Some Conjectures in Chromatic Topological Graph Theory Joan P. Hutchinson Macalester College, emerita
|
|
|
- Randolf Simpson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Some Conjectures in Chromatic Topological Graph Theory Joan P. Hutchinson Macalester College, emerita Thanks to Stan Wagon for the colorful graphics. Ñ
2 ALMOST FOUR-COLORING ON SURFACES: #1. M.O. Albertson s favorite CONJECTURE (1980): All vertices of a triangulation of the torus can be 4-colored except for at most three vertices. Motivation: Every graph on the torus can be 7-colored, and every 7-chromatic toroidal graph contains K 7, a triangulation of the torus. Every 6-chromatic toroidal graph contains one of four graphs. [Thomassen 1994] The list for 5-chromatic toroidal graphs is infinite... An affirmative answer to this conjecture implies the Four Color Theorem.
3 In Jensen & Toft, Graph Coloring Problems, Albertson s Four-Color Problem. CONJECTURE: For every surface S, there is an integer f HSL such that all but f HSL vertices of a graph embeddable on S can be 4-colored.
4 TWO & THREE-COLORING ON SURFACES #2. The easiest coloring result states that every plane graph can be two-colored provided every face is bounded by an even number of edges. What is true on surfaces? Locally bipartite (aka evenly embedded) graphs are those embedded on a surface with all faces bounded by an even number of edges. There is a Heawood/Ringel type theorem for locally bipartite graphs on surfaces. The more modern question asks about locally planar,
5 The more modern question asks about locally planar, locally bipartite graphs on surfaces: Locally planar (Albertson & Stromquist 1980) means that all noncontractible cycles are long, as long as needed for the conjecture/question/theorem at hand. Thm. (H 1995) A locally planar, locally bipartite graph on an orientable surface can be three-colored. The chromatic number of locally planar, locally bipartite graphs on nonorientable surfaces have been determined by Mohar & Seymour, 1999.
6 QUESTION (Kawarabayashi) Can locally planar, locally bipartite graphs be 3-list-colored? Or 4-list-colored? Theorem (Thomassen 1993) A locally planar graph on any surface can be 5-colored. Theorem (DeVos, Kawarabayashi, Mohar 2008; Postle & Thomas 2012) A locally planar graph on any surface can be 5-list-colored.
7 PLANAR THREE-COLORING #3. The next easiest coloring result states that a planar triangulation can be three-colored if and only if every vertex has even degree (Heawood s theorem). Theorem (Król 1973) A planar graph is three-colorable if and only if it is a subgraph of an even-degree-d triangulation. ;
8 ; QUESTION: Is the chromatic number of great-circle graphs (no three meet at a point) on the sphere three? (Felsner, Hurtado, Noy, Streinu, 2000) S. Felsner, F. Hurtado, M. Noy, and I. Streinu, Hamiltonicity and coloring properties of arrangement graphs, in Proc. Symp. on Disc. Algorithms, ACM Press H2000L
9 It s easy to show that the upper hemisphere of greatcircles can be three-colored (Kocay & Wagon)
10 using the easy proof that the graph of straight lines in the plane (no three through a point) can be three-colored. But can the two hemispheres be meshed to be threecolored?
11 PLANAR LIST-COLORING: 8c,d< 8a,b,c,d< 8a,b,c,d< 8a,b< 8a,b< 8a,b,c,d< 8a,b,c,d< 8c,d< 8c,d< 8a,b,c,d< 8a,b,c,d< 8a,b< #4. QUESTION (B. Richter): If G ¹ K 4 is planar, 3-connected and for each v L Hv L ³ min 8deg Hv L, 6<, is G L- list-colorable? Thomassen asked whether there is any k such that L Hv L ³ min 8deg Hv L, k<, then planar, 3-connected G is L-list-colorable.
12 We know G can be L-list-colored when L Hv L ³ deg Hv L for every v, provided G is not a Gallai tree (Borodin 1977). K 5 We know G can be 5-list-colored (Thomassen 1994). Question (B. Richter): If G ¹ K 4 is planar, 3-connected, and for each v L Hv L ³ min 8degHv L, k<, is G L-list-colorable when k = 6? Yes for outerplanar graphs (H 2008)
13 Best results due to Cranston, Pruchnewski, Tuza, Voigt (J. Graph Theory 2012) They ask for which Hr, kl, G a K 5 -minor-free, r-connected graph that is not a Gallai tree is G L-list-colorable whenever L Hv L ³ min 8deg Hv L, k<.
14 PLANAR PRE-COLORING EXTENDING TO A LIST-COL- ORING: #5. Theorem (Thomassen 1994) If G is a plane graph with a distinguished face F, if two consecutive vertices of F are precolored, if all other vertices of F have 3-lists, and if all other vertices have 5-lists, then G can be list-colored. 5-lists 3-lists What if the precolored vertices are not adjacent?
15 5-lists 3-lists No, even for outerplanar graphs. Nor with a 1- and a 2-list: 1-list 8G,B<
16 Yes, for 2-connected, outerplanar graphs with two 2- lists. 2-list 2-list QUESTION If G is a plane graph with a distinguished face F, if two vertices of F have 2-lists, if all other vertices of F have 3-lists, and if all other vertices have 5-lists, can G be list-colored? Yes by Postle & Thomas, 2012.
17 And their work leads toward their solution of another question: Albertson QUESTION (1998): Is there a d > 0 such that in a planar graph G, with 5-lists on each vertex, if a set of vertices, mutually at distance at least d apart, are precolored, the precoloring extends to a list-coloring of G? YES with d = 20, 000 (Dvořák, Lidický, Mohar & Postle, ms 2011; independently Postle & Thomas 2012). Albertson answered his question in the affirmative for 5- coloring.
18 Theorem (A&H 2002) If G is planar, G@P D is bipartite with dist HP L ³ 8, a 5-coloring of G@P D in which each component is 2-colored extends to a 5-coloring of G. #6 QUESTION (2013): Is there a d > 0 such that in a planar graph G, if G@P D is bipartite with distance between components at least d, a 2-coloring of each component of G@P D extends to a 5-list-coloring of G? (Before working on this, check with Luke Postle who has some partial results.)
