Answer any FIVE questions 5 x 10 = 50. Graph traversal algorithms process all the vertices of a graph in a systematic fashion.
|
|
|
- Alicia Berry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PES Institute of Technology, Bangalore South Campus (Hosur Road, 1KM before Electronic City, Bangalore ) Solution Set Test III Subject & Code: Design and Analysis of Algorithms(10MCA44) Name of faculty: Ms. A. D. Ashwini Department: MCA IV SEM. Max Marks: 50 Answer any FIVE questions 5 x 10 = Write algorithm for DFS and BFS. Graph Traversal Graph traversal algorithms process all the vertices of a graph in a systematic fashion. They are useful for many graph problems such as checking connectivity, checking acyclicity, connected components, finding articulation points, and topological sorting. First all the vertices are marked as unvisited. Then an unvisited vertex is selected, marked as visited, and all unvisited vertices reachable from that vertex are marked as visited. Repeat above step until all vertices are visited. Graph Marking Algorithm algorithm MarkGraph(G) // Marks vertices and calls traversal algorithm // Input: Graph G = (V, E) // Output: Vertices marked in traversal order mark each vertex in V with 0 // means unvisited count 0 // count is global for each vertex v in v do if v is marked with 0 call traversal algorithm with v
2 BFS: algorithm BFS(v) // Visits unvisited vertices from v // Input: Vertex v // Output: Unvisited vertices from v are marked count count + 1; mark v with count initialize a queue with v while the queue is not empty do u remove vertex from the queue for each vertex w adjacent from u do if w is marked with 0 count count + 1 mark w with count add w to the queue DFS: algorithm DFS(v) // Recursively visits unvisited vertices from v // Input: Vertex v // Output: Unvisited vertices from v are marked count count + 1 mark v with count for each vertex u adjacent from v do if v is marked with 0 DF S(u)
3 2. a. Write briefly about Decrease and Conquer. Decrease and conquer is an approach to solving a problem by: Change an instance into one smaller instance of the problem. Solve the smaller instance. Convert the solution of the smaller instance into a solution for the larger instance. b. Write a program for Topological sorting. #include<stdio.h> #definemax20 int n,adj[max][max]; int front= 1,rear= 1,queue[MAX]; void main() int i,j=0,k; int topsort[max],indeg[max]; create_graph(); printf( The adjacency matrix is:\n ); display(); for(i=1;i<+n;i++) indeg[i]=indegree(i); if(indeg[i]==0) insert_queue(i); while(front<=rear) k=delete_queue(); topsort[j++]=k; for(i=1;i<=n;i++) if(adj[k][i]==1) adj[k][i]=0; indeg[i]=indeg[i] 1; if(indeg[i]==0) insert_queue(i);
4 printf("nodes after topological sorting are:\n"); for(i=0;i<=n;i++) printf("%d",topsort[i]); printf("\n"); create_graph() int i,max_edges,origin,destin; printf("\n Enter number of vertices:"); scamf("%d",&n); max_edges=n*(n 1); for(i=1;i<=max_edges;i++) printf("\n Enter edge %d (00 to quit):",i); scanf("%d%d",&origin,&destin); if((origin==0)&&(destin==0)) printf("invalid edge!!\n"); i ; else adj[origin][destin]=1; return; display() int i,j; for(i=0;i<=n;i++) for(j=1;jrear) printf( Queue Underflow ); return; else del_item=queue[front]; front=front+1; return del_item; int indegree(int node) int i,in_deg=0; for(i=1;i<=n;i++) if(adj[i][node]==1) in_deg++; returnin_deg;
5 3. a. Explain the below with proper examples. P, NP, and NP Complete P, NP, and NP Complete If there s an algorithm to solve a problem that runs in polynomial time, the problem is said to be in the set P If the outcome of an algorithm to solve a problem can be verified in polynomial time, the problem is said to be in the set NP (non deterministic polynomial, the non determinism refers to the outcome of the algorithm, not the verification) There is a set of problems in NP for which if there s a polynomial solution to one there will be a polynomial solution to all the set is called NP Complete b. Define the following with example: Trivial Lower bound Trivial lower bounds are based on counting the number of items that must be processed in input and generated as output to solve a problem. Some examples: Generating all permutations of a set of n elements has a trivial lower bound of Ω(n!) since all n! permutations must be generated. This lower bound is tight since we have algorithms to do this that operate in Θ(n!) 4. a. What is Backtracking approach? Write generic algorithm for backtracking. Backtracking is a refinement of the brute force approach, which systematically searches for a solution to a problem among all available options. It does so by assuming that the solutions are represented by vectors (v 1,..., v m ) of values and by traversing, in a depth first manner, the domains of the vectors until the solutions are found. When invoked, the algorithm starts with an empty vector. At each stage it extends the partial vector with a new value. Upon reaching a partial vector (v 1,..., v i ) which can t represent a partial solution, the algorithm backtracks by removing the trailing value from the vector, and then proceeds by trying to extend the vector with alternative values. ALGORITHM try(v1,...,vi) IF (v1,...,vi) is a solution THEN RETURN (v1,...,vi) FOR each v DO IF (v1,...,vi,v) is acceptable vector THEN sol = try(v1,...,vi,v) IF sol!= () THEN RETURN sol END END RETURN () If S i is the domain of v i, then S 1... S m is the solution space of the problem. The validity criteria used in checking for acceptable vectors determines what portion of that space needs to be searched, and so it also determines the resources required by the algorithm.
6 b. Define Branch and Bound. Compare Backtracking, Branch and Bound approaches. Backtracking is a problem solving method according to which one systematically searches for one or all solutions to a problem by repeatedly trying to extend an approximate solution in all possible ways. Whenever it turns out that such a solution fails, one backtracks to the last point of choice where there are still alternatives available. For most problems it is of the utmost importance to spot early on that an approximate solution can not be extended to a full solution, so that a huge amount of failing trials can be saved. This is called cutting down the search space. It may diminish the running time of the algorithm by several orders of magnitude. Now suppose that it is required to find not just any one or all solutions, but an optimal one. In this case one can apply the same method, but every time a solution is encountered the search space can be reduced even further: from then onwards one need not try to extend approximate solutions if it is sure that their extensions can not be as good as the currently optimal one. In this case we speak of Branch and Bound 5. a. Constract Hamiltonian circuit. A hamiltonian path in a graph is a path that passes through every vertex in the graph exactly once. A hamiltonain path does not necessarily pass through all the edges of the graph, however. A hamiltonian path which ends in the same place in which it began is called a hamiltonian circuit or a hamiltonain cycle. 6. Explain about Approximation algorithm for NP hard problem.
