Scalable K-Means++ Bahman Bahmani Stanford University
|
|
|
- Ethelbert Caldwell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Scalable K-Means++ Bahman Bahmani Stanford University
2 K-means Clustering Fundamental problem in data analysis and machine learning By far the most popular clustering algorithm used in scientific and industrial applications [Berkhin 02] Identified as one of the top 10 algorithms in data mining [Wu et al 07] 2
3 Problem Statement A scalable algorithm for K-means clustering with theoretical guarantees and good practical performance 3
4 K-means Clustering Input: A set X={x 1, x 2,, x n } of n data points Number of clusters k For a set C={c 1, c 2,, c k } of cluster centers define: $ x#x " X (C) = d(x,c) 2 where d(x,c) = distance from x to closest center in C Goal: To find a set C of centers that minimizes the objective function φ X (C) 4
5 K-means Clustering: Example 5 K = 4
6 Lloyd Algorithm Start with k arbitrary centers {c 1, c 2,, c k } (typically chosen uniformly at random from data points) Performs an EM-type local search till convergence Main advantages: Simplicity, scalability 6
7 What s wrong with Lloyd Algorithm? Takes many iterations to converge Very sensitive to initialization Random initialization can easily get two centers in the same cluster K-means gets stuck in a local optimum 7
8 Lloyd Algorithm: Initialization 8 Figure credited to David Arthur
9 Lloyd Algorithm: Initialization 9 Figure credited to David Arthur
10 Lloyd Algorithm: Initialization 10 Figure credited to David Arthur
11 Lloyd Algorithm: Initialization 11 Figure credited to David Arthur
12 K-means++ [Arthur et al. 07] Spreads out the centers Choose first center, c 1, uniformly at random from the data set Repeat for 2 i k: Choose c i to be equal to a data point x 0 sampled from the distribution: d(x 0,C) 2 " X (C) # d(x 0,C) 2 Theorem: O(log k)-approximation to optimum, right after initialization 12
13 13 K-means++ Initialization
14 14 K-means++ Initialization
15 15 K-means++ Initialization
16 16 K-means++ Initialization
17 17 K-means++ Initialization
18 What s wrong with K-means++? Needs K passes over the data In large data applications, not only the data is massive, but also K is typically large (e.g., easily 1000). Does not scale! 18
19 Intuition for a solution K-means++ samples one point per iteration and updates its distribution What if we oversample by sampling each point independently with a larger probability? Intuitively equivalent to updating the distribution much less frequently Coarser sampling Turns out to be sufficient: K-means 19
20 K-means Initialization K=4, Oversampling factor =3 20
21 K-means Initialization K=4, Oversampling factor =3 21
22 K-means Initialization K=4, Oversampling factor =3 22
23 K-means Initialization K=4, Oversampling factor =3 23
24 K-means Initialization K=4, Oversampling factor =3 24 Cluster the intermediate centers
25 K-means [Bahmani et al. 12] Choose l>1 [Think l= (k)] Initialize C to an arbitrary set of points For R iterations do: Sample each point x in X independently with probability p x = ld 2 (x,c)/φ X (C). Add all the sampled points to C Cluster the (weighted) points in C to find the final k centers 25
26 K-means : Intuition An interpolation between Lloyd and K-means++ Number of iterations (R) R=k: Simulating K-means++ (l=1) à Strong guarantee Small R: K-means à Can it possibly give any guarantees? 26 R=0: Lloyd à No guarantees
27 Theorem Theorem: If φ and φ are the costs of the clustering at the beginning and end of an iteration, and OPT is the cost of the optimum clustering: Corollary: E["'] # O(OPT) + k el " Let = cost of initial clustering K-means produces a constant-factor approximation to OPT, using only O(log ( /OPT)) iterations Using K-means++ for clustering the intermediate centers, the overall approximation factor = O(log k) 27
28 Experimental Results: Quality Clustering Cost Right After Initialization Random NA 22,000 K-means K-means GAUSSMIXTURE: 10,000 points in 15 dimensions K=50 Costs scaled down by 10 4 Clustering Cost After Lloyd Convergence K-means much harder than K-means++ to get confused with noisy outliers 28
29 Experimental Results: Convergence K-means reduces number of Lloyd iterations even more than K-means++ Random 167 K-means++ 42 K-means 28 Number of Lloyd Iterations till Convergence SPAM: 4,601 points in 58 dimensions K=50 29
30 Experimental Results K-means needs a small number of intermediate centers Better than K-means++ as soon as ~K centers chosen Clustering Cost (Scaled down by ) Number of intermediate centers Random 6.4 * 10 7 NA 489 Partition * K-means KDDCUP1999: 4.8M points in 42 dimensions K=1000 Tme (In Minutes) 30
31 Algorithmic Theme Quickly decrease the size of the data in a distributed fashion while maintaining the important features of the data Solve the small instance on a single machine 31
32 32 Thank You!