19 References Mma figs. File::PrintingSettings::PageSetup::talk (under US letter) View::FullScreen (esc to leave)
Graphs and Combinatorics
 Graphs and Combinatorics (2006) 22:289 295 Digital Object Identifier (DOI) 10.1007/s00373-006-0653-4 Graphs and Combinatorics Springer-Verlag 2006 Coloring Vertices and Faces of Locally Planar Graphs Michael
Graphs and Combinatorics (2006) 22:289 295 Digital Object Identifier (DOI) 10.1007/s00373-006-0653-4 Graphs and Combinatorics Springer-Verlag 2006 Coloring Vertices and Faces of Locally Planar Graphs Michael
4-critical graphs on surfaces without contractible cycles of length at most 4
 4-critical graphs on surfaces without contractible cycles of length at most 4 Zdeněk Dvořák, Bernard Lidický Charles University in Prague University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign SIAM DM 2012 Halifax
4-critical graphs on surfaces without contractible cycles of length at most 4 Zdeněk Dvořák, Bernard Lidický Charles University in Prague University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign SIAM DM 2012 Halifax
List colorings of K 5 -minor-free graphs with special list assignments
 List colorings of K 5 -minor-free graphs with special list assignments Daniel W. Cranston, Anja Pruchnewski, Zsolt Tuza, Margit Voigt 22 March 2010 Abstract A list assignment L of a graph G is a function
List colorings of K 5 -minor-free graphs with special list assignments Daniel W. Cranston, Anja Pruchnewski, Zsolt Tuza, Margit Voigt 22 March 2010 Abstract A list assignment L of a graph G is a function
TORUS KAREN L. COLLINS AND JOAN P. HUTCHINSON. Dedicated to Herbert S. Wilf in honor of his 65th birthday, and to. 1. Introduction
 FOUR-COLORING SIX-REGULAR GRAPHS ON THE TORUS KAREN L. COLLINS AND JOAN P. HUTCHINSON Dedicated to Herbert S. Wilf in honor of his 65th birthday, and to Phyllis Cassidy in honor of her retirement from
FOUR-COLORING SIX-REGULAR GRAPHS ON THE TORUS KAREN L. COLLINS AND JOAN P. HUTCHINSON Dedicated to Herbert S. Wilf in honor of his 65th birthday, and to Phyllis Cassidy in honor of her retirement from
The following is a summary, hand-waving certain things which actually should be proven.
 1 Basics of Planar Graphs The following is a summary, hand-waving certain things which actually should be proven. 1.1 Plane Graphs A plane graph is a graph embedded in the plane such that no pair of lines
1 Basics of Planar Graphs The following is a summary, hand-waving certain things which actually should be proven. 1.1 Plane Graphs A plane graph is a graph embedded in the plane such that no pair of lines
Every planar graph is 4-colourable and 5-choosable a joint proof
 Peter Dörre Fachhochschule Südwestfalen (University of Applied Sciences) Frauenstuhlweg, D-58644 Iserlohn, Germany doerre@fh-swf.de Mathematics Subject Classification: 05C5 Abstract A new straightforward
Peter Dörre Fachhochschule Südwestfalen (University of Applied Sciences) Frauenstuhlweg, D-58644 Iserlohn, Germany doerre@fh-swf.de Mathematics Subject Classification: 05C5 Abstract A new straightforward
Dominating Sets in Triangulations on Surfaces
 Dominating Sets in Triangulations on Surfaces Hong Liu Department of Mathematics University of Illinois This is a joint work with Michael Pelsmajer May 14, 2011 Introduction A dominating set D V of a graph
Dominating Sets in Triangulations on Surfaces Hong Liu Department of Mathematics University of Illinois This is a joint work with Michael Pelsmajer May 14, 2011 Introduction A dominating set D V of a graph
Graph Coloring Problems
 Graph Coloring Problems TOMMY R. JENSEN BJARNE TOFT Odense University A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction
Graph Coloring Problems TOMMY R. JENSEN BJARNE TOFT Odense University A Wiley-Interscience Publication JOHN WILEY & SONS New York Chichester Brisbane Toronto Singapore Contents Preface xv 1 Introduction
List Coloring Graphs
 List Coloring Graphs January 29, 2004 CHROMATIC NUMBER Defn 1 A k coloring of a graph G is a function c : V (G) {1, 2,... k}. A proper k coloring of a graph G is a coloring of G with k colors so that no
List Coloring Graphs January 29, 2004 CHROMATIC NUMBER Defn 1 A k coloring of a graph G is a function c : V (G) {1, 2,... k}. A proper k coloring of a graph G is a coloring of G with k colors so that no
[8] that this cannot happen on the projective plane (cf. also [2]) and the results of Robertson, Seymour, and Thomas [5] on linkless embeddings of gra
![[8] that this cannot happen on the projective plane (cf. also [2]) and the results of Robertson, Seymour, and Thomas [5] on linkless embeddings of gra [8] that this cannot happen on the projective plane (cf. also [2]) and the results of Robertson, Seymour, and Thomas [5] on linkless embeddings of gra](/thumbs/85/93035794.jpg) Apex graphs with embeddings of face-width three Bojan Mohar Department of Mathematics University of Ljubljana Jadranska 19, 61111 Ljubljana Slovenia bojan.mohar@uni-lj.si Abstract Aa apex graph is a graph
Apex graphs with embeddings of face-width three Bojan Mohar Department of Mathematics University of Ljubljana Jadranska 19, 61111 Ljubljana Slovenia bojan.mohar@uni-lj.si Abstract Aa apex graph is a graph
Approximation algorithms for Euler genus and related problems
 Approximation algorithms for Euler genus and related problems Chandra Chekuri Anastasios Sidiropoulos February 3, 2014 Slides based on a presentation of Tasos Sidiropoulos Graphs and topology Graphs and
Approximation algorithms for Euler genus and related problems Chandra Chekuri Anastasios Sidiropoulos February 3, 2014 Slides based on a presentation of Tasos Sidiropoulos Graphs and topology Graphs and
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 Apr 2011
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 Apr 2011 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 4 Apr 2011](/thumbs/94/118782109.jpg) arxiv:1104.0510v1 [math.co] 4 Apr 2011 Minimal non-extensible precolorings and implicit-relations José Antonio Martín H. Abstract. In this paper I study a variant of the general vertex coloring problem
arxiv:1104.0510v1 [math.co] 4 Apr 2011 Minimal non-extensible precolorings and implicit-relations José Antonio Martín H. Abstract. In this paper I study a variant of the general vertex coloring problem
HW Graph Theory Name (andrewid) - X. 1: Draw K 7 on a torus with no edge crossings.
