f(x, y, z)dv = As remarked above, triple integrals can be evaluated as iterated integrals.
|
|
|
- Richard Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 7.5 Triple Integrals These are just like double integrals, but with another integration to perform. Although this is conceptually a simple extension of the idea, in practice it can get very complicated. For example, in two variables, there are just two different ways to integrate by iteration, depending on how we order the variables. But since there are six different orderings of three variables, there are now six different types of iterated integrals. In this section we shall illustrate the basic ideas, and not go into very much detail or complexity. We begin with the definition of the integral of a function w = f(x, y, z) over a region in three dimensions. Cover with a grid formed of the coordinate planes. and form the sum f(x, y, z) V over all the cubes of the grid in, where f is evaluated at a point of the cube, and V is the volume of the cube. Taking the limit as the grid becomes infinitely fine, we obtain () f(x, y, z)dv. As remarked above, triple integrals can be evaluated as iterated integrals. Proposition 7.5. Suppose that w = f(x, y, z) is a continuous function on the rectangular parallelipiped : a x b, c y d, p z q. Then the triple integral () can be evaluated by iteration in any of six ways, depending upon which variable is chosen first. For example, if the variables are chosen in the order x, y, z, we have (3) f(x, y, z)dv = b a d q f(x, y, z)dz ] dy ] dx. c p Example. Find the integral of x + yz over the region : x, y 4, z 5. If we iterate in the order x, y, z we get The first integration gives (x + yz)dv = 5 (x + yz)dz ] dy ] dx. The next integral is 5 (x + yz)dz = (x z + yz ) 5 = 5x + 5 y. (5x + 5 y)dy = (5x y y ) 4 = x + 5x = 5x
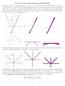
2 Finally, the last integration gives the desired result: (5x x3 )dx = x = 455. If we iterate in another order, the calculations are different (and could be easier or more difficult), but lead to the same answer. For example, let us iterate in the order y, z, x: (x + yz)dv = 5 (x + yz)dx ] dz ] dy. The first integral is The next integration leads to x yzx = yz yz z 5 = 5y + 4 3, and the final integration is (5y )dy = 5y = 455. Now, for the integral over a general region, the situation can easily become quite complicated. Here is one of the possibilities; Proposition 7.6 Suppose that w = f(x, y, z) is a continuous function on the region. If can be described as (x, y, z) such that a x b, u(x) y v(x), ψ(x, y) z φ(x, y), then (4) f(x, y, z)dv = b a v(x) φ(x,y) f(x, y, z)dz ] dy ] dx. u(x) ψ(x,y) Each ordering of the variables leads to a different possibility of calculating the triple integral by iteration; some of which may not work, and some of which may be easier than others. Example Find the volume of the region in the first octant bounded by the plane 3x + y + z =. First we draw a diagram of the figure. Figure 6
3 We see that we can order the variable in any way we please. Describing the region by the inequalities x 4, y 3x, z 3x y we obtain the iterated integral 3x 3x y dz ] dy ] dx. The first integration gives 3x y, and the second is 3x ( 3x y)dy = ( 3x)y y 3x = ( 3x), and finally ( ( 3x) ( 3x)3 )dx = 4 8 = 96. Example. Find the z-coordinate of the centroid of the region of example. To do that, we find the moment of the region about the plane z = : Mom {z=} = zdv. In general, if we have a choice, it is best to leave the most involved integration to the last; thus we may want to take the variables in the order z, x, y. This gives us the iterated integral 6 z ( z y)/3 Mom {z=} = zdx ] dy ] dz. The first integral leads to z( z y)/3, and the second is z z( z y)dy = z y (( z)y 3 3 ) z = z 6 ( z). After a little algebra, we obtain Mom {z=} = 3 6 (36z z + z 3 )dz = 7. z = Mom {z=} Mass = 7 96 =.75. Example 3. Let be the region bounded by the xy-plane, the plane x = and under the surface z = x y. Find the centroid of. First we draw a diagram of the figure. 3
4 Figure 6 We see that we can describe the region as: x, x y x, z x y. x x y dz]dy]dx = x Mom {x=} = x x(x y )dy = 4 x 3 dx = 3 3, x x y xdz]dy]dx = 4 x 4 dx = 4 x 3 5. The moment about the plane y = is zero because of symmetry. Finally, Mom {z=} = x x y zdz]dy]dx = x (x y ) dydx. x x Working out the square, we find the inner integral to be x x (x 4 x y + y 4 )dy = (x 4 y 3 x y 3 + y5 5 ) x x = x5 ( ) = 6 5 x5. and Mom {z=} = 8 x 5 dx = , x = 4/5 /3 = 4 5, ȳ =. z = 4/45 /3 = 4 5. Integration in other coordinates. First, we recall that the volume of the parallelipiped spanned by the three vectors U, V, W is U (V W) = det(u, V, W), where the determinant is that of the matrix whose rows are the components of U, V, W. Now, suppose that we want to evaluate the triple integral (5) fdxdydz where corresponds to a region S in u, v, w space under a change of variables (6) X = X(u, v, w) = x(u, v, w)i + y(u, v, w)j + z(u, v, w)k. By a change of variables, we mean that the coordinates (u, v, w) in S uniquely determine a point in ; that is, in principle, we could solve the equations (6) for u, v, w in terms of x, y, z. Now, we can perform the integration in u, v, w space by selecting a fine grid in S, covering by the image of the grid, and forming the sum f(x) V, where V is the 4
5 volume of the figure in corresponding to a typical cube in the grid on S. This will be an approximation to (5), which gets better as the grid gets finer. If the grid is sufficiently fine, we can, at each cube, approximate by the linear approximation to the change of variables: dx = X u du + X v dv + X w dw. A cube in S of side lengths du, dv, dw corresponds to the parallelipiped in spanned by the vectors X u du, X v dv, X w dw, and the volume of that parallelipiped is (7) dv = det(x u, X v, X w ) dudvdw. The factor in (7) is called the Jacobian of the variable change, and is calculated as the (absolute value of the) determinant of the matrix whose rows are X u, X v, X w. This matrix is denoted by (x, y, z) (u, v, w) = x u x v x w Proposition 7.7. Suppose that we are given the change of variables (6) so that the region in (x, y, z) space corresponds to the region S in (u, v, w) space. Then we can calculate triple integrals by integrating over S as follows: f(x)dxdydz = S y u y v y w z u z v z w. f(x(u, v, w)) (x, y, z) dudvdw. (u, v, w) Example 4. Find the volume of the region given by the inequalities z 4, y + z 3, x + y + z 5. This region is a parallelipiped, so by the appropriate change of coordinates, can be made to correspond to a rectangular parallelipiped. That is, we make the change of variables u = x + y + z, v = y + z, w = z so that corresponds to the region S given by the inequalities u 5, v 3, w 4. dxdydz = S (x, y, z) dudvdw. (u, v, w) Now, to calculate the Jacobian, we solve for x, y, z in terms of u, v, w: x = u v, y = v w, z = w, 5
