FastSim tutorial for beginners
|
|
|
- Bryce Warren
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 FastSim tutorial for beginners Matteo Rama Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati 1st SuperB Collaboration meeting London, September 2011
2 Part I FastSim overview M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 2
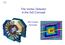
3 Schematic view of FastSim 1 Event Generators 2 EvtGen KK2F Backgrounds Rad. Bhabha e + e - e + e - e + e - neutrons (Geant4) 4 3 Interaction of particles with detector Simplified material x-sections Showering, decay, brems, Voxel-based navigation SimTracks (+SimHits) Configuration data (EDML) Detector geometry Material properties Measurement parameters BaBar Analysis Composite reconstruction Event selection Physics reach evaluation Reco Tracks, Clusters, PID Reconstruction Simulation Parameterized detector response Kalman Filter track fit Hit merging and pat. rec. errors Energy merging and clustering ROOT Tree Output M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 3
4 Physics events Event generation Generators available: Event type e + e - Y(4S) BBbar e + e - qqbar (q=u,d,s,c) e + e - Psi(3770) DDbar e + e - t + t - e + e - m + m - e + e - e + e - (large polar angle) single particles (for det. studies) Generator EvtGen + JETSET Kk2f + tauola Kk2f Bhwide SingleParticle M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 4
5 Backgrounds Backgrounds can be optionally overlapped to the physics event radiative Bhabhas e+e- pairs elastic Bhabhas Event generation Backgrounds particles are generated previously in separate productions and stored in ROOT files Radiative Bhabhas generated with Bruno e+e- pairs and elastic Bhabhas generated with FastSim When FastSim generates the physics event, background particles are overlapped according to their expected rates M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 5
6 Event generation physics event background particles generated previously overlapped event M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 6
7 Event generation From this point on, the simulation makes no distinction between particles from backgrounds and particles from the physics event But NB: particles from the physics event and from background differ for the time distribution. The formers are peaked at t~0 (by definition). overlapped event M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 7
8 Event generation Examples to include backgrounds are in package PacProduction and later in this tutorial. See also overlapped event M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 8
9 Detector simulation cylindrical symmetry detector elements modeled as surface sections cylinders, rings, cones, rectangles configuration via XML (EDML) defines: geometries materials measurement parameters The SuperB detector master file is PacDetector/pacrat_SuperB.xml M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 9
10 from PacDetector/pacrat_SuperB.xml: Detector simulation <!-- the following includes add volumes and elements to the detector, and define the specific measurements and configurations of those detectors. They need to be included in order from the IP outwards --> <include file="pacdetector/ip_superb_shielded.xml" /> <include file="pactrk/si_superb.xml" /> <include file="pactrk/dch_superb.xml" /> <include file="pacemc/pacemcgeom_superb.xml" /> <include file="pacemc/emcbwd_superb.xml" /> <include file="pacdirc/dirc_superb.xml" /> <include file="pacforwardpid/forwardpid_superb.xml" /> <include file="pacemc/emc_superb.xml" /> <include file="pacifr/ifr_superb.xml" /> <include file="pacdetector/machine_superb.xml" /> <!-- generic configuration --> <include file="pactrk/track_reconstruction.xml" /> <include file="pacsim/material_simulation.xml" /> <include file="pacdetector/superbvolume.xml" /> M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 10
11 Example: DCH PacTrk/Dch_SuperB.xml PacTrk/Dch_SuperB_Geom_baseline.xml PacTrk/Dch_SuperB_Measures.xml from PacTrk/ Dch_SuperB_Geom_baseline.xml: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <edml> <included> <define> <constant name="wirezmin" value="-101.5"></constant> <constant name="wirezmax" value="174.9"></constant> </define> <detector> <volume name="drift_tracking"> Example: drift chamber shaped as cylindrical layers of wires and gas inner wall gas wires <cyl name="dchinnercyl" id="101" zmin="wirezmin" zmax="wirezmax" radius="23.60" thick="0.1000" mat="dch-cfiber" /> <cyl name="dch-wires" id="151" zmin="wirezmin" zmax="wirezmax" radius="26.05" thick="0.0120" mat="dch-wires" gap="0.985" /> <cyl name="dch-he-ibu" id="152" zmin="wirezmin" zmax="wirezmax" radius="26.06" thick="1.4300" mat="dch-he-ibu" meas="axial,dchdedx" /> <cyl name="dch-wires" id="153" zmin="wirezmin" zmax="wirezmax" radius="27.24" thick="0.0120" mat="dch-wires" gap="0.986" /> <cyl name="dch-he-ibu" id="154" zmin="wirezmin" zmax="wirezmax" radius="27.25" thick="1.4300" mat="dch-he-ibu" meas="axial,dchdedx" /> <cyl name="dch-wires" id="155" zmin="wirezmin" zmax="wirezmax" radius="28.43" thick="0.0120" mat="dch-wires" gap="0.987" /> Physical properties of materials stored in file database (PacEnv/MaterialsList.data) density, A, Z, radiation/int. lenghts M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 11
12 Example: DCH PacTrk/Dch_SuperB.xml PacTrk/Dch_SuperB_Geom_baseline.xml PacTrk/Dch_SuperB_Measures.xml from PacTrk/ Dch_SuperB_Geom_baseline.xml: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <edml> <included> <define> <constant name="wirezmin" value="-101.5"></constant> <constant name="wirezmax" value="174.9"></constant> </define> <detector> <volume name="drift_tracking"> Example: drift chamber shaped as cylindrical layers of wires and gas inner wall gas wires <cyl name="dchinnercyl" id="101" zmin="wirezmin" zmax="wirezmax" radius="23.60" thick="0.1000" mat="dch-cfiber" /> <cyl name="dch-wires" id="151" zmin="wirezmin" zmax="wirezmax" radius="26.05" thick="0.0120" mat="dch-wires" gap="0.985" /> <cyl name="dch-he-ibu" id="152" zmin="wirezmin" zmax="wirezmax" radius="26.06" thick="1.4300" mat="dch-he-ibu" meas="axial,dchdedx" /> <cyl name="dch-wires" id="153" zmin="wirezmin" zmax="wirezmax" radius="27.24" thick="0.0120" mat="dch-wires" gap="0.986" /> <cyl name="dch-he-ibu" id="154" zmin="wirezmin" zmax="wirezmax" radius="27.25" thick="1.4300" mat="dch-he-ibu" meas="axial,dchdedx" /> <cyl name="dch-wires" id="155" zmin="wirezmin" zmax="wirezmax" radius="28.43" thick="0.0120" mat="dch-wires" gap="0.987" /> from PacTrk/ Dch_SuperB_Measures.xml: parameters defining the cells: sensitive time window, spatial resolution, hit efficiency, cell width, stereo angle <device name="axial" type="driftchamber" sensitivetimewindow="0.5e-6" rms_par0=" " rms_par1="0" rms_par2=" " rms_par3=" " rms_par4=" " rms_par5=" " eff_par0="0.98" eff_par1="0.83" cell_size="1.8" angle="0" /> M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 12
13 Detector simulation 3-dim picture of PacDetector/pacrat_SuperB.xml produced using PacDisplay M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 13
14 Detector simulation 2-dim picture of PacDetector/pacrat_SuperB.xml IFR bwd EMC solenoid barrel EMC DCH SVT fwd EMC ftof beam pipe M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 14
15 From the generated particle to the reconstructed particle step by step M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 15