 1: Draw K 7 on a torus with no edge crossings. A quick calculation reveals that an embedding of K 7 on the torus is a -cell embedding. At that point, it is hard to go wrong if you start drawing C 3 faces,
1: Draw K 7 on a torus with no edge crossings. A quick calculation reveals that an embedding of K 7 on the torus is a -cell embedding. At that point, it is hard to go wrong if you start drawing C 3 faces,
Lift Contractions. Petr Golovach 1 Marcin Kamiński 2 Daniël Paulusma 1 Dimitrios Thilikos 3. 1 September 2011
 Lift Contractions Petr Golovach 1 Marcin Kamiński 2 Daniël Paulusma 1 Dimitrios Thilikos 3 1 Durham University, UK 2 Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium 3 National and Kapodistrian University of Athens,
Lift Contractions Petr Golovach 1 Marcin Kamiński 2 Daniël Paulusma 1 Dimitrios Thilikos 3 1 Durham University, UK 2 Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium 3 National and Kapodistrian University of Athens,
3-coloring planar graphs with four triangles
 3-coloring planar graphs with four triangles Oleg V. Borodin, Zdeněk Dvořák, Alexandr V. Kostochka, Bernard Lidický, Matthew Yancey Sobolev Institute of Mathematics and Novosibirsk State University Charles
3-coloring planar graphs with four triangles Oleg V. Borodin, Zdeněk Dvořák, Alexandr V. Kostochka, Bernard Lidický, Matthew Yancey Sobolev Institute of Mathematics and Novosibirsk State University Charles
Technische Universität Ilmenau Institut für Mathematik
 Technische Universität Ilmenau Institut für Mathematik Preprint No. M 07/26 Precoloring extension for K4-minorfree graphs Pruchnewski, Anja; Voigt, Margit November 2007 Impressum: Hrsg.: Leiter des Instituts
Technische Universität Ilmenau Institut für Mathematik Preprint No. M 07/26 Precoloring extension for K4-minorfree graphs Pruchnewski, Anja; Voigt, Margit November 2007 Impressum: Hrsg.: Leiter des Instituts
arxiv: v2 [math.co] 27 Jul 2015
![arxiv: v2 [math.co] 27 Jul 2015 arxiv: v2 [math.co] 27 Jul 2015](/thumbs/74/69874112.jpg) BOXICITY AND TOPOLOGICAL INVARIANTS LOUIS ESPERET arxiv:1503.05765v2 [math.co] 27 Jul 2015 Abstract. The boxicity of a graph G = (V,E) is the smallest integer k for which there exist k interval graphs
BOXICITY AND TOPOLOGICAL INVARIANTS LOUIS ESPERET arxiv:1503.05765v2 [math.co] 27 Jul 2015 Abstract. The boxicity of a graph G = (V,E) is the smallest integer k for which there exist k interval graphs
Short proofs of coloring theorems on planar graphs
 Short proofs of coloring theorems on planar graphs Oleg V. Borodin Alexandr V. Kostochka Bernard Lidický Matthew Yancey February 28, 20 Abstract A recent lower bound on the number of edges in a k-critical
Short proofs of coloring theorems on planar graphs Oleg V. Borodin Alexandr V. Kostochka Bernard Lidický Matthew Yancey February 28, 20 Abstract A recent lower bound on the number of edges in a k-critical
In Memory of Michael O. Albertson, : a collection of his outstanding conjectures and questions in graph theory.
 In Memory of Michael O. Albertson, 1946-2009: a collection of his outstanding conjectures and questions in graph theory. June 19, 2009 Michael Albertson died in March after a short, intense battle with
In Memory of Michael O. Albertson, 1946-2009: a collection of his outstanding conjectures and questions in graph theory. June 19, 2009 Michael Albertson died in March after a short, intense battle with
Hamiltonian cycles in bipartite quadrangulations on the torus
 Hamiltonian cycles in bipartite quadrangulations on the torus Atsuhiro Nakamoto and Kenta Ozeki Abstract In this paper, we shall prove that every bipartite quadrangulation G on the torus admits a simple
Hamiltonian cycles in bipartite quadrangulations on the torus Atsuhiro Nakamoto and Kenta Ozeki Abstract In this paper, we shall prove that every bipartite quadrangulation G on the torus admits a simple
Computing Linkless and Flat Embeddings of Graphs in R 3
 Computing Linkless and Flat Embeddings of Graphs in R 3 Stephan Kreutzer Technical University Berlin based on joint work with Ken-ichi Kawarabayashi, Bojan Mohar and Bruce Reed Graph Theory @ Georgie Tech
Computing Linkless and Flat Embeddings of Graphs in R 3 Stephan Kreutzer Technical University Berlin based on joint work with Ken-ichi Kawarabayashi, Bojan Mohar and Bruce Reed Graph Theory @ Georgie Tech
On the structure of 1-planar graphs
 Institute of Mathematics, P.J. Šafárik University, Košice, Slovakia 20.11.2008 Planar graphs Within the graph theory, one of oldest areas of research is the study of planar and plane graphs (the beginnings
Institute of Mathematics, P.J. Šafárik University, Košice, Slovakia 20.11.2008 Planar graphs Within the graph theory, one of oldest areas of research is the study of planar and plane graphs (the beginnings
Structure and hamiltonicity of 3-connected graphs with excluded minors
 E0 Structure and hamiltonicity of 3-connected graphs with excluded minors Mark Ellingham* Emily Marshall* Vanderbilt University, USA Kenta Ozeki National Institute of Informatics, Japan Shoichi Tsuchiya
E0 Structure and hamiltonicity of 3-connected graphs with excluded minors Mark Ellingham* Emily Marshall* Vanderbilt University, USA Kenta Ozeki National Institute of Informatics, Japan Shoichi Tsuchiya
EXTREMAL PROBLEMS IN GRAPH THEORY CHRISTOPHER M. HARTMAN. B.S., University of Alaska, Fairbanks, 1991 THESIS. Urbana, Illinois
 EXTREMAL PROBLEMS IN GRAPH THEORY BY CHRISTOPHER M. HARTMAN B.S., University of Alaska, Fairbanks, 1991 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
EXTREMAL PROBLEMS IN GRAPH THEORY BY CHRISTOPHER M. HARTMAN B.S., University of Alaska, Fairbanks, 1991 THESIS Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Chapter 12 and 11.1 Planar graphs, regular polyhedra, and graph colorings
 Chapter 12 and 11.1 Planar graphs, regular polyhedra, and graph colorings Prof. Tesler Math 184A Fall 2017 Prof. Tesler Ch. 12: Planar Graphs Math 184A / Fall 2017 1 / 45 12.1 12.2. Planar graphs Definition
Chapter 12 and 11.1 Planar graphs, regular polyhedra, and graph colorings Prof. Tesler Math 184A Fall 2017 Prof. Tesler Ch. 12: Planar Graphs Math 184A / Fall 2017 1 / 45 12.1 12.2. Planar graphs Definition
Bar k-visibility Graphs: Bounds on the Number of Edges, Chromatic Number, and Thickness
 Bar k-visibility Graphs: Bounds on the Number of Edges, Chromatic Number, and Thickness Alice M. Dean, William Evans, Ellen Gethner 3,JoshuaD.Laison, Mohammad Ali Safari 5, and William T. Trotter 6 Department
Bar k-visibility Graphs: Bounds on the Number of Edges, Chromatic Number, and Thickness Alice M. Dean, William Evans, Ellen Gethner 3,JoshuaD.Laison, Mohammad Ali Safari 5, and William T. Trotter 6 Department
Math 777 Graph Theory, Spring, 2006 Lecture Note 1 Planar graphs Week 1 Weak 2
 Math 777 Graph Theory, Spring, 006 Lecture Note 1 Planar graphs Week 1 Weak 1 Planar graphs Lectured by Lincoln Lu Definition 1 A drawing of a graph G is a function f defined on V (G) E(G) that assigns
Math 777 Graph Theory, Spring, 006 Lecture Note 1 Planar graphs Week 1 Weak 1 Planar graphs Lectured by Lincoln Lu Definition 1 A drawing of a graph G is a function f defined on V (G) E(G) that assigns
8 Colouring Planar Graphs
 8 Colouring Planar Graphs The Four Colour Theorem Lemma 8.1 If G is a simple planar graph, then (i) 12 v V (G)(6 deg(v)) with equality for triangulations. (ii) G has a vertex of degree 5. Proof: For (i),
8 Colouring Planar Graphs The Four Colour Theorem Lemma 8.1 If G is a simple planar graph, then (i) 12 v V (G)(6 deg(v)) with equality for triangulations. (ii) G has a vertex of degree 5. Proof: For (i),
Problem Set 3. MATH 776, Fall 2009, Mohr. November 30, 2009
 Problem Set 3 MATH 776, Fall 009, Mohr November 30, 009 1 Problem Proposition 1.1. Adding a new edge to a maximal planar graph of order at least 6 always produces both a T K 5 and a T K 3,3 subgraph. Proof.
