REVIEW OF CORDIC ARCHITECTURES
|
|
|
- Jeffery Bradley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REVIEW OF CORDIC ARCHITECTURES T.SUBHA SRI #1, K.SESHU KUMAR #2, R. MUTTAIAH #3 School of Computing, M.Tech VLSI design, SASTRA University Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, , India #1 #2 Abstract Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer (CORDIC) first introduced by volder and Jack E. The consequence is lies on reality i.e., Small operations of shift-add and it also perform numerous computation operations. CORDIC used in various applications like image and signal processing, robotics systems and also communication systems and technical totalling. In this paper we presenting a brief outline and also growth in the CORDIC algorithm and architectures. Keyword- CORDIC Algorithm; CORDIC Architectures I. INTRODUCTION In 1956 Jack Volder introduced CORDIC algorithm, it was most effective, robust and low difficulty method to calculate many functions [1]. The CORDIC used wide-ranging applications; those are numerical coprocessors, pocket calculators, and radar signal processing. Later on CORDIC became replacement for the analog navigation computers system used in aircraft. CORDIC airborne navigational computer constructed to outperform the conservative modern of PCs by a factor of 7, and also binary to BCD number representation. In 1971 Walther [2,3] introduced procedure to calculate rotations in the manner of hyperbolic and circular methods and also linear coordinate systems. Afterwards, CORDIC is best choice for scientific calculator and also used in HP and HP-35 desktop calculators, and HP-2152A co-processor [4, 3]. The CORDIC arithmetic processor will perform all the rotation. Later on algorithm used in linear transformations [6], for DSP applications introduced CORDIC processor with single chip [5], digital filters [7], and for signal processing algorithms introduced matrix based methods [8]. Now a days used VLSI technology and EDA tools also in the neural networks [9], and software defined radio [10], field of biomedical signal processing.though CORDIC is not fastest method to perform all these operations, due to some reasons like low cost and efficient implementation it is most attractive. For real time DSP computations they did several modifications in CORDIC algorithm from past 20 years to deliver low cost and high performance hardware solutions. These have mainly focused on latency reduction and thus increase the CORDIC algorithm throughput. Hekstra proposed latest arithmetic operation called as orthonormal rotations or fast rotations by use of fixed angles. This will performs the least amount of shift add operations these are required for rotations. Vander Kolkand Lee said that appropriate fast rotation in the effective and fast selection and it shows the advantage to be extended when applied to (EVD) Enhanced Versatile Disc. Lang and Bruguera [11] introduced a higher radix method instead of radix-2 method, for this operation requires less iteration. The higher radix method mainly suggests that the constant scale factor. They did on-line calculation and subsequent compensation logarithm of the scale factor. Lau, and Delosme [12] introduced 4-D householder CORDIC transform instead of using multi-dimensional transform. This is done by using 2-D CORDIC operations in sequence manner; it is used in singular value deposition (SVD). Swartzlander and Choi [13] introduced sign prediction and addition to overawe the critical path. This done by calculating both outcomes of the sign, and finally it will select the suitable one at the end of final iteration. II. CORDIC ALGORITHM CORDIC offers vector rotations of arbitrary angles, iterative process performed by using only shift and add operations. The Volder algorithm [1], is resulting from the general rotation transform [14] x sin ø + y cos ø = y' (1) x cos ø y sin ø = x' (2) This Cartesian plane rotates by ø angle. ISSN : Vol 5 No 2 Apr-May
2 Fig 1: Vector rotation by ø angle. The above equations can readjusted as: [ y + x tan ø ] cos ø = y' (3) [ x - y tan ø ] cos ø = x' (4) These rotation of angles constrained so tan ø = ±2 -i. This will reduces tangent multiplication by simple shift operation. Another rotation of arbitrary angles can easily accessible by the execution of elementary rotations in simple way. CORDIC, however, it will implement the rotations by a order of micro-rotations by elementary angles (α i ). These are obtained by decomposing ø into elementary rotations in sequence manner: ø =Σ α i (5) By using these we can form simple iterative rotations [y i + x i tan α i ] cos α i = y i+1 (6) [ x i y i tan α i ] cos α i = x i+1 (7) From trigonometric identities we have: cos α i = 1/ (1+tan2 α i ) 1/2 (8) Substituting equation (8) in equation (6) and (7) we have: [ y i + x i tan α i ] / ( 1 + tan2 α i ) 1/2 = y i+1 (9) [ x i y i tan α i ] / (1 + tan2α i ) 1/2 = x i+1 (10) To assure that the tangent multiplication reduced to small shifting operation, the rotation angles obtained from following relation: tan α i = ±2 -i (11) Here i is total number of iteration. And tan α i replaced in above equation Substituting equation (12) in (9) and (10), we have: [ y i + x i.d i. 2 -i ].K i = y i+1 (12) [ x i y i.d i. 2 -i ].K i = x i+1 (13) Here, 1/ (1+2-2i ) 1/ 2 = Ki, denoted as constant scale. di = ±1, it s denoted as decision function. Shift-add algorithm eliminates the constant scale value from yields of obtained equations of vector rotation. Product term K i s is applied in the system. The product value reaches to by using infinite number of iterations. A n denoted as rotation algorithm gain, An = Π [1+2-2i ] 1/2 (14) For infinite iterations, the gain is approximately equal to However gain can be calculated by the help of total number of iterations, and also it depends on composite rotation angle is distinct by sequence of elementary rotations in the directions manner. These sequences denoted as decision vector. And all these vectors used for angular measurement system, based on the values of binary arctangents. Conversions done by using a look-up table between angular system and any other systems. An improved conversion technique uses additional subtract or adder unit, for each iteration it mount up the elementary rotation angles. These angels are expressed by ISSN : Vol 5 No 2 Apr-May
3 convenient angular unit. A small lookup table supplies the angular values, and also we can use hardwired, depending on suitable implementation. Accumulator angle can add the 3 rd value of difference equation to CORDIC: z i α i = Z i+1 z i d i tan -1 (2 -i ) = Z i+1 Thus, only one CORDIC micro-rotation equations can be written as: x i y i. 2 -I.d i = x i+1 y i + x i. 2 -I.d i = y i+1 z i d i tan -1 ( 2 -i ) = z i+1 III.CORDIC MODES Two modes are there in CORDIC. The first one is Rotation mode [15], in this mode input vector value rotated by a specified angle. Second one is Vectoring mode; in this mode input vector rotates to x-axis. A. ROTATION MODE In this mode angle accumulator is set to some preferred rotation angle. Here rotation angle serves as an argument for which we intend to find the trigonometric, hyperbolic or some other transcendental values. Angle accumulator will take care about rotation decision. The decision made at each iteration and evaluated. CORDIC equations in rotation mode are: x i y i. 2 -I.d i = x i+1 y i + x i. 2 -I.d i = y i+1 z i d i tan -1 ( 2 -i ) = z i+1 Here, d i = -1 if z i < 0 +1, else n iterations after it produces following results: z n = 0 [y 0 cosz 0 + x 0 sinz 0 ] An = Y n [x 0 cosz 0 y 0 sinz 0 ] An = X n B. VECTORING MODE In vectoring mode input vector rotates through any angle towards x axis with resultant vector. Scaled magnitude and rotation angle and is the resultant for vectoring operation. The residual vector at each rotation it reduce the y component. y component sign residual used for determining the next rotation direction. Initially angle accumulator is set to zero, it continuous the traversed angle up to the final iterations. A CORDIC equation in vectoring mode follows: x i+1 = x i y i.d i. 2 -i y i+1 = y i + x i.d i. 2 -i z i+1 = z i d i tan -1 ( 2 -i ) Here, di = +1 if yi < 0-1, else n iterations after it produces following results: x n = A n (x 2 0 +y 2 0 ) 1/2 z n = tan -1 (y 0 / x 0 ) +Z 0 y n = 0 IV. CORDIC ARCHITECTURES CORDIC algorithm contains different architectures for mapping into hardware. Normally these are classified into folded and unfolded (figure 1). These operations done by comprehension of 3 iterative equations [14]. First method architecture of folded implemented by copying every difference equations of CORDIC into time multiplexing and hardware. In a single functional unit all these operations are done, so it will provide trading area for speed [16]. It can be classified into two types; those are word-serial and bit-serial architectures. It will check the functional unit implementation logic for the every one bit or word of CORDIC in each iteration. ISSN : Vol 5 No 2 Apr-May
4 Fig: 1 Nomenclature of CORDIC A. FOLDED WORD SERIAL ARCHITECTURE This is done by duplicate the three difference equations in each. This is also called as iterative bit-parallel design [2, 17], the hardware as shown in figure 2. Each block contains a shift unit, subtraction-adder unit block, and one register used for output buffering. Initial values are given to register by the multiplexer for first level calculation. Here z-branch of MSB stored value determines the operation mode for the adder-subtraction unit. X and y outlet Signals passes to block of shift unit and finally subtracted or added to un-shifted signal value in reverse path. Fig:2 Folded Word Serial design The z branch mathematically mixing the registers values, lookup table passes these values, then each number of operations the address value is changed. After n operations output is passes again to register block before primary values are fed in again and these final value can be access as output. Normal FSM needs to control the addressing of the constant values and multiplexers. All the initial values are given hardwired in a word wide manner when it is implemented in FPGA. Both subtracted and adder component are passed out separately. Angle accumulator controls the multiplexer. Routing signals is required to find distinguish between subtraction and addition. For changing the shift distance value shift operations are used, with the no of iterations even it require maximum speed and also high fan-in value for the application [ 3, 4]. Shifters not suitable for FPGA architectures because it wants several layers of logic. Then the resultant shows for large number of logic cells the design is slow. B. FOLDED BIT SERIAL DESIGN In engineering applications we are facing some problems like algebraic and nonlinear equations repeated evaluation in the field of signal processing areas and robotics, graphics in engineering. Complicated equation calculation will take huge time to calculate in software, even though we are using co-processors, and also contain large number transcendental and of nonlinear functions. Two designs of iterative bit-parallel and unrolled shows draw bag in path delays and complexity these are placed between single stages, these are large number of cross connections. Now we are going for bit-serial iterative architecture to reduce the complexity of ISSN : Vol 5 No 2 Apr-May
