A* Algorithm BY WARREN RUSSELL
|
|
|
- Beverly Peters
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A* Algorithm BY WARREN RUSSELL
2 Dijkstra s Algorithm In real time, finding a path can be time consuming. Especially with all the extra cells visited. Is this practical? Could we do better?
3 A* (A Star) This is a shortest path algorithm that avoids exhaustive searches by only looking at promising nodes that are calculated using heuristics. A heuristic is a process or method In this case, it is the process used to provided a better guess for shortest path searches. Works by maintaining two lists, the open list and closed list. Open list holds all nodes found and waiting to be considered. Closed list holds all nodes already considered.
4 G, H, and F Each node is evaluated based on three important scores. G Score is the cost so far, or simply the incremental cost of moving from the start node to this node G(n) = g(n.parent) + g(n.parent, n) H Score is the heuristic estimate, or the guess for how far the goal is from the current node. It is usually computationally easy to calculate which is what makes A* so efficient. F Score is simply the addition of G score and H Score. It is calculated for each node.
5 Pseudo Code Initialize Variables function findpath( startnode, destinationnode ):Array { _openlist = new Array(); _closedlist = new Array(); currentnode = startnode; var testnode:node; var connectednodes:array; var g:number; var h:number; var f:number; currentnode.g = 0; currentnode.h = heuristic(currentnode, destinationnode, currentnode.travelcost); currentnode.f = currentnode.g + currentnode.h;
6 Pseudo Code (Cont.) // loop variables while (currentnode!= destinationnode) { connectednodes = connectednodefunction( currentnode ); int length = connectednodes.length; for (int i = 0; i < length; ++i) { testnode = connectednodes[i]; if ( testnode == currentnode testnode.traversable == false ) continue; g = currentnode.g + currentnode.travelcost; h = heuristic( testnode, destinationnode, currentnode.travelcost); f = g + h;
7 Pseudo Code (Cont.) if ( Pathfinding.isOpen(testNode, _openlist) Pathfinding.isClosed( testnode, _closedlist) ) { if(testnode.f > f) { testnode.f = f; testnode.g = g; testnode.h = h; testnode.parentnode = currentnode; } } else { testnode.f = f; testnode.g = g; testnode.h = h; testnode.parentnode = currentnode; _openlist.push(testnode); } _closedlist.push( currentnode );
8 Pseudo Code (Last.) } } if (_openlist.length == 0) { return null; } _openlist.sort(comparef); currentnode = _openlist.shift() as Node; ++numofloops; if ( numofloops <= iterations ) return buildpath(destinationnode, firstnode); else return null;
9 Simple Example using tie-breaker oldest lowest f first g = 3 h = 5 f = 8 g = 4 h = 4 f = 8 g = 5 h = 3 f = 8 g = 2 h = 4 g = 3 h = 3 g = 4 h = 2 Wall Goal g = 6 h = 0 g = 1 h = 5 g = 2 h = 4 g = 3 h = 3 Wall g = 5 h = 1 Start g = 0 h = 6 g = 1 h = 5 g = 2 h = 4 g = 3 h = 3 g = 4 h = 2 g = 1 h = 7 f = 8 g = 2 h = 6 f = 8 g = 3 h = 5 f = 8 g = 4 h = 4 f = 8 g = 5 h = 3 f = 8
10 Special Cases with heuristics in A* What if the H value is zero? Only G value plays a role in the heuristic. A* turns back into Dijkstra s Algorithm! Guaranteed to find the shortest path. What if the G value is set to zero? Only H value plays a role in the heuristic. A* transforms into the greedy algorithm called Best-First-Search or B* Dijkstra s Best First Search
11 Heuristics Manhattan distance Best used when movement is restricted to 4 directions h(n) = Cost * (abs(n.x-goal.x) + abs(n.y-goal.y)) Diagonal/Chebyshev Used when movement is in 8 directions h(n) = Cost * max(abs(n.x-goal.x), abs(n.y-goal.y))
12 Heuristics (cont.) Diagonal/Chebyshev More sophisticated version if cost of moving diagonally is not equivalent to moving horizontally or vertically. h_diagonal(n) = min(abs(n.x-goal.x), abs(n.y-goal.y)) h_straight(n) = (abs(n.x-goal.x) + abs(n.y-goal.y)) h(n) = DiagonalCost * h_diagonal(n) + Cost * (h_straight(n) - 2*h_diagonal(n))) h_diagonal(n) = the number of steps you can take along a diagonal. h_straight(n) = the Manhattan distance Then combine the two by considering all diagonal steps to cost DiagonalCost. Then all remaining straight steps cost D.
13 More Heuristics Euclidean/straight line distance Used when any direction of movement is allowed. h(n) = Cost * sqrt((n.x-goal.x)^2 + (n.y-goal.y)^2)
14 Demo A* using Manhatten/Taxicab heuristic with movement in 4 directions A* using Diagonal/Chebyshev heuristic with movement in 8 directions
15 Conditions for an Optimal Solution A* always finds the solution if it exists, but to be the optimal solution, the heuristic has to be consistent and admissible A consistent (or monotone) heuristic function is a function that estimates the distance to the goal, and is always at most equal to the estimated distance from any neighboring vertex plus the step cost of reaching that neighbor. h(n) < c(n,p) + h(p) and h(goal) = 0 A heuristic function is said to be admissible if it never overestimates the cost of reaching the goal, i.e. the cost it estimates to reach the goal is not higher than the lowest possible cost from the current point in the path. An admissible heuristic is also known as an optimistic heuristic.
16 Running Time of A* The time complexity of A* depends on the heuristic. In the worst case, the number of nodes expanded is exponential in the length of the solution (the shortest path), but it is polynomial when the: search space is a tree, there is a single goal, and the heuristic function h meets the following condition: h(x) - h*(x) = O(log h*(x))
17 Improvements Beam Search Limit the size of the OpenList. When OpenList is full, drop the nodes with the worst chance of providing a good path. Drawback: OpenList needs to be kept sorted all the time. Limits possible data structures you can use. Using less nodes is the number one improvement that can be made. It is common to use meshes instead.
