7. Vertical Layering
|
|
|
- Meredith Parrish
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 7.1 Make Horizons 7. Vertical Layering The vertical layering process consists of 4 steps: 1. Make Horizons: Insert the input surfaces into the 3D Grid. The inputs can be surfaces from seismic or well tops, line interpretations from seismic, or any other point or line data defining the surface. 2. Depth Conversion: If the inserted horizons and faults are built in time, the grid must be depth converted. This process is skipped if the faults and input horizons are already in depth. 3. Make Zones: Additional horizons are inserted into the 3D Grid by stacking isochors up or down from the previously input horizons. 4. Make Layers: The final step is to make the fine-scale layering, necessary for property modeling. These layers define the top and base of the cells of the 3D Grid. The final step in structural modeling is to insert the stratigraphic horizons into the pillar grid, honoring the grid increment and the faults, defined in the previous steps. The result after the Pillar Gridding process as a 3D grid consisting of a set of pillars connecting the Base, Mid and Top Skeletons. All the faults to be incorporated into the model have been defined, and the pillars have been placed along and between the faults. For the faulted areas, the horizons are blanked (deleted) in a user given area around the faults and an extrapolation is performed to "stretch" the surface back onto the fault plane. This will ensure that rollovers or pull-ups near faults are eliminated and a high quality layering of the 3D grid is preserved. It should be noted that the skeleton grids are modified if the top- and/or base- of the input data extend above or below the Top- and/or Base- Shape Points respectively. The Key Pillars should extend above top horizon and below base horizon to avoid negative volumes in the 3D grid hence an extrapolation is performed. Summary of the Process: Append item in table, Use multiple drop, Select input data, Drop using blue arrow, Define type. To create horizons, follow the steps: Go to Structural Modeling item in the Process Diagram tab, Double click on the Make Horizons process. The process dialog for Make Horizons will pop up called Make Horizons with HAH/3D Grid as shown by Fig Note that the Petrel Explorer will display the Input window for easier access to the input data, 97
2 Select the Horizons tab as it contains the primary controls for making horizons, Fig. 7.1: Make Horizons with HAH/3D Grid dialog box Use the Set number of items in table and specify how many horizons to be inserted as shown in Fig. 7.2, or by either using( Append item in table ), Fig. 7.2: The Set number of items in the table tool tip In this case, insert 4 horizons as shown in the next dialog box, 98
3 Select the data to use to create the horizon (Surfaces data), Make sure your input horizons are sorted in the correct stratigraphic order in the Petrel Explorer respectively ( Base cretaceous, Top Tarbert, Top Ness, Top Etive) as shown by Fig. 7.3, By highlighting this file s name (make bold) in the Petrel Explorer and then Click on the blue arrow to the left of the Input #1 column, and check that the name of the active data object is inserted into the input field, see Fig. 7.4, Remember to insert the correct data object active and the name of the horizon is set equal to the name of the inserted data object. The user is free to change this name. Fig. 7.3: The correct stratigraphic sequence displayed in the input #1 field Fig. 7.4: The correct stratigraphic sequence displayed in the Petrel Explorer 99
4 Make sure that the Multiple drop icon toggled on, this allows you to drop a range of data by only selecting the first in a arrow, as shown by Fig. 7.5, Fig. 7.5: Multiple drops in the table button clicked Press Apply and OK, By clicking OK the Horizons will be generated. See that the Horizons folder in the Petrel Explorer, Models window, now has the new horizons inserted, Define the horizon s geological character (stratigraphy), by clicking on the Horizon Type column for specify horizon, Set Base Cretaceous to be erosional and the other surfaces to be conformable, as shown by Fig. 7.6, Press Apply and OK, see Fig Fig. 7.6: Horizons Type option defined 100
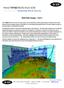
5 Fig. 7.7: Horizons displayed in a 3D window with their Edges 101
6 7.2 Depth Conversion If your 3D grid with inserted horizons and faults is in time, you need to depth convert it to get it into the depth domain. The depth conversion is a vertical process, beginning from a DATUM and progressing downwards, HORIZON by HORIZON and NODE by NODE. This conversion is applied for each node in the 3D grid. Each node corresponds with the intersection of one surface with one pillar. The last step after the conversion of the horizons is the reconstruction of the pillar geometry, faulted or non-faulted. The user is free to force the program to follow the shape given to the pillar during the fault modeling (Vertical, Linear, Listric, and Curved). The nodes are moved horizontally to reconstruct the initial shape of the pillars. Fig. 7.8: Depth Conversion Settings DATUM: must be defined. It can be Mean sea level or it can be any other surface. You can also use surfaces above the 3D grid area as input for the depth conversion even if these surfaces are not part of the 3D grid. Inserting horizons: When you open the Depth Conversion process, all the horizons from the 3D grid will have been inserted into the table. If you want to use any other surface as input, then you insert it into the table using the icons. Note that the Time Horizons must be the horizons that exist in the 3D grid, not the surfaces from the Petrel Explorer s Input window! (Exception is of course surfaces that do not exist in the 3D grid, like the Seabed in the example above). Velocity: For velocity you can either use a constant velocity (V=VO) or a linear expression for velocity (V=VO+kZ). Further, VO can either be a constant value or given by a surface. The k is a constant or a surface. Since Z is negative below MSL k is a negative value. Well Adjustment: If you want to adjust the depth converted horizons to well tops, you must enter the well tops under the Depth Well Tops tab, specify the averaging method, and, if you want a report, do this under the Wells tab. Note that you can specify which wells to be used for conditioning when doing the depth conversion under the Well Tops Spreadsheet. 102
7 7.3 Make Zones The Make Zones process is the next step in defining the vertical resolution of the 3D grid. The process creates zones between each horizon. Zones can be added to the model by introducing thickness data in the form of isochores, constant thickness and percentages. Well points can also be used to tie top structures to the well picks. This process step may be skipped when no zonation is given. To create zones follow the steps: Go to Structural Modeling item in the Process Diagram tab, Double click on the Make Zones process. A window pop up called Make Zones with HAH/3D Grid as shown by Fig. 7.9, Fig. 7.9: Make Zones with HAH/3D Grid dialog box Select the Stratigraphic interval option to be worked first for the definition of the zones, from the pull-down menu in the upper right part of the dialog. This interval will be completed (parameters specified) and the Apply button must be pressed before moving to the next interval. These main intervals are the intervals defined in the Make Horizons process. Note that only one interval can be calculated at a time and each horizon delimits a stratigraphic interval, For the Top Tarbert Top Ness interval there are three isochors (therefore 3 zones). For the Top Ness Top Etive interval these are two isochors (2 zones). There will be no zonation for the other stratigraphic intervals listed, 103
8 Click on the Set number of items in table button and specify how many zones you want in the current stratigraphic interval, or you can click on Append item in the table icon, as shown by Fig. 7.10, in this case insert 6 zones note that one click inserts three rows with two zone icons and one horizon icon (if the chosen stratigraphic interval are either Top Mid or Mid Base). The zone icons represent the isochores used for calculating the new intermediate horizon, Fig. 7.10: Make Zones with HAH/3D Grid while Append item in the table and Set number of items in the table appears Insert the Isochores from the Isochores folder and the subfolder that corresponds with the stratigraphic interval you are working on, Insert isochores by clicking on the blue arrow next to the input field called Input, as shown by Fig. 7.11, 104
9 Fig. 7.11: Isochores placed in input Insert well tops between the isochores by going to Well Tops> Sorted on Type and select the Well Tops that correspond with the Stratigraphic interval you working on, Select Build from base horizon and distribute the volume correction Proportionally among the various sub intervals, Select Build along Vertical Thickness (TVT), Don't forget to repeat procedure for the other Stratigraphic interval, Go to Setting tab and de-select the option that says: According to the setting in the Making Horizons process as shown by Fig. 7.12, Fig. 7.12: Make Zones with HAH/3D Grid dialog box 105
