Exercises for Discrete Maths
|
|
|
- Jordan Kelley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Exercises for Discrete Maths Discrete Maths Teacher: Alessandro Artale Teaching Assistants: Elena Botoeva, Daniele Porello Week 6 Computer Science Free University of Bozen-Bolzano Disclaimer. The course exercises are meant for the students of the course of Discrete Mathematics and Logic at the Free University of Bozen-Bolzano.
2 Graph Theory 1 Exercise Set 10.2: Euler Circuits In the following cases, answer to this question: Does the graph have an Euler circuit? Justify your answers. Recall that: An Euler circuit for G is a circuit that contains every vertex and every edge of G. (That is, an Euler circuit for G is a sequence of adjacent vertices and edges in G that has at least one edge, starts and ends at the same vertex, uses every vertex of G at least once, and uses every edge of G exactly once.) Theorem A graph G has an Euler circuit if, and only if, G is connected and every vertex of G has positive even degree. Exercise 9. a. G is a connected graph with five vertices of degrees 2, 2, 3, 3, and 4. Answer. No, since there are vertices with odd degrees. b. G is a connected graph with five vertices of degrees 2, 2, 4, 4, and 6. Answer. Yes, since all degrees are even and the graph is connected. c. G is a graph with five vertices of degrees 2, 2, 4, 4, and 6. Answer. Not necessarily. Take a graph G with vertices A, B, C, D, E, each with a loop. Let G have two edges connecting A and B, and two other edges connecting A and C. Then G has five vertices of degrees 2, 2, 4, 4, 6, and it is not connected. Thus it does not have an Euler circuit. c (sligthly modified). G is a graph without parallel edges and with five vertices of degrees 2, 2, 4, 4, and 6. Answer. Since the graph has no parallel edges, the vertex of degree 6 must have 4 distinct connected vertices, and a loop. Then the graph is connected with vertices of positive degrees only. Therefore the graph has an Euler circuit.
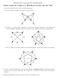
3 2 Exercise 12 & 13 (Homework). Check if the graphs in Fig. 1 and Fig. 2 have an Euler circuit. If the graph does not have an Euler circuit, explain why not. If it does have an Euler circuit, describe one. Figure 1. Graph for Exercise 12 Figure 2. Graph for Exercise 13 Answer. Answer. Ex.12: Yes. One Euler circuit is e4e5e6e3e2e7e8e1. Ex.13: No, since it has vertices with odd degree.
4 3 Exercise Set 10.4: Graph Isomorphisms Determine whether the graphs shown are isomorphic or not. Figure 3. Graph for Exercise 1 Exercise 1. Answer. They are isomorphic. Figure 4. Graph for Exercise 2 Exercise 2. Answer. They are not since deg is an invariant and deg(v2) = 5 and there is not w in G with such a degree. Figure 5. Graph for Exercise 6 Exercise 6 (Homework). Answer. Yes they are isomorphic.
5 4 Figure 6. Graph for Exercise 7 Exercise 7 (Homework). Answer. Yes they are. Pull w 2 below w 3. Take the mapping v1 w1, v2 w3, v4 w4, v3 w2. It preserves the edge relation, i.e., if there is an edge between v n and v m then there is an edge between the images of v n and v m. Figure 7. Graph for Exercise 8 Exercise 8. Answer. The two graphs are not isomorphic. G has a circuit of length 3 while G does not.
6 5 Figure 8. Graph for Exercise 9 Exercise 9 (Homework). Answer. a u b v f z c y e w d x Yes. The function is the following: Figure 9. Graph for Exercise 10 Exercise 10 (Homework). Answer. The graph are isomorphic. Firstly pull a and c down. Then move e to the left of g. The mapping is now easier to spot. Exercise 14. Draw all non-isomorphic simple graphs with three vertices. Solution. See Figure 10.
7 6 Figure 10. Solution for Exercise 14 Exercise Set 10.5: Trees Exercise 3. What is the total degree of a tree with n vertices? Why? Solution. 2n 2 (For any n N, any tree with n vertices has n 1 edges; the degree of a tree/graph is 2 number of edges). Exercise 8. Is there a tree with 9 vertices and 9 edges? Answer. No, due to the previous theorem: any tree with n vertices has n 1 edges. Exercise 12 (Homework). Is there a tree with 5 vertices and total degree 8? Answer. The tree has 4 = 5 1 edges, and hence total degree 2 4 = 8. Yes, there can be such a tree. For instance, one has two leaves (each with degree 1). The other vertices are internal of degree 2 and connected to each other and the other two vertices. Exercise Set 10.6: Binary Trees In each of the following exercises, either draw a graph with the given specifications, or explain why no such graph exists. Exercise 11. A binary tree with height 3 and 9 terminal vertices. Solution. Remember the following: if T is any binary tree with height h and t terminal vertices, then 9 = t 2 h = 8. So no.
8 Exercise 12. A full binary tree, 8 internal vertices (k), and 7 terminal vertices. Solution. Remember the following: If T is a full binary tree with k > 0 internal vertices, then T has a total of 2k + 1 vertices and has k + 1 terminal vertices. So the number of terminal vertices is k + 1 = So no. Exercise 18 (Homework). Tree, 5 vertices, total degree 10. Solution. No. By Ex. 3, Set 10.5, the total degree of a tree with n vertices is 2n-2. Hence 10 = which is false. 7
γ(ɛ) (a, b) (a, d) (d, a) (a, b) (c, d) (d, d) (e, e) (e, a) (e, e) (a) Draw a picture of G.