5 the design. In this process one bit is processed. Then one bit-wide data paths [1] are comes from cross connections. The modified bit serial design logic and interconnect work at high clock rate than bit parallel design. This design model contain 3 shift registers, 3 bit serial subtraction- adder units, and serial ROM. word width length equal to shift register. Also it contain multiplexer block to select the shift registers taps, this is used for a cross terms of right shifted. This architecture is shown in figure 3. Here for n iterations w clock periods are needed. Precision adder is w here. It initializes the x, y and z registers with w clock periods for a load multiplexers. Once data is loaded, then the data is shifted to serial subtraction- adder block and finally return to register in left end. W clock periods require for each and every iteration to return register result value. Fig:3 Folded Bit Serial Design C. UNFOLDED PARALLEL ARCHITECTURE The CORDIC processor discussed above is iterative algorithm, it means processor need to perform n iterations at the given data rate. This is an unfolded operation [17, 18] it means always performs the same iteration at n times processing elements. It shows in figure 4. This will result the value in two simplifications. First one is fixed shifts at shifters; by using wiring we can implement it. Another one based on lookup table. Here angle accumulator distributed the LUT values as constants to each adder; this is chain process in accumulator angle. Instead of using requiring storage space we are using constants, those are hardwired. The whole CORDIC processor can be modified into grouping of subtraction-adder unit in interconnected manner. Now we do not require registers, building of this unrolled processor stringently combinatorial. Finally resulting circuit delay should be substantial; now processing time is decreased compare to iterative circuit. Mostly and particularly in FPGA do not make any sense of using combinatorial large circuit what we required. This design of unrolled processor can be easily pipelined [19].this is done by in-between the subtraction- adder unit block we are inserting registers. More FPGAs already contain registers in each logic cell, so this pipeline registers process do not increase the hardware cost due to already presented registers in the logic block. ISSN : Vol 5 No 2 Apr-May
6 Fig:4 Unfolded Parallel Architecture D. PARALLEL AND PIPELINED ADDERS Pipelining concept mostly used in signal processing applications. If you consider simple example 128- bit adder constructed by using four consecutive 32-bit adders. This parallel adder shown in Figure 5 [20]. Here circuit computation time is almost equal to an 4.T, here T indicated as computation time of each 32-bit adder, now maximum sample rate will be equal to 1/(4.T) of input operands x and y. The pipelined circuit for corresponding data is shown in Figure 6. In this one register placed between the computations resources. These resources are allocated to consecutive cycles, in this way new addition is started when it completes the first cycle of the preceding addition. It is done T seconds. Now latency value is equal to 4.T. Then sample rate of 1/(4.T) is changed to 1/T. Fig: 5 Parallel Adder ISSN : Vol 5 No 2 Apr-May
7 Fig:6 Pipelined Adder Normally basic cell FPGA contain flip flops so pipeline registers insertion do not have necessity to increase the value of total cost, by using basic cells we are computed these values. The flip-flops in pipeline registers are not used in the version of Non-pipelined. V.CONCLUSION The CORDIC splendor is prospective for united solution for hefty set of tasks concerning the computation of multiplication, logarithmic and square-root, division, assessment of transcendental functions and trigonometric, elucidation of linear systems. CORDIC algorithm can be implemented via simple hardware through continual shift-add operations. Computation latency endures to be fore most disadvantage of CORDIC algorithm, ever since we do not have proficient algorithms for its parallel implementation. With enrichment of its throughput and diminution of its latency it is anticipated that CORDIC would be positive for various real-time and highspeed applications. From fast decade, numerous architectures and algorithms have been urbanized to speed up CORDIC algorithm by plummeting its iteration counts by implementation of pipelined architecture. Further way to exploit CORDIC competently, is to go for Redundant Arithmetic. REFERENCES [1] Volder J. E., The CORDIC trigonometric computing technique, IRE Trans. Electronic Computing, Volume EC-8, pp , [2] Walther J. S., A unified algorithm for elementary functions, in Proceedings of the AFIPS Spring Joint Computer Conference, pp , May [3] Walther J. S., The story of Unified CORDIC, Journal of VLSI Signal Processing, vol. 25, no. 2, pp , [4] Andraka R, A survey of CORDIC algorithms for FPGA based computers, FPGA 98, ACM/SIGDA International Symposium on Field Programmable Gate Arrays, pp [5] De Lange A. A. J., Van der Hoeven A. J., Deprettere E. F., and Bu J., Optimal floating-point pipeline CMOS CORDIC processor, Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS 88), vol. 3, pp , June [6] Despain A. M., Fourier transform computers using CORDIC iterations, IEEE Transactions on Computers, vol. 23, no. 10, pp , [7] Ahmed H. M., Delosme J. M., and Morf M., Highly concurrent computing structures for matrix arithmetic and signal processing, Computer, vol. 15, no. 1, pp , [8] Cavallaro J. R. and Luk F. T., CORDIC arithmetic for an SVD processor, Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing, vol. 5, no. 3, pp , ISSN : Vol 5 No 2 Apr-May
8 [9] Lee J. A. and Lang T., SVD by constant-factor-redundant- CORDIC, Proceedings of the 10th IEEE Symposium on Computer Arithmetic, pp , June [10] Meyer A., Watzel R., Meyer U., and Foo S., A parallel CORDIC architecture dedicated to compute the Gaussian potential function in neural networks, Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, vol. 16, no. 7-8, pp , [11] Kang C. Y. and Swartzlander E. E., Digit-pipelined direct digital frequency synthesis based on differential CORDIC, IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I, vol. 53, no. 5, pp , [12] Antelo E., Lang T. and Bruguera J. D., Very-High Radix CORDIC Rotation Based on Selection by Rounding, Journal of VLSI Signal Processing, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, Vol.25, , [13] Delosme M. J.,Lau C. Y. and Hsiao S. F., Redundant Constant-Factor Implementation of Multi-Dimensional CORDIC and Its Application to Complex SVD, Journal of VLSI Signal Processing, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, Volume 25, pp , [14] Choi J. H., Kwak J. H. and Swartzlander, Journal of VLSI Signal Processing, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands, Volume 25, [15] Meggitt J. E., Pseudo division and pseudo multiplication processes IBM Journal, vol. 6, no. 2, pp , [16] Deprettere E., Dewilde P., and Udo R., "Pipelined CORDIC Architecture for Fast VLSI Filtering and Array Processing," Proc. ICASSP'84, 1984, pp. 41.A A.6.4. [17] Lin C. H. and Wu A. Y., Algorithm and Architecture for High-Performance Vector Rotational DSP Applications, Regular IEEE Transactions: Circuits and Systems I, Volume 52, pp , November [18] Erecegovac M. D. and Lang T., Digital Arithmetic, Elsevier, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, [19] Hu Y. H., Pipelined CORDIC architecture for the implementation of rotational based algorithm, in Proceedings of the International Symposium on VLSI Technology, Systems and Applications, p. 259, May [20] De Lange A. A., van der Hoeven A. J., Deprettere E. F., and Bu J., An optimal floating-point pipeline CMOS CORDIC Processor," IEEE ISCAS'88, pp , [21] Burhan Khurshid FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multistage Pipelined Adder Based CORDIC Structure for Large Operand Word Lengths :International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2012] ISSN : Vol 5 No 2 Apr-May
FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multistage Pipelined Adder Based CORDIC Structure for Large Operand Word Lengths
 International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2012] 105 ISSN 2047-3338 FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multistage Pipelined Adder Based CORDIC Structure for
International Journal of Computer Science and Telecommunications [Volume 3, Issue 5, May 2012] 105 ISSN 2047-3338 FPGA Implementation of a High Speed Multistage Pipelined Adder Based CORDIC Structure for
Performance Analysis of CORDIC Architectures Targeted by FPGA Devices
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Performance Analysis of CORDIC Architectures Targeted by FPGA Devices Guddeti Nagarjuna Reddy 1, R.Jayalakshmi 2, Dr.K.Umapathy
International OPEN ACCESS Journal Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Performance Analysis of CORDIC Architectures Targeted by FPGA Devices Guddeti Nagarjuna Reddy 1, R.Jayalakshmi 2, Dr.K.Umapathy
Implementation of Area Efficient Multiplexer Based Cordic
 Implementation of Area Efficient Multiplexer Based Cordic M. Madhava Rao 1, G. Suresh 2 1 M.Tech student M.L.E College, S. Konda, Prakasam (DIST), India 2 Assoc.prof in ECE Department, M.L.E College, S.