10 Go to Well Adjustment tab and specify that you want to create a report from the Well report options, Check Make well report option as shown by Fig. 7.13, Fig. 7.13: Make Zones with HAH/3D Grid dialog box Press Apply to generate the intermediate horizons and zone, Press OK, See Figs Fig. 7.14: well report for 'HAH/3D Grid' appears 106
11 Fig. 7.15: Zones created in a 3D window while Pillar Gridding appears Fig. 7.16: Zones created in 3D window along with their wells and faults 107
12 Fig. 7.17: Zones displayed while zones under Zones Filter created Fig. 7.18: Zones displayed in a 3D window while Intersections are displayed 108
13 Notice: The colors of the zones can be changed from the Setting menu for each zone, found under the Zones filter in the bottom of the 3D Grid (DC) Quality Control (QC) Using Intersection Planes In order to move an intersection it must first be active (bold) in the Petrel Explorer. All intersections can be displayed in the Display window at the same time but only one can be moved at a time. More intersections in either direction can be inserted from the pull-down menu of the Intersection folder or from the Function bar. Playing trough the intersections in the main directions, I- and J-direction, are a good method to QC the 3D grid. The intersections will show how the pillars in the grid are situated next to each other. The 3D grid will get a vertical layering and definition when horizons are inserted in the next process step, but since the vertical definition will not change the pillars in the grid, a QC with intersections can also be done after this step. When quality controlling the 3D grid, it is important to look for neighboring pillars that have very different angles. This can introduce errors when inserting horizons and zones to the grid. Intersections in the I- or J-direction are created when generating the grid. They can be viewed in the Display window by opening the Intersection folder and selecting one or both of them. A new set of icons will be visible on the Status bar in the bottom of the Petrel window. For details on how to use the intersections, see How to use the I and J intersections. 109
14 7.4 Make Layers The Make Zones and Make Sub Zones processes are the two last steps in defining the vertical resolution of the 3D grid. The Make Zones process is used when a geological zonation (isochores) is available. This process step may be skipped when no zonation is given. The Make Sub Zones process enables the user to define the final vertical resolution of the grid by setting the cell thickness or the number of desired cell layers. The final step in building the structural framework is to define the thickness and orientation of the layers between horizons of the 3D Grid. These layers in conjunction with the pillars define the cells of the 3D Grid that are assigned attributes during property modeling. The Make Layer process will only make a finer resolution of the grid and no input data are used for this process. The user can define the vertical resolution of the grid by setting the cell thickness, define a number of cells or use a fraction code. When specifying the cell thickness the zone division can either follow the base or the top of the zone. The layers should be defined based on the properties to be modeled. Usually, the layer thickness should be the thickness of the thinnest facies to be modeled. However, it is important to keep in mind that the number of cells increases when the layer thickness decreases, so you should not put in more detail than necessary. When making the fine-scaled layering, you should try to make layers thin enough to capture the important flow units. However, the layers should not be too thin since that will increase computing time! It s important to focus on flow units when defining the size of the layers, no just on the thickness of each facies. Depending on the geology, you can choose to build the layers from the top, the bottom or use proportional layering. In the layering process, select the method to be used and specify the cell thickness or the number of cells (layers). Making layers may be done based on field geology as follows: Follow base: The layers will be truncated towards the top horizon. The user defines the cell thickness. Follow Top: The layers will be truncated towards the base horizon. For the above two options you can also choose to use a reference surface, i.e. specify a surface which will be used as the surface to build from. The surface can take any shape, and it must exist in the Petrel Explorer in order to be used. Proportional: The sum of layers will be constant in the entire zone, independent of thickness of zone. The user specifies the number of layers to insert. Fraction: This is actually a proportional way of building the layers but you can specify relative thickness between layers. For instance: 1, 2, 1 will generate three layers and the mid layer will be twice as thick as the top and base layers. Combination: e.g. follow top and using depositional surface to guide how the layers will be placed. 110
15 To create layers follow the steps: Go to Structural Modeling item in the Process Diagram tab, Double click on the Layering process. A window pop up called Layering with HAH/3D Grid as shown by Fig. 7.19, this dialog has only one tab. In principle it works the same way as the Make Horizon and Make Zones dialogs - a spreadsheet with the zones as rows and the specific zone settings as columns, Fig 7.19: Layering with HAH/3D Grid dialog box The dialog lists the zones generated in the Make Horizons and Make Zones processes. For each zone select the desired resolution and layering layout. Make sure you have one or both of the I and J intersections displayed in the graphics. Zoom in to see the full vertical interval. Create the internal layering of the zones by clicking OK, and observe the results, Change the option under the Zone Division as shown in Fig. 7.20, The Horizons, Zones and Layering can be removed by clicking with the right mouse button on the 3D grid icon and selecting one of the Remove options, See Fig. 7.21,
16 Fig. 7.20: Changing the setting on Layering with HAH/3D Grid dialog box Fig. 7.21: Layers created in a 3D window while Layering with HAH/3D Grid' appears 112
17 Fig. 7.22: Layers created in a 3D window along with their Fault Polygons, wells, Well Tops, Fault Sticks, Surfaces, Pillar Gridding, Horizones, and Zones You can change in the number of layers from Fig. 7.20, and select option called Proportional and chooses the desire number of layers. 113
Fig. 1.1: Petrel Workflow Tools
 1. Introduction In this project, a 3D geological (static) model of a sample petroleum reservoir will be built. All steps will be shown in detail with screen shots of the necessary figures. The software
1. Introduction In this project, a 3D geological (static) model of a sample petroleum reservoir will be built. All steps will be shown in detail with screen shots of the necessary figures. The software
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM
 Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Using the Make Simple Grid Process to Build Un faulted Frameworks Un faulted reservoirs are relatively rare but do occur and provide a wonderful break
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Using the Make Simple Grid Process to Build Un faulted Frameworks Un faulted reservoirs are relatively rare but do occur and provide a wonderful break
3. Input Data Editing
 3. Input Data Editing There are few editing steps that must be completed before a 3D geological model is created. The steps include: 1. Creating Reservoir Boundary 2. Creating 3D Surfaces 3. Editing the
3. Input Data Editing There are few editing steps that must be completed before a 3D geological model is created. The steps include: 1. Creating Reservoir Boundary 2. Creating 3D Surfaces 3. Editing the
12. Defining Fluid Contacts
 12. Defining Fluid Contacts 12.1 Creating a New Contact Set After having built a Petrel 3D grid and prior to running the volume calculation, the various contacts should be defined in the Make Contacts
12. Defining Fluid Contacts 12.1 Creating a New Contact Set After having built a Petrel 3D grid and prior to running the volume calculation, the various contacts should be defined in the Make Contacts
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM
 Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Well Path Design Part II This TIPS&TRICKS is the second of a three part series intended to aid the geoscientist working in Petrel and tasked with providing
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Well Path Design Part II This TIPS&TRICKS is the second of a three part series intended to aid the geoscientist working in Petrel and tasked with providing
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM
 Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Digitizing and Gridding Contours in Petrel SCM trainers and consultants use Petrel s contour digitizing and contour gridding tools on most projects.
