Circumference of a Circle
|
|
|
- Annabel Barnett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Circumference of a Circle The line segment AB, AB = 2r, and its interior point X are given. The sum of the lengths of semicircles over the diameters AX and XB is 3πr; πr; 3 2 πr; 5 4 πr; 1 2 πr; Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
2 Circumscribed circle Circumcircle of a polygon is a circle which passes through all the vertices of the polygon. Inscribed circle Incircle of a polygon is a circle touches (is tangent to) all sides of the polygon. Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
3 Circle Inscribed in Hexagon The ratio of the area of a regular hexagon with side a to the area of the circle inscribed in it is 2 3 : π, 3 : π, 2 2 : π, 3 2 : π, 2 : π, Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
4 Inscribed triangle Consider an equilateral triangle ABC with the side length a and an inscribed equilateral triangle DEF, where D AB, E BC, F CA and the area of the triangle DEF is equal to one third of the area of the triangle ABC. The length of the side of the triangle DEF is a 2 ; a 2 ; a 4 ; a 6 ; a 3 ; Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
5 Consider an equilateral triangle ABC with the side length a and an inscribed equilateral triangle DEF, where D AB, E BC, F CA and the area of the triangle DEF is equal to one half of the area of the triangle ABC. The length of the side of the triangle DEF is a 2 ; a 3 ; a 4 ; a 2 ; a 6 ; Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
6 Cartesian Coordinate System in the Plane Any point P in the plane can be located by unique ordered pair on numbers coordinates. We write P[x, y] or P = (x, y). Example Describe and sketch the regions given by following sets {(x, y); x 0} {(x, y); y = 1} {(x, y); y < 1} Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
7 Square in CCS Determine coordinates of vetices C, D of the square ABCD, where A[1, 1], B[5, 1] 1 1 square Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
8 Lines Slope form of the equation Slope m measure of the steepness. The slope of line AB is m = y x. Let line l passes through a given point A = (x A, y A ) and has slope m. X = (x, y) l y y A x x A = m y y A = m(x x A ) y = mx x A + y A Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
9 Lines Slope and general equation Example Write the equation of the line l = AB, where A = (2, 1) and B = (0, 3). Determine: The slope m of the line l. Intersection points with coordinate axes, P = l x, Q = l y. whether the line l goes through the point P = (3, 4). Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
10 Identical Straight Lines 2 Straight lines 6x + by + c = 0 and AB, where A[1, 2], B[2, 1], are identical only if b = 4 c = 10 b = 4 c = 14 b = 2 c = 10 b = 4 c = 2 b = 2 c = 10 2 IdenticalLines.ggb Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
11 Lines Parametric equations Directional vector of line AB is any vector parallel with u = B A. Directional vector u is perpendicular to normal vector n, i.e. u n = 0. Let line l passes through a given point A = (x A, y A ) and has directional vector u. X = (x, y) l AX = t u X A = t u X = A + t u Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
12 Point of Intersection 3 A straight line x + 2y 7 = 0 and a line segment x = 1 + 4t, y = 1 + 2t, t 0, 1, do not intersect intersect at point [5, 1] intersect at point [1, 3] intersect at point [3, 2] intersect at point [4, 3 2 ] 3 IntersectionPoint.ggb Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
13 Perpendicular Bisector 4 A straight line ax 2y + c = 0 is the axis of the line segment AB, where A[1, 5], B[ 3, 3], only if a = 4 c = 4 a = 1 c = 3 a = 4 c = 4 a = 2 c = 2 a = 7 c = 0 4 PerpendicularBisector Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
14 Reflection in Line5 Given a line a and a point P. Reflection P 0 of P in a is the point such that PP 0 is perpendicular to a, and PM = MP 0, where M is the point of intersection of PP 0 and a. In other words, P 0 is located on the other side of axis, but at the same distance from a as P. P 0 is said to be a mirror of P. S a rka Vora c ova Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
15 Reflection in Line 6 Axial symmetry with an axis p : x y = 0 maps a point A[3, 0] to a point A[?,?] 6 ReflectionLine.ggb Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
16 Reflection in Line Axial symmetry with an axis p : x 2y + 1 = 0 maps a point A[4, 0] to a point [0, 4] [0, 3] [3, 2] [2, 2] [2, 4] Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
17 Altitude of a Triangle 7 A straight line containing the height h a of the triangle ABC, where A[0, 1], B[6, 0], C[4, 3], has an equation 7 AltitudeTriangle.ggb Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
18 Altitude of a Triangle A straight line containing the height h c of the triangle ABC, where A[ 1, 1], B[3, 2], C[2, 5], has an equation 4x y 3 = 0 x + 4y 22 = 0 x 4y + 18 = 0 x + 4y + 13 = 0 4x + y 13 = 0 Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
19 Equation of the Circle Circle is the set of all points X in a plane that are at a given distance r from a given point, the centre O. X [x, y]; O[m, n] r = OX = (X O) = (x m) 2 + (x n) 2 r 2 = (x m) 2 + (y n) 2 Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
20 Circumcircle and Incircle 8 Write the equation for circle inscribed(circumscribed) in a square ABCD, where A[1, 1], B[2, 2] 8 InscribedSquare.ggb Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
21 Circumcircle about Rectangle The equation of a circle circumscribed about the rectangle ABCD, where A[2, 3], C[8, 3], is (x 3) 2 + (y 3) 2 = 36 x x + y 2 18 = 0 x 2 10x + y = 0 (x 10) 2 + y 2 72 = 0 x 2 10x + y = 0 Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
22 Inscribed Circle The equation of a circle inscribed in the square ABCD, where A[2, 1], C[4, 11], is x 2 + y 2 6x 12y + 32 = 0 x 2 + y 2 3x 6y 29 = 0 x 2 + y 2 + 6x + 12y 32 = 0 x 2 + y 2 + 6x 12y + 32 = 0 x 2 + y 2 6x + 12y + 29 = 0 Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
23 Circumcircle about Triangle Write the equation of the circle c circumscribed about the triangle ABC, where A[0, 0], B[2, 0], C[0, 2] Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
24 The equation of a circle circumscribed about the triangle ABC, where A[1, 5], B[9, 1], C[1, 1], is x 2 + y 2 10x 6y + 14 = 0 x 2 + y 2 5x 3y + 20 = 0 x 2 + y 2 10x + 6y 20 = 0 x 2 + y x + 6y 54 = 0 x 2 + y 2 + 5x + 3y + 20 = 0 Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
25 Nearest and Furthest point Consider a circle given by the equation x 2 + y 2 16x 12y + 75 = 0. The ratio of distances of the nearest and furthest points of this circle from the origin of the coordinate system is 1 : 11 1 : 3 2 : 3 1 : 2 3 : 13 Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
26 Circle and Tangent Line 9 Consider a circle with the center S[ 1, 3] and a tangent t given by the equation x 2y + 2 = 0. The equation of this circle is x 2 + y 2 + 2x 6y + 5 = 0 9 CircleTangent.ggb Šárka Voráčová Plane Geometry May 30, / 26
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Geometry. Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section.
 Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
Geometry Geometry is one of the most important topics of Quantitative Aptitude section. Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles are always equal. If any
14-9 Constructions Review. Geometry Period. Constructions Review
 Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
Name Geometry Period 14-9 Constructions Review Date Constructions Review Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties
Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review
 Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
Name 2-7 Review Geometry Period Unit 2 Constructions Review Date 2-1 Construct an Inscribed Regular Hexagon and Inscribed equilateral triangle. -Measuring radius distance to make arcs. -Properties of equilateral
February Regional Geometry Team: Question #1
 February Regional Geometry Team: Question #1 A = area of an equilateral triangle with a side length of 4. B = area of a square with a side length of 3. C = area of a regular hexagon with a side length
February Regional Geometry Team: Question #1 A = area of an equilateral triangle with a side length of 4. B = area of a square with a side length of 3. C = area of a regular hexagon with a side length
General Pyramids. General Cone. Right Circular Cone = "Cone"
 Aim #6: What are general pyramids and cones? CC Geometry H Do Now: Put the images shown below into the groups (A,B,C and D) based on their properties. Group A: General Cylinders Group B: Prisms Group C:
Aim #6: What are general pyramids and cones? CC Geometry H Do Now: Put the images shown below into the groups (A,B,C and D) based on their properties. Group A: General Cylinders Group B: Prisms Group C:
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions. 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system
 CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH6 2.1 Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system Coordinate axes: Two perpendicular lines that intersect at the origin O on each line.
CHAPTER 2 REVIEW COORDINATE GEOMETRY MATH6 2.1 Warm-Up: See Solved Homework questions 2.2 Cartesian coordinate system Coordinate axes: Two perpendicular lines that intersect at the origin O on each line.
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes
 Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Geometry 10 and 11 Notes Area and Volume Name Per Date 10.1 Area is the amount of space inside of a two dimensional object. When working with irregular shapes, we can find its area by breaking it up into
Geometry: Angle Relationships
 Geometry: Angle Relationships I. Define the following angles (in degrees) and draw an example of each. 1. Acute 3. Right 2. Obtuse 4. Straight Complementary angles: Supplementary angles: a + b = c + d
Geometry: Angle Relationships I. Define the following angles (in degrees) and draw an example of each. 1. Acute 3. Right 2. Obtuse 4. Straight Complementary angles: Supplementary angles: a + b = c + d
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department
 Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
Moore Catholic High School Math Department Geometry Vocabulary The following is a list of terms and properties which are necessary for success in a Geometry class. You will be tested on these terms during
January Regional Geometry Team: Question #1. January Regional Geometry Team: Question #2
 January Regional Geometry Team: Question #1 Points P, Q, R, S, and T lie in the plane with S on and R on. If PQ = 5, PS = 3, PR = 5, QS = 3, and RT = 4, what is ST? 3 January Regional Geometry Team: Question
January Regional Geometry Team: Question #1 Points P, Q, R, S, and T lie in the plane with S on and R on. If PQ = 5, PS = 3, PR = 5, QS = 3, and RT = 4, what is ST? 3 January Regional Geometry Team: Question
(1) Find the area of an equilateral triangle if each side is 8. (2) Given the figure to the right with measures as marked, find: mab, m BAF, m.
 (1) ind the area of an equilateral triangle if each side is 8. (2) Given the figure to the right with measures as marked, find: m, m, m, m 100 9 90 (3) ind the length of the arc of a sector of in a circle
(1) ind the area of an equilateral triangle if each side is 8. (2) Given the figure to the right with measures as marked, find: m, m, m, m 100 9 90 (3) ind the length of the arc of a sector of in a circle
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide
 Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Geometry Final Exam - Study Guide 1. Solve for x. True or False? (questions 2-5) 2. All rectangles are rhombuses. 3. If a quadrilateral is a kite, then it is a parallelogram. 4. If two parallel lines are
Midpoint of a Line Segment Pg. 78 # 1, 3, 4-6, 8, 18. Classifying Figures on a Cartesian Plane Quiz ( )
 UNIT 2 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Date Lesson TOPIC Homework Feb. 22 Feb. 23 Feb. 24 Feb. 27 Feb. 28 2.1 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.1-2.3 2.1-2.3 Mar. 1 2.6 2.4 Mar. 2 2.7 2.5 Mar. 3 2.8 2.6 Mar. 6 2.9 2.7 Mar.
UNIT 2 ANALYTIC GEOMETRY Date Lesson TOPIC Homework Feb. 22 Feb. 23 Feb. 24 Feb. 27 Feb. 28 2.1 2.1 2.2 2.2 2.3 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.1-2.3 2.1-2.3 Mar. 1 2.6 2.4 Mar. 2 2.7 2.5 Mar. 3 2.8 2.6 Mar. 6 2.9 2.7 Mar.
Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips
 & present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
& present Shortcuts, Formulas & Tips For MBA, Banking, Civil Services & Other Entrance Examinations Vol. 3: Geometry Lines and Angles Sum of the angles in a straight line is 180 Vertically opposite angles
with slopes m 1 and m 2 ), if and only if its coordinates satisfy the equation y y 0 = 0 and Ax + By + C 2
 CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
CHAPTER 10 Straight lines Learning Objectives (i) Slope (m) of a non-vertical line passing through the points (x 1 ) is given by (ii) If a line makes an angle α with the positive direction of x-axis, then
Geometry. Oklahoma Math Day INSTRUCTIONS:
 Oklahoma Math Day November 16, 016 Geometry INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Do not begin the test until told to do so.. Calculators are not permitted. 3. Be sure to enter your name and high school code on the answer
Oklahoma Math Day November 16, 016 Geometry INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Do not begin the test until told to do so.. Calculators are not permitted. 3. Be sure to enter your name and high school code on the answer
 CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
CHAPTER - 10 STRAIGHT LINES Slope or gradient of a line is defined as m = tan, ( 90 ), where is angle which the line makes with positive direction of x-axis measured in anticlockwise direction, 0 < 180
Log1 Contest Round 2 Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons. 4 points each
 Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
Name: Units do not have to be included. 016 017 Log1 Contest Round Theta Circles, Parabolas and Polygons 4 points each 1 Find the value of x given that 8 x 30 Find the area of a triangle given that it
If three points A (h, 0), P (a, b) and B (0, k) lie on a line, show that: a b 1.
 ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
ASSIGNMENT ON STRAIGHT LINES LEVEL 1 (CBSE/NCERT/STATE BOARDS) 1 Find the angle between the lines joining the points (0, 0), (2, 3) and the points (2, 2), (3, 5). 2 What is the value of y so that the line
DEFINITIONS. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle.
 DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
DEFINITIONS Degree A degree is the 1 th part of a straight angle. 180 Right Angle A 90 angle is called a right angle. Perpendicular Two lines are called perpendicular if they form a right angle. Congruent
Chapter 10 Similarity
 Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Chapter 10 Similarity Def: The ratio of the number a to the number b is the number. A proportion is an equality between ratios. a, b, c, and d are called the first, second, third, and fourth terms. The
Modeling with Geometry
 Modeling with Geometry 6.3 Parallelograms https://mathbitsnotebook.com/geometry/quadrilaterals/qdparallelograms.html Properties of Parallelograms Sides A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs
Modeling with Geometry 6.3 Parallelograms https://mathbitsnotebook.com/geometry/quadrilaterals/qdparallelograms.html Properties of Parallelograms Sides A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with both pairs
UCS Geometry SEMESTER 1 REVIEW GUIDE #2 STU COPY. 1. Translate the preimage A ( 2, 1) left 4 units and down 7 units.
 2015-2016 UCS Geometry SEMESTER 1 REVIEW GUIDE #2 STU COPY 1. Translate the preimage A ( 2, 1) left 4 units and down 7 units. 2. Use the rule (x, y) (x 5, y + 8) to describe in words how the translation
2015-2016 UCS Geometry SEMESTER 1 REVIEW GUIDE #2 STU COPY 1. Translate the preimage A ( 2, 1) left 4 units and down 7 units. 2. Use the rule (x, y) (x 5, y + 8) to describe in words how the translation
ADVANCED EXERCISE 09B: EQUATION OF STRAIGHT LINE
 ADVANCED EXERCISE 09B: EQUATION OF STRAIGHT LINE It is given that the straight line L passes through A(5, 5) and is perpendicular to the straight line L : x+ y 5= 0 (a) Find the equation of L (b) Find
ADVANCED EXERCISE 09B: EQUATION OF STRAIGHT LINE It is given that the straight line L passes through A(5, 5) and is perpendicular to the straight line L : x+ y 5= 0 (a) Find the equation of L (b) Find
Point A location in geometry. A point has no dimensions without any length, width, or depth. This is represented by a dot and is usually labelled.
 Test Date: November 3, 2016 Format: Scored out of 100 points. 8 Multiple Choice (40) / 8 Short Response (60) Topics: Points, Angles, Linear Objects, and Planes Recognizing the steps and procedures for
Test Date: November 3, 2016 Format: Scored out of 100 points. 8 Multiple Choice (40) / 8 Short Response (60) Topics: Points, Angles, Linear Objects, and Planes Recognizing the steps and procedures for
Index COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Symbols & Numerics
 Symbols & Numerics. (dot) character, point representation, 37 symbol, perpendicular lines, 54 // (double forward slash) symbol, parallel lines, 54, 60 : (colon) character, ratio of quantity representation
Symbols & Numerics. (dot) character, point representation, 37 symbol, perpendicular lines, 54 // (double forward slash) symbol, parallel lines, 54, 60 : (colon) character, ratio of quantity representation
Acknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILAR TRIANGLES. 1. Definition: A ratio represents the comparison of two quantities.
