Velocity (Vs) Display (1-D Profile)
|
|
|
- Leonard Douglas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PS User Guide Series 2015 Velocity (Vs) Display (1-D Profile) Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. January 2015
2 Table of Contents Page 1. Overview 2 2. Files 6 3. View 7 4. Edit 9 5. Chart Layer Dispersion Inversion Seismic 23 1
3 1. Overview This module is specifically for the 1-D layered-earth model (*.LYR) that is obtained from the inversion of one measured dispersion curve (*.DC). In addition to display, this module can perform editing of the model such as changing velocities and depths of layers and remapping current layer model into different depth model, etc. It can also apply certain processes such as calculating average shear-wave velocity (Vs) for a certain depth (or layer) range (e.g., Vs30m), combining with other models, generating an average model from multiple models, exporting current 1-D (depth) velocity (Vs) structure into an existing 2-D Vs file, etc. Furthermore, those forward modeling schemes are also included that can generate theoretical dispersion curves, seismic records, and dispersion images by using the current model displayed as input. To display a layered-earth file (*.LYR), in the main menu go to "Display" "S-Velocity (Vs) Data" "1-D Vs Profile (*.LYR)" and then select such a file as illustrated below. The program will ask if the linked (measured and modeled) dispersion curves are also to be displayed. The information about them is encoded in the input LYR file. If it is chosen by clicking "Yes" as shown below, then a message box will appear that instructs how to manually edit the input layered-earth model. This means the "real-time manual inversion" is enabled as shown below. 2
4 The display below shows the shear-wave velocity (Vs) profile of the input LYR file among other additional parameters included in the file [i.e., Vp, Poissons' ratio ( ), density ( ), and Q values (Qs and Qp)]. The two dispersion curves are also displayed with one of the two vertical axes converted to a frequency (Hz) axis. The match between the two is indicated on top of the form [e.g., "Dispersion Curve Match (%): 87.69"]. As velocities are manually changed by using the mouse, the corresponding modeled dispersion curve will be updated and the new match will be displayed on top so that the manual inversion can be "steered" in the most favorable direction. In addition, an automatic inversion can be launched at any stage in the sequence of manual inversion that will use the current model as the initial model to search for a "better" model that gives an improved match in dispersion curves. This is further explained in section 8 ("Inversion"). In the vertical tool panel displayed on the right side of the form are arranged those buttons that can display layer parameters such as depth ("Z"), shear-wave velocity ("Vs"), P-wave velocity ("Vp"), Poisson's ratio (" "), density (" "), and Q-values ("Qs" and "Qp"). The "Vs/Vp" button, if depressed, will ensure the ratio between the two velocities (Vs and Vp) remains unchanged when either of the two is manually changed. Otherwise, the Poisson's ratio ( ) will be updated in response to the change of either velocity (Vs or Vp). The "Vs30m" button will evaluate the seismic site classification code based on the designation by National Earthquake Hazard Reduction Program (NEHRP) and the International Building Code (IBC) and display the result inside the chart. Examples of all these cases are illustrated below. 3
5 Velocities (Vs and Vp) are displayed on the left, and Poisson's ratio ( ) is displayed on the right. Density ( ) (on the left) and Q values (Qs and Qp) (on the right) are displayed below. The "Vs30m" is calculated and seismic site class ('C') has been assigned in the chart below. 4
6 The top tool panel contains eight (8) tabs: "Files", "View", "Edit", "Chart", "Layer", "Dispersion", "Inversion", and "Seismic." The type of task performed by each tab is explained below. Files View Edit Chart Layer Dispersion Inversion Seismic Another file can be opened to replace the current file or to be added into the current display. The current layered-earth model can be saved into another file (*.LYR) or its image can be saved as a graphic file (*.BMP; *.JPG). The current chart image can be printed, or its contents (i.e., numbers and text) can be printed. Dispersion curve(s) can also be imported as a comparison with modeled dispersion curve. Chart graphic related parameters can be changed such as axis scales, grid lines, etc. Contents of the current file (*.LYR) can be viewed in a separate window. The seismic site classification table (*.PDF) can also be displayed. The current model can be changed manually by using the mouse or typing values in the appropriate boxes displayed in a tabular form. A new layer model can be created. All chart controls are included that can control display attributes of layer parameters. Layer-related operations can be performed such as stretching the depth scale, calculating average velocity (Vs or Vp) for a specified range, generating an average layer model (*.LYR) from multiple models, summing (or subtracting) two models, remapping into another "reference" depth model, etc. Theoretical dispersion curves of any mode (e.g., fundamental, 1st higher, 2nd higher, etc.) can be generated via forward modeling by using current velocity (Vs and Vp) and density ( ) model as input. Detailed explanations about this modeling are provided in the PS User Guide "Modeling Dispersion Curves." Automatic inversion can be performed that uses the current velocity (Vs) model as the initial model. Complete inversion parameters can be controlled that are fully explained in the PS User Guide "Inversion." A seismic record and the corresponding dispersion image can be generated from the current model that includes velocities (Vs and Vp), density ( ), and Q values (Qs and Qp). Details about this modeling is provided in the PS User Guide "Modeling Seismic Data." 5
7 2. Files Open Opens a different layered-earth file (*.LYR) to replace the current one. New Opens another layered-earth file (*.LYR) to display in the same chart. Save Saves the current layered-earth file as a separate file (*.LYR). *.bmp Saves the current chart image as a graphic file (*.BMP, *.JPG). Print ( ) Prints the current chart image. Print ( ) Prints contents (i.e., numbers and texts) of the current layered-earth file (*.LYR). Open DC Opens and displays a dispersion curve file (*.DC). 6
8 3. View Grids Displays dotted horizontal and vertical grid lines on the chart. X* Increases (right click = decreases) horizontal axis scale. Y* Increases (right click = decreases) vertical axis scale. Data Displays data values of a layered-earth file for a complete set of variables as shown below. Contents History Bounds Shows complete contents (i.e., data values and processing history) of the file. Shows only the processing history portion of the file. Displays (as illustrated below) numerical limits (lower and upper bounds) of each layer's velocity (Vs) that fall under 99% confidence of inversion. This evaluation is based on the numerical sensitivity of the Jacobian matrix used during the inversion process. 7
9 DC's If the displayed file (*.LYR) is an inversion output, then the corresponding dispersion curves (i.e., "measured" and "modeled" curves) can be displayed, if chosen (i.e., "Yes" below). Delete Vs30m Dispersion curves currently displayed (except for the "modeled" curve) will be deleted. Displays the seismic site classification table (*.PDF) adopted by National Earthquake Hazard Reduction Program (NEHRP) and the International Building Code (IBC) as shown below. 8
10 4. Edit Edit LYR ( ) Depress the Edit LYR button to enable editing of the model displayed in the chart. A message box (shown below) will appear to instruct how to do it. To change the value of any layer, click and drag the layer's bar (vertical) line horizontally (left and right). To change the depth of any layer, click and drag the (top or bottom) boundary (horizontal) line vertically (up and down). For this, the depth ('Z') button in the tool panel on the right side must be depressed. Instead of using the mouse, values can be typed in when the "Show" button is depressed as explained next. [Why italics?] Show If this button is depressed, a separate panel will appear on the top of the chart (shown below) where edit boxes are arranged. Value of individual variables (e.g., Vs, Vp, etc.) in the displayed model (*.LYR) can be changed by typing in the appropriate box. Display of the model will be accordingly updated as values are changed. Edit LYR ( ) Click the button for a separate display where numerical values of all layer variables are displayed in a table (shown below). Individual items can be changed by manually typing. 9