Pathfinding. Advaith Siddharthan
 Pathfinding Advaith Siddharthan Context What is Intelligence? Rational? Search Optimisation Reasoning Impulsive? Quicker response Less predictable Personality/Emotions: Angry/Bored/Curious Overview The
Pathfinding Advaith Siddharthan Context What is Intelligence? Rational? Search Optimisation Reasoning Impulsive? Quicker response Less predictable Personality/Emotions: Angry/Bored/Curious Overview The
Informed search strategies (Section ) Source: Fotolia
 Informed search strategies (Section 3.5-3.6) Source: Fotolia Review: Tree search Initialize the frontier using the starting state While the frontier is not empty Choose a frontier node to expand according
Informed search strategies (Section 3.5-3.6) Source: Fotolia Review: Tree search Initialize the frontier using the starting state While the frontier is not empty Choose a frontier node to expand according
CS 331: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search. Informed Search
 CS 331: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search 1 Informed Search How can we make search smarter? Use problem-specific knowledge beyond the definition of the problem itself Specifically, incorporate knowledge
CS 331: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search 1 Informed Search How can we make search smarter? Use problem-specific knowledge beyond the definition of the problem itself Specifically, incorporate knowledge
CS 331: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search. Informed Search
 CS 331: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search 1 Informed Search How can we make search smarter? Use problem-specific knowledge beyond the definition of the problem itself Specifically, incorporate knowledge
CS 331: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search 1 Informed Search How can we make search smarter? Use problem-specific knowledge beyond the definition of the problem itself Specifically, incorporate knowledge
Route planning / Search Movement Group behavior Decision making
 Game AI Where is the AI Route planning / Search Movement Group behavior Decision making General Search Algorithm Design Keep a pair of set of states: One, the set of states to explore, called the open
Game AI Where is the AI Route planning / Search Movement Group behavior Decision making General Search Algorithm Design Keep a pair of set of states: One, the set of states to explore, called the open
A.I.: Informed Search Algorithms. Chapter III: Part Deux
 A.I.: Informed Search Algorithms Chapter III: Part Deux Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Outline Overview Informed Search: uses problem-specific knowledge. General approach:
A.I.: Informed Search Algorithms Chapter III: Part Deux Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Outline Overview Informed Search: uses problem-specific knowledge. General approach:
Informed search. Soleymani. CE417: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Sharif University of Technology Spring 2016
 Informed search CE417: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Sharif University of Technology Spring 2016 Soleymani Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, Chapter 3 Outline Best-first search Greedy
Informed search CE417: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Sharif University of Technology Spring 2016 Soleymani Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, Chapter 3 Outline Best-first search Greedy
Informed Search. CS 486/686 University of Waterloo May 10. cs486/686 Lecture Slides 2005 (c) K. Larson and P. Poupart
 Informed Search CS 486/686 University of Waterloo May 0 Outline Using knowledge Heuristics Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Other variations of A* Back to heuristics 2 Recall from last
Informed Search CS 486/686 University of Waterloo May 0 Outline Using knowledge Heuristics Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Other variations of A* Back to heuristics 2 Recall from last
Outline. Best-first search
 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Admissible Heuristics Graph Search Consistent Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing
Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Admissible Heuristics Graph Search Consistent Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing
Informed/Heuristic Search
 Informed/Heuristic Search Outline Limitations of uninformed search methods Informed (or heuristic) search uses problem-specific heuristics to improve efficiency Best-first A* Techniques for generating
Informed/Heuristic Search Outline Limitations of uninformed search methods Informed (or heuristic) search uses problem-specific heuristics to improve efficiency Best-first A* Techniques for generating
Outline. Best-first search
 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A* search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Beam search Simulated annealing search Genetic algorithms Constraint Satisfaction Problems
Notes. Video Game AI: Lecture 5 Planning for Pathfinding. Lecture Overview. Knowledge vs Search. Jonathan Schaeffer this Friday
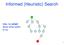
 Notes Video Game AI: Lecture 5 Planning for Pathfinding Nathan Sturtevant COMP 3705 Jonathan Schaeffer this Friday Planning vs localization We cover planning today Localization is just mapping a real-valued
Notes Video Game AI: Lecture 5 Planning for Pathfinding Nathan Sturtevant COMP 3705 Jonathan Schaeffer this Friday Planning vs localization We cover planning today Localization is just mapping a real-valued
Informed Search and Exploration for Agents
 Informed Search and Exploration for Agents R&N: 3.5, 3.6 Michael Rovatsos University of Edinburgh 29 th January 2015 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Admissibility
Informed Search and Exploration for Agents R&N: 3.5, 3.6 Michael Rovatsos University of Edinburgh 29 th January 2015 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Admissibility
Heuristic (Informed) Search
 Heuristic (Informed) Search (Where we try to choose smartly) R&N: Chap. 4, Sect. 4.1 3 1 Recall that the ordering of FRINGE defines the search strategy Search Algorithm #2 SEARCH#2 1. INSERT(initial-node,FRINGE)
Heuristic (Informed) Search (Where we try to choose smartly) R&N: Chap. 4, Sect. 4.1 3 1 Recall that the ordering of FRINGE defines the search strategy Search Algorithm #2 SEARCH#2 1. INSERT(initial-node,FRINGE)
Informed search methods
 Informed search methods Tuomas Sandholm Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University Read Section 3.5-3.7 of Russell and Norvig Informed Search Methods Heuristic = to find, to discover Heuristic