7 An approximate algorithm is a way of dealing with NP completeness for optimization problem. This technique does not guarantee the best solution. The goal of an approximation algorithm is to come as close as possible to the optimum value in a reasonable amount of time which is at most polynomial time. Suppose we have some optimization problem instance i, which has a large number of feasible solutions. Also let c(i) be the cost of solution produced by approximate algorithm and c*(i) be the cost of optimal solution. For minimization problem, we are interested in finding a solution of a given instance i in the set of feasible solutions, such that c(i)/c*(i) be as small as possible. On the other hand, for maximization problem, we are interested in finding a solution in the feasible solution set such that c*(i)/c(i) be as small as possible. We say that an approximation algorithm for the given problem instance i, has a ratio bound of p(n) if for any input of sign n, the cost c of the solution produced by the approximation algorithm is within a factor of p(n) of the cost c* of an optimal solution. That is max(c(i)/c*(i), c*(i)/c(i)) p(n) This definition applies for both minimization and maximization problems. Note that p(n) is always greater than or equal to 1. If solution produced by approximation algorithm is true optimal solution then clearly we have p(n) = 1. For a minimization problem, 0 < c*(i) c(i), and the ratio c(i)/c*(i) gives the factor by which the cost of the approximate solution is larger than the cost of an optimal solution. Similarly, for a maximization problem, 0 < c(i) c*(i), and the ratio c*(i)/c(i) gives the factor by which the cost of an optimal solution is larger than the cost of the approximate solution. Relative Error We define the relative error of the approximate algorithm for any input size as mod[c(i) c*(i)/ c*(i)] We say that an approximate algorithm has a relative bound of ε( n) if mod[c(i) c*(i)/ c*(i)] ε( n) 7. Briefly write about Horspool's algorithm with an example. The Boyer Moore algorithm uses two heuristics in order to determine the shift distance of the pattern in case of a mismatch: the bad character and the good suffix heuristics. Since the good suffix heuristics is rather complicated to implement there is a need for a simple algorithm that is based merely on the bad character heuristics. Due to an idea of Horspool [Hor 80], instead of the "bad character" that caused the mismatch, in each case the rightmost character of the current text window is used for determining the shift distance. Example: a b c a b d a a c b a b c a a b b c a a b a b c a b d a a c b a b c a a b b c a a b
8 (a) Boyer Moore (b) Horspool In this example, t 0,..., t 4 = a b c a b is the current text window that is compared with the pattern. Its suffix a b has matched, but the comparison c a causes a mismatch. The badcharacter heuristics of the Boyer Moore algorithm (a) uses the "bad" text character c to determine the shift distance. The Horspool algorithm (b) uses the rightmost character b of the current text window. The pattern can be shifted until the rightmost occurrence of b in the pattern matches the text character b, where the occurence at the last position of the pattern does not count. Like the Boyer Moore algorithm, the Horspool algorithm assumes its best case if every time in the first comparison a text symbol is found that does not occur at all in the pattern. Then the algorithm performs just O(n/m) comparisons. Preprocessing The function occ required for the bad character heuristics is computed slightly different as in the Boyer Moore algorithm. For every alphabet symbol a, the function value occ(p, a) is equal to the rightmost position of a in p 0... p m 2, or 1, if a does not occur at all. Observe that the last symbol p m 1 of the pattern is not taken into account. Example: occ(text, x) = 2 occ(text, t) = 0 occ(next, t) = 1 The occurrence function for a certain pattern p is stored in an array occ that is indexed by the alphabet symbols. For every symbol a A the entry occ[a] holds the corresponding function value occ(p, a). Given a pattern p, the following function horspoolinitocc computes the occurrence function. void horspoolinitocc() int j; char a; for (a=0; a<alphabetsize; a++) occ[a]= 1; for (j=0; j<m 1; j++) a=p[j]; occ[a]=j;
9 Searching algorithm As in the Boyer Moore algorithm, the pattern is compared from right to left with the text. After a complete match or in case of a mismatch, the pattern is shifted according to the precomputed function occ. void horspoolsearch() int i=0, j; while (i<=n m) j=m 1; while (j>=0 && p[j]==t[i+j]) j ; if (j<0) report(i); i+=m 1; i =occ[t[i]]; 8. Explain List ranking and Graph problems. List ranking Input: A linked list L of n elements. L is given in an array S such that the entry S(i) contains the index of the node which is the successor of the node i in L. Output: The distance of each node i from the end of the list. Sequential list ranking algorithm List ranking can be solved in O(n) time sequentially for a list of length n. A simple parallel list ranking algorithm Output: For each 1 i n, the distance R(i) of node i from the end of the list. begin for 1 i n do in parallel if S(i) 0 then R(i) := 1 else R(i) := 0 endfor while S(i) 0 and S(S(i)) 0 do Set R(i) := R(i) + R(S(i)) Set S(i) := S(S(i)) end
Backtracking is a refinement of the brute force approach, which systematically searches for a
 Backtracking Backtracking is a refinement of the brute force approach, which systematically searches for a solution to a problem among all available options. It does so by assuming that the solutions are
Backtracking Backtracking is a refinement of the brute force approach, which systematically searches for a solution to a problem among all available options. It does so by assuming that the solutions are
Outline. Graphs. Divide and Conquer.
 GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
GRAPHS COMP 321 McGill University These slides are mainly compiled from the following resources. - Professor Jaehyun Park slides CS 97SI - Top-coder tutorials. - Programming Challenges books. Outline Graphs.
Brute Force: Selection Sort
 Brute Force: Intro Brute force means straightforward approach Usually based directly on problem s specs Force refers to computational power Usually not as efficient as elegant solutions Advantages: Applicable
Brute Force: Intro Brute force means straightforward approach Usually based directly on problem s specs Force refers to computational power Usually not as efficient as elegant solutions Advantages: Applicable
PESIT Bangalore South Campus Hosur road, 1km before Electronic City, Bengaluru -100 Department of MCA
 INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : 30/3/15 Max Marks : 50 Name of faculty : Sabeeha Sultana Subject & Code : ADA(13MCA41) Answer any five full question: 1.Illustrate Mergesort for the dataset 8,3,2,9,7,1,5,4.
INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST 2 Date : 30/3/15 Max Marks : 50 Name of faculty : Sabeeha Sultana Subject & Code : ADA(13MCA41) Answer any five full question: 1.Illustrate Mergesort for the dataset 8,3,2,9,7,1,5,4.
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
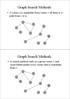 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Computer Science 385 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Siena College Spring Topic Notes: Brute-Force Algorithms
 Computer Science 385 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Siena College Spring 2019 Topic Notes: Brute-Force Algorithms Our first category of algorithms are called brute-force algorithms. Levitin defines
Computer Science 385 Design and Analysis of Algorithms Siena College Spring 2019 Topic Notes: Brute-Force Algorithms Our first category of algorithms are called brute-force algorithms. Levitin defines
Dr. Amotz Bar-Noy s Compendium of Algorithms Problems. Problems, Hints, and Solutions
 Dr. Amotz Bar-Noy s Compendium of Algorithms Problems Problems, Hints, and Solutions Chapter 1 Searching and Sorting Problems 1 1.1 Array with One Missing 1.1.1 Problem Let A = A[1],..., A[n] be an array
Dr. Amotz Bar-Noy s Compendium of Algorithms Problems Problems, Hints, and Solutions Chapter 1 Searching and Sorting Problems 1 1.1 Array with One Missing 1.1.1 Problem Let A = A[1],..., A[n] be an array
Chapter 5. Decrease-and-Conquer. Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved.
 Chapter 5 Decrease-and-Conquer Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Decrease-and-Conquer 1. Reduce problem instance to smaller instance of the same problem 2. Solve smaller instance
Chapter 5 Decrease-and-Conquer Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. Decrease-and-Conquer 1. Reduce problem instance to smaller instance of the same problem 2. Solve smaller instance
String matching algorithms تقديم الطالب: سليمان ضاهر اشراف المدرس: علي جنيدي
 String matching algorithms تقديم الطالب: سليمان ضاهر اشراف المدرس: علي جنيدي للعام الدراسي: 2017/2016 The Introduction The introduction to information theory is quite simple. The invention of writing occurred
String matching algorithms تقديم الطالب: سليمان ضاهر اشراف المدرس: علي جنيدي للعام الدراسي: 2017/2016 The Introduction The introduction to information theory is quite simple. The invention of writing occurred
CS 310 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms
 CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
CS 31 Advanced Data Structures and Algorithms Graphs July 18, 17 Tong Wang UMass Boston CS 31 July 18, 17 1 / 4 Graph Definitions Graph a mathematical construction that describes objects and relations
CSC Design and Analysis of Algorithms. Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms. Brute-Force Approach
 CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
CSC 8301- Design and Analysis of Algorithms Lecture 4 Brute Force, Exhaustive Search, Graph Traversal Algorithms Brute-Force Approach Brute force is a straightforward approach to solving a problem, usually
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal
 Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
Lecture 9 Graph Traversal Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) SWE00: Principles in Programming Spring 0 Euiseong Seo (euiseong@skku.edu) Need for Graphs One of unifying themes of computer science Closely
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs
 CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
CS/COE 1501 cs.pitt.edu/~bill/1501/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 0 2 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(0, 1),
PSD1A. DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS Unit : I-V
 PSD1A DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS Unit : I-V UNIT I -- Introduction -- Definition of Algorithm -- Pseudocode conventions -- Recursive algorithms -- Time and space complexity -- Big- o notation --
PSD1A DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS Unit : I-V UNIT I -- Introduction -- Definition of Algorithm -- Pseudocode conventions -- Recursive algorithms -- Time and space complexity -- Big- o notation --
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12. Questions? Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first Search. (Introduce permutation and subset generation)
 MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Interpolation Search Insertion Sort quick review DFS, BFS Topological Sort MA/CSSE 473 Day 12 Questions? Interpolation Search Insertion sort analysis Depth first Search Breadth first
CS302 - Data Structures using C++
 CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
CS302 - Data Structures using C++ Topic: Graphs - Introduction Kostas Alexis Terminology In the context of our course, graphs represent relations among data items G = {V,E} A graph is a set of vertices
Graph Search Methods. Graph Search Methods
 Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
Graph Search Methods A vertex u is reachable from vertex v iff there is a path from v to u. 0 Graph Search Methods A search method starts at a given vertex v and visits/labels/marks every vertex that is
UNIT Name the different ways of representing a graph? a.adjacencymatrix b. Adjacency list
 UNIT-4 Graph: Terminology, Representation, Traversals Applications - spanning trees, shortest path and Transitive closure, Topological sort. Sets: Representation - Operations on sets Applications. 1. Name
UNIT-4 Graph: Terminology, Representation, Traversals Applications - spanning trees, shortest path and Transitive closure, Topological sort. Sets: Representation - Operations on sets Applications. 1. Name
Lecture 3. Brute Force
 Lecture 3 Brute Force 1 Lecture Contents 1. Selection Sort and Bubble Sort 2. Sequential Search and Brute-Force String Matching 3. Closest-Pair and Convex-Hull Problems by Brute Force 4. Exhaustive Search
Lecture 3 Brute Force 1 Lecture Contents 1. Selection Sort and Bubble Sort 2. Sequential Search and Brute-Force String Matching 3. Closest-Pair and Convex-Hull Problems by Brute Force 4. Exhaustive Search
Theory of Computing. Lecture 4/5 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck
 Theory of Computing Lecture 4/5 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck How fast can we sort? There are deterministic algorithms that sort in worst case time O(n log n) Do better algorithms exist? Example [Andersson et
Theory of Computing Lecture 4/5 MAS 714 Hartmut Klauck How fast can we sort? There are deterministic algorithms that sort in worst case time O(n log n) Do better algorithms exist? Example [Andersson et
Chapter 14. Graphs Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1
 Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
Chapter 14 Graphs 2011 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved 14 A-1 Terminology G = {V, E} A graph G consists of two sets A set V of vertices, or nodes A set E of edges A subgraph Consists of a subset
UNIT 4 Branch and Bound
 UNIT 4 Branch and Bound General method: Branch and Bound is another method to systematically search a solution space. Just like backtracking, we will use bounding functions to avoid generating subtrees
UNIT 4 Branch and Bound General method: Branch and Bound is another method to systematically search a solution space. Just like backtracking, we will use bounding functions to avoid generating subtrees
LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS
 Department of Computer Science University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS By Faculty of Science for Women( SCIW), University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@uobabylon.edu.iq
Department of Computer Science University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS By Faculty of Science for Women( SCIW), University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@uobabylon.edu.iq
UNIT 5 GRAPH. Application of Graph Structure in real world:- Graph Terminologies:
 UNIT 5 CSE 103 - Unit V- Graph GRAPH Graph is another important non-linear data structure. In tree Structure, there is a hierarchical relationship between, parent and children that is one-to-many relationship.