11 New LYR Click this button to replace the current layered-earth model (displayed in the chart) with a new model with initial values that can be specified in the dialog as shown below. Remap The current layered-earth model can be remapped according to a new depth model, which is defined by another ("reference") model. The following message will appear and then a file for the new depth model will have to be imported as shown below. The current layered-earth model will be accordingly updated on the display. Unit Click this button to change the distance unit of the model. Two options are available; (1) simple change of labeling and (2) converting values of related data into those of the other unit. The dialog shown below illustrates the two options. 10
12 5. Chart Show All Displays the following control dialog that contains all the chart-related controls. A full description of common chart controls is provided in the PS User Guide Chart Controls." The "Curve To Apply" box at the bottom of the dialog below is unique to this module of 1-D Vs display. Click an appropriate item in the box to select the corresponding variable in the model to apply the changes. Data Axis Label Panel Displays the dialog above with the "Data" tab opened. Displays the dialog above with the "Axis" tab opened. Displays the dialog above with the "Labeling" tab opened. Displays the dialog above with the "Panel" tab opened. 11
13 6. Layer Scale* Depth scale of current layer model can be enlarged (normal click) or reduced (right click) by a preset amount (10 %) each time the button is clicked. The example below shows how the original layer model (left) is enlarged in depth scale after a few normal clicks (right). Vave Average velocity (Vs or Vp) can be calculated for a specified range of depth or Layers. A control dialog will appear as shown below where the type of velocity ["S-Velocity (Vs)" or "P-Velocity (Vp)"] can be selected. Type of average can also be selected in the "Average type" box where either "Depth" (left) or "Layers" (right) can be selected. If the former is selected, then the maximum depth is specified in the "Maximum depth (Zmax)" box. If the latter ("Layers") is selected, then a separate box will appear where the layer range is specified in the "Start No." and "End No." boxes. If the last layer ("Half Space") is included in the range, then its depth ratio (used during the calculation of relative contribution) is specified in the "Half-Space (HS) Ratio*" box. Click "OK" button to show the calculated average velocity. The two examples shown below illustrate the output values in the above two cases of average type. 12
14 Average This will produce an average model (*.LYR) from multiple models (*.LYR's) to be imported. The existing model(s) currently displayed will not be automatically included in the average process. On clicking the button, this information will be displayed in the message box shown below ("INFO" box). Then, a multiple number of LYR files will have to be imported that may have different depth models (i.e., different number of layers and different maximum depths) as shown below ("Open" dialog). Then, another message box (2nd "INFO" box) will indicate a "reference" file will have to be imported that will be used as the depth model for the output file (*.LYR) (2nd "Open" dialog). Then, the last message box (last "INFO" box) will instruct how to specify the output file name (*.LYR) ("Save As" dialog). Then, the output will be displayed in the current form by replacing the previous model as shown below. 13
15 Bounds Theoretical limits of velocity for each layer (i.e., lower and upper bounds) can be calculated based on each layer's sensitivity on the "reference" dispersion curve. Then, calculated bounds can be used as relative confidence levels if the model (*.LYR) is an inversion output from a measured dispersion curve (*.DC). In this case the velocity range between the two limits may indicate such a range within which the "true" solution can exist with a certain probability, for example, of 99%. In this sense, the bounds of each layer can represent relative confidence levels. On the other hand, if the current model is not an output from inversion and there is no measured and modeled dispersions curve linked to it, then a "fictitious" dispersion curve can be modeled within a specified frequency range and then the bounds calculated based on this curve. In this case, the calculated bounds can represent the relative "accuracy" level of each layer that can be evaluated from a possible MASW survey over such a velocity model. If the current model (*.LYR) is an output from the inversion of a measured dispersion curve (*.DC), then the program will calculate the bounds based on the measured dispersion curve specified within the model file (*.LYR). In this case, existing bounds (calculated during the inversion process) will be replaced by the new calculations as informed by a message box shown below (on the left). If there is no dispersion curve linked to current model (*.LYR) (or if the measured dispersion curve is not found), the following dialog (on the right) will appear where the frequency range can be specified to design a "fictitious" curve in the "Start..." and "End..." boxes. The "Bounds limit..." is an arbitrary amount of overall change in dispersion curve to calculate the bounds. "Account for mode jump" and "Use 'Lamb-Wave' approximation" are applied only when the velocity model includes "significant" velocity inversion on top (see PS User Guide "Modeling Dispersion Curves" for more details). Calculated bounds will be displayed in the chart at the end. 14
16 +/- ( ) Two layered-earth model files (LYR's) (one currently displayed and one to be imported) can be added (+) or subtracted (-). When this button is clicked, the following dialog will appear where the operation type ["Subtract (-)" or "Add (+)"] is specified. Then, another dialog will ask if output is to be in percent (%). (The example below shows a choice of "No.") Then, open the other file (*.LYR) and specify output file name (*.LYR). (The example below opens the same file for demonstration purposes.) The output summed file (in red) is displayed below along with the original file (in blue) to illustrate what it looks like. The two files have to have a common (the same) depth model to perform this operation. 15
17 2-D Vs Current 1-D shear-wave velocity (Vs) model can be written as part of the 2-D velocity (Vs) cross section. It can be added to an existing file if the "Append output" box is checked. Check the "Export confidence data if exists" box if the confidence estimation (calculated from bounds of each layer) is also written in the separate file, whose file name has a post fix of "(2DConf).txt" after the output file name specified by clicking the "Output File Name [*(2DVs).txt]" button. Surface (X) location can be specified in the "Output surface (X) coordinate" box where the default value is copied from the input file (*.LYR) if it has such information in it. 16
18 7. Dispersion RUN Generates dispersion curve(s) from the current layered-earth model (*.LYR) displayed in the chart by running forward modeling. On clicking the button, the control dialog (on the left) will appear where parameters of the dispersion curve (e.g., frequency range, frequency interval, number of data points, etc.) can be specified. See PS User Guide "Modeling Dispersion Curves" for detailed explanation about this dialog. Click "OK" and the calculated dispersion curve will be displayed on the chart as illustrated below. It can be noticed one of the two vertical axes is now converted into the frequency (Hz) axis. Edit RUN If this button is depressed, then the dispersion-curve generation will take place in real time as a response to an edit of the layer model by using the mouse (e.g., changing velocity or depth of a layer). The message box below (on the left) informs about this. However, for this to take place, the layer-edit mode has to have been enabled by depressing the "Edit LYR" button in the "Edit" tab of top tool panel. Otherwise, the program will instruct as illustrated below (on the right). The following example illustrates how the 5th layer's velocity (Vs) is changed by using the mouse after depressing the "Edit RUN" button; the calculated dispersion curve is displayed with one of the two vertical axes (right axis) converted into a frequency (Hz) axis. A control dialog for dispersion-curve generation may appear first if not previously displayed. 17
