Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) use in the simulation of the death end ventilation in tunnels and galleries
|
|
|
- Andrea Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI 113 Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) use in the simulation of the death end ventilation in tunnels and galleries J. Toraño, R. Rodríguez & I. Diego GIMOC, Mining Engineering and Civil Works Research Group, Oviedo School of Mines, University of Oviedo, Oviedo, Spain Abstract In the framework of the Research Project CTM /TECNO, Prediction models and prevention systems in the particle atmospheric contamination in an industrial environment of the Spanish National R+D Plan of the Ministry of Education and Science, period, a CFD model has been developed to simulate air flows in tunnels and galleries, including its detailed comparison with available experimental data. Taking into account the importance of the air velocity distribution in the tunnels or galleries where there is continuous transport of particulated material by means of conveyor belts, and where PM10 or PM50 particulated material can be easily thrown in suspension, we quickly identify the necessity of studying the air behaviour using CFD software. Several models were developed using the commercial code Ansys CFX 10.0, starting from several 3D meshes of different resolutions generated using ICEM CFD Medium complexity turbulence models were selected in order to obtain acceptable resolution times in single processor machines, as well as following advices contained in related bibliography. Zero Equation (constant turbulent eddy viscosity), k-epsilon and Spallart-Allmaras models were used, comparing their results with detailed experimental measurements obtained from the use of hot wire anemometers. Results show good agreement between the simulated data and the experimental measurements depending on the turbulence model: areas close to the tunnel end are best simulated using k-e, but areas far from the tunnel end, in the developed flow area, are best simulated using Spalart-Allmaras. As was expected the constant turbulent eddy viscosity model gave results which were not very approximated. Keywords: death end ventilation, particulated material, CFD, turbulence. doi: /afm06012
2 114 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI 1 Introduction Taking into account the importance of the velocity distribution in the ventilation of the tunnels or galleries where there is continuous transport of particulated material using conveyor belts, from which there can easily appear PM10 and PM50 airborne dust, it was clearly shown the necessity of studying the air flow behaviour through a state of the art tool, CFD or computational Fluid dynamics. Among the hundreds of data that has to be introduced to start a CFD simulation one of the most important is the selection of the method that is going to perform the turbulence modelling. Generally speaking the model is selected depending on the technician expertise, the help of the CFD software support service, or related bibliography, [2], [3] or [7] in our case. This paper shows the use of three relative simple turbulence models that allow its future use in extensive meshes of complex geometries or multiphase modelling. The knowledge acquired with these simulations will allow setting the bases for the subsequent simulations that will include dust behaviour. The dust movement will be checked against experimental measurements done using optical dust samplers, as was previously done by the research team that has developed this study, e.g. Toraño et al [5] and [6]. 2 Measurements in an disused mine gallery Measurements have been done in a death end gallery in a disused mine area. It is a gallery supported by a 2UA type roof support, approximately 72 meters ahead from the axis of the main gallery from it is started. Gallery is curved slightly to the right. d Q 2,0m 1,1m x 0,9m y 1,8 m 2,9m y z L 36 m Figure 1: Draft of the disused mine gallery. During the experiment the air was blown to the gallery end through a ventilation duct, using the power of an electric fan. The duct is flexible in its final part and goes parallel to the gallery wall. Its diameter is 600 mm and finishes its run 6 meters from the gallery end. Environmental conditions during the tests where 22-23ºC and 75-80% of humidity. Air velocity measurements where done with a hot wire anemometer, TSI IFA 100. Two different probes were used, one omnidirectional (measures the velocity under 0,8 m/s) and a film probe (measures the velocity module within 0 to 20 m/s). There were done around 50 measurements in each one of the gallery
3 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI 115 cross sections studied, and a total number of 16 cross sections were studied. This means a number of velocity measurement points as high as 800. Estimated precision in the velocity measurement is around +-5%. Measured data were shown and empirically treated in the development of a PhD of the University of Oviedo, see [8]. 3 CFD simulation The CFD commercial code Ansys CFX was used to develop a simulation model that allows the comparison of the experimental results and the simulated ones. The model considers a straight gallery and a section approximately semicircular, quite similar to the one that accommodated the experimental measurements. 3.1 Geometry The simulated gallery has an approximate cross section of 9 m 2 and an overall length of 36 m. In this simulation there has been considered a ventilation pipe of 600 mm of diameter, that guides an airflow of 3,39 m 3 /s. The 3D Geometry has been done with the software Solidworks. Figure 2: 3D geometry of the model. On top of the surfaces needed to create the model, other auxiliary surfaces were created for a better subsequent meshing: one in the outlet of the gallery, the input and output covers of the ventilation pipe and an intermediate surface that will serve as divide the air in two regions with different meshing sizes. 3.2 Meshing The meshing has been done using commercial software ANSYS ICEM CFD 10.0, importing the geometry from Solidworks through IGES format. First a geometry cleaning is done, deleting unnecessary geometry features and checking for physical incongruence.
4 116 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI The mesh was done using tetrahedrical and prismatic cells, and after several tests and initial CFD calculations it was seen that there were not significantly differences in the calculation using meshes over 500k elements. The mesh was not easy to develop, even using fool-proof software as ICEM, due to difficulties selecting appropriate mesh sizes to solve curved surfaces and the space between the pipe and the wall. The mesh finally used will be different depending on the model area, coarse mesh of 500 mm of tetra size far from the gallery end, a fine mesh of 250 mm of tetra size near the gallery end and three times less in the ventilation tube area. Figure 3: Meshing. Walls will be meshed using prisms. After finishing the mesh and its optimization we finally get a mesh of 634k elements (shown in figure 3). 3.3 CFD simulation Introduction The physical characteristics of the problem are defined in CFX-Pre. Three different simulations will be done, depending on the turbulence model used: Zero equation, K-epsilon and Spallart-Allmaras. CFX offers a wide selection of turbulence models, from the quite simple Zero Equation models to LES and RANS, highly demanding in computing time and hardware requirements. The selection of these 3 more or less complex models is based on related bibliography, e.g. [2], [3] and [4] Resolution conditions Problem will be solved as stationary, with three domains separated by domain interfaces corresponding to the ventilation pipe, fine mesh and coarse mesh, and isothermal conditions at 23ºC The boundary conditions used are: - Wall, with default characteristics and smooth roughness, located in all walls. - Outlet, located in the gallery air outlet, defined by a condition of Average Static Pressure 0 atm. This air outlet could be also defined as an opening, but convergence behaviour seen with all simulations showed no recirculation presence at this plane.