Problem Set 3 MATH 776, Fall 009, Mohr November 30, 009 1 Problem Proposition 1.1. Adding a new edge to a maximal planar graph of order at least 6 always produces both a T K 5 and a T K 3,3 subgraph. Proof.
Characterizations of graph classes by forbidden configurations
 Characterizations of graph classes by forbidden configurations Zdeněk Dvořák September 14, 2015 We consider graph classes that can be described by excluding some fixed configurations. Let us give some
Characterizations of graph classes by forbidden configurations Zdeněk Dvořák September 14, 2015 We consider graph classes that can be described by excluding some fixed configurations. Let us give some
Discrete Mathematics I So Practice Sheet Solutions 1
 Discrete Mathematics I So 2016 Tibor Szabó Shagnik Das Practice Sheet Solutions 1 Provided below are possible solutions to the questions from the practice sheet issued towards the end of the course. Exercise
Discrete Mathematics I So 2016 Tibor Szabó Shagnik Das Practice Sheet Solutions 1 Provided below are possible solutions to the questions from the practice sheet issued towards the end of the course. Exercise
Coloring planar graphs
 : coloring and higher genus surfaces Math 104, Graph Theory April 2, 201 Coloring planar graphs Six Color Let G be a planar graph. Then c(g) apple 6. Proof highlights. I Proof type: Induction on V (G).
: coloring and higher genus surfaces Math 104, Graph Theory April 2, 201 Coloring planar graphs Six Color Let G be a planar graph. Then c(g) apple 6. Proof highlights. I Proof type: Induction on V (G).
Bar k-visibility Graphs
 Bar k-visibility Graphs Alice M. Dean Department of Mathematics Skidmore College adean@skidmore.edu William Evans Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia will@cs.ubc.ca Ellen Gethner
Bar k-visibility Graphs Alice M. Dean Department of Mathematics Skidmore College adean@skidmore.edu William Evans Department of Computer Science University of British Columbia will@cs.ubc.ca Ellen Gethner
CLASSIFICATION OF SURFACES
 CLASSIFICATION OF SURFACES JUSTIN HUANG Abstract. We will classify compact, connected surfaces into three classes: the sphere, the connected sum of tori, and the connected sum of projective planes. Contents
CLASSIFICATION OF SURFACES JUSTIN HUANG Abstract. We will classify compact, connected surfaces into three classes: the sphere, the connected sum of tori, and the connected sum of projective planes. Contents
Some Open Problems in Graph T
 Some Open Problems in Graph T February 11, 2004 0-0 Sources Graph Theory Open Problems - Six problems suitable f uate research projects http://dimacs.rutgers.edu/ hochberg/undopen/graphth Douglas West
Some Open Problems in Graph T February 11, 2004 0-0 Sources Graph Theory Open Problems - Six problems suitable f uate research projects http://dimacs.rutgers.edu/ hochberg/undopen/graphth Douglas West
Face covers and the genus of apex graphs Bojan Mohar Department of Mathematics, University of Ljubljana, 1111 Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Face covers and the genus of apex graphs Bojan Mohar Department of Mathematics, University of Ljubljana, 1111 Ljubljana, Slovenia bojan.mohar@uni-lj.si Abstract A graph G is an apex graph if it contains
Face covers and the genus of apex graphs Bojan Mohar Department of Mathematics, University of Ljubljana, 1111 Ljubljana, Slovenia bojan.mohar@uni-lj.si Abstract A graph G is an apex graph if it contains
ADJACENCY POSETS OF PLANAR GRAPHS
 ADJACENCY POSETS OF PLANAR GRAPHS STEFAN FELSNER, CHING MAN LI, AND WILLIAM T. TROTTER Abstract. In this paper, we show that the dimension of the adjacency poset of a planar graph is at most 8. From below,
ADJACENCY POSETS OF PLANAR GRAPHS STEFAN FELSNER, CHING MAN LI, AND WILLIAM T. TROTTER Abstract. In this paper, we show that the dimension of the adjacency poset of a planar graph is at most 8. From below,
Jordan Curves. A curve is a subset of IR 2 of the form
 Jordan Curves A curve is a subset of IR 2 of the form α = {γ(x) : x [0, 1]}, where γ : [0, 1] IR 2 is a continuous mapping from the closed interval [0, 1] to the plane. γ(0) and γ(1) are called the endpoints
Jordan Curves A curve is a subset of IR 2 of the form α = {γ(x) : x [0, 1]}, where γ : [0, 1] IR 2 is a continuous mapping from the closed interval [0, 1] to the plane. γ(0) and γ(1) are called the endpoints
Non-zero disjoint cycles in highly connected group labelled graphs
 Non-zero disjoint cycles in highly connected group labelled graphs Ken-ichi Kawarabayashi Paul Wollan Abstract Let G = (V, E) be an oriented graph whose edges are labelled by the elements of a group Γ.
Non-zero disjoint cycles in highly connected group labelled graphs Ken-ichi Kawarabayashi Paul Wollan Abstract Let G = (V, E) be an oriented graph whose edges are labelled by the elements of a group Γ.
Note on list star edge-coloring of subcubic graphs
 Note on list star edge-coloring of subcubic graphs Borut Lužar, Martina Mockovčiaková, Roman Soták October 5, 018 arxiv:1709.0393v1 [math.co] 11 Sep 017 Abstract A star edge-coloring of a graph is a proper
Note on list star edge-coloring of subcubic graphs Borut Lužar, Martina Mockovčiaková, Roman Soták October 5, 018 arxiv:1709.0393v1 [math.co] 11 Sep 017 Abstract A star edge-coloring of a graph is a proper
CS6702 GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATIONS QUESTION BANK
 CS6702 GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATIONS 2 MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1 UNIT I INTRODUCTION CS6702 GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATIONS QUESTION BANK 1. Define Graph. 2. Define Simple graph. 3. Write few problems
CS6702 GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATIONS 2 MARKS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 1 UNIT I INTRODUCTION CS6702 GRAPH THEORY AND APPLICATIONS QUESTION BANK 1. Define Graph. 2. Define Simple graph. 3. Write few problems
6 Planar Graphs. 6.1 Euler's Formula
 6 Planar Graphs Roughly speaking, a graph is planar if and only if it can be drawn in the plane without any two of its edges crossing. More formally, an embedding of a graph G = (V; E) is a function f
6 Planar Graphs Roughly speaking, a graph is planar if and only if it can be drawn in the plane without any two of its edges crossing. More formally, an embedding of a graph G = (V; E) is a function f
Prism-hamiltonicity of triangulations
 Prism-hamiltonicity of triangulations Daniel P. Biebighauser and M. N. Ellingham September 23, 2005 Abstract The prism over a graph G is the Cartesian product G K 2 of G with the complete graph K 2. If
Prism-hamiltonicity of triangulations Daniel P. Biebighauser and M. N. Ellingham September 23, 2005 Abstract The prism over a graph G is the Cartesian product G K 2 of G with the complete graph K 2. If
Star coloring planar graphs from small lists
 Star coloring planar graphs from small lists André Kündgen Craig Timmons June 4, 2008 Abstract A star coloring of a graph is a proper vertex-coloring such that no path on four vertices is 2-colored. We
Star coloring planar graphs from small lists André Kündgen Craig Timmons June 4, 2008 Abstract A star coloring of a graph is a proper vertex-coloring such that no path on four vertices is 2-colored. We
Lower Bounds on the Crossing Number of Surface-Embedded Graphs I: Up to Torus.