Implementation of Area Efficient Multiplexer Based Cordic M. Madhava Rao 1, G. Suresh 2 1 M.Tech student M.L.E College, S. Konda, Prakasam (DIST), India 2 Assoc.prof in ECE Department, M.L.E College, S.
A Modified CORDIC Processor for Specific Angle Rotation based Applications
 IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 4, Issue 2, Ver. II (Mar-Apr. 2014), PP 29-37 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 A Modified CORDIC Processor for Specific Angle Rotation
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 4, Issue 2, Ver. II (Mar-Apr. 2014), PP 29-37 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 A Modified CORDIC Processor for Specific Angle Rotation
High Speed Radix 8 CORDIC Processor
 High Speed Radix 8 CORDIC Processor Smt. J.M.Rudagi 1, Dr. Smt. S.S ubbaraman 2 1 Associate Professor, K.L.E CET, Chikodi, karnataka, India. 2 Professor, W C E Sangli, Maharashtra. 1 js_itti@yahoo.co.in
High Speed Radix 8 CORDIC Processor Smt. J.M.Rudagi 1, Dr. Smt. S.S ubbaraman 2 1 Associate Professor, K.L.E CET, Chikodi, karnataka, India. 2 Professor, W C E Sangli, Maharashtra. 1 js_itti@yahoo.co.in
Implementation of Optimized CORDIC Designs
 IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 3 August 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-6010 Implementation of Optimized CORDIC Designs Bibinu Jacob M Tech Student
IJIRST International Journal for Innovative Research in Science & Technology Volume 1 Issue 3 August 2014 ISSN(online) : 2349-6010 Implementation of Optimized CORDIC Designs Bibinu Jacob M Tech Student
Implementation of CORDIC Algorithms in FPGA
 Summer Project Report Implementation of CORDIC Algorithms in FPGA Sidharth Thomas Suyash Mahar under the guidance of Dr. Bishnu Prasad Das May 2017 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
Summer Project Report Implementation of CORDIC Algorithms in FPGA Sidharth Thomas Suyash Mahar under the guidance of Dr. Bishnu Prasad Das May 2017 Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
FPGA Design, Implementation and Analysis of Trigonometric Generators using Radix 4 CORDIC Algorithm
 International Journal of Microcircuits and Electronic. ISSN 0974-2204 Volume 4, Number 1 (2013), pp. 1-9 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com FPGA Design, Implementation and
International Journal of Microcircuits and Electronic. ISSN 0974-2204 Volume 4, Number 1 (2013), pp. 1-9 International Research Publication House http://www.irphouse.com FPGA Design, Implementation and
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF CORDIC ALGORITHM ARCHITECTURE
 FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF CORDIC ALGORITHM ARCHITECTURE Ramanpreet Kaur 1, Parminder Singh Jassal 2 Department of Electronics And Communication Engineering, Punjabi University Yadavindra College of Engineering,
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF CORDIC ALGORITHM ARCHITECTURE Ramanpreet Kaur 1, Parminder Singh Jassal 2 Department of Electronics And Communication Engineering, Punjabi University Yadavindra College of Engineering,
An Enhanced Mixed-Scaling-Rotation CORDIC algorithm with Weighted Amplifying Factor
 SEAS-WP-2016-10-001 An Enhanced Mixed-Scaling-Rotation CORDIC algorithm with Weighted Amplifying Factor Jaina Mehta jaina.mehta@ahduni.edu.in Pratik Trivedi pratik.trivedi@ahduni.edu.in Serial: SEAS-WP-2016-10-001
SEAS-WP-2016-10-001 An Enhanced Mixed-Scaling-Rotation CORDIC algorithm with Weighted Amplifying Factor Jaina Mehta jaina.mehta@ahduni.edu.in Pratik Trivedi pratik.trivedi@ahduni.edu.in Serial: SEAS-WP-2016-10-001
Low Power and Memory Efficient FFT Architecture Using Modified CORDIC Algorithm
 Low Power and Memory Efficient FFT Architecture Using Modified CORDIC Algorithm 1 A.Malashri, 2 C.Paramasivam 1 PG Student, Department of Electronics and Communication K S Rangasamy College Of Technology,
Low Power and Memory Efficient FFT Architecture Using Modified CORDIC Algorithm 1 A.Malashri, 2 C.Paramasivam 1 PG Student, Department of Electronics and Communication K S Rangasamy College Of Technology,
Realization of Fixed Angle Rotation for Co-Ordinate Rotation Digital Computer
 International Journal of Innovative Research in Electronics and Communications (IJIREC) Volume 2, Issue 1, January 2015, PP 1-7 ISSN 2349-4042 (Print) & ISSN 2349-4050 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Realization
International Journal of Innovative Research in Electronics and Communications (IJIREC) Volume 2, Issue 1, January 2015, PP 1-7 ISSN 2349-4042 (Print) & ISSN 2349-4050 (Online) www.arcjournals.org Realization
Three Dimensional CORDIC with reduced iterations
 Three Dimensional CORDIC with reduced iterations C.T. Clarke and G.R. Nudd Department of Computer Science University of Warwick Coventry CV4 7AL United Kingdom Abstract This paper describes a modification
Three Dimensional CORDIC with reduced iterations C.T. Clarke and G.R. Nudd Department of Computer Science University of Warwick Coventry CV4 7AL United Kingdom Abstract This paper describes a modification
Modified CORDIC Architecture for Fixed Angle Rotation
 International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology EISSN 2277 4106, PISSN 2347 5161 2015INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Binu M
International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology EISSN 2277 4106, PISSN 2347 5161 2015INPRESSCO, All Rights Reserved Available at http://inpressco.com/category/ijcet Research Article Binu M
A CORDIC-BASED METHOD FOR IMPROVING DECIMAL CALCULATIONS
 Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational and Mathematical Methods in Science and Engineering, CMMSE 2008 13 17 June 2008. A CORDIC-BASED METHOD FOR IMPROVING DECIMAL CALCULATIONS Jose-Luis
Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational and Mathematical Methods in Science and Engineering, CMMSE 2008 13 17 June 2008. A CORDIC-BASED METHOD FOR IMPROVING DECIMAL CALCULATIONS Jose-Luis
A CORDIC Algorithm with Improved Rotation Strategy for Embedded Applications
 A CORDIC Algorithm with Improved Rotation Strategy for Embedded Applications Kui-Ting Chen Research Center of Information, Production and Systems, Waseda University, Fukuoka, Japan Email: nore@aoni.waseda.jp
A CORDIC Algorithm with Improved Rotation Strategy for Embedded Applications Kui-Ting Chen Research Center of Information, Production and Systems, Waseda University, Fukuoka, Japan Email: nore@aoni.waseda.jp
Efficient Double-Precision Cosine Generation
 Efficient Double-Precision Cosine Generation Derek Nowrouzezahrai Brian Decker William Bishop dnowrouz@uwaterloo.ca bjdecker@uwaterloo.ca wdbishop@uwaterloo.ca Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Efficient Double-Precision Cosine Generation Derek Nowrouzezahrai Brian Decker William Bishop dnowrouz@uwaterloo.ca bjdecker@uwaterloo.ca wdbishop@uwaterloo.ca Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering
Sine/Cosine using CORDIC Algorithm
 Sine/Cosine using CORDIC Algorithm Prof. Kris Gaj Gaurav Doshi, Hiren Shah Outlines Introduction Basic Idea CORDIC Principles Hardware Implementation FPGA & ASIC Results Conclusion Introduction CORDIC
Sine/Cosine using CORDIC Algorithm Prof. Kris Gaj Gaurav Doshi, Hiren Shah Outlines Introduction Basic Idea CORDIC Principles Hardware Implementation FPGA & ASIC Results Conclusion Introduction CORDIC
Review Article CORDIC Architectures: A Survey
 VLSI Design Volume 2010, Article ID 794891, 19 pages doi:10.1155/2010/794891 Review Article CORDIC Architectures: A Survey B. Lakshmi and A. S. Dhar Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication
VLSI Design Volume 2010, Article ID 794891, 19 pages doi:10.1155/2010/794891 Review Article CORDIC Architectures: A Survey B. Lakshmi and A. S. Dhar Department of Electronics and Electrical Communication
FPGA Implementation of Discrete Fourier Transform Using CORDIC Algorithm
 AMSE JOURNALS-AMSE IIETA publication-2017-series: Advances B; Vol. 60; N 2; pp 332-337 Submitted Apr. 04, 2017; Revised Sept. 25, 2017; Accepted Sept. 30, 2017 FPGA Implementation of Discrete Fourier Transform
