edge 7 cube: 3 cm on each edge 9 prism: l = 15 in., w = 12 in., h = 2 in. 11 cube: 4 cm on each edge 1 cm 1 cm 1 cm 1 cm 6 prism: l = 6 in., w = 9 in., h = 3 in. 8 prism: l = 8 in., w = 6 in., h = 4 in. 10 cube: 5 cm on each edge 12 prism: l = 1 ft 2 in., w = 8 in., h = 3 in. 468 in cm 2 32 cm in cm 2 48 cm 2 96 cm 2 6 cm in in cm 2 54 cm 2 24 Objective: Find the surface area of a rectangular prism.
27 Rolling Along Find the surface area of the cylinder rounded to the nearest whole number. Use π Use the formula for the surface area of a cylinder: Surface area = 2πr 2 + 2πr h where r is the radius of the base and h is the height of the cylinder. SA = 2πr 2 + 2πrh 2(3.14)(12 cm) 2 + 2(3.14) (12 cm)(15 cm) 2, cm 2 So, the surface area of the cylinder is approximately 2,035 cm 2. Find the surface area of the cylinder rounded to the nearest whole number. Use π base: r = 11 cm, h = 14 cm 7 base: d = 26 cm, h = 0.19 m 9 base: d = 0.3 m, h = 0.17 m 11 base: r = 1 ft 1 in., h = 9 in. 6 base: r = 16 in., h = 8 in. 8 base: d = 1 ft 2 in., h = 10 in. 10 base: r = 0.12 m, h = 8 cm 12 base: d = 240 mm, h = 18 cm 791 in cm 2 2,412 in. 2 1,407 cm in. 2 3,014 cm 2 2,612 cm 2 1,507 cm 2 2,261 cm in. 2 1,796 in. 2 1,727 cm 2 Objective: Find the surface area of a cylinder. 25
28 Volumes of Prisms Find the volume of the prism. Use the formula for the volume of a prism: Volume = area of base height V = B H So, the volume of the prism is 252 in. 3 V = BH, where B = 1 2 bh V = (9 in. 4 in.) 2 14 in. = 252 in. 3 Find the volume of the prism rectangular: l = 1 ft, w = 0.75 ft, h = 2 ft 2 in. 7 triangular: b = 14 in., h = 10 in., H = 1 ft 9 triangular: b = 1 ft 4 in., h = 0.5 ft, H = 1 ft 3 in. 11 rectangular: l = 2 ft, w = 5 in., h = ft 6 rectangular: l = 18 in., w = 1 ft 3 in., h = 1 2 ft 8 triangular: b = 0.25 m, h = 16 cm, H = 0.4 m 10 rectangular: l = 1 ft, w = 1 ft, h = 1 ft 12 rectangular: l = 19 in., w = 9 in., h = ft 1,620 in. 3 8,000 cm 3 1,920 cm 3 1,728 in cm 3 2,160 in. 3 2,565 in in in cm 3 2,808 in in Objective: Find the volume of a rectangular or triangular prism.
29 Volumes of Cylinders Find the volume of the cylinder rounded to the nearest whole number. Use π Use the formula for the volume of a cylinder. Volume = area of the base height. V = πr 2 h V = πr 2 h 3.14(3 ft) 2 (7 ft) ft 3 So, the volume of the cylinder is approximately 198 ft 3. Find the volume of the cylinder rounded to the nearest whole number. Use π r = 16 in., h = 10 in. 8 d = 18 cm, h = 130 mm 11 r = 3 4 ft, h = ft 6 r = 6 cm, h = 12 cm 9 d = 0.12 m, h = 14 cm 12 d = 220 mm, h = 13 cm 7 r = 1 ft 4 in., h = 0.5 ft 10 r = 10 in., h = 1 ft 6 in. 4,939 cm 3 3,306 cm 3 1,583 cm 3 1,846 in. 3 5,652 in. 3 4,823 in. 3 4,069 cm 3 1,356 cm 3 8,038 in. 3 3,815 in. 3 3,617 cm 3 6,359 in. 3 Objective: Find the volume of a cylinder. 27
30 Egyptian or Mexican Design? Find the volume of the pyramid rounded to the nearest whole number. Use the formula for the volume of a pyramid: V = 1 3 BH Volume = 1 3 area of the base height = 1 3 (9 in. 8 in.)(7 in.) V = 1 3 BH = 1 3 (504 in.3 ) So, the volume of the pyramid is 168 in. 3 = 168 in. 3 Find the volume of the pyramid rounded to the nearest whole number cm cm 9 cm 11 cm 8 cm 6 cm 10 cm 5 B = 84 cm 2, H = 8 cm 7 B = 74.6 cm 2, H = 0.15 m 9 a pyramid with a square base 13 cm on a side and height is 15 cm 11 a pyramid whose base is a right triangle with legs 9 cm and 12 cm, and height is 10 cm 6 B = in. 2, H = in. 8 B = 122 in. 2, H = 6 in. 10 a pyramid whose base is a triangle with area 45 in. 2 and height is 20 in. 12 a pyramid whose base is a rectangle with length 24 in. and width 16 in. and whose height is 1 ft 268 cm cm in cm 3 3,227 in in cm cm in cm 3 1,536 in in Objective: Find the volume of a pyramid.