19 Ctrls Displays the control dialog shown below that contains all the parameters related to the forward modeling of dispersion curve(s). See PS User Guide "Modeling Dispersion Curves" for details. Frq Root The control dialog will appear with the "Frequency (Hz)" tab selected where frequency related parameters can be specified as illustrated above. The control dialog will appear with the "Searching option" tab selected where "root searching" parameters (in solving the characteristic equation) can be specified as illustrated below. 18
20 Inverse The control dialog will appear with the "Inverse velocity (Vs)" tab selected where those parameters related to "inverse velocity" structure of input velocity (Vs) model can be specified as illustrated below. 19
21 8. Inversion This inversion tab enables the inversion of a measured dispersion curve through forward modeling. Therefore, the layered-earth model (*.LYR) currently displayed must be an inversion output and the corresponding measured dispersion curve has to be displayed also. The message dialog (below left) indicates the input file is an inversion output file and asks if the measured dispersion curve should be displayed. Click "Yes" to display it and then another message box will appear as shown (below right) that instructs how to change an individual layer s velocity and depth. When the file (*.LYR) is displayed with corresponding (measured and modeled) dispersion curves as shown below, then the match between the two curves is displayed on top of the form [e.g., "Dispersion Curve Match (%): 87.69"] that is the best match found from the previous inversion process. Then, all the buttons (i.e., options) will have been set so that the manual layer edit by mouse is enabled and the corresponding real-time update of modeled dispersion curve is also enabled. Then, the new match will be displayed on top to indicate whether the updated velocity model is a "better solution" or not. The example shown below illustrates this improvement of match that changed from % to % (indicated by red arrow) after the 5th layer's velocity has been changed (indicated by the yellow arrow). 20
22 RUN Clicking this button will launch the "automatic" inversion that uses the current layeredearth model displayed on the chart as the initial model. The process will update the model only when it can find a "better solution" as described above. The example below illustrates a case in which the match further improved from 87.94% to 91.08%. By properly combining the manual inversion described above and this automatic inversion, it is possible to find a velocity model that is most accurate from the numerical perspective and yet more realistic. 21
23 Ctrls Display the following control dialog that contains all the parameters related to the automatic inversion. See PS User Guide "Inversion" for detailed description of these parameters. 22
24 9. Seismic Multichannel seismic record(s) can be modeled using the current 1-D (depth) model (*.LYR) displayed on the chart as an input layered-earth model. This is the modeling by the reflectivity method described in the PS User Guide "Modeling Seismic Data." On clicking the button, the following control dialog will appear that contains all the parameters related to the modeling. See the PS User Guide ("Modeling Seismic Data") for detailed description of these parameters. The following illustrates the modeling output of a seismic record (left) and the corresponding dispersion image (right) calculated from the layered-earth model last displayed. 23
PS User Guide Series Velocity (Vs) Display (2-D Cross Section)
 PS User Guide Series 2015 Velocity (Vs) Display (2-D Cross Section) Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents Page 1. Overview 2 2. Files 4 3. View 5 4. Edit 7 5. Process 9 6. Chart
PS User Guide Series 2015 Velocity (Vs) Display (2-D Cross Section) Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents Page 1. Overview 2 2. Files 4 3. View 5 4. Edit 7 5. Process 9 6. Chart
PS User Guide Series Dispersion-Data Display
 PS User Guide Series 2015 Dispersion-Data Display Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents Page 1. Overview 2 2. Dispersion Curve (*.DC) 5 2.1 Files 5 2.2 Curves 6 2.3 Scale 7 2.4
PS User Guide Series 2015 Dispersion-Data Display Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents Page 1. Overview 2 2. Dispersion Curve (*.DC) 5 2.1 Files 5 2.2 Curves 6 2.3 Scale 7 2.4
PS User Guide Series Utility
 PS User Guide Series 2015 Utility Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents Page 1. Overview 2 2. Format SEG-2 Files 5 3. Format TEXT data 7 4. Make Common Seismic Gathers 9 5. Make
PS User Guide Series 2015 Utility Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents Page 1. Overview 2 2. Format SEG-2 Files 5 3. Format TEXT data 7 4. Make Common Seismic Gathers 9 5. Make
About This Version ParkSEIS 2.0
 PS User Guide Series - About This Version 2.0 2016 About This Version ParkSEIS 2.0 Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. September 2016 Table of Contents Page 1. Summary 2 2. Velocity (Vs) Cross Section - Topographic
PS User Guide Series - About This Version 2.0 2016 About This Version ParkSEIS 2.0 Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. September 2016 Table of Contents Page 1. Summary 2 2. Velocity (Vs) Cross Section - Topographic
Dispersion Curve Extraction (1-D Profile)
 PS User Guide Series 2015 Dispersion Curve Extraction (1-D Profile) Working with Sample Data ("Vs1DMASW.dat") Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents Page 1. Overview 2 2. Bounds
PS User Guide Series 2015 Dispersion Curve Extraction (1-D Profile) Working with Sample Data ("Vs1DMASW.dat") Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents Page 1. Overview 2 2. Bounds
About This Version ParkSEIS 3.0
 PS User Guide Series - About This Version 3.0 2017 About This Version ParkSEIS 3.0 Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. September 2017 Table of Contents Page 1. Summary 2 2. AUTO - Automatic Generation of
PS User Guide Series - About This Version 3.0 2017 About This Version ParkSEIS 3.0 Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. September 2017 Table of Contents Page 1. Summary 2 2. AUTO - Automatic Generation of
PS User Guide Series Dispersion Image Generation
 PS User Guide Series 2015 Dispersion Image Generation Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents Page 1. Overview 2 2. Importing Input Data 3 3. Main Dialog 4 4. Frequency/Velocity
PS User Guide Series 2015 Dispersion Image Generation Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents Page 1. Overview 2 2. Importing Input Data 3 3. Main Dialog 4 4. Frequency/Velocity
Tutorial on Multichannel Analysis of Surface Wave (MASW) in the RadExPro Software
 Tutorial on Multichannel Analysis of Surface Wave (MASW) in the RadExPro Software (Revision of 23.11.2016) DECO Geophysical SC Moscow State University Science Park 1-77 Leninskie Gory Moscow 119992, Russia
Tutorial on Multichannel Analysis of Surface Wave (MASW) in the RadExPro Software (Revision of 23.11.2016) DECO Geophysical SC Moscow State University Science Park 1-77 Leninskie Gory Moscow 119992, Russia
Pre-Lab Excel Problem
 Pre-Lab Excel Problem Read and follow the instructions carefully! Below you are given a problem which you are to solve using Excel. If you have not used the Excel spreadsheet a limited tutorial is given
Pre-Lab Excel Problem Read and follow the instructions carefully! Below you are given a problem which you are to solve using Excel. If you have not used the Excel spreadsheet a limited tutorial is given
MASW Short Course - Park Seismic LLC
 Course Title: Multichannel Analysis of Surface Waves (MASW) Format: Two-Half-Day Course (PM Session in Day 1 and AM Session in Day 2) Date and Location: April 6, 2016 (location to be announced later) Instructor:
Course Title: Multichannel Analysis of Surface Waves (MASW) Format: Two-Half-Day Course (PM Session in Day 1 and AM Session in Day 2) Date and Location: April 6, 2016 (location to be announced later) Instructor:
Abstract. Introduction