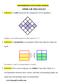 1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
1 cknowledgement: Scott, Foresman. Geometry. SIMILR TRINGLS 1. efinition: ratio represents the comparison of two quantities. In figure, ratio of blue squares to white squares is 3 : 5 2. efinition: proportion
ME 111: Engineering Drawing. Geometric Constructions
 ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 2 01-08-2011 Geometric Constructions Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 Geometric Construction Construction of primitive geometric forms (points,
ME 111: Engineering Drawing Lecture 2 01-08-2011 Geometric Constructions Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Guwahati 781039 Geometric Construction Construction of primitive geometric forms (points,
 1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
1 www.gradestack.com/ssc Dear readers, ADVANCE MATHS - GEOMETRY DIGEST Geometry is a very important topic in numerical ability section of SSC Exams. You can expect 14-15 questions from Geometry in SSC
Geometry Mathematics Content Standards
 85 The geometry skills and concepts developed in this discipline are useful to all students. Aside from learning these skills and concepts, students will develop their ability to construct formal, logical
85 The geometry skills and concepts developed in this discipline are useful to all students. Aside from learning these skills and concepts, students will develop their ability to construct formal, logical
a) 1/3 area of triangle ABC b) 3.6 c) 3 d) e) Euclid s fifth postulate is equivalent to: Given a line and a point not on that line
 1. Given is a right triangle with AD a perpendicular from the right angle to the hypotenuse, find the length of AD given AB = 6, BC = 10 and AC = 8. B D A C a) 7.5 b) 6.5 c) 4.8 d) e) 2. Using the figure
1. Given is a right triangle with AD a perpendicular from the right angle to the hypotenuse, find the length of AD given AB = 6, BC = 10 and AC = 8. B D A C a) 7.5 b) 6.5 c) 4.8 d) e) 2. Using the figure
Day 5: Inscribing and Circumscribing Getting Closer to π: Inscribing and Circumscribing Polygons - Archimedes Method. Goals:
 Day 5: Inscribing and Circumscribing Getting Closer to π: Inscribing and Circumscribing Polygons - Archimedes Method Goals: Construct an inscribed hexagon and dodecagon. Construct a circumscribed hexagon
Day 5: Inscribing and Circumscribing Getting Closer to π: Inscribing and Circumscribing Polygons - Archimedes Method Goals: Construct an inscribed hexagon and dodecagon. Construct a circumscribed hexagon
Note: For all questions, answer (E) NOTA means none of the above answers is correct. Unless otherwise specified, all angles are measured in degrees.
 Note: For all questions, answer means none of the above answers is correct. Unless otherwise specified, all angles are measured in degrees. 1. The three angles of a triangle have measures given by 3 5,
Note: For all questions, answer means none of the above answers is correct. Unless otherwise specified, all angles are measured in degrees. 1. The three angles of a triangle have measures given by 3 5,
SOAR2001 GEOMETRY SUMMER 2001
 SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
SR2001 GEMETRY SUMMER 2001 1. Introduction to plane geometry This is the short version of the notes for one of the chapters. The proofs are omitted but some hints are given. Try not to use the hints first,
The scale factor between the blue diamond and the green diamond is, so the ratio of their areas is.
 For each pair of similar figures, find the area of the green figure. 1. The scale factor between the blue diamond and the green diamond is, so the ratio of their areas is. The area of the green diamond
For each pair of similar figures, find the area of the green figure. 1. The scale factor between the blue diamond and the green diamond is, so the ratio of their areas is. The area of the green diamond
Geometry 2 Final Review
 Name: Period: Date: Geometry 2 Final Review 1 Find x in ABC. 5 Find x in ABC. 2 Find x in STU. 6 Find cos A in ABC. 3 Find y in XYZ. 7 Find x to the nearest tenth. 4 Find x in HJK. 8 Find the angle of
Name: Period: Date: Geometry 2 Final Review 1 Find x in ABC. 5 Find x in ABC. 2 Find x in STU. 6 Find cos A in ABC. 3 Find y in XYZ. 7 Find x to the nearest tenth. 4 Find x in HJK. 8 Find the angle of
FORMULAS to UNDERSTAND & MEMORIZE
 1 of 6 FORMULAS to UNDERSTAND & MEMORIZE Now we come to the part where you need to just bear down and memorize. To make the process a bit simpler, I am providing all of the key info that they re going
1 of 6 FORMULAS to UNDERSTAND & MEMORIZE Now we come to the part where you need to just bear down and memorize. To make the process a bit simpler, I am providing all of the key info that they re going
Geometry Rules. Triangles:
 Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
Triangles: Geometry Rules 1. Types of Triangles: By Sides: Scalene - no congruent sides Isosceles - 2 congruent sides Equilateral - 3 congruent sides By Angles: Acute - all acute angles Right - one right
MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS
 MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS KEY IDEAS 1. To copy a segment, follow the steps given: Given: AB Construct: PQ congruent to AB 1. Use a straightedge to draw a line, l. 2. Choose a point on line l and label
MAKE GEOMETRIC CONSTRUCTIONS KEY IDEAS 1. To copy a segment, follow the steps given: Given: AB Construct: PQ congruent to AB 1. Use a straightedge to draw a line, l. 2. Choose a point on line l and label
Mathematics
 Mathematics Total Score 80 Time 2 ½ hours Instructions Read the instructions against each question before answering them Logical explanations should be given wherever necessary If two questions have OR
Mathematics Total Score 80 Time 2 ½ hours Instructions Read the instructions against each question before answering them Logical explanations should be given wherever necessary If two questions have OR
Chapter 11 Review. Period:
 Chapter 11 Review Name: Period: 1. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a pentagon. 6. Find the area of an equilateral triangle with side 1.. Find the sum of the measures of the interior
Chapter 11 Review Name: Period: 1. Find the sum of the measures of the interior angles of a pentagon. 6. Find the area of an equilateral triangle with side 1.. Find the sum of the measures of the interior
EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS
 EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS Steps to Find the Median of a Triangle: -Find the midpoint of a segment using the midpoint formula. -Use the vertex and midpoint to find the
EQUATIONS OF ALTITUDES, MEDIANS, and PERPENDICULAR BISECTORS Steps to Find the Median of a Triangle: -Find the midpoint of a segment using the midpoint formula. -Use the vertex and midpoint to find the
Perimeter. Area. Surface Area. Volume. Circle (circumference) C = 2πr. Square. Rectangle. Triangle. Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh
 Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Perimeter Circle (circumference) C = 2πr Square P = 4s Rectangle P = 2b + 2h Area Circle A = πr Triangle A = bh Rectangle/Parallelogram A = bh Rhombus/Kite A = d d Trapezoid A = b + b h A area a apothem
Mathematical derivations of some important formula in 2D-Geometry by HCR
 From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Summer March 31, 2018 Mathematical derivations of some important formula in 2D-Geometry by HCR Harish Chandra Rajpoot, HCR Available at: https://works.bepress.com/harishchandrarajpoot_hcrajpoot/61/
From the SelectedWorks of Harish Chandra Rajpoot H.C. Rajpoot Summer March 31, 2018 Mathematical derivations of some important formula in 2D-Geometry by HCR Harish Chandra Rajpoot, HCR Available at: https://works.bepress.com/harishchandrarajpoot_hcrajpoot/61/
EUCLID S GEOMETRY. Raymond Hoobler. January 27, 2008
 EUCLID S GEOMETRY Raymond Hoobler January 27, 2008 Euclid rst codi ed the procedures and results of geometry, and he did such a good job that even today it is hard to improve on his presentation. He lived
EUCLID S GEOMETRY Raymond Hoobler January 27, 2008 Euclid rst codi ed the procedures and results of geometry, and he did such a good job that even today it is hard to improve on his presentation. He lived
Entrance Exam Wiskunde B
 CENTRALE COMMISSIE VOORTENTAMEN WISKUNDE Entrance Exam Wiskunde B Date: 16 January 2015 Time: 13.30 16.30 Questions: 5 Please read the instructions below carefully before answering the questions. There
CENTRALE COMMISSIE VOORTENTAMEN WISKUNDE Entrance Exam Wiskunde B Date: 16 January 2015 Time: 13.30 16.30 Questions: 5 Please read the instructions below carefully before answering the questions. There
7. 2 More Things Under. Construction. A Develop Understanding Task
 7 Construction A Develop Understanding Task Like a rhombus, an equilateral triangle has three congruent sides. Show and describe how you might locate the third vertex point on an equilateral triangle,
7 Construction A Develop Understanding Task Like a rhombus, an equilateral triangle has three congruent sides. Show and describe how you might locate the third vertex point on an equilateral triangle,
1. AREAS. Geometry 199. A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh. B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh. C. Rhombus = 1 product of the diagonals = 1 dd
 Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
Geometry 199 1. AREAS A. Rectangle = base altitude = bh Area = 40 B. Parallelogram = base altitude = bh Area = 40 Notice that the altitude is different from the side. It is always shorter than the second
SOL Chapter Due Date
 Name: Block: Date: Geometry SOL Review SOL Chapter Due Date G.1 2.2-2.4 G.2 3.1-3.5 G.3 1.3, 4.8, 6.7, 9 G.4 N/A G.5 5.5 G.6 4.1-4.7 G.7 6.1-6.6 G.8 7.1-7.7 G.9 8.2-8.6 G.10 1.6, 8.1 G.11 10.1-10.6, 11.5,
Name: Block: Date: Geometry SOL Review SOL Chapter Due Date G.1 2.2-2.4 G.2 3.1-3.5 G.3 1.3, 4.8, 6.7, 9 G.4 N/A G.5 5.5 G.6 4.1-4.7 G.7 6.1-6.6 G.8 7.1-7.7 G.9 8.2-8.6 G.10 1.6, 8.1 G.11 10.1-10.6, 11.5,
MANHATTAN HUNTER SCIENCE HIGH SCHOOL GEOMETRY CURRICULUM
 COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
COORDINATE Geometry Plotting points on the coordinate plane. Using the Distance Formula: Investigate, and apply the Pythagorean Theorem as it relates to the distance formula. (G.GPE.7, 8.G.B.7, 8.G.B.8)
Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units
 Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units affine linear equation: an equation in which both sides are sums of terms that are either a number times y or a number times x or just a number [SlL2-D5]
Glossary of dictionary terms in the AP geometry units affine linear equation: an equation in which both sides are sums of terms that are either a number times y or a number times x or just a number [SlL2-D5]
Angles. An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex.
 Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
Angles An angle is: the union of two rays having a common vertex. Angles can be measured in both degrees and radians. A circle of 360 in radian measure is equal to 2π radians. If you draw a circle with
MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 4th YEAR
 European Schools Office of the Secretary-General Pedagogical Development Unit Ref.: 2010-D-581-en-2 Orig.: EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 4th YEAR 4 period/week course APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING
European Schools Office of the Secretary-General Pedagogical Development Unit Ref.: 2010-D-581-en-2 Orig.: EN MATHEMATICS SYLLABUS SECONDARY 4th YEAR 4 period/week course APPROVED BY THE JOINT TEACHING
Common Core State Standards High School Geometry Constructions
 ommon ore State Standards High School Geometry onstructions HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying a line segment HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying an angle HSG.O..12 onstruction: isecting a line segment HSG.O..12
ommon ore State Standards High School Geometry onstructions HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying a line segment HSG.O..12 onstruction: opying an angle HSG.O..12 onstruction: isecting a line segment HSG.O..12
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties
 Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Videos, Constructions, Definitions, Postulates, Theorems, and Properties Videos Proof Overview: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof Modules 9 and 10: http://tinyurl.com/riehlproof2 Module 9 Review: http://tinyurl.com/module9livelesson-recording
Section Congruence Through Constructions
 Section 10.1 - Congruence Through Constructions Definitions: Similar ( ) objects have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Congruent ( =) objects have the same size as well as the same shape.
Section 10.1 - Congruence Through Constructions Definitions: Similar ( ) objects have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. Congruent ( =) objects have the same size as well as the same shape.