k-means, k-means++ Barna Saha March 8, 2016
 k-means, k-means++ Barna Saha March 8, 2016 K-Means: The Most Popular Clustering Algorithm k-means clustering problem is one of the oldest and most important problem. K-Means: The Most Popular Clustering
k-means, k-means++ Barna Saha March 8, 2016 K-Means: The Most Popular Clustering Algorithm k-means clustering problem is one of the oldest and most important problem. K-Means: The Most Popular Clustering
MapReduce ML & Clustering Algorithms
 MapReduce ML & Clustering Algorithms Reminder MapReduce: A trade-off between ease of use & possible parallelism Graph Algorithms Approaches: Reduce input size (filtering) Graph specific optimizations (Pregel
MapReduce ML & Clustering Algorithms Reminder MapReduce: A trade-off between ease of use & possible parallelism Graph Algorithms Approaches: Reduce input size (filtering) Graph specific optimizations (Pregel
K-Means. Algorithmic Methods of Data Mining M. Sc. Data Science Sapienza University of Rome. Carlos Castillo
 K-Means Class Program University Semester Slides by Algorithmic Methods of Data Mining M. Sc. Data Science Sapienza University of Rome Fall 2017 Carlos Castillo http://chato.cl/ Sources: Mohammed J. Zaki,
K-Means Class Program University Semester Slides by Algorithmic Methods of Data Mining M. Sc. Data Science Sapienza University of Rome Fall 2017 Carlos Castillo http://chato.cl/ Sources: Mohammed J. Zaki,
Clustering. (Part 2)
 Clustering (Part 2) 1 k-means clustering 2 General Observations on k-means clustering In essence, k-means clustering aims at minimizing cluster variance. It is typically used in Euclidean spaces and works
Clustering (Part 2) 1 k-means clustering 2 General Observations on k-means clustering In essence, k-means clustering aims at minimizing cluster variance. It is typically used in Euclidean spaces and works
Clustering Algorithms. Margareta Ackerman
 Clustering Algorithms Margareta Ackerman A sea of algorithms As we discussed last class, there are MANY clustering algorithms, and new ones are proposed all the time. They are very different from each
Clustering Algorithms Margareta Ackerman A sea of algorithms As we discussed last class, there are MANY clustering algorithms, and new ones are proposed all the time. They are very different from each
Scalable Data Analysis
 Scalable Data Analysis David M. Blei April 26, 2012 1 Why? Olden days: Small data sets Careful experimental design Challenge: Squeeze as much as we can out of the data Modern data analysis: Very large
Scalable Data Analysis David M. Blei April 26, 2012 1 Why? Olden days: Small data sets Careful experimental design Challenge: Squeeze as much as we can out of the data Modern data analysis: Very large
Fast Clustering using MapReduce
 Fast Clustering using MapReduce Alina Ene Sungjin Im Benjamin Moseley September 6, 2011 Abstract Clustering problems have numerous applications and are becoming more challenging as the size of the data
Fast Clustering using MapReduce Alina Ene Sungjin Im Benjamin Moseley September 6, 2011 Abstract Clustering problems have numerous applications and are becoming more challenging as the size of the data
Clustering. K-means clustering
 Clustering K-means clustering Clustering Motivation: Identify clusters of data points in a multidimensional space, i.e. partition the data set {x 1,...,x N } into K clusters. Intuition: A cluster is a
Clustering K-means clustering Clustering Motivation: Identify clusters of data points in a multidimensional space, i.e. partition the data set {x 1,...,x N } into K clusters. Intuition: A cluster is a
Clustering. Unsupervised Learning
 Clustering. Unsupervised Learning Maria-Florina Balcan 04/06/2015 Reading: Chapter 14.3: Hastie, Tibshirani, Friedman. Additional resources: Center Based Clustering: A Foundational Perspective. Awasthi,
Clustering. Unsupervised Learning Maria-Florina Balcan 04/06/2015 Reading: Chapter 14.3: Hastie, Tibshirani, Friedman. Additional resources: Center Based Clustering: A Foundational Perspective. Awasthi,
K-Means++: The Advantages of Careful Seeding
 K-Means++: The Advantages of Careful Seeding PAPER BY DAVID ARTHUR & SERGEI VASSILVITSKII PRESENTATION BY STEVEN ROHR What is it and why do we need it? By Augmenting k-means with a very simple, randomized
K-Means++: The Advantages of Careful Seeding PAPER BY DAVID ARTHUR & SERGEI VASSILVITSKII PRESENTATION BY STEVEN ROHR What is it and why do we need it? By Augmenting k-means with a very simple, randomized
Lecture 2 The k-means clustering problem
 CSE 29: Unsupervised learning Spring 2008 Lecture 2 The -means clustering problem 2. The -means cost function Last time we saw the -center problem, in which the input is a set S of data points and the
CSE 29: Unsupervised learning Spring 2008 Lecture 2 The -means clustering problem 2. The -means cost function Last time we saw the -center problem, in which the input is a set S of data points and the
Lecture 25 November 26, 2013
 CS 229r: Algorithms for Big Data Fall 2013 Prof. Jelani Nelson Lecture 25 November 26, 2013 Scribe: Thomas Steinke 1 Overview Tody is the last lecture. We will finish our discussion of MapReduce by covering
CS 229r: Algorithms for Big Data Fall 2013 Prof. Jelani Nelson Lecture 25 November 26, 2013 Scribe: Thomas Steinke 1 Overview Tody is the last lecture. We will finish our discussion of MapReduce by covering
CSE 40171: Artificial Intelligence. Learning from Data: Unsupervised Learning
 CSE 40171: Artificial Intelligence Learning from Data: Unsupervised Learning 32 Homework #6 has been released. It is due at 11:59PM on 11/7. 33 CSE Seminar: 11/1 Amy Reibman Purdue University 3:30pm DBART
CSE 40171: Artificial Intelligence Learning from Data: Unsupervised Learning 32 Homework #6 has been released. It is due at 11:59PM on 11/7. 33 CSE Seminar: 11/1 Amy Reibman Purdue University 3:30pm DBART
Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning
 Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning Yufei Tao Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 / 29 Y Tao Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning In this lecture, we
Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning Yufei Tao Department of Computer Science and Engineering Chinese University of Hong Kong 1 / 29 Y Tao Clustering: Centroid-Based Partitioning In this lecture, we
Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University. K- Means + GMMs
 10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University K- Means + GMMs Clustering Readings: Murphy 25.5 Bishop 12.1, 12.3 HTF 14.3.0 Mitchell
10-601 Introduction to Machine Learning Machine Learning Department School of Computer Science Carnegie Mellon University K- Means + GMMs Clustering Readings: Murphy 25.5 Bishop 12.1, 12.3 HTF 14.3.0 Mitchell
Analysis of Extended Performance for clustering of Satellite Images Using Bigdata Platform Spark
 Analysis of Extended Performance for clustering of Satellite Images Using Bigdata Platform Spark PL.Marichamy 1, M.Phil Research Scholar, Department of Computer Application, Alagappa University, Karaikudi,
Analysis of Extended Performance for clustering of Satellite Images Using Bigdata Platform Spark PL.Marichamy 1, M.Phil Research Scholar, Department of Computer Application, Alagappa University, Karaikudi,
Unsupervised Learning
 Outline Unsupervised Learning Basic concepts K-means algorithm Representation of clusters Hierarchical clustering Distance functions Which clustering algorithm to use? NN Supervised learning vs. unsupervised
Outline Unsupervised Learning Basic concepts K-means algorithm Representation of clusters Hierarchical clustering Distance functions Which clustering algorithm to use? NN Supervised learning vs. unsupervised
Clustering. Unsupervised Learning
 Clustering. Unsupervised Learning Maria-Florina Balcan 03/02/2016 Clustering, Informal Goals Goal: Automatically partition unlabeled data into groups of similar datapoints. Question: When and why would
Clustering. Unsupervised Learning Maria-Florina Balcan 03/02/2016 Clustering, Informal Goals Goal: Automatically partition unlabeled data into groups of similar datapoints. Question: When and why would
CLUSTERING BIG DATA USING NORMALIZATION BASED k-means ALGORITHM
 Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology ISSN 2320 088X IMPACT FACTOR: 5.258 IJCSMC,
Available Online at www.ijcsmc.com International Journal of Computer Science and Mobile Computing A Monthly Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology ISSN 2320 088X IMPACT FACTOR: 5.258 IJCSMC,
Introduction to Computer Science
 DM534 Introduction to Computer Science Clustering and Feature Spaces Richard Roettger: About Me Computer Science (Technical University of Munich and thesis at the ICSI at the University of California at
DM534 Introduction to Computer Science Clustering and Feature Spaces Richard Roettger: About Me Computer Science (Technical University of Munich and thesis at the ICSI at the University of California at
Kapitel 4: Clustering
 Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Institut für Informatik Lehr- und Forschungseinheit für Datenbanksysteme Knowledge Discovery in Databases WiSe 2017/18 Kapitel 4: Clustering Vorlesung: Prof. Dr.
