SOME PROPERTIES OF PARABOLAS TANGENT TO TWO SIDES OF A TRIANGLE
|
|
|
- Phyllis Hampton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Mathematical Sciences: Advances and Applications Volume 48, 017, Pages 47-5 Available at DOI: SOME PROPERTIES OF PARABOLAS TANGENT TO TWO SIDES OF A TRIANGLE A. BAYAR, Z. AKÇA*, A. ALTINTAŞ and S. EKMEKÇI Department of Mathematics - Computer Sciences Eskişehir Osmangazi University 6480 Eskişehir Turkey zakca@ogu.edu.tr Abstract In this work, we study some properties of parabolas whose vertex and focus are on bisector line and tangent to two sides of a given triangle. Also, we give the relationships among the vertex, the focus, and the intersection angle of the tangents. For the triangles with particular angles, we associate these parabolas with Euler line of the triangle ABC. 1. Introduction A parabola is the set of points in a plane that are equidistant from a fixed point F (called the focus) and a fixed line (called the directrix). It is well known that the point called the vertex halfway between the focus and the directrix lies on the parabola and the line called the axis of the parabola through the focus perpendicular to the directrix [6]. 010 Mathematics Subject Classification: 51N0. Keywords and phrases: tangent parabolas, Euler line. *Corresponding author Z. Akça. Received November 0, Scientific Advances Publishers
2 48 A. BAYAR et al. The parabolas which are tangent to two sides of a triangle where the tangent points are two vertices and the other side of the triangle is a chord of the corresponding parabola were first described by Artzt in 1884, []. When the sides of a triangle are tangents to a parabola, the triangle is said to circumscribe the parabola. But it must be clearly understood that the triangle does not enclose the parabola, for no finite triangle can enclose a parabola, which is infinite in extent. When a triangle circumscribes a parabola, the parabola is really escribed to it, that is, it touches one side of the triangle and the other two sides produced [1]. Some properties of these parabolas are mentioned in [], [4], [5], and [6]. In this work, we establish some properties of parabolas whose vertex and focus are on bisector line and tangent to two sides of triangle. It is given the ratio of the distance between the vertex of parabola and the intersection point of tangents to the distance between the vertex and the focus. Also, in case that the vertex and the focus of parabola coincide with the special points on Euler line of the triangle, we determine the internal angle of the tangent sides of the triangle. Theorem 1. Let ABC be a triangle with m ( C) α, and a parabola with the vertex P and the focus F on the internal bisector of the angle C. If the parabola is tangent to sides AC and BC of the triangle ABC, the distance between the vertex P and the focus F of the parabola is times the distance between P and the vertex C of triangle ABC. tan α Proof. Consider a triangle ABC formed by tangents at the points D and E of a parabola. Let the focus F be on the internal bisector of the angle C of the triangle ABC and let the vertex C with angle α be the intersection point of the tangents of the parabola. Since the translations and the rotations preserve the distances in Euclidean plane, we can take the coordinates of points F ( 0, 0), D( x, y), P( 0, a), and C (, y ), where 0 0 a, y0, x, y R. Since the distance of the point D to the directrix of
3 SOME PROPERTIES OF PARABOLAS TANGENT 49 parabola equals to the distance of the focus F, the equation of the parabola is, x + 4ay 4a 0. Tangent line DC is obtained as α y cot x + y0. This will meet the parabola where, x α + 4a cot x + 4ay0 4a 0. For a tangent, the roots of the equation must be coincident and therefore; y 0 1 a sin. α The ratio of length of PF to the length of DC; PF a. y 0 a 1 For y 0 a, α sin PF tan α is obtained. Corollary. Let the measure of the included angle C by two adjacent sides, AC and BC, of the triangle ABC be,, and, respectively. If a parabola which has the vertex P and the focus F on the internal bisector of the angle C is tangent to the sides AC and BC of the triangle ABC, then PF 1 the ratio is equal to 1,, and, respectively.
4 50 A. BAYAR et al. Proof. In Theorem 1, if α is taken as,, and, then the ratio PF 1 is obtained as 1,, and, respectively. Theorem. Let ABC be a triangle with m ( C), O be the circumcircle center, a parabola with the vertex P and the focus F on the internal bisector of the angle C and the side AB be tangent to sides AC and BC of the triangle ABC. Then this parabola is tangent to sides OA and OB of the triangle OAB. Proof. Let the measure of the included angle C by two adjacent sides, AC and BC, of the triangle ABC be. Since the translations and the rotations preserve the distances in Euclidean plane, we can take the coordinates of points F ( 0, 0), P( 0, a), and C ( 0, 4a), a R. Then the equation of the parabola tangent to sides AC and BC of the triangle ABC is x + 4ay 4a 0. If it is taken the coordinate of the point A as ( x 1, x1 + 4a ), the coordinates of the vertex B and the circumcircle center O are calculated as ax1 a( x1 + 4a ), x + a x + a 1 1 and x1 + ax1 x1 + ax1 + a,. It is easily seen that this parabola 1 1 x + a x + a is tangent to the sides OA and OB of the triangle OAB. Corollary 4. Let ABC be an equilateral triangle and a parabola with the vertex P and the focus F on the internal bisector of the angle C and the side AB be tangent to sides AC and BC of the triangle ABC. Then, this parabola is tangent to the internal bisectors of the angles A and B. Proof. Let ABC be an equilateral triangle. Since the circumcircle coincides with the orthocenter in an equilateral triangle ABC, the corollary is obtained from the previous theorem.