AMSE JOURNALS-AMSE IIETA publication-2017-series: Advances B; Vol. 60; N 2; pp 332-337 Submitted Apr. 04, 2017; Revised Sept. 25, 2017; Accepted Sept. 30, 2017 FPGA Implementation of Discrete Fourier Transform
Pipelined Quadratic Equation based Novel Multiplication Method for Cryptographic Applications
 , Vol 7(4S), 34 39, April 204 ISSN (Print): 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Pipelined Quadratic Equation based Novel Multiplication Method for Cryptographic Applications B. Vignesh *, K. P. Sridhar
, Vol 7(4S), 34 39, April 204 ISSN (Print): 0974-6846 ISSN (Online) : 0974-5645 Pipelined Quadratic Equation based Novel Multiplication Method for Cryptographic Applications B. Vignesh *, K. P. Sridhar
Power and Area Optimization for Pipelined CORDIC Processor
 Power and Area Optimization for Pipelined CORDIC Processor Architecture in VLSI G.Sandhya**, Syed Inthiyaz*, Dr. Fazal Noor Basha*** ** (M.Tech VLSI student, Department of ECE, KL University, and Vijayawada)
Power and Area Optimization for Pipelined CORDIC Processor Architecture in VLSI G.Sandhya**, Syed Inthiyaz*, Dr. Fazal Noor Basha*** ** (M.Tech VLSI student, Department of ECE, KL University, and Vijayawada)
ECEn 621 Computer Arithmetic Project #3. CORDIC History
 ECEn 621 Computer Arithmetic Project #3 CORDIC Algorithms Slide #1 CORDIC History Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer Invented in late 1950 s Based on the observation that: if you rotate a unit-length
ECEn 621 Computer Arithmetic Project #3 CORDIC Algorithms Slide #1 CORDIC History Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer Invented in late 1950 s Based on the observation that: if you rotate a unit-length
VHDL Implementation of DIT-FFT using CORDIC
 Available online www.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2015, 2(6): 98-102 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X VHDL Implementation of DIT-FFT using CORDIC M Paavani 1, A
Available online www.ejaet.com European Journal of Advances in Engineering and Technology, 2015, 2(6): 98-102 Research Article ISSN: 2394-658X VHDL Implementation of DIT-FFT using CORDIC M Paavani 1, A
IEEE-754 compliant Algorithms for Fast Multiplication of Double Precision Floating Point Numbers
 International Journal of Research in Computer Science ISSN 2249-8257 Volume 1 Issue 1 (2011) pp. 1-7 White Globe Publications www.ijorcs.org IEEE-754 compliant Algorithms for Fast Multiplication of Double
International Journal of Research in Computer Science ISSN 2249-8257 Volume 1 Issue 1 (2011) pp. 1-7 White Globe Publications www.ijorcs.org IEEE-754 compliant Algorithms for Fast Multiplication of Double
Fast evaluation of nonlinear functions using FPGAs
 Adv. Radio Sci., 6, 233 237, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Advances in Radio Science Fast evaluation of nonlinear functions using FPGAs
Adv. Radio Sci., 6, 233 237, 2008 Author(s) 2008. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License. Advances in Radio Science Fast evaluation of nonlinear functions using FPGAs
FPGA Implementation of the CORDIC Algorithm for Fingerprints Recognition Systems
 FPGA Implementation of the CORDIC Algorithm for Fingerprints Recognition Systems Nihel Neji, Anis Boudabous, Wajdi Kharrat, Nouri Masmoudi University of Sfax, Electronics and Information Technology Laboratory,
FPGA Implementation of the CORDIC Algorithm for Fingerprints Recognition Systems Nihel Neji, Anis Boudabous, Wajdi Kharrat, Nouri Masmoudi University of Sfax, Electronics and Information Technology Laboratory,
Implementation techniques of CORDIC: a review
 Implementation techniques of CORDIC: a review 1 Gadhiya Ravindra B., 2 Prof. Manisha C. Patel 1 PG Scholar, 2 Assistant Professor 1 Instrumentation and Control Department, 1 NL.D. College of Engineering,
Implementation techniques of CORDIC: a review 1 Gadhiya Ravindra B., 2 Prof. Manisha C. Patel 1 PG Scholar, 2 Assistant Professor 1 Instrumentation and Control Department, 1 NL.D. College of Engineering,
International Journal of Innovative and Emerging Research in Engineering. e-issn: p-issn:
 Available online at www.ijiere.com International Journal of Innovative and Emerging Research in Engineering e-issn: 2394-3343 p-issn: 2394-5494 Design and Implementation of FFT Processor using CORDIC Algorithm
Available online at www.ijiere.com International Journal of Innovative and Emerging Research in Engineering e-issn: 2394-3343 p-issn: 2394-5494 Design and Implementation of FFT Processor using CORDIC Algorithm
Fast Evaluation of the Square Root and Other Nonlinear Functions in FPGA
 Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Pre. 20 2008 Fast Evaluation of the Square Root and Other Nonlinear Functions in FPGA Stefan Lachowicz Edith Cowan University Hans-Joerg Pfleiderer
Edith Cowan University Research Online ECU Publications Pre. 20 2008 Fast Evaluation of the Square Root and Other Nonlinear Functions in FPGA Stefan Lachowicz Edith Cowan University Hans-Joerg Pfleiderer
Implementation Of Quadratic Rotation Decomposition Based Recursive Least Squares Algorithm
 157 Implementation Of Quadratic Rotation Decomposition Based Recursive Least Squares Algorithm Manpreet Singh 1, Sandeep Singh Gill 2 1 University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala-India
157 Implementation Of Quadratic Rotation Decomposition Based Recursive Least Squares Algorithm Manpreet Singh 1, Sandeep Singh Gill 2 1 University College of Engineering, Punjabi University, Patiala-India
Introduction to Field Programmable Gate Arrays
 Introduction to Field Programmable Gate Arrays Lecture 2/3 CERN Accelerator School on Digital Signal Processing Sigtuna, Sweden, 31 May 9 June 2007 Javier Serrano, CERN AB-CO-HT Outline Digital Signal
Introduction to Field Programmable Gate Arrays Lecture 2/3 CERN Accelerator School on Digital Signal Processing Sigtuna, Sweden, 31 May 9 June 2007 Javier Serrano, CERN AB-CO-HT Outline Digital Signal
Research Article Design and Implementation of Hybrid CORDIC Algorithm Based on Phase Rotation Estimation for NCO
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation e Scientific World Journal Volume 214, Article ID 897381, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/897381 Research Article Design and Implementation of Hybrid CORDIC Algorithm
Hindawi Publishing Corporation e Scientific World Journal Volume 214, Article ID 897381, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/1.1155/214/897381 Research Article Design and Implementation of Hybrid CORDIC Algorithm
Realization of Hardware Architectures for Householder Transformation based QR Decomposition using Xilinx System Generator Block Sets
 IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 08 February 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Realization of Hardware Architectures for Householder Transformation based QR
IJSTE - International Journal of Science Technology & Engineering Volume 2 Issue 08 February 2016 ISSN (online): 2349-784X Realization of Hardware Architectures for Householder Transformation based QR
ISSN (Online), Volume 1, Special Issue 2(ICITET 15), March 2015 International Journal of Innovative Trends and Emerging Technologies
 VLSI IMPLEMENTATION OF HIGH PERFORMANCE DISTRIBUTED ARITHMETIC (DA) BASED ADAPTIVE FILTER WITH FAST CONVERGENCE FACTOR G. PARTHIBAN 1, P.SATHIYA 2 PG Student, VLSI Design, Department of ECE, Surya Group
VLSI IMPLEMENTATION OF HIGH PERFORMANCE DISTRIBUTED ARITHMETIC (DA) BASED ADAPTIVE FILTER WITH FAST CONVERGENCE FACTOR G. PARTHIBAN 1, P.SATHIYA 2 PG Student, VLSI Design, Department of ECE, Surya Group
HIGH PERFORMANCE QUATERNARY ARITHMETIC LOGIC UNIT ON PROGRAMMABLE LOGIC DEVICE
 International Journal of Advances in Applied Science and Engineering (IJAEAS) ISSN (P): 2348-1811; ISSN (E): 2348-182X Vol. 2, Issue 1, Feb 2015, 01-07 IIST HIGH PERFORMANCE QUATERNARY ARITHMETIC LOGIC
International Journal of Advances in Applied Science and Engineering (IJAEAS) ISSN (P): 2348-1811; ISSN (E): 2348-182X Vol. 2, Issue 1, Feb 2015, 01-07 IIST HIGH PERFORMANCE QUATERNARY ARITHMETIC LOGIC
Design and Analysis of Kogge-Stone and Han-Carlson Adders in 130nm CMOS Technology