6 so that (x, y, z) (u, v, w) = det =. 5 3 dudvdw = 6. When we make a linear change of variables the Jacobian is a constant (but not always, as above). By using the following fact about determinants, we need not actually solve for x, y, z in terms of u, v, w: (8) (x, y, z) (u, v, w) (u, v, w) (x, y, z) =. Example 5. Let u = 3x y + z, v = x + y + z, w = x z. Find the volume of the parallelipiped given by the inequalities u 3, v 4, u 7. We calculate, by (8), so that (u, v, w) (x, y, z) = det 3 = 7. (x, y, z) (u, v, w) = 7, 3 7 dudvdw = 7 7. Usually, we change coordinates only when the statement of the problem strongly suggests a different set of coordinates., if the problem has symmetry about the z- axis, we may change to spherical coordinates, and if there is symmetry about the origin, an change to spherical coordinates is indicated. The calculation of thejacobians for cylindrical and spherical coordinates leads to these expressions: Cylindrical coordinates: dv = rdrdθdz. Spherical coordinates: dv = ρ sin φdρdθdφ. Example 6. Find the volume and the centroid of the region bounded by the hyperboloid x + y z = and the planes z =, z =. Here, because of the symmetry about the z-axis, we are led to cylindrical coordinates. In these coordinates, the region is given by θ π, z, r + z. π +z dxdydz = rdrdzdθ = rdr]dz]dθ. 6
7 The inner integral is and the next integral is +z + z rdr = + z dz = z + z3 6 = 7 3, and the final integration gives the volume as 4π/3. x =, ȳ =. To calculate z, we need Mom {z=} = zrdrdzdθ = π This time the first integral gives us z( + )/, and the next is, Now, because of the symmetry, +z zrdr]dz]dθ. so that Mom {z=} = 6π. z + z 3 dz = z 4 + z4 8 = 3, z = 6π 4π/3 = 9/7. Example 7. The region between the spheres of radius 4 and 5 is filled with a material whose density is given by δ(x, y, z) = + x + y. Find the mass of this region. In spherical coordinates, the region is given by the inequalities θ π, φ π, 4 ρ 5, and δ = + ρ sin φ. Mass = The innermost integral is π π 5 4 ( + ρ sin φ)ρ sin φdρ]dφ]dθ. 5 4 ( + ρ sin φ)ρ sin φdρ = 6 3 sin φ + 5 sin 3 φ. Now, to integrate with respect to φ, we calculate π sin φdφ =, π sin 3 φdφ = π ( cos φ) sin φdφ = 4 3, and the integration with respect to θ introduces a factor of π. Mass = π( 6 4 () + ) =.87π =
MATH 261 EXAM III PRACTICE PROBLEMS
 MATH 6 EXAM III PRACTICE PROBLEMS These practice problems are pulled from actual midterms in previous semesters. Exam 3 typically has 5 (not 6!) problems on it, with no more than one problem of any given
MATH 6 EXAM III PRACTICE PROBLEMS These practice problems are pulled from actual midterms in previous semesters. Exam 3 typically has 5 (not 6!) problems on it, with no more than one problem of any given
f (Pijk ) V. may form the Riemann sum: . Definition. The triple integral of f over the rectangular box B is defined to f (x, y, z) dv = lim
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals..1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections.2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals.3
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals..1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections.2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals.3
Applications of Triple Integrals
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 ouble Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 ouble Integrals over more general regions, efinition, Evaluation of ouble Integrals, Properties of ouble Integrals
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 ouble Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 ouble Integrals over more general regions, efinition, Evaluation of ouble Integrals, Properties of ouble Integrals
Coordinate Transformations in Advanced Calculus
 Coordinate Transformations in Advanced Calculus by Sacha Nandlall T.A. for MATH 264, McGill University Email: sacha.nandlall@mail.mcgill.ca Website: http://www.resanova.com/teaching/calculus/ Fall 2006,
Coordinate Transformations in Advanced Calculus by Sacha Nandlall T.A. for MATH 264, McGill University Email: sacha.nandlall@mail.mcgill.ca Website: http://www.resanova.com/teaching/calculus/ Fall 2006,
MATH203 Calculus. Dr. Bandar Al-Mohsin. School of Mathematics, KSU
 School of Mathematics, KSU Theorem The rectangular coordinates (x, y, z) and the cylindrical coordinates (r, θ, z) of a point P are related as follows: x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ, tan θ = y x, r 2 = x 2
School of Mathematics, KSU Theorem The rectangular coordinates (x, y, z) and the cylindrical coordinates (r, θ, z) of a point P are related as follows: x = r cos θ, y = r sin θ, tan θ = y x, r 2 = x 2
MATH 200 WEEK 9 - WEDNESDAY TRIPLE INTEGRALS
 MATH WEEK 9 - WEDNESDAY TRIPLE INTEGRALS MATH GOALS Be able to set up and evaluate triple integrals using rectangular, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates MATH TRIPLE INTEGRALS We integrate functions
MATH WEEK 9 - WEDNESDAY TRIPLE INTEGRALS MATH GOALS Be able to set up and evaluate triple integrals using rectangular, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates MATH TRIPLE INTEGRALS We integrate functions
Chapter 15 Notes, Stewart 7e
 Contents 15.2 Iterated Integrals..................................... 2 15.3 Double Integrals over General Regions......................... 5 15.4 Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates..........................
Contents 15.2 Iterated Integrals..................................... 2 15.3 Double Integrals over General Regions......................... 5 15.4 Double Integrals in Polar Coordinates..........................
UNIVERSITI TEKNOLOGI MALAYSIA SSCE 1993 ENGINEERING MATHEMATICS II TUTORIAL 2. 1 x cos dy dx x y dy dx. y cosxdy dx
 UNIVESITI TEKNOLOI MALAYSIA SSCE 99 ENINEEIN MATHEMATICS II TUTOIAL. Evaluate the following iterated integrals. (e) (g) (i) x x x sinx x e x y dy dx x dy dx y y cosxdy dx xy x + dxdy (f) (h) (y + x)dy
UNIVESITI TEKNOLOI MALAYSIA SSCE 99 ENINEEIN MATHEMATICS II TUTOIAL. Evaluate the following iterated integrals. (e) (g) (i) x x x sinx x e x y dy dx x dy dx y y cosxdy dx xy x + dxdy (f) (h) (y + x)dy
MA 174: Multivariable Calculus Final EXAM (practice) NO CALCULATORS, BOOKS, OR PAPERS ARE ALLOWED. Use the back of the test pages for scrap paper.
 MA 174: Multivariable alculus Final EXAM (practice) NAME lass Meeting Time: NO ALULATOR, BOOK, OR PAPER ARE ALLOWED. Use the back of the test pages for scrap paper. Points awarded 1. (5 pts). (5 pts).