16 Generated particle x-y view Generated particles are GTracks (or Tparticles) A GTrack represents the particle at its production vertex: 4-momentum (E,p) vertex (t,x) charge Q E,p x t,x helix if Q!=0 straight line if Q=0 M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 16
17 Simulated particle The generated particle is propagated through the detector elements and interacts with the material. x-y view In general the interaction changes the particle momentum. Thus the simulated trajectory is a set of helix pieces (Q!=0) or segment pieces (Q=0) M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 17
18 Simulated particle The intersection between the trajectory and a detector element is represented by a PacSimHit object x-y view A PacSimHit has access to the relevant information related to the hit: (x,t) of the hit p at entrance and at exit type of interaction properties of the detector element etc M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 18
19 Simulated particle The set of PacSimHits and trajectories pieces of a particle is represented by a PacSimTrack object x-y view A PacSimTrack thus represents the simulated particle. It has access to its PacSimHits trajectory pieces original GTrack M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 19
20 Simulated particle The following interaction processes are modeled: x-y view brems photon radiation by electron compt compton scattering, with electron emission - N/A yet - normal adiabatic energy loss and scattering interact hadronic (nuclear) interaction, with destruction of original particle and daughter creation convert photon conversion into e+e- pair M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 20
21 Simulated particle The following interaction processes are modeled x-y view decay electroweak decay shower EM cascade. hadshower hadronic cascade M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 21
22 Simulated particle Depending on the interaction with the material layer a PacSimTrack will stop or continue, and one or more new particles may be created as GTracks. x-y view The new GTracks are propagated through the space and simulated the same way as the original particle. (iterative procedure) M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 22
23 Simulated particle Example: x-y view e+ B e- A g e- The electron emits a bremsstrahlung photon in A and continues with a new p. The photon is generated in A and the corresponding GTrack and PacSimTrack are created. The PacSimTrack stops in B following the conversion to e+e-. Two GTracks for the e+e- pairs are created, and so on e- M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 23
24 Simulated particle Particles can decay. The PacSimTrack stops and the GTracks of the particle daughters are created and propagated as usual. (obviously, neutrinos are ignored ) x-y view m+ n K+ M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 24
25 Reconstructed particle The simulation step (creation of the PacSimTracks) is followed by the reconstruction. x-y view The first step is tracking. Reco hits (PacHitOnTrk) are simulated for each PacSimHit associated to a tracker measurement layer. Si striplets (SVT L0) MAPs (SVT L0) Si microstrips (SVT L1-5) wires axial/stereo (DCH) etc M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 25
26 resolution resolution Reconstructed particle The reco hit position is generated according to an efficiency and resolution function specific to each measurement layer and configurable via EDML. Example: the DCH resolution function x-y view BaBar data FastSim signed distance from wire The reco hit position w.r.t. the true value is determined from a Gaussian distribution whose width is determined from a random sample of the above function (tuned on Babar data). M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 26
27 Reconstructed particle Once the track hits are simulated they are passed to the Babar Kalman filter track fit, which gives the measured track parameters. x-y view TrkRecoTrk The reconstructed track is represented by the TrkRecoTrk class. Hit merging and pattern recognition confusion effects can be taken into account. M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 27
28 Reconstructed particle x-y view Q C, err(q C ), #g(sig), #g(bkg) fdirc quartz bar A PacSimHit associated to the measurement layer of a given detector triggers the corresponding signal reconstruction. For example the simulation of the fdirc includes the measurement of thetac, s(thetac), #signal phot, #bkg photons SuperB subsystems implemented in FastSim: SVT, DCH, fdirc, ftof, barrel/fwd/bwd EMC, IFR Adding new ones is straighforward M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 28
29 Reconstructed particle PacSimHits representing the EM shower >1 discrete interaction within a material layer will start a shower (EM or had depending on the interaction). x-y view fdirc quartz bar EMC The barrel EMC is simplified as set of cylindrical layers: crystals are not modeled individually. Energy loss distributed according to the shower profile over a grid representing the crystal segmentation Fluctuations included The EMC clusters reconstruction is not trivial M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 29
30 Reconstructed particle PacMC/src/PmcReconstructionSequence.cc M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 30
31 tracking from fastsim to the event analysis fdirc BtaCandidate Composition/ vertexing tools Analysis EMC IFR M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 31
32 Analysis tools Set of tools inherited from Babar Vertexing/composition tools, ntuple maker, Others are being developed for SuperB A few examples in the practical tutorial SuperB documentation has holes Important task. Volunteers needed. Plan to use/adapt Babar documentation. M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 32
33 a personal special thank to David Brown master of Babar code and core Fastsim M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 33
34 FastSim User Guide M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 34
35 Part II Tutorial M. Rama - 1st SuperB Collaboration Meeting QMUL - 35
DCH and SVT studies with FastSim. Matteo Rama Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati
 DCH and SVT studies with FastSim Matteo Rama Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati 17 June 2009 Configurations I Start with the current configuration in FastSim (default config. in the following) DCH 10 SuperLayers
DCH and SVT studies with FastSim Matteo Rama Laboratori Nazionali di Frascati 17 June 2009 Configurations I Start with the current configuration in FastSim (default config. in the following) DCH 10 SuperLayers
PXD Simulation and Optimisation Studies
 PXD Simulation and Optimisation Studies Z. Drásal, A. Moll, K. Prothmann with special thanks to: C. Kiesling, A. Raspereza, Prague people Charles University Prague MPI Munich ILC Software Framework Summary
PXD Simulation and Optimisation Studies Z. Drásal, A. Moll, K. Prothmann with special thanks to: C. Kiesling, A. Raspereza, Prague people Charles University Prague MPI Munich ILC Software Framework Summary
First studies in the detector geometry working group
 First studies in the detector geometry working group Matteo Rama - INFN Lab. Nazionali Frascati Achille Stocchi - LAL, Orsay for the Detector Geometry working group SuperB meeting, Orsay, Feb. 2009 detector
First studies in the detector geometry working group Matteo Rama - INFN Lab. Nazionali Frascati Achille Stocchi - LAL, Orsay for the Detector Geometry working group SuperB meeting, Orsay, Feb. 2009 detector
05/09/07 CHEP2007 Stefano Spataro. Simulation and Event Reconstruction inside the PandaRoot Framework. Stefano Spataro. for the collaboration