5 SOME PROPERTIES OF PARABOLAS TANGENT 51 The most famous line in the subject of triangle geometry is the Euler line, named in honor of Leonhard Euler (pronounced Oiler), who penned more pages of original mathematics than any other human being. If G centroid, O circumcenter, H the orthocenter, N ninepoint center of any triangle ABC, these well-known points lie on the Euler line and when you vary the shape of triangle ABC, the relative distances between the points G, O, H, N remain the same: G always lies 1 of the way from O to H; N always lies 1 of the way from O to H. In the following theorems deal with the tangent parabolas and Euler line. Theorem 5. Let H, G, O, N be the orthocenter, the centroid, the circumcircle center, and the ninepoint center in any scalene triangle ABC, respectively. If the measure of the included angle at the vertex C is, the parabola tangent to the altitudes from the vertices A and B has the vertex N and the focus G.. Proof. Suppose the measure of the included angle at the vertex C is Then the measure of angle H, the angle between the altitudes from the vertices A and B is and Euler line is the internal bisector of the angle H. It is well-known that the distance from the ninepoint center N to the orthocenter H is always three times the distance of the ninepoint center N to the centroid G on the Euler line. From Corollary, the parabola tangent to the altitudes from the vertices A and B has the vertex N and the focus G. Theorem 6. Let H, G, N be the orthocenter, the centroid, and the ninepoint center in any isoscales triangle ABC, CA CB, respectively. There is the parabola with the vertex N and the focus H tangent to the medians from the vertices A and B. Also the included angle between these medians is.
6 5 A. BAYAR et al. Proof. Let any isoscales triangle be ABC with CA CB. Then Euler line coincides with the internal bisector of the angles C and G. It is well known that the distance from the ninepoint center N to the orthocenter H is always three times of the distance from the ninepoint center N to the centroid G on the Euler line. From Theorem 1, the parabola with the vertex N and the focus H is tangent to the medians from the vertices A and B. And the measure of angle G, the angle between the medians from the vertices A and B is. Theorem 7. Let H, O, N be the orthocenter, the circumcircle center and the ninepoint center in any isoscales triangle ABC, CA CB, respectively. The parabola with the vertex N and the focus H is tangent to both the sides AC and BC and the radii from the vertices A and B of the triangle ABC. Proof. Let any isoscales triangle be ABC with CA CB. So, Euler line is the internal bisector of the angle C. The distance from the ninepoint center N to the orthocenter H is always equal to the distance from the ninepoint center N to the centroid O. From Theorem 1, the parabola with the vertex N and the focus H is tangent to the radii from the vertices A and B. And the measure of angle O, the angle between the radii from the vertices A and B is. Since the measure of the included NH angle at the vertex C is and for the parabola with the 4 NC vertex N and the focus H, this parabola is tangent to both sides AC and BC of the triangle ABC.
7 SOME PROPERTIES OF PARABOLAS TANGENT 5 References [1] E. H. Askwith, A Course of Pure Geometry, Cambridge University Press, [] August Artzt, Untersuchungen über ähnliche punktreihen auf den Seiten eines Dreiecks und auf deren Mittelsenkrechten, sowie über kongruente Strahlen-büschel aus den Ecken desselben; ein Beitrag zur geometrie des Brocardschen Kreises, Programm des Gymnasiums zu Recklinghausen 54 (1884), -. [] N. Dergiades, Conics tangent at the vertices to two sides of a triangle, Forum Geometricorum 10 (010), [4] J. A. Bullard, Properties of parabolas inscribed in a triangle, Amer. Math. Monthly 4(10) (195), [5] J. A. Bullard, Further properties of parabolas inscribed in a triangle, Amer. Math. Monthly 44(6) (197), [6] A. Altintaş, Properties of parabolas inscribed in a triangle, Roma. Math. Magazine (017), (to appear). g
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra
 Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
Visualizing Triangle Centers Using Geogebra Sanjay Gulati Shri Shankaracharya Vidyalaya, Hudco, Bhilai (Chhattisgarh) India http://mathematicsbhilai.blogspot.com/ sanjaybhil@gmail.com ABSTRACT. In this
If three points A (h, 0), P (a, b) and B (0, k) lie on a line, show that: a b 1.
 ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
DEFINITIONS. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle.
 DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
SOAR2001 GEOMETRY SUMMER 2001
 SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011
 MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011 Open the document Getting Started with GeoGebra and follow the instructions either to download and install it on your computer or to run it as a Webstart
MATH 341 FALL 2011 ASSIGNMENT 6 October 3, 2011 Open the document Getting Started with GeoGebra and follow the instructions either to download and install it on your computer or to run it as a Webstart
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
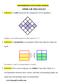 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
Segment Addition Postulate: If B is BETWEEN A and C, then AB + BC = AC. If AB + BC = AC, then B is BETWEEN A and C.
 Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
Ruler Postulate: The points on a line can be matched one to one with the REAL numbers. The REAL number that corresponds to a point is the COORDINATE of the point. The DISTANCE between points A and B, written
Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never
 1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
1stSemesterReviewTrueFalse.nb 1 Geometry (H) Worksheet: 1st Semester Review:True/False, Always/Sometimes/Never Classify each statement as TRUE or FALSE. 1. Three given points are always coplanar. 2. A
H.Geometry Chapter 3 Definition Sheet
 Section 3.1 Measurement Tools Construction Tools Sketch Draw Construct Constructing the Duplicate of a Segment 1.) Start with a given segment. 2.) 3.) Constructing the Duplicate of an angle 1.) Start with
Section 3.1 Measurement Tools Construction Tools Sketch Draw Construct Constructing the Duplicate of a Segment 1.) Start with a given segment. 2.) 3.) Constructing the Duplicate of an angle 1.) Start with
SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS
 SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS A system of linear equations is a set of two equations of lines. A solution of a system of linear equations is the set of ordered pairs that makes each equation true. That is
SYSTEMS OF LINEAR EQUATIONS A system of linear equations is a set of two equations of lines. A solution of a system of linear equations is the set of ordered pairs that makes each equation true. That is
Unit 1 Unit 1 A M. M.Sigley, Baker MS. Unit 1 Unit 1. 3 M.Sigley, Baker MS
 A M S 1 2 G O E A B 3 4 LINE POINT Undefined No thickness Extends infinitely in two directions Designated with two points Named with two capital letters or Undefined No size Named with a capital letter
A M S 1 2 G O E A B 3 4 LINE POINT Undefined No thickness Extends infinitely in two directions Designated with two points Named with two capital letters or Undefined No size Named with a capital letter
Chapter 10 Similarity
 Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties
 Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures
 MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
Orbiting Vertex: Follow That Triangle Center!
 Orbiting Vertex: Follow That Triangle Center! Justin Dykstra Clinton Peterson Ashley Rall Erika Shadduck March 1, 2006 1 Preliminaries 1.1 Introduction The number of triangle centers is astounding. Upwards
Orbiting Vertex: Follow That Triangle Center! Justin Dykstra Clinton Peterson Ashley Rall Erika Shadduck March 1, 2006 1 Preliminaries 1.1 Introduction The number of triangle centers is astounding. Upwards
Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips
 & present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
& present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle
 Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle Arseniy V. Akopyan Abstract Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
Conjugation of lines with respect to a triangle Arseniy V. Akopyan Abstract Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
 1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
Term: Definition: Picture:
 10R Unit 7 Triangle Relationships CW 7.8 HW: Finish this CW 7.8 Review for Test Answers: See Teacher s Website Theorem/Definition Study Sheet! Term: Definition: Picture: Exterior Angle Theorem: Triangle
10R Unit 7 Triangle Relationships CW 7.8 HW: Finish this CW 7.8 Review for Test Answers: See Teacher s Website Theorem/Definition Study Sheet! Term: Definition: Picture: Exterior Angle Theorem: Triangle
CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE
 CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE ARSENIY V. AKOPYAN Abstract. Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
CONJUGATION OF LINES WITH RESPECT TO A TRIANGLE ARSENIY V. AKOPYAN Abstract. Isotomic and isogonal conjugate with respect to a triangle is a well-known and well studied map frequently used in classical
Geometry. Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section.
 Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
with slopes m 1 and m 2 ), if and only if its coordinates satisfy the equation y y 0 = 0 and Ax + By + C 2
 CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
Geometry Rules. Triangles:
 Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
a triangle with all acute angles acute triangle angles that share a common side and vertex adjacent angles alternate exterior angles
 acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
acute triangle a triangle with all acute angles adjacent angles angles that share a common side and vertex alternate exterior angles two non-adjacent exterior angles on opposite sides of the transversal;
TImath.com. Geometry. Special Segments in Triangles
 Special Segments in Triangles ID: 8672 Time required 90 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore medians, altitudes, angle bisectors, and perpendicular bisectors of triangles. They
Special Segments in Triangles ID: 8672 Time required 90 minutes Activity Overview In this activity, students explore medians, altitudes, angle bisectors, and perpendicular bisectors of triangles. They
arxiv: v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013
![arxiv: v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013 arxiv: v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013](/thumbs/74/70304288.jpg) Solution of Sondow s problem: a synthetic proof of the tangency property of the parbelos Emmanuel Tsukerman arxiv:1210.5580v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013 Abstract In a recent paper titled The parbelos, a parabolic
Solution of Sondow s problem: a synthetic proof of the tangency property of the parbelos Emmanuel Tsukerman arxiv:1210.5580v2 [math.mg] 24 Jul 2013 Abstract In a recent paper titled The parbelos, a parabolic
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Drill Exercise -. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ).. Prove that the points (a, 4a) (a, 6a) and (a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral triangle.