MA 174: Multivariable alculus Final EXAM (practice) NAME lass Meeting Time: NO ALULATOR, BOOK, OR PAPER ARE ALLOWED. Use the back of the test pages for scrap paper. Points awarded 1. (5 pts). (5 pts).
Math 241, Exam 3 Information.
 Math 241, xam 3 Information. 11/28/12, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. xam 3 will be based on: Sections 15.2-15.4, 15.6-15.8. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241fa12/241.html)
Math 241, xam 3 Information. 11/28/12, LC 310, 11:15-12:05. xam 3 will be based on: Sections 15.2-15.4, 15.6-15.8. The corresponding assigned homework problems (see http://www.math.sc.edu/ boylan/sccourses/241fa12/241.html)
) in the k-th subbox. The mass of the k-th subbox is M k δ(x k, y k, z k ) V k. Thus,
 1 Triple Integrals Mass problem. Find the mass M of a solid whose density (the mass per unit volume) is a continuous nonnegative function δ(x, y, z). 1. Divide the box enclosing into subboxes, and exclude
1 Triple Integrals Mass problem. Find the mass M of a solid whose density (the mass per unit volume) is a continuous nonnegative function δ(x, y, z). 1. Divide the box enclosing into subboxes, and exclude
Calculus IV. Exam 2 November 13, 2003
 Name: Section: Calculus IV Math 1 Fall Professor Ben Richert Exam November 1, Please do all your work in this booklet and show all the steps. Calculators and note-cards are not allowed. Problem Possible
Name: Section: Calculus IV Math 1 Fall Professor Ben Richert Exam November 1, Please do all your work in this booklet and show all the steps. Calculators and note-cards are not allowed. Problem Possible
Contents. MATH 32B-2 (18W) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables. 1 Homework 1 - Solutions 3. 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 13
 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Homework - Solutions 3 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 3 3 Homework 3 - Solutions 9 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus
MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus of Several Variables Contents Homework - Solutions 3 2 Homework 2 - Solutions 3 3 Homework 3 - Solutions 9 MATH 32B-2 (8) (L) G. Liu / (TA) A. Zhou Calculus
Math 265 Exam 3 Solutions
 C Roettger, Fall 16 Math 265 Exam 3 Solutions Problem 1 Let D be the region inside the circle r 5 sin θ but outside the cardioid r 2 + sin θ. Find the area of D. Note that r and θ denote polar coordinates.
C Roettger, Fall 16 Math 265 Exam 3 Solutions Problem 1 Let D be the region inside the circle r 5 sin θ but outside the cardioid r 2 + sin θ. Find the area of D. Note that r and θ denote polar coordinates.
MIDTERM. Section: Signature:
 MIDTERM Math 32B 8/8/2 Name: Section: Signature: Read all of the following information before starting the exam: Check your exam to make sure all pages are present. NO CALCULATORS! Show all work, clearly
MIDTERM Math 32B 8/8/2 Name: Section: Signature: Read all of the following information before starting the exam: Check your exam to make sure all pages are present. NO CALCULATORS! Show all work, clearly
12.5 Triple Integrals
 1.5 Triple Integrals Arkansas Tech University MATH 94: Calculus III r. Marcel B Finan In Sections 1.1-1., we showed how a function of two variables can be integrated over a region in -space and how integration
1.5 Triple Integrals Arkansas Tech University MATH 94: Calculus III r. Marcel B Finan In Sections 1.1-1., we showed how a function of two variables can be integrated over a region in -space and how integration
Triple Integrals. Be able to set up and evaluate triple integrals over rectangular boxes.
 SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: Triple Integrals As you work through the problems listed below, you should reference Chapters 4.5 & 4.6 of the recommended textbook (or the equivalent chapter in your alternative
SUGGESTED REFERENCE MATERIAL: Triple Integrals As you work through the problems listed below, you should reference Chapters 4.5 & 4.6 of the recommended textbook (or the equivalent chapter in your alternative
Math 253, Section 102, Fall 2006 Practice Final Solutions
 Math 253, Section 102, Fall 2006 Practice Final Solutions 1 2 1. Determine whether the two lines L 1 and L 2 described below intersect. If yes, find the point of intersection. If not, say whether they
Math 253, Section 102, Fall 2006 Practice Final Solutions 1 2 1. Determine whether the two lines L 1 and L 2 described below intersect. If yes, find the point of intersection. If not, say whether they
Parametric Surfaces. Substitution
 Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Surfaces. Substitution Recall that a curve in space is given by parametric equations as a function of single parameter t x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t). A curve is a one-dimensional
Calculus Lia Vas Parametric Surfaces. Substitution Recall that a curve in space is given by parametric equations as a function of single parameter t x = x(t) y = y(t) z = z(t). A curve is a one-dimensional
Math 11 Fall 2016 Section 1 Monday, October 17, 2016
 Math 11 Fall 16 Section 1 Monday, October 17, 16 First, some important points from the last class: f(x, y, z) dv, the integral (with respect to volume) of f over the three-dimensional region, is a triple
Math 11 Fall 16 Section 1 Monday, October 17, 16 First, some important points from the last class: f(x, y, z) dv, the integral (with respect to volume) of f over the three-dimensional region, is a triple
Worksheet 3.5: Triple Integrals in Spherical Coordinates. Warm-Up: Spherical Coordinates (ρ, φ, θ)
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.5: Triple Integrals in Spherical Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know what the volume element dv represents. Be able to find
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.5: Triple Integrals in Spherical Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know what the volume element dv represents. Be able to find
Double Integrals over Polar Coordinate
 1. 15.4 DOUBLE INTEGRALS OVER POLAR COORDINATE 1 15.4 Double Integrals over Polar Coordinate 1. Polar Coordinates. The polar coordinates (r, θ) of a point are related to the rectangular coordinates (x,y)
1. 15.4 DOUBLE INTEGRALS OVER POLAR COORDINATE 1 15.4 Double Integrals over Polar Coordinate 1. Polar Coordinates. The polar coordinates (r, θ) of a point are related to the rectangular coordinates (x,y)
Mathematics 205 HWK 21 Solutions Section 16.5 p766
 Mathematics 5 HK 1 Solutions Section 16.5 p766 Problem 5, 16.5, p766. For the region shown (a rectangular slab of dimensions 1 5; see the text), choose coordinates and set up a triple integral, including
Mathematics 5 HK 1 Solutions Section 16.5 p766 Problem 5, 16.5, p766. For the region shown (a rectangular slab of dimensions 1 5; see the text), choose coordinates and set up a triple integral, including
Math 2130 Practice Problems Sec Name. Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate.