UNIT 5 CSE 103 - Unit V- Graph GRAPH Graph is another important non-linear data structure. In tree Structure, there is a hierarchical relationship between, parent and children that is one-to-many relationship.
DARSHAN INST. OF ENGG. & TECH.
 (1) Explain with example how games can be formulated using graphs? Consider the following game. It is one of the many variants of Nim, also known as the Marienbad game. Initially there is a heap of matches
(1) Explain with example how games can be formulated using graphs? Consider the following game. It is one of the many variants of Nim, also known as the Marienbad game. Initially there is a heap of matches
CS/COE
 CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
CS/COE 151 www.cs.pitt.edu/~lipschultz/cs151/ Graphs 5 3 2 4 1 Graphs A graph G = (V, E) Where V is a set of vertices E is a set of edges connecting vertex pairs Example: V = {, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5} E = {(,
CS61BL. Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting
 CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
COMP4128 Programming Challenges
 Multi- COMP4128 Programming Challenges School of Computer Science and Engineering UNSW Australia Table of Contents 2 Multi- 1 2 Multi- 3 3 Multi- Given two strings, a text T and a pattern P, find the first
Multi- COMP4128 Programming Challenges School of Computer Science and Engineering UNSW Australia Table of Contents 2 Multi- 1 2 Multi- 3 3 Multi- Given two strings, a text T and a pattern P, find the first
Coping with the Limitations of Algorithm Power Exact Solution Strategies Backtracking Backtracking : A Scenario
 Coping with the Limitations of Algorithm Power Tackling Difficult Combinatorial Problems There are two principal approaches to tackling difficult combinatorial problems (NP-hard problems): Use a strategy
Coping with the Limitations of Algorithm Power Tackling Difficult Combinatorial Problems There are two principal approaches to tackling difficult combinatorial problems (NP-hard problems): Use a strategy
CSCE 350: Chin-Tser Huang. University of South Carolina
 CSCE 350: Data Structures and Algorithms Chin-Tser Huang huangct@cse.sc.edu University of South Carolina Announcement Homework 2 will be returned on Thursday; solution will be available on class website
CSCE 350: Data Structures and Algorithms Chin-Tser Huang huangct@cse.sc.edu University of South Carolina Announcement Homework 2 will be returned on Thursday; solution will be available on class website
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS
 QUESTION BANK DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS UNIT1: INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVE: Algorithms play the central role in both the science and the practice of computing. There are compelling reasons to study
QUESTION BANK DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS UNIT1: INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVE: Algorithms play the central role in both the science and the practice of computing. There are compelling reasons to study
Text Algorithms (6EAP) Lecture 3: Exact pa;ern matching II
 Text Algorithms (6EAP) Lecture 3: Exact pa;ern matching II Jaak Vilo 2010 fall Jaak Vilo MTAT.03.190 Text Algorithms 1 Find occurrences in text P S 2 Algorithms Brute force O(nm) Knuth- Morris- Pra; O(n)
Text Algorithms (6EAP) Lecture 3: Exact pa;ern matching II Jaak Vilo 2010 fall Jaak Vilo MTAT.03.190 Text Algorithms 1 Find occurrences in text P S 2 Algorithms Brute force O(nm) Knuth- Morris- Pra; O(n)
11/22/2016. Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms. Introduction. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions. Definitions
 Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Introduction Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 2 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be slow if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E)
Lecture 25 Spanning Trees
 Lecture 25 Spanning Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning, Iliano Cervesato The following is a simple example of a connected, undirected graph with 5 vertices (A,
Lecture 25 Spanning Trees 15-122: Principles of Imperative Computation (Fall 2018) Frank Pfenning, Iliano Cervesato The following is a simple example of a connected, undirected graph with 5 vertices (A,
CS Algorithms and Complexity
 CS 350 - Algorithms and Complexity Graph Theory, Midterm Review Sean Anderson 2/6/18 Portland State University Table of contents 1. Graph Theory 2. Graph Problems 3. Uninformed Exhaustive Search 4. Informed
CS 350 - Algorithms and Complexity Graph Theory, Midterm Review Sean Anderson 2/6/18 Portland State University Table of contents 1. Graph Theory 2. Graph Problems 3. Uninformed Exhaustive Search 4. Informed
Sankalchand Patel College of Engineering - Visnagar Department of Computer Engineering and Information Technology. Assignment
 Class: V - CE Sankalchand Patel College of Engineering - Visnagar Department of Computer Engineering and Information Technology Sub: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Analysis of Algorithm: Assignment
Class: V - CE Sankalchand Patel College of Engineering - Visnagar Department of Computer Engineering and Information Technology Sub: Design and Analysis of Algorithms Analysis of Algorithm: Assignment
Graph Theory. Many problems are mapped to graphs. Problems. traffic VLSI circuits social network communication networks web pages relationship
 Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
Graph Graph Usage I want to visit all the known famous places starting from Seoul ending in Seoul Knowledge: distances, costs Find the optimal(distance or cost) path Graph Theory Many problems are mapped
CMSC 451: Lecture 22 Approximation Algorithms: Vertex Cover and TSP Tuesday, Dec 5, 2017