Informed search methods Tuomas Sandholm Computer Science Department Carnegie Mellon University Read Section 3.5-3.7 of Russell and Norvig Informed Search Methods Heuristic = to find, to discover Heuristic
Informed search algorithms. Chapter 4
 Informed search algorithms Chapter 4 Material Chapter 4 Section 1 - Exclude memory-bounded heuristic search 3 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Local search algorithms
Informed search algorithms Chapter 4 Material Chapter 4 Section 1 - Exclude memory-bounded heuristic search 3 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Local search algorithms
CS171 Introduction to Computer Science II. Graphs
 CS171 Introduction to Computer Science II Graphs Announcements/Reminders Median grades of midterms Midterm 2: 88 Midterm 1: 90 Median grades of quizzes Quiz 3: 91 Quiz 2: 81 Quiz 1: 89 Quiz 4 on Friday
CS171 Introduction to Computer Science II Graphs Announcements/Reminders Median grades of midterms Midterm 2: 88 Midterm 1: 90 Median grades of quizzes Quiz 3: 91 Quiz 2: 81 Quiz 1: 89 Quiz 4 on Friday
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computers and Informatics, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Informed search algorithms
Artificial Intelligence Dr Ahmed Rafat Abas Computer Science Dept, Faculty of Computers and Informatics, Zagazig University arabas@zu.edu.eg http://www.arsaliem.faculty.zu.edu.eg/ Informed search algorithms
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE. Informed search
 INFOB2KI 2017-2018 Utrecht University The Netherlands ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE Informed search Lecturer: Silja Renooij These slides are part of the INFOB2KI Course Notes available from www.cs.uu.nl/docs/vakken/b2ki/schema.html
INFOB2KI 2017-2018 Utrecht University The Netherlands ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE Informed search Lecturer: Silja Renooij These slides are part of the INFOB2KI Course Notes available from www.cs.uu.nl/docs/vakken/b2ki/schema.html
Informed Search Methods
 Informed Search Methods How can we improve searching strategy by using intelligence? Map example: Heuristic: Expand those nodes closest in as the crow flies distance to goal 8-puzzle: Heuristic: Expand
Informed Search Methods How can we improve searching strategy by using intelligence? Map example: Heuristic: Expand those nodes closest in as the crow flies distance to goal 8-puzzle: Heuristic: Expand
Informed search algorithms. (Based on slides by Oren Etzioni, Stuart Russell)
 Informed search algorithms (Based on slides by Oren Etzioni, Stuart Russell) Outline Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Simulated annealing search
Informed search algorithms (Based on slides by Oren Etzioni, Stuart Russell) Outline Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing search Simulated annealing search
CS 771 Artificial Intelligence. Informed Search
 CS 771 Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Outline Review limitations of uninformed search methods Informed (or heuristic) search Uses problem-specific heuristics to improve efficiency Best-first,
CS 771 Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Outline Review limitations of uninformed search methods Informed (or heuristic) search Uses problem-specific heuristics to improve efficiency Best-first,
Overview. Path Cost Function. Real Life Problems. COMP219: Artificial Intelligence. Lecture 10: Heuristic Search
 COMP219: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 10: Heuristic Search Overview Last time Depth-limited, iterative deepening and bi-directional search Avoiding repeated states Today Show how applying knowledge
COMP219: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 10: Heuristic Search Overview Last time Depth-limited, iterative deepening and bi-directional search Avoiding repeated states Today Show how applying knowledge
Basic Motion Planning Algorithms
 Basic Motion Planning Algorithms Sohaib Younis Intelligent Robotics 7 January, 2013 1 Outline Introduction Environment Map Dijkstra's algorithm A* algorithm Summary 2 Introduction Definition: Motion Planning
Basic Motion Planning Algorithms Sohaib Younis Intelligent Robotics 7 January, 2013 1 Outline Introduction Environment Map Dijkstra's algorithm A* algorithm Summary 2 Introduction Definition: Motion Planning
Informed Search A* Algorithm
 Informed Search A* Algorithm CE417: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Sharif University of Technology Spring 2018 Soleymani Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, Chapter 3 Most slides have
Informed Search A* Algorithm CE417: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Sharif University of Technology Spring 2018 Soleymani Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, Chapter 3 Most slides have
Outline for today s lecture. Informed Search. Informed Search II. Review: Properties of greedy best-first search. Review: Greedy best-first search:
 Outline for today s lecture Informed Search II Informed Search Optimal informed search: A* (AIMA 3.5.2) Creating good heuristic functions Hill Climbing 2 Review: Greedy best-first search: f(n): estimated
Outline for today s lecture Informed Search II Informed Search Optimal informed search: A* (AIMA 3.5.2) Creating good heuristic functions Hill Climbing 2 Review: Greedy best-first search: f(n): estimated
CMPUT 396 Sliding Tile Puzzle
 CMPUT 396 Sliding Tile Puzzle Sliding Tile Puzzle 2x2 Sliding Tile States Exactly half of the states are solvable, the other half are not. In the case of 2x2 puzzles, I can solve it if I start with a configuration
CMPUT 396 Sliding Tile Puzzle Sliding Tile Puzzle 2x2 Sliding Tile States Exactly half of the states are solvable, the other half are not. In the case of 2x2 puzzles, I can solve it if I start with a configuration
Problem Solving: Informed Search
 Problem Solving: Informed Search References Russell and Norvig, Artificial Intelligence: A modern approach, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, 2003 (Chapters 1,2, and 4) Nilsson, Artificial intelligence: A New synthesis.
Problem Solving: Informed Search References Russell and Norvig, Artificial Intelligence: A modern approach, 2nd ed. Prentice Hall, 2003 (Chapters 1,2, and 4) Nilsson, Artificial intelligence: A New synthesis.
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Prof. Scott Niekum University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on ones created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley.
CS 343: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Prof. Scott Niekum University of Texas at Austin [These slides based on ones created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley.