Ludwig-Maximilians-Universität München Institut für Informatik Lehr- und Forschungseinheit für Datenbanksysteme Knowledge Discovery in Databases WiSe 2017/18 Kapitel 4: Clustering Vorlesung: Prof. Dr.
Clustering. So far in the course. Clustering. Clustering. Subhransu Maji. CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning. dist(x, y) = x y 2 2
 So far in the course Clustering Subhransu Maji : Machine Learning 2 April 2015 7 April 2015 Supervised learning: learning with a teacher You had training data which was (feature, label) pairs and the goal
So far in the course Clustering Subhransu Maji : Machine Learning 2 April 2015 7 April 2015 Supervised learning: learning with a teacher You had training data which was (feature, label) pairs and the goal
Clustering. CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring Soleymani
 Clustering CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring 2016 Soleymani Outline Clustering Definition Clustering main approaches Partitional (flat) Hierarchical Clustering validation
Clustering CE-717: Machine Learning Sharif University of Technology Spring 2016 Soleymani Outline Clustering Definition Clustering main approaches Partitional (flat) Hierarchical Clustering validation
K-Means. Oct Youn-Hee Han
 K-Means Oct. 2015 Youn-Hee Han http://link.koreatech.ac.kr ²K-Means algorithm An unsupervised clustering algorithm K stands for number of clusters. It is typically a user input to the algorithm Some criteria
K-Means Oct. 2015 Youn-Hee Han http://link.koreatech.ac.kr ²K-Means algorithm An unsupervised clustering algorithm K stands for number of clusters. It is typically a user input to the algorithm Some criteria
Local Search Methods for k-means with Outliers
 Local Search Methods for -Means with Outliers Shalmoli Gupta University of Illinois 201 N. Goodwin Ave. Urbana, IL, 61801 sgupta49@illinois.edu Ravi Kumar Google 1600 Amphitheater Parway Mountain View,
Local Search Methods for -Means with Outliers Shalmoli Gupta University of Illinois 201 N. Goodwin Ave. Urbana, IL, 61801 sgupta49@illinois.edu Ravi Kumar Google 1600 Amphitheater Parway Mountain View,
Clustering. Subhransu Maji. CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning. 2 April April 2015
 Clustering Subhransu Maji CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning 2 April 2015 7 April 2015 So far in the course Supervised learning: learning with a teacher You had training data which was (feature, label) pairs
Clustering Subhransu Maji CMPSCI 689: Machine Learning 2 April 2015 7 April 2015 So far in the course Supervised learning: learning with a teacher You had training data which was (feature, label) pairs
An Efficient Clustering for Crime Analysis
 An Efficient Clustering for Crime Analysis Malarvizhi S 1, Siddique Ibrahim 2 1 UG Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Kumaraguru College Of Technology, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India
An Efficient Clustering for Crime Analysis Malarvizhi S 1, Siddique Ibrahim 2 1 UG Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Kumaraguru College Of Technology, Coimbatore, Tamilnadu, India
The K-modes and Laplacian K-modes algorithms for clustering
 The K-modes and Laplacian K-modes algorithms for clustering Miguel Á. Carreira-Perpiñán Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California, Merced http://faculty.ucmerced.edu/mcarreira-perpinan
The K-modes and Laplacian K-modes algorithms for clustering Miguel Á. Carreira-Perpiñán Electrical Engineering and Computer Science University of California, Merced http://faculty.ucmerced.edu/mcarreira-perpinan
CS664 Lecture #19: Layers, RANSAC, panoramas, epipolar geometry
 CS664 Lecture #19: Layers, RANSAC, panoramas, epipolar geometry Some material taken from: David Lowe, UBC Jiri Matas, CMP Prague http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~matas/papers/presentations/matas_beyondransac_cvprac05.ppt
CS664 Lecture #19: Layers, RANSAC, panoramas, epipolar geometry Some material taken from: David Lowe, UBC Jiri Matas, CMP Prague http://cmp.felk.cvut.cz/~matas/papers/presentations/matas_beyondransac_cvprac05.ppt
Clustering. Unsupervised Learning
 Clustering. Unsupervised Learning Maria-Florina Balcan 11/05/2018 Clustering, Informal Goals Goal: Automatically partition unlabeled data into groups of similar datapoints. Question: When and why would
Clustering. Unsupervised Learning Maria-Florina Balcan 11/05/2018 Clustering, Informal Goals Goal: Automatically partition unlabeled data into groups of similar datapoints. Question: When and why would
1 Case study of SVM (Rob)
 DRAFT a final version will be posted shortly COS 424: Interacting with Data Lecturer: Rob Schapire and David Blei Lecture # 8 Scribe: Indraneel Mukherjee March 1, 2007 In the previous lecture we saw how
DRAFT a final version will be posted shortly COS 424: Interacting with Data Lecturer: Rob Schapire and David Blei Lecture # 8 Scribe: Indraneel Mukherjee March 1, 2007 In the previous lecture we saw how
Algorithms, Spring 2014, CSE, OSU Greedy algorithms II. Instructor: Anastasios Sidiropoulos
 6331 - Algorithms, Spring 2014, CSE, OSU Greedy algorithms II Instructor: Anastasios Sidiropoulos Greedy algorithms Fast Easy to implement At every step, the algorithm makes a choice that seems locally
6331 - Algorithms, Spring 2014, CSE, OSU Greedy algorithms II Instructor: Anastasios Sidiropoulos Greedy algorithms Fast Easy to implement At every step, the algorithm makes a choice that seems locally
A Weighted Majority Voting based on Normalized Mutual Information for Cluster Analysis
 A Weighted Majority Voting based on Normalized Mutual Information for Cluster Analysis Meshal Shutaywi and Nezamoddin N. Kachouie Department of Mathematical Sciences, Florida Institute of Technology Abstract