 Math 10 Practice Problems Sec 1.-1. Name Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate. 1) 5 5 - x dy dx -5 0 A) 5 B) C) 15 D) 5 ) 0 0-8 - 6 - x (8 + ln 9) A) 1 1 + x
Math 10 Practice Problems Sec 1.-1. Name Change the Cartesian integral to an equivalent polar integral, and then evaluate. 1) 5 5 - x dy dx -5 0 A) 5 B) C) 15 D) 5 ) 0 0-8 - 6 - x (8 + ln 9) A) 1 1 + x
Multiple Integrals. max x i 0
 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals Definite integrals appear when one solves Area problem. Find the area A of the region bounded above by the curve y = f(x), below by the x-axis, and on the sides by
Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals Definite integrals appear when one solves Area problem. Find the area A of the region bounded above by the curve y = f(x), below by the x-axis, and on the sides by
MATH 52 MIDTERM I APRIL 22, 2009
 MATH 52 MIDTERM I APRIL 22, 2009 THIS IS A CLOSED BOOK, CLOSED NOTES EXAM. NO CALCULATORS OR OTHER ELECTRONIC DEVICES ARE PERMITTED. YOU DO NOT NEED TO EVALUATE ANY INTEGRALS IN ANY PROBLEM. THERE ARE
MATH 52 MIDTERM I APRIL 22, 2009 THIS IS A CLOSED BOOK, CLOSED NOTES EXAM. NO CALCULATORS OR OTHER ELECTRONIC DEVICES ARE PERMITTED. YOU DO NOT NEED TO EVALUATE ANY INTEGRALS IN ANY PROBLEM. THERE ARE
2. Give an example of a non-constant function f(x, y) such that the average value of f over is 0.
 Midterm 3 Review Short Answer 2. Give an example of a non-constant function f(x, y) such that the average value of f over is 0. 3. Compute the Riemann sum for the double integral where for the given grid
Midterm 3 Review Short Answer 2. Give an example of a non-constant function f(x, y) such that the average value of f over is 0. 3. Compute the Riemann sum for the double integral where for the given grid
38. Triple Integration over Rectangular Regions
 8. Triple Integration over Rectangular Regions A rectangular solid region S in R can be defined by three compound inequalities, a 1 x a, b 1 y b, c 1 z c, where a 1, a, b 1, b, c 1 and c are constants.
8. Triple Integration over Rectangular Regions A rectangular solid region S in R can be defined by three compound inequalities, a 1 x a, b 1 y b, c 1 z c, where a 1, a, b 1, b, c 1 and c are constants.
First we consider how to parameterize a surface (similar to a parameterized curve for line integrals). Surfaces will need two parameters.
 Math 55 - Vector Calculus II Notes 14.6 urface Integrals Let s develop some surface integrals. First we consider how to parameterize a surface (similar to a parameterized curve for line integrals). urfaces
Math 55 - Vector Calculus II Notes 14.6 urface Integrals Let s develop some surface integrals. First we consider how to parameterize a surface (similar to a parameterized curve for line integrals). urfaces
MAC2313 Test 3 A E g(x, y, z) dy dx dz
 MAC2313 Test 3 A (5 pts) 1. If the function g(x, y, z) is integrated over the cylindrical solid bounded by x 2 + y 2 = 3, z = 1, and z = 7, the correct integral in Cartesian coordinates is given by: A.
MAC2313 Test 3 A (5 pts) 1. If the function g(x, y, z) is integrated over the cylindrical solid bounded by x 2 + y 2 = 3, z = 1, and z = 7, the correct integral in Cartesian coordinates is given by: A.
Integration. Example Find x 3 dx.
 Integration A function F is called an antiderivative of the function f if F (x)=f(x). The set of all antiderivatives of f is called the indefinite integral of f with respect to x and is denoted by f(x)dx.
Integration A function F is called an antiderivative of the function f if F (x)=f(x). The set of all antiderivatives of f is called the indefinite integral of f with respect to x and is denoted by f(x)dx.
Math 241, Final Exam. 12/11/12.
 Math, Final Exam. //. No notes, calculator, or text. There are points total. Partial credit may be given. ircle or otherwise clearly identify your final answer. Name:. (5 points): Equation of a line. Find
Math, Final Exam. //. No notes, calculator, or text. There are points total. Partial credit may be given. ircle or otherwise clearly identify your final answer. Name:. (5 points): Equation of a line. Find
Math Exam III Review
 Math 213 - Exam III Review Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 10, 2019 Homework Exam III is tonight at 5 PM Exam III will cover 15.1 15.3, 15.6 15.9, 16.1 16.2, and identifying conservative vector
Math 213 - Exam III Review Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky April 10, 2019 Homework Exam III is tonight at 5 PM Exam III will cover 15.1 15.3, 15.6 15.9, 16.1 16.2, and identifying conservative vector
MATH 234. Excercises on Integration in Several Variables. I. Double Integrals
 MATH 234 Excercises on Integration in everal Variables I. Double Integrals Problem 1. D = {(x, y) : y x 1, 0 y 1}. Compute D ex3 da. Problem 2. Find the volume of the solid bounded above by the plane 3x
MATH 234 Excercises on Integration in everal Variables I. Double Integrals Problem 1. D = {(x, y) : y x 1, 0 y 1}. Compute D ex3 da. Problem 2. Find the volume of the solid bounded above by the plane 3x
Integration using Transformations in Polar, Cylindrical, and Spherical Coordinates
 ections 15.4 Integration using Transformations in Polar, Cylindrical, and pherical Coordinates Cylindrical Coordinates pherical Coordinates MATH 127 (ection 15.5) Applications of Multiple Integrals The
ections 15.4 Integration using Transformations in Polar, Cylindrical, and pherical Coordinates Cylindrical Coordinates pherical Coordinates MATH 127 (ection 15.5) Applications of Multiple Integrals The
Homework 8. Due: Tuesday, March 31st, 2009
 MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 9 Homework 8 Due: Tuesday, March 3st, 9 Section 6.5, pg. 54: 7, 3. Section 6.6, pg. 58:, 3. Section 6.7, pg. 66: 3, 5, 47. Section 6.8, pg. 73: 33, 38. Section
MATH 55 Applied Honors Calculus III Winter 9 Homework 8 Due: Tuesday, March 3st, 9 Section 6.5, pg. 54: 7, 3. Section 6.6, pg. 58:, 3. Section 6.7, pg. 66: 3, 5, 47. Section 6.8, pg. 73: 33, 38. Section
Exam 2 Preparation Math 2080 (Spring 2011) Exam 2: Thursday, May 12.