Today. Informed Search. Graph Search. Heuristics Greedy Search A* Search
 Informed Search [These slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188 materials are available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.] Today Informed Search Heuristics
Informed Search [These slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188 materials are available at http://ai.berkeley.edu.] Today Informed Search Heuristics
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Informed Search and Exploration Chapter 4 (4.1 4.2) A General Search algorithm: Chapter 3: Search Strategies Task : Find a sequence of actions leading from the initial state to
Artificial Intelligence Informed Search and Exploration Chapter 4 (4.1 4.2) A General Search algorithm: Chapter 3: Search Strategies Task : Find a sequence of actions leading from the initial state to
Lecture 4: Informed/Heuristic Search
 Lecture 4: Informed/Heuristic Search Outline Limitations of uninformed search methods Informed (or heuristic) search uses problem-specific heuristics to improve efficiency Best-first A* RBFS SMA* Techniques
Lecture 4: Informed/Heuristic Search Outline Limitations of uninformed search methods Informed (or heuristic) search uses problem-specific heuristics to improve efficiency Best-first A* RBFS SMA* Techniques
CSE 473. Chapter 4 Informed Search. CSE AI Faculty. Last Time. Blind Search BFS UC-BFS DFS DLS Iterative Deepening Bidirectional Search
 CSE 473 Chapter 4 Informed Search CSE AI Faculty Blind Search BFS UC-BFS DFS DLS Iterative Deepening Bidirectional Search Last Time 2 1 Repeated States Failure to detect repeated states can turn a linear
CSE 473 Chapter 4 Informed Search CSE AI Faculty Blind Search BFS UC-BFS DFS DLS Iterative Deepening Bidirectional Search Last Time 2 1 Repeated States Failure to detect repeated states can turn a linear
CS 354R: Computer Game Technology
 CS 354R: Computer Game Technology A* Heuristics Fall 2018 A* Search f(n): The current best estimate for the best path through a node: f(n)=g(n)+h(n) g(n): current known best cost for getting to a node
CS 354R: Computer Game Technology A* Heuristics Fall 2018 A* Search f(n): The current best estimate for the best path through a node: f(n)=g(n)+h(n) g(n): current known best cost for getting to a node
COMP9414: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search
 COMP9, Monday 9 March, 0 Informed Search COMP9: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Wayne Wobcke Room J- wobcke@cse.unsw.edu.au Based on slides by Maurice Pagnucco Overview Heuristics Informed Search
COMP9, Monday 9 March, 0 Informed Search COMP9: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Wayne Wobcke Room J- wobcke@cse.unsw.edu.au Based on slides by Maurice Pagnucco Overview Heuristics Informed Search
COMP219: Artificial Intelligence. Lecture 10: Heuristic Search
 COMP219: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 10: Heuristic Search 1 Class Tests Class Test 1 (Prolog): Tuesday 8 th November (Week 7) 13:00-14:00 LIFS-LT2 and LIFS-LT3 Class Test 2 (Everything but Prolog)
COMP219: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 10: Heuristic Search 1 Class Tests Class Test 1 (Prolog): Tuesday 8 th November (Week 7) 13:00-14:00 LIFS-LT2 and LIFS-LT3 Class Test 2 (Everything but Prolog)
CE 473: Artificial Intelligence. Autumn 2011
 CE 473: Artificial Intelligence Autumn 2011 A* Search Luke Zettlemoyer Based on slides from Dan Klein Multiple slides from Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Today A* Search Heuristic Design Graph search Recap:
CE 473: Artificial Intelligence Autumn 2011 A* Search Luke Zettlemoyer Based on slides from Dan Klein Multiple slides from Stuart Russell or Andrew Moore Today A* Search Heuristic Design Graph search Recap:
4 INFORMED SEARCH AND EXPLORATION. 4.1 Heuristic Search Strategies
 55 4 INFORMED SEARCH AND EXPLORATION We now consider informed search that uses problem-specific knowledge beyond the definition of the problem itself This information helps to find solutions more efficiently
55 4 INFORMED SEARCH AND EXPLORATION We now consider informed search that uses problem-specific knowledge beyond the definition of the problem itself This information helps to find solutions more efficiently
HW#1 due today. HW#2 due Monday, 9/09/13, in class Continue reading Chapter 3
 9-04-2013 Uninformed (blind) search algorithms Breadth-First Search (BFS) Uniform-Cost Search Depth-First Search (DFS) Depth-Limited Search Iterative Deepening Best-First Search HW#1 due today HW#2 due
9-04-2013 Uninformed (blind) search algorithms Breadth-First Search (BFS) Uniform-Cost Search Depth-First Search (DFS) Depth-Limited Search Iterative Deepening Best-First Search HW#1 due today HW#2 due
Informed Search and Exploration
 Informed Search and Exploration Chapter 4 (4.1-4.3) CS 2710 1 Introduction Ch.3 searches good building blocks for learning about search But vastly inefficient eg: Can we do better? Breadth Depth Uniform
Informed Search and Exploration Chapter 4 (4.1-4.3) CS 2710 1 Introduction Ch.3 searches good building blocks for learning about search But vastly inefficient eg: Can we do better? Breadth Depth Uniform
Chapter 5.4 Artificial Intelligence: Pathfinding
 Chapter 5.4 Artificial Intelligence: Pathfinding Introduction Almost every game requires pathfinding Agents must be able to find their way around the game world Pathfinding is not a trivial problem The
Chapter 5.4 Artificial Intelligence: Pathfinding Introduction Almost every game requires pathfinding Agents must be able to find their way around the game world Pathfinding is not a trivial problem The
Informed Search. Best-first search. Greedy best-first search. Intelligent Systems and HCI D7023E. Romania with step costs in km
 Informed Search Intelligent Systems and HCI D7023E Lecture 5: Informed Search (heuristics) Paweł Pietrzak [Sec 3.5-3.6,Ch.4] A search strategy which searches the most promising branches of the state-space
Informed Search Intelligent Systems and HCI D7023E Lecture 5: Informed Search (heuristics) Paweł Pietrzak [Sec 3.5-3.6,Ch.4] A search strategy which searches the most promising branches of the state-space
mywbut.com Informed Search Strategies-I
 Informed Search Strategies-I 1 3.1 Introduction We have outlined the different types of search strategies. In the earlier chapter we have looked at different blind search strategies. Uninformed search
Informed Search Strategies-I 1 3.1 Introduction We have outlined the different types of search strategies. In the earlier chapter we have looked at different blind search strategies. Uninformed search
COMP9414: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search
 COMP9, Wednesday March, 00 Informed Search COMP9: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Wayne Wobcke Room J- wobcke@cse.unsw.edu.au Based on slides by Maurice Pagnucco Overview Heuristics Informed Search
COMP9, Wednesday March, 00 Informed Search COMP9: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Wayne Wobcke Room J- wobcke@cse.unsw.edu.au Based on slides by Maurice Pagnucco Overview Heuristics Informed Search
Informed Search. Notes about the assignment. Outline. Tree search: Reminder. Heuristics. Best-first search. Russell and Norvig chap.
 Notes about the assignment Informed Search Russell and Norvig chap. 4 If it says return True or False, return True or False, not "True" or "False Comment out or remove print statements before submitting.
Notes about the assignment Informed Search Russell and Norvig chap. 4 If it says return True or False, return True or False, not "True" or "False Comment out or remove print statements before submitting.