Section 12.1 Translations and Rotations
 Section 12.1 Translations and Rotations Any rigid motion that preserves length or distance is an isometry. We look at two types of isometries in this section: translations and rotations. Translations A
Section 12.1 Translations and Rotations Any rigid motion that preserves length or distance is an isometry. We look at two types of isometries in this section: translations and rotations. Translations A
3. The sides of a rectangle are in ratio fo 3:5 and the rectangle s area is 135m2. Find the dimensions of the rectangle.
 Geometry B Honors Chapter Practice Test 1. Find the area of a square whose diagonal is. 7. Find the area of the triangle. 60 o 12 2. Each rectangle garden below has an area of 0. 8. Find the area of the
Geometry B Honors Chapter Practice Test 1. Find the area of a square whose diagonal is. 7. Find the area of the triangle. 60 o 12 2. Each rectangle garden below has an area of 0. 8. Find the area of the
Study Guide - Geometry
 Study Guide - Geometry (NOTE: This does not include every topic on the outline. Take other steps to review those.) Page 1: Rigid Motions Page 3: Constructions Page 12: Angle relationships Page 14: Angle
Study Guide - Geometry (NOTE: This does not include every topic on the outline. Take other steps to review those.) Page 1: Rigid Motions Page 3: Constructions Page 12: Angle relationships Page 14: Angle
Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist
 3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
3 undefined terms: point, line, plane Definition / Postulates / Theorems Checklist Section Definition Postulate Theorem 1.2 Space Collinear Non-collinear Coplanar Non-coplanar Intersection 1.3 Segment
Postulates, Theorems, and Corollaries. Chapter 1
 Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Chapter 1 Post. 1-1-1 Through any two points there is exactly one line. Post. 1-1-2 Through any three noncollinear points there is exactly one plane containing them. Post. 1-1-3 If two points lie in a
Geometry - Chapter 1 - Corrective #1
 Class: Date: Geometry - Chapter 1 - Corrective #1 Short Answer 1. Sketch a figure that shows two coplanar lines that do not intersect, but one of the lines is the intersection of two planes. 2. Name two
Class: Date: Geometry - Chapter 1 - Corrective #1 Short Answer 1. Sketch a figure that shows two coplanar lines that do not intersect, but one of the lines is the intersection of two planes. 2. Name two
SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal)
 1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
1 SOME IMPORTANT PROPERTIES/CONCEPTS OF GEOMETRY (Compiled by Ronnie Bansal) 1. Basic Terms and Definitions: a) Line-segment: A part of a line with two end points is called a line-segment. b) Ray: A part
Mgr. ubomíra Tomková GEOMETRY
 GEOMETRY NAMING ANGLES: any angle less than 90º is an acute angle any angle equal to 90º is a right angle any angle between 90º and 80º is an obtuse angle any angle between 80º and 60º is a reflex angle
GEOMETRY NAMING ANGLES: any angle less than 90º is an acute angle any angle equal to 90º is a right angle any angle between 90º and 80º is an obtuse angle any angle between 80º and 60º is a reflex angle
Night Classes Geometry - 2
 Geometry - 2 Properties of four centres in a triangle Median: Area of ABD = area of ADC Angle Bisector: Properties of four centres in a triangle Angle Bisector: Properties of four centres in a triangle
Geometry - 2 Properties of four centres in a triangle Median: Area of ABD = area of ADC Angle Bisector: Properties of four centres in a triangle Angle Bisector: Properties of four centres in a triangle
EOC Review: Practice: 1. In the circle below, AB = 2BC. What is the probability of hitting the shaded region with a random dart?
 EOC Review: Focus Areas: Trigonometric Ratios Area and Volume including Changes in Area/Volume Geometric Probability Proofs and Deductive Reasoning including Conditionals Properties of Polygons and Circles
EOC Review: Focus Areas: Trigonometric Ratios Area and Volume including Changes in Area/Volume Geometric Probability Proofs and Deductive Reasoning including Conditionals Properties of Polygons and Circles
ARML Practice Problems Arvind Thiagarajan, May 7, 2006
 1 Geometry Problems ARML Practice Problems Arvind Thiagarajan, 005-006 May 7, 006 1. Find the coordinates of the point on the circle with equation (x 6) + (y 5) = 5 that is nearest the point (, 11). (TJ
1 Geometry Problems ARML Practice Problems Arvind Thiagarajan, 005-006 May 7, 006 1. Find the coordinates of the point on the circle with equation (x 6) + (y 5) = 5 that is nearest the point (, 11). (TJ
Indiana State Math Contest Geometry
 Indiana State Math Contest 018 Geometry This test was prepared by faculty at Indiana University - Purdue University Columbus Do not open this test booklet until you have been advised to do so by the test
Indiana State Math Contest 018 Geometry This test was prepared by faculty at Indiana University - Purdue University Columbus Do not open this test booklet until you have been advised to do so by the test
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1
 P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
P1 REVISION EXERCISE: 1 1. Solve the simultaneous equations: x + y = x +y = 11. For what values of p does the equation px +4x +(p 3) = 0 have equal roots? 3. Solve the equation 3 x 1 =7. Give your answer
Angles. Classification Acute Right Obtuse. Complementary s 2 s whose sum is 90 Supplementary s 2 s whose sum is 180. Angle Addition Postulate
 ngles Classification cute Right Obtuse Complementary s 2 s whose sum is 90 Supplementary s 2 s whose sum is 180 ngle ddition Postulate If the exterior sides of two adj s lie in a line, they are supplementary
ngles Classification cute Right Obtuse Complementary s 2 s whose sum is 90 Supplementary s 2 s whose sum is 180 ngle ddition Postulate If the exterior sides of two adj s lie in a line, they are supplementary
fall08ge Geometry Regents Exam Test Sampler fall08 4 The diagram below shows the construction of the perpendicular bisector of AB.
 fall08ge 1 Isosceles trapezoid ABCD has diagonals AC and BD. If AC = 5x + 13 and BD = 11x 5, what is the value of x? 1) 8 4 The diagram below shows the construction of the perpendicular bisector of AB.
fall08ge 1 Isosceles trapezoid ABCD has diagonals AC and BD. If AC = 5x + 13 and BD = 11x 5, what is the value of x? 1) 8 4 The diagram below shows the construction of the perpendicular bisector of AB.