31 One Scoop or Two? Find the volume of the cone rounded to the nearest whole number. Use π Use the formula for the volume of a cone: V = 1 3 πr2 h Volume = 1 3 area of a circle height 1 3 (3.14)(9 in.)2 (13 in.) V = 1 3 πr 2 h 1, in. 3 So, the volume of the cone is approximately 1,102 in. 3 Find the volume of the cone rounded to the nearest whole number. Use π cm 26 cm 5 area of base = in. 2, h = 9 in. 7 r = 14 in., h = 5 in. 9 d = 1 ft 8 in., h = 1 ft 11 d = 2 ft, h = 1 ft 6 area of base = cm 2, h = 6 cm 8 r = 30 mm, h = 17 cm 10 d = 18 cm, h = 0.18 m 12 r = 14 cm, h = 220 mm 1,026 in. 3 1,526 cm in. 3 1,809 in. 3 4,513 cm cm 3 8,470 in cm 3 1,256 in. 3 8,308 in. 3 3,919 cm cm 3 Objective: Find the volume of a cone. 29
32 Using a Model You may wish to draw a model of the information to help you. Solve the problem. 1 How many minutes will it take to cut a 15-ft piece of wood into five 3-ft sections if each cut takes 4 min? 2 How many minutes will it take to cut a 20-ft piece of pipe into four 5-ft sections if each cut takes 5 min? 3 How many square feet will be in the largest rectangle that can be formed from 24 ft of fencing? 4 If each side of the rectangle described in question 3 is increased by 3 ft, by how many square feet will the area increase? 5 A rectangular garden is to be fenced. Posts are placed every 3 ft. If 12 total posts are used and the width of the garden is 6 ft, how many square feet are in the area of the garden? 6 If the gardener decides to keep the size and shape of the garden unchanged, but places posts every 2 ft, how many posts will be needed? 7 What is the greatest number of 3 in. by 6 in. rectangles that can be cut from a sheet of cardboard that is 3 ft by 6 ft? 30
33 8 There are 25 marbles arranged in a square at the bottom of a pyramid. How many marbles are in the entire pyramid? 9 How many marbles will be in the bottom layer when there are 8 layers? 10 A pegboard in the shape of a square has 11 pegs in each row. If the area of the smallest square that can be made on the board is 1 square unit, how many square units is the largest square? 11 A school bus leaves its garage, drives west for 8 mi, north for 3 mi, east for 2 mi, south for 5 mi, east for 12 mi, and finally, north 2 mi to school. How many miles from the garage is the school now? 12 A straight cut through a rectangle makes 2 sections. What is the greatest number of sections that can be made by 4 straight cuts? Objective: Solve a problem by using a model of the figure. 31
34 Volumes of Irregular Figures Find the volume of the figure rounded to the nearest whole number. Use π Determine the basic figures that make up the irregular figure. Find the volumes of the basic figures in. 3 5,220 cm cm 3 1,693 in. 3 1,232 cm 3 4,494 cm 3 6,120 in in. 3 2,736 in. 3 1,340 in. 3 5,769 cm in Objective: Find the volume of an irregular figure by combining the volume of its parts.
35
36 Getting Started with Four Easy Steps Make VersaTiles Simple to Use! Set up your VersaTiles Answer Case by placing the numbered tiles in order from 1 12 in the top 2 rows. Now you are ready to begin your activity. 1 Answer Questions Complete each question by placing the number tile on the letter in the Answer Case that corresponds to the correct answer. 2 close and flip Close the Answer Case and flip it over. Open the case and look at the pattern on the tiles. 3 match Check the tile pattern against the pattern in the Activity Book. If it matches, all answers are correct. If not, remove tiles that do not match and flip the case over again. 4 learn Rethink the incorrect answer and flip the Answer Case over again. Once the pattern in the case and the book match, the activity has been successfully completed! hand2mind.com Connect with us.
Geometry eday #2 Assignment
 Name Date Score Quadrilaterals Geometry eday #2 Assignment 1. If the diagonals of a quadrilateral are perpendicular bisectors of equal length, then the quadrilateral is a. (Give the strongest condition.)
Name Date Score Quadrilaterals Geometry eday #2 Assignment 1. If the diagonals of a quadrilateral are perpendicular bisectors of equal length, then the quadrilateral is a. (Give the strongest condition.)
Geometry Practice. 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles.
 Geometry Practice Name 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles. 2. Planes that meet to form right angles are called planes. 3. Lines that cross are called lines. 4.
Geometry Practice Name 1. Angles located next to one another sharing a common side are called angles. 2. Planes that meet to form right angles are called planes. 3. Lines that cross are called lines. 4.
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume
 Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Geometric Figures & Their Properties; Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (4.6) The student will validate conclusions about geometric figures and
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes
 Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Answer Key. 1.1 The Three Dimensions. Chapter 1 Basics of Geometry. CK-12 Geometry Honors Concepts 1. Answers
 1.1 The Three Dimensions 1. Possible answer: You need only one number to describe the location of a point on a line. You need two numbers to describe the location of a point on a plane. 2. vary. Possible
1.1 The Three Dimensions 1. Possible answer: You need only one number to describe the location of a point on a line. You need two numbers to describe the location of a point on a plane. 2. vary. Possible
2-dimensional figure. 3-dimensional figure. about. acute angle. addend. addition. angle. area. array. bar graph. capacity
 2-dimensional figure a plane figure that has length and width 3-dimensional figure a solid figure that has length, width, and height about used to indicate approximation/ estimation; indicates rounding
2-dimensional figure a plane figure that has length and width 3-dimensional figure a solid figure that has length, width, and height about used to indicate approximation/ estimation; indicates rounding
Pre-Algebra, Unit 10: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes
 Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
Pre-Algebra, Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Notes Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Objective: (4.6) The student will classify polygons. Take this opportunity to review vocabulary and previous
GEOMETRY REVIEW PACKET
 Obstacles are those frightful things you see when you take your eyes off your goal -Henry Ford As of Spring 2016, geometry is no longer a prerequisite for MTH101 and MTH165 Spend time with the material
Obstacles are those frightful things you see when you take your eyes off your goal -Henry Ford As of Spring 2016, geometry is no longer a prerequisite for MTH101 and MTH165 Spend time with the material
Geometry. Geometry is the study of shapes and sizes. The next few pages will review some basic geometry facts. Enjoy the short lesson on geometry.
 Geometry Introduction: We live in a world of shapes and figures. Objects around us have length, width and height. They also occupy space. On the job, many times people make decision about what they know
Geometry Introduction: We live in a world of shapes and figures. Objects around us have length, width and height. They also occupy space. On the job, many times people make decision about what they know
Geometry Vocabulary. Name Class
 Geometry Vocabulary Name Class Definition/Description Symbol/Sketch 1 point An exact location in space. In two dimensions, an ordered pair specifies a point in a coordinate plane: (x,y) 2 line 3a line
Geometry Vocabulary Name Class Definition/Description Symbol/Sketch 1 point An exact location in space. In two dimensions, an ordered pair specifies a point in a coordinate plane: (x,y) 2 line 3a line
A. 180 B. 108 C. 360 D. 540
 Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM - GEOMETRY 2 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C.