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Digitizing and Gridding Contours in Petrel SCM trainers and consultants use Petrel s contour digitizing and contour gridding tools on most projects.
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM
 E&P SOLUTIONS Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Cropped & Flattened Volumes in *Petrel Geophysicists who use D volumes often want to work on a smaller part of the volume or they want
E&P SOLUTIONS Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Cropped & Flattened Volumes in *Petrel Geophysicists who use D volumes often want to work on a smaller part of the volume or they want
3D Horizon/Fault Interpretation Exercise Using Seismic Micro-Technology s PC based 2d/3dPAK Seismic Interpretation Software
 3D Horizon/Fault Interpretation Exercise Using Seismic Micro-Technology s PC based 2d/3dPAK Seismic Interpretation Software Prepared by Tom Wilson, Appalachian Region Resource Center, Petroleum Technology
3D Horizon/Fault Interpretation Exercise Using Seismic Micro-Technology s PC based 2d/3dPAK Seismic Interpretation Software Prepared by Tom Wilson, Appalachian Region Resource Center, Petroleum Technology
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM
 Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Well Sections in Petrel 2010 Geologists who use Petrel to create and use Well Sections have noticed a significant change in this area between Petrel
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Well Sections in Petrel 2010 Geologists who use Petrel to create and use Well Sections have noticed a significant change in this area between Petrel
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM
 Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Well Path Design Part I This TIPS&TRICKS is the first of a three part series intended to aid the geoscientist working in Petrel and tasked with providing
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Well Path Design Part I This TIPS&TRICKS is the first of a three part series intended to aid the geoscientist working in Petrel and tasked with providing
Tutorial 7. Water Table and Bedrock Surface
 Tutorial 7 Water Table and Bedrock Surface Table of Contents Objective. 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Data Input. 2 Step 1: Open Adaptive Groundwater Input (.agw) File. 2 Step 2: Assign Material
Tutorial 7 Water Table and Bedrock Surface Table of Contents Objective. 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Data Input. 2 Step 1: Open Adaptive Groundwater Input (.agw) File. 2 Step 2: Assign Material
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM
 E&P SOLUTIONS Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Petrel Inspector The Petrel Inspector was introduced in Petrel 2012 and was augmented with new features in Petrel 2013. It contains a variety
E&P SOLUTIONS Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Petrel Inspector The Petrel Inspector was introduced in Petrel 2012 and was augmented with new features in Petrel 2013. It contains a variety
Basic Modeling 1 Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006
 Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents Contents 3 1 5 1.1 Start Tekla Structures 6 1.2 Create a New Model BasicModel1 7 1.3 Create Grids 10 1.4
Tekla Structures 12.0 Basic Training September 19, 2006 Copyright 2006 Tekla Corporation Contents Contents 3 1 5 1.1 Start Tekla Structures 6 1.2 Create a New Model BasicModel1 7 1.3 Create Grids 10 1.4
Jan-12
 Model Building, Modeling & Processing using Well-log data -examples- www.tesseral-geo.com Jan-12 1 Thin-layered Model by 1 well -Example 1- Illustration of practical work with the Tesseral package for
Model Building, Modeling & Processing using Well-log data -examples- www.tesseral-geo.com Jan-12 1 Thin-layered Model by 1 well -Example 1- Illustration of practical work with the Tesseral package for
Geology 554 Environmental and Exploration Geophysics II Final Exam
 Geology 554 Environmental and Exploration Geophysics II Final Exam In this exam, you are asked to apply some of the seismic interpretation skills you ve learned during the semester to the analysis of another
Geology 554 Environmental and Exploration Geophysics II Final Exam In this exam, you are asked to apply some of the seismic interpretation skills you ve learned during the semester to the analysis of another
Th Volume Based Modeling - Automated Construction of Complex Structural Models
 Th-04-06 Volume Based Modeling - Automated Construction of Complex Structural Models L. Souche* (Schlumberger), F. Lepage (Schlumberger) & G. Iskenova (Schlumberger) SUMMARY A new technology for creating,
Th-04-06 Volume Based Modeling - Automated Construction of Complex Structural Models L. Souche* (Schlumberger), F. Lepage (Schlumberger) & G. Iskenova (Schlumberger) SUMMARY A new technology for creating,
Using Kingdom Suite for 3D Horizon/Fault Interpretation Parts 3 & 4 - Horizon Interpretation and Correlation
 Using Kingdom Suite for 3D Horizon/Fault Interpretation Parts 3 & 4 - Horizon Interpretation and Correlation Wilson (2010) 1 A footnote to last week's exercise Double Vision? - Last week when you were
Using Kingdom Suite for 3D Horizon/Fault Interpretation Parts 3 & 4 - Horizon Interpretation and Correlation Wilson (2010) 1 A footnote to last week's exercise Double Vision? - Last week when you were
Manipulating the Boundary Mesh
 Chapter 7. Manipulating the Boundary Mesh The first step in producing an unstructured grid is to define the shape of the domain boundaries. Using a preprocessor (GAMBIT or a third-party CAD package) you
Chapter 7. Manipulating the Boundary Mesh The first step in producing an unstructured grid is to define the shape of the domain boundaries. Using a preprocessor (GAMBIT or a third-party CAD package) you
11. Petrophysical Modeling
 11. Petrophysical Modeling 11.1 Deterministic Modeling When the well logs have been scaled up to the resolution of the cells in the 3D grid, the values for each cell along the well trajectory can be interpolated
11. Petrophysical Modeling 11.1 Deterministic Modeling When the well logs have been scaled up to the resolution of the cells in the 3D grid, the values for each cell along the well trajectory can be interpolated
Geology Interpretation Project Big Injun Sand & Trenton-Black River plays, Central Appalachian Basin, WV
 Geology 554 - Interpretation Project Big Injun Sand & Trenton-Black River plays, Central Appalachian Basin, WV Part 1 - Access and Basic Interpretation of the Seismic Data Using Kingdom T. H. Wilson (2005)