 Lower Bounds on the Crossing Number of Surface-Embedded Graphs I: Up to Torus. Petr Hliněný Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University Botanická 68a, 602 00 Brno, Czech Rep. http://www.fi.muni.cz/~hlineny
Lower Bounds on the Crossing Number of Surface-Embedded Graphs I: Up to Torus. Petr Hliněný Faculty of Informatics, Masaryk University Botanická 68a, 602 00 Brno, Czech Rep. http://www.fi.muni.cz/~hlineny
Discrete Applied Mathematics
 Discrete Applied Mathematics 160 (2012) 505 512 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Discrete Applied Mathematics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dam 1-planarity of complete multipartite
Discrete Applied Mathematics 160 (2012) 505 512 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Discrete Applied Mathematics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/dam 1-planarity of complete multipartite
Coloring Subgraphs with Restricted Amounts of Hues
 Coloring Subgraphs with Restricted Amounts of Hues Wayne Goddard School of Computing and Dept of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University goddard@clemson.edu Robert Melville Dept of Mathematics Abstract
Coloring Subgraphs with Restricted Amounts of Hues Wayne Goddard School of Computing and Dept of Mathematical Sciences Clemson University goddard@clemson.edu Robert Melville Dept of Mathematics Abstract
Diskrete Mathematik und Optimierung
 Diskrete Mathematik und Optimierung Stephan Dominique Andres: Game-perfect digraphs paths and cycles Technical Report feu-dmo015.09 Contact: dominique.andres@fernuni-hagen.de FernUniversität in Hagen Fakultät
Diskrete Mathematik und Optimierung Stephan Dominique Andres: Game-perfect digraphs paths and cycles Technical Report feu-dmo015.09 Contact: dominique.andres@fernuni-hagen.de FernUniversität in Hagen Fakultät
Planar Graphs. 1 Graphs and maps. 1.1 Planarity and duality
 Planar Graphs In the first half of this book, we consider mostly planar graphs and their geometric representations, mostly in the plane. We start with a survey of basic results on planar graphs. This chapter
Planar Graphs In the first half of this book, we consider mostly planar graphs and their geometric representations, mostly in the plane. We start with a survey of basic results on planar graphs. This chapter
Discrete Mathematics
 Discrete Mathematics 312 (2012) 2735 2740 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Discrete Mathematics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/disc Facial parity edge colouring of plane pseudographs
Discrete Mathematics 312 (2012) 2735 2740 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Discrete Mathematics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/disc Facial parity edge colouring of plane pseudographs
Math 3012 Applied Combinatorics Lecture 12
 September 29, 2015 Math 3012 Applied Combinatorics Lecture 12 William T. Trotter trotter@math.gatech.edu Planar Graphs Definition A graph G is planar if it can be drawn in the plane with no edge crossings.
September 29, 2015 Math 3012 Applied Combinatorics Lecture 12 William T. Trotter trotter@math.gatech.edu Planar Graphs Definition A graph G is planar if it can be drawn in the plane with no edge crossings.
On Choosability with Separation of Planar Graphs with Forbidden Cycles
 On Choosability with Separation of Planar Graphs with Forbidden Cycles Ilkyoo Choi Bernard Lidický Derrick Stolee March, 203 Abstract We study choosability with separation which is a constrained version
On Choosability with Separation of Planar Graphs with Forbidden Cycles Ilkyoo Choi Bernard Lidický Derrick Stolee March, 203 Abstract We study choosability with separation which is a constrained version
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
 Page 1 of 7 Planar graph From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In graph theory, a planar graph is a graph that can be embedded in the plane, i.e., it can be drawn on the plane in such a way that its edges
Page 1 of 7 Planar graph From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia In graph theory, a planar graph is a graph that can be embedded in the plane, i.e., it can be drawn on the plane in such a way that its edges
List edge-colorings of series-parallel graphs
 List edge-colorings of series-parallel graphs Martin Juvan Department of Mathematics, University of Ljubljana 1111 Ljubljana, Slovenia martin.juvan@fmf.uni-lj.si Bojan Mohar Department of Mathematics,
List edge-colorings of series-parallel graphs Martin Juvan Department of Mathematics, University of Ljubljana 1111 Ljubljana, Slovenia martin.juvan@fmf.uni-lj.si Bojan Mohar Department of Mathematics,
How many colors are needed to color a map?
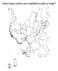 How many colors are needed to color a map? Is 4 always enough? Two relevant concepts How many colors do we need to color a map so neighboring countries get different colors? Simplifying assumption (not
How many colors are needed to color a map? Is 4 always enough? Two relevant concepts How many colors do we need to color a map so neighboring countries get different colors? Simplifying assumption (not
LAMC Advanced Circle October 9, Oleg Gleizer. Warm-up
 LAMC Advanced Circle October 9, 2016 Oleg Gleizer prof1140g@math.ucla.edu Warm-up Problem 1 Prove that a straight line tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius connecting the tangency point to
LAMC Advanced Circle October 9, 2016 Oleg Gleizer prof1140g@math.ucla.edu Warm-up Problem 1 Prove that a straight line tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius connecting the tangency point to
Treewidth and graph minors
 Treewidth and graph minors Lectures 9 and 10, December 29, 2011, January 5, 2012 We shall touch upon the theory of Graph Minors by Robertson and Seymour. This theory gives a very general condition under
Treewidth and graph minors Lectures 9 and 10, December 29, 2011, January 5, 2012 We shall touch upon the theory of Graph Minors by Robertson and Seymour. This theory gives a very general condition under
Correspondence coloring and its application to list-coloring planar graphs without cycles of lengths 4 to 8
 arxiv:1508.03437v [math.co] 8 Oct 016 Correspondence coloring and its application to list-coloring planar graphs without cycles of lengths 4 to 8 Zdeněk Dvořák Luke Postle Abstract We introduce a new variant
arxiv:1508.03437v [math.co] 8 Oct 016 Correspondence coloring and its application to list-coloring planar graphs without cycles of lengths 4 to 8 Zdeněk Dvořák Luke Postle Abstract We introduce a new variant
Note Asymmetric Directed Graph Coloring Games
 Note Asymmetric Directed Graph Coloring Games Stephan Dominique Andres Zentrum für angewandte Informatik Köln, University of Cologne, Weyertal 80, 50931 Köln, Germany Abstract This note generalizes the
Note Asymmetric Directed Graph Coloring Games Stephan Dominique Andres Zentrum für angewandte Informatik Köln, University of Cologne, Weyertal 80, 50931 Köln, Germany Abstract This note generalizes the
Planarity: dual graphs
 : dual graphs Math 104, Graph Theory March 28, 2013 : dual graphs Duality Definition Given a plane graph G, the dual graph G is the plane graph whose vtcs are the faces of G. The correspondence between
: dual graphs Math 104, Graph Theory March 28, 2013 : dual graphs Duality Definition Given a plane graph G, the dual graph G is the plane graph whose vtcs are the faces of G. The correspondence between
c 2010 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics
 SIAM J. DISCRETE MATH. Vol. 24, No. 4, pp. 1632 1637 c 2010 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics THOMASSEN S CHOOSABILITY ARGUMENT REVISITED DAVID R. WOOD AND SVANTE LINUSSON Abstract. Thomassen
SIAM J. DISCRETE MATH. Vol. 24, No. 4, pp. 1632 1637 c 2010 Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics THOMASSEN S CHOOSABILITY ARGUMENT REVISITED DAVID R. WOOD AND SVANTE LINUSSON Abstract. Thomassen
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 5: Planar graphs and coloring
 Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 5: Planar graphs and coloring David Glickenstein October 10, 2014 1 Planar graphs The Three Houses and Three Utilities Problem: Given three houses and three utilities, can
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 5: Planar graphs and coloring David Glickenstein October 10, 2014 1 Planar graphs The Three Houses and Three Utilities Problem: Given three houses and three utilities, can
λ -Harmonious Graph Colouring
 λ -Harmonious Graph Colouring Lauren DeDieu McMaster University Southwestern Ontario Graduate Mathematics Conference June 4th, 201 What is a graph? What is vertex colouring? 1 1 1 2 2 Figure : Proper Colouring.