 A COMPARISON OF SHEAR WAVE VELOCITIES OBTAINED FROM THE CROSSHOLE SEISMIC, SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE WAVES AND MULTIPLE IMPACTS OF SURFACE WAVES METHODS Patrick K. Miller, Olson Engineering, Wheat Ridge,
A COMPARISON OF SHEAR WAVE VELOCITIES OBTAINED FROM THE CROSSHOLE SEISMIC, SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE WAVES AND MULTIPLE IMPACTS OF SURFACE WAVES METHODS Patrick K. Miller, Olson Engineering, Wheat Ridge,
Geogiga Seismic Pro 9.0 Release Notes
 Geogiga Seismic Pro 9.0 Release Notes Copyright 2018, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Introduction...1 Part 1 New Modules...3 Modeling2D...3 Surface RT...4 Part 2 General Enhancements...5 Part 3
Geogiga Seismic Pro 9.0 Release Notes Copyright 2018, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Introduction...1 Part 1 New Modules...3 Modeling2D...3 Surface RT...4 Part 2 General Enhancements...5 Part 3
MASW Horizontal Resolution in 2D Shear-Velocity (Vs) Mapping
 MASW Horizontal Resolution in 2D Shear-Velocity (Vs) Mapping by Choon B. Park Kansas Geological Survey University of Kansas 1930 Constant Avenue, Campus West Lawrence, Kansas 66047-3726 Tel: 785-864-2162
MASW Horizontal Resolution in 2D Shear-Velocity (Vs) Mapping by Choon B. Park Kansas Geological Survey University of Kansas 1930 Constant Avenue, Campus West Lawrence, Kansas 66047-3726 Tel: 785-864-2162
Introduction to CS graphs and plots in Excel Jacek Wiślicki, Laurent Babout,
 MS Excel 2010 offers a large set of graphs and plots for data visualization. For those who are familiar with older version of Excel, the layout is completely different. The following exercises demonstrate
MS Excel 2010 offers a large set of graphs and plots for data visualization. For those who are familiar with older version of Excel, the layout is completely different. The following exercises demonstrate
KCS Motion. Video Motion Analysis Software
 Video Motion Analysis Software Software and supporting material is property of G. Mason, Seattle University, 2007 Overview Overview KCS Motion tracks moving objects in a video clip and analyzes their position,
Video Motion Analysis Software Software and supporting material is property of G. Mason, Seattle University, 2007 Overview Overview KCS Motion tracks moving objects in a video clip and analyzes their position,
DW Tomo 8.1 User Guide
 DW Tomo 8.1 User Guide Copyright 2016, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Preface...1 Conventions Used in This Guide...1 Where to Find Information...1 Technical Support...2 Feedback...2 Chapter 1 Introducing
DW Tomo 8.1 User Guide Copyright 2016, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Preface...1 Conventions Used in This Guide...1 Where to Find Information...1 Technical Support...2 Feedback...2 Chapter 1 Introducing
Jan-12
 Model Building, Modeling & Processing using Well-log data -examples- www.tesseral-geo.com Jan-12 1 Thin-layered Model by 1 well -Example 1- Illustration of practical work with the Tesseral package for
Model Building, Modeling & Processing using Well-log data -examples- www.tesseral-geo.com Jan-12 1 Thin-layered Model by 1 well -Example 1- Illustration of practical work with the Tesseral package for
Limitations of Rayleigh Dispersion Curve Obtained from Simulated Ambient Vibrations
 Limitations of Rayleigh Dispersion Curve Obtained from Simulated Ambient Vibrations KEN TOKESHI and CARLOS CUADRA Department of Architecture and Environment Systems Akita Prefectural University 84-4 Ebinokuchi,
Limitations of Rayleigh Dispersion Curve Obtained from Simulated Ambient Vibrations KEN TOKESHI and CARLOS CUADRA Department of Architecture and Environment Systems Akita Prefectural University 84-4 Ebinokuchi,
MAPPING POISSON S RATIO OF UNCONSOLIDATED MATERIALS FROM A JOINT ANALYSIS OF SURFACE-WAVE AND REFRACTION EVENTS INTRODUCTION
 MAPPING POISSON S RATIO OF UNCONSOLIDATED MATERIALS FROM A JOINT ANALYSIS OF SURFACE-WAVE AND REFRACTION EVENTS Julian Ivanov, Choon B. Park, Richard D. Miller, and Jianghai Xia Kansas Geological Survey
MAPPING POISSON S RATIO OF UNCONSOLIDATED MATERIALS FROM A JOINT ANALYSIS OF SURFACE-WAVE AND REFRACTION EVENTS Julian Ivanov, Choon B. Park, Richard D. Miller, and Jianghai Xia Kansas Geological Survey
Refractor 8.1 User Guide
 Refractor 8.1 User Guide Copyright 2016, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Preface...1 Conventions Used in This Guide...1 Where to Find Information...1 Technical Support...2 Feedback...2 Chapter 1
Refractor 8.1 User Guide Copyright 2016, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Preface...1 Conventions Used in This Guide...1 Where to Find Information...1 Technical Support...2 Feedback...2 Chapter 1
Multichannel analysis of surface waves (MASW) active and passive methods
 Multichannel analysis of surface waves (MASW) active and passive methods CHOON B. PARK, RICHARD D. MILLER, JIANGHAI XIA, AND JULIAN IVANOV, Kansas Geological Survey, Lawrence, USA Downloaded 01/20/13 to
Multichannel analysis of surface waves (MASW) active and passive methods CHOON B. PARK, RICHARD D. MILLER, JIANGHAI XIA, AND JULIAN IVANOV, Kansas Geological Survey, Lawrence, USA Downloaded 01/20/13 to
Stepwise instructions for getting started
 Multiparameter Numerical Medium for Seismic Modeling, Planning, Imaging & Interpretation Worldwide Tesseral Geo Modeling Tesseral 2D Tutorial Stepwise instructions for getting started Contents Useful information...1
Multiparameter Numerical Medium for Seismic Modeling, Planning, Imaging & Interpretation Worldwide Tesseral Geo Modeling Tesseral 2D Tutorial Stepwise instructions for getting started Contents Useful information...1
Geogiga Seismic Pro 8.1 Release Notes
 Geogiga Seismic Pro 8.1 Release Notes Copyright 2016, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Introduction...1 Part 1 General Enhancements...3 Well Data...4 Data Format...6 Data Import...7 Trace Magnifier...8
Geogiga Seismic Pro 8.1 Release Notes Copyright 2016, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Introduction...1 Part 1 General Enhancements...3 Well Data...4 Data Format...6 Data Import...7 Trace Magnifier...8
MET 107 Drawing Tool (Shapes) Notes Day 3
 MET 107 Drawing Tool (Shapes) Notes Day 3 Shapes: (Insert Tab Shapes) Example: Select on the rounded rectangle Then use the mouse to position the upper left corner and produce the size by dragging out
MET 107 Drawing Tool (Shapes) Notes Day 3 Shapes: (Insert Tab Shapes) Example: Select on the rounded rectangle Then use the mouse to position the upper left corner and produce the size by dragging out
How do you roll? Fig. 1 - Capstone screen showing graph areas and menus
 How do you roll? Purpose: Observe and compare the motion of a cart rolling down hill versus a cart rolling up hill. Develop a mathematical model of the position versus time and velocity versus time for
How do you roll? Purpose: Observe and compare the motion of a cart rolling down hill versus a cart rolling up hill. Develop a mathematical model of the position versus time and velocity versus time for
NSE 1.7. SEG/Houston 2005 Annual Meeting 1057
 Finite-difference Modeling of High-frequency Rayleigh waves Yixian Xu, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, 430074, China; Jianghai Xia, and Richard D. Miller, Kansas Geological Survey, The University
Finite-difference Modeling of High-frequency Rayleigh waves Yixian Xu, China University of Geosciences, Wuhan, 430074, China; Jianghai Xia, and Richard D. Miller, Kansas Geological Survey, The University
Virtual MODELA USER'S MANUAL
 Virtual MODELA USER'S MANUAL Virtual MODELA is a program that simulates the movement of the tool on the screen. Contents Contents Part 1 Introduction 1-1 System Requirements... 4 1-2 Overview of Virtual
Virtual MODELA USER'S MANUAL Virtual MODELA is a program that simulates the movement of the tool on the screen. Contents Contents Part 1 Introduction 1-1 System Requirements... 4 1-2 Overview of Virtual
PCB List Panel. Contents
 PCB List Panel Contents Function Content and Use Defining Panel Display Scope Working with Filtered Objects Displaying Workspace Selection Displaying Filtering Results Using the Panel to Select Objects
PCB List Panel Contents Function Content and Use Defining Panel Display Scope Working with Filtered Objects Displaying Workspace Selection Displaying Filtering Results Using the Panel to Select Objects
NaysEddy ver 1.0. Example MANUAL. By: Mohamed Nabi, Ph.D. Copyright 2014 iric Project. All Rights Reserved.