 MAD 3105 Spring 2006 Solutions for Review for Test 2 1. Define a graph G with V (G) = {a, b, c, d, e}, E(G) = {r, s, t, u, v, w, x, y, z} and γ, the function defining the edges, is given by the table ɛ
MAD 3105 Spring 2006 Solutions for Review for Test 2 1. Define a graph G with V (G) = {a, b, c, d, e}, E(G) = {r, s, t, u, v, w, x, y, z} and γ, the function defining the edges, is given by the table ɛ
Introduction III. Graphs. Motivations I. Introduction IV
 Introduction I Graphs Computer Science & Engineering 235: Discrete Mathematics Christopher M. Bourke cbourke@cse.unl.edu Graph theory was introduced in the 18th century by Leonhard Euler via the Königsberg
Introduction I Graphs Computer Science & Engineering 235: Discrete Mathematics Christopher M. Bourke cbourke@cse.unl.edu Graph theory was introduced in the 18th century by Leonhard Euler via the Königsberg
Math.3336: Discrete Mathematics. Chapter 10 Graph Theory
 Math.3336: Discrete Mathematics Chapter 10 Graph Theory Instructor: Dr. Blerina Xhabli Department of Mathematics, University of Houston https://www.math.uh.edu/ blerina Email: blerina@math.uh.edu Fall
Math.3336: Discrete Mathematics Chapter 10 Graph Theory Instructor: Dr. Blerina Xhabli Department of Mathematics, University of Houston https://www.math.uh.edu/ blerina Email: blerina@math.uh.edu Fall
CHAPTER 2. Graphs. 1. Introduction to Graphs and Graph Isomorphism
 CHAPTER 2 Graphs 1. Introduction to Graphs and Graph Isomorphism 1.1. The Graph Menagerie. Definition 1.1.1. A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of a set V of vertices and a set E of edges, represented
CHAPTER 2 Graphs 1. Introduction to Graphs and Graph Isomorphism 1.1. The Graph Menagerie. Definition 1.1.1. A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of a set V of vertices and a set E of edges, represented
Unit 7 Day 4 Notes: graph coloring, Graph theory review & Quiz
 Unit 7 Day 4 Notes: graph coloring, Graph theory review & Quiz Warm-Up Phones OFF & in Blue Pockets! Get out paper for notes! Agenda Notes first, Then do practice and HW questions Quiz at the end Notes:
Unit 7 Day 4 Notes: graph coloring, Graph theory review & Quiz Warm-Up Phones OFF & in Blue Pockets! Get out paper for notes! Agenda Notes first, Then do practice and HW questions Quiz at the end Notes:
MA 111 Review for Exam 3
 MA 111 Review for Exam 3 Exam 3 (given in class on Tuesday, March 27, 2012) will cover Chapter 5. You should: know what a graph is and how to use graphs to model geographic relationships. know how to describe
MA 111 Review for Exam 3 Exam 3 (given in class on Tuesday, March 27, 2012) will cover Chapter 5. You should: know what a graph is and how to use graphs to model geographic relationships. know how to describe
INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY. 1. Definitions
 INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY D. JAKOBSON 1. Definitions A graph G consists of vertices {v 1, v 2,..., v n } and edges {e 1, e 2,..., e m } connecting pairs of vertices. An edge e = (uv) is incident with
INTRODUCTION TO GRAPH THEORY D. JAKOBSON 1. Definitions A graph G consists of vertices {v 1, v 2,..., v n } and edges {e 1, e 2,..., e m } connecting pairs of vertices. An edge e = (uv) is incident with
GRAPHS, GRAPH MODELS, GRAPH TERMINOLOGY, AND SPECIAL TYPES OF GRAPHS
 GRAPHS, GRAPH MODELS, GRAPH TERMINOLOGY, AND SPECIAL TYPES OF GRAPHS DR. ANDREW SCHWARTZ, PH.D. 10.1 Graphs and Graph Models (1) A graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes)
GRAPHS, GRAPH MODELS, GRAPH TERMINOLOGY, AND SPECIAL TYPES OF GRAPHS DR. ANDREW SCHWARTZ, PH.D. 10.1 Graphs and Graph Models (1) A graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes)
Math 15 - Spring Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so:
 Math 15 - Spring 2017 - Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so: dm = {0: [1,15], 1: [2,16,31], 2: [3,17,32], 3: [4,18,33], 4: [5,19,34],
Math 15 - Spring 2017 - Homework 2.6 Solutions 1. (2.6 # 20) The following graph has 45 vertices. In Sagemath, we can define it like so: dm = {0: [1,15], 1: [2,16,31], 2: [3,17,32], 3: [4,18,33], 4: [5,19,34],
Graphs (MTAT , 6 EAP) Lectures: Mon 14-16, hall 404 Exercises: Wed 14-16, hall 402
 Graphs (MTAT.05.080, 6 EAP) Lectures: Mon 14-16, hall 404 Exercises: Wed 14-16, hall 402 homepage: http://courses.cs.ut.ee/2012/graafid (contains slides) For grade: Homework + three tests (during or after
Graphs (MTAT.05.080, 6 EAP) Lectures: Mon 14-16, hall 404 Exercises: Wed 14-16, hall 402 homepage: http://courses.cs.ut.ee/2012/graafid (contains slides) For grade: Homework + three tests (during or after
Math236 Discrete Maths with Applications
 Math236 Discrete Maths with Applications P. Ittmann UKZN, Pietermaritzburg Semester 1, 2012 Ittmann (UKZN PMB) Math236 2012 1 / 19 Degree Sequences Let G be a graph with vertex set V (G) = {v 1, v 2, v
Math236 Discrete Maths with Applications P. Ittmann UKZN, Pietermaritzburg Semester 1, 2012 Ittmann (UKZN PMB) Math236 2012 1 / 19 Degree Sequences Let G be a graph with vertex set V (G) = {v 1, v 2, v
WUCT121. Discrete Mathematics. Graphs
 WUCT121 Discrete Mathematics Graphs WUCT121 Graphs 1 Section 1. Graphs 1.1. Introduction Graphs are used in many fields that require analysis of routes between locations. These areas include communications,
WUCT121 Discrete Mathematics Graphs WUCT121 Graphs 1 Section 1. Graphs 1.1. Introduction Graphs are used in many fields that require analysis of routes between locations. These areas include communications,
Week 8: The fundamentals of graph theory; Planar Graphs 25 and 27 October, 2017
 (1/25) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 8: The fundamentals of graph theory; Planar Graphs 25 and 27 October, 2017 1 Definitions 1. A graph 2. Paths and connected graphs 3. Complete graphs 4. Vertex degree
(1/25) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 8: The fundamentals of graph theory; Planar Graphs 25 and 27 October, 2017 1 Definitions 1. A graph 2. Paths and connected graphs 3. Complete graphs 4. Vertex degree
Circuits and Paths. April 13, 2014
 Circuits and Paths April 13, 2014 Warm Up Problem Quandroland is an insect country that has four cities. Draw all possible ways tunnels can join the cities in Quadroland. (Remember that some cities might