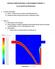
5 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI Inlet : characterized by the velocity obtained from the theoretical operating point of the fan installed in the experiment. Turbulence will be considered medium, intensity=5%. Convergence is set to reach a 1E-05 level in all governing equations, which is accurate enough as per CFX support documentation. In case of the Zero Equation turbulence model, and after several tests, the Eddy Length Scale is set at 1.25 m. The Spallart-Allmaras model is experimentally implemented in CFX 10.0, and CCL, CFX Command Language, must to be used to be able to start this model, as it is not available in the CFX-Pre GUI (Graphic User Interface). 4 Results comparison Each one of the simulations done is compared with the existent experimental data. Comparisons are resumed in two ways: first a general flow comparison and secondly a detailed one in several remarkable sections. 4.1 General view of flow Figure 4 shows simultaneously cut planes for the velocity flow field, representing velocity contours in following planes: XY at 0.5, 8, 18 and 29 meters from the gallery end, ZX at 0.4 meters from bottom and YZ at 0.5 m from left in the outflow adventional sense. (As seen in the figure, Z is aligned with the gallery axis, Y is the vertical and X is the cross direction axis). The airflow is mainly characterized by its turn in the middle of the studied domain, as well as its highly turbulent behaviour near the gallery end, with an area of highly separated layers. The simplest model, the Zero Equation, shows how the air flow gets out of the tube, turns and quickly fits to the down left (as seen in figure 4) corner of the gallery, which will not leave for the complete length of the gallery. The k-epsilon model shows similar behaviour (not considering turbulence effects close to the FRENTE) up to the end of the studied domain (around 25 meters). At that distance the flow turns to the right for 4 meters and then again to the left. The same effect is seen in case of the Spallart-Allmaras model, but this turn is seen closer to the FRENTE, at 16 meters from it. As we will see later on in the cross sections the Spallart-Allmaras is the best fit, as the experimental data section at 18 meters clearly shows the flow going by the right side of the gallery. 4.2 Detailed comparison Cross sections Data available at 200 cm from the gallery end will be compared now (see figure 5). All figures, including the experimental data show a highly negative area (blue), in the output of the tube, and a positive area (red) that indicates output flow towards the beginning of the gallery. The intermediate areas (yellows or white in B/W prints) show the area where there is a change in the sense of the flow, the separated flow.
6 118 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI Figure 4: Velocity contours, K-E (up), Zero Equation (middle) and Spalart- Allmaras (down).
7 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI 119 Measurements Z=200 CFD K-epsilon Z=200 CFD Zero Equation Z=200 CFD Spallart-Allmaras Z=200 Figure 5: Velocity contours at Z=200 cm. In all cases the left down area has positive velocities ranging from 0 to 2 m/s, occupying a wide area of the bottom. Experimental data shows this area to be very wide, best reflected by the k-epsilon model. The area immediately in front of the tube output shows a highly negative velocity, again best simulated by the k-epsilon model. The middle of the gallery shows an experimental velocity between 0 and 1 m/s. This area is again well predicted by the k-epsilon model. In any case differences between k-epsilon and Spallart-Allmaras models are not important. Figure 6 shows equivalent velocity contours in XY planes at 18 meters from gallery end. We can see in the upper left image, the experimental data, that the airflow is now fully developed and velocity values are all below 1 m/s. The output flow has displaced clearly to the right of the gallery, below the ventilation pipe, and at a medium height. Values below zero, flow towards the gallery end, only appears in the upper part of the gallery, over the ventilation tube. The only model that predicts this effect is the Spallart-Allmaras, with a 1m/s velocity area in the middle of the gallery, clearly displaced to the right of the image, as in the reality. Both k-epsilon and Zero Equation show the flow in the
8 120 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI left, stuck to the wall, although k-epsilon shows a more developed flow with almost no areas with velocity below 0,1 m/s. This effect can be also clearly seen in figure 4, analysis completed with the fact already commented that the flow turn to the right shown at 18 meters is only seen in case of the k-epsilon model at 25 meters from the gallery end. Measurements Z=1800 CFD K-epsilon Z=1800 CFD Zero Equation Z=1800 CFD Spalart Allmaras Z=1800 Figure 6: Velocity contours at Z= Conclusions Air flow in a death end gallery can be adequately calculated using CFD methods, serving as a base to the injection of particles to simulate dust behaviour in this environment. The comparison of the results shows good agreement between the experimental data and the simulations done using the Spallart-Allmaras model in the majority of the calculation domain. The area close to the gallery end is best simulated using the k-epsilon model. The flow makes a characteristic turn around 16 meters from the FRENTE and this turn is simulated in that point by the Spallart-Allmaras model. The K-epsilon model also simulates this turn, but at 25 meters of distance. The simplest model, the Zero Equation, or constant turbulent eddy viscosity model, does not simulate this separation at all, as was expected by the advices referring to its limited use contained in the CFX documentation.
9 Advances in Fluid Mechanics VI 121 After the successful velocity field simulation, currently we are developing the study of the evolution of the particulated material inside this airflow, as well as the subsequent comparison with the experimental data obtained by means of optical particle samplers. We want to acknowledge the help and advices from the Ansys CFX Technical Support Team in the development of these studies. References [1] CFD Help, ANSYS CFX-Solver, Release 10.0: Modelling, pp 98. [2] K.W. Moloney, I.S. Lowndes and G.K. Hargrave, Analysis of flow patterns in drivages with auxiliary ventilation, Trans. Instn Min. Metall. 108, pp (1999). [3] A. Wala, J. Jacob, J. Brown and G. Huang, New approaches to mine-face ventilation, Mining engineering, March 2003, pp (2003). [4] K.W. Moloney and I.S. Lowndes, Comparison of measured underground air velocities and air flows simulated by computational fluid dynamics, Trans. Instn Min. Metall. 108, pp (1999). [5] J. Toraño, R. Rodriguez, I. Diego and A. Pelegry, Contamination by particulated material in blasts: analysis, application and adaptation of the existent calculation formulas and software. Environmental Health Risk III, pp , (2004). [6] J. Toraño, R. Rodriguez, J.M. Rivas and A. Pelegry, Diminishing of the dust quantity during the management of granular material in an underground space, XII International Conference on Modelling Monitoring and management of Air Pollution. (2004). [7] S.A. Silvester, I.S. Lowndes and S.W. Kingman, The ventilation of an underground crushing plant, Mining Technology (Trans. Inst. Min. Metall. A), Vol. 113, pp (2004). [8] López Muñiz, Luis Manuel, PhD. Explosion retaining through active water barriers, Universidad de Oviedo
Dust barriers in open pit blasts. Multiphase Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations
 Air Pollution XVI 85 Dust barriers in open pit blasts. Multiphase Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations J. T. Alvarez, I. D. Alvarez & S. T. Lougedo GIMOC, Mining Engineering and Civil Works Research
Air Pollution XVI 85 Dust barriers in open pit blasts. Multiphase Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations J. T. Alvarez, I. D. Alvarez & S. T. Lougedo GIMOC, Mining Engineering and Civil Works Research
CFD modelling of thickened tailings Final project report
 26.11.2018 RESEM Remote sensing supporting surveillance and operation of mines CFD modelling of thickened tailings Final project report Lic.Sc.(Tech.) Reeta Tolonen and Docent Esa Muurinen University of