Part I - Multiple Choice - Circle your answer: REVIEW FOR FINAL EXAM - GEOMETRY 2 1. Find the area of the shaded sector. Q O 8 P A. 2 π B. 4 π C. 8 π D. 16 π 2. An octagon has sides. A. five B. six C.
5-Minute Check Solve.
 5-Minute Check (over Chapter 9) Use with Lesson 10-1 Solve. 1. There are 12 balls in a hat and 3 are red. What is the probability of drawing a red ball? 2. Use the Fundamental Counting Principle to find
5-Minute Check (over Chapter 9) Use with Lesson 10-1 Solve. 1. There are 12 balls in a hat and 3 are red. What is the probability of drawing a red ball? 2. Use the Fundamental Counting Principle to find
Number/Computation. addend Any number being added. digit Any one of the ten symbols: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9
 14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
14 Number/Computation addend Any number being added algorithm A step-by-step method for computing array A picture that shows a number of items arranged in rows and columns to form a rectangle associative
1. AREAS. Geometry 199. A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh. B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh. C. Rhombus = 1 product of the diagonals = 1 dd
 Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Section 1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes
 Section 1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes I CAN. Identify and model points, lines, and planes. Identify collinear and coplanar points and intersecting lines and planes in space. Undefined Term- Words, usually
Section 1-1 Points, Lines, and Planes I CAN. Identify and model points, lines, and planes. Identify collinear and coplanar points and intersecting lines and planes in space. Undefined Term- Words, usually
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6
 acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
acute angle An angle with a measure less than that of a right angle. Houghton Mifflin Co. 2 Grade 5 Unit 6 angle An angle is formed by two rays with a common end point. Houghton Mifflin Co. 3 Grade 5 Unit
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Excel Math Glossary Fourth Grade
 Excel Math Glossary Fourth Grade Mathematical Term [Lesson #] TE Page # A acute angle Acute Angle an angle that measures less than 90º [Lesson 78] 187 Addend any number being added [Lesson 1] 003 AM (ante
Excel Math Glossary Fourth Grade Mathematical Term [Lesson #] TE Page # A acute angle Acute Angle an angle that measures less than 90º [Lesson 78] 187 Addend any number being added [Lesson 1] 003 AM (ante
Class Generated Review Sheet for Math 213 Final
 Class Generated Review Sheet for Math 213 Final Key Ideas 9.1 A line segment consists of two point on a plane and all the points in between them. Complementary: The sum of the two angles is 90 degrees
Class Generated Review Sheet for Math 213 Final Key Ideas 9.1 A line segment consists of two point on a plane and all the points in between them. Complementary: The sum of the two angles is 90 degrees
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 10: Measurement, Area, and Volume
 HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (5.6) The student will classify polygons. (5.5) The student will validate conclusions
HS Pre-Algebra Notes Unit 0: Measurement, Area, and Volume Triangles, Quadrilaterals, and Polygons Syllabus Objectives: (5.6) The student will classify polygons. (5.5) The student will validate conclusions
Geometry Vocabulary. acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees
 Geometry Vocabulary acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees angle-the turn or bend between two intersecting lines, line segments, rays, or planes angle bisector-an angle bisector is a ray that
Geometry Vocabulary acute angle-an angle measuring less than 90 degrees angle-the turn or bend between two intersecting lines, line segments, rays, or planes angle bisector-an angle bisector is a ray that
The radius for a regular polygon is the same as the radius of the circumscribed circle.
 Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Perimeter and Area The perimeter and area of geometric shapes are basic properties that we need to know. The more complex a shape is, the more complex the process can be in finding its perimeter and area.
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships
 Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Unit 10 Study Guide: Plane Figures
 Unit 10 Study Guide: Plane Figures *Be sure to watch all videos within each lesson* You can find geometric shapes in art. Whether determining the amount of leading or the amount of glass needed for a piece
Unit 10 Study Guide: Plane Figures *Be sure to watch all videos within each lesson* You can find geometric shapes in art. Whether determining the amount of leading or the amount of glass needed for a piece
Page 1 CCM6+7+ UNIT 9 GEOMETRY 2D and 3D. Angle Relationships, Area, and Perimeter/Circumference Surface Area and Volume
 Page 1 CCM6+7+ UNIT 9 GEOMETRY 2D and 3D UNIT 9 2015-16 Angle Relationships, Area, and Perimeter/Circumference Surface Area and Volume CCM6+7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: MAIN CONCEPT(S) PAGE(S)
Page 1 CCM6+7+ UNIT 9 GEOMETRY 2D and 3D UNIT 9 2015-16 Angle Relationships, Area, and Perimeter/Circumference Surface Area and Volume CCM6+7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: MAIN CONCEPT(S) PAGE(S)
Study Guide and Review
 State whether each sentence is or false. If false, replace the underlined term to make a sentence. 1. Euclidean geometry deals with a system of points, great circles (lines), and spheres (planes). false,
State whether each sentence is or false. If false, replace the underlined term to make a sentence. 1. Euclidean geometry deals with a system of points, great circles (lines), and spheres (planes). false,
Pre-AP Geometry Spring Semester Exam Review 2015
 hapter 8 1. Find.. 25.4. 11.57. 3 D. 28 3. Find.. 3.73. 4. 2 D. 8.77 5. Find, y, k, and m. = k= Pre-P Geometry Spring Semester Eam Review 2015 40 18 25 y= m= 2. Find.. 5 2.. 5 D. 2 4. Find.. 3 2. 2. D.
hapter 8 1. Find.. 25.4. 11.57. 3 D. 28 3. Find.. 3.73. 4. 2 D. 8.77 5. Find, y, k, and m. = k= Pre-P Geometry Spring Semester Eam Review 2015 40 18 25 y= m= 2. Find.. 5 2.. 5 D. 2 4. Find.. 3 2. 2. D.