Circuits and Paths April 13, 2014 Warm Up Problem Quandroland is an insect country that has four cities. Draw all possible ways tunnels can join the cities in Quadroland. (Remember that some cities might
GRAPH THEORY: AN INTRODUCTION
 GRAPH THEORY: AN INTRODUCTION BEGINNERS 3/4/2018 1. GRAPHS AND THEIR PROPERTIES A graph G consists of two sets: a set of vertices V, and a set of edges E. A vertex is simply a labeled point. An edge is
GRAPH THEORY: AN INTRODUCTION BEGINNERS 3/4/2018 1. GRAPHS AND THEIR PROPERTIES A graph G consists of two sets: a set of vertices V, and a set of edges E. A vertex is simply a labeled point. An edge is
DEFINITION OF GRAPH GRAPH THEORY GRAPHS ACCORDING TO THEIR VERTICES AND EDGES EXAMPLE GRAPHS ACCORDING TO THEIR VERTICES AND EDGES
 DEFINITION OF GRAPH GRAPH THEORY Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Discrete Math by Kenneth H. Rosen A graph G = (V,E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes) and E, a set of edges. Each
DEFINITION OF GRAPH GRAPH THEORY Prepared by Engr. JP Timola Reference: Discrete Math by Kenneth H. Rosen A graph G = (V,E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes) and E, a set of edges. Each
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, February 22, 2017 Graph Theory III
 1 Eulerian Graphs Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, February 22, 2017 Graph Theory III Let s begin this section with a problem that you may remember from lecture 1. Consider the layout of land and water
1 Eulerian Graphs Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, February 22, 2017 Graph Theory III Let s begin this section with a problem that you may remember from lecture 1. Consider the layout of land and water
An Introduction to Graph Theory
 An Introduction to Graph Theory Evelyne Smith-Roberge University of Waterloo March 22, 2017 What is a graph? Definition A graph G is: a set V (G) of objects called vertices together with: a set E(G), of
An Introduction to Graph Theory Evelyne Smith-Roberge University of Waterloo March 22, 2017 What is a graph? Definition A graph G is: a set V (G) of objects called vertices together with: a set E(G), of
Lecture 5: Graphs. Rajat Mittal. IIT Kanpur
 Lecture : Graphs Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur Combinatorial graphs provide a natural way to model connections between different objects. They are very useful in depicting communication networks, social networks
Lecture : Graphs Rajat Mittal IIT Kanpur Combinatorial graphs provide a natural way to model connections between different objects. They are very useful in depicting communication networks, social networks
Graph Theory Questions from Past Papers
 Graph Theory Questions from Past Papers Bilkent University, Laurence Barker, 19 October 2017 Do not forget to justify your answers in terms which could be understood by people who know the background theory
Graph Theory Questions from Past Papers Bilkent University, Laurence Barker, 19 October 2017 Do not forget to justify your answers in terms which could be understood by people who know the background theory
Trees and Tree Encodings
 Trees and Tree Encodings January, 08 Introduction: Today, we are going to be looking at a special class of graph theory called trees. These structures are an important discipline in mathematics and have
Trees and Tree Encodings January, 08 Introduction: Today, we are going to be looking at a special class of graph theory called trees. These structures are an important discipline in mathematics and have
Introduction to Graphs
 Introduction to Graphs Historical Motivation Seven Bridges of Königsberg Königsberg (now Kaliningrad, Russia) around 1735 Problem: Find a walk through the city that would cross each bridge once and only
Introduction to Graphs Historical Motivation Seven Bridges of Königsberg Königsberg (now Kaliningrad, Russia) around 1735 Problem: Find a walk through the city that would cross each bridge once and only
Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, Graph Theory
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, 2017 Graph Theory Solutions Example 1 1. To represent
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, 2017 Graph Theory Solutions Example 1 1. To represent
v V Question: How many edges are there in a graph with 10 vertices each of degree 6?
 ECS20 Handout Graphs and Trees March 4, 2015 (updated 3/9) Notion of a graph 1. A graph G = (V,E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes) and E, a set of pairs of elements of V called edges.
ECS20 Handout Graphs and Trees March 4, 2015 (updated 3/9) Notion of a graph 1. A graph G = (V,E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes) and E, a set of pairs of elements of V called edges.
MC 302 GRAPH THEORY 10/1/13 Solutions to HW #2 50 points + 6 XC points
 MC 0 GRAPH THEORY 0// Solutions to HW # 0 points + XC points ) [CH] p.,..7. This problem introduces an important class of graphs called the hypercubes or k-cubes, Q, Q, Q, etc. I suggest that before you
MC 0 GRAPH THEORY 0// Solutions to HW # 0 points + XC points ) [CH] p.,..7. This problem introduces an important class of graphs called the hypercubes or k-cubes, Q, Q, Q, etc. I suggest that before you
Graphs. Pseudograph: multiple edges and loops allowed
 Graphs G = (V, E) V - set of vertices, E - set of edges Undirected graphs Simple graph: V - nonempty set of vertices, E - set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices (no multiple edges or loops) Multigraph:
Graphs G = (V, E) V - set of vertices, E - set of edges Undirected graphs Simple graph: V - nonempty set of vertices, E - set of unordered pairs of distinct vertices (no multiple edges or loops) Multigraph:
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes
 Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes David Glickenstein September 3, 2008 1 Introduction We will begin by considering several problems which may be solved using graphs, directed graphs (digraphs), and networks.
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes David Glickenstein September 3, 2008 1 Introduction We will begin by considering several problems which may be solved using graphs, directed graphs (digraphs), and networks.