26.11.2018 RESEM Remote sensing supporting surveillance and operation of mines CFD modelling of thickened tailings Final project report Lic.Sc.(Tech.) Reeta Tolonen and Docent Esa Muurinen University of
Healthy Buildings 2017 Europe July 2-5, 2017, Lublin, Poland
 Healthy Buildings 2017 Europe July 2-5, 2017, Lublin, Poland Paper ID 0122 ISBN: 978-83-7947-232-1 Numerical Investigation of Transport and Deposition of Liquid Aerosol Particles in Indoor Environments
Healthy Buildings 2017 Europe July 2-5, 2017, Lublin, Poland Paper ID 0122 ISBN: 978-83-7947-232-1 Numerical Investigation of Transport and Deposition of Liquid Aerosol Particles in Indoor Environments
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING
 CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
CFD MODELING FOR PNEUMATIC CONVEYING Arvind Kumar 1, D.R. Kaushal 2, Navneet Kumar 3 1 Associate Professor YMCAUST, Faridabad 2 Associate Professor, IIT, Delhi 3 Research Scholar IIT, Delhi e-mail: arvindeem@yahoo.co.in
Introduction to ANSYS CFX
 Workshop 03 Fluid flow around the NACA0012 Airfoil 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS CFX 2015 ANSYS, Inc. March 13, 2015 1 Release 16.0 Workshop Description: The flow simulated is an external aerodynamics
Workshop 03 Fluid flow around the NACA0012 Airfoil 16.0 Release Introduction to ANSYS CFX 2015 ANSYS, Inc. March 13, 2015 1 Release 16.0 Workshop Description: The flow simulated is an external aerodynamics
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE METERING SITUATIONS UNDER ABNORMAL CONFIGURATIONS
 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE METERING SITUATIONS UNDER ABNORMAL CONFIGURATIONS Dr W. Malalasekera Version 3.0 August 2013 1 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE METERING SITUATIONS UNDER ABNORMAL CONFIGURATIONS Dr W. Malalasekera Version 3.0 August 2013 1 COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS ANALYSIS OF ORIFICE PLATE
Simulation and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows
 Simulation and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Oct. 10, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan Kim,
Simulation and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows ENGR:2510 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 17.1; Last Updated: Oct. 10, 2016) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan Kim,
Optimization of Parameters to Improve Ventilation in Underground Mine Working using CFD
 Optimization of Parameters to Improve Ventilation in Underground Mine Working using CFD A THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULLFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF Master of Technology In Mining Engineering
Optimization of Parameters to Improve Ventilation in Underground Mine Working using CFD A THESIS SUBMITTED IN PARTIAL FULLFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF Master of Technology In Mining Engineering
Three Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow Over Spillways
 Three Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow Over Spillways Latif Bouhadji ASL-AQFlow Inc., Sidney, British Columbia, Canada Email: lbouhadji@aslenv.com ABSTRACT Turbulent flows over a spillway
Three Dimensional Numerical Simulation of Turbulent Flow Over Spillways Latif Bouhadji ASL-AQFlow Inc., Sidney, British Columbia, Canada Email: lbouhadji@aslenv.com ABSTRACT Turbulent flows over a spillway
Tutorial 1. Introduction to Using FLUENT: Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow
 Tutorial 1. Introduction to Using FLUENT: Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Introduction This tutorial illustrates the setup and solution of the two-dimensional turbulent fluid flow and heat
Tutorial 1. Introduction to Using FLUENT: Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Introduction This tutorial illustrates the setup and solution of the two-dimensional turbulent fluid flow and heat
Investigation of mixing chamber for experimental FGD reactor
 Investigation of mixing chamber for experimental FGD reactor Jan Novosád 1,a, Petra Danová 1 and Tomáš Vít 1 1 Department of Power Engineering Equipment, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Technical University
Investigation of mixing chamber for experimental FGD reactor Jan Novosád 1,a, Petra Danová 1 and Tomáš Vít 1 1 Department of Power Engineering Equipment, Faculty of Mechanical Engineering, Technical University
Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe
 Tutorial 4. Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D turbulent fluid flow in a pipe. The pipe networks are common
Tutorial 4. Simulation of Flow Development in a Pipe Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to illustrate the setup and solution of a 3D turbulent fluid flow in a pipe. The pipe networks are common
Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray
 Tutorial 17. Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray Introduction In this tutorial, the air-blast atomizer model in ANSYS FLUENT is used to predict the behavior of an evaporating methanol spray. Initially, the
Tutorial 17. Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray Introduction In this tutorial, the air-blast atomizer model in ANSYS FLUENT is used to predict the behavior of an evaporating methanol spray. Initially, the
CIBSE Application Manual AM11 Building Performance Modelling Chapter 6: Ventilation Modelling
 Contents Background Ventilation modelling tool categories Simple tools and estimation techniques Analytical methods Zonal network methods Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Semi-external spaces Summary
Contents Background Ventilation modelling tool categories Simple tools and estimation techniques Analytical methods Zonal network methods Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Semi-external spaces Summary
APPLIED COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS-PROJECT-3
 APPLIED COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS-PROJECT-3 BY SAI CHAITANYA MANGAVELLI Common Setup Data: 1) Mesh Proximity and Curvature with Refinement of 2. 2) Double Precision and second order for methods in Solver.
APPLIED COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS-PROJECT-3 BY SAI CHAITANYA MANGAVELLI Common Setup Data: 1) Mesh Proximity and Curvature with Refinement of 2. 2) Double Precision and second order for methods in Solver.
ISSN(PRINT): ,(ONLINE): ,VOLUME-1,ISSUE-1,
 NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE TUBE BANK PRESSURE DROP OF A SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER Kartik Ajugia, Kunal Bhavsar Lecturer, Mechanical Department, SJCET Mumbai University, Maharashtra Assistant Professor,
NUMERICAL ANALYSIS OF THE TUBE BANK PRESSURE DROP OF A SHELL AND TUBE HEAT EXCHANGER Kartik Ajugia, Kunal Bhavsar Lecturer, Mechanical Department, SJCET Mumbai University, Maharashtra Assistant Professor,
Simulation of Laminar Pipe Flows
 Simulation of Laminar Pipe Flows 57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD PRELAB 1 By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Maysam Mousaviraad, Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering
Simulation of Laminar Pipe Flows 57:020 Mechanics of Fluids and Transport Processes CFD PRELAB 1 By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Maysam Mousaviraad, Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering
Coupled Analysis of FSI
 Coupled Analysis of FSI Qin Yin Fan Oct. 11, 2008 Important Key Words Fluid Structure Interface = FSI Computational Fluid Dynamics = CFD Pressure Displacement Analysis = PDA Thermal Stress Analysis = TSA
Coupled Analysis of FSI Qin Yin Fan Oct. 11, 2008 Important Key Words Fluid Structure Interface = FSI Computational Fluid Dynamics = CFD Pressure Displacement Analysis = PDA Thermal Stress Analysis = TSA
Unique Airflow Visualization Techniques for the Design and Validation of Above-Plenum Data Center CFD Models
 Unique Airflow Visualization Techniques for the Design and Validation of Above-Plenum Data Center CFD Models The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Unique Airflow Visualization Techniques for the Design and Validation of Above-Plenum Data Center CFD Models The MIT Faculty has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits
Flow Around Nuclear Rod Bundles Simulations Based on RANS and LES Method Respectively