Geometry First Semester Practice Final (cont)
 49. Determine the width of the river, AE, if A. 6.6 yards. 10 yards C. 12.8 yards D. 15 yards Geometry First Semester Practice Final (cont) 50. In the similar triangles shown below, what is the value of
49. Determine the width of the river, AE, if A. 6.6 yards. 10 yards C. 12.8 yards D. 15 yards Geometry First Semester Practice Final (cont) 50. In the similar triangles shown below, what is the value of
Area. Angle where two rays. Acute angle. Addend. a number to be added. an angle measuring less than 90 degrees. or line segments share an endpoint
 Acute angle Addend an angle measuring less than 90 degrees a number to be added Angle where two rays or line segments share an endpoint Area the measure of space inside a figure. Area is measured in square
Acute angle Addend an angle measuring less than 90 degrees a number to be added Angle where two rays or line segments share an endpoint Area the measure of space inside a figure. Area is measured in square
Page 1 CCM6+7+ UNIT 9 GEOMETRY 2D and 3D 2D & 3D GEOMETRY PERIMETER/CIRCUMFERENCE & AREA SURFACE AREA & VOLUME
 Page 1 CCM6+7+ UNIT 9 GEOMETRY 2D and 3D UNIT 9 2016-17 2D & 3D GEOMETRY PERIMETER/CIRCUMFERENCE & AREA SURFACE AREA & VOLUME CCM6+7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: MAIN CONCEPT(S) PAGE(S) Vocabulary
Page 1 CCM6+7+ UNIT 9 GEOMETRY 2D and 3D UNIT 9 2016-17 2D & 3D GEOMETRY PERIMETER/CIRCUMFERENCE & AREA SURFACE AREA & VOLUME CCM6+7+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: MAIN CONCEPT(S) PAGE(S) Vocabulary
MR. JIMENEZ FINAL EXAM REVIEW GEOMETRY 2011
 PAGE 1 1. The area of a circle is 25.5 in. 2. Find the circumference of the circle. Round your answers to the nearest tenth. 2. The circumference of a circle is 13.1 in. Find the area of the circle. Round
PAGE 1 1. The area of a circle is 25.5 in. 2. Find the circumference of the circle. Round your answers to the nearest tenth. 2. The circumference of a circle is 13.1 in. Find the area of the circle. Round
Jumpstarters for Geometry. Table of Contents. Table of Contents
 Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Lines, Rays, and Line Segments...2 Classifying Angles...3 Measuring and Drawing Angles...4 Classifying Pairs of Lines...5 Special Pairs
Table of Contents Table of Contents Introduction to the Teacher...1 Lines, Rays, and Line Segments...2 Classifying Angles...3 Measuring and Drawing Angles...4 Classifying Pairs of Lines...5 Special Pairs
S P. Geometry Final Exam Review. Name R S P Q P S. Chapter 7 1. If you reflect the point (2, -6) in the x-axis, the coordinates of the image would be:
 Geometry Final Exam Review Chapter 7 1. If you reflect the point (2, -6) in the x-axis, the coordinates of the image would be: Name 6. Use the graph below to complete the sentence. 2. If you reflect the
Geometry Final Exam Review Chapter 7 1. If you reflect the point (2, -6) in the x-axis, the coordinates of the image would be: Name 6. Use the graph below to complete the sentence. 2. If you reflect the
Polygons. 5 sides 5 angles. pentagon. no no R89. Name
 Lesson 11.1 Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number of angles
Lesson 11.1 Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number of angles
Geometry 2 Final Review
 Name: Period: Date: Geometry 2 Final Review 1 Find x in ABC. 5 Find x in ABC. 2 Find x in STU. 6 Find cos A in ABC. 3 Find y in XYZ. 7 Find x to the nearest tenth. 4 Find x in HJK. 8 Find the angle of
Name: Period: Date: Geometry 2 Final Review 1 Find x in ABC. 5 Find x in ABC. 2 Find x in STU. 6 Find cos A in ABC. 3 Find y in XYZ. 7 Find x to the nearest tenth. 4 Find x in HJK. 8 Find the angle of
EOC Review: Practice: 1. In the circle below, AB = 2BC. What is the probability of hitting the shaded region with a random dart?
 EOC Review: Focus Areas: Trigonometric Ratios Area and Volume including Changes in Area/Volume Geometric Probability Proofs and Deductive Reasoning including Conditionals Properties of Polygons and Circles
EOC Review: Focus Areas: Trigonometric Ratios Area and Volume including Changes in Area/Volume Geometric Probability Proofs and Deductive Reasoning including Conditionals Properties of Polygons and Circles
Dear Parents/Students,
 Dear Parents/Students, In the summer time, many necessary mathematical skills are lost due to the absence of daily exposure. The loss of skills may result in a lack of success and unnecessary frustration
Dear Parents/Students, In the summer time, many necessary mathematical skills are lost due to the absence of daily exposure. The loss of skills may result in a lack of success and unnecessary frustration
Geometry Spring Semester Review
 hapter 5 Geometry Spring Semester Review 1. In PM,. m P > m. m P > m M. m > m P. m M > m P 7 M 2. Find the shortest side of the figure QU. Q Q 80 4. QU. U. 50 82 U 3. In EFG, m E = 5 + 2, m F = -, and
hapter 5 Geometry Spring Semester Review 1. In PM,. m P > m. m P > m M. m > m P. m M > m P 7 M 2. Find the shortest side of the figure QU. Q Q 80 4. QU. U. 50 82 U 3. In EFG, m E = 5 + 2, m F = -, and
Math 2 Plane Geometry part 1 Unit Updated January 13, 2017
 Complementary angles (two angles whose sum is 90 ) and supplementary angles (two angles whose sum is 180. A straight line = 180. In the figure below and to the left, angle EFH and angle HFG form a straight
Complementary angles (two angles whose sum is 90 ) and supplementary angles (two angles whose sum is 180. A straight line = 180. In the figure below and to the left, angle EFH and angle HFG form a straight
Vocabulary. Term Page Definition Clarifying Example. cone. cube. cylinder. edge of a threedimensional. figure. face of a polyhedron.