Majority and Friendship Paradoxes
 Majority and Friendship Paradoxes Majority Paradox Example: Small town is considering a bond initiative in an upcoming election. Some residents are in favor, some are against. Consider a poll asking the
Majority and Friendship Paradoxes Majority Paradox Example: Small town is considering a bond initiative in an upcoming election. Some residents are in favor, some are against. Consider a poll asking the
Week 11: Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs; Trees. 15 and 17 November, 2017
 (1/22) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 11: Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs; Trees http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/~niall/ma284/ 15 and 17 November, 2017 Hamilton s Icosian Game (Library or the Royal Irish
(1/22) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 11: Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs; Trees http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/~niall/ma284/ 15 and 17 November, 2017 Hamilton s Icosian Game (Library or the Royal Irish
Planar Graph (7A) Young Won Lim 6/20/18
 Planar Graph (7A) Copyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
Planar Graph (7A) Copyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
An Introduction to Graph Theory
 An Introduction to Graph Theory CIS008-2 Logic and Foundations of Mathematics David Goodwin david.goodwin@perisic.com 12:00, Friday 17 th February 2012 Outline 1 Graphs 2 Paths and cycles 3 Graphs and
An Introduction to Graph Theory CIS008-2 Logic and Foundations of Mathematics David Goodwin david.goodwin@perisic.com 12:00, Friday 17 th February 2012 Outline 1 Graphs 2 Paths and cycles 3 Graphs and
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES. Alessandro Artale UniBZ - artale/z
 CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/z SECTION 10.4 Isomorphisms of Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Isomorphisms of Graphs The two
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/z SECTION 10.4 Isomorphisms of Graphs Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Isomorphisms of Graphs The two
Varying Applications (examples)
 Graph Theory Varying Applications (examples) Computer networks Distinguish between two chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures Solve shortest path problems between cities
Graph Theory Varying Applications (examples) Computer networks Distinguish between two chemical compounds with the same molecular formula but different structures Solve shortest path problems between cities
Section 8.2 Graph Terminology. Undirected Graphs. Definition: Two vertices u, v in V are adjacent or neighbors if there is an edge e between u and v.
 Section 8.2 Graph Terminology Undirected Graphs Definition: Two vertices u, v in V are adjacent or neighbors if there is an edge e between u and v. The edge e connects u and v. The vertices u and v are
Section 8.2 Graph Terminology Undirected Graphs Definition: Two vertices u, v in V are adjacent or neighbors if there is an edge e between u and v. The edge e connects u and v. The vertices u and v are
Discrete Mathematics (2009 Spring) Graphs (Chapter 9, 5 hours)
 Discrete Mathematics (2009 Spring) Graphs (Chapter 9, 5 hours) Chih-Wei Yi Dept. of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University June 1, 2009 9.1 Graphs and Graph Models What are Graphs? General meaning
Discrete Mathematics (2009 Spring) Graphs (Chapter 9, 5 hours) Chih-Wei Yi Dept. of Computer Science National Chiao Tung University June 1, 2009 9.1 Graphs and Graph Models What are Graphs? General meaning
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao,David Tse Note 8
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao,David Tse Note 8 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2009 Satish Rao,David Tse Note 8 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite
Paths, Circuits, and Connected Graphs
 Paths, Circuits, and Connected Graphs Paths and Circuits Definition: Let G = (V, E) be an undirected graph, vertices u, v V A path of length n from u to v is a sequence of edges e i = {u i 1, u i} E for
Paths, Circuits, and Connected Graphs Paths and Circuits Definition: Let G = (V, E) be an undirected graph, vertices u, v V A path of length n from u to v is a sequence of edges e i = {u i 1, u i} E for
MATH 101: Introduction to Contemporary Mathematics
 MATH 101: Introduction to Contemporary Mathematics Sections 201-206 Instructor: H. R. Hughes Course web page: http://www.math.siu.edu/hughes/math101.htm Summer 2013 Lecture sessions meet: MTWF 12:10-1:10
MATH 101: Introduction to Contemporary Mathematics Sections 201-206 Instructor: H. R. Hughes Course web page: http://www.math.siu.edu/hughes/math101.htm Summer 2013 Lecture sessions meet: MTWF 12:10-1:10
Elements of Graph Theory
 Elements of Graph Theory Quick review of Chapters 9.1 9.5, 9.7 (studied in Mt1348/2008) = all basic concepts must be known New topics we will mostly skip shortest paths (Chapter 9.6), as that was covered
Elements of Graph Theory Quick review of Chapters 9.1 9.5, 9.7 (studied in Mt1348/2008) = all basic concepts must be known New topics we will mostly skip shortest paths (Chapter 9.6), as that was covered
University of Toronto Department of Mathematics
 University of Toronto Department of Mathematics MAT332H1F, Graph Theory Midterm, October 21, 2014 Instructor: Kasra Rafi First Last Student Number Instructions: No aids allowed. Write solutions on the
University of Toronto Department of Mathematics MAT332H1F, Graph Theory Midterm, October 21, 2014 Instructor: Kasra Rafi First Last Student Number Instructions: No aids allowed. Write solutions on the
Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Note 13. An Introduction to Graphs
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Note 13 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite to writing a
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics for CS Spring 2008 David Wagner Note 13 An Introduction to Graphs Formulating a simple, precise specification of a computational problem is often a prerequisite to writing a
Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory
 Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory Chapter 8: Topics in Graph Theory Section 8.1: Examples {1,2,3} Section 8.2: Examples {1,2,4} Section 8.3: Examples {1} 8.1 Graphs Graph A graph G consists of a finite
Chapter 8 Topics in Graph Theory Chapter 8: Topics in Graph Theory Section 8.1: Examples {1,2,3} Section 8.2: Examples {1,2,4} Section 8.3: Examples {1} 8.1 Graphs Graph A graph G consists of a finite
Discrete mathematics
 Discrete mathematics Petr Kovář petr.kovar@vsb.cz VŠB Technical University of Ostrava DiM 470-2301/02, Winter term 2018/2019 About this file This file is meant to be a guideline for the lecturer. Many
Discrete mathematics Petr Kovář petr.kovar@vsb.cz VŠB Technical University of Ostrava DiM 470-2301/02, Winter term 2018/2019 About this file This file is meant to be a guideline for the lecturer. Many
(5.2) 151 Math Exercises. Graph Terminology and Special Types of Graphs. Malek Zein AL-Abidin
 King Saud University College of Science Department of Mathematics 151 Math Exercises (5.2) Graph Terminology and Special Types of Graphs Malek Zein AL-Abidin ه Basic Terminology First, we give some terminology