Searching. Assume goal- or utilitybased. Next task to achieve is to determine the best path to the goal
 Searching Assume goal- or utilitybased agents: state information ability to perform actions goals to achieve Next task to achieve is to determine the best path to the goal CSC384 Lecture Slides Steve Engels,
Searching Assume goal- or utilitybased agents: state information ability to perform actions goals to achieve Next task to achieve is to determine the best path to the goal CSC384 Lecture Slides Steve Engels,
Informed search algorithms. Chapter 4
 Informed search algorithms Chapter 4 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Memory Bounded A* Search Best-first search Idea: use an evaluation function f(n) for each node
Informed search algorithms Chapter 4 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Memory Bounded A* Search Best-first search Idea: use an evaluation function f(n) for each node
Heuris'c Search. Reading note: Chapter 4 covers heuristic search.
 Heuris'c Search Reading note: Chapter 4 covers heuristic search. Credits: Slides in this deck are drawn from or inspired by a multitude of sources including: Shaul Markovitch Jurgen Strum Sheila McIlraith
Heuris'c Search Reading note: Chapter 4 covers heuristic search. Credits: Slides in this deck are drawn from or inspired by a multitude of sources including: Shaul Markovitch Jurgen Strum Sheila McIlraith
CS414-Artificial Intelligence
 CS414-Artificial Intelligence Lecture 6: Informed Search Algorithms Waheed Noor Computer Science and Information Technology, University of Balochistan, Quetta, Pakistan Waheed Noor (CS&IT, UoB, Quetta)
CS414-Artificial Intelligence Lecture 6: Informed Search Algorithms Waheed Noor Computer Science and Information Technology, University of Balochistan, Quetta, Pakistan Waheed Noor (CS&IT, UoB, Quetta)
Moving On. 10. Single-agent Search. Applications. Why Alpha-Beta First?
 Moving On 10. Single-agent Search Jonathan Schaeffer jonathan@cs.ualberta.ca www.cs.ualberta.ca/~jonathan Two-player adversary search is nice, but not all interesting problems can be mapped to games Large
Moving On 10. Single-agent Search Jonathan Schaeffer jonathan@cs.ualberta.ca www.cs.ualberta.ca/~jonathan Two-player adversary search is nice, but not all interesting problems can be mapped to games Large
Informed search methods
 CS 2710 Foundations of AI Lecture 5 Informed search methods Milos Hauskrecht milos@pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Announcements Homework assignment 2 is out Due on Tuesday, September 19, 2017 before the
CS 2710 Foundations of AI Lecture 5 Informed search methods Milos Hauskrecht milos@pitt.edu 5329 Sennott Square Announcements Homework assignment 2 is out Due on Tuesday, September 19, 2017 before the
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Tomáš Horváth 16 rd November, 2011 Informed Search and Exploration Example (again) Informed strategy we use a problem-specific
Artificial Intelligence Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Tomáš Horváth 16 rd November, 2011 Informed Search and Exploration Example (again) Informed strategy we use a problem-specific
Lecture 4: Search 3. Victor R. Lesser. CMPSCI 683 Fall 2010
 Lecture 4: Search 3 Victor R. Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2010 First Homework 1 st Programming Assignment 2 separate parts (homeworks) First part due on (9/27) at 5pm Second part due on 10/13 at 5pm Send homework
Lecture 4: Search 3 Victor R. Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2010 First Homework 1 st Programming Assignment 2 separate parts (homeworks) First part due on (9/27) at 5pm Second part due on 10/13 at 5pm Send homework
CS 380: Artificial Intelligence Lecture #4
 CS 380: Artificial Intelligence Lecture #4 William Regli Material Chapter 4 Section 1-3 1 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing
CS 380: Artificial Intelligence Lecture #4 William Regli Material Chapter 4 Section 1-3 1 Outline Best-first search Greedy best-first search A * search Heuristics Local search algorithms Hill-climbing
Artificial Intelligence Informed search. Peter Antal
 Artificial Intelligence Informed search Peter Antal antal@mit.bme.hu 1 Informed = use problem-specific knowledge Which search strategies? Best-first search and its variants Heuristic functions? How to
Artificial Intelligence Informed search Peter Antal antal@mit.bme.hu 1 Informed = use problem-specific knowledge Which search strategies? Best-first search and its variants Heuristic functions? How to
Chapter 3: Informed Search and Exploration. Dr. Daisy Tang
 Chapter 3: Informed Search and Exploration Dr. Daisy Tang Informed Search Definition: Use problem-specific knowledge beyond the definition of the problem itself Can find solutions more efficiently Best-first
Chapter 3: Informed Search and Exploration Dr. Daisy Tang Informed Search Definition: Use problem-specific knowledge beyond the definition of the problem itself Can find solutions more efficiently Best-first
Artificial Intelligence Informed Search
 Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Instructors: David Suter and Qince Li Course Delivered @ Harbin Institute of Technology [Many slides adapted from those created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for
Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Instructors: David Suter and Qince Li Course Delivered @ Harbin Institute of Technology [Many slides adapted from those created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Tomáš Horváth 10 rd November, 2010 Informed Search and Exploration Example (again) Informed strategy we use a problem-specific
Artificial Intelligence Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Tomáš Horváth 10 rd November, 2010 Informed Search and Exploration Example (again) Informed strategy we use a problem-specific
Informed search algorithms. (Based on slides by Oren Etzioni, Stuart Russell)
 Informed search algorithms (Based on slides by Oren Etzioni, Stuart Russell) The problem # Unique board configurations in search space 8-puzzle 9! = 362880 15-puzzle 16! = 20922789888000 10 13 24-puzzle
Informed search algorithms (Based on slides by Oren Etzioni, Stuart Russell) The problem # Unique board configurations in search space 8-puzzle 9! = 362880 15-puzzle 16! = 20922789888000 10 13 24-puzzle
CSCI 446: Artificial Intelligence
 CSCI 446: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Instructor: Michele Van Dyne [These slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188 materials are available
CSCI 446: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Instructor: Michele Van Dyne [These slides were created by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel for CS188 Intro to AI at UC Berkeley. All CS188 materials are available
EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS
 EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS Lecture 4, 4/11/2005 University of Washington, Department of Electrical Engineering Spring 2005 Instructor: Professor Jeff A. Bilmes Today: Informed search algorithms
EE562 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE FOR ENGINEERS Lecture 4, 4/11/2005 University of Washington, Department of Electrical Engineering Spring 2005 Instructor: Professor Jeff A. Bilmes Today: Informed search algorithms
COMP219: Artificial Intelligence. Lecture 10: Heuristic Search
 COMP219: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 10: Heuristic Search 1 Class Tests Class Test 1 (Prolog): Friday 17th November (Week 8), 15:00-17:00. Class Test 2 (Everything but Prolog) Friday 15th December
COMP219: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 10: Heuristic Search 1 Class Tests Class Test 1 (Prolog): Friday 17th November (Week 8), 15:00-17:00. Class Test 2 (Everything but Prolog) Friday 15th December
Graph Representation DFS BFS Dijkstra A* Search Bellman-Ford Floyd-Warshall Iterative? Non-iterative? MST Flow Edmond-Karp
 Charles Lin Graph Representation DFS BFS Dijkstra A* Search Bellman-Ford Floyd-Warshall Iterative? Non-iterative? MST Flow Edmond-Karp Adjacency Matrix bool way[100][100]; cin >> i >> j; way[i][j] = true;
Charles Lin Graph Representation DFS BFS Dijkstra A* Search Bellman-Ford Floyd-Warshall Iterative? Non-iterative? MST Flow Edmond-Karp Adjacency Matrix bool way[100][100]; cin >> i >> j; way[i][j] = true;
Informed (Heuristic) Search. Idea: be smart about what paths to try.