Geology 554 - Interpretation Project Big Injun Sand & Trenton-Black River plays, Central Appalachian Basin, WV Part 1 - Access and Basic Interpretation of the Seismic Data Using Kingdom T. H. Wilson (2005)
Stepwise instructions for getting started
 Multiparameter Numerical Medium for Seismic Modeling, Planning, Imaging & Interpretation Worldwide Tesseral Geo Modeling Tesseral 2D Tutorial Stepwise instructions for getting started Contents Useful information...1
Multiparameter Numerical Medium for Seismic Modeling, Planning, Imaging & Interpretation Worldwide Tesseral Geo Modeling Tesseral 2D Tutorial Stepwise instructions for getting started Contents Useful information...1
Petrel* Schlumberger Public
 Petrel* Schlumberger Public Copyright Notice Copyright 1998-2010 Schlumberger. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or translated in any form or
Petrel* Schlumberger Public Copyright Notice Copyright 1998-2010 Schlumberger. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or translated in any form or
Depth Conversion Methods & Petrel Workflows
 Depth Conversion Methods & Petrel Workflows Course Information Alan Atkinson March 2016 Depth Conversion Methods & Petrel Workflows 2016 Alan Atkinson, AA Geophysical Ltd Course Description Depth Conversion
Depth Conversion Methods & Petrel Workflows Course Information Alan Atkinson March 2016 Depth Conversion Methods & Petrel Workflows 2016 Alan Atkinson, AA Geophysical Ltd Course Description Depth Conversion
MODFLOW Generating Data from Solids Using solid models to represent complex stratigraphy with MODFLOW
 v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial MODFLOW Generating Data from Solids Using solid models to represent complex stratigraphy with MODFLOW Objectives Learn the steps necessary to convert solid models to MODFLOW data
v. 10.3 GMS 10.3 Tutorial MODFLOW Generating Data from Solids Using solid models to represent complex stratigraphy with MODFLOW Objectives Learn the steps necessary to convert solid models to MODFLOW data
Geology 554 3D Horizon/Fault Interpretation Labs 1 & 2 - Fault Interpretation and Correlation
 Geology 554 3D Horizon/Fault Interpretation Labs 1 & 2 - Fault Interpretation and Correlation Wilson (2005) *This workshop is based on procedural steps developed by Mike Enomoto of Seismic MicroTechnology
Geology 554 3D Horizon/Fault Interpretation Labs 1 & 2 - Fault Interpretation and Correlation Wilson (2005) *This workshop is based on procedural steps developed by Mike Enomoto of Seismic MicroTechnology
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM
 Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Smoothing 2D Grids in Petrel 2D Grids are the foundation of much of the work done in Petrel. They are used for display, volume calculations, input for
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Smoothing 2D Grids in Petrel 2D Grids are the foundation of much of the work done in Petrel. They are used for display, volume calculations, input for
Appropriate algorithm method for Petrophysical properties to construct 3D modeling for Mishrif formation in Amara oil field Jawad K.
 Appropriate algorithm method for Petrophysical properties to construct 3D modeling for Mishrif formation in Amara oil field Jawad K. Radhy AlBahadily Department of geology, college of science, Baghdad
Appropriate algorithm method for Petrophysical properties to construct 3D modeling for Mishrif formation in Amara oil field Jawad K. Radhy AlBahadily Department of geology, college of science, Baghdad
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies
 Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
Autodesk Inventor Design Exercise 2: F1 Team Challenge Car Developed by Tim Varner Synergis Technologies Tim Varner - 2004 The Inventor User Interface Command Panel Lists the commands that are currently
Refractor 8.1 User Guide
 Refractor 8.1 User Guide Copyright 2016, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Preface...1 Conventions Used in This Guide...1 Where to Find Information...1 Technical Support...2 Feedback...2 Chapter 1
Refractor 8.1 User Guide Copyright 2016, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Preface...1 Conventions Used in This Guide...1 Where to Find Information...1 Technical Support...2 Feedback...2 Chapter 1
Desktop Studio: Charts. Version: 7.3
 Desktop Studio: Charts Version: 7.3 Copyright 2015 Intellicus Technologies This document and its content is copyrighted material of Intellicus Technologies. The content may not be copied or derived from,
Desktop Studio: Charts Version: 7.3 Copyright 2015 Intellicus Technologies This document and its content is copyrighted material of Intellicus Technologies. The content may not be copied or derived from,
RSPile. Tutorial 3 Grouped Pile Analysis. Pile Analysis Software. Grouped Pile Analysis
 RSPile Pile Analysis Software Tutorial 3 Grouped Pile Analysis Grouped Pile Analysis Introduction This tutorial will demonstrate how to model grouped piles under a cap. The finished product of this tutorial
RSPile Pile Analysis Software Tutorial 3 Grouped Pile Analysis Grouped Pile Analysis Introduction This tutorial will demonstrate how to model grouped piles under a cap. The finished product of this tutorial
Pre-Lab Excel Problem
 Pre-Lab Excel Problem Read and follow the instructions carefully! Below you are given a problem which you are to solve using Excel. If you have not used the Excel spreadsheet a limited tutorial is given
Pre-Lab Excel Problem Read and follow the instructions carefully! Below you are given a problem which you are to solve using Excel. If you have not used the Excel spreadsheet a limited tutorial is given
New Features. Version (0)
 New Features Version 2015 contact@eliis.fr - +33(0) 4.67.41.31.16 Copyright Notice All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or translated in any form
New Features Version 2015 contact@eliis.fr - +33(0) 4.67.41.31.16 Copyright Notice All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or translated in any form
GMS 8.0 Tutorial MODFLOW Generating Data from Solids Using solid models to represent complex stratigraphy with MODFLOW
 v. 8.0 GMS 8.0 Tutorial MODFLOW Generating Data from Solids Using solid models to represent complex stratigraphy with MODFLOW Objectives Learn the steps necessary to convert solid models to MODFLOW data
v. 8.0 GMS 8.0 Tutorial MODFLOW Generating Data from Solids Using solid models to represent complex stratigraphy with MODFLOW Objectives Learn the steps necessary to convert solid models to MODFLOW data
DW Tomo 8.1 User Guide