King Saud University College of Science Department of Mathematics 151 Math Exercises (5.2) Graph Terminology and Special Types of Graphs Malek Zein AL-Abidin ه Basic Terminology First, we give some terminology
The University of Sydney MATH2969/2069. Graph Theory Tutorial 2 (Week 9) 2008
 The University of Sydney MATH99/09 Graph Theory Tutorial (Week 9) 00. Show that the graph on the left is Hamiltonian, but that the other two are not. To show that the graph is Hamiltonian, simply find
The University of Sydney MATH99/09 Graph Theory Tutorial (Week 9) 00. Show that the graph on the left is Hamiltonian, but that the other two are not. To show that the graph is Hamiltonian, simply find
Week 9: Planar and non-planar graphs. 1st and 3rd of November, 2017
 (1/26) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 9: Planar and non-planar graphs http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/~niall/ma284/ 1st and 3rd of November, 2017 1 Recall... planar graphs and Euler s formula 2 Non-planar
(1/26) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 9: Planar and non-planar graphs http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/~niall/ma284/ 1st and 3rd of November, 2017 1 Recall... planar graphs and Euler s formula 2 Non-planar
HOMEWORK 4 SOLUTIONS. Solution: The Petersen graph contains a cycle of odd length as a subgraph. Hence,
 HOMEWORK 4 SOLUTIONS (1) Determine the chromatic number of the Petersen graph. Solution: The Petersen graph contains a cycle of odd length as a subgraph. Hence, 3 χ(c 5 ) χ(p ). As the Petersen graph is
HOMEWORK 4 SOLUTIONS (1) Determine the chromatic number of the Petersen graph. Solution: The Petersen graph contains a cycle of odd length as a subgraph. Hence, 3 χ(c 5 ) χ(p ). As the Petersen graph is
March 20/2003 Jayakanth Srinivasan,
 Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Definition : A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Definition : In a multigraph G = (V, E) two or
Basics of Graph Theory
 Basics of Graph Theory 1 Basic notions A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Simple graphs have their
Basics of Graph Theory 1 Basic notions A simple graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices, and E, a set of unordered pairs of distinct elements of V called edges. Simple graphs have their
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES. Alessandro Artale UniBZ - artale/z
 CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/z SECTION 10.1 Graphs: Definitions and Basic Properties Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Graphs: Definitions
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/z SECTION 10.1 Graphs: Definitions and Basic Properties Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Graphs: Definitions
-Discrete Math 504 Homework Assignment #8 TO: Dr. Jim Gleason FROM: Deborah Britt, ACCLAIM Cohort 2 Date: March 1, 2005
 -Discrete Math 504 Homework Assignment #8 TO: Dr. Jim leason FOM: Deborah ritt, ACCLAIM Cohort 2 Date: March 1, 2005 Section 4.6 Exploratory #3 Exercises (2,4,6,10,11) Section 5.1 Exercises (4,5,6,10,14)
-Discrete Math 504 Homework Assignment #8 TO: Dr. Jim leason FOM: Deborah ritt, ACCLAIM Cohort 2 Date: March 1, 2005 Section 4.6 Exploratory #3 Exercises (2,4,6,10,11) Section 5.1 Exercises (4,5,6,10,14)
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2013 Vazirani Note 7
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2013 Vazirani Note 7 An Introduction to Graphs A few centuries ago, residents of the city of Königsberg, Prussia were interested in a certain problem.
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2013 Vazirani Note 7 An Introduction to Graphs A few centuries ago, residents of the city of Königsberg, Prussia were interested in a certain problem.
13. (a) G,G. A circuit of length 1 is a loop. 14. (a) E,E. (c) A,B,C,A. 16. (a) BF, FG
 13. (a) G,G. A circuit of length 1 is a loop. There are none. Such a circuit would consist of two vertices and two (different) edges connecting the vertices. 10. (a) 11. (a) C, B, A, H, F Other answers
13. (a) G,G. A circuit of length 1 is a loop. There are none. Such a circuit would consist of two vertices and two (different) edges connecting the vertices. 10. (a) 11. (a) C, B, A, H, F Other answers
Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, Graph Theory
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, 2017 Graph Theory Introduction Graph Theory is the
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grades 7 & 8, Math Circles 31 October/1/2 November, 2017 Graph Theory Introduction Graph Theory is the
NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER II EXAMINATION MH 1301 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS
 NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER II EXAMINATION 2015-2016 MH 1301 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS May 2016 TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This examination paper contains FIVE (5) questions
NANYANG TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY SEMESTER II EXAMINATION 2015-2016 MH 1301 DISCRETE MATHEMATICS May 2016 TIME ALLOWED: 2 HOURS INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES 1. This examination paper contains FIVE (5) questions
Extremal Graph Theory: Turán s Theorem
 Bridgewater State University Virtual Commons - Bridgewater State University Honors Program Theses and Projects Undergraduate Honors Program 5-9-07 Extremal Graph Theory: Turán s Theorem Vincent Vascimini
Bridgewater State University Virtual Commons - Bridgewater State University Honors Program Theses and Projects Undergraduate Honors Program 5-9-07 Extremal Graph Theory: Turán s Theorem Vincent Vascimini
Graph Theory Day Four
 Graph Theory Day Four February 8, 018 1 Connected Recall from last class, we discussed methods for proving a graph was connected. Our two methods were 1) Based on the definition, given any u, v V(G), there
Graph Theory Day Four February 8, 018 1 Connected Recall from last class, we discussed methods for proving a graph was connected. Our two methods were 1) Based on the definition, given any u, v V(G), there
Math 100 Homework 4 B A C E
 Math 100 Homework 4 Part 1 1. nswer the following questions for this graph. (a) Write the vertex set. (b) Write the edge set. (c) Is this graph connected? (d) List the degree of each vertex. (e) oes the
Math 100 Homework 4 Part 1 1. nswer the following questions for this graph. (a) Write the vertex set. (b) Write the edge set. (c) Is this graph connected? (d) List the degree of each vertex. (e) oes the
PRIMES Circle: High School Math Enrichment at MIT
 PRIMES Circle: High School Math Enrichment at MIT Department of Mathematics, MIT ivogt@mit.edu June 25th, 2015 PRIMES Umbrella organization: research and outreach Four programs: MIT PRIMES: research on
PRIMES Circle: High School Math Enrichment at MIT Department of Mathematics, MIT ivogt@mit.edu June 25th, 2015 PRIMES Umbrella organization: research and outreach Four programs: MIT PRIMES: research on
Proposition 1. The edges of an even graph can be split (partitioned) into cycles, no two of which have an edge in common.