 Design and Analysis of Kogge-Stone and Han-Carlson Adders in 130nm CMOS Technology Senthil Ganesh R & R. Kalaimathi 1 Assistant Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering, Info Institute of Engineering,
Design and Analysis of Kogge-Stone and Han-Carlson Adders in 130nm CMOS Technology Senthil Ganesh R & R. Kalaimathi 1 Assistant Professor, Electronics and Communication Engineering, Info Institute of Engineering,
A fast algorithm for coordinate rotation without using transcendental functions
 42 Int'l Conf. Scientific Computing CSC'15 A fast algorithm for coordinate rotation without using transcendental functions Jorge Resa 1, Domingo Cortes 1, and David Navarro 1 1 Instituto Politecnico Nacional
42 Int'l Conf. Scientific Computing CSC'15 A fast algorithm for coordinate rotation without using transcendental functions Jorge Resa 1, Domingo Cortes 1, and David Navarro 1 1 Instituto Politecnico Nacional
Design of FPGA Based Radix 4 FFT Processor using CORDIC
 Design of FPGA Based Radix 4 FFT Processor using CORDIC Chetan Korde 1, Dr. P. Malathi 2, Sudhir N. Shelke 3, Dr. Manish Sharma 4 1,2,4 Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering, DYPCOE,
Design of FPGA Based Radix 4 FFT Processor using CORDIC Chetan Korde 1, Dr. P. Malathi 2, Sudhir N. Shelke 3, Dr. Manish Sharma 4 1,2,4 Department of Electronics and Telecommunication Engineering, DYPCOE,
VLSI ARCHITECTURE FOR NANO WIRE BASED ADVANCED ENCRYPTION STANDARD (AES) WITH THE EFFICIENT MULTIPLICATIVE INVERSE UNIT
 VLSI ARCHITECTURE FOR NANO WIRE BASED ADVANCED ENCRYPTION STANDARD (AES) WITH THE EFFICIENT MULTIPLICATIVE INVERSE UNIT K.Sandyarani 1 and P. Nirmal Kumar 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of ECE, Sathyabama
VLSI ARCHITECTURE FOR NANO WIRE BASED ADVANCED ENCRYPTION STANDARD (AES) WITH THE EFFICIENT MULTIPLICATIVE INVERSE UNIT K.Sandyarani 1 and P. Nirmal Kumar 2 1 Research Scholar, Department of ECE, Sathyabama
Design of a Multiplier Architecture Based on LUT and VHBCSE Algorithm For FIR Filter
 African Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences 9 (1): 53-58, 2017 ISSN 2079-2034 IDOSI Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajbas.2017.53.58 Design of a Multiplier Architecture Based on LUT and VHBCSE Algorithm
African Journal of Basic & Applied Sciences 9 (1): 53-58, 2017 ISSN 2079-2034 IDOSI Publications, 2017 DOI: 10.5829/idosi.ajbas.2017.53.58 Design of a Multiplier Architecture Based on LUT and VHBCSE Algorithm
THE coordinate rotational digital computer (CORDIC)
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 52, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2005 2385 Mixed-Scaling-Rotation CORDIC (MSR-CORDIC) Algorithm and Architecture for High-Performance Vector Rotational
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS I: REGULAR PAPERS, VOL. 52, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2005 2385 Mixed-Scaling-Rotation CORDIC (MSR-CORDIC) Algorithm and Architecture for High-Performance Vector Rotational
DIGITAL ARITHMETIC. Miloš D. Ercegovac Computer Science Department University of California Los Angeles and
 1 DIGITAL ARITHMETIC Miloš D. Ercegovac Computer Science Department University of California Los Angeles and Tomás Lang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California at Irvine
1 DIGITAL ARITHMETIC Miloš D. Ercegovac Computer Science Department University of California Los Angeles and Tomás Lang Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of California at Irvine
Design and Implementation of 3-D DWT for Video Processing Applications
 Design and Implementation of 3-D DWT for Video Processing Applications P. Mohaniah 1, P. Sathyanarayana 2, A. S. Ram Kumar Reddy 3 & A. Vijayalakshmi 4 1 E.C.E, N.B.K.R.IST, Vidyanagar, 2 E.C.E, S.V University
Design and Implementation of 3-D DWT for Video Processing Applications P. Mohaniah 1, P. Sathyanarayana 2, A. S. Ram Kumar Reddy 3 & A. Vijayalakshmi 4 1 E.C.E, N.B.K.R.IST, Vidyanagar, 2 E.C.E, S.V University
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF FLOATING POINT ADDER AND MULTIPLIER UNDER ROUND TO NEAREST
 FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF FLOATING POINT ADDER AND MULTIPLIER UNDER ROUND TO NEAREST SAKTHIVEL Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, Coimbatore Institute of Engineering and Technology Abstract- FPGA is
FPGA IMPLEMENTATION OF FLOATING POINT ADDER AND MULTIPLIER UNDER ROUND TO NEAREST SAKTHIVEL Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, Coimbatore Institute of Engineering and Technology Abstract- FPGA is
Design of a Floating-Point Fused Add-Subtract Unit Using Verilog
 International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1007 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Design of a Floating-Point Fused Add-Subtract Unit Using Verilog Mayank Sharma,
International Journal of Electronics and Computer Science Engineering 1007 Available Online at www.ijecse.org ISSN- 2277-1956 Design of a Floating-Point Fused Add-Subtract Unit Using Verilog Mayank Sharma,
International Journal of Advanced Research in Electrical, Electronics and Instrumentation Engineering
 An Efficient Implementation of Double Precision Floating Point Multiplier Using Booth Algorithm Pallavi Ramteke 1, Dr. N. N. Mhala 2, Prof. P. R. Lakhe M.Tech [IV Sem], Dept. of Comm. Engg., S.D.C.E, [Selukate],
An Efficient Implementation of Double Precision Floating Point Multiplier Using Booth Algorithm Pallavi Ramteke 1, Dr. N. N. Mhala 2, Prof. P. R. Lakhe M.Tech [IV Sem], Dept. of Comm. Engg., S.D.C.E, [Selukate],
ISSN Vol.08,Issue.12, September-2016, Pages:
 ISSN 2348 2370 Vol.08,Issue.12, September-2016, Pages:2273-2277 www.ijatir.org G. DIVYA JYOTHI REDDY 1, V. ROOPA REDDY 2 1 PG Scholar, Dept of ECE, TKR Engineering College, Hyderabad, TS, India, E-mail:
ISSN 2348 2370 Vol.08,Issue.12, September-2016, Pages:2273-2277 www.ijatir.org G. DIVYA JYOTHI REDDY 1, V. ROOPA REDDY 2 1 PG Scholar, Dept of ECE, TKR Engineering College, Hyderabad, TS, India, E-mail:
Xilinx Based Simulation of Line detection Using Hough Transform
 Xilinx Based Simulation of Line detection Using Hough Transform Vijaykumar Kawde 1 Assistant Professor, Department of EXTC Engineering, LTCOE, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India 1 ABSTRACT: In auto focusing
Xilinx Based Simulation of Line detection Using Hough Transform Vijaykumar Kawde 1 Assistant Professor, Department of EXTC Engineering, LTCOE, Navi Mumbai, Maharashtra, India 1 ABSTRACT: In auto focusing
Prachi Sharma 1, Rama Laxmi 2, Arun Kumar Mishra 3 1 Student, 2,3 Assistant Professor, EC Department, Bhabha College of Engineering
 A Review: Design of 16 bit Arithmetic and Logical unit using Vivado 14.7 and Implementation on Basys 3 FPGA Board Prachi Sharma 1, Rama Laxmi 2, Arun Kumar Mishra 3 1 Student, 2,3 Assistant Professor,
A Review: Design of 16 bit Arithmetic and Logical unit using Vivado 14.7 and Implementation on Basys 3 FPGA Board Prachi Sharma 1, Rama Laxmi 2, Arun Kumar Mishra 3 1 Student, 2,3 Assistant Professor,
IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ADAPTIVE FIR FILTER USING HIGH SPEED DISTRIBUTED ARITHMETIC
 IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ADAPTIVE FIR FILTER USING HIGH SPEED DISTRIBUTED ARITHMETIC Thangamonikha.A 1, Dr.V.R.Balaji 2 1 PG Scholar, Department OF ECE, 2 Assitant Professor, Department of ECE 1, 2 Sri Krishna
IMPLEMENTATION OF AN ADAPTIVE FIR FILTER USING HIGH SPEED DISTRIBUTED ARITHMETIC Thangamonikha.A 1, Dr.V.R.Balaji 2 1 PG Scholar, Department OF ECE, 2 Assitant Professor, Department of ECE 1, 2 Sri Krishna
Performance of Constant Addition Using Enhanced Flagged Binary Adder
 Performance of Constant Addition Using Enhanced Flagged Binary Adder Sangeetha A UG Student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam,
Performance of Constant Addition Using Enhanced Flagged Binary Adder Sangeetha A UG Student, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam,
OPTIMIZING THE POWER USING FUSED ADD MULTIPLIER
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 11, November 2014,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology IJCSMC, Vol. 3, Issue. 11, November 2014,