 for the collaboration Overview Introduction on Panda Structure of the framework Event generation Detector implementation Reconstruction The Panda experiment AntiProton Annihilations at Darmstadt Multi
for the collaboration Overview Introduction on Panda Structure of the framework Event generation Detector implementation Reconstruction The Panda experiment AntiProton Annihilations at Darmstadt Multi
Charged Particle Tracking at Cornell: Gas Detectors and Event Reconstruction
 Charged Particle Tracking at Cornell: Gas Detectors and Event Reconstruction Dan Peterson, Cornell University The Cornell group has constructed, operated and maintained the charged particle tracking detectors
Charged Particle Tracking at Cornell: Gas Detectors and Event Reconstruction Dan Peterson, Cornell University The Cornell group has constructed, operated and maintained the charged particle tracking detectors
Track reconstruction for the Mu3e experiment based on a novel Multiple Scattering fit Alexandr Kozlinskiy (Mainz, KPH) for the Mu3e collaboration
 Track reconstruction for the Mu3e experiment based on a novel Multiple Scattering fit Alexandr Kozlinskiy (Mainz, KPH) for the Mu3e collaboration CTD/WIT 2017 @ LAL-Orsay Mu3e Experiment Mu3e Experiment:
Track reconstruction for the Mu3e experiment based on a novel Multiple Scattering fit Alexandr Kozlinskiy (Mainz, KPH) for the Mu3e collaboration CTD/WIT 2017 @ LAL-Orsay Mu3e Experiment Mu3e Experiment:
Klaus Dehmelt EIC Detector R&D Weekly Meeting November 28, 2011 GEM SIMULATION FRAMEWORK
 Klaus Dehmelt EIC Detector R&D Weekly Meeting November 28, 2011 GEM SIMULATION FRAMEWORK Overview GEM Simulation Framework in the context of Simulation Studies for a High Resolution Time Projection Chamber
Klaus Dehmelt EIC Detector R&D Weekly Meeting November 28, 2011 GEM SIMULATION FRAMEWORK Overview GEM Simulation Framework in the context of Simulation Studies for a High Resolution Time Projection Chamber
Charged Particle Tracking at Cornell: Gas Detectors and Event Reconstruction
 Charged Particle Tracking at Cornell: Gas Detectors and Event Reconstruction Dan Peterson, Cornell University The Cornell group has constructed, operated and maintained the charged particle tracking detectors
Charged Particle Tracking at Cornell: Gas Detectors and Event Reconstruction Dan Peterson, Cornell University The Cornell group has constructed, operated and maintained the charged particle tracking detectors
The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment. Conference Report. Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland
 Available on CMS information server CMS CR -2008/100 The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland 02 December 2008 (v2, 03 December 2008)
Available on CMS information server CMS CR -2008/100 The Compact Muon Solenoid Experiment Conference Report Mailing address: CMS CERN, CH-1211 GENEVA 23, Switzerland 02 December 2008 (v2, 03 December 2008)
8.882 LHC Physics. Track Reconstruction and Fitting. [Lecture 8, March 2, 2009] Experimental Methods and Measurements
![8.882 LHC Physics. Track Reconstruction and Fitting. [Lecture 8, March 2, 2009] Experimental Methods and Measurements 8.882 LHC Physics. Track Reconstruction and Fitting. [Lecture 8, March 2, 2009] Experimental Methods and Measurements](/thumbs/84/91007011.jpg) 8.882 LHC Physics Experimental Methods and Measurements Track Reconstruction and Fitting [Lecture 8, March 2, 2009] Organizational Issues Due days for the documented analyses project 1 is due March 12
8.882 LHC Physics Experimental Methods and Measurements Track Reconstruction and Fitting [Lecture 8, March 2, 2009] Organizational Issues Due days for the documented analyses project 1 is due March 12
Muon Reconstruction and Identification in CMS
 Muon Reconstruction and Identification in CMS Marcin Konecki Institute of Experimental Physics, University of Warsaw, Poland E-mail: marcin.konecki@gmail.com An event reconstruction at LHC is a challenging
Muon Reconstruction and Identification in CMS Marcin Konecki Institute of Experimental Physics, University of Warsaw, Poland E-mail: marcin.konecki@gmail.com An event reconstruction at LHC is a challenging
Cut per region. Marc Verderi GEANT4 collaboration meeting 01/10/2002
 Cut per region Marc Verderi GEANT4 collaboration meeting 01/10/2002 Introduction Cut here = «production threshold»; Not tracking cut; GEANT4 originally designed to allow a unique cut in range; Unique cut
Cut per region Marc Verderi GEANT4 collaboration meeting 01/10/2002 Introduction Cut here = «production threshold»; Not tracking cut; GEANT4 originally designed to allow a unique cut in range; Unique cut
π ± Charge Exchange Cross Section on Liquid Argon
 π ± Charge Exchange Cross Section on Liquid Argon Kevin Nelson REU Program, College of William and Mary Mike Kordosky College of William and Mary, Physics Dept. August 5, 2016 Abstract The observation
π ± Charge Exchange Cross Section on Liquid Argon Kevin Nelson REU Program, College of William and Mary Mike Kordosky College of William and Mary, Physics Dept. August 5, 2016 Abstract The observation
GEANT4 is used for simulating: RICH testbeam data, HCAL testbeam data. GAUSS Project: LHCb Simulation using GEANT4 with GAUDI.
 Status of GEANT4 in LHCb S. Easo, RAL, 30-9-2002 The LHCbexperiment. GEANT4 is used for simulating: RICH testbeam data, HCAL testbeam data. GAUSS Project: LHCb Simulation using GEANT4 with GAUDI. Summary.
Status of GEANT4 in LHCb S. Easo, RAL, 30-9-2002 The LHCbexperiment. GEANT4 is used for simulating: RICH testbeam data, HCAL testbeam data. GAUSS Project: LHCb Simulation using GEANT4 with GAUDI. Summary.
Electron and Photon Reconstruction and Identification with the ATLAS Detector
 Electron and Photon Reconstruction and Identification with the ATLAS Detector IPRD10 S12 Calorimetry 7th-10th June 2010 Siena, Italy Marine Kuna (CPPM/IN2P3 Univ. de la Méditerranée) on behalf of the ATLAS
Electron and Photon Reconstruction and Identification with the ATLAS Detector IPRD10 S12 Calorimetry 7th-10th June 2010 Siena, Italy Marine Kuna (CPPM/IN2P3 Univ. de la Méditerranée) on behalf of the ATLAS
Detector Response Simulation
 Simulating the Silicon Detector Norman Graf SLAC March 17, 2005 Detector Response Simulation Use Geant4 toolkit to describe interaction of particles with matter. Thin layer of LC-specific C++ provides
Simulating the Silicon Detector Norman Graf SLAC March 17, 2005 Detector Response Simulation Use Geant4 toolkit to describe interaction of particles with matter. Thin layer of LC-specific C++ provides
Physics and Detector Simulations. Norman Graf (SLAC) 2nd ECFA/DESY Workshop September 24, 2000
 Physics and Detector Simulations Norman Graf (SLAC) 2nd ECFA/DESY Workshop September 24, 2000 Simulation studies for a future Linear Collider We believe that the physics case for the LC has been made.
Physics and Detector Simulations Norman Graf (SLAC) 2nd ECFA/DESY Workshop September 24, 2000 Simulation studies for a future Linear Collider We believe that the physics case for the LC has been made.
Performance of the GlueX Detector Systems
 Performance of the GlueX Detector Systems GlueX-doc-2775 Gluex Collaboration August 215 Abstract This document summarizes the status of calibration and performance of the GlueX detector as of summer 215.
Performance of the GlueX Detector Systems GlueX-doc-2775 Gluex Collaboration August 215 Abstract This document summarizes the status of calibration and performance of the GlueX detector as of summer 215.