A Weighted Majority Voting based on Normalized Mutual Information for Cluster Analysis Meshal Shutaywi and Nezamoddin N. Kachouie Department of Mathematical Sciences, Florida Institute of Technology Abstract
Clustering. SC4/SM4 Data Mining and Machine Learning, Hilary Term 2017 Dino Sejdinovic
 Clustering SC4/SM4 Data Mining and Machine Learning, Hilary Term 2017 Dino Sejdinovic Clustering is one of the fundamental and ubiquitous tasks in exploratory data analysis a first intuition about the
Clustering SC4/SM4 Data Mining and Machine Learning, Hilary Term 2017 Dino Sejdinovic Clustering is one of the fundamental and ubiquitous tasks in exploratory data analysis a first intuition about the
Efficiency of k-means and K-Medoids Algorithms for Clustering Arbitrary Data Points
 Efficiency of k-means and K-Medoids Algorithms for Clustering Arbitrary Data Points Dr. T. VELMURUGAN Associate professor, PG and Research Department of Computer Science, D.G.Vaishnav College, Chennai-600106,
Efficiency of k-means and K-Medoids Algorithms for Clustering Arbitrary Data Points Dr. T. VELMURUGAN Associate professor, PG and Research Department of Computer Science, D.G.Vaishnav College, Chennai-600106,
Faster Algorithms for the Constrained k-means Problem
 Faster Algorithms for the Constrained k-means Problem CSE, IIT Delhi June 16, 2015 [Joint work with Anup Bhattacharya (IITD) and Amit Kumar (IITD)] k-means Clustering Problem Problem (k-means) Given n
Faster Algorithms for the Constrained k-means Problem CSE, IIT Delhi June 16, 2015 [Joint work with Anup Bhattacharya (IITD) and Amit Kumar (IITD)] k-means Clustering Problem Problem (k-means) Given n
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING
 CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10. Cluster
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10. Cluster
SYDE Winter 2011 Introduction to Pattern Recognition. Clustering
 SYDE 372 - Winter 2011 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Clustering Alexander Wong Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo Outline 1 2 3 4 5 All the approaches we have learned
SYDE 372 - Winter 2011 Introduction to Pattern Recognition Clustering Alexander Wong Department of Systems Design Engineering University of Waterloo Outline 1 2 3 4 5 All the approaches we have learned
Online Algorithms. Lecture 11
 Online Algorithms Lecture 11 Today DC on trees DC on arbitrary metrics DC on circle Scheduling K-server on trees Theorem The DC Algorithm is k-competitive for the k server problem on arbitrary tree metrics.
Online Algorithms Lecture 11 Today DC on trees DC on arbitrary metrics DC on circle Scheduling K-server on trees Theorem The DC Algorithm is k-competitive for the k server problem on arbitrary tree metrics.
Hard clustering. Each object is assigned to one and only one cluster. Hierarchical clustering is usually hard. Soft (fuzzy) clustering
 An unsupervised machine learning problem Grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another) to each other than to those in other
An unsupervised machine learning problem Grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (a cluster) are more similar (in some sense or another) to each other than to those in other
Clustering Part 3. Hierarchical Clustering
 Clustering Part Dr Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville Hierarchical Clustering Two main types: Agglomerative Start with the points
Clustering Part Dr Sanjay Ranka Professor Computer and Information Science and Engineering University of Florida, Gainesville Hierarchical Clustering Two main types: Agglomerative Start with the points
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING
 CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University 09/25/2017 Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10.
CSE 5243 INTRO. TO DATA MINING Cluster Analysis: Basic Concepts and Methods Huan Sun, CSE@The Ohio State University 09/25/2017 Slides adapted from UIUC CS412, Fall 2017, by Prof. Jiawei Han 2 Chapter 10.
Approximation Algorithms for NP-Hard Clustering Problems
 Approximation Algorithms for NP-Hard Clustering Problems Ramgopal R. Mettu Dissertation Advisor: Greg Plaxton Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Austin What Is Clustering? The goal of
Approximation Algorithms for NP-Hard Clustering Problems Ramgopal R. Mettu Dissertation Advisor: Greg Plaxton Department of Computer Science University of Texas at Austin What Is Clustering? The goal of
Clustering: Overview and K-means algorithm
 Clustering: Overview and K-means algorithm Informal goal Given set of objects and measure of similarity between them, group similar objects together K-Means illustrations thanks to 2006 student Martin
Clustering: Overview and K-means algorithm Informal goal Given set of objects and measure of similarity between them, group similar objects together K-Means illustrations thanks to 2006 student Martin
princeton univ. F 15 cos 521: Advanced Algorithm Design Lecture 2: Karger s Min Cut Algorithm
 princeton univ. F 5 cos 5: Advanced Algorithm Design Lecture : Karger s Min Cut Algorithm Lecturer: Pravesh Kothari Scribe:Pravesh (These notes are a slightly modified version of notes from previous offerings
princeton univ. F 5 cos 5: Advanced Algorithm Design Lecture : Karger s Min Cut Algorithm Lecturer: Pravesh Kothari Scribe:Pravesh (These notes are a slightly modified version of notes from previous offerings
A Mixed Hierarchical Algorithm for Nearest Neighbor Search
 A Mixed Hierarchical Algorithm for Nearest Neighbor Search Carlo del Mundo Virginia Tech 222 Kraft Dr. Knowledge Works II Building Blacksburg, VA cdel@vt.edu ABSTRACT The k nearest neighbor (knn) search
A Mixed Hierarchical Algorithm for Nearest Neighbor Search Carlo del Mundo Virginia Tech 222 Kraft Dr. Knowledge Works II Building Blacksburg, VA cdel@vt.edu ABSTRACT The k nearest neighbor (knn) search
Keywords Hadoop, Map Reduce, K-Means, Data Analysis, Storage, Clusters.