 CMSC 451: Lecture 22 Approximation Algorithms: Vertex Cover and TSP Tuesday, Dec 5, 2017 Reading: Section 9.2 of DPV. Section 11.3 of KT presents a different approximation algorithm for Vertex Cover. Coping
CMSC 451: Lecture 22 Approximation Algorithms: Vertex Cover and TSP Tuesday, Dec 5, 2017 Reading: Section 9.2 of DPV. Section 11.3 of KT presents a different approximation algorithm for Vertex Cover. Coping
CSCE 321/3201 Analysis and Design of Algorithms. Prof. Amr Goneid. Fall 2016
 CSCE 321/3201 Analysis and Design of Algorithms Prof. Amr Goneid Fall 2016 CSCE 321/3201 Analysis and Design of Algorithms Prof. Amr Goneid Course Resources Instructor: Prof. Amr Goneid E-mail: goneid@aucegypt.edu
CSCE 321/3201 Analysis and Design of Algorithms Prof. Amr Goneid Fall 2016 CSCE 321/3201 Analysis and Design of Algorithms Prof. Amr Goneid Course Resources Instructor: Prof. Amr Goneid E-mail: goneid@aucegypt.edu
CS 491 CAP Introduction to Graphs and Search
 CS 491 CAP Introduction to Graphs and Search Jingbo Shang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Sep 9, 2016 Outline Graphs Adjacency Matrix vs. Adjacency List Special Graphs Depth-first and Breadth-first
CS 491 CAP Introduction to Graphs and Search Jingbo Shang University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign Sep 9, 2016 Outline Graphs Adjacency Matrix vs. Adjacency List Special Graphs Depth-first and Breadth-first
Graph: representation and traversal
 Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Graph: representation and traversal CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang! Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook
Indexing and Searching
 Indexing and Searching Introduction How to retrieval information? A simple alternative is to search the whole text sequentially Another option is to build data structures over the text (called indices)
Indexing and Searching Introduction How to retrieval information? A simple alternative is to search the whole text sequentially Another option is to build data structures over the text (called indices)
Backtracking and Branch-and-Bound
 Backtracking and Branch-and-Bound Usually for problems with high complexity Exhaustive Search is too time consuming Cut down on some search using special methods Idea: Construct partial solutions and extend
Backtracking and Branch-and-Bound Usually for problems with high complexity Exhaustive Search is too time consuming Cut down on some search using special methods Idea: Construct partial solutions and extend
GRAPHICAL ALGORITHMS. UNIT _II Lecture-12 Slides No. 3-7 Lecture Slides No Lecture Slides No
 GRAPHICAL ALGORITHMS UNIT _II Lecture-12 Slides No. 3-7 Lecture-13-16 Slides No. 8-26 Lecture-17-19 Slides No. 27-42 Topics Covered Graphs & Trees ( Some Basic Terminologies) Spanning Trees (BFS & DFS)
GRAPHICAL ALGORITHMS UNIT _II Lecture-12 Slides No. 3-7 Lecture-13-16 Slides No. 8-26 Lecture-17-19 Slides No. 27-42 Topics Covered Graphs & Trees ( Some Basic Terminologies) Spanning Trees (BFS & DFS)
Solution for Data Structure
 Solution for Data Structure May 2016 INDEX Q1 a 2-3 b 4 c. 4-6 d 7 Q2- a 8-12 b 12-14 Q3 a 15-18 b 18-22 Q4- a 22-35 B..N.A Q5 a 36-38 b N.A Q6- a 39-42 b 43 1 www.brainheaters.in Q1) Ans: (a) Define ADT
Solution for Data Structure May 2016 INDEX Q1 a 2-3 b 4 c. 4-6 d 7 Q2- a 8-12 b 12-14 Q3 a 15-18 b 18-22 Q4- a 22-35 B..N.A Q5 a 36-38 b N.A Q6- a 39-42 b 43 1 www.brainheaters.in Q1) Ans: (a) Define ADT
CS8391-DATA STRUCTURES QUESTION BANK UNIT I
 CS8391-DATA STRUCTURES QUESTION BANK UNIT I 2MARKS 1.Define data structure. The data structure can be defined as the collection of elements and all the possible operations which are required for those
CS8391-DATA STRUCTURES QUESTION BANK UNIT I 2MARKS 1.Define data structure. The data structure can be defined as the collection of elements and all the possible operations which are required for those
Introduction to Algorithms: Brute-Force Algorithms
 Introduction to Algorithms: Brute-Force Algorithms Introduction to Algorithms Brute Force Powering a Number Selection Sort Exhaustive Search 0/1 Knapsack Problem Assignment Problem CS 421 - Analysis of
Introduction to Algorithms: Brute-Force Algorithms Introduction to Algorithms Brute Force Powering a Number Selection Sort Exhaustive Search 0/1 Knapsack Problem Assignment Problem CS 421 - Analysis of
CS 8391 DATA STRUCTURES
 DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK CS 8391 DATA STRUCTURES UNIT- I PART A 1. Define: data structure. A data structure is a way of storing and organizing data in the memory for
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING QUESTION BANK CS 8391 DATA STRUCTURES UNIT- I PART A 1. Define: data structure. A data structure is a way of storing and organizing data in the memory for
String Matching. Pedro Ribeiro 2016/2017 DCC/FCUP. Pedro Ribeiro (DCC/FCUP) String Matching 2016/ / 42
 String Matching Pedro Ribeiro DCC/FCUP 2016/2017 Pedro Ribeiro (DCC/FCUP) String Matching 2016/2017 1 / 42 On this lecture The String Matching Problem Naive Algorithm Deterministic Finite Automata Knuth-Morris-Pratt
String Matching Pedro Ribeiro DCC/FCUP 2016/2017 Pedro Ribeiro (DCC/FCUP) String Matching 2016/2017 1 / 42 On this lecture The String Matching Problem Naive Algorithm Deterministic Finite Automata Knuth-Morris-Pratt
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures Chapter 9 Graph s 2 Definitions Definitions an undirected graph is a finite set
Design and Analysis of Algorithms - - Assessment
 X Courses» Design and Analysis of Algorithms Week 1 Quiz 1) In the code fragment below, start and end are integer values and prime(x) is a function that returns true if x is a prime number and false otherwise.
X Courses» Design and Analysis of Algorithms Week 1 Quiz 1) In the code fragment below, start and end are integer values and prime(x) is a function that returns true if x is a prime number and false otherwise.