 DW Tomo 8.1 User Guide Copyright 2016, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Preface...1 Conventions Used in This Guide...1 Where to Find Information...1 Technical Support...2 Feedback...2 Chapter 1 Introducing
DW Tomo 8.1 User Guide Copyright 2016, All rights reserved. Table of Contents Preface...1 Conventions Used in This Guide...1 Where to Find Information...1 Technical Support...2 Feedback...2 Chapter 1 Introducing
Create ruler guides. Create a ruler guide
 Create ruler guides Ruler guides are different from grids in that they can be positioned freely on a page or on a pasteboard. You can create two kinds of ruler guides: page guides, which appear only on
Create ruler guides Ruler guides are different from grids in that they can be positioned freely on a page or on a pasteboard. You can create two kinds of ruler guides: page guides, which appear only on
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM
 E&P SOLUTIONS Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Petrel Studio Part 1 The Petrel Studio was new to Petrel 2011, was augmented with new features in Petrel 2012 and contains a variety of
E&P SOLUTIONS Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Petrel Studio Part 1 The Petrel Studio was new to Petrel 2011, was augmented with new features in Petrel 2012 and contains a variety of
Desktop Studio: Charts
 Desktop Studio: Charts Intellicus Enterprise Reporting and BI Platform Intellicus Technologies info@intellicus.com www.intellicus.com Working with Charts i Copyright 2011 Intellicus Technologies This document
Desktop Studio: Charts Intellicus Enterprise Reporting and BI Platform Intellicus Technologies info@intellicus.com www.intellicus.com Working with Charts i Copyright 2011 Intellicus Technologies This document
Designed by Jason Wagner, Course Web Programmer, Office of e-learning NOTE ABOUT CELL REFERENCES IN THIS DOCUMENT... 1
 Excel Essentials Designed by Jason Wagner, Course Web Programmer, Office of e-learning NOTE ABOUT CELL REFERENCES IN THIS DOCUMENT... 1 FREQUENTLY USED KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS... 1 FORMATTING CELLS WITH PRESET
Excel Essentials Designed by Jason Wagner, Course Web Programmer, Office of e-learning NOTE ABOUT CELL REFERENCES IN THIS DOCUMENT... 1 FREQUENTLY USED KEYBOARD SHORTCUTS... 1 FORMATTING CELLS WITH PRESET
Tutorial 6. Pumping Well and River
 Tutorial 6 Pumping Well and River Table of Contents Objective. 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Data Input. 2 Step 1: Open Adaptive Groundwater Input (.agw) File. 2 Step 2: Pumping Well Design Database
Tutorial 6 Pumping Well and River Table of Contents Objective. 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Data Input. 2 Step 1: Open Adaptive Groundwater Input (.agw) File. 2 Step 2: Pumping Well Design Database
Geology 554 Interpretation Project Big Injun Sand, Trenton/Black River Plays, Central Appalachian Basin, WV
 Geology 554 Interpretation Project Big Injun Sand, Trenton/Black River Plays, Central Appalachian Basin, WV Lab Exercise- Horizon Interpretation and Correlation Wilson (2005) 1 Team effort on these interpretation
Geology 554 Interpretation Project Big Injun Sand, Trenton/Black River Plays, Central Appalachian Basin, WV Lab Exercise- Horizon Interpretation and Correlation Wilson (2005) 1 Team effort on these interpretation
v SMS 12.2 Tutorial Observation Prerequisites Requirements Time minutes
 v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Observation Objectives This tutorial will give an overview of using the observation coverage in SMS. Observation points will be created to measure the numerical analysis with
v. 12.2 SMS 12.2 Tutorial Observation Objectives This tutorial will give an overview of using the observation coverage in SMS. Observation points will be created to measure the numerical analysis with
SUM - This says to add together cells F28 through F35. Notice that it will show your result is
 COUNTA - The COUNTA function will examine a set of cells and tell you how many cells are not empty. In this example, Excel analyzed 19 cells and found that only 18 were not empty. COUNTBLANK - The COUNTBLANK
COUNTA - The COUNTA function will examine a set of cells and tell you how many cells are not empty. In this example, Excel analyzed 19 cells and found that only 18 were not empty. COUNTBLANK - The COUNTBLANK
Background on Kingdom Suite for the Imperial Barrel Competition 3D Horizon/Fault Interpretation Parts 1 & 2 - Fault Interpretation and Correlation
 Background on Kingdom Suite for the Imperial Barrel Competition 3D Horizon/Fault Interpretation Parts 1 & 2 - Fault Interpretation and Correlation Wilson (2010) 1 Fault/Horizon Interpretation Using Seismic
Background on Kingdom Suite for the Imperial Barrel Competition 3D Horizon/Fault Interpretation Parts 1 & 2 - Fault Interpretation and Correlation Wilson (2010) 1 Fault/Horizon Interpretation Using Seismic
Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu.
 4. MEMBRANE MODEL 1.1. Preprocessing with surface elements Start New Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu. Create a
4. MEMBRANE MODEL 1.1. Preprocessing with surface elements Start New Start AxisVM by double-clicking the AxisVM icon in the AxisVM folder, found on the Desktop, or in the Start, Programs Menu. Create a
Observation Coverage SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM. 1 Introduction. 2 Opening the Data
 SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM Observation Coverage 1 Introduction An important part of any computer model is the verification of results. Surface water modeling is no exception. Before using a surface
SURFACE WATER MODELING SYSTEM Observation Coverage 1 Introduction An important part of any computer model is the verification of results. Surface water modeling is no exception. Before using a surface
Budget Exercise for Intermediate Excel
 Budget Exercise for Intermediate Excel Follow the directions below to create a 12 month budget exercise. Read through each individual direction before performing it, like you are following recipe instructions.
Budget Exercise for Intermediate Excel Follow the directions below to create a 12 month budget exercise. Read through each individual direction before performing it, like you are following recipe instructions.
Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals
 1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
1-1 Lesson 1 Parametric Modeling Fundamentals Create Simple Parametric Models. Understand the Basic Parametric Modeling Process. Create and Profile Rough Sketches. Understand the "Shape before size" approach.