 Volume 6, Issue 3, March 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Special Issue
Volume 6, Issue 3, March 2016 ISSN: 2277 128X International Journal of Advanced Research in Computer Science and Software Engineering Research Paper Available online at: www.ijarcsse.com Special Issue
Lecture 10: Semantic Segmentation and Clustering
 Lecture 10: Semantic Segmentation and Clustering Vineet Kosaraju, Davy Ragland, Adrien Truong, Effie Nehoran, Maneekwan Toyungyernsub Department of Computer Science Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305
Lecture 10: Semantic Segmentation and Clustering Vineet Kosaraju, Davy Ragland, Adrien Truong, Effie Nehoran, Maneekwan Toyungyernsub Department of Computer Science Stanford University Stanford, CA 94305
Approximation-stability and proxy objectives
 Harnessing implicit assumptions in problem formulations: Approximation-stability and proxy objectives Avrim Blum Carnegie Mellon University Based on work joint with Pranjal Awasthi, Nina Balcan, Anupam
Harnessing implicit assumptions in problem formulations: Approximation-stability and proxy objectives Avrim Blum Carnegie Mellon University Based on work joint with Pranjal Awasthi, Nina Balcan, Anupam
COMP Online Algorithms. k-server Problem & Advice. Shahin Kamali. Lecture 13 - Oct. 24, 2017 University of Manitoba
 COMP 7720 - Online Algorithms k-server Problem & Advice Shahin Kamali Lecture 13 - Oct. 24, 2017 University of Manitoba COMP 7720 - Online Algorithms k-server Problem & Advice 1 / 20 Review & Plan COMP
COMP 7720 - Online Algorithms k-server Problem & Advice Shahin Kamali Lecture 13 - Oct. 24, 2017 University of Manitoba COMP 7720 - Online Algorithms k-server Problem & Advice 1 / 20 Review & Plan COMP
Numerical Integration
 Lecture 12: Numerical Integration (with a focus on Monte Carlo integration) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2015 Review: fundamental theorem of calculus Z b f(x)dx = F (b) F (a) a f(x) = d dx
Lecture 12: Numerical Integration (with a focus on Monte Carlo integration) Computer Graphics CMU 15-462/15-662, Fall 2015 Review: fundamental theorem of calculus Z b f(x)dx = F (b) F (a) a f(x) = d dx
Machine Learning using MapReduce
 Machine Learning using MapReduce What is Machine Learning Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence concerned with techniques that allow computers to improve their outputs based on previous
Machine Learning using MapReduce What is Machine Learning Machine learning is a subfield of artificial intelligence concerned with techniques that allow computers to improve their outputs based on previous
Community Detection. Jian Pei: CMPT 741/459 Clustering (1) 2
 Clustering Community Detection http://image.slidesharecdn.com/communitydetectionitilecturejune0-0609559-phpapp0/95/community-detection-in-social-media--78.jpg?cb=3087368 Jian Pei: CMPT 74/459 Clustering
Clustering Community Detection http://image.slidesharecdn.com/communitydetectionitilecturejune0-0609559-phpapp0/95/community-detection-in-social-media--78.jpg?cb=3087368 Jian Pei: CMPT 74/459 Clustering
Introduction to Mobile Robotics
 Introduction to Mobile Robotics Clustering Wolfram Burgard Cyrill Stachniss Giorgio Grisetti Maren Bennewitz Christian Plagemann Clustering (1) Common technique for statistical data analysis (machine learning,
Introduction to Mobile Robotics Clustering Wolfram Burgard Cyrill Stachniss Giorgio Grisetti Maren Bennewitz Christian Plagemann Clustering (1) Common technique for statistical data analysis (machine learning,
Clustering Lecture 14
 Clustering Lecture 14 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, Carlos Guestrin, Andrew Moore, Dan Klein Clustering: Unsupervised learning Clustering Requires
Clustering Lecture 14 David Sontag New York University Slides adapted from Luke Zettlemoyer, Vibhav Gogate, Carlos Guestrin, Andrew Moore, Dan Klein Clustering: Unsupervised learning Clustering Requires
Clustering: Overview and K-means algorithm
 Clustering: Overview and K-means algorithm Informal goal Given set of objects and measure of similarity between them, group similar objects together K-Means illustrations thanks to 2006 student Martin
Clustering: Overview and K-means algorithm Informal goal Given set of objects and measure of similarity between them, group similar objects together K-Means illustrations thanks to 2006 student Martin
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University
 CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu [Kumar et al. 99] 2/13/2013 Jure Leskovec, Stanford CS246: Mining Massive Datasets, http://cs246.stanford.edu
CS246: Mining Massive Datasets Jure Leskovec, Stanford University http://cs246.stanford.edu [Kumar et al. 99] 2/13/2013 Jure Leskovec, Stanford CS246: Mining Massive Datasets, http://cs246.stanford.edu
February 2017 (1/20) 2 Piecewise Polynomial Interpolation 2.2 (Natural) Cubic Splines. MA378/531 Numerical Analysis II ( NA2 )
 f f f f f (/2).9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2. S Knots.7.6.5.4.3.2. 5 5.2.8.6.4.2 S Knots.2 5 5.9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2..9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2. S Knots 5 5 S Knots 5 5 5 5.35.3.25.2.5..5 5 5.6.5.4.3.2. 5 5 4 x 3 3.5 3 2.5 2.5.5 5
f f f f f (/2).9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2. S Knots.7.6.5.4.3.2. 5 5.2.8.6.4.2 S Knots.2 5 5.9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2..9.8.7.6.5.4.3.2. S Knots 5 5 S Knots 5 5 5 5.35.3.25.2.5..5 5 5.6.5.4.3.2. 5 5 4 x 3 3.5 3 2.5 2.5.5 5
Scalable and Practical Probability Density Estimators for Scientific Anomaly Detection
 Scalable PDEs p.1/107 Scalable and Practical Probability Density Estimators for Scientific Anomaly Detection Dan Pelleg Andrew Moore (chair) Manuela Veloso Geoff Gordon Nir Friedman, the Hebrew University
Scalable PDEs p.1/107 Scalable and Practical Probability Density Estimators for Scientific Anomaly Detection Dan Pelleg Andrew Moore (chair) Manuela Veloso Geoff Gordon Nir Friedman, the Hebrew University
High Dimensional Indexing by Clustering
 Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland Recall that, our discussion so far has assumed that the dimensionality d is moderately high, such that it can be regarded as a constant. This means that d should
Yufei Tao ITEE University of Queensland Recall that, our discussion so far has assumed that the dimensionality d is moderately high, such that it can be regarded as a constant. This means that d should
Data Informatics. Seon Ho Kim, Ph.D.