 Informed (Heuristic) Search Idea: be smart about what paths to try. 1 Blind Search vs. Informed Search What s the difference? How do we formally specify this? A node is selected for expansion based on
Informed (Heuristic) Search Idea: be smart about what paths to try. 1 Blind Search vs. Informed Search What s the difference? How do we formally specify this? A node is selected for expansion based on
Robotic Motion Planning: A* and D* Search
 Robotic Motion Planning: A* and D* Search Robotics Institute 6-75 http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~motion Howie Choset http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~choset 6-75, Howie Choset with slides from G. Ayorker
Robotic Motion Planning: A* and D* Search Robotics Institute 6-75 http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~motion Howie Choset http://voronoi.sbp.ri.cmu.edu/~choset 6-75, Howie Choset with slides from G. Ayorker
Lecture 5 Heuristics. Last Time: A* Search
 CSE 473 Lecture 5 Heuristics CSE AI Faculty Last Time: A* Search Use an evaluation function f(n) for node n. f(n) = estimated total cost of path thru n to goal f(n) = g(n) + h(n) g(n) = cost so far to
CSE 473 Lecture 5 Heuristics CSE AI Faculty Last Time: A* Search Use an evaluation function f(n) for node n. f(n) = estimated total cost of path thru n to goal f(n) = g(n) + h(n) g(n) = cost so far to
Heuristic (Informed) Search
 Heuristic (Informed) Search (Where we try to choose smartly) R&N: Chap., Sect..1 3 1 Search Algorithm #2 SEARCH#2 1. INSERT(initial-node,Open-List) 2. Repeat: a. If empty(open-list) then return failure
Heuristic (Informed) Search (Where we try to choose smartly) R&N: Chap., Sect..1 3 1 Search Algorithm #2 SEARCH#2 1. INSERT(initial-node,Open-List) 2. Repeat: a. If empty(open-list) then return failure
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence CSC348 Unit 3: Problem Solving and Search Syedur Rahman Lecturer, CSE Department North South University syedur.rahman@wolfson.oxon.org Artificial Intelligence: Lecture Notes The
Artificial Intelligence CSC348 Unit 3: Problem Solving and Search Syedur Rahman Lecturer, CSE Department North South University syedur.rahman@wolfson.oxon.org Artificial Intelligence: Lecture Notes The
2006/2007 Intelligent Systems 1. Intelligent Systems. Prof. dr. Paul De Bra Technische Universiteit Eindhoven
 test gamma 2006/2007 Intelligent Systems 1 Intelligent Systems Prof. dr. Paul De Bra Technische Universiteit Eindhoven debra@win.tue.nl 2006/2007 Intelligent Systems 2 Informed search and exploration Best-first
test gamma 2006/2007 Intelligent Systems 1 Intelligent Systems Prof. dr. Paul De Bra Technische Universiteit Eindhoven debra@win.tue.nl 2006/2007 Intelligent Systems 2 Informed search and exploration Best-first
Informed search algorithms
 Informed search algorithms This lecture topic Chapter 3.5-3.7 Next lecture topic Chapter 4.1-4.2 (Please read lecture topic material before and after each lecture on that topic) Outline Review limitations
Informed search algorithms This lecture topic Chapter 3.5-3.7 Next lecture topic Chapter 4.1-4.2 (Please read lecture topic material before and after each lecture on that topic) Outline Review limitations
Algorithm. December 7, Shortest path using A Algorithm. Phaneendhar Reddy Vanam. Introduction. History. Components of A.
 December 7, 2011 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 The A is a best-first search algorithm that finds the least cost path from an initial configuration to a final configuration. The most essential part of the A is a good heuristic
December 7, 2011 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 The A is a best-first search algorithm that finds the least cost path from an initial configuration to a final configuration. The most essential part of the A is a good heuristic
Map coloring. 4 colors. From coloring to CSP. Informed Search Methods. Constrained Satisfaction Search. Constrained Satisfaction Search.