Chapter 1. Linear Equations and Straight Lines. 2 of 71. Copyright 2014, 2010, 2007 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Straight Lines 2 of 71 Outline 1.1 Coordinate Systems and Graphs 1.4 The Slope of a Straight Line 1.3 The Intersection Point of a Pair of Lines 1.2 Linear Inequalities 1.5
Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Straight Lines 2 of 71 Outline 1.1 Coordinate Systems and Graphs 1.4 The Slope of a Straight Line 1.3 The Intersection Point of a Pair of Lines 1.2 Linear Inequalities 1.5
Geometry Vocabulary Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1
 Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
Math Fundamentals Reference Sheet Page 1 Acute Angle An angle whose measure is between 0 and 90 Acute Triangle A that has all acute Adjacent Alternate Interior Angle Two coplanar with a common vertex and
LT 1.2 Linear Measure (*) LT 1.3 Distance and Midpoints (*) LT 1.4 Angle Measure (*) LT 1.5 Angle Relationships (*) LT 1.6 Two-Dimensional Figures (*)
 PS1 Tools of Geometry: Students will be able to find distances between points and midpoints of line segments; identify angle relationships; and find perimeters, areas, surface areas and volumes. LT 1.1
PS1 Tools of Geometry: Students will be able to find distances between points and midpoints of line segments; identify angle relationships; and find perimeters, areas, surface areas and volumes. LT 1.1
Introduction to Geometry
 Introduction to Geometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (211 topics + 6 additional topics)
Introduction to Geometry This course covers the topics outlined below. You can customize the scope and sequence of this course to meet your curricular needs. Curriculum (211 topics + 6 additional topics)
TENTH YEAR MATHEMATICS
 10 The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION TENTH YEAR MATHEMATICS Wednesday, August 16, 1967-8 :30 to 11 :30 a.m., only The last page of the booklet is the answer sheet,
10 The University of the State of New York REGENTS HIGH SCHOOL EXAMINATION TENTH YEAR MATHEMATICS Wednesday, August 16, 1967-8 :30 to 11 :30 a.m., only The last page of the booklet is the answer sheet,
Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry
 Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry 1 Mark Questions 1. Where do these following points lie (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) A. Given points (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) The x coordinates of each point is zero.
Chapter 7 Coordinate Geometry 1 Mark Questions 1. Where do these following points lie (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) A. Given points (0, 3), (0, 8), (0, 6), (0, 4) The x coordinates of each point is zero.
Chapter 10 Practice Test
 Chapter 10 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the area. The figure is not drawn to scale. 7.6 cm 3.7 cm a. b. c. d. 2.
Chapter 10 Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Find the area. The figure is not drawn to scale. 7.6 cm 3.7 cm a. b. c. d. 2.
Class Generated Review Sheet for Math 213 Final
 Class Generated Review Sheet for Math 213 Final Key Ideas 9.1 A line segment consists of two point on a plane and all the points in between them. Complementary: The sum of the two angles is 90 degrees
Class Generated Review Sheet for Math 213 Final Key Ideas 9.1 A line segment consists of two point on a plane and all the points in between them. Complementary: The sum of the two angles is 90 degrees
10.6 Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons
 10.6. Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons www.ck12.org 10.6 Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons Learning Objectives Calculate the area and perimeter of a regular polygon. Review Queue 1. What is
10.6. Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons www.ck12.org 10.6 Area and Perimeter of Regular Polygons Learning Objectives Calculate the area and perimeter of a regular polygon. Review Queue 1. What is
Geometry Semester 1 Model Problems (California Essential Standards) Short Answer
 Geometry Semester 1 Model Problems (California Essential Standards) Short Answer GE 1.0 1. List the undefined terms in Geometry. 2. Match each of the terms with the corresponding example a. A theorem.
Geometry Semester 1 Model Problems (California Essential Standards) Short Answer GE 1.0 1. List the undefined terms in Geometry. 2. Match each of the terms with the corresponding example a. A theorem.
Name Honors Geometry Final Exam Review
 2014-2015 Name Honors Geometry Final Eam Review Chapter 5 Use the picture at the right to answer the following questions. 1. AC= 2. m BFD = 3. m CAE = A 29 C B 71⁰ 19 D 16 F 65⁰ E 4. Find the equation
2014-2015 Name Honors Geometry Final Eam Review Chapter 5 Use the picture at the right to answer the following questions. 1. AC= 2. m BFD = 3. m CAE = A 29 C B 71⁰ 19 D 16 F 65⁰ E 4. Find the equation
4. Find the exact circumference of a circle with diameter 12 in.
 TMTA Geometry Test 008 1. The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is 0 inches. The area in square inches is 5 50 5 a ) 5 5. Which of the following pairs of angles are complementary? 1,77 180 45,90 6,
TMTA Geometry Test 008 1. The perimeter of an equilateral triangle is 0 inches. The area in square inches is 5 50 5 a ) 5 5. Which of the following pairs of angles are complementary? 1,77 180 45,90 6,
February Regional Geometry Individual Test
 Calculators are NOT to be used for this test. For all problems, answer choice E, NOTA, means none of the above answers is correct. Assume all measurements to be in units unless otherwise specified; angle
Calculators are NOT to be used for this test. For all problems, answer choice E, NOTA, means none of the above answers is correct. Assume all measurements to be in units unless otherwise specified; angle
GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders
 GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders Paddy Johnson and Tim Brophy www.ul.ie/cemtl/ Table of Contents 1. Square Construction and Measurement 2 2. Circumscribed Circle of a Triangle
GeoGebra Workbook 2 More Constructions, Measurements and Sliders Paddy Johnson and Tim Brophy www.ul.ie/cemtl/ Table of Contents 1. Square Construction and Measurement 2 2. Circumscribed Circle of a Triangle
Theta Circles & Polygons 2015 Answer Key 11. C 2. E 13. D 4. B 15. B 6. C 17. A 18. A 9. D 10. D 12. C 14. A 16. D
 Theta Circles & Polygons 2015 Answer Key 1. C 2. E 3. D 4. B 5. B 6. C 7. A 8. A 9. D 10. D 11. C 12. C 13. D 14. A 15. B 16. D 17. A 18. A 19. A 20. B 21. B 22. C 23. A 24. C 25. C 26. A 27. C 28. A 29.