 Data Informatics Seon Ho Kim, Ph.D. seonkim@usc.edu Clustering Overview Supervised vs. Unsupervised Learning Supervised learning (classification) Supervision: The training data (observations, measurements,
Data Informatics Seon Ho Kim, Ph.D. seonkim@usc.edu Clustering Overview Supervised vs. Unsupervised Learning Supervised learning (classification) Supervision: The training data (observations, measurements,
f xx + f yy = F (x, y)
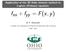 Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
Application of the 2D finite element method to Laplace (Poisson) equation; f xx + f yy = F (x, y) M. R. Hadizadeh Computer Club, Department of Physics and Astronomy, Ohio University 4 Nov. 2013 Domain
Fast Personalized PageRank On MapReduce Authors: Bahman Bahmani, Kaushik Chakrabart, Dong Xin In SIGMOD 2011 Presenter: Adams Wei Yu
 Fast Personalized PageRank On MapReduce Authors: Bahman Bahmani, Kaushik Chakrabart, Dong Xin In SIGMOD 2011 Presenter: Adams Wei Yu March 2015, CMU Graph data is Ubiquitous Basic Problem in Graphs: How
Fast Personalized PageRank On MapReduce Authors: Bahman Bahmani, Kaushik Chakrabart, Dong Xin In SIGMOD 2011 Presenter: Adams Wei Yu March 2015, CMU Graph data is Ubiquitous Basic Problem in Graphs: How
CS 1675 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 18. Clustering. Clustering. Groups together similar instances in the data sample
 CS 1675 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 18 Clustering Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Clustering Groups together similar instances in the data sample Basic clustering problem:
CS 1675 Introduction to Machine Learning Lecture 18 Clustering Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Clustering Groups together similar instances in the data sample Basic clustering problem:
Progress Report: Collaborative Filtering Using Bregman Co-clustering
 Progress Report: Collaborative Filtering Using Bregman Co-clustering Wei Tang, Srivatsan Ramanujam, and Andrew Dreher April 4, 2008 1 Introduction Analytics are becoming increasingly important for business
Progress Report: Collaborative Filtering Using Bregman Co-clustering Wei Tang, Srivatsan Ramanujam, and Andrew Dreher April 4, 2008 1 Introduction Analytics are becoming increasingly important for business
[7.3, EA], [9.1, CMB]
![[7.3, EA], [9.1, CMB] [7.3, EA], [9.1, CMB]](/thumbs/76/73876791.jpg) K-means Clustering Ke Chen Reading: [7.3, EA], [9.1, CMB] Outline Introduction K-means Algorithm Example How K-means partitions? K-means Demo Relevant Issues Application: Cell Neulei Detection Summary
K-means Clustering Ke Chen Reading: [7.3, EA], [9.1, CMB] Outline Introduction K-means Algorithm Example How K-means partitions? K-means Demo Relevant Issues Application: Cell Neulei Detection Summary
On Initial Effects of the k-means Clustering
 200 Int'l Conf. Scientific Computing CSC'15 On Initial Effects of the k-means Clustering Sherri Burks, Greg Harrell, and Jin Wang Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Valdosta State University,
200 Int'l Conf. Scientific Computing CSC'15 On Initial Effects of the k-means Clustering Sherri Burks, Greg Harrell, and Jin Wang Department of Mathematics and Computer Science Valdosta State University,
Parallel K-Means Algorithm for Shared Memory Multiprocessors
 Journal of Computer and Communications, 2014, 2, 15-23 Published Online September 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jcc http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jcc.2014.211002 Parallel K-Means Algorithm for
Journal of Computer and Communications, 2014, 2, 15-23 Published Online September 2014 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/jcc http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/jcc.2014.211002 Parallel K-Means Algorithm for
Clustering COMS 4771
 Clustering COMS 4771 1. Clustering Unsupervised classification / clustering Unsupervised classification Input: x 1,..., x n R d, target cardinality k N. Output: function f : R d {1,..., k} =: [k]. Typical
Clustering COMS 4771 1. Clustering Unsupervised classification / clustering Unsupervised classification Input: x 1,..., x n R d, target cardinality k N. Output: function f : R d {1,..., k} =: [k]. Typical
A Course in Machine Learning
 A Course in Machine Learning Hal Daumé III 13 UNSUPERVISED LEARNING If you have access to labeled training data, you know what to do. This is the supervised setting, in which you have a teacher telling
A Course in Machine Learning Hal Daumé III 13 UNSUPERVISED LEARNING If you have access to labeled training data, you know what to do. This is the supervised setting, in which you have a teacher telling