 Math 3116 Dr. Franz Rothe June 5, 2012 08SUM\3116_2012t1.tex Name: Use the back pages for extra space 1 Solution of Test 1.1 Eulerian graphs Proposition 1. The edges of an even graph can be split (partitioned)
Math 3116 Dr. Franz Rothe June 5, 2012 08SUM\3116_2012t1.tex Name: Use the back pages for extra space 1 Solution of Test 1.1 Eulerian graphs Proposition 1. The edges of an even graph can be split (partitioned)
Graphs and Algorithms
 Graphs and Algorithms Graphs are a mathematical concept readily adapted into computer programming. Graphs are not just data structures, that is, they are not solutions to simple data storage problems.
Graphs and Algorithms Graphs are a mathematical concept readily adapted into computer programming. Graphs are not just data structures, that is, they are not solutions to simple data storage problems.
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes
 Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes David Glickenstein September 8, 2014 1 Introduction We will begin by considering several problems which may be solved using graphs, directed graphs (digraphs), and networks.
Math 443/543 Graph Theory Notes David Glickenstein September 8, 2014 1 Introduction We will begin by considering several problems which may be solved using graphs, directed graphs (digraphs), and networks.
Graph Theory. 1 Introduction to Graphs. Martin Stynes Department of Mathematics, UCC January 26, 2011
 Graph Theory Martin Stynes Department of Mathematics, UCC email: m.stynes@ucc.ie January 26, 2011 1 Introduction to Graphs 1 A graph G = (V, E) is a non-empty set of nodes or vertices V and a (possibly
Graph Theory Martin Stynes Department of Mathematics, UCC email: m.stynes@ucc.ie January 26, 2011 1 Introduction to Graphs 1 A graph G = (V, E) is a non-empty set of nodes or vertices V and a (possibly
Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]
![Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks] Topic 10 Part 2 [474 marks]](/thumbs/89/97991710.jpg) Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
Topic Part 2 [474 marks] The complete graph H has the following cost adjacency matrix Consider the travelling salesman problem for H a By first finding a minimum spanning tree on the subgraph of H formed
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & BUILT ENVIRONMENT. Mathematics. An Introduction to Graph Theory
 SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & BUILT ENVIRONMENT Mathematics An Introduction to Graph Theory. Introduction. Definitions.. Vertices and Edges... The Handshaking Lemma.. Connected Graphs... Cut-Points and Bridges.
SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & BUILT ENVIRONMENT Mathematics An Introduction to Graph Theory. Introduction. Definitions.. Vertices and Edges... The Handshaking Lemma.. Connected Graphs... Cut-Points and Bridges.
Week 10: Colouring graphs, and Euler s paths. 14 and 16 November, 2018
 MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 10: Colouring graphs, and Euler s paths http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ 14 and 16 November, 2018 1 Colouring The Four Colour Theorem 2 Graph colouring Chromatic
MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 10: Colouring graphs, and Euler s paths http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ 14 and 16 November, 2018 1 Colouring The Four Colour Theorem 2 Graph colouring Chromatic
BIL694-Lecture 1: Introduction to Graphs
 BIL694-Lecture 1: Introduction to Graphs Lecturer: Lale Özkahya Resources for the presentation: http://www.math.ucsd.edu/ gptesler/184a/calendar.html http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/courses/dmmr/ Outline
BIL694-Lecture 1: Introduction to Graphs Lecturer: Lale Özkahya Resources for the presentation: http://www.math.ucsd.edu/ gptesler/184a/calendar.html http://www.inf.ed.ac.uk/teaching/courses/dmmr/ Outline
Computer Science 280 Fall 2002 Homework 10 Solutions
 Computer Science 280 Fall 2002 Homework 10 Solutions Part A 1. How many nonisomorphic subgraphs does W 4 have? W 4 is the wheel graph obtained by adding a central vertex and 4 additional "spoke" edges
Computer Science 280 Fall 2002 Homework 10 Solutions Part A 1. How many nonisomorphic subgraphs does W 4 have? W 4 is the wheel graph obtained by adding a central vertex and 4 additional "spoke" edges
MC302 GRAPH THEORY SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK #1 9/19/13 68 points + 6 extra credit points
 MC02 GRAPH THEORY SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK #1 9/19/1 68 points + 6 extra credit points 1. [CH] p. 1, #1... a. In each case, for the two graphs you say are isomorphic, justify it by labeling their vertices
MC02 GRAPH THEORY SOLUTIONS TO HOMEWORK #1 9/19/1 68 points + 6 extra credit points 1. [CH] p. 1, #1... a. In each case, for the two graphs you say are isomorphic, justify it by labeling their vertices
Math 485, Graph Theory: Homework #3
 Math 485, Graph Theory: Homework #3 Stephen G Simpson Due Monday, October 26, 2009 The assignment consists of Exercises 2129, 2135, 2137, 2218, 238, 2310, 2313, 2314, 2315 in the West textbook, plus the
Math 485, Graph Theory: Homework #3 Stephen G Simpson Due Monday, October 26, 2009 The assignment consists of Exercises 2129, 2135, 2137, 2218, 238, 2310, 2313, 2314, 2315 in the West textbook, plus the
Discrete Mathematics
 Discrete Mathematics Lecturer: Mgr. Tereza Kovářová, Ph.D. tereza.kovarova@vsb.cz Guarantor: doc. Mgr. Petr Kovář, Ph.D. Department of Applied Mathematics, VŠB Technical University of Ostrava About this
Discrete Mathematics Lecturer: Mgr. Tereza Kovářová, Ph.D. tereza.kovarova@vsb.cz Guarantor: doc. Mgr. Petr Kovář, Ph.D. Department of Applied Mathematics, VŠB Technical University of Ostrava About this
Number Theory and Graph Theory
 1 Number Theory and Graph Theory Chapter 7 Graph properties By A. Satyanarayana Reddy Department of Mathematics Shiv Nadar University Uttar Pradesh, India E-mail: satya8118@gmail.com 2 Module-2: Eulerian
1 Number Theory and Graph Theory Chapter 7 Graph properties By A. Satyanarayana Reddy Department of Mathematics Shiv Nadar University Uttar Pradesh, India E-mail: satya8118@gmail.com 2 Module-2: Eulerian