Tracking and Vertexing in 3D B-field
 Tracking and Vertexing in 3D B-field Norman Graf (SLAC) HPS Collaboration Meeting, JLab October 26, 2015 Track Extrapolation At the heart of both track and vertex fitting in the presence of a non-uniform
Tracking and Vertexing in 3D B-field Norman Graf (SLAC) HPS Collaboration Meeting, JLab October 26, 2015 Track Extrapolation At the heart of both track and vertex fitting in the presence of a non-uniform
Update of the BESIII Event Display System
 Update of the BESIII Event Display System Shuhui Huang, Zhengyun You Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, 510275, China E-mail: huangshh28@mail2.sysu.edu.cn, youzhy5@mail.sysu.edu.cn Abstract. The BESIII
Update of the BESIII Event Display System Shuhui Huang, Zhengyun You Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, 510275, China E-mail: huangshh28@mail2.sysu.edu.cn, youzhy5@mail.sysu.edu.cn Abstract. The BESIII
Updated impact parameter resolutions of the ATLAS Inner Detector
 Updated impact parameter resolutions of the ATLAS Inner Detector ATLAS Internal Note Inner Detector 27.09.2000 ATL-INDET-2000-020 06/10/2000 Szymon Gadomski, CERN 1 Abstract The layout of the ATLAS pixel
Updated impact parameter resolutions of the ATLAS Inner Detector ATLAS Internal Note Inner Detector 27.09.2000 ATL-INDET-2000-020 06/10/2000 Szymon Gadomski, CERN 1 Abstract The layout of the ATLAS pixel
PoS(High-pT physics09)036
 Triggering on Jets and D 0 in HLT at ALICE 1 University of Bergen Allegaten 55, 5007 Bergen, Norway E-mail: st05886@alf.uib.no The High Level Trigger (HLT) of the ALICE experiment is designed to perform
Triggering on Jets and D 0 in HLT at ALICE 1 University of Bergen Allegaten 55, 5007 Bergen, Norway E-mail: st05886@alf.uib.no The High Level Trigger (HLT) of the ALICE experiment is designed to perform
CMS Conference Report
 Available on CMS information server CMS CR 2005/021 CMS Conference Report 29 Septemebr 2005 Track and Vertex Reconstruction with the CMS Detector at LHC S. Cucciarelli CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract
Available on CMS information server CMS CR 2005/021 CMS Conference Report 29 Septemebr 2005 Track and Vertex Reconstruction with the CMS Detector at LHC S. Cucciarelli CERN, Geneva, Switzerland Abstract
MIP Reconstruction Techniques and Minimum Spanning Tree Clustering
 SLAC-PUB-11359 July 25 MIP Reconstruction Techniques and Minimum Spanning Tree Clustering Wolfgang F. Mader The University of Iowa, 23 Van Allen Hall, 52242 Iowa City, IA The development of a tracking
SLAC-PUB-11359 July 25 MIP Reconstruction Techniques and Minimum Spanning Tree Clustering Wolfgang F. Mader The University of Iowa, 23 Van Allen Hall, 52242 Iowa City, IA The development of a tracking
Performance of the ATLAS Inner Detector at the LHC
 Performance of the ALAS Inner Detector at the LHC hijs Cornelissen for the ALAS Collaboration Bergische Universität Wuppertal, Gaußstraße 2, 4297 Wuppertal, Germany E-mail: thijs.cornelissen@cern.ch Abstract.
Performance of the ALAS Inner Detector at the LHC hijs Cornelissen for the ALAS Collaboration Bergische Universität Wuppertal, Gaußstraße 2, 4297 Wuppertal, Germany E-mail: thijs.cornelissen@cern.ch Abstract.
Track reconstruction with the CMS tracking detector
 Track reconstruction with the CMS tracking detector B. Mangano (University of California, San Diego) & O.Gutsche (Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory) Overview The challenges The detector Track reconstruction
Track reconstruction with the CMS tracking detector B. Mangano (University of California, San Diego) & O.Gutsche (Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory) Overview The challenges The detector Track reconstruction
SiD VXD Conceptual Design Su Dong SLAC
 SiD VXD Conceptual Design Su Dong SLAC Aug/23/05 Su Dong Snowmass 05 VTX WG: SiD VXD conceptual Design 1 Common Design Features Like other detector concepts, SiD VXD design is open to all sensor technology
SiD VXD Conceptual Design Su Dong SLAC Aug/23/05 Su Dong Snowmass 05 VTX WG: SiD VXD conceptual Design 1 Common Design Features Like other detector concepts, SiD VXD design is open to all sensor technology
Topics for the TKR Software Review Tracy Usher, Leon Rochester
 Topics for the TKR Software Review Tracy Usher, Leon Rochester Progress in reconstruction Reconstruction short-term plans Simulation Calibration issues Balloon-specific support Personnel and Schedule TKR
Topics for the TKR Software Review Tracy Usher, Leon Rochester Progress in reconstruction Reconstruction short-term plans Simulation Calibration issues Balloon-specific support Personnel and Schedule TKR
ALICE tracking system
 ALICE tracking system Marian Ivanov, GSI Darmstadt, on behalf of the ALICE Collaboration Third International Workshop for Future Challenges in Tracking and Trigger Concepts 1 Outlook Detector description
ALICE tracking system Marian Ivanov, GSI Darmstadt, on behalf of the ALICE Collaboration Third International Workshop for Future Challenges in Tracking and Trigger Concepts 1 Outlook Detector description
Update of the BESIII Event Display System
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Update of the BESIII Event Display System To cite this article: Shuhui Huang and Zhengyun You 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1085 042027 View the article
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Update of the BESIII Event Display System To cite this article: Shuhui Huang and Zhengyun You 2018 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 1085 042027 View the article
A New Segment Building Algorithm for the Cathode Strip Chambers in the CMS Experiment
 EPJ Web of Conferences 108, 02023 (2016) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 201610802023 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 A New Segment Building Algorithm for the Cathode Strip Chambers in the
EPJ Web of Conferences 108, 02023 (2016) DOI: 10.1051/ epjconf/ 201610802023 C Owned by the authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2016 A New Segment Building Algorithm for the Cathode Strip Chambers in the
Work in Tbilisi. David Mchedlishvili (SMART EDM_lab of TSU) GGSWBS , Tbilisi. Shota Rustaveli National Science Foundation
 Mitglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft David Mchedlishvili (SMART EDM_lab of TSU) Work in Tbilisi GGSWBS 18 23.08.2018, Tbilisi JEDI: Charged-Particle EDM Search Main principle: Inject polarized particles
Mitglied der Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft David Mchedlishvili (SMART EDM_lab of TSU) Work in Tbilisi GGSWBS 18 23.08.2018, Tbilisi JEDI: Charged-Particle EDM Search Main principle: Inject polarized particles
Cluster errors and Truth information Algorithms
 Cluster errors and Truth information Algorithms Mikael Berggren 1 1 DESY, Hamburg ILD Software Workshop, DESY-HH, Feb 22-26, 2016 Mikael Berggren (DESY-HH) Truth Algorithms ILD SWWS, Feb 2016 1 / 14 Cluster
Cluster errors and Truth information Algorithms Mikael Berggren 1 1 DESY, Hamburg ILD Software Workshop, DESY-HH, Feb 22-26, 2016 Mikael Berggren (DESY-HH) Truth Algorithms ILD SWWS, Feb 2016 1 / 14 Cluster
TPC Detector Response Simulation and Track Reconstruction
 TPC Detector Response Simulation and Track Reconstruction Physics goals at the Linear Collider drive the detector performance goals: charged particle track reconstruction resolution: δ reconstruction efficiency:
TPC Detector Response Simulation and Track Reconstruction Physics goals at the Linear Collider drive the detector performance goals: charged particle track reconstruction resolution: δ reconstruction efficiency:
SoLID GEM Detectors in US
 SoLID GEM Detectors in US Kondo Gnanvo University of Virginia SoLID Collaboration Meeting @ JLab, 08/26/2016 Outline Design Optimization U-V strips readout design Large GEMs for PRad in Hall B Requirements
SoLID GEM Detectors in US Kondo Gnanvo University of Virginia SoLID Collaboration Meeting @ JLab, 08/26/2016 Outline Design Optimization U-V strips readout design Large GEMs for PRad in Hall B Requirements
TPC Detector Response Simulation and Track Reconstruction
 TPC Detector Response Simulation and Track Reconstruction Physics goals at the Linear Collider drive the detector performance goals: charged particle track reconstruction resolution: δ reconstruction efficiency:
TPC Detector Response Simulation and Track Reconstruction Physics goals at the Linear Collider drive the detector performance goals: charged particle track reconstruction resolution: δ reconstruction efficiency:
Performance of FPCCD vertex detector. T. Nagamine Tohoku University Feb 6, 2007 ACFA 9, IHEP,Beijin
 Performance of FPCCD vertex detector T. Nagamine Tohoku University Feb 6, 27 ACFA 9, IHEP,Beijin Outline FPCCD and Vertex Detector Structure Impact Parameter Resolution Pair Background in Vertex Detector
Performance of FPCCD vertex detector T. Nagamine Tohoku University Feb 6, 27 ACFA 9, IHEP,Beijin Outline FPCCD and Vertex Detector Structure Impact Parameter Resolution Pair Background in Vertex Detector