 CHAPTER 10 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 10. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. cone Term Page Definition
CHAPTER 10 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 10. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. cone Term Page Definition
Geometry SIA #3. Name: Class: Date: Short Answer. 1. Find the perimeter of parallelogram ABCD with vertices A( 2, 2), B(4, 2), C( 6, 1), and D(0, 1).
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Geometry SIA #3 Short Answer 1. Find the perimeter of parallelogram ABCD with vertices A( 2, 2), B(4, 2), C( 6, 1), and D(0, 1). 2. If the perimeter of a square is 72 inches, what
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Geometry SIA #3 Short Answer 1. Find the perimeter of parallelogram ABCD with vertices A( 2, 2), B(4, 2), C( 6, 1), and D(0, 1). 2. If the perimeter of a square is 72 inches, what
A triangle that has three acute angles Example:
 1. acute angle : An angle that measures less than a right angle (90 ). 2. acute triangle : A triangle that has three acute angles 3. angle : A figure formed by two rays that meet at a common endpoint 4.
1. acute angle : An angle that measures less than a right angle (90 ). 2. acute triangle : A triangle that has three acute angles 3. angle : A figure formed by two rays that meet at a common endpoint 4.
Chapter 11 Areas of Polygons and Circles
 Section 11-1: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles SOL: G.14 The student will use similar geometric objects in two- or three-dimensions to a) compare ratios between side lengths, perimeters, areas, and
Section 11-1: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles SOL: G.14 The student will use similar geometric objects in two- or three-dimensions to a) compare ratios between side lengths, perimeters, areas, and
Exploring Triangles. We can name triangles by the number of equal sides.
 UNIT 6 1 STUDENT BOOK Exploring Triangles LESSO N Quick Review At At Home Sc h o o l We can name triangles by the number of equal sides. An equilateral triangle has 3 equal sides. It has three 60 angles.
UNIT 6 1 STUDENT BOOK Exploring Triangles LESSO N Quick Review At At Home Sc h o o l We can name triangles by the number of equal sides. An equilateral triangle has 3 equal sides. It has three 60 angles.
Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever.
 Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever. Point an exact location Line a straight path that has no thickness and extends forever in opposite directions Ray Part of a line that
Lines Plane A flat surface that has no thickness and extends forever. Point an exact location Line a straight path that has no thickness and extends forever in opposite directions Ray Part of a line that
Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes
 Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess
Math 7, Unit 8: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My guess
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION
 SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 9-1 Chapter 9 Geometry 9.1 Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles Basic Terms A line segment is part of a line between two points, including the endpoints.
SEVENTH EDITION and EXPANDED SEVENTH EDITION Slide 9-1 Chapter 9 Geometry 9.1 Points, Lines, Planes, and Angles Basic Terms A line segment is part of a line between two points, including the endpoints.
To find the surface area of a pyramid and a cone
 11-3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones Common Core State Standards G-MG.A.1 Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects. MP 1, MP 3, MP 4, MP 6, MP 7 Objective To find
11-3 Surface Areas of Pyramids and Cones Common Core State Standards G-MG.A.1 Use geometric shapes, their measures, and their properties to describe objects. MP 1, MP 3, MP 4, MP 6, MP 7 Objective To find
GEOMETRY SPRING SEMESTER FINALS REVIEW PACKET
 Name Date Class GEOMETRY SPRING SEMESTER FINALS REVIEW PACKET For 1 2, use the graph. 6. State the converse of the statement. Then determine whether the converse is true. Explain. If two angles are vertical
Name Date Class GEOMETRY SPRING SEMESTER FINALS REVIEW PACKET For 1 2, use the graph. 6. State the converse of the statement. Then determine whether the converse is true. Explain. If two angles are vertical
Math 1 Plane Geometry Part 1
 Math 1 Plane Geometry Part 1 1 Intersecting lines: When two lines intersect, adjacent angles are supplementary (they make a line and add up to 180 degrees, and vertical angles (angles across from each
Math 1 Plane Geometry Part 1 1 Intersecting lines: When two lines intersect, adjacent angles are supplementary (they make a line and add up to 180 degrees, and vertical angles (angles across from each
C in. 2. D in Find the volume of a 7-inch tall drinking glass with a 4-inch diameter. C lateral faces. A in. 3 B in.
 Standardized Test A For use after Chapter Multiple Choice. Which figure is a polyhedron? A B 7. Find the surface area of the regular pyramid. A 300 ft 2 B 340 ft 2 C 400 ft 2 C D D 700 ft 2 2. A polyhedron
Standardized Test A For use after Chapter Multiple Choice. Which figure is a polyhedron? A B 7. Find the surface area of the regular pyramid. A 300 ft 2 B 340 ft 2 C 400 ft 2 C D D 700 ft 2 2. A polyhedron
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition
 Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 #51-90 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes
Kansas City Area Teachers of Mathematics 2018 KCATM Math Competition GEOMETRY AND MEASUREMENT TEST GRADE 6 #51-90 INSTRUCTIONS Do not open this booklet until instructed to do so. Time limit: 20 minutes
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships
 Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Math 6, Unit 8 Notes: Geometric Relationships Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays As we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful.
Let a line l and a point P not lying on it be given. By using properties of a transversal and parallel lines, a line which passes through the point P
 Let a line l and a point P not lying on it be given. By using properties of a transversal and parallel lines, a line which passes through the point P and parallel to l, can be drawn. A triangle can be
Let a line l and a point P not lying on it be given. By using properties of a transversal and parallel lines, a line which passes through the point P and parallel to l, can be drawn. A triangle can be
PRACTICAL GEOMETRY SYMMETRY AND VISUALISING SOLID SHAPES
 UNIT 12 PRACTICAL GEOMETRY SYMMETRY AND VISUALISING SOLID SHAPES (A) Main Concepts and Results Let a line l and a point P not lying on it be given. By using properties of a transversal and parallel lines,
UNIT 12 PRACTICAL GEOMETRY SYMMETRY AND VISUALISING SOLID SHAPES (A) Main Concepts and Results Let a line l and a point P not lying on it be given. By using properties of a transversal and parallel lines,
Measurement and Geometry
 8A A Family Letter: Area Dear Family, The student will learn how to convert between units within the customary and metric measuring systems. The table below shows the conversions for the customary system.