10. MLSP intro. (Clustering: K-means, EM, GMM, etc.)
 10. MLSP intro. (Clustering: K-means, EM, GMM, etc.) Rahil Mahdian 01.04.2016 LSV Lab, Saarland University, Germany What is clustering? Clustering is the classification of objects into different groups,
10. MLSP intro. (Clustering: K-means, EM, GMM, etc.) Rahil Mahdian 01.04.2016 LSV Lab, Saarland University, Germany What is clustering? Clustering is the classification of objects into different groups,
APPM/MATH Problem Set 4 Solutions
 APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
APPM/MATH 465 Problem Set 4 Solutions This assignment is due by 4pm on Wednesday, October 16th. You may either turn it in to me in class on Monday or in the box outside my office door (ECOT 35). Minimal
Clustering: K-means and Kernel K-means
 Clustering: K-means and Kernel K-means Piyush Rai Machine Learning (CS771A) Aug 31, 2016 Machine Learning (CS771A) Clustering: K-means and Kernel K-means 1 Clustering Usually an unsupervised learning problem
Clustering: K-means and Kernel K-means Piyush Rai Machine Learning (CS771A) Aug 31, 2016 Machine Learning (CS771A) Clustering: K-means and Kernel K-means 1 Clustering Usually an unsupervised learning problem
Unsupervised Learning: Clustering
 Unsupervised Learning: Clustering Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from Carlos Guestrin, Dan Klein & Luke Zettlemoyer Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised Learning: Clustering Vibhav Gogate The University of Texas at Dallas Slides adapted from Carlos Guestrin, Dan Klein & Luke Zettlemoyer Machine Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning
Clustering: Classic Methods and Modern Views
 Clustering: Classic Methods and Modern Views Marina Meilă University of Washington mmp@stat.washington.edu June 22, 2015 Lorentz Center Workshop on Clusters, Games and Axioms Outline Paradigms for clustering
Clustering: Classic Methods and Modern Views Marina Meilă University of Washington mmp@stat.washington.edu June 22, 2015 Lorentz Center Workshop on Clusters, Games and Axioms Outline Paradigms for clustering
DS Machine Learning and Data Mining I. Alina Oprea Associate Professor, CCIS Northeastern University
 DS 4400 Machine Learning and Data Mining I Alina Oprea Associate Professor, CCIS Northeastern University September 20 2018 Review Solution for multiple linear regression can be computed in closed form
DS 4400 Machine Learning and Data Mining I Alina Oprea Associate Professor, CCIS Northeastern University September 20 2018 Review Solution for multiple linear regression can be computed in closed form
Enhancing K-means Clustering Algorithm with Improved Initial Center
 Enhancing K-means Clustering Algorithm with Improved Initial Center Madhu Yedla #1, Srinivasa Rao Pathakota #2, T M Srinivasa #3 # Department of Computer Science and Engineering, National Institute of
Enhancing K-means Clustering Algorithm with Improved Initial Center Madhu Yedla #1, Srinivasa Rao Pathakota #2, T M Srinivasa #3 # Department of Computer Science and Engineering, National Institute of
Clustering (Basic concepts and Algorithms) Entscheidungsunterstützungssysteme
 Clustering (Basic concepts and Algorithms) Entscheidungsunterstützungssysteme Why do we need to find similarity? Similarity underlies many data science methods and solutions to business problems. Some
Clustering (Basic concepts and Algorithms) Entscheidungsunterstützungssysteme Why do we need to find similarity? Similarity underlies many data science methods and solutions to business problems. Some
CS 2750 Machine Learning. Lecture 19. Clustering. CS 2750 Machine Learning. Clustering. Groups together similar instances in the data sample
 Lecture 9 Clustering Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Clustering Groups together similar instances in the data sample Basic clustering problem: distribute data into k different groups
Lecture 9 Clustering Milos Hauskrecht milos@cs.pitt.edu 539 Sennott Square Clustering Groups together similar instances in the data sample Basic clustering problem: distribute data into k different groups
K-Means Clustering With Initial Centroids Based On Difference Operator
 K-Means Clustering With Initial Centroids Based On Difference Operator Satish Chaurasiya 1, Dr.Ratish Agrawal 2 M.Tech Student, School of Information and Technology, R.G.P.V, Bhopal, India Assistant Professor,
K-Means Clustering With Initial Centroids Based On Difference Operator Satish Chaurasiya 1, Dr.Ratish Agrawal 2 M.Tech Student, School of Information and Technology, R.G.P.V, Bhopal, India Assistant Professor,
Today. Lecture 4: Last time. The EM algorithm. We examine clustering in a little more detail; we went over it a somewhat quickly last time
 Today Lecture 4: We examine clustering in a little more detail; we went over it a somewhat quickly last time The CAD data will return and give us an opportunity to work with curves (!) We then examine
Today Lecture 4: We examine clustering in a little more detail; we went over it a somewhat quickly last time The CAD data will return and give us an opportunity to work with curves (!) We then examine
ADVANCED MACHINE LEARNING MACHINE LEARNING. Kernel for Clustering kernel K-Means
 1 MACHINE LEARNING Kernel for Clustering ernel K-Means Outline of Today s Lecture 1. Review principle and steps of K-Means algorithm. Derive ernel version of K-means 3. Exercise: Discuss the geometrical
1 MACHINE LEARNING Kernel for Clustering ernel K-Means Outline of Today s Lecture 1. Review principle and steps of K-Means algorithm. Derive ernel version of K-means 3. Exercise: Discuss the geometrical
k-means Clustering David S. Rosenberg April 24, 2018 New York University
 k-means Clustering David S. Rosenberg New York University April 24, 2018 David S. Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 / CSCI-GA 2567 April 24, 2018 1 / 19 Contents 1 k-means Clustering 2 k-means:
k-means Clustering David S. Rosenberg New York University April 24, 2018 David S. Rosenberg (New York University) DS-GA 1003 / CSCI-GA 2567 April 24, 2018 1 / 19 Contents 1 k-means Clustering 2 k-means:
TELCOM2125: Network Science and Analysis
 School of Information Sciences University of Pittsburgh TELCOM2125: Network Science and Analysis Konstantinos Pelechrinis Spring 2015 Figures are taken from: M.E.J. Newman, Networks: An Introduction 2
School of Information Sciences University of Pittsburgh TELCOM2125: Network Science and Analysis Konstantinos Pelechrinis Spring 2015 Figures are taken from: M.E.J. Newman, Networks: An Introduction 2
10703 Deep Reinforcement Learning and Control
 10703 Deep Reinforcement Learning and Control Russ Salakhutdinov Machine Learning Department rsalakhu@cs.cmu.edu Policy Gradient I Used Materials Disclaimer: Much of the material and slides for this lecture
10703 Deep Reinforcement Learning and Control Russ Salakhutdinov Machine Learning Department rsalakhu@cs.cmu.edu Policy Gradient I Used Materials Disclaimer: Much of the material and slides for this lecture