IV/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION. Design and Analysis of Algorithms (CS/IT 414) Scheme of Evaluation
 IV/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION Design and Analysis of Algorithms (CS/IT 414) Scheme of Evaluation Maximum: 60 Marks 1. Write briefly about the following 1*12= 12 Marks a) Give the characteristics
IV/IV B.Tech (Regular) DEGREE EXAMINATION Design and Analysis of Algorithms (CS/IT 414) Scheme of Evaluation Maximum: 60 Marks 1. Write briefly about the following 1*12= 12 Marks a) Give the characteristics
CS 350 Final Algorithms and Complexity. It is recommended that you read through the exam before you begin. Answer all questions in the space provided.
 It is recommended that you read through the exam before you begin. Answer all questions in the space provided. Name: Answer whether the following statements are true or false and briefly explain your answer
It is recommended that you read through the exam before you begin. Answer all questions in the space provided. Name: Answer whether the following statements are true or false and briefly explain your answer
Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS, Topological sort
 Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS, Topological sort Graphs and BFS Graph G = (V, E) Graph Representations (V G ) v1 v n V(G) = V - Set of all vertices in G E(G) = E - Set of all edges (u,v) in
Practical Session No. 12 Graphs, BFS, DFS, Topological sort Graphs and BFS Graph G = (V, E) Graph Representations (V G ) v1 v n V(G) = V - Set of all vertices in G E(G) = E - Set of all edges (u,v) in
L.J. Institute of Engineering & Technology Semester: VIII (2016)
 Subject Name: Design & Analysis of Algorithm Subject Code:1810 Faculties: Mitesh Thakkar Sr. UNIT-1 Basics of Algorithms and Mathematics No 1 What is an algorithm? What do you mean by correct algorithm?
Subject Name: Design & Analysis of Algorithm Subject Code:1810 Faculties: Mitesh Thakkar Sr. UNIT-1 Basics of Algorithms and Mathematics No 1 What is an algorithm? What do you mean by correct algorithm?
Basic Graph Definitions
 CMSC 341 Graphs Basic Graph Definitions A graph G = (V,E) consists of a finite set of vertices, V, and a finite set of edges, E. Each edge is a pair (v,w) where v, w V. V and E are sets, so each vertex
CMSC 341 Graphs Basic Graph Definitions A graph G = (V,E) consists of a finite set of vertices, V, and a finite set of edges, E. Each edge is a pair (v,w) where v, w V. V and E are sets, so each vertex
Seach algorithms The travelling salesman problem The Towers of Hanoi Playing games. Comp24412: Symbolic AI. Lecture 4: Search. Ian Pratt-Hartmann
 Comp24412: Symbolic AI Lecture 4: Search Ian Pratt-Hartmann Room KB2.38: email: ipratt@cs.man.ac.uk 2016 17 Outline Seach algorithms The travelling salesman problem The Towers of Hanoi Playing games Typical
Comp24412: Symbolic AI Lecture 4: Search Ian Pratt-Hartmann Room KB2.38: email: ipratt@cs.man.ac.uk 2016 17 Outline Seach algorithms The travelling salesman problem The Towers of Hanoi Playing games Typical
Graph traversal is a generalization of tree traversal except we have to keep track of the visited vertices.
 Traversal Techniques for Graphs Graph traversal is a generalization of tree traversal except we have to keep track of the visited vertices. Applications: Strongly connected components, topological sorting,
Traversal Techniques for Graphs Graph traversal is a generalization of tree traversal except we have to keep track of the visited vertices. Applications: Strongly connected components, topological sorting,
Graph Traversals. CS200 - Graphs 1
 Graph Traversals CS200 - Graphs 1 Tree traversal reminder A Pre order A B D G H C E F I B C In order G D H B A E C F I D E F Post order G H D B E I F C A G H I Level order A B C D E F G H I Connected Components
Graph Traversals CS200 - Graphs 1 Tree traversal reminder A Pre order A B D G H C E F I B C In order G D H B A E C F I D E F Post order G H D B E I F C A G H I Level order A B C D E F G H I Connected Components
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms
 Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
Chapter 9 Graph Algorithms 2 Introduction graph theory useful in practice represent many real-life problems can be if not careful with data structures 3 Definitions an undirected graph G = (V, E) is a
String Matching Algorithms
 String Matching Algorithms Georgy Gimel farb (with basic contributions from M. J. Dinneen, Wikipedia, and web materials by Ch. Charras and Thierry Lecroq, Russ Cox, David Eppstein, etc.) COMPSCI 369 Computational
String Matching Algorithms Georgy Gimel farb (with basic contributions from M. J. Dinneen, Wikipedia, and web materials by Ch. Charras and Thierry Lecroq, Russ Cox, David Eppstein, etc.) COMPSCI 369 Computational
Elementary Graph Algorithms. Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph:
 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. Representing a graph: Graph G(V, E): V set of nodes (vertices); E set of edges. Notation: n = V and m = E. (Vertices are numbered
Text Algorithms (6EAP) Lecture 3: Exact paaern matching II
 Text Algorithms (6EA) Lecture 3: Exact paaern matching II Jaak Vilo 2012 fall Jaak Vilo MTAT.03.190 Text Algorithms 1 2 Algorithms Brute force O(nm) Knuth- Morris- raa O(n) Karp- Rabin hir- OR, hir- AND
Text Algorithms (6EA) Lecture 3: Exact paaern matching II Jaak Vilo 2012 fall Jaak Vilo MTAT.03.190 Text Algorithms 1 2 Algorithms Brute force O(nm) Knuth- Morris- raa O(n) Karp- Rabin hir- OR, hir- AND
Practice Problems for the Final
 ECE-250 Algorithms and Data Structures (Winter 2012) Practice Problems for the Final Disclaimer: Please do keep in mind that this problem set does not reflect the exact topics or the fractions of each
ECE-250 Algorithms and Data Structures (Winter 2012) Practice Problems for the Final Disclaimer: Please do keep in mind that this problem set does not reflect the exact topics or the fractions of each
Mystery Algorithm! ALGORITHM MYSTERY( G = (V,E), start_v ) mark all vertices in V as unvisited mystery( start_v )
 Mystery Algorithm! 0 2 ALGORITHM MYSTERY( G = (V,E), start_v ) mark all vertices in V as unvisited mystery( start_v ) 3 1 4 7 6 5 mystery( v ) mark vertex v as visited PRINT v for each vertex w adjacent
Mystery Algorithm! 0 2 ALGORITHM MYSTERY( G = (V,E), start_v ) mark all vertices in V as unvisited mystery( start_v ) 3 1 4 7 6 5 mystery( v ) mark vertex v as visited PRINT v for each vertex w adjacent
UNIT III TREES. A tree is a non-linear data structure that is used to represents hierarchical relationships between individual data items.