Simulation and Physics Studies for SiD. Norman Graf (for the Simulation & Reconstruction Team)
 Simulation and Physics Studies for SiD Norman Graf (for the Simulation & Reconstruction Team) SLAC DOE Program Review June 13, 2007 Linear Collider Detector Environment Detectors designed to exploit the
Simulation and Physics Studies for SiD Norman Graf (for the Simulation & Reconstruction Team) SLAC DOE Program Review June 13, 2007 Linear Collider Detector Environment Detectors designed to exploit the
ATLAS ITk Layout Design and Optimisation
 ATLAS ITk Layout Design and Optimisation Noemi Calace noemi.calace@cern.ch On behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration 3rd ECFA High Luminosity LHC Experiments Workshop 3-6 October 2016 Aix-Les-Bains Overview
ATLAS ITk Layout Design and Optimisation Noemi Calace noemi.calace@cern.ch On behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration 3rd ECFA High Luminosity LHC Experiments Workshop 3-6 October 2016 Aix-Les-Bains Overview
Deeply Virtual Compton Scattering at Jefferson Lab
 Deeply Virtual Compton Scattering at Jefferson Lab June 16-17, 2016 Frederic Georges (PhD student) PhD Supervisor: Carlos Muñoz Camacho Institut de Physique Nucléaire d Orsay CNRS-IN2P3 Université Paris-Sud,
Deeply Virtual Compton Scattering at Jefferson Lab June 16-17, 2016 Frederic Georges (PhD student) PhD Supervisor: Carlos Muñoz Camacho Institut de Physique Nucléaire d Orsay CNRS-IN2P3 Université Paris-Sud,
TPC Detector Response Simulation and Track Reconstruction
 TPC Detector Response Simulation and Track Reconstruction Physics goals at the Linear Collider drive the detector performance goals: charged particle track reconstruction resolution: δ(1/p)= ~ 4 x 10-5
TPC Detector Response Simulation and Track Reconstruction Physics goals at the Linear Collider drive the detector performance goals: charged particle track reconstruction resolution: δ(1/p)= ~ 4 x 10-5
DD4hep Based Event Reconstruction
 CLICdp-Conf-2017-002 06 February 2017 DD4hep Based Event Reconstruction Andre Sailer, Markus Frank, Frank Gaede, Daniel Hynds, Shaojun Lu, Nikiforos Nikiforou, Marko Petric, Rosa Simoniello, Georgios Voutsinas
CLICdp-Conf-2017-002 06 February 2017 DD4hep Based Event Reconstruction Andre Sailer, Markus Frank, Frank Gaede, Daniel Hynds, Shaojun Lu, Nikiforos Nikiforou, Marko Petric, Rosa Simoniello, Georgios Voutsinas
Muon Software Tutorial. Rick Wilkinson Caltech
 Muon Software Tutorial Rick Wilkinson Caltech The Basics Q: Is there a Muon class? A : No. A muon is just a RecTrack, the same class as the Tracker uses. Q: What information can I get from a RecTrack?
Muon Software Tutorial Rick Wilkinson Caltech The Basics Q: Is there a Muon class? A : No. A muon is just a RecTrack, the same class as the Tracker uses. Q: What information can I get from a RecTrack?
TPC digitization and track reconstruction: efficiency dependence on noise
 TPC digitization and track reconstruction: efficiency dependence on noise Daniel Peterson, Cornell University, DESY, May-2007 A study of track reconstruction efficiency in a TPC using simulation of the
TPC digitization and track reconstruction: efficiency dependence on noise Daniel Peterson, Cornell University, DESY, May-2007 A study of track reconstruction efficiency in a TPC using simulation of the
Introduction. Bill Cooper LDC Meeting May 25,
 The Vertex Detector in the SiD Concept Bill Cooper Fermilab (Layer 1) (Layer 5) VXD Introduction SiD is a closely integrated detector. Designs of the outer tracker and the vertex detector have been developed
The Vertex Detector in the SiD Concept Bill Cooper Fermilab (Layer 1) (Layer 5) VXD Introduction SiD is a closely integrated detector. Designs of the outer tracker and the vertex detector have been developed
An important feature of CLEO III track finding is the diagnostics package providing information on the conditions encountered & decisions met in selec
 CLEO III track finding uses cell level information in the initial phase, does not depend on intrinsic device resolution, is ideal for high (radial) density, low precision, information. CLEO III track finding
CLEO III track finding uses cell level information in the initial phase, does not depend on intrinsic device resolution, is ideal for high (radial) density, low precision, information. CLEO III track finding
PoS(Baldin ISHEPP XXII)134
 Implementation of the cellular automaton method for track reconstruction in the inner tracking system of MPD at NICA, G.A. Ososkov and A.I. Zinchenko Joint Institute of Nuclear Research, 141980 Dubna,
Implementation of the cellular automaton method for track reconstruction in the inner tracking system of MPD at NICA, G.A. Ososkov and A.I. Zinchenko Joint Institute of Nuclear Research, 141980 Dubna,
Charged Particle Reconstruction in HIC Detectors
 Charged Particle Reconstruction in HIC Detectors Ralf-Arno Tripolt, Qiyan Li [http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/marienburg_(mosel)] H-QM Lecture Week on Introduction to Heavy Ion Physics Kloster Marienburg/Mosel,
Charged Particle Reconstruction in HIC Detectors Ralf-Arno Tripolt, Qiyan Li [http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/marienburg_(mosel)] H-QM Lecture Week on Introduction to Heavy Ion Physics Kloster Marienburg/Mosel,
Tracking and Vertex reconstruction at LHCb for Run II
 Tracking and Vertex reconstruction at LHCb for Run II Hang Yin Central China Normal University On behalf of LHCb Collaboration The fifth Annual Conference on Large Hadron Collider Physics, Shanghai, China
Tracking and Vertex reconstruction at LHCb for Run II Hang Yin Central China Normal University On behalf of LHCb Collaboration The fifth Annual Conference on Large Hadron Collider Physics, Shanghai, China
A Topologic Approach to Particle Flow PandoraPFA
 A Topologic Approach to Particle Flow PandoraPFA Mark Thomson University of Cambridge This Talk: Philosophy The Algorithm Some New Results Confusion Conclusions Outlook Cambridge 5/4/06 Mark Thomson 1
A Topologic Approach to Particle Flow PandoraPFA Mark Thomson University of Cambridge This Talk: Philosophy The Algorithm Some New Results Confusion Conclusions Outlook Cambridge 5/4/06 Mark Thomson 1
Studies of the KS and KL lifetimes and
 Studies of the KS and KL lifetimes and BR(K ) with KLOE ± ± + Simona S. Bocchetta* on behalf of the KLOE Collaboration KAON09 Tsukuba June 9th 2009 * INFN and University of Roma Tre Outline DA NE and KLOE
Studies of the KS and KL lifetimes and BR(K ) with KLOE ± ± + Simona S. Bocchetta* on behalf of the KLOE Collaboration KAON09 Tsukuba June 9th 2009 * INFN and University of Roma Tre Outline DA NE and KLOE
ATLAS Tracking Detector Upgrade studies using the Fast Simulation Engine
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS ATLAS Tracking Detector Upgrade studies using the Fast Simulation Engine To cite this article: Noemi Calace et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 664 072005
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS ATLAS Tracking Detector Upgrade studies using the Fast Simulation Engine To cite this article: Noemi Calace et al 2015 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 664 072005
Description and performance of track and primaryvertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker
 Journal of Instrumentation OPEN ACCESS Description and performance of track and primaryvertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker o cite this article: he CMS Collaboration 04 JINS 9 P009 View the article
Journal of Instrumentation OPEN ACCESS Description and performance of track and primaryvertex reconstruction with the CMS tracker o cite this article: he CMS Collaboration 04 JINS 9 P009 View the article
Machine Learning approach to neutrino experiment track reconstruction. Robert Sulej Connecting The Dots / Intelligent Trackers March 2017
 Machine Learning approach to neutrino experiment track reconstruction Robert Sulej Connecting The Dots / Intelligent Trackers 2017 9 March 2017 Aim of the talk Very briefly about physics itself A bit more
Machine Learning approach to neutrino experiment track reconstruction Robert Sulej Connecting The Dots / Intelligent Trackers 2017 9 March 2017 Aim of the talk Very briefly about physics itself A bit more
Direct photon measurements in ALICE. Alexis Mas for the ALICE collaboration
 Direct photon measurements in ALICE Alexis Mas for the ALICE collaboration 1 Outline I - Physics motivations for direct photon measurements II Direct photon measurements in ALICE i - Conversion method
Direct photon measurements in ALICE Alexis Mas for the ALICE collaboration 1 Outline I - Physics motivations for direct photon measurements II Direct photon measurements in ALICE i - Conversion method
PoS(EPS-HEP2017)492. Performance and recent developments of the real-time track reconstruction and alignment of the LHCb detector.