I. Introduction. India; 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering, SRIT, Jabalpur (M.P.
 A Decimal / Binary Multi-operand Adder using a Fast Binary to Decimal Converter-A Review Ruchi Bhatt, Divyanshu Rao, Ravi Mohan 1 M. Tech Scholar, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering,
A Decimal / Binary Multi-operand Adder using a Fast Binary to Decimal Converter-A Review Ruchi Bhatt, Divyanshu Rao, Ravi Mohan 1 M. Tech Scholar, Department of Electronics & Communication Engineering,
Keywords: Fast Fourier Transforms (FFT), Multipath Delay Commutator (MDC), Pipelined Architecture, Radix-2 k, VLSI.
 ww.semargroup.org www.ijvdcs.org ISSN 2322-0929 Vol.02, Issue.05, August-2014, Pages:0294-0298 Radix-2 k Feed Forward FFT Architectures K.KIRAN KUMAR 1, M.MADHU BABU 2 1 PG Scholar, Dept of VLSI & ES,
ww.semargroup.org www.ijvdcs.org ISSN 2322-0929 Vol.02, Issue.05, August-2014, Pages:0294-0298 Radix-2 k Feed Forward FFT Architectures K.KIRAN KUMAR 1, M.MADHU BABU 2 1 PG Scholar, Dept of VLSI & ES,
Fault Tolerant Parallel Filters Based On Bch Codes
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Fault Tolerant Parallel Filters Based On Bch Codes K.Mohana Krishna 1, Mrs.A.Maria Jossy 2 1 Student, M-TECH(VLSI Design) SRM UniversityChennai, India 2 Assistant Professor
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Fault Tolerant Parallel Filters Based On Bch Codes K.Mohana Krishna 1, Mrs.A.Maria Jossy 2 1 Student, M-TECH(VLSI Design) SRM UniversityChennai, India 2 Assistant Professor
A SIMULINK-TO-FPGA MULTI-RATE HIERARCHICAL FIR FILTER DESIGN
 A SIMULINK-TO-FPGA MULTI-RATE HIERARCHICAL FIR FILTER DESIGN Xiaoying Li 1 Fuming Sun 2 Enhua Wu 1, 3 1 University of Macau, Macao, China 2 University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China
A SIMULINK-TO-FPGA MULTI-RATE HIERARCHICAL FIR FILTER DESIGN Xiaoying Li 1 Fuming Sun 2 Enhua Wu 1, 3 1 University of Macau, Macao, China 2 University of Science and Technology Beijing, Beijing, China
PROJECT REPORT IMPLEMENTATION OF LOGARITHM COMPUTATION DEVICE AS PART OF VLSI TOOLS COURSE
 PROJECT REPORT ON IMPLEMENTATION OF LOGARITHM COMPUTATION DEVICE AS PART OF VLSI TOOLS COURSE Project Guide Prof Ravindra Jayanti By Mukund UG3 (ECE) 200630022 Introduction The project was implemented
PROJECT REPORT ON IMPLEMENTATION OF LOGARITHM COMPUTATION DEVICE AS PART OF VLSI TOOLS COURSE Project Guide Prof Ravindra Jayanti By Mukund UG3 (ECE) 200630022 Introduction The project was implemented
Available online at ScienceDirect
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 64 ( 2013 ) 56 64 International Conference On DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING, IConDM 2013 High Precision and High Speed handheld Scientific
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia Engineering 64 ( 2013 ) 56 64 International Conference On DESIGN AND MANUFACTURING, IConDM 2013 High Precision and High Speed handheld Scientific
Low Latency CORDIC Architecture in FFT
 Low Latency CORDIC Architecture in FFT Ms. Nidhin K.V, M.Tech Student, Ms. Meera Thampy, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Electronics & Communication Engineering, SNGCE, Kadayiruppu, Ernakulam, Kerala Abstract
Low Latency CORDIC Architecture in FFT Ms. Nidhin K.V, M.Tech Student, Ms. Meera Thampy, Assistant Professor, Dept. of Electronics & Communication Engineering, SNGCE, Kadayiruppu, Ernakulam, Kerala Abstract
FPGA Implementation of FFT using CORDIC Processor for Fingerprint Application
 FPGA Implementation of FFT using CORDIC Processor for Fingerprint Application Abstract Fingerprint applications are widely used to identify person s authenticity. It is an important part of Biometric system
FPGA Implementation of FFT using CORDIC Processor for Fingerprint Application Abstract Fingerprint applications are widely used to identify person s authenticity. It is an important part of Biometric system
Computations Of Elementary Functions Based On Table Lookup And Interpolation
 RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Computations Of Elementary Functions Based On Table Lookup And Interpolation Syed Aliasgar 1, Dr.V.Thrimurthulu 2, G Dillirani 3 1 Assistant Professor, Dept.of ECE, CREC, Tirupathi,
RESEARCH ARTICLE OPEN ACCESS Computations Of Elementary Functions Based On Table Lookup And Interpolation Syed Aliasgar 1, Dr.V.Thrimurthulu 2, G Dillirani 3 1 Assistant Professor, Dept.of ECE, CREC, Tirupathi,
A Novel Carry-look ahead approach to an Unified BCD and Binary Adder/Subtractor
 A Novel Carry-look ahead approach to an Unified BCD and Binary Adder/Subtractor Abstract Increasing prominence of commercial, financial and internet-based applications, which process decimal data, there
A Novel Carry-look ahead approach to an Unified BCD and Binary Adder/Subtractor Abstract Increasing prominence of commercial, financial and internet-based applications, which process decimal data, there
UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT
 UNIT-III 1 KNREDDY UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT Register Transfer: Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Micro operations Logic
UNIT-III 1 KNREDDY UNIT-III REGISTER TRANSFER LANGUAGE AND DESIGN OF CONTROL UNIT Register Transfer: Register Transfer Language Register Transfer Bus and Memory Transfers Arithmetic Micro operations Logic
COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital
 Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital hardware modules that accomplish a specific information-processing task. Digital systems vary in
Register Transfer and Micro-operations 1. Introduction A digital system is an interconnection of digital hardware modules that accomplish a specific information-processing task. Digital systems vary in
International Journal of Engineering and Techniques - Volume 4 Issue 2, April-2018
 RESEARCH ARTICLE DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF RADIX-16 BOOTH PARTIAL PRODUCT GENERATOR FOR 64-BIT BINARY MULTIPLIERS K.Deepthi 1, Dr.T.Lalith Kumar 2 OPEN ACCESS 1 PG Scholar,Dept. Of ECE,Annamacharya Institute
RESEARCH ARTICLE DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF RADIX-16 BOOTH PARTIAL PRODUCT GENERATOR FOR 64-BIT BINARY MULTIPLIERS K.Deepthi 1, Dr.T.Lalith Kumar 2 OPEN ACCESS 1 PG Scholar,Dept. Of ECE,Annamacharya Institute
Computation of Decimal Transcendental Functions Using the CORDIC Algorithm
 2009 19th IEEE International Symposium on Computer Arithmetic Computation of Decimal Transcendental Functions Using the CORDIC Algorithm Álvaro Vázquez, Julio Villalba and Elisardo Antelo University of
2009 19th IEEE International Symposium on Computer Arithmetic Computation of Decimal Transcendental Functions Using the CORDIC Algorithm Álvaro Vázquez, Julio Villalba and Elisardo Antelo University of
A Binary Floating-Point Adder with the Signed-Digit Number Arithmetic
 Proceedings of the 2007 WSEAS International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications, Gold Coast, Australia, January 17-19, 2007 528 A Binary Floating-Point Adder with the Signed-Digit Number
Proceedings of the 2007 WSEAS International Conference on Computer Engineering and Applications, Gold Coast, Australia, January 17-19, 2007 528 A Binary Floating-Point Adder with the Signed-Digit Number
Available online at ScienceDirect. IERI Procedia 7 (2014 ) Engineering
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect IERI Procedia 7 (2014 ) 21 27 2013 International Conference on Applied Computing, Computer Science, and Computer Engineering Design and Performance
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect IERI Procedia 7 (2014 ) 21 27 2013 International Conference on Applied Computing, Computer Science, and Computer Engineering Design and Performance
A Single/Double Precision Floating-Point Reciprocal Unit Design for Multimedia Applications
 A Single/Double Precision Floating-Point Reciprocal Unit Design for Multimedia Applications Metin Mete Özbilen 1 and Mustafa Gök 2 1 Mersin University, Engineering Faculty, Department of Computer Science,
A Single/Double Precision Floating-Point Reciprocal Unit Design for Multimedia Applications Metin Mete Özbilen 1 and Mustafa Gök 2 1 Mersin University, Engineering Faculty, Department of Computer Science,
DUE to the high computational complexity and real-time