 UNIT III TREES A tree is a non-linear data structure that is used to represents hierarchical relationships between individual data items. Tree: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that, there
UNIT III TREES A tree is a non-linear data structure that is used to represents hierarchical relationships between individual data items. Tree: A tree is a finite set of one or more nodes such that, there
Lecturers: Sanjam Garg and Prasad Raghavendra March 20, Midterm 2 Solutions
 U.C. Berkeley CS70 : Algorithms Midterm 2 Solutions Lecturers: Sanjam Garg and Prasad aghavra March 20, 207 Midterm 2 Solutions. (0 points) True/False Clearly put your answers in the answer box in front
U.C. Berkeley CS70 : Algorithms Midterm 2 Solutions Lecturers: Sanjam Garg and Prasad aghavra March 20, 207 Midterm 2 Solutions. (0 points) True/False Clearly put your answers in the answer box in front
Copyright 2000, Kevin Wayne 1
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. Directed
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II
 CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
CS 206 Introduction to Computer Science II 04 / 06 / 2018 Instructor: Michael Eckmann Today s Topics Questions? Comments? Graphs Definition Terminology two ways to represent edges in implementation traversals
Graph Algorithms. Definition
 Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
Graph Algorithms Many problems in CS can be modeled as graph problems. Algorithms for solving graph problems are fundamental to the field of algorithm design. Definition A graph G = (V, E) consists of
Topics. Trees Vojislav Kecman. Which graphs are trees? Terminology. Terminology Trees as Models Some Tree Theorems Applications of Trees CMSC 302
 Topics VCU, Department of Computer Science CMSC 302 Trees Vojislav Kecman Terminology Trees as Models Some Tree Theorems Applications of Trees Binary Search Tree Decision Tree Tree Traversal Spanning Trees
Topics VCU, Department of Computer Science CMSC 302 Trees Vojislav Kecman Terminology Trees as Models Some Tree Theorems Applications of Trees Binary Search Tree Decision Tree Tree Traversal Spanning Trees
Undirected Graphs. V = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 } E = { 1-2, 1-3, 2-3, 2-4, 2-5, 3-5, 3-7, 3-8, 4-5, 5-6 } n = 8 m = 11
 Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
Chapter 3 - Graphs Undirected Graphs Undirected graph. G = (V, E) V = nodes. E = edges between pairs of nodes. Captures pairwise relationship between objects. Graph size parameters: n = V, m = E. V = {
1 5,9,2,7,6,10,4,3,8,1 The first number (5) is automatically the first number of the sorted list
 Algorithms One of the more challenging aspects of Computer Science are algorithms. An algorithm is a plan that solves a problem. When assembling a bicycle based on the included instructions, in this case,
Algorithms One of the more challenging aspects of Computer Science are algorithms. An algorithm is a plan that solves a problem. When assembling a bicycle based on the included instructions, in this case,
Graphs. Part I: Basic algorithms. Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College
 Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College Undirected graphs Concepts: connectivity, connected components paths (undirected) cycles Basic problems, given undirected graph G: is G connected how many
Laura Toma Algorithms (csci2200), Bowdoin College Undirected graphs Concepts: connectivity, connected components paths (undirected) cycles Basic problems, given undirected graph G: is G connected how many
Graph Representation
 Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
Graph Representation Adjacency list representation of G = (V, E) An array of V lists, one for each vertex in V Each list Adj[u] contains all the vertices v such that there is an edge between u and v Adj[u]
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS
 CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
CSE 100: GRAPH ALGORITHMS 2 Graphs: Example A directed graph V5 V = { V = E = { E Path: 3 Graphs: Definitions A directed graph V5 V6 A graph G = (V,E) consists of a set of vertices V and a set of edges
Project and Production Management Prof. Arun Kanda Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi
 Project and Production Management Prof. Arun Kanda Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 8 Consistency and Redundancy in Project networks In today s lecture
Project and Production Management Prof. Arun Kanda Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi Lecture - 8 Consistency and Redundancy in Project networks In today s lecture
MOST attention in the literature of network codes has
 3862 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 56, NO. 8, AUGUST 2010 Efficient Network Code Design for Cyclic Networks Elona Erez, Member, IEEE, and Meir Feder, Fellow, IEEE Abstract This paper introduces
3862 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON INFORMATION THEORY, VOL. 56, NO. 8, AUGUST 2010 Efficient Network Code Design for Cyclic Networks Elona Erez, Member, IEEE, and Meir Feder, Fellow, IEEE Abstract This paper introduces
CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms Practice Final Exam
 CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms Practice Final Exam Name: ID: Instructions: Answer the questions directly on the exam pages. Show all your work for each question. Providing more detail including
CMPSCI 311: Introduction to Algorithms Practice Final Exam Name: ID: Instructions: Answer the questions directly on the exam pages. Show all your work for each question. Providing more detail including
Exact Algorithms for NP-hard problems
 24 mai 2012 1 Why do we need exponential algorithms? 2 3 Why the P-border? 1 Practical reasons (Jack Edmonds, 1965) For practical purposes the difference between algebraic and exponential order is more
24 mai 2012 1 Why do we need exponential algorithms? 2 3 Why the P-border? 1 Practical reasons (Jack Edmonds, 1965) For practical purposes the difference between algebraic and exponential order is more
DATA STRUCTURE : A MCQ QUESTION SET Code : RBMCQ0305
 Q.1 If h is any hashing function and is used to hash n keys in to a table of size m, where n
Q.1 If h is any hashing function and is used to hash n keys in to a table of size m, where n
Directed Graphs (II) Hwansoo Han
 Directed Graphs (II) Hwansoo Han Traversals of Directed Graphs To solve many problems dealing with digraphs, we need to visit vertexes and arcs in a systematic way Depth-first search (DFS) A generalization
Directed Graphs (II) Hwansoo Han Traversals of Directed Graphs To solve many problems dealing with digraphs, we need to visit vertexes and arcs in a systematic way Depth-first search (DFS) A generalization
Solution for Homework set 3
 TTIC 300 and CMSC 37000 Algorithms Winter 07 Solution for Homework set 3 Question (0 points) We are given a directed graph G = (V, E), with two special vertices s and t, and non-negative integral capacities
TTIC 300 and CMSC 37000 Algorithms Winter 07 Solution for Homework set 3 Question (0 points) We are given a directed graph G = (V, E), with two special vertices s and t, and non-negative integral capacities
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms
 CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
CSI 604 Elementary Graph Algorithms Ref: Chapter 22 of the text by Cormen et al. (Second edition) 1 / 25 Graphs: Basic Definitions Undirected Graph G(V, E): V is set of nodes (or vertices) and E is the
22.3 Depth First Search
 22.3 Depth First Search Depth-First Search(DFS) always visits a neighbour of the most recently visited vertex with an unvisited neighbour. This means the search moves forward when possible, and only backtracks
22.3 Depth First Search Depth-First Search(DFS) always visits a neighbour of the most recently visited vertex with an unvisited neighbour. This means the search moves forward when possible, and only backtracks
Search means finding a path or traversal between a start node and one of a set of goal nodes. Search is a study of states and their transitions.