 Performance and recent developments of the real-time track reconstruction and alignment of the LHCb detector. CERN E-mail: agnieszka.dziurda@cern.ch he LHCb detector is a single-arm forward spectrometer
Performance and recent developments of the real-time track reconstruction and alignment of the LHCb detector. CERN E-mail: agnieszka.dziurda@cern.ch he LHCb detector is a single-arm forward spectrometer
HepRep: a Generic Interface Definition for HEP Event Display Representables
 SLAC-PUB-8332 HepRep: a Generic Interface Definition for HEP Event Display Representables J. Perl 1 1 SLAC, Stanford University, California Abstract HepRep, the Generic Interface Definition for HEP Event
SLAC-PUB-8332 HepRep: a Generic Interface Definition for HEP Event Display Representables J. Perl 1 1 SLAC, Stanford University, California Abstract HepRep, the Generic Interface Definition for HEP Event
Alignment of the ATLAS Inner Detector tracking system
 Alignment of the ATLAS Inner Detector tracking system Instituto de Física Corpuscular (IFIC), Centro Mixto UVEG-CSIC, Apdo.22085, ES-46071 Valencia, E-mail: Regina.Moles@ific.uv.es The ATLAS experiment
Alignment of the ATLAS Inner Detector tracking system Instituto de Física Corpuscular (IFIC), Centro Mixto UVEG-CSIC, Apdo.22085, ES-46071 Valencia, E-mail: Regina.Moles@ific.uv.es The ATLAS experiment
ATLAS Dr. C. Lacasta, Dr. C. Marinas
 ATLAS Dr. C. Lacasta, Dr. C. Marinas cmarinas@uni-bonn.de 1 http://www.atlas.ch/multimedia/# Why? In particle physics, the processes occur on a scale that is either too brief or too small to be observed
ATLAS Dr. C. Lacasta, Dr. C. Marinas cmarinas@uni-bonn.de 1 http://www.atlas.ch/multimedia/# Why? In particle physics, the processes occur on a scale that is either too brief or too small to be observed
Fast simulation in ATLAS
 Fast simulation in ATLAS A. Salzburger, CERN for the ATLAS collaboration 1 Simulation load & requirements typical MC campaign in ATLAS 2011 - O( 9) events
Fast simulation in ATLAS A. Salzburger, CERN for the ATLAS collaboration 1 Simulation load & requirements typical MC campaign in ATLAS 2011 - O( 9) events
Disentangling P ANDA s time-based data stream
 Disentangling P ANDA s time-based data stream M. Tiemens on behalf of the PANDA Collaboration KVI - Center For Advanced Radiation Technology, University of Groningen, Zernikelaan 25, 9747 AA Groningen,
Disentangling P ANDA s time-based data stream M. Tiemens on behalf of the PANDA Collaboration KVI - Center For Advanced Radiation Technology, University of Groningen, Zernikelaan 25, 9747 AA Groningen,
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
 Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title A new inner vertex detector for STAR Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/1863684z Authors Wieman, H. Beiser, F.
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory Title A new inner vertex detector for STAR Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/1863684z Authors Wieman, H. Beiser, F.
Status of the DCBA experiment
 Status of the DCBA experiment 9 November, 2016 Hidekazu Kakuno Tokyo Metropolitan University International Workshop on Double Beta Decay and Underground Science, DBD16 Osaka University, JAPAN bb experiments
Status of the DCBA experiment 9 November, 2016 Hidekazu Kakuno Tokyo Metropolitan University International Workshop on Double Beta Decay and Underground Science, DBD16 Osaka University, JAPAN bb experiments
Code characteristics
 The PENELOPE Computer code M.J. Anagnostakis Nuclear Engineering Department National Technical University of Athens The PENELOPE code system PENetration and Energy LOss of Positrons and Electrons in matter
The PENELOPE Computer code M.J. Anagnostakis Nuclear Engineering Department National Technical University of Athens The PENELOPE code system PENetration and Energy LOss of Positrons and Electrons in matter
GLAST tracking reconstruction Status Report
 GLAST collaboration meeting, UCSC June 22-24 1999 GLAST tracking reconstruction Status Report Bill Atwood, Jose A. Hernando, Robert P. Johnson, Hartmut Sadrozinski Naomi Cotton, Dennis Melton University
GLAST collaboration meeting, UCSC June 22-24 1999 GLAST tracking reconstruction Status Report Bill Atwood, Jose A. Hernando, Robert P. Johnson, Hartmut Sadrozinski Naomi Cotton, Dennis Melton University
FAMOS: A Dynamically Configurable System for Fast Simulation and Reconstruction for CMS
 FAMOS: A Dynamically Configurable System for Fast Simulation and Reconstruction for CMS St. Wynhoff Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544, USA Detailed detector simulation and reconstruction of physics
FAMOS: A Dynamically Configurable System for Fast Simulation and Reconstruction for CMS St. Wynhoff Princeton University, Princeton, NJ 08544, USA Detailed detector simulation and reconstruction of physics
Obtainment of Prototypical images and Detector performance simulations. Guillaume Potdevin for the XFEL-HPAD-Consortium
 Obtainment of Prototypical images and Detector performance simulations Overview of the analysis Outlook Prototypical images: Single object imaging & XPCS short presentation (reminder ) Presentation of
Obtainment of Prototypical images and Detector performance simulations Overview of the analysis Outlook Prototypical images: Single object imaging & XPCS short presentation (reminder ) Presentation of
LCDG4 Status. Dhiman Chakraborty, Guilherme Lima, Jeremy McCormick, Vishnu Zutshi. LC Simulations Workshop Argonne, June 02 05, 2004
 LCDG4 Status Dhiman Chakraborty, Guilherme Lima, Jeremy McCormick, Vishnu Zutshi LC Simulations Workshop Argonne, June 02 05, 2004 Outline Overview LCDG4 features XML geometry representation SIO contents
LCDG4 Status Dhiman Chakraborty, Guilherme Lima, Jeremy McCormick, Vishnu Zutshi LC Simulations Workshop Argonne, June 02 05, 2004 Outline Overview LCDG4 features XML geometry representation SIO contents
Optimisation Studies for the CLIC Vertex-Detector Geometry
 CLICdp-Note04-002 4 July 204 Optimisation Studies for the CLIC Vertex-Detector Geometry Niloufar Alipour Tehrani, Philipp Roloff CERN, Switzerland, ETH Zürich, Switzerland Abstract An improved CLIC detector
CLICdp-Note04-002 4 July 204 Optimisation Studies for the CLIC Vertex-Detector Geometry Niloufar Alipour Tehrani, Philipp Roloff CERN, Switzerland, ETH Zürich, Switzerland Abstract An improved CLIC detector
Event reconstruction in STAR
 Chapter 4 Event reconstruction in STAR 4.1 Data aquisition and trigger The STAR data aquisition system (DAQ) [54] receives the input from multiple detectors at different readout rates. The typical recorded
Chapter 4 Event reconstruction in STAR 4.1 Data aquisition and trigger The STAR data aquisition system (DAQ) [54] receives the input from multiple detectors at different readout rates. The typical recorded
3D-Triplet Tracking for LHC and Future High Rate Experiments
 3D-Triplet Tracking for LHC and Future High Rate Experiments André Schöning Physikalisches Institut, Universität Heidelberg Workshop on Intelligent Trackers WIT 2014 University of Pennsylvania May 14-16,