 Multivariable Calculus Exam 2 Preparation Math 28 (Spring 2) Exam 2: Thursday, May 2. Friday May, is a day off! Instructions: () There are points on the exam and an extra credit problem worth an additional
Multivariable Calculus Exam 2 Preparation Math 28 (Spring 2) Exam 2: Thursday, May 2. Friday May, is a day off! Instructions: () There are points on the exam and an extra credit problem worth an additional
MA 243 Calculus III Fall Assignment 1. Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals)
 MA 43 Calculus III Fall 8 Dr. E. Jacobs Assignments Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals) Assignment. Spheres and Other Surfaces Read. -. and.6 Section./Problems
MA 43 Calculus III Fall 8 Dr. E. Jacobs Assignments Reading assignments are found in James Stewart s Calculus (Early Transcendentals) Assignment. Spheres and Other Surfaces Read. -. and.6 Section./Problems
Triple Integrals. MATH 311, Calculus III. J. Robert Buchanan. Fall Department of Mathematics. J. Robert Buchanan Triple Integrals
 Triple Integrals MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 211 Riemann Sum Approach Suppose we wish to integrate w f (x, y, z), a continuous function, on the box-shaped region
Triple Integrals MATH 311, Calculus III J. Robert Buchanan Department of Mathematics Fall 211 Riemann Sum Approach Suppose we wish to integrate w f (x, y, z), a continuous function, on the box-shaped region
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Calculus III-Final review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the corresponding position vector. 1) Define the points P = (-,
Calculus III-Final review Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. Find the corresponding position vector. 1) Define the points P = (-,
To find the maximum and minimum values of f(x, y, z) subject to the constraints
 Midterm 3 review Math 265 Fall 2007 14.8. Lagrange Multipliers. Case 1: One constraint. To find the maximum and minimum values of f(x, y, z) subject to the constraint g(x, y, z) = k: Step 1: Find all values
Midterm 3 review Math 265 Fall 2007 14.8. Lagrange Multipliers. Case 1: One constraint. To find the maximum and minimum values of f(x, y, z) subject to the constraint g(x, y, z) = k: Step 1: Find all values
MATH 010B - Spring 2018 Worked Problems - Section 6.2. ze x2 +y 2
 MATH B - Spring 8 orked Problems - Section 6.. Compute the following double integral x +y 9 z 3 ze x +y dv Solution: Here, we can t hope to integrate this directly in Cartesian coordinates, since the the
MATH B - Spring 8 orked Problems - Section 6.. Compute the following double integral x +y 9 z 3 ze x +y dv Solution: Here, we can t hope to integrate this directly in Cartesian coordinates, since the the
Worksheet 3.4: Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates. Warm-Up: Cylindrical Volume Element d V
 Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.4: Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know what the volume element dv represents. Be able to find
Boise State Math 275 (Ultman) Worksheet 3.4: Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates From the Toolbox (what you need from previous classes) Know what the volume element dv represents. Be able to find
Ma MULTIPLE INTEGRATION
 Ma 7 - MULTIPLE INTEGATION emark: The concept of a function of one variable in which y gx may be extended to two or more variables. If z is uniquely determined by values of the variables x and y, thenwesayz
Ma 7 - MULTIPLE INTEGATION emark: The concept of a function of one variable in which y gx may be extended to two or more variables. If z is uniquely determined by values of the variables x and y, thenwesayz
1 Double Integrals over Rectangular Regions
 Contents ouble Integrals over Rectangular Regions ouble Integrals Over General Regions 7. Introduction.................................... 7. Areas of General Regions............................. 9.3 Region
Contents ouble Integrals over Rectangular Regions ouble Integrals Over General Regions 7. Introduction.................................... 7. Areas of General Regions............................. 9.3 Region
QUIZ 4 (CHAPTER 17) SOLUTIONS MATH 252 FALL 2008 KUNIYUKI SCORED OUT OF 125 POINTS MULTIPLIED BY % POSSIBLE
 QUIZ 4 (CHAPTER 17) SOLUTIONS MATH 5 FALL 8 KUNIYUKI SCORED OUT OF 15 POINTS MULTIPLIED BY.84 15% POSSIBLE 1) Reverse the order of integration, and evaluate the resulting double integral: 16 y dx dy. Give
QUIZ 4 (CHAPTER 17) SOLUTIONS MATH 5 FALL 8 KUNIYUKI SCORED OUT OF 15 POINTS MULTIPLIED BY.84 15% POSSIBLE 1) Reverse the order of integration, and evaluate the resulting double integral: 16 y dx dy. Give
Second Midterm Exam Math 212 Fall 2010
 Second Midterm Exam Math 22 Fall 2 Instructions: This is a 9 minute exam. You should work alone, without access to any book or notes. No calculators are allowed. Do not discuss this exam with anyone other
Second Midterm Exam Math 22 Fall 2 Instructions: This is a 9 minute exam. You should work alone, without access to any book or notes. No calculators are allowed. Do not discuss this exam with anyone other
10.7 Triple Integrals. The Divergence Theorem of Gauss
 10.7 riple Integrals. he Divergence heorem of Gauss We begin by recalling the definition of the triple integral f (x, y, z) dv, (1) where is a bounded, solid region in R 3 (for example the solid ball {(x,
10.7 riple Integrals. he Divergence heorem of Gauss We begin by recalling the definition of the triple integral f (x, y, z) dv, (1) where is a bounded, solid region in R 3 (for example the solid ball {(x,
1 Double Integral. 1.1 Double Integral over Rectangular Domain
 Double Integral. Double Integral over Rectangular Domain As the definite integral of a positive function of one variable represents the area of the region between the graph and the x-asis, the double integral
Double Integral. Double Integral over Rectangular Domain As the definite integral of a positive function of one variable represents the area of the region between the graph and the x-asis, the double integral
18.02 Final Exam. y = 0
 No books, notes or calculators. 5 problems, 50 points. 8.0 Final Exam Useful formula: cos (θ) = ( + cos(θ)) Problem. (0 points) a) (5 pts.) Find the equation in the form Ax + By + z = D of the plane P
No books, notes or calculators. 5 problems, 50 points. 8.0 Final Exam Useful formula: cos (θ) = ( + cos(θ)) Problem. (0 points) a) (5 pts.) Find the equation in the form Ax + By + z = D of the plane P
Contents. 3 Multiple Integration. 3.1 Double Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates
 Calculus III (part 3): Multiple Integration (by Evan Dummit, 8, v. 3.) Contents 3 Multiple Integration 3. Double Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates............................... 3.. Double Integrals
Calculus III (part 3): Multiple Integration (by Evan Dummit, 8, v. 3.) Contents 3 Multiple Integration 3. Double Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates............................... 3.. Double Integrals
Chapter 15 Vector Calculus
 Chapter 15 Vector Calculus 151 Vector Fields 152 Line Integrals 153 Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path 153 Conservative Fields and Potential Functions 154 Green s Theorem 155 urface Integrals
Chapter 15 Vector Calculus 151 Vector Fields 152 Line Integrals 153 Fundamental Theorem and Independence of Path 153 Conservative Fields and Potential Functions 154 Green s Theorem 155 urface Integrals
= f (a, b) + (hf x + kf y ) (a,b) +
 Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
Chapter 14 Multiple Integrals 1 Double Integrals, Iterated Integrals, Cross-sections 2 Double Integrals over more general regions, Definition, Evaluation of Double Integrals, Properties of Double Integrals
MATH. 2153, Spring 16, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 January 25, 2016 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points.