 NaysEddy ver 1.0 Example MANUAL By: Mohamed Nabi, Ph.D. Copyright 2014 iric Project. All Rights Reserved. Contents Introduction... 3 Getting started... 4 Simulation of flow over dunes... 6 1. Purpose of
NaysEddy ver 1.0 Example MANUAL By: Mohamed Nabi, Ph.D. Copyright 2014 iric Project. All Rights Reserved. Contents Introduction... 3 Getting started... 4 Simulation of flow over dunes... 6 1. Purpose of
Saratoga Springs City School District/Office of Continuing Education Introduction to Microsoft Excel 04 Charts. 1. Chart Types and Dimensions
 1949 1954 1959 1964 1969 1974 1979 1984 1989 1994 1999 2004 Saratoga Springs City School District/Office of Continuing Education Introduction to Microsoft Excel 04 Charts 1. Chart Types and Dimensions
1949 1954 1959 1964 1969 1974 1979 1984 1989 1994 1999 2004 Saratoga Springs City School District/Office of Continuing Education Introduction to Microsoft Excel 04 Charts 1. Chart Types and Dimensions
SurfSeis Active and Passive MASW
 SurfSeis Active and Passive MASW Seismic Processing Software for use with Microsoft Windows (Supplementary) User s Manual v 2.0 (Beta) written by Choon B. Park and compiled and edited by Mary Brohammer
SurfSeis Active and Passive MASW Seismic Processing Software for use with Microsoft Windows (Supplementary) User s Manual v 2.0 (Beta) written by Choon B. Park and compiled and edited by Mary Brohammer
Getting to Know FlexPro in just 15 Minutes
 Getting to Know FlexPro in just 15 Minutes This tutorial provides you with a brief overview of the structure of FlexPro and the basic command methods. 3 Managing Data with FlexPro FlexPro stores all objects
Getting to Know FlexPro in just 15 Minutes This tutorial provides you with a brief overview of the structure of FlexPro and the basic command methods. 3 Managing Data with FlexPro FlexPro stores all objects
Managing the Displays in IX1D v 3 A Tutorial
 Managing the Displays in IX1D v 3 A Tutorial Version 1.0 2006 Interpex Limited All rights reserved Adjusting Display Parameters IX1D v 3 has several commands and dialogs that are used to manage the views
Managing the Displays in IX1D v 3 A Tutorial Version 1.0 2006 Interpex Limited All rights reserved Adjusting Display Parameters IX1D v 3 has several commands and dialogs that are used to manage the views
Geogiga Seismic Pro 8.3 Release Notes
 Geogiga Seismic Pro 8.3 Release Notes Copyright 2017, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Introduction...1 Part 1 Utility Modules...2 Part 2 Reflection Modules...4 Updates in SF Imager...5 Updates in
Geogiga Seismic Pro 8.3 Release Notes Copyright 2017, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Introduction...1 Part 1 Utility Modules...2 Part 2 Reflection Modules...4 Updates in SF Imager...5 Updates in
Geogiga Seismic Pro 8.0 Release Notes
 Geogiga Seismic Pro 8.0 Release Notes Copyright 2015, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Introduction...1 Part 1 General Enhancements...3 Trace Display...4 Color Section Display...6 Curve Plotting...8
Geogiga Seismic Pro 8.0 Release Notes Copyright 2015, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Introduction...1 Part 1 General Enhancements...3 Trace Display...4 Color Section Display...6 Curve Plotting...8
Technical Documentation Version 7.3 Output
 Technical Documentation Version 7.3 Output These documents are copyrighted by the Regents of the University of Colorado. No part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted
Technical Documentation Version 7.3 Output These documents are copyrighted by the Regents of the University of Colorado. No part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted
ProShake 2.0. The first step in this tutorial exercise is to start the ProShake 2.0 program. Click on the ProShake 2.0 icon to start the program.
 PROSHAKE 2.0 TUTORIAL The easiest way to learn the basics of ProShake s organization and operation is to complete the tutorial exercise detailed in this section. This tutorial will take you through nearly
PROSHAKE 2.0 TUTORIAL The easiest way to learn the basics of ProShake s organization and operation is to complete the tutorial exercise detailed in this section. This tutorial will take you through nearly
Open Excel by following the directions listed below: Click on Start, select Programs, and the click on Microsoft Excel.
 Candy is Dandy Grading Rubric You have been hired to conduct some market research about M&M's. First, you had your team purchase 4 large bags and the results are given for the contents of those bags. You
Candy is Dandy Grading Rubric You have been hired to conduct some market research about M&M's. First, you had your team purchase 4 large bags and the results are given for the contents of those bags. You
Guideline for a Sonic Studio Model
 Sonic Studio Model Pg.1 Guideline for a Sonic Studio Model A model will be constructed to demonstrate a how to demonstrate how to use Sonic Studio in UTAPWeLS. The model will be created to represent soft
Sonic Studio Model Pg.1 Guideline for a Sonic Studio Model A model will be constructed to demonstrate a how to demonstrate how to use Sonic Studio in UTAPWeLS. The model will be created to represent soft
Lab 4 Projectile Motion
 b Lab 4 Projectile Motion What You Need To Know: x = x v = v v o ox = v + v ox ox + at 1 t + at + a x FIGURE 1 Linear Motion Equations The Physics So far in lab you ve dealt with an object moving horizontally
b Lab 4 Projectile Motion What You Need To Know: x = x v = v v o ox = v + v ox ox + at 1 t + at + a x FIGURE 1 Linear Motion Equations The Physics So far in lab you ve dealt with an object moving horizontally
AQ7932 OTDR Emulation Software Operation Manual
 User s Manual Model 735070 AQ7932 OTDR Emulation Software Operation Manual IM 735070-04E 3rd Edition Introduction Thank you for your purchasing of this AQ7932 OTDR Emulation Software. This user's manual
User s Manual Model 735070 AQ7932 OTDR Emulation Software Operation Manual IM 735070-04E 3rd Edition Introduction Thank you for your purchasing of this AQ7932 OTDR Emulation Software. This user's manual
Scientific Graphing in Excel 2013
 Scientific Graphing in Excel 2013 When you start Excel, you will see the screen below. Various parts of the display are labelled in red, with arrows, to define the terms used in the remainder of this overview.
Scientific Graphing in Excel 2013 When you start Excel, you will see the screen below. Various parts of the display are labelled in red, with arrows, to define the terms used in the remainder of this overview.
For more info and downloads go to: Gerrit Stols
 For more info and downloads go to: http://school-maths.com Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source (free) software for learning and teaching mathematics in schools. It
For more info and downloads go to: http://school-maths.com Gerrit Stols Acknowledgements GeoGebra is dynamic mathematics open source (free) software for learning and teaching mathematics in schools. It
Microsoft Excel Using Excel in the Science Classroom
 Microsoft Excel Using Excel in the Science Classroom OBJECTIVE Students will take data and use an Excel spreadsheet to manipulate the information. This will include creating graphs, manipulating data,
Microsoft Excel Using Excel in the Science Classroom OBJECTIVE Students will take data and use an Excel spreadsheet to manipulate the information. This will include creating graphs, manipulating data,
Introduction to seismic body waves Tomography
 Introduction to seismic body waves Tomography Presented by Han Zhang Prepared by group work of Justin Wilgus and Han Zhang Outlines 1. Velocity derived from wave equation 2. Two commonly used reference
Introduction to seismic body waves Tomography Presented by Han Zhang Prepared by group work of Justin Wilgus and Han Zhang Outlines 1. Velocity derived from wave equation 2. Two commonly used reference
(1B) Click Browse and select the AASPI-format file (*.H) that you want to display. After you browse the file, the Colorbar file name (1C), plot title
 QC PLOTTING OF AASPI-FORMAT DATA AND ATTRIBUTES Program aaspi_plot The AASPI QC Plotting tab To further quality control the conversion process, you will wish to plot your data before computing seismic
QC PLOTTING OF AASPI-FORMAT DATA AND ATTRIBUTES Program aaspi_plot The AASPI QC Plotting tab To further quality control the conversion process, you will wish to plot your data before computing seismic
GET TO KNOW FLEXPRO IN ONLY 15 MINUTES
 GET TO KNOW FLEXPRO IN ONLY 15 MINUTES Data Analysis and Presentation Software GET TO KNOW FLEXPRO IN ONLY 15 MINUTES This tutorial provides you with a brief overview of the structure of FlexPro and the
GET TO KNOW FLEXPRO IN ONLY 15 MINUTES Data Analysis and Presentation Software GET TO KNOW FLEXPRO IN ONLY 15 MINUTES This tutorial provides you with a brief overview of the structure of FlexPro and the
Tutorial 2: Particles convected with the flow along a curved pipe.