8A A Family Letter: Area Dear Family, The student will learn how to convert between units within the customary and metric measuring systems. The table below shows the conversions for the customary system.
Honors Geometry Final Study Guide 2014
 Honors Geometry Final Study Guide 2014 1. Find the sum of the measures of the angles of the figure. 2. What is the sum of the angle measures of a 37-gon? 3. Complete this statement: A polygon with all
Honors Geometry Final Study Guide 2014 1. Find the sum of the measures of the angles of the figure. 2. What is the sum of the angle measures of a 37-gon? 3. Complete this statement: A polygon with all
Mgr. ubomíra Tomková GEOMETRY
 GEOMETRY NAMING ANGLES: any angle less than 90º is an acute angle any angle equal to 90º is a right angle any angle between 90º and 80º is an obtuse angle any angle between 80º and 60º is a reflex angle
GEOMETRY NAMING ANGLES: any angle less than 90º is an acute angle any angle equal to 90º is a right angle any angle between 90º and 80º is an obtuse angle any angle between 80º and 60º is a reflex angle
Volume of Cylinders. Volume of Cones. Example Find the volume of the cylinder. Round to the nearest tenth.
 Volume of Cylinders As with prisms, the area of the base of a cylinder tells the number of cubic units in one layer. The height tells how many layers there are in the cylinder. The volume V of a cylinder
Volume of Cylinders As with prisms, the area of the base of a cylinder tells the number of cubic units in one layer. The height tells how many layers there are in the cylinder. The volume V of a cylinder
Math 10 C Measurement Unit
 Math 10 C Measurement Unit Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which imperial unit is most appropriate
Math 10 C Measurement Unit Name: Class: Date: ID: A Chapter Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which imperial unit is most appropriate
FSA Geometry End-of-Course Review Packet. Circles Geometric Measurement and Geometric Properties
 FSA Geometry End-of-Course Review Packet Circles Geometric Measurement and Geometric Properties Table of Contents MAFS.912.G-C.1.1 EOC Practice... 3 MAFS.912.G-C.1.2 EOC Practice... 5 MAFS.912.G-C.1.3
FSA Geometry End-of-Course Review Packet Circles Geometric Measurement and Geometric Properties Table of Contents MAFS.912.G-C.1.1 EOC Practice... 3 MAFS.912.G-C.1.2 EOC Practice... 5 MAFS.912.G-C.1.3
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide
 Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Polygons. 5 sides 5 angles. pentagon. Name
 Lesson 11.1 Reteach Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number
Lesson 11.1 Reteach Polygons A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. You can classify a polygon by the number of sides and the number
Part I Multiple Choice
 Oregon Focus on Surface Area and Volume Practice Test ~ Surface Area Name Period Date Long/Short Term Learning Targets MA.MS.07.ALT.05: I can solve problems and explain formulas involving surface area
Oregon Focus on Surface Area and Volume Practice Test ~ Surface Area Name Period Date Long/Short Term Learning Targets MA.MS.07.ALT.05: I can solve problems and explain formulas involving surface area
MATH DICTIONARY. Number Sense. Number Families. Operations. Counting (Natural) Numbers The numbers we say when we count. Example: {0, 1, 2, 3, 4 }
 Number Sense Number Families MATH DICTIONARY Counting (Natural) Numbers The numbers we say when we count Example: {1, 2, 3, 4 } Whole Numbers The counting numbers plus zero Example: {0, 1, 2, 3, 4 } Positive
Number Sense Number Families MATH DICTIONARY Counting (Natural) Numbers The numbers we say when we count Example: {1, 2, 3, 4 } Whole Numbers The counting numbers plus zero Example: {0, 1, 2, 3, 4 } Positive
Vocabulary. Term Page Definition Clarifying Example. apothem. center of a circle. center of a regular polygon. central angle of a regular polygon
 CHAPTER 9 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 9. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. apothem Term Page Definition
CHAPTER 9 Vocabulary The table contains important vocabulary terms from Chapter 9. As you work through the chapter, fill in the page number, definition, and a clarifying example. apothem Term Page Definition
MATH-G Geometry SOL Test 2015 Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions
 MATH-G Geometry SOL Test 2015 Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2LKRLG 1 Which Venn diagram accurately represents the information in the following statement? If a triangle is equilateral,
MATH-G Geometry SOL Test 2015 Exam not valid for Paper Pencil Test Sessions [Exam ID:2LKRLG 1 Which Venn diagram accurately represents the information in the following statement? If a triangle is equilateral,
Math Tool: Grid Paper
 Math Tool: Grid Paper A2 math tools Reproducible page, for classroom use only. 20 Triumph Learning, LLC Math Tool: Grid Paper Reproducible page, for classroom use only. 20 Triumph Learning, LLC math tools
Math Tool: Grid Paper A2 math tools Reproducible page, for classroom use only. 20 Triumph Learning, LLC Math Tool: Grid Paper Reproducible page, for classroom use only. 20 Triumph Learning, LLC math tools
SHAPE AND STRUCTURE. Shape and Structure. An explanation of Mathematical terminology
 Shape and Structure An explanation of Mathematical terminology 2005 1 POINT A dot Dots join to make lines LINE A line is 1 dimensional (length) A line is a series of points touching each other and extending
Shape and Structure An explanation of Mathematical terminology 2005 1 POINT A dot Dots join to make lines LINE A line is 1 dimensional (length) A line is a series of points touching each other and extending
2nd Semester Exam Review
 Geometry 2nd Semester Exam Review Name: Date: Per: Trig & Special Right Triangles 1. At a certain time of the day, a 30 meter high building cast a shadow that is 31 meters long. What is the angle of elevation
Geometry 2nd Semester Exam Review Name: Date: Per: Trig & Special Right Triangles 1. At a certain time of the day, a 30 meter high building cast a shadow that is 31 meters long. What is the angle of elevation
The Geometry of Solids
 CONDENSED LESSON 10.1 The Geometry of Solids In this lesson you will Learn about polyhedrons, including prisms and pyramids Learn about solids with curved surfaces, including cylinders, cones, and spheres
CONDENSED LESSON 10.1 The Geometry of Solids In this lesson you will Learn about polyhedrons, including prisms and pyramids Learn about solids with curved surfaces, including cylinders, cones, and spheres
Geometry Vocabulary Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
3 Dimensional Solids. Table of Contents. 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres
 Table of Contents 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres Surface Area Prisms Pyramids Cylinders Spheres More Practice/ Review 3 Dimensional Solids Polyhedron A
Table of Contents 3 Dimensional Solids Nets Volume Prisms and Cylinders Pyramids, Cones & Spheres Surface Area Prisms Pyramids Cylinders Spheres More Practice/ Review 3 Dimensional Solids Polyhedron A