 MATH. 2153, Spring 16, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 January 25, 2016 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points. 1. Evaluate the area A of the triangle with the vertices
MATH. 2153, Spring 16, MWF 12:40 p.m. QUIZ 1 January 25, 2016 PRINT NAME A. Derdzinski Show all work. No calculators. The problem is worth 10 points. 1. Evaluate the area A of the triangle with the vertices
Exam in Calculus. Wednesday June 1st First Year at The TEK-NAT Faculty and Health Faculty
 Exam in Calculus Wednesday June 1st 211 First Year at The TEK-NAT Faculty and Health Faculty The present exam consists of 7 numbered pages with a total of 12 exercises. It is allowed to use books, notes,
Exam in Calculus Wednesday June 1st 211 First Year at The TEK-NAT Faculty and Health Faculty The present exam consists of 7 numbered pages with a total of 12 exercises. It is allowed to use books, notes,
8(x 2) + 21(y 1) + 6(z 3) = 0 8x + 21y + 6z = 55.
 MATH 24 -Review for Final Exam. Let f(x, y, z) x 2 yz + y 3 z x 2 + z, and a (2,, 3). Note: f (2xyz 2x, x 2 z + 3y 2 z, x 2 y + y 3 + ) f(a) (8, 2, 6) (a) Find all stationary points (if any) of f. et f.
MATH 24 -Review for Final Exam. Let f(x, y, z) x 2 yz + y 3 z x 2 + z, and a (2,, 3). Note: f (2xyz 2x, x 2 z + 3y 2 z, x 2 y + y 3 + ) f(a) (8, 2, 6) (a) Find all stationary points (if any) of f. et f.
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 2003
 Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Math 113 Calculus III Final Exam Practice Problems Spring 23 1. Let g(x, y, z) = 2x 2 + y 2 + 4z 2. (a) Describe the shapes of the level surfaces of g. (b) In three different graphs, sketch the three cross
Grad operator, triple and line integrals. Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures
 Grad operator, triple and line integrals Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures 1 .1 The grad operator Let f(x 1, x,..., x n ) be a function of the n variables
Grad operator, triple and line integrals Notice: this material must not be used as a substitute for attending the lectures 1 .1 The grad operator Let f(x 1, x,..., x n ) be a function of the n variables
MATH SPRING 2000 (Test 01) FINAL EXAM INSTRUCTIONS
 MATH 61 - SPRING 000 (Test 01) Name Signature Instructor Recitation Instructor Div. Sect. No. FINAL EXAM INSTRUCTIONS 1. You must use a # pencil on the mark-sense sheet (answer sheet).. If you have test
MATH 61 - SPRING 000 (Test 01) Name Signature Instructor Recitation Instructor Div. Sect. No. FINAL EXAM INSTRUCTIONS 1. You must use a # pencil on the mark-sense sheet (answer sheet).. If you have test
f x = 2e xy +y(2x+y)e xy = (2+2xy+y 2 )e xy.
 gri (rg38778) Homework 11 gri (11111) 1 This print-out should have 3 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. Find lim (x,y) (,) 1
gri (rg38778) Homework 11 gri (11111) 1 This print-out should have 3 questions. Multiple-choice questions may continue on the next column or page find all choices before answering. Find lim (x,y) (,) 1
18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007
 MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. CV. Changing Variables in
MIT OpenCourseWare http://ocw.mit.edu 18.02 Multivariable Calculus Fall 2007 For information about citing these materials or our Terms of Use, visit: http://ocw.mit.edu/terms. CV. Changing Variables in
Dr. Allen Back. Nov. 21, 2014
 Dr. Allen Back of Nov. 21, 2014 The most important thing you should know (e.g. for exams and homework) is how to setup (and perhaps compute if not too hard) surface integrals, triple integrals, etc. But
Dr. Allen Back of Nov. 21, 2014 The most important thing you should know (e.g. for exams and homework) is how to setup (and perhaps compute if not too hard) surface integrals, triple integrals, etc. But
27. Tangent Planes & Approximations
 27. Tangent Planes & Approximations If z = f(x, y) is a differentiable surface in R 3 and (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is a point on this surface, then it is possible to construct a plane passing through this point,
27. Tangent Planes & Approximations If z = f(x, y) is a differentiable surface in R 3 and (x 0, y 0, z 0 ) is a point on this surface, then it is possible to construct a plane passing through this point,
Calculus III. Math 233 Spring In-term exam April 11th. Suggested solutions
 Calculus III Math Spring 7 In-term exam April th. Suggested solutions This exam contains sixteen problems numbered through 6. Problems 5 are multiple choice problems, which each count 5% of your total
Calculus III Math Spring 7 In-term exam April th. Suggested solutions This exam contains sixteen problems numbered through 6. Problems 5 are multiple choice problems, which each count 5% of your total
Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two
 Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Thursday, February 28, class time. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration: sections 13.3,
Multivariate Calculus Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Thursday, February 28, class time. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration: sections 13.3,
Final Exam Review. Name: Class: Date: Short Answer
 Name: Class: Date: ID: A Final Exam Review Short Answer 1. Find the distance between the sphere (x 1) + (y + 1) + z = 1 4 and the sphere (x 3) + (y + ) + (z + ) = 1. Find, a a + b, a b, a, and 3a + 4b
Name: Class: Date: ID: A Final Exam Review Short Answer 1. Find the distance between the sphere (x 1) + (y + 1) + z = 1 4 and the sphere (x 3) + (y + ) + (z + ) = 1. Find, a a + b, a b, a, and 3a + 4b
MATH 2023 Multivariable Calculus
 MATH 2023 Multivariable Calculus Problem Sets Note: Problems with asterisks represent supplementary informations. You may want to read their solutions if you like, but you don t need to work on them. Set
MATH 2023 Multivariable Calculus Problem Sets Note: Problems with asterisks represent supplementary informations. You may want to read their solutions if you like, but you don t need to work on them. Set
Section Parametrized Surfaces and Surface Integrals. (I) Parametrizing Surfaces (II) Surface Area (III) Scalar Surface Integrals
 Section 16.4 Parametrized Surfaces and Surface Integrals (I) Parametrizing Surfaces (II) Surface Area (III) Scalar Surface Integrals MATH 127 (Section 16.4) Parametrized Surfaces and Surface Integrals