Creating & Using Tables
 Creating & Using Tables in Microsoft Word 2000 Created by and for: Internet and Technology Training Services Office of Information Technology What is a Table? A table is a structure that is divided into
Creating & Using Tables in Microsoft Word 2000 Created by and for: Internet and Technology Training Services Office of Information Technology What is a Table? A table is a structure that is divided into
Candy is Dandy Project (Project #12)
 Candy is Dandy Project (Project #12) You have been hired to conduct some market research about M&M's. First, you had your team purchase 4 large bags and the results are given for the contents of those
Candy is Dandy Project (Project #12) You have been hired to conduct some market research about M&M's. First, you had your team purchase 4 large bags and the results are given for the contents of those
LESSON 2 MODELING BASICS
 LESSON 2 MODELING BASICS In this lesson we ll start to model a multi-story office building from scratch. We ll construct the base grid, create the two towers and place slabs between the stories. Also we
LESSON 2 MODELING BASICS In this lesson we ll start to model a multi-story office building from scratch. We ll construct the base grid, create the two towers and place slabs between the stories. Also we
SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND
 1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
1 SETTLEMENT OF A CIRCULAR FOOTING ON SAND In this chapter a first application is considered, namely the settlement of a circular foundation footing on sand. This is the first step in becoming familiar
START>PROGRAMS>ARCGIS>
 Department of Urban Studies and Planning Spring 2006 Department of Architecture Site and Urban Systems Planning 11.304J / 4.255J GIS EXERCISE 2 Objectives: To generate the following maps using ArcGIS Software:
Department of Urban Studies and Planning Spring 2006 Department of Architecture Site and Urban Systems Planning 11.304J / 4.255J GIS EXERCISE 2 Objectives: To generate the following maps using ArcGIS Software:
Mesh Quality Tutorial
 Mesh Quality Tutorial Figure 1: The MeshQuality model. See Figure 2 for close-up of bottom-right area This tutorial will illustrate the importance of Mesh Quality in PHASE 2. This tutorial will also show
Mesh Quality Tutorial Figure 1: The MeshQuality model. See Figure 2 for close-up of bottom-right area This tutorial will illustrate the importance of Mesh Quality in PHASE 2. This tutorial will also show
Kinematic Interactivity
 Kinematic Interactivity Interactivity controls have been introduced in the 2D and 3D Kinematic Modelling Modules in Move to make them easier to use and to improve the user experience. Minimising the number
Kinematic Interactivity Interactivity controls have been introduced in the 2D and 3D Kinematic Modelling Modules in Move to make them easier to use and to improve the user experience. Minimising the number
Tutorial For LamTopo
 Tutorial For LamTopo Automatic Grid Generation for LaModel One of the nicest features introduced in LaModel 2.0 was the capability of building the seam and topographic grid automatically from AutoCAD files.
Tutorial For LamTopo Automatic Grid Generation for LaModel One of the nicest features introduced in LaModel 2.0 was the capability of building the seam and topographic grid automatically from AutoCAD files.
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial MODPATH The MODPATH Interface in GMS Prerequisite Tutorials None Time minutes
 v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial The Interface in GMS Objectives Setup a simulation in GMS and view the results. Learn about assigning porosity, creating starting locations, different ways to display pathlines,
v. 9.0 GMS 9.0 Tutorial The Interface in GMS Objectives Setup a simulation in GMS and view the results. Learn about assigning porosity, creating starting locations, different ways to display pathlines,
Tutorial 3. Correlated Random Hydraulic Conductivity Field
 Tutorial 3 Correlated Random Hydraulic Conductivity Field Table of Contents Objective. 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Generation of Correlated Random Hydraulic Conductivity Field 2 Step 1: Open
Tutorial 3 Correlated Random Hydraulic Conductivity Field Table of Contents Objective. 1 Step-by-Step Procedure... 2 Section 1 Generation of Correlated Random Hydraulic Conductivity Field 2 Step 1: Open
Excel Tips to help you with the PS477/577 Final Paper Project
 Excel Tips to help you with the PS477/577 Final Paper Project Please try working through this sheet BEFORE the training session -- it will allow you to learn much more at the training session. Best of
Excel Tips to help you with the PS477/577 Final Paper Project Please try working through this sheet BEFORE the training session -- it will allow you to learn much more at the training session. Best of
Microsoft Excel 2007
 Microsoft Excel 2007 1 Excel is Microsoft s Spreadsheet program. Spreadsheets are often used as a method of displaying and manipulating groups of data in an effective manner. It was originally created
Microsoft Excel 2007 1 Excel is Microsoft s Spreadsheet program. Spreadsheets are often used as a method of displaying and manipulating groups of data in an effective manner. It was originally created
Mapping the Subsurface in 3-D Using Seisworks Part 1 - Structure Mapping
 Mapping the Subsurface in 3-D Using Seisworks Part 1 - Structure Mapping The purpose of this exercise is to introduce you to the art of mapping geologic surfaces from 3-D seismic data using Seisworks.
Mapping the Subsurface in 3-D Using Seisworks Part 1 - Structure Mapping The purpose of this exercise is to introduce you to the art of mapping geologic surfaces from 3-D seismic data using Seisworks.
4D Embroidery Software Exercise Fan Dance Quilt Block
 4D Embroidery Software Exercise Fan Dance Quilt Block By Shirley Rosenbrock 1. Open 4D Embroidery Extra. 2. Quick Link to 4D Configure. Under system, set measurement to Millimeters. 3. Click on the Preference
4D Embroidery Software Exercise Fan Dance Quilt Block By Shirley Rosenbrock 1. Open 4D Embroidery Extra. 2. Quick Link to 4D Configure. Under system, set measurement to Millimeters. 3. Click on the Preference
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM
 Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Merging Overlapping Files into One 2D Grid Often several files (grids or data) covering adjacent and overlapping areas must be combined into one 2D Grid.
Petrel TIPS&TRICKS from SCM Knowledge Worth Sharing Merging Overlapping Files into One 2D Grid Often several files (grids or data) covering adjacent and overlapping areas must be combined into one 2D Grid.
ArcGIS Extension User's Guide
 ArcGIS Extension 2010 - User's Guide Table of Contents OpenSpirit ArcGIS Extension 2010... 1 Installation ( ArcGIS 9.3 or 9.3.1)... 3 Prerequisites... 3 Installation Steps... 3 Installation ( ArcGIS 10)...
ArcGIS Extension 2010 - User's Guide Table of Contents OpenSpirit ArcGIS Extension 2010... 1 Installation ( ArcGIS 9.3 or 9.3.1)... 3 Prerequisites... 3 Installation Steps... 3 Installation ( ArcGIS 10)...
Tutorial: Conceptual Modeling Tutorial. Integrated Conceptual & Numerical Groundwater Modeling Software by Waterloo Hydrogeologic
 Tutorial: Visual MODFLOW Flex 5.1 Integrated Conceptual & Numerical Groundwater Modeling Software 1 1 Visual MODFLOW Flex 5.1 The following example is a quick walk-through of the basics of building a conceptual
Tutorial: Visual MODFLOW Flex 5.1 Integrated Conceptual & Numerical Groundwater Modeling Software 1 1 Visual MODFLOW Flex 5.1 The following example is a quick walk-through of the basics of building a conceptual
3.1 Conceptual Modeling
 Quick Start Tutorials 35 3.1 Conceptual Modeling Conceptual Modeling Tutorial The following example is a quick walk through of the basics of building a conceptual model and converting this to a numerical
Quick Start Tutorials 35 3.1 Conceptual Modeling Conceptual Modeling Tutorial The following example is a quick walk through of the basics of building a conceptual model and converting this to a numerical
Project curves, points, or sketches onto faces and planes.