Drill Exercise - 1. Drill Exercise - 2. Drill Exercise - 3
 Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
Drill Exercise - 1 1. Find the distance between the pair of points, (a sin, b cos ) and ( a cos, b sin ). 2. Prove that the points (2a, 4a) (2a, 6a) and (2a + 3 a, 5a) are the vertices of an equilateral
 CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
Semester Test Topic Review. Correct Version
 Semester Test Topic Review Correct Version List of Questions Questions to answer: What does the perpendicular bisector theorem say? What is true about the slopes of parallel lines? What is true about the
Semester Test Topic Review Correct Version List of Questions Questions to answer: What does the perpendicular bisector theorem say? What is true about the slopes of parallel lines? What is true about the
Definitions. Topology/Geometry of Geodesics. Joseph D. Clinton. SNEC June Magnus J. Wenninger
 Topology/Geometry of Geodesics Joseph D. Clinton SNEC-04 28-29 June 2003 Magnus J. Wenninger Introduction Definitions Topology Goldberg s polyhedra Classes of Geodesic polyhedra Triangular tessellations
Topology/Geometry of Geodesics Joseph D. Clinton SNEC-04 28-29 June 2003 Magnus J. Wenninger Introduction Definitions Topology Goldberg s polyhedra Classes of Geodesic polyhedra Triangular tessellations
The focus and the median of a non-tangential quadrilateral in the isotropic plane
 MATHEMATICAL COMMUNICATIONS 117 Math. Commun., Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 117-17 (010) The focus and the median of a non-tangential quadrilateral in the isotropic plane Vladimir Volenec 1,, Jelena Beban-Brkić
MATHEMATICAL COMMUNICATIONS 117 Math. Commun., Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 117-17 (010) The focus and the median of a non-tangential quadrilateral in the isotropic plane Vladimir Volenec 1,, Jelena Beban-Brkić
8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry
 8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry 8.1 The circum-center Figure 8.1: In hyperbolic geometry, the perpendicular bisectors can be parallel as shown but this figure is impossible in Euclidean geometry.
8 Standard Euclidean Triangle Geometry 8.1 The circum-center Figure 8.1: In hyperbolic geometry, the perpendicular bisectors can be parallel as shown but this figure is impossible in Euclidean geometry.
Postulates, Theorems, and Corollaries. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry
 NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and
NAEP Released Items Aligned to the Iowa Core: Geometry Congruence G-CO Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and
Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles
 1 Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles or contains a right angle. D D 2 Solution to Example
1 Example G1: Triangles with circumcenter on a median. Prove that if the circumcenter of a triangle lies on a median, the triangle either is isosceles or contains a right angle. D D 2 Solution to Example
SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal)
 1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
Conic Solution of Euler s Triangle Determination Problem
 Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 12 (2008), o. 1, 1 6. Conic Solution of Euler s Triangle Determination Problem Paul Yiu Dept. of Mathematical Sciences, Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton,
Journal for Geometry and Graphics Volume 12 (2008), o. 1, 1 6. Conic Solution of Euler s Triangle Determination Problem Paul Yiu Dept. of Mathematical Sciences, Florida Atlantic University Boca Raton,
We have already studied equations of the line. There are several forms:
 Chapter 13-Coordinate Geometry extended. 13.1 Graphing equations We have already studied equations of the line. There are several forms: slope-intercept y = mx + b point-slope y - y1=m(x - x1) standard
Chapter 13-Coordinate Geometry extended. 13.1 Graphing equations We have already studied equations of the line. There are several forms: slope-intercept y = mx + b point-slope y - y1=m(x - x1) standard
notes13.1inclass May 01, 2015
 Chapter 13-Coordinate Geometry extended. 13.1 Graphing equations We have already studied equations of the line. There are several forms: slope-intercept y = mx + b point-slope y - y1=m(x - x1) standard
Chapter 13-Coordinate Geometry extended. 13.1 Graphing equations We have already studied equations of the line. There are several forms: slope-intercept y = mx + b point-slope y - y1=m(x - x1) standard
Along the Euler Line Berkeley Math Circle Intermediate
 Along the Euler Line Berkeley Math Circle Intermediate by Zvezdelina Stankova Berkeley Math Circle Director October 11, 17 2011 Note: We shall work on the problems below over the next two circle sessions
Along the Euler Line Berkeley Math Circle Intermediate by Zvezdelina Stankova Berkeley Math Circle Director October 11, 17 2011 Note: We shall work on the problems below over the next two circle sessions
Circumference of a Circle
 Circumference of a Circle The line segment AB, AB = 2r, and its interior point X are given. The sum of the lengths of semicircles over the diameters AX and XB is 3πr; πr; 3 2 πr; 5 4 πr; 1 2 πr; Šárka
Circumference of a Circle The line segment AB, AB = 2r, and its interior point X are given. The sum of the lengths of semicircles over the diameters AX and XB is 3πr; πr; 3 2 πr; 5 4 πr; 1 2 πr; Šárka
VOCABULARY. Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8. WORD IMAGE DEFINITION An angle with measure between 0 and A triangle with three acute angles.
 Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Acute VOCABULARY Chapters 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 9, and 8 WORD IMAGE DEFINITION Acute angle An angle with measure between 0 and 90 56 60 70 50 A with three acute. Adjacent Alternate interior Altitude of a Angle
Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units
 Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units affine linear equation: an equation in which both sides are sums of terms that are either a number times y or a number times x or just a number [SlL2-D5]
Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units affine linear equation: an equation in which both sides are sums of terms that are either a number times y or a number times x or just a number [SlL2-D5]
If B is the If two angles are
 If If B is between A and C, then 1 2 If P is in the interior of RST, then If B is the If two angles are midpoint of AC, vertical, then then 3 4 If angles are adjacent, then If angles are a linear pair,
If If B is between A and C, then 1 2 If P is in the interior of RST, then If B is the If two angles are midpoint of AC, vertical, then then 3 4 If angles are adjacent, then If angles are a linear pair,
We have already studied equations of the line. There are several forms:
 Chapter 13-Coordinate Geometry extended. 13.1 Graphing equations We have already studied equations of the line. There are several forms: slope-intercept y = mx + b point-slope y - y1=m(x - x1) standard
Chapter 13-Coordinate Geometry extended. 13.1 Graphing equations We have already studied equations of the line. There are several forms: slope-intercept y = mx + b point-slope y - y1=m(x - x1) standard
Coordinate Systems, Locus and Straight Line
 Coordinate Systems Locus Straight Line. A line makes zero intercepts on - ax - ax it perpendicular to the line. Then the equation (Karnataka CET 00). If p the length if the perpendicular from the origin
Coordinate Systems Locus Straight Line. A line makes zero intercepts on - ax - ax it perpendicular to the line. Then the equation (Karnataka CET 00). If p the length if the perpendicular from the origin
Geometry IB Date: 2/18/2013 ID Check Objective: Students will identify and use medians and altitudes in triangles. Bell Ringer: Complete Constructions
 Geometry IB Date: 2/18/2013 ID Check Objective: Students will identify and use medians and altitudes in triangles. Bell Ringer: Complete Constructions HW Requests: pg 327 #17-25 odds 45, 46, pg 338 #11,
Geometry IB Date: 2/18/2013 ID Check Objective: Students will identify and use medians and altitudes in triangles. Bell Ringer: Complete Constructions HW Requests: pg 327 #17-25 odds 45, 46, pg 338 #11,
GEOMETRY R Unit 4: More Transformations / Compositions. Day Classwork Homework Monday 10/16. Perpendicular Bisector Relationship to Transformations
 GEOMETRY R Unit 4: More Transformations / Compositions Day Classwork Homework Monday 10/16 Perpendicular Bisector Relationship to Transformations HW 4.1 Tuesday 10/17 Construction of Parallel Lines Through
GEOMETRY R Unit 4: More Transformations / Compositions Day Classwork Homework Monday 10/16 Perpendicular Bisector Relationship to Transformations HW 4.1 Tuesday 10/17 Construction of Parallel Lines Through
a) 1/3 area of triangle ABC b) 3.6 c) 3 d) e) Euclid s fifth postulate is equivalent to: Given a line and a point not on that line
 1. Given is a right triangle with AD a perpendicular from the right angle to the hypotenuse, find the length of AD given AB = 6, BC = 10 and AC = 8. B D A C a) 7.5 b) 6.5 c) 4.8 d) e) 2. Using the figure
1. Given is a right triangle with AD a perpendicular from the right angle to the hypotenuse, find the length of AD given AB = 6, BC = 10 and AC = 8. B D A C a) 7.5 b) 6.5 c) 4.8 d) e) 2. Using the figure
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 3 Constructions Review
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 3 Constructions Review Complete all questions. Questions 7-18 must be completed on looseleaf paper. Constructions & Definitions to know: Altitudes Orthocenter Centers to know:
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 3 Constructions Review Complete all questions. Questions 7-18 must be completed on looseleaf paper. Constructions & Definitions to know: Altitudes Orthocenter Centers to know:
Buds Public School, Dubai
 Buds Public School, Dubai Subject: Maths Grade: 11 AB Topic: Statistics, Probability, Trigonometry, 3D, Conic Section, Straight lines and Limits and Derivatives Statistics and Probability: 1. Find the
Buds Public School, Dubai Subject: Maths Grade: 11 AB Topic: Statistics, Probability, Trigonometry, 3D, Conic Section, Straight lines and Limits and Derivatives Statistics and Probability: 1. Find the
Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments
 Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments Concept 9 Parallel Lines and Triangles (Section 3.5) ANGLE Classifications Acute: Obtuse: Right: SIDE Classifications Scalene: Isosceles:
Geometry - Concepts 9-12 Congruent Triangles and Special Segments Concept 9 Parallel Lines and Triangles (Section 3.5) ANGLE Classifications Acute: Obtuse: Right: SIDE Classifications Scalene: Isosceles:
5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited
 230 Chapter 5. AREAS 5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited 259. Theorem. The areas of squares constructed on the legs of a right triangle add up to the area of the square constructed on its hypotenuse. This
230 Chapter 5. AREAS 5 The Pythagorean theorem revisited 259. Theorem. The areas of squares constructed on the legs of a right triangle add up to the area of the square constructed on its hypotenuse. This