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 15, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 445 A Memory-Efficient Realization of Cyclic Convolution and Its Application to Discrete Cosine Transform Hun-Chen
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS FOR VIDEO TECHNOLOGY, VOL. 15, NO. 3, MARCH 2005 445 A Memory-Efficient Realization of Cyclic Convolution and Its Application to Discrete Cosine Transform Hun-Chen
A proposed efficient architecture for OFDM MIMO systems using SVD
 A proposed efficient architecture for OFDM MIMO systems using SVD Naveen Rathee Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering CMJ University, Shilong Dr.S.C.Gupta Department of Electronics and
A proposed efficient architecture for OFDM MIMO systems using SVD Naveen Rathee Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering CMJ University, Shilong Dr.S.C.Gupta Department of Electronics and
Floating Point Square Root under HUB Format
 Floating Point Square Root under HUB Format Julio Villalba-Moreno Dept. of Computer Architecture University of Malaga Malaga, SPAIN jvillalba@uma.es Javier Hormigo Dept. of Computer Architecture University
Floating Point Square Root under HUB Format Julio Villalba-Moreno Dept. of Computer Architecture University of Malaga Malaga, SPAIN jvillalba@uma.es Javier Hormigo Dept. of Computer Architecture University
Redundant Data Formats for Faster Floating Point Addition. Abstract
 Redundant Data Formats for Faster Floating Point Addition Abstract This paper presents an approach that minimizes the latency of a floating point adder by leaving outputs in a redundant form. As long as
Redundant Data Formats for Faster Floating Point Addition Abstract This paper presents an approach that minimizes the latency of a floating point adder by leaving outputs in a redundant form. As long as
The Serial Commutator FFT
 The Serial Commutator FFT Mario Garrido Gálvez, Shen-Jui Huang, Sau-Gee Chen and Oscar Gustafsson Journal Article N.B.: When citing this work, cite the original article. 2016 IEEE. Personal use of this
The Serial Commutator FFT Mario Garrido Gálvez, Shen-Jui Huang, Sau-Gee Chen and Oscar Gustafsson Journal Article N.B.: When citing this work, cite the original article. 2016 IEEE. Personal use of this
Speed Optimised CORDIC Based Fast Algorithm for DCT
 GRD Journals Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering International Conference on Innovations in Engineering and Technology (ICIET) - 2016 July 2016 e-issn: 2455-5703 Speed Optimised CORDIC
GRD Journals Global Research and Development Journal for Engineering International Conference on Innovations in Engineering and Technology (ICIET) - 2016 July 2016 e-issn: 2455-5703 Speed Optimised CORDIC
Binary Adders. Ripple-Carry Adder
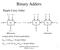 Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Ripple-Carry Adder Binary Adders x n y n x y x y c n FA c n - c 2 FA c FA c s n MSB position Longest delay (Critical-path delay): d c(n) = n d carry = 2n gate delays d s(n-) = (n-) d carry +d sum = 2n
Optimized Design and Implementation of a 16-bit Iterative Logarithmic Multiplier
 Optimized Design and Implementation a 16-bit Iterative Logarithmic Multiplier Laxmi Kosta 1, Jaspreet Hora 2, Rupa Tomaskar 3 1 Lecturer, Department Electronic & Telecommunication Engineering, RGCER, Nagpur,India,
Optimized Design and Implementation a 16-bit Iterative Logarithmic Multiplier Laxmi Kosta 1, Jaspreet Hora 2, Rupa Tomaskar 3 1 Lecturer, Department Electronic & Telecommunication Engineering, RGCER, Nagpur,India,
Fused Floating Point Arithmetic Unit for Radix 2 FFT Implementation
 IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 6, Issue 2, Ver. I (Mar. -Apr. 2016), PP 58-65 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 www.iosrjournals.org Fused Floating Point Arithmetic
IOSR Journal of VLSI and Signal Processing (IOSR-JVSP) Volume 6, Issue 2, Ver. I (Mar. -Apr. 2016), PP 58-65 e-issn: 2319 4200, p-issn No. : 2319 4197 www.iosrjournals.org Fused Floating Point Arithmetic
VLSI Design Of a Novel Pre Encoding Multiplier Using DADDA Multiplier. Guntur(Dt),Pin:522017
 VLSI Design Of a Novel Pre Encoding Multiplier Using DADDA Multiplier 1 Katakam Hemalatha,(M.Tech),Email Id: hema.spark2011@gmail.com 2 Kundurthi Ravi Kumar, M.Tech,Email Id: kundurthi.ravikumar@gmail.com
VLSI Design Of a Novel Pre Encoding Multiplier Using DADDA Multiplier 1 Katakam Hemalatha,(M.Tech),Email Id: hema.spark2011@gmail.com 2 Kundurthi Ravi Kumar, M.Tech,Email Id: kundurthi.ravikumar@gmail.com
Carry Select Adder with High Speed and Power Efficiency
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal ISSN: 2249-6645 Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Carry Select Adder with High Speed and Power Efficiency V P C Reddy, Chenchela V K Reddy 2, V Ravindra Reddy 3 (ECE
International OPEN ACCESS Journal ISSN: 2249-6645 Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Carry Select Adder with High Speed and Power Efficiency V P C Reddy, Chenchela V K Reddy 2, V Ravindra Reddy 3 (ECE
FPGA Implementation of Low-Area Floating Point Multiplier Using Vedic Mathematics
 FPGA Implementation of Low-Area Floating Point Multiplier Using Vedic Mathematics R. Sai Siva Teja 1, A. Madhusudhan 2 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Assistant Professor, Dept of ECE, Anurag Group of Institutions
FPGA Implementation of Low-Area Floating Point Multiplier Using Vedic Mathematics R. Sai Siva Teja 1, A. Madhusudhan 2 1 M.Tech Student, 2 Assistant Professor, Dept of ECE, Anurag Group of Institutions
Baseline V IRAM Trimedia. Cycles ( x 1000 ) N
 CS 252 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE MAY 2000 An Investigation of the QR Decomposition Algorithm on Parallel Architectures Vito Dai and Brian Limketkai Abstract This paper presents an implementation of a QR decomposition
CS 252 COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE MAY 2000 An Investigation of the QR Decomposition Algorithm on Parallel Architectures Vito Dai and Brian Limketkai Abstract This paper presents an implementation of a QR decomposition
Volume 5, Issue 5 OCT 2016
 DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF REDUNDANT BASIS HIGH SPEED FINITE FIELD MULTIPLIERS Vakkalakula Bharathsreenivasulu 1 G.Divya Praneetha 2 1 PG Scholar, Dept of VLSI & ES, G.Pullareddy Eng College,kurnool
DESIGN AND IMPLEMENTATION OF REDUNDANT BASIS HIGH SPEED FINITE FIELD MULTIPLIERS Vakkalakula Bharathsreenivasulu 1 G.Divya Praneetha 2 1 PG Scholar, Dept of VLSI & ES, G.Pullareddy Eng College,kurnool
Design and Implementation of Low-Complexity Redundant Multiplier Architecture for Finite Field
 Design and Implementation of Low-Complexity Redundant Multiplier Architecture for Finite Field Veerraju kaki Electronics and Communication Engineering, India Abstract- In the present work, a low-complexity
Design and Implementation of Low-Complexity Redundant Multiplier Architecture for Finite Field Veerraju kaki Electronics and Communication Engineering, India Abstract- In the present work, a low-complexity
ARITHMETIC operations based on residue number systems
 IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 53, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 133 Improved Memoryless RNS Forward Converter Based on the Periodicity of Residues A. B. Premkumar, Senior Member,
IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 53, NO. 2, FEBRUARY 2006 133 Improved Memoryless RNS Forward Converter Based on the Periodicity of Residues A. B. Premkumar, Senior Member,
FIR Filter Architecture for Fixed and Reconfigurable Applications
 FIR Filter Architecture for Fixed and Reconfigurable Applications Nagajyothi 1,P.Sayannna 2 1 M.Tech student, Dept. of ECE, Sudheer reddy college of Engineering & technology (w), Telangana, India 2 Assosciate
FIR Filter Architecture for Fixed and Reconfigurable Applications Nagajyothi 1,P.Sayannna 2 1 M.Tech student, Dept. of ECE, Sudheer reddy college of Engineering & technology (w), Telangana, India 2 Assosciate
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK DESIGN OF QUATERNARY ADDER FOR HIGH SPEED APPLICATIONS MS. PRITI S. KAPSE 1, DR.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PURE AND APPLIED RESEARCH IN ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY A PATH FOR HORIZING YOUR INNOVATIVE WORK DESIGN OF QUATERNARY ADDER FOR HIGH SPEED APPLICATIONS MS. PRITI S. KAPSE 1, DR.