 Tutorial 2: Particles convected with the flow along a curved pipe. Part 1: Creating an elbow In part 1 of this tutorial, you will create a model of a 90 elbow featuring a long horizontal inlet and a short
Tutorial 2: Particles convected with the flow along a curved pipe. Part 1: Creating an elbow In part 1 of this tutorial, you will create a model of a 90 elbow featuring a long horizontal inlet and a short
ST5 - Weld Design. FRILO Software GmbH as of
 ST5 - Weld Design FRILO Software GmbH www.frilo.com info@frilo.com as of 29.03.2016 ST5 ST5 Weld Design Contents Application options 4 Basis of calculation 4 Verification of welding seams 4 Constructive
ST5 - Weld Design FRILO Software GmbH www.frilo.com info@frilo.com as of 29.03.2016 ST5 ST5 Weld Design Contents Application options 4 Basis of calculation 4 Verification of welding seams 4 Constructive
Settle 3D 3.0 is here! Become a Rocscience Beta Tester
 Settle 3D 3.0 is here! Become a Rocscience Beta Tester RocNews Winter 2014 Settle 3D 3.0 An Exciting New Upgrade! Settle 3D is a 3-dimensional program for the analysis of vertical consolidation and settlement
Settle 3D 3.0 is here! Become a Rocscience Beta Tester RocNews Winter 2014 Settle 3D 3.0 An Exciting New Upgrade! Settle 3D is a 3-dimensional program for the analysis of vertical consolidation and settlement
User Manual Version 1.1 January 2015
 User Manual Version 1.1 January 2015 - 2 / 112 - V1.1 Variegator... 7 Variegator Features... 7 1. Variable elements... 7 2. Static elements... 7 3. Element Manipulation... 7 4. Document Formats... 7 5.
User Manual Version 1.1 January 2015 - 2 / 112 - V1.1 Variegator... 7 Variegator Features... 7 1. Variable elements... 7 2. Static elements... 7 3. Element Manipulation... 7 4. Document Formats... 7 5.
IX Oct Operation Guide. Application Software. Vf File Analyzer 3. Ver. 2.4
 IX000265 Oct. 2015 Operation Guide Application Software Vf File Analyzer 3 Ver. 2.4 About This Guide Contents This PDF version of the Operation Guide is provided so that you can print all or any portion
IX000265 Oct. 2015 Operation Guide Application Software Vf File Analyzer 3 Ver. 2.4 About This Guide Contents This PDF version of the Operation Guide is provided so that you can print all or any portion
Separate Text Across Cells The Convert Text to Columns Wizard can help you to divide the text into columns separated with specific symbols.
 Chapter 7 Highlights 7.1 The Use of Formulas and Functions 7.2 Creating Charts 7.3 Using Chart Toolbar 7.4 Changing Source Data of a Chart Separate Text Across Cells The Convert Text to Columns Wizard
Chapter 7 Highlights 7.1 The Use of Formulas and Functions 7.2 Creating Charts 7.3 Using Chart Toolbar 7.4 Changing Source Data of a Chart Separate Text Across Cells The Convert Text to Columns Wizard
A Simple First-Model Using the Berkeley-Madonna Program
 A Simple First-Model Using the Berkeley-Madonna Program For this introduction, we will be creating a model of a simple system with two compartments analogous to containers of a liquid which can flow between
A Simple First-Model Using the Berkeley-Madonna Program For this introduction, we will be creating a model of a simple system with two compartments analogous to containers of a liquid which can flow between
Making and Editing a Table in Microsoft Word 2007
 Making and Editing a Table in Microsoft Word 2007 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Creating a Table... 2 1. Finding the "Table" button... 2 2. Methods for making a table... 3 Editing Table Dimensions...
Making and Editing a Table in Microsoft Word 2007 Table of Contents Introduction... 2 Creating a Table... 2 1. Finding the "Table" button... 2 2. Methods for making a table... 3 Editing Table Dimensions...
Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows
 1 Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 1, 2017) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan
1 Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 1, 2017) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan
PRACTICAL EXPERIENCE USING A SIMPLIFIED PROCEDURE TO MEASURE AVERAGE SHEAR-WAVE VELOCITY TO A DEPTH OF 30 METERS (V S 30)
 13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 952 PRACTICAL EXPERIENCE USING A SIMPLIFIED PROCEDURE TO MEASURE AVERAGE SHEAR-WAVE VELOCITY TO A DEPTH
13 th World Conference on Earthquake Engineering Vancouver, B.C., Canada August 1-6, 24 Paper No. 952 PRACTICAL EXPERIENCE USING A SIMPLIFIED PROCEDURE TO MEASURE AVERAGE SHEAR-WAVE VELOCITY TO A DEPTH
Th LHR5 08 Multi-modal Surface Wave Inversion and Application to North Sea OBN Data
 Th LHR5 08 Multi-modal Surface Wave Inversion and pplication to North Sea ON Data S. Hou (CGG), D. Zheng (CGG), X.G. Miao* (CGG) & R.R. Haacke (CGG) SUMMRY Surface-wave inversion (SWI) for S-wave velocity
Th LHR5 08 Multi-modal Surface Wave Inversion and pplication to North Sea ON Data S. Hou (CGG), D. Zheng (CGG), X.G. Miao* (CGG) & R.R. Haacke (CGG) SUMMRY Surface-wave inversion (SWI) for S-wave velocity
u = v is the Laplacian and represents the sum of the second order derivatives of the wavefield spatially.
 Seismic Elastic Modelling Satinder Chopra, Arcis Corporation, Calgary, Canada Summary Seismic modeling experiments were performed to understand the seismic responses associated with a variety of subsurface
Seismic Elastic Modelling Satinder Chopra, Arcis Corporation, Calgary, Canada Summary Seismic modeling experiments were performed to understand the seismic responses associated with a variety of subsurface
Scientific Graphing in Excel 2007
 Scientific Graphing in Excel 2007 When you start Excel, you will see the screen below. Various parts of the display are labelled in red, with arrows, to define the terms used in the remainder of this overview.
Scientific Graphing in Excel 2007 When you start Excel, you will see the screen below. Various parts of the display are labelled in red, with arrows, to define the terms used in the remainder of this overview.
PS User Guide Series Passive MASW Data Acquisition and Processing
 PS User Guide Series 2015 Passive MASW Data Acquisition and Processing Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents Page 1. Overview 2 2. Passive MASW Sample Data Sets 8 2.1 Passive
PS User Guide Series 2015 Passive MASW Data Acquisition and Processing Prepared By Choon B. Park, Ph.D. January 2015 Table of Contents Page 1. Overview 2 2. Passive MASW Sample Data Sets 8 2.1 Passive
Using Charts in a Presentation 6
 Using Charts in a Presentation 6 LESSON SKILL MATRIX Skill Exam Objective Objective Number Building Charts Create a chart. Import a chart. Modifying the Chart Type and Data Change the Chart Type. 3.2.3
Using Charts in a Presentation 6 LESSON SKILL MATRIX Skill Exam Objective Objective Number Building Charts Create a chart. Import a chart. Modifying the Chart Type and Data Change the Chart Type. 3.2.3
JASCO CANVAS PROGRAM OPERATION MANUAL
 JASCO CANVAS PROGRAM OPERATION MANUAL P/N: 0302-1840A April 1999 Contents 1. What is JASCO Canvas?...1 1.1 Features...1 1.2 About this Manual...1 2. Installation...1 3. Operating Procedure - Tutorial...2
JASCO CANVAS PROGRAM OPERATION MANUAL P/N: 0302-1840A April 1999 Contents 1. What is JASCO Canvas?...1 1.1 Features...1 1.2 About this Manual...1 2. Installation...1 3. Operating Procedure - Tutorial...2
In this chapter we explain the structure and use of BestDose, with examples.