Geometry 5-1 Bisector of Triangles- Live lesson
 Geometry 5-1 Bisector of Triangles- Live lesson Draw a Line Segment Bisector: Draw an Angle Bisectors: Perpendicular Bisector A perpendicular bisector is a line, segment, or ray that is perpendicular to
Geometry 5-1 Bisector of Triangles- Live lesson Draw a Line Segment Bisector: Draw an Angle Bisectors: Perpendicular Bisector A perpendicular bisector is a line, segment, or ray that is perpendicular to
G.CO.C.10: Centroid, Orthocenter, Incenter and Circumcenter
 1 Which geometric principle is used in the construction shown below? 2 In the diagram below of ABC, CD is the bisector of BCA, AE is the bisector of CAB, and BG is drawn. 1) The intersection of the angle
1 Which geometric principle is used in the construction shown below? 2 In the diagram below of ABC, CD is the bisector of BCA, AE is the bisector of CAB, and BG is drawn. 1) The intersection of the angle
PARABOLA SYNOPSIS 1.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP
 PARABOLA SYNOPSIS.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP PM = where PM is perpendicular to the directrix, then the locus of P is a parabola... S ax + hxy
PARABOLA SYNOPSIS.S is the focus and the line l is the directrix. If a variable point P is such that SP PM = where PM is perpendicular to the directrix, then the locus of P is a parabola... S ax + hxy
S56 (5.3) Higher Straight Line.notebook June 22, 2015
 Daily Practice 5.6.2015 Q1. Simplify Q2. Evaluate L.I: Today we will be revising over our knowledge of the straight line. Q3. Write in completed square form x 2 + 4x + 7 Q4. State the equation of the line
Daily Practice 5.6.2015 Q1. Simplify Q2. Evaluate L.I: Today we will be revising over our knowledge of the straight line. Q3. Write in completed square form x 2 + 4x + 7 Q4. State the equation of the line
Unit Number of Days Dates. 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/ Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9
 8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
8 th Grade Geometry Curriculum Map Overview 2016-2017 Unit Number of Days Dates 1 Angles, Lines and Shapes 14 8/2 8/19 2 - Reasoning and Proof with Lines and Angles 14 8/22 9/9 3 - Congruence Transformations
14-9 Constructions Review. Geometry Period. Constructions Review
 Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
Solutions to the Test. Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written?
 Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
Solutions to the Test Problem 1. 1) Who is the author of the first comprehensive text on geometry? When and where was it written? Answer: The first comprehensive text on geometry is called The Elements
Midpoint of a Line Segment Pg. 78 # 1, 3, 4-6, 8, 18. Classifying Figures on a Cartesian Plane Quiz ( )
 UNIT 2 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Date Lesson TOPIC Homework Feb. 22 Feb. 23 Feb. 24 Feb. 27 Feb. 28 2.1 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.1-2.3 2.1-2.3 Mar. 1 2.6 2.4 Mar. 2 2.7 2.5 Mar. 3 2.8 2.6 Mar. 6 2.9 2.7 Mar.
UNIT 2 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Date Lesson TOPIC Homework Feb. 22 Feb. 23 Feb. 24 Feb. 27 Feb. 28 2.1 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.1-2.3 2.1-2.3 Mar. 1 2.6 2.4 Mar. 2 2.7 2.5 Mar. 3 2.8 2.6 Mar. 6 2.9 2.7 Mar.
Modeling with Geometry
 Modeling with Geometry 6.3 Parallelograms https://mathbitsnotebook.com/geometry/quadrilaterals/qdparallelograms.html Properties of Parallelograms Sides A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs
Modeling with Geometry 6.3 Parallelograms https://mathbitsnotebook.com/geometry/quadrilaterals/qdparallelograms.html Properties of Parallelograms Sides A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA
 GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA PART ONE: TRIANGLES Notations AB ( AB ) [ AB ] ] AB [ [ AB ) distance between the points A and B line through the points A and B segment between the two points A and B (A and B included)
GEOMETRY WITH GEOGEBRA PART ONE: TRIANGLES Notations AB ( AB ) [ AB ] ] AB [ [ AB ) distance between the points A and B line through the points A and B segment between the two points A and B (A and B included)
Point A location in geometry. A point has no dimensions without any length, width, or depth. This is represented by a dot and is usually labelled.
 Test Date: November 3, 2016 Format: Scored out of 100 points. 8 Multiple Choice (40) / 8 Short Response (60) Topics: Points, Angles, Linear Objects, and Planes Recognizing the steps and procedures for
Test Date: November 3, 2016 Format: Scored out of 100 points. 8 Multiple Choice (40) / 8 Short Response (60) Topics: Points, Angles, Linear Objects, and Planes Recognizing the steps and procedures for
Question2: Which statement is true about the two triangles in the diagram?
 Question1: The diagram shows three aid stations in a national park. Choose the values of x, y, and z that COULD represent the distances between the stations. (a) x = 7 miles, y = 8 miles, z = 18 miles
Question1: The diagram shows three aid stations in a national park. Choose the values of x, y, and z that COULD represent the distances between the stations. (a) x = 7 miles, y = 8 miles, z = 18 miles
A parabola has a focus at the point (6, 0), and the equation of the directrix is
 1 A parabola has a focus at the point (6, 0), and the equation of the directrix is Part A Determine the vertex of the parabola. Explain your answer. Part B Prove that point (12, 8) is on the parabola.
1 A parabola has a focus at the point (6, 0), and the equation of the directrix is Part A Determine the vertex of the parabola. Explain your answer. Part B Prove that point (12, 8) is on the parabola.