 Constrained Satisfaction Search Informed Search Methods Example: 8-Queens Problem States: , where V is the row occupied by the ith queen. Constraint satisfaction search Heuristics Best
Constrained Satisfaction Search Informed Search Methods Example: 8-Queens Problem States: , where V is the row occupied by the ith queen. Constraint satisfaction search Heuristics Best
Problem Solving and Search
 Artificial Intelligence Problem Solving and Search Dae-Won Kim School of Computer Science & Engineering Chung-Ang University Outline Problem-solving agents Problem types Problem formulation Example problems
Artificial Intelligence Problem Solving and Search Dae-Won Kim School of Computer Science & Engineering Chung-Ang University Outline Problem-solving agents Problem types Problem formulation Example problems
Heuristic Optimisation
 Heuristic Optimisation Lecture 10: Properties of A* Dr. Sándor Zoltán Németh nemeths@for.mat.bham.ac.uk http://web.mat.bham.ac.uk/s.z.nemeth HO p.1 The properties to be studied Completeness Admissibility
Heuristic Optimisation Lecture 10: Properties of A* Dr. Sándor Zoltán Németh nemeths@for.mat.bham.ac.uk http://web.mat.bham.ac.uk/s.z.nemeth HO p.1 The properties to be studied Completeness Admissibility
Today s s lecture. Lecture 3: Search - 2. Problem Solving by Search. Agent vs. Conventional AI View. Victor R. Lesser. CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004
 Today s s lecture Search and Agents Material at the end of last lecture Lecture 3: Search - 2 Victor R. Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004 Continuation of Simple Search The use of background knowledge to accelerate
Today s s lecture Search and Agents Material at the end of last lecture Lecture 3: Search - 2 Victor R. Lesser CMPSCI 683 Fall 2004 Continuation of Simple Search The use of background knowledge to accelerate
Algorithms and Path Planning
 Algorithms and Path Planning Topics Simple Search Depth First Search Breadth First Search Dijkstra s Search Greedy Search A* Search Classes of interest ECE400: Computer Systems Programming CS4700: Foundations
Algorithms and Path Planning Topics Simple Search Depth First Search Breadth First Search Dijkstra s Search Greedy Search A* Search Classes of interest ECE400: Computer Systems Programming CS4700: Foundations
Mustafa Jarrar: Lecture Notes on Artificial Intelligence Birzeit University, Chapter 3 Informed Searching. Mustafa Jarrar. University of Birzeit
 Mustafa Jarrar: Lecture Notes on Artificial Intelligence Birzeit University, 2018 Chapter 3 Informed Searching Mustafa Jarrar University of Birzeit Jarrar 2018 1 Watch this lecture and download the slides
Mustafa Jarrar: Lecture Notes on Artificial Intelligence Birzeit University, 2018 Chapter 3 Informed Searching Mustafa Jarrar University of Birzeit Jarrar 2018 1 Watch this lecture and download the slides
Chapters 3-5 Problem Solving using Search
 CSEP 573 Chapters 3-5 Problem Solving using Search First, they do an on-line search CSE AI Faculty Example: The 8-puzzle Example: The 8-puzzle 1 2 3 8 4 7 6 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 Example: Route Planning
CSEP 573 Chapters 3-5 Problem Solving using Search First, they do an on-line search CSE AI Faculty Example: The 8-puzzle Example: The 8-puzzle 1 2 3 8 4 7 6 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 2 Example: Route Planning
Informed State Space Search B4B36ZUI, LS 2018
 Informed State Space Search B4B36ZUI, LS 2018 Branislav Bošanský, Martin Schaefer, David Fiedler, Jaromír Janisch {name.surname}@agents.fel.cvut.cz Artificial Intelligence Center, Czech Technical University
Informed State Space Search B4B36ZUI, LS 2018 Branislav Bošanský, Martin Schaefer, David Fiedler, Jaromír Janisch {name.surname}@agents.fel.cvut.cz Artificial Intelligence Center, Czech Technical University
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Today Informed Search Informed Search Heuristics Greedy Search A* Search Instructor: Marco Alvarez University of Rhode Island (These slides were created/modified by Dan
CS 188: Artificial Intelligence Today Informed Search Informed Search Heuristics Greedy Search A* Search Instructor: Marco Alvarez University of Rhode Island (These slides were created/modified by Dan
CS 520: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence. Lectures on Search
 CS 520: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Prof. Louis Steinberg Lecture : uninformed search uninformed search Review Lectures on Search Formulation of search problems. State Spaces Uninformed (blind)
CS 520: Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Prof. Louis Steinberg Lecture : uninformed search uninformed search Review Lectures on Search Formulation of search problems. State Spaces Uninformed (blind)
S A E RC R H C I H NG N G IN N S T S A T T A E E G R G A R PH P S
 LECTURE 2 SEARCHING IN STATE GRAPHS Introduction Idea: Problem Solving as Search Basic formalism as State-Space Graph Graph explored by Tree Search Different algorithms to explore the graph Slides mainly
LECTURE 2 SEARCHING IN STATE GRAPHS Introduction Idea: Problem Solving as Search Basic formalism as State-Space Graph Graph explored by Tree Search Different algorithms to explore the graph Slides mainly
Artificial Intelligence
 Artificial Intelligence Search Marc Toussaint University of Stuttgart Winter 2015/16 (slides based on Stuart Russell s AI course) Outline Problem formulation & examples Basic search algorithms 2/100 Example:
Artificial Intelligence Search Marc Toussaint University of Stuttgart Winter 2015/16 (slides based on Stuart Russell s AI course) Outline Problem formulation & examples Basic search algorithms 2/100 Example:
Solving Problems by Searching
 INF5390 Kunstig intelligens Solving Problems by Searching Roar Fjellheim Outline Problem-solving agents Example problems Search programs Uninformed search Informed search Summary AIMA Chapter 3: Solving
INF5390 Kunstig intelligens Solving Problems by Searching Roar Fjellheim Outline Problem-solving agents Example problems Search programs Uninformed search Informed search Summary AIMA Chapter 3: Solving
COMP9414/ 9814/ 3411: Artificial Intelligence. 5. Informed Search. Russell & Norvig, Chapter 3. UNSW c Alan Blair,
 COMP9414/ 9814/ 3411: Artificial Intelligence 5. Informed Search Russell & Norvig, Chapter 3. COMP9414/9814/3411 15s1 Informed Search 1 Search Strategies General Search algorithm: add initial state to
COMP9414/ 9814/ 3411: Artificial Intelligence 5. Informed Search Russell & Norvig, Chapter 3. COMP9414/9814/3411 15s1 Informed Search 1 Search Strategies General Search algorithm: add initial state to
CS 343H: Artificial Intelligence
 CS 343H: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 4: Informed Search 1/23/2014 Slides courtesy of Dan Klein at UC-Berkeley Unless otherwise noted Today Informed search Heuristics Greedy search A* search Graph search