Section 16.4 Parametrized Surfaces and Surface Integrals (I) Parametrizing Surfaces (II) Surface Area (III) Scalar Surface Integrals MATH 127 (Section 16.4) Parametrized Surfaces and Surface Integrals
Dr. Allen Back. Nov. 19, 2014
 Why of Dr. Allen Back Nov. 19, 2014 Graph Picture of T u, T v for a Lat/Long Param. of the Sphere. Why of Graph Basic Picture Why of Graph Why Φ(u, v) = (x(u, v), y(u, v), z(u, v)) Tangents T u = (x u,
Why of Dr. Allen Back Nov. 19, 2014 Graph Picture of T u, T v for a Lat/Long Param. of the Sphere. Why of Graph Basic Picture Why of Graph Why Φ(u, v) = (x(u, v), y(u, v), z(u, v)) Tangents T u = (x u,
Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates
 Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates P. Sam Johnson April 10, 2017 P. Sam Johnson (NIT Karnataka) Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates April 10, 2017 1 / 28 Overview We use triple integrals
Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates P. Sam Johnson April 10, 2017 P. Sam Johnson (NIT Karnataka) Triple Integrals in Rectangular Coordinates April 10, 2017 1 / 28 Overview We use triple integrals
Math 32B Discussion Session Week 2 Notes January 17 and 24, 2017
 Math 3B Discussion Session Week Notes January 7 and 4, 7 This week we ll finish discussing the double integral for non-rectangular regions (see the last few pages of the week notes) and then we ll touch
Math 3B Discussion Session Week Notes January 7 and 4, 7 This week we ll finish discussing the double integral for non-rectangular regions (see the last few pages of the week notes) and then we ll touch
Background for Surface Integration
 Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
Background for urface Integration 1 urface Integrals We have seen in previous work how to define and compute line integrals in R 2. You should remember the basic surface integrals that we will need to
1.(6pts) Which integral computes the area of the quarter-disc of radius a centered at the origin in the first quadrant? rdr d
 .(6pts) Which integral computes the area of the quarter-disc of radius a centered at the origin in the first quadrant? (a) / Z a rdr d (b) / Z a rdr d (c) Z a dr d (d) / Z a dr d (e) / Z a a rdr d.(6pts)
.(6pts) Which integral computes the area of the quarter-disc of radius a centered at the origin in the first quadrant? (a) / Z a rdr d (b) / Z a rdr d (c) Z a dr d (d) / Z a dr d (e) / Z a a rdr d.(6pts)
Math 52 Homework 2 Solutions
 Math 52 Homework 2 Solutions October 3, 28 Problem. If is a verticall simple region then we know that the double integral da computes the area of. On the other hand, one can also compute the area of as
Math 52 Homework 2 Solutions October 3, 28 Problem. If is a verticall simple region then we know that the double integral da computes the area of. On the other hand, one can also compute the area of as
MAC2313 Final A. a. The vector r u r v lies in the tangent plane of S at a given point. b. S f(x, y, z) ds = R f(r(u, v)) r u r v du dv.
 MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. Let f(x, y, z) be a function continuous in R 3 and let S be a surface parameterized by r(u, v) with the domain of the parameterization given by R; how many of the following are
MAC2313 Final A (5 pts) 1. Let f(x, y, z) be a function continuous in R 3 and let S be a surface parameterized by r(u, v) with the domain of the parameterization given by R; how many of the following are
Math Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates
 Math 213 - Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky November 2, 218 Homework Re-read section 15.7 Work on section 15.7, problems 1-13 (odd), 17-21 (odd) from Stewart
Math 213 - Triple Integrals in Cylindrical Coordinates Peter A. Perry University of Kentucky November 2, 218 Homework Re-read section 15.7 Work on section 15.7, problems 1-13 (odd), 17-21 (odd) from Stewart
Math 2374 Spring 2007 Midterm 3 Solutions - Page 1 of 6 April 25, 2007
 Math 374 Spring 7 Midterm 3 Solutions - Page of 6 April 5, 7. (3 points) Consider the surface parametrized by (x, y, z) Φ(x, y) (x, y,4 (x +y )) between the planes z and z 3. (i) (5 points) Set up the
Math 374 Spring 7 Midterm 3 Solutions - Page of 6 April 5, 7. (3 points) Consider the surface parametrized by (x, y, z) Φ(x, y) (x, y,4 (x +y )) between the planes z and z 3. (i) (5 points) Set up the
Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two
 Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Tuesday, August 16. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration. You should review the double
Multivariate Calculus: Review Problems for Examination Two Note: Exam Two is on Tuesday, August 16. The coverage is multivariate differential calculus and double integration. You should review the double
Topic 5-6: Parameterizing Surfaces and the Surface Elements ds and ds. Big Ideas. What We Are Doing Today... Notes. Notes. Notes
 Topic 5-6: Parameterizing Surfaces and the Surface Elements ds and ds. Textbook: Section 16.6 Big Ideas A surface in R 3 is a 2-dimensional object in 3-space. Surfaces can be described using two variables.
Topic 5-6: Parameterizing Surfaces and the Surface Elements ds and ds. Textbook: Section 16.6 Big Ideas A surface in R 3 is a 2-dimensional object in 3-space. Surfaces can be described using two variables.
Lesson 10. Transforming 3D Integrals
 Lesson 10 Transforming D Integrals Example 1: Triple Integrals to Compute Volume ecall that in previous chapters we could find the length of an interval I by computing dx or the area of a region by computing
Lesson 10 Transforming D Integrals Example 1: Triple Integrals to Compute Volume ecall that in previous chapters we could find the length of an interval I by computing dx or the area of a region by computing
A1:Orthogonal Coordinate Systems
 A1:Orthogonal Coordinate Systems A1.1 General Change of Variables Suppose that we express x and y as a function of two other variables u and by the equations We say that these equations are defining a
A1:Orthogonal Coordinate Systems A1.1 General Change of Variables Suppose that we express x and y as a function of two other variables u and by the equations We say that these equations are defining a
Name: Class: Date: 1. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint.
 . Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint. f (x, y) = x y, x + y = 8. Set up the triple integral of an arbitrary continuous function
. Use Lagrange multipliers to find the maximum and minimum values of the function subject to the given constraint. f (x, y) = x y, x + y = 8. Set up the triple integral of an arbitrary continuous function
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS. Page. 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary Assignments...2
 PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary...1 3. Assignments...2 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2010 Assignment Date to be Posted
PURE MATHEMATICS 212 Multivariable Calculus CONTENTS Page 1. Assignment Summary... i 2. Summary...1 3. Assignments...2 i PMTH212, Multivariable Calculus Assignment Summary 2010 Assignment Date to be Posted
Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation
 Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation For functions of one variable, y = f (x), the rate of change of the dependent variable can dy be found unambiguously by differentiation: f x. In this chapter we explore
Chapter 5 Partial Differentiation For functions of one variable, y = f (x), the rate of change of the dependent variable can dy be found unambiguously by differentiation: f x. In this chapter we explore
Updated: March 31, 2016 Calculus III Section Math 232. Calculus III. Brian Veitch Fall 2015 Northern Illinois University
 Updated: March 3, 26 Calculus III Section 5.6 Math 232 Calculus III Brian Veitch Fall 25 Northern Illinois University 5.6 Triple Integrals In order to build up to a triple integral let s start back at
Updated: March 3, 26 Calculus III Section 5.6 Math 232 Calculus III Brian Veitch Fall 25 Northern Illinois University 5.6 Triple Integrals In order to build up to a triple integral let s start back at
Lecture 17 - Friday May 8th
 Lecture 17 - Friday May 8th jacques@ucsd.edu Key words: Multiple integrals Key concepts: Know how to evaluate multiple integrals 17.1 Multiple Integrals A rectangular parallelepiped in R n is a set of
Lecture 17 - Friday May 8th jacques@ucsd.edu Key words: Multiple integrals Key concepts: Know how to evaluate multiple integrals 17.1 Multiple Integrals A rectangular parallelepiped in R n is a set of
MH2800/MAS183 - Linear Algebra and Multivariable Calculus
 MH28/MAS83 - Linear Algebra and Multivariable Calculus SEMESTER II EXAMINATION 2-22 Solved by Tao Biaoshuai Email: taob@e.ntu.edu.sg QESTION Let A 2 2 2. Solve the homogeneous linear system Ax and write
MH28/MAS83 - Linear Algebra and Multivariable Calculus SEMESTER II EXAMINATION 2-22 Solved by Tao Biaoshuai Email: taob@e.ntu.edu.sg QESTION Let A 2 2 2. Solve the homogeneous linear system Ax and write
Math 32B Discussion Session Week 2 Notes April 5 and 7, 2016
 Math 3B Discussion Session Week Notes April 5 and 7, 6 We have a little flexibility this week: we can tie up some loose ends from double integrals over vertically or horizontally simple regions, we can
Math 3B Discussion Session Week Notes April 5 and 7, 6 We have a little flexibility this week: we can tie up some loose ends from double integrals over vertically or horizontally simple regions, we can
R f da (where da denotes the differential of area dxdy (or dydx)
 Math 28H Topics for the second exam (Technically, everything covered on the first exam, plus) Constrained Optimization: Lagrange Multipliers Most optimization problems that arise naturally are not unconstrained;
Math 28H Topics for the second exam (Technically, everything covered on the first exam, plus) Constrained Optimization: Lagrange Multipliers Most optimization problems that arise naturally are not unconstrained;
We can conclude that if f is differentiable in an interval containing a, then. f(x) L(x) = f(a) + f (a)(x a).
 = sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
= sin( x) = 8 Lecture :Linear Approximations and Differentials Consider a point on a smooth curve y = f(x), say P = (a, f(a)), If we draw a tangent line to the curve at the point P, we can see from the
There are 10 problems, with a total of 150 points possible. (a) Find the tangent plane to the surface S at the point ( 2, 1, 2).
 Instructions Answer each of the questions on your own paper, and be sure to show your work so that partial credit can be adequately assessed. Put your name on each page of your paper. You may use a scientific
Instructions Answer each of the questions on your own paper, and be sure to show your work so that partial credit can be adequately assessed. Put your name on each page of your paper. You may use a scientific
Hw 4 Due Feb 22. D(fg) x y z (
 Hw 4 Due Feb 22 2.2 Exercise 7,8,10,12,15,18,28,35,36,46 2.3 Exercise 3,11,39,40,47(b) 2.4 Exercise 6,7 Use both the direct method and product rule to calculate where f(x, y, z) = 3x, g(x, y, z) = ( 1
Hw 4 Due Feb 22 2.2 Exercise 7,8,10,12,15,18,28,35,36,46 2.3 Exercise 3,11,39,40,47(b) 2.4 Exercise 6,7 Use both the direct method and product rule to calculate where f(x, y, z) = 3x, g(x, y, z) = ( 1
Parametric Surfaces and Surface Area
 Parametric Surfaces and Surface Area What to know: 1. Be able to parametrize standard surfaces, like the ones in the handout.. Be able to understand what a parametrized surface looks like (for this class,
Parametric Surfaces and Surface Area What to know: 1. Be able to parametrize standard surfaces, like the ones in the handout.. Be able to understand what a parametrized surface looks like (for this class,
To graph the point (r, θ), simply go out r units along the initial ray, then rotate through the angle θ. The point (1, 5π 6
 Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
Polar Coordinates Any point in the plane can be described by the Cartesian coordinates (x, y), where x and y are measured along the corresponding axes. However, this is not the only way to represent points
MATH 251 Fall 2016 EXAM III - VERSION A
 MATH 51 Fall 16 EXAM III - VERSION A LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: SECTION NUMBER: UIN: DIRECTIONS: 1. You may use a calculator on this exam.. TURN OFF cell phones and put them away. If a cell phone is seen during
MATH 51 Fall 16 EXAM III - VERSION A LAST NAME: FIRST NAME: SECTION NUMBER: UIN: DIRECTIONS: 1. You may use a calculator on this exam.. TURN OFF cell phones and put them away. If a cell phone is seen during
Changing Variables in Multiple Integrals
 Changing Variables in Multiple Integrals 3. Examples and comments; putting in limits. If we write the change of variable formula as (x, y) (8) f(x, y)dx dy = g(u, v) dudv, (u, v) where (x, y) x u x v (9)
Changing Variables in Multiple Integrals 3. Examples and comments; putting in limits. If we write the change of variable formula as (x, y) (8) f(x, y)dx dy = g(u, v) dudv, (u, v) where (x, y) x u x v (9)
MATH 116 REVIEW PROBLEMS for the FINAL EXAM
 MATH 116 REVIEW PROBLEMS for the FINAL EXAM The following questions are taken from old final exams of various calculus courses taught in Bilkent University 1. onsider the line integral (2xy 2 z + y)dx
MATH 116 REVIEW PROBLEMS for the FINAL EXAM The following questions are taken from old final exams of various calculus courses taught in Bilkent University 1. onsider the line integral (2xy 2 z + y)dx
Curves: We always parameterize a curve with a single variable, for example r(t) =
 Final Exam Topics hapters 16 and 17 In a very broad sense, the two major topics of this exam will be line and surface integrals. Both of these have versions for scalar functions and vector fields, and
Final Exam Topics hapters 16 and 17 In a very broad sense, the two major topics of this exam will be line and surface integrals. Both of these have versions for scalar functions and vector fields, and
Math 210, Exam 2, Spring 2010 Problem 1 Solution
 Math, Exam, Spring Problem Solution. Find and classify the critical points of the function f(x,y) x 3 +3xy y 3. Solution: By definition, an interior point (a,b) in the domain of f is a critical point of
Math, Exam, Spring Problem Solution. Find and classify the critical points of the function f(x,y) x 3 +3xy y 3. Solution: By definition, an interior point (a,b) in the domain of f is a critical point of