 Proceedings of the World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 20-21, 2015 Paper No. 285 Flow Around Nuclear Rod Bundles Simulations Based on RANS
Proceedings of the World Congress on Mechanical, Chemical, and Material Engineering (MCM 2015) Barcelona, Spain July 20-21, 2015 Paper No. 285 Flow Around Nuclear Rod Bundles Simulations Based on RANS
CFD Modelling in the Cement Industry
 CFD Modelling in the Cement Industry Victor J. Turnell, P.E., Turnell Corp., USA, describes computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation and its benefits in applications in the cement industry. Introduction
CFD Modelling in the Cement Industry Victor J. Turnell, P.E., Turnell Corp., USA, describes computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation and its benefits in applications in the cement industry. Introduction
Tutorial: Hydrodynamics of Bubble Column Reactors
 Tutorial: Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to provide guidelines and recommendations for solving a gas-liquid bubble column problem using the multiphase mixture model, including advice on solver
Tutorial: Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to provide guidelines and recommendations for solving a gas-liquid bubble column problem using the multiphase mixture model, including advice on solver
LIDAR technique application to the analysis of environmental pollution
 Waste Management and the Environment V 301 LIDAR technique application to the analysis of environmental pollution S. Torno, J. Toraño, M. Menendez, M. Gent & C. Allende School of Mines, University of Oviedo,
Waste Management and the Environment V 301 LIDAR technique application to the analysis of environmental pollution S. Torno, J. Toraño, M. Menendez, M. Gent & C. Allende School of Mines, University of Oviedo,
Pressure Losses Analysis in Air Duct Flow Using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
 International Academic Institute for Science and Technology International Academic Journal of Science and Engineering Vol. 3, No. 9, 2016, pp. 55-70. ISSN 2454-3896 International Academic Journal of Science
International Academic Institute for Science and Technology International Academic Journal of Science and Engineering Vol. 3, No. 9, 2016, pp. 55-70. ISSN 2454-3896 International Academic Journal of Science
CFD validation of the thermal comfort in a room using draft rates
 CFD validation of the thermal comfort in a room using draft rates Authors: Mika Ruponen 1 and John A. Tinker 1 1 School of Civil Engineering, University of Leeds, UK Corresponding email: mika.ruponen@halton.com
CFD validation of the thermal comfort in a room using draft rates Authors: Mika Ruponen 1 and John A. Tinker 1 1 School of Civil Engineering, University of Leeds, UK Corresponding email: mika.ruponen@halton.com
Validation of a Multi-physics Simulation Approach for Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter Design Application
 Validation of a Multi-physics Simulation Approach for Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter Design Application Setup Numerical Turbulence ing by March 15, 2015 Markets Insertion electromagnetic flowmeters
Validation of a Multi-physics Simulation Approach for Insertion Electromagnetic Flowmeter Design Application Setup Numerical Turbulence ing by March 15, 2015 Markets Insertion electromagnetic flowmeters
THE APPLICATION OF AN ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER TO EVALUATE TRUCK AERODYNAMICS IN CFD
 THE APPLICATION OF AN ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER TO EVALUATE TRUCK AERODYNAMICS IN CFD A SOLUTION FOR A REAL-WORLD ENGINEERING PROBLEM Ir. Niek van Dijk DAF Trucks N.V. CONTENTS Scope & Background Theory:
THE APPLICATION OF AN ATMOSPHERIC BOUNDARY LAYER TO EVALUATE TRUCK AERODYNAMICS IN CFD A SOLUTION FOR A REAL-WORLD ENGINEERING PROBLEM Ir. Niek van Dijk DAF Trucks N.V. CONTENTS Scope & Background Theory:
CFD Analysis of a Fully Developed Turbulent Flow in a Pipe with a Constriction and an Obstacle
 CFD Analysis of a Fully Developed Turbulent Flow in a Pipe with a Constriction and an Obstacle C, Diyoke Mechanical Engineering Department Enugu State University of Science & Tech. Enugu, Nigeria U, Ngwaka
CFD Analysis of a Fully Developed Turbulent Flow in a Pipe with a Constriction and an Obstacle C, Diyoke Mechanical Engineering Department Enugu State University of Science & Tech. Enugu, Nigeria U, Ngwaka
Tutorial 17. Using the Mixture and Eulerian Multiphase Models
 Tutorial 17. Using the Mixture and Eulerian Multiphase Models Introduction: This tutorial examines the flow of water and air in a tee junction. First you will solve the problem using the less computationally-intensive
Tutorial 17. Using the Mixture and Eulerian Multiphase Models Introduction: This tutorial examines the flow of water and air in a tee junction. First you will solve the problem using the less computationally-intensive
Team 194: Aerodynamic Study of Airflow around an Airfoil in the EGI Cloud
 Team 194: Aerodynamic Study of Airflow around an Airfoil in the EGI Cloud CFD Support s OpenFOAM and UberCloud Containers enable efficient, effective, and easy access and use of MEET THE TEAM End-User/CFD
Team 194: Aerodynamic Study of Airflow around an Airfoil in the EGI Cloud CFD Support s OpenFOAM and UberCloud Containers enable efficient, effective, and easy access and use of MEET THE TEAM End-User/CFD
Computational Fluid Dynamics modeling of a Water Flow Over an Ogee Profile
 FINITE ELEMENT METHOD TECHNICAL REPORT Computational Fluid Dynamics modeling of a Water Flow Over an Ogee Profile ANSYS CFX 12 ENME 547 Dr. Sudak Matias Sessarego Written Report Due Date: Friday December
FINITE ELEMENT METHOD TECHNICAL REPORT Computational Fluid Dynamics modeling of a Water Flow Over an Ogee Profile ANSYS CFX 12 ENME 547 Dr. Sudak Matias Sessarego Written Report Due Date: Friday December
Using the Eulerian Multiphase Model for Granular Flow
 Tutorial 21. Using the Eulerian Multiphase Model for Granular Flow Introduction Mixing tanks are used to maintain solid particles or droplets of heavy fluids in suspension. Mixing may be required to enhance
Tutorial 21. Using the Eulerian Multiphase Model for Granular Flow Introduction Mixing tanks are used to maintain solid particles or droplets of heavy fluids in suspension. Mixing may be required to enhance
NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOW BEHAVIOR INTO THE INLET GUIDE VANE SYSTEM (IGV)
 University of West Bohemia» Department of Power System Engineering NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOW BEHAVIOR INTO THE INLET GUIDE VANE SYSTEM (IGV) Publication was supported by project: Budování excelentního
University of West Bohemia» Department of Power System Engineering NUMERICAL INVESTIGATION OF THE FLOW BEHAVIOR INTO THE INLET GUIDE VANE SYSTEM (IGV) Publication was supported by project: Budování excelentního
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010
 An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Flat Plate Boundary Layer Objectives Creating
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2010 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS www.sdcpublications.com Schroff Development Corporation Chapter 2 Flat Plate Boundary Layer Objectives Creating
On the numerical accuracy of particle dispersion simulation in operating theatres
 On the numerical accuracy of particle dispersion simulation in operating theatres Wiebe Zoon 1,*, Marcel Loomans 1 and Jan Hensen 1 1 Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, the Netherlands * Corresponding
On the numerical accuracy of particle dispersion simulation in operating theatres Wiebe Zoon 1,*, Marcel Loomans 1 and Jan Hensen 1 1 Eindhoven University of Technology, Eindhoven, the Netherlands * Corresponding
CFD Modeling of a Radiator Axial Fan for Air Flow Distribution
 CFD Modeling of a Radiator Axial Fan for Air Flow Distribution S. Jain, and Y. Deshpande Abstract The fluid mechanics principle is used extensively in designing axial flow fans and their associated equipment.
CFD Modeling of a Radiator Axial Fan for Air Flow Distribution S. Jain, and Y. Deshpande Abstract The fluid mechanics principle is used extensively in designing axial flow fans and their associated equipment.
Ashwin Shridhar et al. Int. Journal of Engineering Research and Applications ISSN : , Vol. 5, Issue 6, ( Part - 5) June 2015, pp.