λ -Harmonious Graph Colouring Lauren DeDieu McMaster University Southwestern Ontario Graduate Mathematics Conference June 4th, 201 What is a graph? What is vertex colouring? 1 1 1 2 2 Figure : Proper Colouring.
GRAPH THEORY and APPLICATIONS. Planar Graphs
 GRAPH THEORY and APPLICATIONS Planar Graphs Planar Graph A graph is planar if it can be drawn on a plane surface with no two edges intersecting. G is said to be embedded in the plane. We can extend the
GRAPH THEORY and APPLICATIONS Planar Graphs Planar Graph A graph is planar if it can be drawn on a plane surface with no two edges intersecting. G is said to be embedded in the plane. We can extend the
16 1. The Basics. x = t 1 >...>t k <...<t n = y
 16 1. The Basics [8.2.3] [8.6.8] Lemma 1.5.5. Let T be a normal tree in G. (i) Any two vertices x, y T are separated in G by the set x y. (ii) If S V (T )=V(G) and S is down-closed, then the components
16 1. The Basics [8.2.3] [8.6.8] Lemma 1.5.5. Let T be a normal tree in G. (i) Any two vertices x, y T are separated in G by the set x y. (ii) If S V (T )=V(G) and S is down-closed, then the components
Graph and Digraph Glossary
 1 of 15 31.1.2004 14:45 Graph and Digraph Glossary A B C D E F G H I-J K L M N O P-Q R S T U V W-Z Acyclic Graph A graph is acyclic if it contains no cycles. Adjacency Matrix A 0-1 square matrix whose
1 of 15 31.1.2004 14:45 Graph and Digraph Glossary A B C D E F G H I-J K L M N O P-Q R S T U V W-Z Acyclic Graph A graph is acyclic if it contains no cycles. Adjacency Matrix A 0-1 square matrix whose
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 11: Graph minors and Kuratowski s Theorem
 Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 11: Graph minors and Kuratowski s Theorem David Glickenstein November 26, 2008 1 Graph minors Let s revisit some de nitions. Let G = (V; E) be a graph. De nition 1 Removing
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes 11: Graph minors and Kuratowski s Theorem David Glickenstein November 26, 2008 1 Graph minors Let s revisit some de nitions. Let G = (V; E) be a graph. De nition 1 Removing
Coloring Eulerian triangulations of the Klein bottle
 Coloring Eulerian triangulations of the Klein bottle Daniel Král Bojan Mohar Atsuhiro Nakamoto Ondřej Pangrác Yusuke Suzuki Abstract We sho that an Eulerian triangulation of the Klein bottle has chromatic
Coloring Eulerian triangulations of the Klein bottle Daniel Král Bojan Mohar Atsuhiro Nakamoto Ondřej Pangrác Yusuke Suzuki Abstract We sho that an Eulerian triangulation of the Klein bottle has chromatic
Tomaz Pisanski, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia. Thomas W. Tucker, Colgate University. Arjana Zitnik, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia
 Eulerian Embeddings of Graphs Tomaz Pisanski, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia Thomas W. Tucker, Colgate University Arjana Zitnik, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia Abstract A straight-ahead walk in an
Eulerian Embeddings of Graphs Tomaz Pisanski, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia Thomas W. Tucker, Colgate University Arjana Zitnik, University of Ljubljana, Slovenia Abstract A straight-ahead walk in an
The chromatic number of the square of subcubic planar graphs
 The chromatic number of the square of subcubic planar graphs Stephen G. Hartke Sogol Jahanbekam Brent Thomas April 7, 20 Abstract Wegner conjectured in 977 that the square of every planar graph with maximum
The chromatic number of the square of subcubic planar graphs Stephen G. Hartke Sogol Jahanbekam Brent Thomas April 7, 20 Abstract Wegner conjectured in 977 that the square of every planar graph with maximum
A simple algorithm for 4-coloring 3-colorable planar graphs
 A simple algorithm for 4-coloring 3-colorable planar graphs Ken-ichi Kawarabayashi 1 National Institute of Informatics, 2-1-2 Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-8430, Japan Kenta Ozeki 2 Department of
A simple algorithm for 4-coloring 3-colorable planar graphs Ken-ichi Kawarabayashi 1 National Institute of Informatics, 2-1-2 Hitotsubashi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-8430, Japan Kenta Ozeki 2 Department of
Topological Graph Theory and Graphs of Positive Combinatorial Curvature. Marissa L. Childs
 Topological Graph Theory and Graphs of Positive Combinatorial Curvature by Marissa L. Childs A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for graduation with Honors in Mathematics. Whitman
Topological Graph Theory and Graphs of Positive Combinatorial Curvature by Marissa L. Childs A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for graduation with Honors in Mathematics. Whitman
Dominating Sets in Planar Graphs 1
 Dominating Sets in Planar Graphs 1 Lesley R. Matheson 2 Robert E. Tarjan 2; May, 1994 Abstract Motivated by an application to unstructured multigrid calculations, we consider the problem of asymptotically
Dominating Sets in Planar Graphs 1 Lesley R. Matheson 2 Robert E. Tarjan 2; May, 1994 Abstract Motivated by an application to unstructured multigrid calculations, we consider the problem of asymptotically
Kyle Gettig. Mentor Benjamin Iriarte Fourth Annual MIT PRIMES Conference May 17, 2014
 Linear Extensions of Directed Acyclic Graphs Kyle Gettig Mentor Benjamin Iriarte Fourth Annual MIT PRIMES Conference May 17, 2014 Motivation Individuals can be modeled as vertices of a graph, with edges
Linear Extensions of Directed Acyclic Graphs Kyle Gettig Mentor Benjamin Iriarte Fourth Annual MIT PRIMES Conference May 17, 2014 Motivation Individuals can be modeled as vertices of a graph, with edges
MATH 350 GRAPH THEORY & COMBINATORICS. Contents
 MATH 350 GRAPH THEORY & COMBINATORICS PROF. SERGEY NORIN, FALL 2013 Contents 1. Basic definitions 1 2. Connectivity 2 3. Trees 3 4. Spanning Trees 3 5. Shortest paths 4 6. Eulerian & Hamiltonian cycles
MATH 350 GRAPH THEORY & COMBINATORICS PROF. SERGEY NORIN, FALL 2013 Contents 1. Basic definitions 1 2. Connectivity 2 3. Trees 3 4. Spanning Trees 3 5. Shortest paths 4 6. Eulerian & Hamiltonian cycles