3D-Triplet Tracking for LHC and Future High Rate Experiments André Schöning Physikalisches Institut, Universität Heidelberg Workshop on Intelligent Trackers WIT 2014 University of Pennsylvania May 14-16,
Pattern recognition and event reconstruction in particle physics experiments
 INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Rep. Prog. Phys. 67 (2004) 553 622 REPORTS ON PROGRESS IN PHYSICS PII: S0034-4885(04)04034-5 Pattern recognition and event reconstruction in particle physics experiments
INSTITUTE OF PHYSICS PUBLISHING Rep. Prog. Phys. 67 (2004) 553 622 REPORTS ON PROGRESS IN PHYSICS PII: S0034-4885(04)04034-5 Pattern recognition and event reconstruction in particle physics experiments
Overview of the American Detector Models
 Overview of the American Detector Models Univ. of Oregon The American study groups have investigated two specific models Choosing any particular detector design is a compromise between competing constraints
Overview of the American Detector Models Univ. of Oregon The American study groups have investigated two specific models Choosing any particular detector design is a compromise between competing constraints
GEANT4 Simulation of MOLLER Experiment
 GEANT4 Simulation of MOLLER Experiment Mark Dalton UVa (for Dustin McNulty, Luis Mercado and the MOLLER Collaboration) Outline Introduction to the MOLLER experiment Simulation Overview Spectrometer Design
GEANT4 Simulation of MOLLER Experiment Mark Dalton UVa (for Dustin McNulty, Luis Mercado and the MOLLER Collaboration) Outline Introduction to the MOLLER experiment Simulation Overview Spectrometer Design
CMS Simulation Software
 CMS Simulation Software Dmitry Onoprienko Kansas State University on behalf of the CMS collaboration 10th Topical Seminar on Innovative Particle and Radiation Detectors 1-5 October 2006. Siena, Italy Simulation
CMS Simulation Software Dmitry Onoprienko Kansas State University on behalf of the CMS collaboration 10th Topical Seminar on Innovative Particle and Radiation Detectors 1-5 October 2006. Siena, Italy Simulation
Fast pattern recognition with the ATLAS L1Track trigger for the HL-LHC
 Fast pattern recognition with the ATLAS L1Track trigger for the HL-LHC On behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration Uppsala Universitet E-mail: mikael.martensson@cern.ch ATL-DAQ-PROC-2016-034 09/01/2017 A fast
Fast pattern recognition with the ATLAS L1Track trigger for the HL-LHC On behalf of the ATLAS Collaboration Uppsala Universitet E-mail: mikael.martensson@cern.ch ATL-DAQ-PROC-2016-034 09/01/2017 A fast
EicRoot for tracking R&D studies
 EicRoot for tracking R&D studies Alexander Kiselev EIC Software Meeting Jefferson Lab September,24 2015 Contents of the talk Tracking code implementation in EicRoot Few particular applications: Basic forward
EicRoot for tracking R&D studies Alexander Kiselev EIC Software Meeting Jefferson Lab September,24 2015 Contents of the talk Tracking code implementation in EicRoot Few particular applications: Basic forward
Real-time Analysis with the ALICE High Level Trigger.
 Real-time Analysis with the ALICE High Level Trigger C. Loizides 1,3, V.Lindenstruth 2, D.Röhrich 3, B.Skaali 4, T.Steinbeck 2, R. Stock 1, H. TilsnerK.Ullaland 3, A.Vestbø 3 and T.Vik 4 for the ALICE
Real-time Analysis with the ALICE High Level Trigger C. Loizides 1,3, V.Lindenstruth 2, D.Röhrich 3, B.Skaali 4, T.Steinbeck 2, R. Stock 1, H. TilsnerK.Ullaland 3, A.Vestbø 3 and T.Vik 4 for the ALICE
The Pandora Software Development Kit for. - Particle Flow Calorimetry. Journal of Physics: Conference Series. Related content.
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series The Pandora Software Development Kit for Particle Flow Calorimetry To cite this article: J S Marshall and M A Thomson 2012 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 396 022034 Related
Journal of Physics: Conference Series The Pandora Software Development Kit for Particle Flow Calorimetry To cite this article: J S Marshall and M A Thomson 2012 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 396 022034 Related
Track reconstruction of real cosmic muon events with CMS tracker detector
 Track reconstruction of real cosmic muon events with CMS tracker detector Piergiulio Lenzi a, Chiara Genta a, Boris Mangano b a Università degli Studi di Firenze and Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare
Track reconstruction of real cosmic muon events with CMS tracker detector Piergiulio Lenzi a, Chiara Genta a, Boris Mangano b a Università degli Studi di Firenze and Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare
SVT detector Electronics Status
 SVT detector Electronics Status On behalf of the SVT community Mauro Citterio INFN Milano Overview: - SVT design status - F.E. chips - Electronic design - Hit rates and data volumes 1 SVT Design Detectors:
SVT detector Electronics Status On behalf of the SVT community Mauro Citterio INFN Milano Overview: - SVT design status - F.E. chips - Electronic design - Hit rates and data volumes 1 SVT Design Detectors:
EicRoot software framework
 EicRoot software framework Alexander Kiselev EIC Software Meeting Jefferson Lab September,24 2015 Contents of the talk FairRoot software project EicRoot framework structure Typical EicRoot applications
EicRoot software framework Alexander Kiselev EIC Software Meeting Jefferson Lab September,24 2015 Contents of the talk FairRoot software project EicRoot framework structure Typical EicRoot applications
PANDA EMC Trigger and Data Acquisition Algorithms Development
 PANDA EMC Trigger and Data Acquisition Algorithms Development a,b, Dapeng Jin b, Andreas Kopp a, Wolfgang Kühn a, Jens Sören Lang a, Yutie Liang a, Ming Liu a, Zhen-an Liu b, David Münchow a, Björn Spruck
PANDA EMC Trigger and Data Acquisition Algorithms Development a,b, Dapeng Jin b, Andreas Kopp a, Wolfgang Kühn a, Jens Sören Lang a, Yutie Liang a, Ming Liu a, Zhen-an Liu b, David Münchow a, Björn Spruck
The CLICdp Optimization Process
 ILDOptWS, Feb, 2016 A. Sailer: The CLICdp Optimization Process 1/17 The CLICdp Optimization Process André Sailer (CERN-EP-LCD) On Behalf of the CLICdp Collaboration ILD Software and Optimisation Workshop
ILDOptWS, Feb, 2016 A. Sailer: The CLICdp Optimization Process 1/17 The CLICdp Optimization Process André Sailer (CERN-EP-LCD) On Behalf of the CLICdp Collaboration ILD Software and Optimisation Workshop
for the DESY/ ECFA study detector
 The TPC Tracker for the DESY/ ECFA study detector Ties Behnke DESY 1-May-1999 the TPC tracker requirements from physics a TPC at TESLA: can this work? results from simulation technical issues conclusion
The TPC Tracker for the DESY/ ECFA study detector Ties Behnke DESY 1-May-1999 the TPC tracker requirements from physics a TPC at TESLA: can this work? results from simulation technical issues conclusion
Muon imaging for innovative tomography of large volume and heterogeneous cemented waste packages