Theta Circles & Polygons 2015 Answer Key 1. C 2. E 3. D 4. B 5. B 6. C 7. A 8. A 9. D 10. D 11. C 12. C 13. D 14. A 15. B 16. D 17. A 18. A 19. A 20. B 21. B 22. C 23. A 24. C 25. C 26. A 27. C 28. A 29.
Geometry / Integrated II TMTA Test units.
 1. An isosceles triangle has a side of length 2 units and another side of length 3 units. Which of the following best completes the statement The length of the third side of this triangle? (a) is (b) is
1. An isosceles triangle has a side of length 2 units and another side of length 3 units. Which of the following best completes the statement The length of the third side of this triangle? (a) is (b) is
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures
 MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
MATH 113 Section 8.2: Two-Dimensional Figures Prof. Jonathan Duncan Walla Walla University Winter Quarter, 2008 Outline 1 Classifying Two-Dimensional Shapes 2 Polygons Triangles Quadrilaterals 3 Other
2.1 Length of a Line Segment
 .1 Length of a Line Segment MATHPOWER TM 10 Ontario Edition pp. 66 7 To find the length of a line segment joining ( 1 y 1 ) and ( y ) use the formula l= ( ) + ( y y ). 1 1 Name An equation of the circle
.1 Length of a Line Segment MATHPOWER TM 10 Ontario Edition pp. 66 7 To find the length of a line segment joining ( 1 y 1 ) and ( y ) use the formula l= ( ) + ( y y ). 1 1 Name An equation of the circle
? Answer:
 A1 What is the value of 1 2 + 2 3 + 3 4 + 4 5 5 2? A2 What is the value of k? 11 2 22 2 33 2 = 66 2 k. A3 The four-digit integers 5634 and 6435 share the following two properties: (i) they consist of four
A1 What is the value of 1 2 + 2 3 + 3 4 + 4 5 5 2? A2 What is the value of k? 11 2 22 2 33 2 = 66 2 k. A3 The four-digit integers 5634 and 6435 share the following two properties: (i) they consist of four
Chapter Test Form A. 173 Holt Geometry. Name Date Class. 1. Find the area of the triangle.
 Form A 1. Find the area of the triangle. 6. A square has a perimeter of 8 inches. Find the area of the square. cm 7. Find the circumference of C in terms of.. Find the area of the parallelogram. 11 cm
Form A 1. Find the area of the triangle. 6. A square has a perimeter of 8 inches. Find the area of the square. cm 7. Find the circumference of C in terms of.. Find the area of the parallelogram. 11 cm
PCTI Geometry. Summer Packet
 PCTI Geometry Summer Packet 2017 1 This packet has been designed to help you review various mathematical topics that will be necessary for your success in Geometry. INSTRUCTIONS: Do all problems without
PCTI Geometry Summer Packet 2017 1 This packet has been designed to help you review various mathematical topics that will be necessary for your success in Geometry. INSTRUCTIONS: Do all problems without
High School Geometry
 High School Geometry This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
High School Geometry This course covers the topics shown below. Students navigate learning paths based on their level of readiness. Institutional users may customize the scope and sequence to meet curricular
2. The pentagon shown is regular. Name Geometry Semester 1 Review Guide Hints: (transformation unit)
 Name Geometry Semester 1 Review Guide 1 2014-2015 1. Jen and Beth are graphing triangles on this coordinate grid. Beth graphed her triangle as shown. Jen must now graph the reflection of Beth s triangle
Name Geometry Semester 1 Review Guide 1 2014-2015 1. Jen and Beth are graphing triangles on this coordinate grid. Beth graphed her triangle as shown. Jen must now graph the reflection of Beth s triangle
Assignment List. Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry. Chapter 2 Reasoning and Proof. Chapter 3 Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
 Geometry Assignment List Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry 1.1 Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 5 #1, 4-38 even, 44-58 even 27 1.2 Use Segments and Congruence 12 #4-36 even, 37-45 all 26 1.3 Use Midpoint
Geometry Assignment List Chapter 1 Essentials of Geometry 1.1 Identify Points, Lines, and Planes 5 #1, 4-38 even, 44-58 even 27 1.2 Use Segments and Congruence 12 #4-36 even, 37-45 all 26 1.3 Use Midpoint
Find the locus of the center of a bicycle wheel touching the floor and two corner walls.
 WFNMC conference - Riga - July 00 Maurice Starck - mstarck@canl.nc Three problems My choice of three problems, ordered in increasing difficulty. The first is elementary, but the last is a very difficult
WFNMC conference - Riga - July 00 Maurice Starck - mstarck@canl.nc Three problems My choice of three problems, ordered in increasing difficulty. The first is elementary, but the last is a very difficult
Geometry Foundations Planning Document
 Geometry Foundations Planning Document Unit 1: Chromatic Numbers Unit Overview A variety of topics allows students to begin the year successfully, review basic fundamentals, develop cooperative learning
Geometry Foundations Planning Document Unit 1: Chromatic Numbers Unit Overview A variety of topics allows students to begin the year successfully, review basic fundamentals, develop cooperative learning
Select the best answer. Bubble the corresponding choice on your scantron. Team 13. Geometry
 Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
Team Geometry . What is the sum of the interior angles of an equilateral triangle? a. 60 b. 90 c. 80 d. 60. The sine of angle A is. What is the cosine of angle A? 6 4 6 a. b. c.. A parallelogram has all