STAR COLORINGS AND ACYCLIC COLORINGS OF LOCALLY PLANAR GRAPHS
 University of Ljubljana Institute of Mathematics, Physics and Mechanics Department of Mathematics Jadranska 19, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia Preprint series, Vol. 44 (2006), 1024 STAR COLORINGS AND ACYCLIC
University of Ljubljana Institute of Mathematics, Physics and Mechanics Department of Mathematics Jadranska 19, 1000 Ljubljana, Slovenia Preprint series, Vol. 44 (2006), 1024 STAR COLORINGS AND ACYCLIC
and Heinz-Jürgen Voss
 Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 22 (2002 ) 193 198 ON k-trestles IN POLYHEDRAL GRAPHS Michal Tkáč Department of Mathematics The Faculty of Business Economics in Košice University of Economics in
Discussiones Mathematicae Graph Theory 22 (2002 ) 193 198 ON k-trestles IN POLYHEDRAL GRAPHS Michal Tkáč Department of Mathematics The Faculty of Business Economics in Košice University of Economics in
Forbidden minors and subdivisions for toroidal graphs with no K 3,3 s
 Forbidden minors and subdivisions for toroidal graphs with no K 3,3 s Andrei Gagarin 2 Laboratoire de Combinatoire et d Informatique Mathématique (LaCIM) Université du Québec à Montréal (UQAM) Montréal,
Forbidden minors and subdivisions for toroidal graphs with no K 3,3 s Andrei Gagarin 2 Laboratoire de Combinatoire et d Informatique Mathématique (LaCIM) Université du Québec à Montréal (UQAM) Montréal,
Star edge coloring of some classes of graphs
 Star edge coloring of some classes of graphs Ľudmila Bezegová, Borut Lužar, Martina Mockovčiaková, Roman Soták, Riste Škrekovski July, 0 arxiv:07.v [math.co] Jul 0 Abstract A star edge coloring of a graph
Star edge coloring of some classes of graphs Ľudmila Bezegová, Borut Lužar, Martina Mockovčiaková, Roman Soták, Riste Škrekovski July, 0 arxiv:07.v [math.co] Jul 0 Abstract A star edge coloring of a graph
Math 575 Exam 3. (t). What is the chromatic number of G?
 Math 575 Exam 3 Name 1 (a) Draw the Grötsch graph See your notes (b) Suppose that G is a graph having 6 vertices and 9 edges and that the chromatic polynomial of G is given below Fill in the missing coefficients
Math 575 Exam 3 Name 1 (a) Draw the Grötsch graph See your notes (b) Suppose that G is a graph having 6 vertices and 9 edges and that the chromatic polynomial of G is given below Fill in the missing coefficients
On ɛ-unit distance graphs
 On ɛ-unit distance graphs Geoffrey Exoo Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Indiana State University Terre Haute, IN 47809 g-exoo@indstate.edu April 9, 003 Abstract We consider a variation on
On ɛ-unit distance graphs Geoffrey Exoo Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Indiana State University Terre Haute, IN 47809 g-exoo@indstate.edu April 9, 003 Abstract We consider a variation on
FORBIDDEN MINORS: FINDING THE FINITE FEW
 FORBIDDEN MINORS: FINDING THE FINITE FEW THOMAS W. MATTMAN arxiv:1608.04066v2 [math.co] 23 Nov 2018 Abstract. The Graph Minor Theorem of Robertson and Seymour asserts that any graph property, whatsoever,
FORBIDDEN MINORS: FINDING THE FINITE FEW THOMAS W. MATTMAN arxiv:1608.04066v2 [math.co] 23 Nov 2018 Abstract. The Graph Minor Theorem of Robertson and Seymour asserts that any graph property, whatsoever,
Approximation Schemes for Planar Graph Problems (1983, 1994; Baker)
 Approximation Schemes for Planar Graph Problems (1983, 1994; Baker) Erik D. Demaine, MIT, theory.csail.mit.edu/ edemaine MohammadTaghi Hajiaghayi, MIT, www.mit.edu/ hajiagha INDEX TERMS: approximation
Approximation Schemes for Planar Graph Problems (1983, 1994; Baker) Erik D. Demaine, MIT, theory.csail.mit.edu/ edemaine MohammadTaghi Hajiaghayi, MIT, www.mit.edu/ hajiagha INDEX TERMS: approximation
The k-in-a-path problem for claw-free graphs
 The k-in-a-path problem for claw-free graphs Jiří Fiala Univerzita Karlova v Praze Bernard Lidický Univerzita Karlova v Praze Marcin Kamiński Université Libre de Bruxelles Daniël Paulusma University of
The k-in-a-path problem for claw-free graphs Jiří Fiala Univerzita Karlova v Praze Bernard Lidický Univerzita Karlova v Praze Marcin Kamiński Université Libre de Bruxelles Daniël Paulusma University of
Minor-monotone crossing number
 Minor-monotone crossing number Drago Bokal, Gašper Fijavž, Bojan Mohar To cite this version: Drago Bokal, Gašper Fijavž, Bojan Mohar. Minor-monotone crossing number. Stefan Felsner. 2005 European Conference
Minor-monotone crossing number Drago Bokal, Gašper Fijavž, Bojan Mohar To cite this version: Drago Bokal, Gašper Fijavž, Bojan Mohar. Minor-monotone crossing number. Stefan Felsner. 2005 European Conference
Approximation Algorithms via Structural Results for Apex-Minor-Free Graphs
 Approximation Algorithms via Structural Results for Apex-Minor-Free Graphs Erik D. Demaine 1, MohammadTaghi Hajiaghayi 2, and Ken-ichi Kawarabayashi 3 1 MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence
Approximation Algorithms via Structural Results for Apex-Minor-Free Graphs Erik D. Demaine 1, MohammadTaghi Hajiaghayi 2, and Ken-ichi Kawarabayashi 3 1 MIT Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence
Edge-disjoint Spanning Trees in Triangulated Graphs on Surfaces and application to node labeling 1
 Edge-disjoint Spanning Trees in Triangulated Graphs on Surfaces and application to node labeling 1 Arnaud Labourel a a LaBRI - Universite Bordeaux 1, France Abstract In 1974, Kundu [4] has shown that triangulated
Edge-disjoint Spanning Trees in Triangulated Graphs on Surfaces and application to node labeling 1 Arnaud Labourel a a LaBRI - Universite Bordeaux 1, France Abstract In 1974, Kundu [4] has shown that triangulated
Straight-ahead walks in Eulerian graphs
 Discrete Mathematics 281 (2004) 237 246 www.elsevier.com/locate/disc Straight-ahead walks in Eulerian graphs Tomaz Pisanski a, Thomas W. Tucker b, Arjana Zitnik a a IMFM, University of Ljubljana, Jadranska