 Muon imaging for innovative tomography of large volume and heterogeneous cemented waste packages This project has received funding from the Euratom research and training programme 2014-2018 under grant
Muon imaging for innovative tomography of large volume and heterogeneous cemented waste packages This project has received funding from the Euratom research and training programme 2014-2018 under grant
Full Simulation of Belle & Belle II SVD Detector (within ILC Framework)
 Full Simulation of Belle & Belle II SVD Detector (within ILC Framework) Z. Drásal Charles University in Prague ILC Software Framework Summary Mokka: Geant 4 based, full simulation tool using a realistic
Full Simulation of Belle & Belle II SVD Detector (within ILC Framework) Z. Drásal Charles University in Prague ILC Software Framework Summary Mokka: Geant 4 based, full simulation tool using a realistic
Synrad3D Photon propagation and scattering simulation
 Synrad3D Photon propagation and scattering simulation G. Dugan, D. Sagan CLASSE, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853 USA Abstract As part of the Bmad software library, a program called Synrad3D has been
Synrad3D Photon propagation and scattering simulation G. Dugan, D. Sagan CLASSE, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY 14853 USA Abstract As part of the Bmad software library, a program called Synrad3D has been
Inside-out tracking at CDF
 Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 538 (25) 249 254 www.elsevier.com/locate/nima Inside-out tracking at CDF Christopher Hays a,, Yimei Huang a, Ashutosh V. Kotwal a, Heather K. Gerberich
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A 538 (25) 249 254 www.elsevier.com/locate/nima Inside-out tracking at CDF Christopher Hays a,, Yimei Huang a, Ashutosh V. Kotwal a, Heather K. Gerberich
Locating the neutrino interaction vertex with the help of electronic detectors in the OPERA experiment
 Locating the neutrino interaction vertex with the help of electronic detectors in the OPERA experiment S.Dmitrievsky Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia LNGS seminar, 2015/04/08 Outline
Locating the neutrino interaction vertex with the help of electronic detectors in the OPERA experiment S.Dmitrievsky Joint Institute for Nuclear Research, Dubna, Russia LNGS seminar, 2015/04/08 Outline
Stefania Beolè (Università di Torino e INFN) for the ALICE Collaboration. TIPP Chicago, June 9-14
 ALICE SDD ITS performance with pp and Pb-Pb beams Stefania Beolè (Università di Torino e INFN) for the ALICE Collaboration - Chicago, June 9-14 Inner Tracking System (I) Six layers of silicon detectors
ALICE SDD ITS performance with pp and Pb-Pb beams Stefania Beolè (Università di Torino e INFN) for the ALICE Collaboration - Chicago, June 9-14 Inner Tracking System (I) Six layers of silicon detectors
The Silicon Tracking System: Mechanical Integration and Alignement
 EUDET The Silicon Tracking System: Mechanical Integration and Alignement SiLC Collaboration 12.12.2009 Abstract A brief review of the impact of some of the SiTRA-JRA2 related activities within the EUDET
EUDET The Silicon Tracking System: Mechanical Integration and Alignement SiLC Collaboration 12.12.2009 Abstract A brief review of the impact of some of the SiTRA-JRA2 related activities within the EUDET
Optical Photon Processes
 Optical Photon Processes GEANT4 is an effective and comprehensive tool capable of realistically modeling the optics of scintillation and Cerenkov detectors and their associated light guides. This is founded
Optical Photon Processes GEANT4 is an effective and comprehensive tool capable of realistically modeling the optics of scintillation and Cerenkov detectors and their associated light guides. This is founded
HEP Experiments: Fixed-Target and Collider
 HEP Experiments: Fixed-Target and Collider Beam Beam Beam Target Inelastic collisions 107 109 1011 Signal events 102 10-2 High energy = high density + high rate CBM (FAIR/GSI) Magnet PID ALICE (CERN) TPC
HEP Experiments: Fixed-Target and Collider Beam Beam Beam Target Inelastic collisions 107 109 1011 Signal events 102 10-2 High energy = high density + high rate CBM (FAIR/GSI) Magnet PID ALICE (CERN) TPC
Event Displays and LArg
 Event Displays and LArg Columbia U. / Nevis Labs Slide 1 Introduction Displays are needed in various ways at different stages of the experiment: Software development: understanding offline & trigger algorithms
Event Displays and LArg Columbia U. / Nevis Labs Slide 1 Introduction Displays are needed in various ways at different stages of the experiment: Software development: understanding offline & trigger algorithms
A GEANT4 Simulation of the Derek Glazier University of Edinburgh
 A GEANT4 Simulation of the CrystalBall@MAMI Derek Glazier University of Edinburgh GEANT4 Overview Geant4 is the successor of GEANT3, the world-standard toolkit for HEP detector simulation Geant4 is an
A GEANT4 Simulation of the CrystalBall@MAMI Derek Glazier University of Edinburgh GEANT4 Overview Geant4 is the successor of GEANT3, the world-standard toolkit for HEP detector simulation Geant4 is an
Identification of Shielding Material Configurations Using NMIS Imaging
 Identification of Shielding Material Configurations Using NMIS Imaging B. R. Grogan, J. T. Mihalczo, S. M. McConchie, and J. A. Mullens Oak Ridge National Laboratory, P.O. Box 2008, MS-6010, Oak Ridge,
Identification of Shielding Material Configurations Using NMIS Imaging B. R. Grogan, J. T. Mihalczo, S. M. McConchie, and J. A. Mullens Oak Ridge National Laboratory, P.O. Box 2008, MS-6010, Oak Ridge,
3d-Topological Reconstruction in Liquid Scintillator
 3d-Topological Reconstruction in Liquid Scintillator Presented by Björn Wonsak on behalf of Felix Benckwitz1, Caren Hagner1, Sebastian Lorenz2, David Meyhöfer1, Henning Rebber1, Michael Wurm2 Dresden,
3d-Topological Reconstruction in Liquid Scintillator Presented by Björn Wonsak on behalf of Felix Benckwitz1, Caren Hagner1, Sebastian Lorenz2, David Meyhöfer1, Henning Rebber1, Michael Wurm2 Dresden,
The Belle II Software From Detector Signals to Physics Results
 The Belle II Software From Detector Signals to Physics Results LMU Munich INSTR17 2017-02-28 Belle II @ SuperKEKB B, charm, τ physics 40 higher luminosity than KEKB Aim: 50 times more data than Belle Significantly
The Belle II Software From Detector Signals to Physics Results LMU Munich INSTR17 2017-02-28 Belle II @ SuperKEKB B, charm, τ physics 40 higher luminosity than KEKB Aim: 50 times more data than Belle Significantly
Monte Carlo methods in proton beam radiation therapy. Harald Paganetti
 Monte Carlo methods in proton beam radiation therapy Harald Paganetti Introduction: Proton Physics Electromagnetic energy loss of protons Distal distribution Dose [%] 120 100 80 60 40 p e p Ionization
Monte Carlo methods in proton beam radiation therapy Harald Paganetti Introduction: Proton Physics Electromagnetic energy loss of protons Distal distribution Dose [%] 120 100 80 60 40 p e p Ionization