 Project Curve Path: Curve tab > Derived Curve group > Project Curve Objectives Project curves, points, or sketches onto faces and planes. Prerequisites File tab > Start > Modeling Projecting Curves to
Project Curve Path: Curve tab > Derived Curve group > Project Curve Objectives Project curves, points, or sketches onto faces and planes. Prerequisites File tab > Start > Modeling Projecting Curves to
Working with Excel CHAPTER 1
 CHAPTER 1 Working with Excel You use Microsoft Excel to create spreadsheets, which are documents that enable you to manipulate numbers and formulas to quickly create powerful mathematical, financial, and
CHAPTER 1 Working with Excel You use Microsoft Excel to create spreadsheets, which are documents that enable you to manipulate numbers and formulas to quickly create powerful mathematical, financial, and
Lesson 6 Adding Graphics
 Lesson 6 Adding Graphics Inserting Graphics Images Graphics files (pictures, drawings, and other images) can be inserted into documents, or into frames within documents. They can either be embedded or
Lesson 6 Adding Graphics Inserting Graphics Images Graphics files (pictures, drawings, and other images) can be inserted into documents, or into frames within documents. They can either be embedded or
Tutorial Base Module
 Tutorial Base Module CONTENTS Part 1 - Introduction to the CycloLog desktop... 7 1.1 Introduction to the CycloLog desktop... 7 1.2 Using Log Data panes... 9 Part 2 - Importing and displaying well log data...
Tutorial Base Module CONTENTS Part 1 - Introduction to the CycloLog desktop... 7 1.1 Introduction to the CycloLog desktop... 7 1.2 Using Log Data panes... 9 Part 2 - Importing and displaying well log data...
Working with Excel involves two basic tasks: building a spreadsheet and then manipulating the
 Working with Excel You use Microsoft Excel to create spreadsheets, which are documents that enable you to manipulate numbers and formulas to create powerful mathematical, financial, and statistical models
Working with Excel You use Microsoft Excel to create spreadsheets, which are documents that enable you to manipulate numbers and formulas to create powerful mathematical, financial, and statistical models
Spreadsheet View and Basic Statistics Concepts
 Spreadsheet View and Basic Statistics Concepts GeoGebra 3.2 Workshop Handout 9 Judith and Markus Hohenwarter www.geogebra.org Table of Contents 1. Introduction to GeoGebra s Spreadsheet View 2 2. Record
Spreadsheet View and Basic Statistics Concepts GeoGebra 3.2 Workshop Handout 9 Judith and Markus Hohenwarter www.geogebra.org Table of Contents 1. Introduction to GeoGebra s Spreadsheet View 2 2. Record
Supply Chain Guru Network Optimization Tutorial. Version 8.2
 Supply Chain Guru Network Optimization Tutorial Version 8.2 Supply Chain Guru 8.2 Network Optimization Tutorial January 2015 Copyright 2015 LLamasoft, Inc. All Rights Reserved. PC*MILER and ALK are registered
Supply Chain Guru Network Optimization Tutorial Version 8.2 Supply Chain Guru 8.2 Network Optimization Tutorial January 2015 Copyright 2015 LLamasoft, Inc. All Rights Reserved. PC*MILER and ALK are registered
Target 3D Geology Surfaces
 Target 3D Geology Surfaces The Target 3D Geology Surfaces (Contact Surface from Geology Grids) tool enables you to create subsurface topography grids, where the "Z" values correspond to the elevation of
Target 3D Geology Surfaces The Target 3D Geology Surfaces (Contact Surface from Geology Grids) tool enables you to create subsurface topography grids, where the "Z" values correspond to the elevation of
Excel 2016 Basics for Windows
 Excel 2016 Basics for Windows Excel 2016 Basics for Windows Training Objective To learn the tools and features to get started using Excel 2016 more efficiently and effectively. What you can expect to learn
Excel 2016 Basics for Windows Excel 2016 Basics for Windows Training Objective To learn the tools and features to get started using Excel 2016 more efficiently and effectively. What you can expect to learn
In this section you will learn some simple data entry, editing, formatting techniques and some simple formulae. Contents
 In this section you will learn some simple data entry, editing, formatting techniques and some simple formulae. Contents Section Topic Sub-topic Pages Section 2 Spreadsheets Layout and Design S2: 2 3 Formulae
In this section you will learn some simple data entry, editing, formatting techniques and some simple formulae. Contents Section Topic Sub-topic Pages Section 2 Spreadsheets Layout and Design S2: 2 3 Formulae
Microsoft Excel 2000 Charts
 You see graphs everywhere, in textbooks, in newspapers, magazines, and on television. The ability to create, read, and analyze graphs are essential parts of a student s education. Creating graphs by hand
You see graphs everywhere, in textbooks, in newspapers, magazines, and on television. The ability to create, read, and analyze graphs are essential parts of a student s education. Creating graphs by hand
GUIDE TO View3D. Introduction to View3D
 View3D Guide Introduction to View3D... 1 Starting Hampson-Russell Software... 2 Starting View3D... 4 A Brief Summary of the View3D Process... 8 Loading the Seismic and Horizon Data... 8 Viewing the Data...
View3D Guide Introduction to View3D... 1 Starting Hampson-Russell Software... 2 Starting View3D... 4 A Brief Summary of the View3D Process... 8 Loading the Seismic and Horizon Data... 8 Viewing the Data...
Math 227 EXCEL / MEGASTAT Guide
 Math 227 EXCEL / MEGASTAT Guide Introduction Introduction: Ch2: Frequency Distributions and Graphs Construct Frequency Distributions and various types of graphs: Histograms, Polygons, Pie Charts, Stem-and-Leaf
Math 227 EXCEL / MEGASTAT Guide Introduction Introduction: Ch2: Frequency Distributions and Graphs Construct Frequency Distributions and various types of graphs: Histograms, Polygons, Pie Charts, Stem-and-Leaf
Creating a Basic Chart in Excel 2007
 Creating a Basic Chart in Excel 2007 A chart is a pictorial representation of the data you enter in a worksheet. Often, a chart can be a more descriptive way of representing your data. As a result, those
Creating a Basic Chart in Excel 2007 A chart is a pictorial representation of the data you enter in a worksheet. Often, a chart can be a more descriptive way of representing your data. As a result, those
v Observations SMS Tutorials Prerequisites Requirements Time Objectives
 v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will give an overview of using the observation coverage in SMS. Observation points will be created to measure the numerical analysis with measured field
v. 13.0 SMS 13.0 Tutorial Objectives This tutorial will give an overview of using the observation coverage in SMS. Observation points will be created to measure the numerical analysis with measured field
Release Notes Software Release HRS-9 / R-1.1
 Release Notes Software Release HRS-9 / R-1.1 New Features and Enhancements Summary Start up (last revision: May 2, 2012) Software Release Date: March 29, 2012 This is a patch release, containing rigorous
Release Notes Software Release HRS-9 / R-1.1 New Features and Enhancements Summary Start up (last revision: May 2, 2012) Software Release Date: March 29, 2012 This is a patch release, containing rigorous
Target Lithology Voxels
 Target Lithology Voxels The Target Lithology Voxels tool enables you to create a 3D grid (voxel) based on data contained in a string channel within a from-to drillhole database. A lithology voxel can be
Target Lithology Voxels The Target Lithology Voxels tool enables you to create a 3D grid (voxel) based on data contained in a string channel within a from-to drillhole database. A lithology voxel can be
Technique or Feature Where Introduced
 Part 6: Keypad 4 Mirrored features Patterned features First extrusion Rounded corners In the earpiece part, you defined a radial pattern, one that created new instances of a feature at intervals around
Part 6: Keypad 4 Mirrored features Patterned features First extrusion Rounded corners In the earpiece part, you defined a radial pattern, one that created new instances of a feature at intervals around
(1B) Click Browse and select the AASPI-format file (*.H) that you want to display. After you browse the file, the Colorbar file name (1C), plot title
 QC PLOTTING OF AASPI-FORMAT DATA AND ATTRIBUTES Program aaspi_plot The AASPI QC Plotting tab To further quality control the conversion process, you will wish to plot your data before computing seismic
QC PLOTTING OF AASPI-FORMAT DATA AND ATTRIBUTES Program aaspi_plot The AASPI QC Plotting tab To further quality control the conversion process, you will wish to plot your data before computing seismic
User-defined compaction curves
 User-defined compaction curves Compaction curves define the decrease in porosity of a given lithology with increasing burial depth. In Move, the 2D Kinematic and 3D Kinematic modules use compaction curves
User-defined compaction curves Compaction curves define the decrease in porosity of a given lithology with increasing burial depth. In Move, the 2D Kinematic and 3D Kinematic modules use compaction curves
Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2007
 Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2007 Microsoft Excel is a very powerful tool for you to use for numeric computations and analysis. Excel can also function as a simple database but that is another class.