VLSI Design and Implementation of High Speed and High Throughput DADDA Multiplier
 VLSI Design and Implementation of High Speed and High Throughput DADDA Multiplier U.V.N.S.Suhitha Student Department of ECE, BVC College of Engineering, AP, India. Abstract: The ever growing need for improved
VLSI Design and Implementation of High Speed and High Throughput DADDA Multiplier U.V.N.S.Suhitha Student Department of ECE, BVC College of Engineering, AP, India. Abstract: The ever growing need for improved
VLSI Implementation of Low Power Area Efficient FIR Digital Filter Structures Shaila Khan 1 Uma Sharma 2
 IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 05, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 VLSI Implementation of Low Power Area Efficient FIR Digital Filter Structures Shaila
IJSRD - International Journal for Scientific Research & Development Vol. 3, Issue 05, 2015 ISSN (online): 2321-0613 VLSI Implementation of Low Power Area Efficient FIR Digital Filter Structures Shaila
CORDIC Based FFT for Signal Processing System
 CORDIC Based FFT for Signal Processing System Karthick S1, Priya P2, Valarmathy S3 1 2 Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam, India PG Scholar ME-
CORDIC Based FFT for Signal Processing System Karthick S1, Priya P2, Valarmathy S3 1 2 Assistant Professor, Department of ECE, Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, Sathyamangalam, India PG Scholar ME-
OPTIMIZATION OF AREA COMPLEXITY AND DELAY USING PRE-ENCODED NR4SD MULTIPLIER.
 OPTIMIZATION OF AREA COMPLEXITY AND DELAY USING PRE-ENCODED NR4SD MULTIPLIER. A.Anusha 1 R.Basavaraju 2 anusha201093@gmail.com 1 basava430@gmail.com 2 1 PG Scholar, VLSI, Bharath Institute of Engineering
OPTIMIZATION OF AREA COMPLEXITY AND DELAY USING PRE-ENCODED NR4SD MULTIPLIER. A.Anusha 1 R.Basavaraju 2 anusha201093@gmail.com 1 basava430@gmail.com 2 1 PG Scholar, VLSI, Bharath Institute of Engineering
High Speed Special Function Unit for Graphics Processing Unit
 High Speed Special Function Unit for Graphics Processing Unit Abd-Elrahman G. Qoutb 1, Abdullah M. El-Gunidy 1, Mohammed F. Tolba 1, and Magdy A. El-Moursy 2 1 Electrical Engineering Department, Fayoum
High Speed Special Function Unit for Graphics Processing Unit Abd-Elrahman G. Qoutb 1, Abdullah M. El-Gunidy 1, Mohammed F. Tolba 1, and Magdy A. El-Moursy 2 1 Electrical Engineering Department, Fayoum
Application of LUT Cascades to Numerical Function Generators
 Application of LUT Cascades to Numerical Function Generators T. Sasao J. T. Butler M. D. Riedel Department of Computer Science Department of Electrical Department of Electrical and Electronics and Computer
Application of LUT Cascades to Numerical Function Generators T. Sasao J. T. Butler M. D. Riedel Department of Computer Science Department of Electrical Department of Electrical and Electronics and Computer
Implementation of FFT Processor using Urdhva Tiryakbhyam Sutra of Vedic Mathematics
 Implementation of FFT Processor using Urdhva Tiryakbhyam Sutra of Vedic Mathematics Yojana Jadhav 1, A.P. Hatkar 2 PG Student [VLSI & Embedded system], Dept. of ECE, S.V.I.T Engineering College, Chincholi,
Implementation of FFT Processor using Urdhva Tiryakbhyam Sutra of Vedic Mathematics Yojana Jadhav 1, A.P. Hatkar 2 PG Student [VLSI & Embedded system], Dept. of ECE, S.V.I.T Engineering College, Chincholi,
Implementation of Ripple Carry and Carry Skip Adders with Speed and Area Efficient
 ISSN (Online) : 2278-1021 Implementation of Ripple Carry and Carry Skip Adders with Speed and Area Efficient PUSHPALATHA CHOPPA 1, B.N. SRINIVASA RAO 2 PG Scholar (VLSI Design), Department of ECE, Avanthi
ISSN (Online) : 2278-1021 Implementation of Ripple Carry and Carry Skip Adders with Speed and Area Efficient PUSHPALATHA CHOPPA 1, B.N. SRINIVASA RAO 2 PG Scholar (VLSI Design), Department of ECE, Avanthi
Implementation and Impact of LNS MAC Units in Digital Filter Application
 Implementation and Impact of LNS MAC Units in Digital Filter Application Hari Krishna Raja.V.S *, Christina Jesintha.R * and Harish.I * * Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Sri Shakthi
Implementation and Impact of LNS MAC Units in Digital Filter Application Hari Krishna Raja.V.S *, Christina Jesintha.R * and Harish.I * * Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, Sri Shakthi
Copyright 2007 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE (Proc. SPIE Vol.
 Copyright 2007 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE (Proc. SPIE Vol. 6937, 69370N, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/12.784572 ) and is made
Copyright 2007 Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE (Proc. SPIE Vol. 6937, 69370N, DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1117/12.784572 ) and is made
Design & Analysis of 16 bit RISC Processor Using low Power Pipelining
 International OPEN ACCESS Journal ISSN: 2249-6645 Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Design & Analysis of 16 bit RISC Processor Using low Power Pipelining Yedla Venkanna 148R1D5710 Branch: VLSI ABSTRACT:-
International OPEN ACCESS Journal ISSN: 2249-6645 Of Modern Engineering Research (IJMER) Design & Analysis of 16 bit RISC Processor Using low Power Pipelining Yedla Venkanna 148R1D5710 Branch: VLSI ABSTRACT:-
IMPLEMENTATION OF LOW-COMPLEXITY REDUNDANT MULTIPLIER ARCHITECTURE FOR FINITE FIELD
 IMPLEMENTATION OF LOW-COMPLEXITY REDUNDANT MULTIPLIER ARCHITECTURE FOR FINITE FIELD JyothiLeonoreDake 1,Sudheer Kumar Terlapu 2 and K. Lakshmi Divya 3 1 M.Tech-VLSID,ECE Department, SVECW (Autonomous),Bhimavaram,
IMPLEMENTATION OF LOW-COMPLEXITY REDUNDANT MULTIPLIER ARCHITECTURE FOR FINITE FIELD JyothiLeonoreDake 1,Sudheer Kumar Terlapu 2 and K. Lakshmi Divya 3 1 M.Tech-VLSID,ECE Department, SVECW (Autonomous),Bhimavaram,