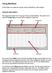 Using BestDose In this chapter we explain the structure and use of BestDose, with examples. General description The image below shows the view you get when you start BestDose. The actual view is called
Using BestDose In this chapter we explain the structure and use of BestDose, with examples. General description The image below shows the view you get when you start BestDose. The actual view is called
Exercise 1: Getting to know ArcGIS
 The Scenario You are working for the California Visitor s Commission. You have been asked to prepare a map of California for several dignitaries from out of the country. Your map will need to include enough
The Scenario You are working for the California Visitor s Commission. You have been asked to prepare a map of California for several dignitaries from out of the country. Your map will need to include enough
Getting Started with DADiSP
 Section 1: Welcome to DADiSP Getting Started with DADiSP This guide is designed to introduce you to the DADiSP environment. It gives you the opportunity to build and manipulate your own sample Worksheets
Section 1: Welcome to DADiSP Getting Started with DADiSP This guide is designed to introduce you to the DADiSP environment. It gives you the opportunity to build and manipulate your own sample Worksheets
Copyright 2016 The evsm Group, All Rights Reserved. Deny. Approve. Customer Incoming Demand. Create Technical Proposal. Qty=50. Create Review Package
 Quick Transactional Pro Tutorial This tutorial will guide you through the steps to draw a simple map, perform common calculations, and plot charts using the Quick Transactional Pro stencil. Z Customer
Quick Transactional Pro Tutorial This tutorial will guide you through the steps to draw a simple map, perform common calculations, and plot charts using the Quick Transactional Pro stencil. Z Customer
Microsoft Excel 2007 Creating a XY Scatter Chart
 Microsoft Excel 2007 Creating a XY Scatter Chart Introduction This document will walk you through the process of creating a XY Scatter Chart using Microsoft Excel 2007 and using the available Excel features
Microsoft Excel 2007 Creating a XY Scatter Chart Introduction This document will walk you through the process of creating a XY Scatter Chart using Microsoft Excel 2007 and using the available Excel features
Selective Space Structures Manual
 Selective Space Structures Manual February 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Overview and Concept 4 1.1 General Concept........................... 4 1.2 Modules................................ 6 2 The 3S Generator
Selective Space Structures Manual February 2017 CONTENTS 1 Contents 1 Overview and Concept 4 1.1 General Concept........................... 4 1.2 Modules................................ 6 2 The 3S Generator
Introducing Gupta Report Builder
 Business Reporting Chapter 1 Introducing Gupta Report Builder You can use Report Builder to design reports. This chapter describes: Our approach to building reports. Some of the reports you can build.
Business Reporting Chapter 1 Introducing Gupta Report Builder You can use Report Builder to design reports. This chapter describes: Our approach to building reports. Some of the reports you can build.
Using Microsoft Excel
 Using Microsoft Excel Introduction This handout briefly outlines most of the basic uses and functions of Excel that we will be using in this course. Although Excel may be used for performing statistical
Using Microsoft Excel Introduction This handout briefly outlines most of the basic uses and functions of Excel that we will be using in this course. Although Excel may be used for performing statistical
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010
 An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Flat Plate Boundary Layer Objectives Creating
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Flat Plate Boundary Layer Objectives Creating
Using DataQuest on a Handheld
 Using DataQuest on a Handheld Appendix B This appendix gives an overview of using the Vernier DataQuest application on a TI-Nspire handheld. It includes information on accessing the common tools in the
Using DataQuest on a Handheld Appendix B This appendix gives an overview of using the Vernier DataQuest application on a TI-Nspire handheld. It includes information on accessing the common tools in the
SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014
 An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
0 Graphical Analysis Use of Excel
 Lab 0 Graphical Analysis Use of Excel What You Need To Know: This lab is to familiarize you with the graphing ability of excels. You will be plotting data set, curve fitting and using error bars on the
Lab 0 Graphical Analysis Use of Excel What You Need To Know: This lab is to familiarize you with the graphing ability of excels. You will be plotting data set, curve fitting and using error bars on the
Published on Online Documentation for Altium Products (https://www.altium.com/documentation)
 Published on Online Documentation for Altium Products (https://www.altium.com/documentation) Home > PCBLIB List A New Era for Documentation Modified by Susan Riege on Jan 24, 2018 Parent Page PCB Panels
Published on Online Documentation for Altium Products (https://www.altium.com/documentation) Home > PCBLIB List A New Era for Documentation Modified by Susan Riege on Jan 24, 2018 Parent Page PCB Panels
Models for Nurses: Quadratic Model ( ) Linear Model Dx ( ) x Models for Doctors:
 The goal of this technology assignment is to graph several formulas in Excel. This assignment assumes that you using Excel 2007. The formula you will graph is a rational function formed from two polynomials,
The goal of this technology assignment is to graph several formulas in Excel. This assignment assumes that you using Excel 2007. The formula you will graph is a rational function formed from two polynomials,
DATA REPORT. SASW Measurements at the NEES Garner Valley Test Site, California
 13 January 2004 DATA REPORT SASW Measurements at the NEES Garner Valley Test Site, California by Kenneth H. Stokoe, II, Ph.D., P.E., Jennie C. and Milton T. Graves Chair in Engineering Asli Kurtulus, M.S.,
13 January 2004 DATA REPORT SASW Measurements at the NEES Garner Valley Test Site, California by Kenneth H. Stokoe, II, Ph.D., P.E., Jennie C. and Milton T. Graves Chair in Engineering Asli Kurtulus, M.S.,
SIMPLE TEXT LAYOUT FOR COREL DRAW. When you start Corel Draw, you will see the following welcome screen.
 SIMPLE TEXT LAYOUT FOR COREL DRAW When you start Corel Draw, you will see the following welcome screen. A. Start a new job by left clicking New Graphic. B. Place your mouse cursor over the page width box.
SIMPLE TEXT LAYOUT FOR COREL DRAW When you start Corel Draw, you will see the following welcome screen. A. Start a new job by left clicking New Graphic. B. Place your mouse cursor over the page width box.