Foundations of Discrete Mathematics
 Foundations of Discrete Mathematics Chapters 9 By Dr. Dalia M. Gil, Ph.D. Graphs Graphs are discrete structures consisting of vertices and edges that connect these vertices. Graphs A graph is a pair (V,
Foundations of Discrete Mathematics Chapters 9 By Dr. Dalia M. Gil, Ph.D. Graphs Graphs are discrete structures consisting of vertices and edges that connect these vertices. Graphs A graph is a pair (V,
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES. Alessandro Artale UniBZ - artale/
 CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/ SECTION 10.5 Trees Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Trees In mathematics, a tree is a connected graph
CHAPTER 10 GRAPHS AND TREES Alessandro Artale UniBZ - http://www.inf.unibz.it/ artale/ SECTION 10.5 Trees Copyright Cengage Learning. All rights reserved. Trees In mathematics, a tree is a connected graph
Discrete Mathematics I So Practice Sheet Solutions 1
 Discrete Mathematics I So 2016 Tibor Szabó Shagnik Das Practice Sheet Solutions 1 Provided below are possible solutions to the questions from the practice sheet issued towards the end of the course. Exercise
Discrete Mathematics I So 2016 Tibor Szabó Shagnik Das Practice Sheet Solutions 1 Provided below are possible solutions to the questions from the practice sheet issued towards the end of the course. Exercise
Solutions to Exercises 9
 Discrete Mathematics Lent 2009 MA210 Solutions to Exercises 9 (1) There are 5 cities. The cost of building a road directly between i and j is the entry a i,j in the matrix below. An indefinite entry indicates
Discrete Mathematics Lent 2009 MA210 Solutions to Exercises 9 (1) There are 5 cities. The cost of building a road directly between i and j is the entry a i,j in the matrix below. An indefinite entry indicates
MATH 103: Contemporary Mathematics Study Guide for Chapter 6: Hamilton Circuits and the TSP
 MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
MTH 3: ontemporary Mathematics Study Guide for hapter 6: Hamilton ircuits and the TSP. nswer the questions above each of the following graphs: (a) ind 3 different Hamilton circuits for the graph below.
2. CONNECTIVITY Connectivity
 2. CONNECTIVITY 70 2. Connectivity 2.1. Connectivity. Definition 2.1.1. (1) A path in a graph G = (V, E) is a sequence of vertices v 0, v 1, v 2,..., v n such that {v i 1, v i } is an edge of G for i =
2. CONNECTIVITY 70 2. Connectivity 2.1. Connectivity. Definition 2.1.1. (1) A path in a graph G = (V, E) is a sequence of vertices v 0, v 1, v 2,..., v n such that {v i 1, v i } is an edge of G for i =
Solutions to In-Class Problems Week 4, Fri
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.042J/18.062J, Fall 02: Mathematics for Computer Science Professor Albert Meyer and Dr. Radhika Nagpal Solutions to In-Class Problems Week 4, Fri Definition: The
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 6.042J/18.062J, Fall 02: Mathematics for Computer Science Professor Albert Meyer and Dr. Radhika Nagpal Solutions to In-Class Problems Week 4, Fri Definition: The
ASSIGNMENT 4 SOLUTIONS
 MATH 71 ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONS 1. If F : X X is a function, define f (x) to be (f f)(x), and inductively define f k (x) (f f k 1 )(x) for each integer k. (So f (x) (f f )(x) f(f(f(x))) for instance.) We
MATH 71 ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONS 1. If F : X X is a function, define f (x) to be (f f)(x), and inductively define f k (x) (f f k 1 )(x) for each integer k. (So f (x) (f f )(x) f(f(f(x))) for instance.) We
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, February 8, 2017 Graph Theory I
 Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, February 8, 2017 Graph Theory I Many of you are probably familiar with the term graph. To you a graph may mean a line or curve defined by a function y = f(x). It may
Intermediate Math Circles Wednesday, February 8, 2017 Graph Theory I Many of you are probably familiar with the term graph. To you a graph may mean a line or curve defined by a function y = f(x). It may
Planar Graph (7A) Young Won Lim 5/21/18
 Planar Graph (7A) Copyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
Planar Graph (7A) Copyright (c) 2015 2018 Young W. Lim. Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.2 or any later
11.2 Eulerian Trails
 11.2 Eulerian Trails K.. onigsberg, 1736 Graph Representation A B C D Do You Remember... Definition A u v trail is a u v walk where no edge is repeated. Do You Remember... Definition A u v trail is a u
11.2 Eulerian Trails K.. onigsberg, 1736 Graph Representation A B C D Do You Remember... Definition A u v trail is a u v walk where no edge is repeated. Do You Remember... Definition A u v trail is a u
Notebook Assignments
 Notebook Assignments These six assignments are a notebook using techniques from class in the single concrete context of graph theory. This is supplemental to your usual assignments, and is designed for
Notebook Assignments These six assignments are a notebook using techniques from class in the single concrete context of graph theory. This is supplemental to your usual assignments, and is designed for
Objective 1.02 Understand Numbering Systems
 Objective.0 Understand Numbering Systems C O M P U T E R P R O G R A M M I N G I Number Systems Number systems we will talk about: Decimal (Base 0 ) Binary (Base ) Hexadecimal (Base 6 ) Decimal The number
Objective.0 Understand Numbering Systems C O M P U T E R P R O G R A M M I N G I Number Systems Number systems we will talk about: Decimal (Base 0 ) Binary (Base ) Hexadecimal (Base 6 ) Decimal The number
Math 311. Trees Name: A Candel CSUN Math
 1. A simple path in a graph is a path with no repeated edges. A simple circuit is a circuit without repeated edges. 2. Trees are special kinds of graphs. A tree is a connected graph with no simple circuits.
1. A simple path in a graph is a path with no repeated edges. A simple circuit is a circuit without repeated edges. 2. Trees are special kinds of graphs. A tree is a connected graph with no simple circuits.