CS 343H: Artificial Intelligence Lecture 4: Informed Search 1/23/2014 Slides courtesy of Dan Klein at UC-Berkeley Unless otherwise noted Today Informed search Heuristics Greedy search A* search Graph search
Automated Route Finding on Digital Terrains
 Automated Route Finding on Digital Terrains D. R. Wichmann and B. C. Wünsche Graphics Group, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Auckland, Private Bag 92019, Auckland, New Zealand. daniel.wichmann@gmail.com,
Automated Route Finding on Digital Terrains D. R. Wichmann and B. C. Wünsche Graphics Group, Dept. of Computer Science, University of Auckland, Private Bag 92019, Auckland, New Zealand. daniel.wichmann@gmail.com,
Class Overview. Introduction to Artificial Intelligence COMP 3501 / COMP Lecture 2. Problem Solving Agents. Problem Solving Agents: Assumptions
 Class Overview COMP 3501 / COMP 4704-4 Lecture 2 Prof. JGH 318 Problem Solving Agents Problem Solving Agents: Assumptions Requires a goal Assume world is: Requires actions Observable What actions? Discrete
Class Overview COMP 3501 / COMP 4704-4 Lecture 2 Prof. JGH 318 Problem Solving Agents Problem Solving Agents: Assumptions Requires a goal Assume world is: Requires actions Observable What actions? Discrete
Announcements. CS 188: Artificial Intelligence
 Announcements Projects: Looking for project partners? --- Come to front after lecture. Try pair programming, not divide-and-conquer Account forms available up front during break and after lecture Assignments
Announcements Projects: Looking for project partners? --- Come to front after lecture. Try pair programming, not divide-and-conquer Account forms available up front during break and after lecture Assignments
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE
 UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 4161/5196 Introduction to Robotics Experiment No. 5 A* Path Planning Overview: The purpose of this experiment
UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECGR 4161/5196 Introduction to Robotics Experiment No. 5 A* Path Planning Overview: The purpose of this experiment
Searching with Partial Information
 Searching with Partial Information Above we (unrealistically) assumed that the environment is fully observable and deterministic Moreover, we assumed that the agent knows what the effects of each action
Searching with Partial Information Above we (unrealistically) assumed that the environment is fully observable and deterministic Moreover, we assumed that the agent knows what the effects of each action
Informed Search Algorithms
 Informed Search Algorithms CITS3001 Algorithms, Agents and Artificial Intelligence Tim French School of Computer Science and Software Engineering The University of Western Australia 2017, Semester 2 Introduction
Informed Search Algorithms CITS3001 Algorithms, Agents and Artificial Intelligence Tim French School of Computer Science and Software Engineering The University of Western Australia 2017, Semester 2 Introduction
521495A: Artificial Intelligence
 521495A: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Lectured by Abdenour Hadid Adjunct Professor, CMVS, University of Oulu Slides adopted from http://ai.berkeley.edu Today Informed Search Heuristics Greedy
521495A: Artificial Intelligence Informed Search Lectured by Abdenour Hadid Adjunct Professor, CMVS, University of Oulu Slides adopted from http://ai.berkeley.edu Today Informed Search Heuristics Greedy
Informed search algorithms. Chapter 3 (Based on Slides by Stuart Russell, Dan Klein, Richard Korf, Subbarao Kambhampati, and UW-AI faculty)
 Informed search algorithms Chapter 3 (Based on Slides by Stuart Russell, Dan Klein, Richard Korf, Subbarao Kambhampati, and UW-AI faculty) Intuition, like the rays of the sun, acts only in an inflexibly
Informed search algorithms Chapter 3 (Based on Slides by Stuart Russell, Dan Klein, Richard Korf, Subbarao Kambhampati, and UW-AI faculty) Intuition, like the rays of the sun, acts only in an inflexibly
Informed (heuristic) search (cont). Constraint-satisfaction search.
 CS 1571 Introduction to AI Lecture 5 Informed (heuristic) search (cont). Constraint-satisfaction search. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Administration PS 1 due today Report before
CS 1571 Introduction to AI Lecture 5 Informed (heuristic) search (cont). Constraint-satisfaction search. Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Administration PS 1 due today Report before
Dr. Mustafa Jarrar. Chapter 4 Informed Searching. Artificial Intelligence. Sina Institute, University of Birzeit
 Lecture Notes on Informed Searching University of Birzeit, Palestine 1 st Semester, 2014 Artificial Intelligence Chapter 4 Informed Searching Dr. Mustafa Jarrar Sina Institute, University of Birzeit mjarrar@birzeit.edu
Lecture Notes on Informed Searching University of Birzeit, Palestine 1 st Semester, 2014 Artificial Intelligence Chapter 4 Informed Searching Dr. Mustafa Jarrar Sina Institute, University of Birzeit mjarrar@birzeit.edu
Shortest path using A Algorithm
 Shortest path using A Algorithm Phaneendhar Reddy Vanam Computer Science Indiana State University Terre Haute, IN, USA December 13, 2011 Contents Abstract The main aim of this project is to find the shortest
Shortest path using A Algorithm Phaneendhar Reddy Vanam Computer Science Indiana State University Terre Haute, IN, USA December 13, 2011 Contents Abstract The main aim of this project is to find the shortest
CS 4700: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence
 CS 4700: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence Bart Selman selman@cs.cornell.edu Module: Informed Search Readings R&N - Chapter 3: 3.5 and 3.6 Search Search strategies determined by choice of node (in
CS 4700: Foundations of Artificial Intelligence Bart Selman selman@cs.cornell.edu Module: Informed Search Readings R&N - Chapter 3: 3.5 and 3.6 Search Search strategies determined by choice of node (in
Informed search algorithms
 Informed search algorithms This lecture topic Chapter 3.5-3.7 Next lecture topic Chapter 4.1-4.2 (Please read lecture topic material before and after each lecture on that topic) Outline Review limitations
Informed search algorithms This lecture topic Chapter 3.5-3.7 Next lecture topic Chapter 4.1-4.2 (Please read lecture topic material before and after each lecture on that topic) Outline Review limitations
Informed search algorithms
 Informed search algorithms This lecture topic Chapter 3.5-3.7 Next lecture topic Chapter 4.1-4.2 (Please read lecture topic material before and after each lecture on that topic) Outline Review limitations
Informed search algorithms This lecture topic Chapter 3.5-3.7 Next lecture topic Chapter 4.1-4.2 (Please read lecture topic material before and after each lecture on that topic) Outline Review limitations