2. A circle is inscribed in a square of diagonal length 12 inches. What is the area of the circle?
 March 24, 2011 1. When a square is cut into two congruent rectangles, each has a perimeter of P feet. When the square is cut into three congruent rectangles, each has a perimeter of P 6 feet. Determine
March 24, 2011 1. When a square is cut into two congruent rectangles, each has a perimeter of P feet. When the square is cut into three congruent rectangles, each has a perimeter of P 6 feet. Determine
Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes
 Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My
Math 7, Unit 08: Geometric Figures Notes Points, Lines and Planes; Line Segments and Rays s we begin any new topic, we have to familiarize ourselves with the language and notation to be successful. My
Day 116 Bellringer. 1. Use the triangle below to answer the questions that follow.
 Day 116 Bellringer 1. Use the triangle below to answer the questions that follow. 3 in 5 in 4 in a) Find the area of the triangle. b) Find the perimeter of the triangle. 2. Use the distance formula to
Day 116 Bellringer 1. Use the triangle below to answer the questions that follow. 3 in 5 in 4 in a) Find the area of the triangle. b) Find the perimeter of the triangle. 2. Use the distance formula to
GM1.1 Consolidation Worksheet Answers
 Cambridge Essentials Mathematics Support 8 GM1.1 Consolidation Worksheet Answers GM1.1 Consolidation Worksheet Answers 1 a a = 60 Angles on a straight line add to 180. b b = 150 Angles on a straight line
Cambridge Essentials Mathematics Support 8 GM1.1 Consolidation Worksheet Answers GM1.1 Consolidation Worksheet Answers 1 a a = 60 Angles on a straight line add to 180. b b = 150 Angles on a straight line
Review: Geometry. Area Composite Figures Surface Area Volume Fractional Edge Length 3-D Figures and Nets Coordinate Graphing
 Review: Geometry Area Composite Figures Surface Area Volume Fractional Edge Length 3-D Figures and Nets Coordinate Graphing Perimeter: the distance around a polygon. Area: the number of square units needed
Review: Geometry Area Composite Figures Surface Area Volume Fractional Edge Length 3-D Figures and Nets Coordinate Graphing Perimeter: the distance around a polygon. Area: the number of square units needed
2.1 Length of a Line Segment
 .1 Length of a Line Segment MATHPOWER TM 10 Ontario Edition pp. 66 7 To find the length of a line segment joining ( 1 y 1 ) and ( y ) use the formula l= ( ) + ( y y ). 1 1 Name An equation of the circle
.1 Length of a Line Segment MATHPOWER TM 10 Ontario Edition pp. 66 7 To find the length of a line segment joining ( 1 y 1 ) and ( y ) use the formula l= ( ) + ( y y ). 1 1 Name An equation of the circle
Geometry Workbook WALCH PUBLISHING
 Geometry Workbook WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Student..............................vii Unit 1: Lines and Triangles Activity 1 Dimensions............................. 1 Activity 2 Parallel
Geometry Workbook WALCH PUBLISHING Table of Contents To the Student..............................vii Unit 1: Lines and Triangles Activity 1 Dimensions............................. 1 Activity 2 Parallel
Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes
 Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes Day 1: Area of Square, Rectangles, and Parallelograms Day 2: Area of Triangles Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Day 3: Quiz over Area of those
Unit Lesson Plan: Measuring Length and Area: Area of shapes Day 1: Area of Square, Rectangles, and Parallelograms Day 2: Area of Triangles Trapezoids, Rhombuses, and Kites Day 3: Quiz over Area of those
Unit 4 End-of-Unit Assessment Study Guide
 Circles Unit 4 End-of-Unit Assessment Study Guide Definitions Radius (r) = distance from the center of a circle to the circle s edge Diameter (d) = distance across a circle, from edge to edge, through
Circles Unit 4 End-of-Unit Assessment Study Guide Definitions Radius (r) = distance from the center of a circle to the circle s edge Diameter (d) = distance across a circle, from edge to edge, through
TOPIC 2 Building Blocks of Geometry. Good Luck To
 Good Luck To Period Date PART I DIRECTIONS: Use the Terms (page 2), Definitions (page 3), and Diagrams (page 4) to complete the table Term (capital letters) 1. Chord 2. Definition (roman numerals) Pictures
Good Luck To Period Date PART I DIRECTIONS: Use the Terms (page 2), Definitions (page 3), and Diagrams (page 4) to complete the table Term (capital letters) 1. Chord 2. Definition (roman numerals) Pictures
February 07, Dimensional Geometry Notebook.notebook. Glossary & Standards. Prisms and Cylinders. Return to Table of Contents
 Prisms and Cylinders Glossary & Standards Return to Table of Contents 1 Polyhedrons 3-Dimensional Solids A 3-D figure whose faces are all polygons Sort the figures into the appropriate side. 2. Sides are
Prisms and Cylinders Glossary & Standards Return to Table of Contents 1 Polyhedrons 3-Dimensional Solids A 3-D figure whose faces are all polygons Sort the figures into the appropriate side. 2. Sides are
Geometry Semester 1 Model Problems (California Essential Standards) Short Answer
 Geometry Semester 1 Model Problems (California Essential Standards) Short Answer GE 1.0 1. List the undefined terms in Geometry. 2. Match each of the terms with the corresponding example a. A theorem.