Assignment 4 Solutions of graph problems
 Assignment 4 Solutions of graph problems 1. Let us assume that G is not a cycle. Consider the maximal path in the graph. Let the end points of the path be denoted as v 1, v k respectively. If either of
Assignment 4 Solutions of graph problems 1. Let us assume that G is not a cycle. Consider the maximal path in the graph. Let the end points of the path be denoted as v 1, v k respectively. If either of
Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths. April 18, 2010
 Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths April 18, 2010 We have talked about insect worlds which consist of cities connected by tunnels. Here is an example of an insect world (Antland) which we saw last
Junior Circle Meeting 3 Circuits and Paths April 18, 2010 We have talked about insect worlds which consist of cities connected by tunnels. Here is an example of an insect world (Antland) which we saw last
1. The following graph is not Eulerian. Make it into an Eulerian graph by adding as few edges as possible.
 1. The following graph is not Eulerian. Make it into an Eulerian graph by adding as few edges as possible. A graph is Eulerian if it has an Eulerian circuit, which occurs if the graph is connected and
1. The following graph is not Eulerian. Make it into an Eulerian graph by adding as few edges as possible. A graph is Eulerian if it has an Eulerian circuit, which occurs if the graph is connected and
Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Midterm 1
 CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Midterm 1 PRINT Your Name:, (last) SIGN Your Name: (first) PRINT Your Student ID: CIRCLE your exam room: 1 Pimentel 141 Mccone
CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Spring 2016 Rao and Walrand Midterm 1 PRINT Your Name:, (last) SIGN Your Name: (first) PRINT Your Student ID: CIRCLE your exam room: 1 Pimentel 141 Mccone
MATH10001 Mathematical Workshop. Graphs, Trees and Algorithms Part 2. Trees. From Trees to Prüfer Codes
 MATH10001 Mathematical Workshop Graphs, Trees and Algorithms Part 2 Trees Recall that a simple graph is one without loops or multiple edges. We are interested in a special type of simple graph: A tree
MATH10001 Mathematical Workshop Graphs, Trees and Algorithms Part 2 Trees Recall that a simple graph is one without loops or multiple edges. We are interested in a special type of simple graph: A tree
CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko. Graphs
 CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko Graphs 2014 Definitions Definition: A graph G = (V,E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge
CS 311 Discrete Math for Computer Science Dr. William C. Bulko Graphs 2014 Definitions Definition: A graph G = (V,E) consists of a nonempty set V of vertices (or nodes) and a set E of edges. Each edge
Week 11: Eulerian and Hamiltonian graphs; Trees. 21 and 23 November, 2018
 (1/22) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 11: Eulerian and amiltonian graphs; Trees http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ amilton s Icosian Game (Library or the Royal Irish Academy) 21 and 23 November,
(1/22) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 11: Eulerian and amiltonian graphs; Trees http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ amilton s Icosian Game (Library or the Royal Irish Academy) 21 and 23 November,
Week 7: Introduction to Graph Theory. 24 and 26 October, 2018
 (1/32) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 7: Introduction to Graph Theory. http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ 24 and 26 October, 2018 1 Graph theory A network of mathematicians Water-Electricity-Broadband
(1/32) MA284 : Discrete Mathematics Week 7: Introduction to Graph Theory. http://www.maths.nuigalway.ie/ niall/ma284/ 24 and 26 October, 2018 1 Graph theory A network of mathematicians Water-Electricity-Broadband
Math 575 Exam 3. (t). What is the chromatic number of G?
 Math 575 Exam 3 Name 1 (a) Draw the Grötsch graph See your notes (b) Suppose that G is a graph having 6 vertices and 9 edges and that the chromatic polynomial of G is given below Fill in the missing coefficients
Math 575 Exam 3 Name 1 (a) Draw the Grötsch graph See your notes (b) Suppose that G is a graph having 6 vertices and 9 edges and that the chromatic polynomial of G is given below Fill in the missing coefficients
Graphs and Algorithms 2015
 Graphs and Algorithms 2015 Teachers: Nikhil Bansal and Jorn van der Pol Webpage: www.win.tue.nl/~nikhil/courses/2wo08 (for up to date information, links to reading material) Goal: Have fun with discrete
Graphs and Algorithms 2015 Teachers: Nikhil Bansal and Jorn van der Pol Webpage: www.win.tue.nl/~nikhil/courses/2wo08 (for up to date information, links to reading material) Goal: Have fun with discrete
MAT 145: PROBLEM SET 4
 MAT 145: PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TO FRIDAY FEB 22 Abstract. This problem set corresponds to the sixth week of the Combinatorics Course in the Winter Quarter 2019. It was posted online on Friday Feb 15 and is
MAT 145: PROBLEM SET 4 DUE TO FRIDAY FEB 22 Abstract. This problem set corresponds to the sixth week of the Combinatorics Course in the Winter Quarter 2019. It was posted online on Friday Feb 15 and is
Yimin Math Centre. Year 10 Term 2 Homework. 3.1 Graphs in the number plane The minimum and maximum value of a quadratic function...
 Year 10 Term 2 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 3 Year 10 Term 2 Week 3 Homework 1 3.1 Graphs in the number plane................................. 1 3.1.1 The parabola....................................
Year 10 Term 2 Homework Student Name: Grade: Date: Score: Table of contents 3 Year 10 Term 2 Week 3 Homework 1 3.1 Graphs in the number plane................................. 1 3.1.1 The parabola....................................
Senior Math Circles November 25, 2009 Graph Theory II
 University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Senior Math Circles November 5, 009 Graph Theory II Planar Graphs A graph that can be drawn in R without
University of Waterloo Faculty of Mathematics Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Senior Math Circles November 5, 009 Graph Theory II Planar Graphs A graph that can be drawn in R without
Graphs. Introduction To Graphs: Exercises. Definitions:
 Graphs Eng.Jehad Aldahdooh Introduction To Graphs: Definitions: A graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes) and E, a set of edges. Each edge has either one or two vertices associated
Graphs Eng.Jehad Aldahdooh Introduction To Graphs: Definitions: A graph G = (V, E) consists of V, a nonempty set of vertices (or nodes) and E, a set of edges. Each edge has either one or two vertices associated