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Conjugate Heat transfer Analysis of helical fins with airfoil crosssection and its comparison with existing circular fin design for air cooled engines employing constant rectangular
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Conjugate Heat transfer Analysis of helical fins with airfoil crosssection and its comparison with existing circular fin design for air cooled engines employing constant rectangular
Pressure Drop Evaluation in a Pilot Plant Hydrocyclone
 Pressure Drop Evaluation in a Pilot Plant Hydrocyclone Fabio Kasper, M.Sc. Emilio Paladino, D.Sc. Marcus Reis, M.Sc. ESSS Carlos A. Capela Moraes, D.Sc. Dárley C. Melo, M.Sc. Petrobras Research Center
Pressure Drop Evaluation in a Pilot Plant Hydrocyclone Fabio Kasper, M.Sc. Emilio Paladino, D.Sc. Marcus Reis, M.Sc. ESSS Carlos A. Capela Moraes, D.Sc. Dárley C. Melo, M.Sc. Petrobras Research Center
CFD Best Practice Guidelines: A process to understand CFD results and establish Simulation versus Reality
 CFD Best Practice Guidelines: A process to understand CFD results and establish Simulation versus Reality Judd Kaiser ANSYS Inc. judd.kaiser@ansys.com 2005 ANSYS, Inc. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Overview
CFD Best Practice Guidelines: A process to understand CFD results and establish Simulation versus Reality Judd Kaiser ANSYS Inc. judd.kaiser@ansys.com 2005 ANSYS, Inc. 1 ANSYS, Inc. Proprietary Overview
SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014
 An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
An Introduction to SolidWorks Flow Simulation 2014 John E. Matsson, Ph.D. SDC PUBLICATIONS Better Textbooks. Lower Prices. www.sdcpublications.com Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Visit the following websites
Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows
 1 Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 1, 2017) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan
1 Verification of Laminar and Validation of Turbulent Pipe Flows 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 1 (ANSYS 18.1; Last Updated: Aug. 1, 2017) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger, Dong-Hwan
Modelling wind driven airflow rate with CFD and verification of. approximation formulas based on wind pressure coefficients
 Modelling wind driven airflow rate with CFD and verification of approximation formulas based on wind pressure coefficients S. Leenknegt 1 *, B. Piret 1, A. Tablada de la Torre 1, D. Saelens 1 (1) Division
Modelling wind driven airflow rate with CFD and verification of approximation formulas based on wind pressure coefficients S. Leenknegt 1 *, B. Piret 1, A. Tablada de la Torre 1, D. Saelens 1 (1) Division
Calculate a solution using the pressure-based coupled solver.
 Tutorial 19. Modeling Cavitation Introduction This tutorial examines the pressure-driven cavitating flow of water through a sharpedged orifice. This is a typical configuration in fuel injectors, and brings
Tutorial 19. Modeling Cavitation Introduction This tutorial examines the pressure-driven cavitating flow of water through a sharpedged orifice. This is a typical configuration in fuel injectors, and brings
Solved with COMSOL Multiphysics 4.2
 Laminar Static Mixer Introduction In static mixers, also called motionless or in-line mixers, a fluid is pumped through a pipe containing stationary blades. This mixing technique is particularly well suited
Laminar Static Mixer Introduction In static mixers, also called motionless or in-line mixers, a fluid is pumped through a pipe containing stationary blades. This mixing technique is particularly well suited
µ = Pa s m 3 The Reynolds number based on hydraulic diameter, D h = 2W h/(w + h) = 3.2 mm for the main inlet duct is = 359
 Laminar Mixer Tutorial for STAR-CCM+ ME 448/548 March 30, 2014 Gerald Recktenwald gerry@pdx.edu 1 Overview Imagine that you are part of a team developing a medical diagnostic device. The device has a millimeter
Laminar Mixer Tutorial for STAR-CCM+ ME 448/548 March 30, 2014 Gerald Recktenwald gerry@pdx.edu 1 Overview Imagine that you are part of a team developing a medical diagnostic device. The device has a millimeter
Modeling and Simulation of Single Phase Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in Packed Beds
 Modeling and Simulation of Single Phase Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in Packed Beds by:- Balaaji Mahadevan Shaurya Sachdev Subhanshu Pareek Amol Deshpande Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani
Modeling and Simulation of Single Phase Fluid Flow and Heat Transfer in Packed Beds by:- Balaaji Mahadevan Shaurya Sachdev Subhanshu Pareek Amol Deshpande Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani
Computational Fluid Dynamics as an advanced module of ESP-r Part 1: The numerical grid - defining resources and accuracy. Jordan A.
 Computational Fluid Dynamics as an advanced module of ESP-r Part 1: The numerical grid - defining resources and accuracy Jordan A. Denev Abstract: The present paper is a first one from a series of papers
Computational Fluid Dynamics as an advanced module of ESP-r Part 1: The numerical grid - defining resources and accuracy Jordan A. Denev Abstract: The present paper is a first one from a series of papers
HIGH PERFORMANCE LARGE EDDY SIMULATION OF TURBULENT FLOWS AROUND PWR MIXING GRIDS
 HIGH PERFORMANCE LARGE EDDY SIMULATION OF TURBULENT FLOWS AROUND PWR MIXING GRIDS U. Bieder, C. Calvin, G. Fauchet CEA Saclay, CEA/DEN/DANS/DM2S P. Ledac CS-SI HPCC 2014 - First International Workshop
HIGH PERFORMANCE LARGE EDDY SIMULATION OF TURBULENT FLOWS AROUND PWR MIXING GRIDS U. Bieder, C. Calvin, G. Fauchet CEA Saclay, CEA/DEN/DANS/DM2S P. Ledac CS-SI HPCC 2014 - First International Workshop
CFD Application in Offshore Structures Design at PETROBRAS
 CFD Application in Offshore Structures Design at PETROBRAS Marcus Reis ESSS CFD Director Mooring System Design of Floating Production Systems; Current and Wind Loads; Wave Induced Drag Coefficients. Case
CFD Application in Offshore Structures Design at PETROBRAS Marcus Reis ESSS CFD Director Mooring System Design of Floating Production Systems; Current and Wind Loads; Wave Induced Drag Coefficients. Case
Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames
 Tutorial 10. Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames Introduction Many engineering problems involve rotating flow domains. One example is the centrifugal blower unit that is typically used in automotive
Tutorial 10. Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames Introduction Many engineering problems involve rotating flow domains. One example is the centrifugal blower unit that is typically used in automotive
COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS USED IN THE DESIGN OF WATERBLAST TOOLING
 2015 WJTA-IMCA Conference and Expo November 2-4 New Orleans, Louisiana Paper COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS USED IN THE DESIGN OF WATERBLAST TOOLING J. Schneider StoneAge, Inc. Durango, Colorado, U.S.A.
2015 WJTA-IMCA Conference and Expo November 2-4 New Orleans, Louisiana Paper COMPUTATIONAL FLUID DYNAMICS USED IN THE DESIGN OF WATERBLAST TOOLING J. Schneider StoneAge, Inc. Durango, Colorado, U.S.A.
Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil
 Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil 1. Purpose 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 2 By Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering The University
Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil 1. Purpose 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 2 By Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering The University
Usage of CFX for Aeronautical Simulations
 Usage of CFX for Aeronautical Simulations Florian Menter Development Manager Scientific Coordination ANSYS Germany GmbH Overview Elements of CFD Technology for aeronautical simulations: Grid generation
Usage of CFX for Aeronautical Simulations Florian Menter Development Manager Scientific Coordination ANSYS Germany GmbH Overview Elements of CFD Technology for aeronautical simulations: Grid generation
Aerodynamic Study of a Realistic Car W. TOUGERON
 Aerodynamic Study of a Realistic Car W. TOUGERON Tougeron CFD Engineer 2016 Abstract This document presents an aerodynamic CFD study of a realistic car geometry. The aim is to demonstrate the efficiency
Aerodynamic Study of a Realistic Car W. TOUGERON Tougeron CFD Engineer 2016 Abstract This document presents an aerodynamic CFD study of a realistic car geometry. The aim is to demonstrate the efficiency
THE INFLUENCE OF MESH CHARACTERISTICS ON OPENFOAM SIMULATIONS OF THE DRIVAER MODEL
 6 th BETA CAE International Conference THE INFLUENCE OF MESH CHARACTERISTICS ON OPENFOAM SIMULATIONS OF THE DRIVAER MODEL Grigoris Fotiadis *, Vangelis Skaperdas, Aristotelis Iordanidis BETA CAE Systems
6 th BETA CAE International Conference THE INFLUENCE OF MESH CHARACTERISTICS ON OPENFOAM SIMULATIONS OF THE DRIVAER MODEL Grigoris Fotiadis *, Vangelis Skaperdas, Aristotelis Iordanidis BETA CAE Systems
Thermal and Flow Modeling & Validation of an Exhaust Gas Particulate Matter Sensor
 Thermal and Flow Modeling & Validation of an Exhaust Gas Particulate Matter Sensor A. Lourdhusamy, B. Henderson, J. Steppan, V. Wang, J. Fitzpatrick, K. Allmendinger EmiSense Technologies, LLC Salt Lake
Thermal and Flow Modeling & Validation of an Exhaust Gas Particulate Matter Sensor A. Lourdhusamy, B. Henderson, J. Steppan, V. Wang, J. Fitzpatrick, K. Allmendinger EmiSense Technologies, LLC Salt Lake
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Compressible Flow in a Nozzle
 ANSYS AIM Tutorial Compressible Flow in a Nozzle Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Pre-Analysis Start-Up Geometry Import Geometry Mesh
ANSYS AIM Tutorial Compressible Flow in a Nozzle Author(s): Sebastian Vecchi Created using ANSYS AIM 18.1 Problem Specification Pre-Analysis & Start Up Pre-Analysis Start-Up Geometry Import Geometry Mesh
Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil
 1 Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 2 (ANSYS 19.1; Last Updated: Aug. 7, 2018) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger,
1 Verification and Validation of Turbulent Flow around a Clark-Y Airfoil 1. Purpose ME:5160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 2 (ANSYS 19.1; Last Updated: Aug. 7, 2018) By Timur Dogan, Michael Conger,
Reproducibility of Complex Turbulent Flow Using Commercially-Available CFD Software
 Reports of Research Institute for Applied Mechanics, Kyushu University No.150 (47 59) March 2016 Reproducibility of Complex Turbulent Using Commercially-Available CFD Software Report 1: For the Case of
Reports of Research Institute for Applied Mechanics, Kyushu University No.150 (47 59) March 2016 Reproducibility of Complex Turbulent Using Commercially-Available CFD Software Report 1: For the Case of
Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics. D. Murrin
 Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics D. Murrin Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat transfer, mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena
Introduction to C omputational F luid Dynamics D. Murrin Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the science of predicting fluid flow, heat transfer, mass transfer, chemical reactions, and related phenomena
McNair Scholars Research Journal
 McNair Scholars Research Journal Volume 2 Article 1 2015 Benchmarking of Computational Models against Experimental Data for Velocity Profile Effects on CFD Analysis of Adiabatic Film-Cooling Effectiveness
McNair Scholars Research Journal Volume 2 Article 1 2015 Benchmarking of Computational Models against Experimental Data for Velocity Profile Effects on CFD Analysis of Adiabatic Film-Cooling Effectiveness
Validation of Computational Models of Auxiliary Ventilation Systems with Experimental Data
 551 Validation of Computational Models of Auxiliary Ventilation Systems with Experimental Data K.W. Moloney/ D.M. Hargreaves/ I.S. Lowndes 1 and W. Pearce 2 1 School of Chemical Environmental and Mining
551 Validation of Computational Models of Auxiliary Ventilation Systems with Experimental Data K.W. Moloney/ D.M. Hargreaves/ I.S. Lowndes 1 and W. Pearce 2 1 School of Chemical Environmental and Mining
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) for Built Environment
 Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) for Built Environment Seminar 4 (For ASHRAE Members) Date: Sunday 20th March 2016 Time: 18:30-21:00 Venue: Millennium Hotel Sponsored by: ASHRAE Oryx Chapter Dr. Ahmad
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) for Built Environment Seminar 4 (For ASHRAE Members) Date: Sunday 20th March 2016 Time: 18:30-21:00 Venue: Millennium Hotel Sponsored by: ASHRAE Oryx Chapter Dr. Ahmad
The study of air distribution in tunnels and large industrial buildings
 Ventilation, Airflow and Contaminant Transport in Buildings The study of air distribution in tunnels and large industrial buildings 13th January 2017 7. Semester Project Indoor Environmental & Energy Engineering
Ventilation, Airflow and Contaminant Transport in Buildings The study of air distribution in tunnels and large industrial buildings 13th January 2017 7. Semester Project Indoor Environmental & Energy Engineering
Verification and Validation in CFD and Heat Transfer: ANSYS Practice and the New ASME Standard
 Verification and Validation in CFD and Heat Transfer: ANSYS Practice and the New ASME Standard Dimitri P. Tselepidakis & Lewis Collins ASME 2012 Verification and Validation Symposium May 3 rd, 2012 1 Outline
Verification and Validation in CFD and Heat Transfer: ANSYS Practice and the New ASME Standard Dimitri P. Tselepidakis & Lewis Collins ASME 2012 Verification and Validation Symposium May 3 rd, 2012 1 Outline
Optimization of under-relaxation factors. and Courant numbers for the simulation of. sloshing in the oil pan of an automobile
 Optimization of under-relaxation factors and Courant numbers for the simulation of sloshing in the oil pan of an automobile Swathi Satish*, Mani Prithiviraj and Sridhar Hari⁰ *National Institute of Technology,
Optimization of under-relaxation factors and Courant numbers for the simulation of sloshing in the oil pan of an automobile Swathi Satish*, Mani Prithiviraj and Sridhar Hari⁰ *National Institute of Technology,
Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray
 Tutorial 16. Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray Introduction In this tutorial, FLUENT s air-blast atomizer model is used to predict the behavior of an evaporating methanol spray. Initially, the air flow
Tutorial 16. Modeling Evaporating Liquid Spray Introduction In this tutorial, FLUENT s air-blast atomizer model is used to predict the behavior of an evaporating methanol spray. Initially, the air flow
c Fluent Inc. May 16,
 Tutorial 1. Office Ventilation Introduction: This tutorial demonstrates how to model an office shared by two people working at computers, using Airpak. In this tutorial, you will learn how to: Open a new
Tutorial 1. Office Ventilation Introduction: This tutorial demonstrates how to model an office shared by two people working at computers, using Airpak. In this tutorial, you will learn how to: Open a new
Application of Wray-Agarwal Turbulence Model for Accurate Numerical Simulation of Flow Past a Three-Dimensional Wing-body
 Washington University in St. Louis Washington University Open Scholarship Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science Independent Study Mechanical Engineering & Materials Science 4-28-2016 Application
Washington University in St. Louis Washington University Open Scholarship Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science Independent Study Mechanical Engineering & Materials Science 4-28-2016 Application
MODELING PARTICLE DEPOSITION IN VENTILATION DUCTS
 MODELING PARTICLE DEPOSITION IN VENTILATION DUCTS MR Sippola 1* and WW Nazaroff 1,2 1 Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA 2 Indoor Environment Dept.,
MODELING PARTICLE DEPOSITION IN VENTILATION DUCTS MR Sippola 1* and WW Nazaroff 1,2 1 Dept. of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of California, Berkeley, CA, USA 2 Indoor Environment Dept.,
Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow
 Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Objectives The main objectives of the project are to learn (i) how to set up and perform flow simulations with heat transfer and mixing, (ii) post-processing and
Flow and Heat Transfer in a Mixing Elbow Objectives The main objectives of the project are to learn (i) how to set up and perform flow simulations with heat transfer and mixing, (ii) post-processing and
Design Verification of Hydraulic Performance. for a Centrifugal Pump using. Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
 Design Verification of Hydraulic Performance for a Centrifugal Pump using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Anil S. Akole (Asst. Manager) Center for Design & Research Pentair Water India Private Limited
Design Verification of Hydraulic Performance for a Centrifugal Pump using Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Anil S. Akole (Asst. Manager) Center for Design & Research Pentair Water India Private Limited
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 02 Using the Discrete Phase Model (DPM)
 Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 02 Using the Discrete Phase Model (DPM) Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry
Express Introductory Training in ANSYS Fluent Workshop 02 Using the Discrete Phase Model (DPM) Dimitrios Sofialidis Technical Manager, SimTec Ltd. Mechanical Engineer, PhD PRACE Autumn School 2013 - Industry
Using a Single Rotating Reference Frame
 Tutorial 9. Using a Single Rotating Reference Frame Introduction This tutorial considers the flow within a 2D, axisymmetric, co-rotating disk cavity system. Understanding the behavior of such flows is
Tutorial 9. Using a Single Rotating Reference Frame Introduction This tutorial considers the flow within a 2D, axisymmetric, co-rotating disk cavity system. Understanding the behavior of such flows is
The Spalart Allmaras turbulence model
 The Spalart Allmaras turbulence model The main equation The Spallart Allmaras turbulence model is a one equation model designed especially for aerospace applications; it solves a modelled transport equation
The Spalart Allmaras turbulence model The main equation The Spallart Allmaras turbulence model is a one equation model designed especially for aerospace applications; it solves a modelled transport equation
FAR-Wake Workshop, Marseille, May 2008
 Wake Vortices generated by an Aircraft Fuselage : Comparison of Wind Tunnel Measurements on the TAK Model with RANS and RANS-LES Simulations T. Louagie, L. Georges & P. Geuzaine Cenaero CFD-Multiphysics
Wake Vortices generated by an Aircraft Fuselage : Comparison of Wind Tunnel Measurements on the TAK Model with RANS and RANS-LES Simulations T. Louagie, L. Georges & P. Geuzaine Cenaero CFD-Multiphysics
SIMULATION OF FREE SURFACE FLOW IN A SPILLWAY WITH THE RIGID LID AND VOLUME OF FLUID METHODS AND VALIDATION IN A SCALE MODEL
 V European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics ECCOMAS CFD 21 J. C. F. Pereira and A. Sequeira (Eds) Lisbon, Portugal, 14 17 June 21 SIMULATION OF FREE SURFACE FLOW IN A SPILLWAY WITH THE RIGID
V European Conference on Computational Fluid Dynamics ECCOMAS CFD 21 J. C. F. Pereira and A. Sequeira (Eds) Lisbon, Portugal, 14 17 June 21 SIMULATION OF FREE SURFACE FLOW IN A SPILLWAY WITH THE RIGID
Simulation of Turbulent Flow in an Asymmetric Diffuser
 Simulation of Turbulent Flow in an Asymmetric Diffuser 1. Purpose 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 3 By Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering The University of Iowa C.
Simulation of Turbulent Flow in an Asymmetric Diffuser 1. Purpose 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 3 By Tao Xing and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering The University of Iowa C.
RBF Morph An Add-on Module for Mesh Morphing in ANSYS Fluent
 RBF Morph An Add-on Module for Mesh Morphing in ANSYS Fluent Gilles Eggenspieler Senior Product Manager 1 Morphing & Smoothing A mesh morpher is a tool capable of performing mesh modifications in order
RBF Morph An Add-on Module for Mesh Morphing in ANSYS Fluent Gilles Eggenspieler Senior Product Manager 1 Morphing & Smoothing A mesh morpher is a tool capable of performing mesh modifications in order
NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF LOCAL LOSS COEFFICIENTS OF VENTILATION DUCT FITTINGS
 Eleventh International IBPSA Conference Glasgow, Scotland July 7-30, 009 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF LOCAL LOSS COEFFICIENTS OF VENTILATION DUCT FITTINGS Vladimir Zmrhal, Jan Schwarzer Department of Environmental
Eleventh International IBPSA Conference Glasgow, Scotland July 7-30, 009 NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF LOCAL LOSS COEFFICIENTS OF VENTILATION DUCT FITTINGS Vladimir Zmrhal, Jan Schwarzer Department of Environmental
Numerical Simulation Study on Aerodynamic Characteristics of the High Speed Train under Crosswind
 2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 Numerical Simulation Study on Aerodynamic Characteristics of the High Speed Train under Crosswind Fan Zhao,
2017 2nd International Conference on Industrial Aerodynamics (ICIA 2017) ISBN: 978-1-60595-481-3 Numerical Simulation Study on Aerodynamic Characteristics of the High Speed Train under Crosswind Fan Zhao,
Simulation of Turbulent Flow over the Ahmed Body
 Simulation of Turbulent Flow over the Ahmed Body 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 4 By Timur K. Dogan, Michael Conger, Maysam Mousaviraad, and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering
Simulation of Turbulent Flow over the Ahmed Body 58:160 Intermediate Mechanics of Fluids CFD LAB 4 By Timur K. Dogan, Michael Conger, Maysam Mousaviraad, and Fred Stern IIHR-Hydroscience & Engineering
NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF FLOW THROUGH AN S-DUCT
 NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF FLOW THROUGH AN S-DUCT 1 Pravin Peddiraju, 1 Arthur Papadopoulos, 2 Vangelis Skaperdas, 3 Linda Hedges 1 BETA CAE Systems USA, Inc., USA, 2 BETA CAE Systems SA, Greece, 3 CFD Consultant,
NUMERICAL SIMULATIONS OF FLOW THROUGH AN S-DUCT 1 Pravin Peddiraju, 1 Arthur Papadopoulos, 2 Vangelis Skaperdas, 3 Linda Hedges 1 BETA CAE Systems USA, Inc., USA, 2 BETA CAE Systems SA, Greece, 3 CFD Consultant,
NUMERICAL 3D TRANSONIC FLOW SIMULATION OVER A WING
 Review of the Air Force Academy No.3 (35)/2017 NUMERICAL 3D TRANSONIC FLOW SIMULATION OVER A WING Cvetelina VELKOVA Department of Technical Mechanics, Naval Academy Nikola Vaptsarov,Varna, Bulgaria (cvetelina.velkova1985@gmail.com)
Review of the Air Force Academy No.3 (35)/2017 NUMERICAL 3D TRANSONIC FLOW SIMULATION OVER A WING Cvetelina VELKOVA Department of Technical Mechanics, Naval Academy Nikola Vaptsarov,Varna, Bulgaria (cvetelina.velkova1985@gmail.com)
STAR-CCM+: Wind loading on buildings SPRING 2018
 STAR-CCM+: Wind loading on buildings SPRING 2018 1. Notes on the software 2. Assigned exercise (submission via Blackboard; deadline: Thursday Week 3, 11 pm) 1. NOTES ON THE SOFTWARE STAR-CCM+ generates
STAR-CCM+: Wind loading on buildings SPRING 2018 1. Notes on the software 2. Assigned exercise (submission via Blackboard; deadline: Thursday Week 3, 11 pm) 1. NOTES ON THE SOFTWARE STAR-CCM+ generates
Performance Analysis of an After Cooler Used In High Power Engine Using CFD
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Performance Analysis of an After Cooler Used In High Power Engine Using CFD M. Safraaj Salaamer 1, Dr. K. S. Amirthagadeswaran 2,
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Performance Analysis of an After Cooler Used In High Power Engine Using CFD M. Safraaj Salaamer 1, Dr. K. S. Amirthagadeswaran 2,
CFD Simulation for Stratified Oil-Water Two-Phase Flow in a Horizontal Pipe
 CFD Simulation for Stratified Oil-Water Two-Phase Flow in a Horizontal Pipe Adib Zulhilmi Mohd Alias, a, Jaswar Koto, a,b,* and Yasser Mohamed Ahmed, a a) Department of Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean
CFD Simulation for Stratified Oil-Water Two-Phase Flow in a Horizontal Pipe Adib Zulhilmi Mohd Alias, a, Jaswar Koto, a,b,* and Yasser Mohamed Ahmed, a a) Department of Aeronautics, Automotive and Ocean
Design Optimization of a Weather Radar Antenna using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
 Design Optimization of a Weather Radar Antenna using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Fernando Prevedello Regis Ataídes Nícolas Spogis Wagner Ortega Guedes Fabiano Armellini
Design Optimization of a Weather Radar Antenna using Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) Fernando Prevedello Regis Ataídes Nícolas Spogis Wagner Ortega Guedes Fabiano Armellini
Ryian Hunter MAE 598
 Setup: The initial geometry was produced using the engineering schematics provided in the project assignment document using the ANSYS DesignModeler application taking advantage of system symmetry. Fig.