Discrete Mathematics 281 (2004) 237 246 www.elsevier.com/locate/disc Straight-ahead walks in Eulerian graphs Tomaz Pisanski a, Thomas W. Tucker b, Arjana Zitnik a a IMFM, University of Ljubljana, Jadranska
CONTRACTIONS OF PLANAR GRAPHS
 Marcin Kamiński Brussels Daniël Paulusma Durham Dimitrios Thilikos Athens ESA 2010 CONTAINMENT RELATIONS \v \e /e 2 CONTAINMENT RELATIONS \v \e /e induced subgraph subgraph minor contraction induced minor
Marcin Kamiński Brussels Daniël Paulusma Durham Dimitrios Thilikos Athens ESA 2010 CONTAINMENT RELATIONS \v \e /e 2 CONTAINMENT RELATIONS \v \e /e induced subgraph subgraph minor contraction induced minor
Three applications of Euler s formula. Chapter 10
 Three applications of Euler s formula Chapter 10 A graph is planar if it can be drawn in the plane R without crossing edges (or, equivalently, on the -dimensional sphere S ). We talk of a plane graph if
Three applications of Euler s formula Chapter 10 A graph is planar if it can be drawn in the plane R without crossing edges (or, equivalently, on the -dimensional sphere S ). We talk of a plane graph if
Embeddings of Small Graphs on the Torus
 June, 00 This article appeared in CUBO (00), - Embeddings of Small Graphs on the Torus Andrei Gagarin, William Kocay* and Daniel Neilson Computer Science Department University of Manitoba Winnipeg, Manitoba,
June, 00 This article appeared in CUBO (00), - Embeddings of Small Graphs on the Torus Andrei Gagarin, William Kocay* and Daniel Neilson Computer Science Department University of Manitoba Winnipeg, Manitoba,
A note on Brooks theorem for triangle-free graphs
 A note on Brooks theorem for triangle-free graphs Bert Randerath Institut für Informatik Universität zu Köln D-50969 Köln, Germany randerath@informatik.uni-koeln.de Ingo Schiermeyer Fakultät für Mathematik
A note on Brooks theorem for triangle-free graphs Bert Randerath Institut für Informatik Universität zu Köln D-50969 Köln, Germany randerath@informatik.uni-koeln.de Ingo Schiermeyer Fakultät für Mathematik
Contractions of graphs on surfaces in polynomial time
 Contractions of graphs on surfaces in polynomial time Marcin Kamiński Daniël Paulusma Dimitrios M. Thilikos December 20, 2010 Abstract We prove that for every integer g 0 and graph H, there exists a polynomial-time
Contractions of graphs on surfaces in polynomial time Marcin Kamiński Daniël Paulusma Dimitrios M. Thilikos December 20, 2010 Abstract We prove that for every integer g 0 and graph H, there exists a polynomial-time
The Topology of Bendless Orthogonal Three-Dimensional Graph Drawing. David Eppstein Computer Science Dept. Univ. of California, Irvine
 The Topology of Bendless Orthogonal Three-Dimensional Graph Drawing David Eppstein Computer Science Dept. Univ. of California, Irvine Graph drawing: visual display of symbolic information Vertices and
The Topology of Bendless Orthogonal Three-Dimensional Graph Drawing David Eppstein Computer Science Dept. Univ. of California, Irvine Graph drawing: visual display of symbolic information Vertices and
The incidence game chromatic number
 The incidence game chromatic number Stephan Dominique Andres Zentrum für angewandte Informatik Köln, University of Cologne, Weyertal 80, 50931 Köln, Germany Abstract We introduce the incidence game chromatic
The incidence game chromatic number Stephan Dominique Andres Zentrum für angewandte Informatik Köln, University of Cologne, Weyertal 80, 50931 Köln, Germany Abstract We introduce the incidence game chromatic
LARGE 6-CONNECTED GRAPHS WITH NO K 6 MINOR. Robin Thomas. School of Mathematics Georgia Institute of Technology
 LARGE 6-CONNECTED GRAPHS WITH NO K 6 MINOR Robin Thomas School of Mathematics Georgia Institute of Technology http://math.gatech.edu/~thomas Joint work with Matthew DeVos Rajneesh Hegde Kenichi Kawarabayashi
LARGE 6-CONNECTED GRAPHS WITH NO K 6 MINOR Robin Thomas School of Mathematics Georgia Institute of Technology http://math.gatech.edu/~thomas Joint work with Matthew DeVos Rajneesh Hegde Kenichi Kawarabayashi
arxiv: v1 [math.co] 31 Jan 2019
![arxiv: v1 [math.co] 31 Jan 2019 arxiv: v1 [math.co] 31 Jan 2019](/thumbs/94/119876416.jpg) Decomposition of cubic graphs related to Wegner s conjecture arxiv:1901.11339v1 [math.co] 31 Jan 2019 János arát University of Pannonia, Department of Mathematics 8200 Veszprém, Egyetem utca 10., Hungary
Decomposition of cubic graphs related to Wegner s conjecture arxiv:1901.11339v1 [math.co] 31 Jan 2019 János arát University of Pannonia, Department of Mathematics 8200 Veszprém, Egyetem utca 10., Hungary
How many colors are needed to color a map?
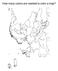 How many colors are needed to color a map? Is 4 always enough? Two relevant concepts How many colors do we need to color a map so neighboring countries get different colors? Simplifying assumption (not
How many colors are needed to color a map? Is 4 always enough? Two relevant concepts How many colors do we need to color a map so neighboring countries get different colors? Simplifying assumption (not
Isometric Diamond Subgraphs
 Isometric Diamond Subgraphs David Eppstein Computer Science Department, University of California, Irvine eppstein@uci.edu Abstract. We test in polynomial time whether a graph embeds in a distancepreserving
Isometric Diamond Subgraphs David Eppstein Computer Science Department, University of California, Irvine eppstein@uci.edu Abstract. We test in polynomial time whether a graph embeds in a distancepreserving
Representing 3-trees as Unit Rectangle-Visibility Graphs
 Representing 3-trees as Unit Rectangle-Visibility Graphs Alice M. Dean Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Skidmore College Saratoga Springs, NY 12866, USA Joan P. Hutchinson Department of Mathematics,
Representing 3-trees as Unit Rectangle-Visibility Graphs Alice M. Dean Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Skidmore College Saratoga Springs, NY 12866, USA Joan P. Hutchinson Department of Mathematics,