Introduction to Microsoft Excel 2007 Microsoft Excel is a very powerful tool for you to use for numeric computations and analysis. Excel can also function as a simple database but that is another class.
WEEK NO. 12 MICROSOFT EXCEL 2007
 WEEK NO. 12 MICROSOFT EXCEL 2007 LESSONS OVERVIEW: GOODBYE CALCULATORS, HELLO SPREADSHEET! 1. The Excel Environment 2. Starting A Workbook 3. Modifying Columns, Rows, & Cells 4. Working with Worksheets
WEEK NO. 12 MICROSOFT EXCEL 2007 LESSONS OVERVIEW: GOODBYE CALCULATORS, HELLO SPREADSHEET! 1. The Excel Environment 2. Starting A Workbook 3. Modifying Columns, Rows, & Cells 4. Working with Worksheets
Chapter 4 Determining Cell Size
 Chapter 4 Determining Cell Size Chapter 4 Determining Cell Size The third tutorial is designed to give you a demonstration in using the Cell Size Calculator to obtain the optimal cell size for your circuit
Chapter 4 Determining Cell Size Chapter 4 Determining Cell Size The third tutorial is designed to give you a demonstration in using the Cell Size Calculator to obtain the optimal cell size for your circuit
Introduction to Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2010
 Introduction to Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS Open PowerPoint 2010... 1 About the Editing Screen... 1 Create a Title Slide... 6 Save Your Presentation... 6 Create a New Slide... 7
Introduction to Microsoft Office PowerPoint 2010 TABLE OF CONTENTS Open PowerPoint 2010... 1 About the Editing Screen... 1 Create a Title Slide... 6 Save Your Presentation... 6 Create a New Slide... 7
Producing a Depth-Converted Seismic Horizon in Z-map
 Producing a Depth-Converted Seismic Horizon in Z-map Summary This is a reference guide to creating a depth-converted seismic horizon in LGC s Z-Map Plus TM. The procedure followed is: 1. Approximately
Producing a Depth-Converted Seismic Horizon in Z-map Summary This is a reference guide to creating a depth-converted seismic horizon in LGC s Z-Map Plus TM. The procedure followed is: 1. Approximately
Autodesk Inventor 2019 and Engineering Graphics
 Autodesk Inventor 2019 and Engineering Graphics An Integrated Approach Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the
Autodesk Inventor 2019 and Engineering Graphics An Integrated Approach Randy H. Shih SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the
Module 4 : Spreadsheets
 Module 4 : Spreadsheets What is a spreadsheet program? A spreadsheet program allows you to store, organise and analyse information. Applications of spreadsheets focus on generating numeric information
Module 4 : Spreadsheets What is a spreadsheet program? A spreadsheet program allows you to store, organise and analyse information. Applications of spreadsheets focus on generating numeric information
Chapter 1: Quick Start
 This chapter gives the steps for reconstructing serial sections. You will learn the basics of using RECONSTRUCT TM to import a series of images, view and align the sections, trace profiles, and generate
This chapter gives the steps for reconstructing serial sections. You will learn the basics of using RECONSTRUCT TM to import a series of images, view and align the sections, trace profiles, and generate
Lesson 5: Board Design Files
 5 Lesson 5: Board Design Files Learning Objectives In this lesson you will: Use the Mechanical Symbol Editor to create a mechanical board symbol Use the PCB Design Editor to create a master board design
5 Lesson 5: Board Design Files Learning Objectives In this lesson you will: Use the Mechanical Symbol Editor to create a mechanical board symbol Use the PCB Design Editor to create a master board design
Display Layers in Geosoft 3D View
 Use the New 2D/3D Workflow features in Target for ArcGIS In Target for ArcGIS version 3.5, there are three new interconnected features that make integrating 2D and 3D data in plan and section maps easier.
Use the New 2D/3D Workflow features in Target for ArcGIS In Target for ArcGIS version 3.5, there are three new interconnected features that make integrating 2D and 3D data in plan and section maps easier.
Introduction to Microsoft Excel
 Create it Introduction to Microsoft Excel It's the beginning of the year (or you just got your new computer) and you want to create an electronic grade book to keep track of student achievement and do
Create it Introduction to Microsoft Excel It's the beginning of the year (or you just got your new computer) and you want to create an electronic grade book to keep track of student achievement and do
Using Microsoft Excel
 Using Microsoft Excel Formatting a spreadsheet means changing the way it looks to make it neater and more attractive. Formatting changes can include modifying number styles, text size and colours. Many
Using Microsoft Excel Formatting a spreadsheet means changing the way it looks to make it neater and more attractive. Formatting changes can include modifying number styles, text size and colours. Many
EXCEL BASICS: PROJECTS
 EXCEL BASICS: PROJECTS In this class, you will be practicing with three basic Excel worksheets to learn a variety of foundational skills necessary for more advanced projects. This class covers: Three Project
EXCEL BASICS: PROJECTS In this class, you will be practicing with three basic Excel worksheets to learn a variety of foundational skills necessary for more advanced projects. This class covers: Three Project
Excel 2010 Charts and Graphs
 Excel 2010 Charts and Graphs In older versions of Excel the chart engine looked tired and old. Little had changed in 15 years in charting. The popular chart wizard has been replaced in Excel 2010 by a
Excel 2010 Charts and Graphs In older versions of Excel the chart engine looked tired and old. Little had changed in 15 years in charting. The popular chart wizard has been replaced in Excel 2010 by a