Setup: The initial geometry was produced using the engineering schematics provided in the project assignment document using the ANSYS DesignModeler application taking advantage of system symmetry. Fig.
Meshing of flow and heat transfer problems
 Meshing of flow and heat transfer problems Luyao Zou a, Zhe Li b, Qiqi Fu c and Lujie Sun d School of, Shandong University of science and technology, Shandong 266590, China. a zouluyaoxf@163.com, b 1214164853@qq.com,
Meshing of flow and heat transfer problems Luyao Zou a, Zhe Li b, Qiqi Fu c and Lujie Sun d School of, Shandong University of science and technology, Shandong 266590, China. a zouluyaoxf@163.com, b 1214164853@qq.com,
Tutorial: Simulating a 3D Check Valve Using Dynamic Mesh 6DOF Model And Diffusion Smoothing
 Tutorial: Simulating a 3D Check Valve Using Dynamic Mesh 6DOF Model And Diffusion Smoothing Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate how to simulate a ball check valve with small displacement
Tutorial: Simulating a 3D Check Valve Using Dynamic Mesh 6DOF Model And Diffusion Smoothing Introduction The purpose of this tutorial is to demonstrate how to simulate a ball check valve with small displacement
Applications of ICFD /SPH Solvers by LS-DYNA to Solve Water Splashing Impact to Automobile Body. Abstract
 Applications of ICFD /SPH Solvers by LS-DYNA to Solve Water Splashing Impact to Automobile Body George Wang (1 ), Kevin Gardner (3), Eric DeHoff (1), Facundo del Pin (2), Inaki Caldichoury (2), Edouard
Applications of ICFD /SPH Solvers by LS-DYNA to Solve Water Splashing Impact to Automobile Body George Wang (1 ), Kevin Gardner (3), Eric DeHoff (1), Facundo del Pin (2), Inaki Caldichoury (2), Edouard
Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames
 Tutorial 9. Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames Introduction Many engineering problems involve rotating flow domains. One example is the centrifugal blower unit that is typically used in automotive
Tutorial 9. Using Multiple Rotating Reference Frames Introduction Many engineering problems involve rotating flow domains. One example is the centrifugal blower unit that is typically used in automotive
NUMERICAL STUDY OF CAVITATING FLOW INSIDE A FLUSH VALVE
 Conference on Modelling Fluid Flow (CMFF 09) The 14th International Conference on Fluid Flow Technologies Budapest, Hungary, September 9-12, 2009 NUMERICAL STUDY OF CAVITATING FLOW INSIDE A FLUSH VALVE
Conference on Modelling Fluid Flow (CMFF 09) The 14th International Conference on Fluid Flow Technologies Budapest, Hungary, September 9-12, 2009 NUMERICAL STUDY OF CAVITATING FLOW INSIDE A FLUSH VALVE
Smoothing the Path to Simulation-Led Device Design
 Smoothing the Path to Simulation-Led Device Design Beverly E. Pryor 1, and Roger W. Pryor, Ph.D. *,2 1 Pryor Knowledge Systems, Inc. 2 Pryor Knowledge Systems, Inc. *Corresponding author: 4918 Malibu Drive,
Smoothing the Path to Simulation-Led Device Design Beverly E. Pryor 1, and Roger W. Pryor, Ph.D. *,2 1 Pryor Knowledge Systems, Inc. 2 Pryor Knowledge Systems, Inc. *Corresponding author: 4918 Malibu Drive,
Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics Mech 122 D. Fabris, K. Lynch, D. Rich
 Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics Mech 122 D. Fabris, K. Lynch, D. Rich 1 Computational Fluid dynamics Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the analysis of systems involving fluid flow, heat
Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics Mech 122 D. Fabris, K. Lynch, D. Rich 1 Computational Fluid dynamics Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) is the analysis of systems involving fluid flow, heat
Keywords: flows past a cylinder; detached-eddy-simulations; Spalart-Allmaras model; flow visualizations
 A TURBOLENT FLOW PAST A CYLINDER *Vít HONZEJK, **Karel FRAŇA *Technical University of Liberec Studentská 2, 461 17, Liberec, Czech Republic Phone:+ 420 485 353434 Email: vit.honzejk@seznam.cz **Technical
A TURBOLENT FLOW PAST A CYLINDER *Vít HONZEJK, **Karel FRAŇA *Technical University of Liberec Studentská 2, 461 17, Liberec, Czech Republic Phone:+ 420 485 353434 Email: vit.honzejk@seznam.cz **Technical
DrivAer-Aerodynamic Investigations for a New Realistic Generic Car Model using ANSYS CFD
 DrivAer-Aerodynamic Investigations for a New Realistic Generic Car Model using ANSYS CFD Thomas Frank (*), BenediktGerlicher (*), Juan Abanto (**) (*) ANSYS Germany, Otterfing, Germany (**) ANSYS Inc.,
DrivAer-Aerodynamic Investigations for a New Realistic Generic Car Model using ANSYS CFD Thomas Frank (*), BenediktGerlicher (*), Juan Abanto (**) (*) ANSYS Germany, Otterfing, Germany (**) ANSYS Inc.,
Computational Flow Analysis of Para-rec Bluff Body at Various Reynold s Number
 International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 5 (2013), pp. 667-674 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Computational Flow Analysis
International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology. ISSN 0974-3154 Volume 6, Number 5 (2013), pp. 667-674 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com Computational Flow Analysis
Validation of CFD Simulation with Scaled Physical Model of Tailings Dissipation Boxes
 Validation of CFD Simulation with Scaled Physical Model of Tailings Dissipation Boxes José Facusse Ingeniero Mecánico Daniel Manzo Ingeniero Hidráulico PRESENTATION TOPICS Company Overview; Problem Description;
Validation of CFD Simulation with Scaled Physical Model of Tailings Dissipation Boxes José Facusse Ingeniero Mecánico Daniel Manzo Ingeniero Hidráulico PRESENTATION TOPICS Company Overview; Problem Description;