Geometry Semester 1 Model Problems (California Essential Standards) Short Answer GE 1.0 1. List the undefined terms in Geometry. 2. Match each of the terms with the corresponding example a. A theorem.
Additional Practice. Name Date Class
 Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
Additional Practice Investigation 1 1. The four nets below will fold into rectangular boxes. Net iii folds into an open box. The other nets fold into closed boxes. Answer the following questions for each
Get Ready. Solving Equations 1. Solve each equation. a) 4x + 3 = 11 b) 8y 5 = 6y + 7
 Get Ready BLM... Solving Equations. Solve each equation. a) 4x + = 8y 5 = 6y + 7 c) z+ = z+ 5 d) d = 5 5 4. Write each equation in the form y = mx + b. a) x y + = 0 5x + y 7 = 0 c) x + 6y 8 = 0 d) 5 0
Get Ready BLM... Solving Equations. Solve each equation. a) 4x + = 8y 5 = 6y + 7 c) z+ = z+ 5 d) d = 5 5 4. Write each equation in the form y = mx + b. a) x y + = 0 5x + y 7 = 0 c) x + 6y 8 = 0 d) 5 0
Name: Date: Class: Honors Geometry Advancement Practice (Part 2)
 Name: Date: lass: Honors Geometry Advancement Practice (Part 2) Part 1 Multiple hoice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Place your answer on the Scantron sheet
Name: Date: lass: Honors Geometry Advancement Practice (Part 2) Part 1 Multiple hoice: Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Place your answer on the Scantron sheet
Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review
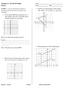 Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review G-GPE.7 I can use the distance formula to compute perimeter and area of triangles and rectangles. Name Period Date 3. Find the area and perimeter of the triangle with
Geometry 2: 2D and 3D shapes Review G-GPE.7 I can use the distance formula to compute perimeter and area of triangles and rectangles. Name Period Date 3. Find the area and perimeter of the triangle with
Reteach. Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes. P point P
 Name Date Class 1-1 Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes A point has no size. It is named using a capital letter. All the figures below contain points. line Figure Characteristics Diagram Words and
Name Date Class 1-1 Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes A point has no size. It is named using a capital letter. All the figures below contain points. line Figure Characteristics Diagram Words and
Extra Practice 1. Name Date. Lesson 1: Exploring Triangles
 Master 6.36 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 1: Exploring Triangles 1. Draw 3 different triangles. Measure and label the side lengths. Name each triangle as equilateral, isosceles, or scalene. 2. Name each triangle
Master 6.36 Extra Practice 1 Lesson 1: Exploring Triangles 1. Draw 3 different triangles. Measure and label the side lengths. Name each triangle as equilateral, isosceles, or scalene. 2. Name each triangle
UNIT 11. Angle Relationships, Area, and Perimeter/Circumference CCM6+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Unit 11 Vocabulary...
 Page 1 CCM6+ Unit 11 Angle Relationships, Area, Perimeter/Circumference 15-16 UNIT 11 Angle Relationships, Area, and Perimeter/Circumference 2016 2017 CCM6+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Unit
Page 1 CCM6+ Unit 11 Angle Relationships, Area, Perimeter/Circumference 15-16 UNIT 11 Angle Relationships, Area, and Perimeter/Circumference 2016 2017 CCM6+ Name: Math Teacher: Projected Test Date: Unit
Name: Target 12.2: Find and apply surface of Spheres and Composites 12.2a: Surface Area of Spheres 12.2b: Surface Area of Composites Solids
 Unit 12: Surface Area and Volume of Solids Target 12.0: Euler s Formula and Introduction to Solids Target 12.1: Find and apply surface area of solids 12.1a: Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.1b:
Unit 12: Surface Area and Volume of Solids Target 12.0: Euler s Formula and Introduction to Solids Target 12.1: Find and apply surface area of solids 12.1a: Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders 12.1b:
Mathematics Assessment Anchor Glossary Grades 3 & 4
 Mathematics Assessment Anchor Glossary Grades 3 & 4 The definitions for this glossary were taken from one or more of the following sources: Webster s Dictionary, various mathematics dictionaries, the PA
Mathematics Assessment Anchor Glossary Grades 3 & 4 The definitions for this glossary were taken from one or more of the following sources: Webster s Dictionary, various mathematics dictionaries, the PA
To the Student...4. Part Part
 Table of Contents To the Student.......................................................4 Session I: Pretest...........................................5 Part 1............................................................6
Table of Contents To the Student.......................................................4 Session I: Pretest...........................................5 Part 1............................................................6
SHAPE, SPACE and MEASUREMENT
 SHAPE, SPACE and MEASUREMENT Types of Angles Acute angles are angles of less than ninety degrees. For example: The angles below are acute angles. Obtuse angles are angles greater than 90 o and less than
SHAPE, SPACE and MEASUREMENT Types of Angles Acute angles are angles of less than ninety degrees. For example: The angles below are acute angles. Obtuse angles are angles greater than 90 o and less than
Mrs. Daniel s Geometry Vocab List
 Mrs. Daniel s Geometry Vocab List Geometry Definition: a branch of mathematics concerned with questions of shape, size, relative position of figures, and the properties of space. Refectional Symmetry Definition:
Mrs. Daniel s Geometry Vocab List Geometry Definition: a branch of mathematics concerned with questions of shape, size, relative position of figures, and the properties of space. Refectional Symmetry Definition:
Practice A Introduction to Three-Dimensional Figures
 Name Date Class Identify the base of each prism or pyramid. Then choose the name of the prism or pyramid from the box. rectangular prism square pyramid triangular prism pentagonal prism square prism triangular
Name Date Class Identify the base of each prism or pyramid. Then choose the name of the prism or pyramid from the box. rectangular prism square pyramid triangular prism pentagonal prism square prism triangular
Big Apple Academy 2017 Mathematics Department
 Big Apple Academy 201 Mathematics Department Grade Homework Math Package It is important that you keep practicing your mathematical Knowledge over the summer to be ready for 5 th grade. In this Package
Big Apple Academy 201 Mathematics Department Grade Homework Math Package It is important that you keep practicing your mathematical Knowledge over the summer to be ready for 5 th grade. In this Package