Multichannel Data logging
 Multichannel Data logging As of version V1.1 Operating manual Bedienungsanleitung EBS 20M / EBS 60M SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 3 SCOPE OF SUPPLY... 3 INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING... 3 DESIGNATED USE... 3
Multichannel Data logging As of version V1.1 Operating manual Bedienungsanleitung EBS 20M / EBS 60M SYSTEM REQUIREMENTS... 3 SCOPE OF SUPPLY... 3 INSTALLATION AND COMMISSIONING... 3 DESIGNATED USE... 3
VIEWZ 1.3 USER MANUAL
 VIEWZ 1.3 USER MANUAL 2007-08 Zeus Numerix ViewZ 1.3.0 User Manual Revision: 200806061429 The latest copy of this PDF may be downloaded from the website. An online (HTML) version is also available. Zeus
VIEWZ 1.3 USER MANUAL 2007-08 Zeus Numerix ViewZ 1.3.0 User Manual Revision: 200806061429 The latest copy of this PDF may be downloaded from the website. An online (HTML) version is also available. Zeus
BioIRC solutions. CFDVasc manual
 BioIRC solutions CFDVasc manual Main window of application is consisted from two parts: toolbar - which consist set of button for accessing variety of present functionalities image area area in which is
BioIRC solutions CFDVasc manual Main window of application is consisted from two parts: toolbar - which consist set of button for accessing variety of present functionalities image area area in which is
The Mathcad Workspace 7
 For information on system requirements and how to install Mathcad on your computer, refer to Chapter 1, Welcome to Mathcad. When you start Mathcad, you ll see a window like that shown in Figure 2-1. By
For information on system requirements and how to install Mathcad on your computer, refer to Chapter 1, Welcome to Mathcad. When you start Mathcad, you ll see a window like that shown in Figure 2-1. By
Interpreting Data in IX1D v 3 A Tutorial
 Interpreting Data in IX1D v 3 A Tutorial Version 1.0 2006 Interpex Limited All rights reserved Select a Sounding from the Map Display using the Mouse If you right-click on the sounding, there are more
Interpreting Data in IX1D v 3 A Tutorial Version 1.0 2006 Interpex Limited All rights reserved Select a Sounding from the Map Display using the Mouse If you right-click on the sounding, there are more
Mapping and migrating reflected ground-roll
 Mapping and migrating reflected ground-roll Craig Hyslop Advisor: Dr. Stewart April 2, 2014 Outline 3D fault imaging Outline: Ground-roll reflection in-line Synthetics Field result 3D fault imaging off-line
Mapping and migrating reflected ground-roll Craig Hyslop Advisor: Dr. Stewart April 2, 2014 Outline 3D fault imaging Outline: Ground-roll reflection in-line Synthetics Field result 3D fault imaging off-line
Chapter 24. Creating Surfaces for Displaying and Reporting Data
 Chapter 24. Creating Surfaces for Displaying and Reporting Data FLUENT allows you to select portions of the domain to be used for visualizing the flow field. The domain portions are called surfaces, and
Chapter 24. Creating Surfaces for Displaying and Reporting Data FLUENT allows you to select portions of the domain to be used for visualizing the flow field. The domain portions are called surfaces, and
7. Vertical Layering
 7.1 Make Horizons 7. Vertical Layering The vertical layering process consists of 4 steps: 1. Make Horizons: Insert the input surfaces into the 3D Grid. The inputs can be surfaces from seismic or well tops,
7.1 Make Horizons 7. Vertical Layering The vertical layering process consists of 4 steps: 1. Make Horizons: Insert the input surfaces into the 3D Grid. The inputs can be surfaces from seismic or well tops,
RSPile. Tutorial 3 Grouped Pile Analysis. Pile Analysis Software. Grouped Pile Analysis
 RSPile Pile Analysis Software Tutorial 3 Grouped Pile Analysis Grouped Pile Analysis Introduction This tutorial will demonstrate how to model grouped piles under a cap. The finished product of this tutorial
RSPile Pile Analysis Software Tutorial 3 Grouped Pile Analysis Grouped Pile Analysis Introduction This tutorial will demonstrate how to model grouped piles under a cap. The finished product of this tutorial
Th C 02 Model-Based Surface Wave Analysis and Attenuation
 Th C 02 Model-Based Surface Wave Analysis and Attenuation J. Bai* (Paradigm Geophysical), O. Yilmaz (Paradigm Geophysical) Summary Surface waves can significantly degrade overall data quality in seismic
Th C 02 Model-Based Surface Wave Analysis and Attenuation J. Bai* (Paradigm Geophysical), O. Yilmaz (Paradigm Geophysical) Summary Surface waves can significantly degrade overall data quality in seismic
TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION...2
 WINGARD PE 6.0 August 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS...1 1. INTRODUCTION...2 2. PROGRAM OVERVIEW...3 2.1. PROGRAM MENUS... 4 2.2. MAIN TOOLBAR... 5 2.3. ANALYSIS... 7 2.4. OUTPUT... 10 2.5. DISPLAY
WINGARD PE 6.0 August 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS TABLE OF CONTENTS...1 1. INTRODUCTION...2 2. PROGRAM OVERVIEW...3 2.1. PROGRAM MENUS... 4 2.2. MAIN TOOLBAR... 5 2.3. ANALYSIS... 7 2.4. OUTPUT... 10 2.5. DISPLAY
Unit 12. Electronic Spreadsheets - Microsoft Excel. Desired Outcomes
 Unit 12 Electronic Spreadsheets - Microsoft Excel Desired Outcomes Student understands Excel workbooks and worksheets Student can navigate in an Excel workbook and worksheet Student can use toolbars and
Unit 12 Electronic Spreadsheets - Microsoft Excel Desired Outcomes Student understands Excel workbooks and worksheets Student can navigate in an Excel workbook and worksheet Student can use toolbars and
Common Core Vocabulary and Representations
 Vocabulary Description Representation 2-Column Table A two-column table shows the relationship between two values. 5 Group Columns 5 group columns represent 5 more or 5 less. a ten represented as a 5-group
Vocabulary Description Representation 2-Column Table A two-column table shows the relationship between two values. 5 Group Columns 5 group columns represent 5 more or 5 less. a ten represented as a 5-group
Select the Points You ll Use. Tech Assignment: Find a Quadratic Function for College Costs
 In this technology assignment, you will find a quadratic function that passes through three of the points on each of the scatter plots you created in an earlier technology assignment. You will need the
In this technology assignment, you will find a quadratic function that passes through three of the points on each of the scatter plots you created in an earlier technology assignment. You will need the
3D shear wave velocity analysis and Earthquake scenario modeling based on CCBD microzonation data base. Travis West Thesis Proposal
 3D shear wave velocity analysis and Earthquake scenario modeling based on CCBD microzonation data base Travis West - 9-30 15 - Thesis Proposal Outline BACKGROUND - ReMi, Vs30 Parcel map, earthquake simulations
3D shear wave velocity analysis and Earthquake scenario modeling based on CCBD microzonation data base Travis West - 9-30 15 - Thesis Proposal Outline BACKGROUND - ReMi, Vs30 Parcel map, earthquake simulations
Algebra 2 Semester 1 (#2221)
 Instructional Materials for WCSD Math Common Finals The Instructional Materials are for student and teacher use and are aligned to the 2016-2017 Course Guides for the following course: Algebra 2 Semester
Instructional Materials for WCSD Math Common Finals The Instructional Materials are for student and teacher use and are aligned to the 2016-2017 Course Guides for the following course: Algebra 2 Semester
Tekla Structures Analysis Guide. Product version 21.0 March Tekla Corporation
 Tekla Structures Analysis Guide Product version 21.0 March 2015 2015 Tekla Corporation Contents 1 Getting started with analysis... 7 1.1 What is an analysis model... 7 Analysis model objects...9 1.2 About
Tekla Structures Analysis Guide Product version 21.0 March 2015 2015 Tekla Corporation Contents 1 Getting started with analysis... 7 1.1 What is an analysis model... 7 Analysis model objects...9 1.2 About
Math 227 EXCEL / MEGASTAT Guide
 Math 227 EXCEL / MEGASTAT Guide Introduction Introduction: Ch2: Frequency Distributions and Graphs Construct Frequency Distributions and various types of graphs: Histograms, Polygons, Pie Charts, Stem-and-Leaf
Math 227 EXCEL / MEGASTAT Guide Introduction Introduction: Ch2: Frequency Distributions and Graphs Construct Frequency Distributions and various types of graphs: Histograms, Polygons, Pie Charts, Stem-and-Leaf
Reflectivity modeling for stratified anelastic media
 Reflectivity modeling for stratified anelastic media Peng Cheng and Gary F. Margrave Reflectivity modeling ABSTRACT The reflectivity method is widely used for the computation of synthetic seismograms for
Reflectivity modeling for stratified anelastic media Peng Cheng and Gary F. Margrave Reflectivity modeling ABSTRACT The reflectivity method is widely used for the computation of synthetic seismograms for
Physics 101, Lab 1: LINEAR KINEMATICS PREDICTION SHEET
 Physics 101, Lab 1: LINEAR KINEMATICS PREDICTION SHEET After reading through the Introduction, Purpose and Principles sections of the lab manual (and skimming through the procedures), answer the following
Physics 101, Lab 1: LINEAR KINEMATICS PREDICTION SHEET After reading through the Introduction, Purpose and Principles sections of the lab manual (and skimming through the procedures), answer the following
Unit 2: Functions and Graphs
 AMHS Precalculus - Unit 16 Unit : Functions and Graphs Functions A function is a rule that assigns each element in the domain to exactly one element in the range. The domain is the set of all possible
AMHS Precalculus - Unit 16 Unit : Functions and Graphs Functions A function is a rule that assigns each element in the domain to exactly one element in the range. The domain is the set of all possible