Entrance Exam Wiskunde B
 CENTRALE COMMISSIE VOORTENTAMEN WISKUNDE Entrance Exam Wiskunde B Date: 16 January 2015 Time: 13.30 16.30 Questions: 5 Please read the instructions below carefully before answering the questions. There
CENTRALE COMMISSIE VOORTENTAMEN WISKUNDE Entrance Exam Wiskunde B Date: 16 January 2015 Time: 13.30 16.30 Questions: 5 Please read the instructions below carefully before answering the questions. There
Geometry Vocabulary Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
3 Identify shapes as two-dimensional (lying in a plane, flat ) or three-dimensional ( solid ).
 Geometry Kindergarten Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1 Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes,
Geometry Kindergarten Identify and describe shapes (squares, circles, triangles, rectangles, hexagons, cubes, cones, cylinders, and spheres). 1 Describe objects in the environment using names of shapes,
, Geometry, Quarter 1
 2017.18, Geometry, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical Proficiency 1.
2017.18, Geometry, Quarter 1 The following Practice Standards and Literacy Skills will be used throughout the course: Standards for Mathematical Practice Literacy Skills for Mathematical Proficiency 1.
Lesson 9: Coordinate Proof - Quadrilaterals Learning Targets
 Lesson 9: Coordinate Proof - Quadrilaterals Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of the way along each median
Lesson 9: Coordinate Proof - Quadrilaterals Learning Targets Using coordinates, I can find the intersection of the medians of a triangle that meet at a point that is two-thirds of the way along each median
EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS
 EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS Steps to Find the Median of a Triangle: -Find the midpoint of a segment using the midpoint formula. -Use the vertex and midpoint to find the
EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS Steps to Find the Median of a Triangle: -Find the midpoint of a segment using the midpoint formula. -Use the vertex and midpoint to find the
Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence
 Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definition ABC =
Chapter 2 Similarity and Congruence Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definitions Definition AB = CD if and only if AB = CD Remember, mab = AB. Definition ABC =
GEOMETRY POSTULATES AND THEOREMS. Postulate 1: Through any two points, there is exactly one line.
 GEOMETRY POSTULATES AND THEOREMS Postulate 1: Through any two points, there is exactly one line. Postulate 2: The measure of any line segment is a unique positive number. The measure (or length) of AB
GEOMETRY POSTULATES AND THEOREMS Postulate 1: Through any two points, there is exactly one line. Postulate 2: The measure of any line segment is a unique positive number. The measure (or length) of AB
Inversive Plane Geometry
 Inversive Plane Geometry An inversive plane is a geometry with three undefined notions: points, circles, and an incidence relation between points and circles, satisfying the following three axioms: (I.1)
Inversive Plane Geometry An inversive plane is a geometry with three undefined notions: points, circles, and an incidence relation between points and circles, satisfying the following three axioms: (I.1)
Chapter 6.1 Medians. Geometry
 Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Chapter 6.1 Medians Identify medians of triangles Find the midpoint of a line using a compass. A median is a segment that joins a vertex of the triangle and the midpoint of the opposite side. Median AD
Suggested List of Mathematical Language. Geometry
 Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Suggested List of Mathematical Language Geometry Problem Solving A additive property of equality algorithm apply constraints construct discover explore generalization inductive reasoning parameters reason
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts
 Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
Mathematics High School Geometry An understanding of the attributes and relationships of geometric objects can be applied in diverse contexts interpreting a schematic drawing, estimating the amount of
On Taxicab Incircle and Circumcircle of a Triangle
 KoG 16 01 Original scientific paper Accepted 8 9 01 T Ermiş, Ö Gelişgen, R Kaya: On Taxica Incircle Circumcircle of a Triangle TEMEL ERMIŞ ÖZCAN GELIŞGEN RUSTEM KAYA On Taxica Incircle Circumcircle of
KoG 16 01 Original scientific paper Accepted 8 9 01 T Ermiş, Ö Gelişgen, R Kaya: On Taxica Incircle Circumcircle of a Triangle TEMEL ERMIŞ ÖZCAN GELIŞGEN RUSTEM KAYA On Taxica Incircle Circumcircle of
of Nebraska - Lincoln
 University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2008 Lester s Circle Julie Hoaglund University of
University of Nebraska - Lincoln DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska - Lincoln MAT Exam Expository Papers Math in the Middle Institute Partnership 7-2008 Lester s Circle Julie Hoaglund University of
Unit 2 Triangles Part 1
 Graded Learning Targets LT 2.1 I can Unit 2 Triangles Part 1 Supporting Learning Targets I can justify, using a formal proof, that the three angles in a triangle add up to 180. I can justify whether or
Graded Learning Targets LT 2.1 I can Unit 2 Triangles Part 1 Supporting Learning Targets I can justify, using a formal proof, that the three angles in a triangle add up to 180. I can justify whether or
2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? Formula: Area of a Trapezoid. 3 Centroid. 4 Midsegment of a triangle
 1 Formula: Area of a Trapezoid 2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? 3 Centroid 4 Midsegment of a triangle 5 Slope formula 6 Point Slope Form of Linear Equation *can
1 Formula: Area of a Trapezoid 2 Formula (given): Volume of a Pyramid V = 1/3 BH What does B represent? 3 Centroid 4 Midsegment of a triangle 5 Slope formula 6 Point Slope Form of Linear Equation *can
Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics. A circle is
 Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
Name: Pre-Calculus Guided Notes: Chapter 10 Conics Section Circles A circle is _ Example 1 Write an equation for the circle with center (3, ) and radius 5. To do this, we ll need the x1 y y1 distance formula:
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined
 MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
MTH 362 Study Guide Exam 1 System of Euclidean Geometry 1. Describe the building blocks of Euclidean geometry. a. Point, line, and plane - undefined terms used to create definitions. Definitions are used
Common Core Cluster. Experiment with transformations in the plane. Unpacking What does this standard mean that a student will know and be able to do?
 Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Congruence G.CO Experiment with transformations in the plane. G.CO.1 Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point,
Course Number: Course Title: Geometry
 Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
Course Number: 1206310 Course Title: Geometry RELATED GLOSSARY TERM DEFINITIONS (89) Altitude The perpendicular distance from the top of a geometric figure to its opposite side. Angle Two rays or two line
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK
 Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
Math 3315: Geometry Vocabulary Review Human Dictionary: WORD BANK [acute angle] [acute triangle] [adjacent interior angle] [alternate exterior angles] [alternate interior angles] [altitude] [angle] [angle_addition_postulate]
Chapter 7. Some triangle centers. 7.1 The Euler line Inferior and superior triangles
 hapter 7 Some triangle centers 7.1 The Euler line 7.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,. The two triangles
hapter 7 Some triangle centers 7.1 The Euler line 7.1.1 nferior and superior triangles G F E G D The inferior triangle of is the triangle DEF whose vertices are the midpoints of the sides,,. The two triangles
5-2 Medians and Altitudes of Triangles. In, P is the centroid, PF = 6, and AD = 15. Find each measure. 1. PC ANSWER: 12 2.
 In, P is the centroid, PF = 6, and AD = 15. Find each measure. In, UJ = 9, VJ = 3, and ZT = 18. Find each length. 1. PC 12 2. AP 10 3. INTERIOR DESIGN An interior designer is creating a custom coffee table
In, P is the centroid, PF = 6, and AD = 15. Find each measure. In, UJ = 9, VJ = 3, and ZT = 18. Find each length. 1. PC 12 2. AP 10 3. INTERIOR DESIGN An interior designer is creating a custom coffee table
Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards. Geometry. Table of Contents. Geometry 1 Statistics and Probability 8
 Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards Geometry Table of Contents Geometry 1 Statistics and Probability 8 Geometry Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions
Unit Activity Correlations to Common Core State Standards Geometry Table of Contents Geometry 1 Statistics and Probability 8 Geometry Experiment with transformations in the plane 1. Know precise definitions
Geom6 3MediansAndAltitudesOfTrianglesNotes.notebook March 23, P Medians and Altitudes of Triangles
 Geometry P33 6 3 Medians and Altitudes of Triangles Review Circumcenter * The Perpendicular Bisectors of the sides of a triangle are concurrent at a point equidistant from the vertices. We call this point
Geometry P33 6 3 Medians and Altitudes of Triangles Review Circumcenter * The Perpendicular Bisectors of the sides of a triangle are concurrent at a point equidistant from the vertices. We call this point
Analytic Geometry Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Important Notes for Teachers:
 Analytic Geometry Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file reflect the vocabulary students taking Coordinate Algebra will need to know and be able
Analytic Geometry Vocabulary Cards and Word Walls Important Notes for Teachers: The vocabulary cards in this file reflect the vocabulary students taking Coordinate Algebra will need to know and be able
Plane Geometry: Reflection Across a Line Does It! at the Marin Math Circle 1
 Plane Geometry: Reflection Across a Line Does It! at the Marin Math Circle 1 by Zvezdelina Stankova Berkeley Math Circle Director September 29 and October 13, 2010 Note: We shall work on the problems below
Plane Geometry: Reflection Across a Line Does It! at the Marin Math Circle 1 by Zvezdelina Stankova Berkeley Math Circle Director September 29 and October 13, 2010 Note: We shall work on the problems below
On the Cyclic Quadrilaterals with the Same Varignon Parallelogram
 Forum Geometricorum Volume 18 (2018) 103 113. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On the Cyclic Quadrilaterals with the Same Varignon Parallelogram Sándor Nagydobai Kiss Abstract. The circumcenters and anticenters
Forum Geometricorum Volume 18 (2018) 103 113. FORUM GEOM ISSN 1534-1178 On the Cyclic Quadrilaterals with the Same Varignon Parallelogram Sándor Nagydobai Kiss Abstract. The circumcenters and anticenters
Common Core Specifications for Geometry
 1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
1 Common Core Specifications for Geometry Examples of how to read the red references: Congruence (G-Co) 2-03 indicates this spec is implemented in Unit 3, Lesson 2. IDT_C indicates that this spec is implemented
EUCLID S GEOMETRY. Raymond Hoobler. January 27, 2008
 EUCLID S GEOMETRY Raymond Hoobler January 27, 2008 Euclid rst codi ed the procedures and results of geometry, and he did such a good job that even today it is hard to improve on his presentation. He lived
EUCLID S GEOMETRY Raymond Hoobler January 27, 2008 Euclid rst codi ed the procedures and results of geometry, and he did such a good job that even today it is hard to improve on his presentation. He lived
Multivariable Calculus
 Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
Multivariable Calculus Chapter 10 Topics in Analytic Geometry (Optional) 1. Inclination of a line p. 5. Circles p. 4 9. Determining Conic Type p. 13. Angle between lines p. 6. Parabolas p. 5 10. Rotation