 UNIT 3 BASIC TRAVERSAL AND SEARCH TECHNIQUES Search means finding a path or traversal between a start node and one of a set of goal nodes. Search is a study of states and their transitions. Search involves
UNIT 3 BASIC TRAVERSAL AND SEARCH TECHNIQUES Search means finding a path or traversal between a start node and one of a set of goal nodes. Search is a study of states and their transitions. Search involves
CSE 417 Branch & Bound (pt 4) Branch & Bound
 CSE 417 Branch & Bound (pt 4) Branch & Bound Reminders > HW8 due today > HW9 will be posted tomorrow start early program will be slow, so debugging will be slow... Review of previous lectures > Complexity
CSE 417 Branch & Bound (pt 4) Branch & Bound Reminders > HW8 due today > HW9 will be posted tomorrow start early program will be slow, so debugging will be slow... Review of previous lectures > Complexity
CSC 421: Algorithm Design Analysis. Spring 2017
 CSC 421: Algorithm Design Analysis Spring 2017 Transform & conquer transform-and-conquer approach presorting, balanced search trees, heaps, Horner's Rule problem reduction space/time tradeoffs heap sort,
CSC 421: Algorithm Design Analysis Spring 2017 Transform & conquer transform-and-conquer approach presorting, balanced search trees, heaps, Horner's Rule problem reduction space/time tradeoffs heap sort,
CISC 320 Midterm Exam
 Name: CISC 320 Midterm Exam Wednesday, Mar 25, 2015 There are 19 questions. The first 15 questions count 4 points each. For the others, points are individually shown. The total is 100 points. Multiple
Name: CISC 320 Midterm Exam Wednesday, Mar 25, 2015 There are 19 questions. The first 15 questions count 4 points each. For the others, points are individually shown. The total is 100 points. Multiple
Graph Theory: Starting Out
 Graph Theory: Starting Out Administrivia To read: Chapter 7, Sections 1-3 (Ensley/Crawley) Problem Set 5 sent out; due Monday 12/8 in class. There will be two review days next week (Wednesday and Friday)
Graph Theory: Starting Out Administrivia To read: Chapter 7, Sections 1-3 (Ensley/Crawley) Problem Set 5 sent out; due Monday 12/8 in class. There will be two review days next week (Wednesday and Friday)
CS-6402 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS
 CS-6402 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS 2 marks UNIT-I 1. Define Algorithm. An algorithm is a sequence of unambiguous instructions for solving a problem in a finite amount of time. 2.Write a short note
CS-6402 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS 2 marks UNIT-I 1. Define Algorithm. An algorithm is a sequence of unambiguous instructions for solving a problem in a finite amount of time. 2.Write a short note
Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS
 Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Directed and Undirected Graphs I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
Inf 2B: Graphs, BFS, DFS Kyriakos Kalorkoti School of Informatics University of Edinburgh Directed and Undirected Graphs I A graph is a mathematical structure consisting of a set of vertices and a set
Homework Assignment #3 Graph
 CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
CISC 4080 Computer Algorithms Spring, 2019 Homework Assignment #3 Graph Some of the problems are adapted from problems in the book Introduction to Algorithms by Cormen, Leiserson and Rivest, and some are
Graph. Vertex. edge. Directed Graph. Undirected Graph
 Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
Module : Graphs Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu Graph Graph is a data structure that is a collection
Copyright 2007 Pearson Addison-Wesley. All rights reserved. A. Levitin Introduction to the Design & Analysis of Algorithms, 2 nd ed., Ch.
 Iterative Improvement Algorithm design technique for solving optimization problems Start with a feasible solution Repeat the following step until no improvement can be found: change the current feasible
Iterative Improvement Algorithm design technique for solving optimization problems Start with a feasible solution Repeat the following step until no improvement can be found: change the current feasible
Lecture 3: Graphs and flows
 Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
Chapter 3 Lecture 3: Graphs and flows Graphs: a useful combinatorial structure. Definitions: graph, directed and undirected graph, edge as ordered pair, path, cycle, connected graph, strongly connected
Randomized Algorithms
 Randomized Algorithms Last time Network topologies Intro to MPI Matrix-matrix multiplication Today MPI I/O Randomized Algorithms Parallel k-select Graph coloring Assignment 2 Parallel I/O Goal of Parallel
Randomized Algorithms Last time Network topologies Intro to MPI Matrix-matrix multiplication Today MPI I/O Randomized Algorithms Parallel k-select Graph coloring Assignment 2 Parallel I/O Goal of Parallel
Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search
 Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search Analysis of Algorithms Week 8, Lecture 1 Prepared by John Reif, Ph.D. Distinguished Professor of Computer Science Duke University Graph Algorithms Using Depth
Graph Algorithms Using Depth First Search Analysis of Algorithms Week 8, Lecture 1 Prepared by John Reif, Ph.D. Distinguished Professor of Computer Science Duke University Graph Algorithms Using Depth
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics
 Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu P, NP-Problems Class
Module 6 NP-Complete Problems and Heuristics Dr. Natarajan Meghanathan Professor of Computer Science Jackson State University Jackson, MS 39217 E-mail: natarajan.meghanathan@jsums.edu P, NP-Problems Class