TDT- An Efficient Clustering Algorithm for Large Database Ms. Kritika Maheshwari, Mr. M.Rajsekaran
 TDT- An Efficient Clustering Algorithm for Large Database Ms. Kritika Maheshwari, Mr. M.Rajsekaran M-Tech Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, SRM University, India Assistant Professor,
TDT- An Efficient Clustering Algorithm for Large Database Ms. Kritika Maheshwari, Mr. M.Rajsekaran M-Tech Scholar, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, SRM University, India Assistant Professor,
Hierarchical Clustering: Objectives & Algorithms. École normale supérieure & CNRS
 Hierarchical Clustering: Objectives & Algorithms Vincent Cohen-Addad Paris Sorbonne & CNRS Frederik Mallmann-Trenn MIT Varun Kanade University of Oxford Claire Mathieu École normale supérieure & CNRS Clustering
Hierarchical Clustering: Objectives & Algorithms Vincent Cohen-Addad Paris Sorbonne & CNRS Frederik Mallmann-Trenn MIT Varun Kanade University of Oxford Claire Mathieu École normale supérieure & CNRS Clustering
Data Clustering Hierarchical Clustering, Density based clustering Grid based clustering
 Data Clustering Hierarchical Clustering, Density based clustering Grid based clustering Team 2 Prof. Anita Wasilewska CSE 634 Data Mining All Sources Used for the Presentation Olson CF. Parallel algorithms
Data Clustering Hierarchical Clustering, Density based clustering Grid based clustering Team 2 Prof. Anita Wasilewska CSE 634 Data Mining All Sources Used for the Presentation Olson CF. Parallel algorithms
Polynomial-Time Approximation Algorithms
 6.854 Advanced Algorithms Lecture 20: 10/27/2006 Lecturer: David Karger Scribes: Matt Doherty, John Nham, Sergiy Sidenko, David Schultz Polynomial-Time Approximation Algorithms NP-hard problems are a vast
6.854 Advanced Algorithms Lecture 20: 10/27/2006 Lecturer: David Karger Scribes: Matt Doherty, John Nham, Sergiy Sidenko, David Schultz Polynomial-Time Approximation Algorithms NP-hard problems are a vast
An Accelerated MapReduce-based K-prototypes for Big Data
 An Accelerated MapReduce-based K-prototypes for Big Data Mohamed Aymen Ben HajKacem, Chiheb-Eddine Ben N'cir, and Nadia Essoussi LARODEC, Université de Tunis, Institut Supérieur de Gestion de Tunis, 41
An Accelerated MapReduce-based K-prototypes for Big Data Mohamed Aymen Ben HajKacem, Chiheb-Eddine Ben N'cir, and Nadia Essoussi LARODEC, Université de Tunis, Institut Supérieur de Gestion de Tunis, 41
Clustering Distance measures K-Means. Lecture 22: Aykut Erdem December 2016 Hacettepe University
 Clustering Distance measures K-Means Lecture 22: Aykut Erdem December 2016 Hacettepe University Last time Boosting Idea: given a weak learner, run it multiple times on (reweighted) training data, then
Clustering Distance measures K-Means Lecture 22: Aykut Erdem December 2016 Hacettepe University Last time Boosting Idea: given a weak learner, run it multiple times on (reweighted) training data, then
Towards the world s fastest k-means algorithm
 Greg Hamerly Associate Professor Computer Science Department Baylor University Joint work with Jonathan Drake May 15, 2014 Objective function and optimization Lloyd s algorithm 1 The k-means clustering
Greg Hamerly Associate Professor Computer Science Department Baylor University Joint work with Jonathan Drake May 15, 2014 Objective function and optimization Lloyd s algorithm 1 The k-means clustering
Random projection for non-gaussian mixture models
 Random projection for non-gaussian mixture models Győző Gidófalvi Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92037 gyozo@cs.ucsd.edu Abstract Recently,
Random projection for non-gaussian mixture models Győző Gidófalvi Department of Computer Science and Engineering University of California, San Diego La Jolla, CA 92037 gyozo@cs.ucsd.edu Abstract Recently,
Data Mining. Jeff M. Phillips. January 9, 2013
 Data Mining Jeff M. Phillips January 9, 2013 Data Mining What is Data Mining? Finding structure in data? Machine learning on large data? Unsupervised learning? Large scale computational statistics? Data
Data Mining Jeff M. Phillips January 9, 2013 Data Mining What is Data Mining? Finding structure in data? Machine learning on large data? Unsupervised learning? Large scale computational statistics? Data
Lecture 7: Segmentation. Thursday, Sept 20
 Lecture 7: Segmentation Thursday, Sept 20 Outline Why segmentation? Gestalt properties, fun illusions and/or revealing examples Clustering Hierarchical K-means Mean Shift Graph-theoretic Normalized cuts
Lecture 7: Segmentation Thursday, Sept 20 Outline Why segmentation? Gestalt properties, fun illusions and/or revealing examples Clustering Hierarchical K-means Mean Shift Graph-theoretic Normalized cuts
Lecture 3 January 22
 EE 38V: Large cale Learning pring 203 Lecture 3 January 22 Lecturer: Caramanis & anghavi cribe: ubhashini Krishsamy 3. Clustering In the last lecture, we saw Locality ensitive Hashing (LH) which uses hash
EE 38V: Large cale Learning pring 203 Lecture 3 January 22 Lecturer: Caramanis & anghavi cribe: ubhashini Krishsamy 3. Clustering In the last lecture, we saw Locality ensitive Hashing (LH) which uses hash
Intelligent Image and Graphics Processing
 Intelligent Image and Graphics Processing 智能图像图形处理图形处理 布树辉 bushuhui@nwpu.edu.cn http://www.adv-ci.com Clustering Clustering Attach label to each observation or data points in a set You can say this unsupervised
Intelligent Image and Graphics Processing 智能图像图形处理图形处理 布树辉 bushuhui@nwpu.edu.cn http://www.adv-ci.com Clustering Clustering Attach label to each observation or data points in a set You can say this unsupervised
Lecture 11: E-M and MeanShift. CAP 5415 Fall 2007
 Lecture 11: E-M and MeanShift CAP 5415 Fall 2007 Review on Segmentation by Clustering Each Pixel Data Vector Example (From Comanciu and Meer) Review of k-means Let's find three clusters in this data These
Lecture 11: E-M and MeanShift CAP 5415 Fall 2007 Review on Segmentation by Clustering Each Pixel Data Vector Example (From Comanciu and Meer) Review of k-means Let's find three clusters in this data These
Data Mining. Jeff M. Phillips. January 7, 2019 CS 5140 / CS 6140
 Data Mining CS 5140 / CS 6140 Jeff M. Phillips January 7, 2019 What is Data Mining? What is Data Mining? Finding structure in data? Machine learning on large data? Unsupervised learning? Large scale computational
Data Mining CS 5140 / CS 6140 Jeff M. Phillips January 7, 2019 What is Data Mining? What is Data Mining? Finding structure in data? Machine learning on large data? Unsupervised learning? Large scale computational
ECLT 5810 Clustering
 ECLT 5810 Clustering What is Cluster Analysis? Cluster: a collection of data objects Similar to one another within the same cluster Dissimilar to the objects in other clusters Cluster analysis Grouping
ECLT 5810 Clustering What is Cluster Analysis? Cluster: a collection of data objects Similar to one another within the same cluster Dissimilar to the objects in other clusters Cluster analysis Grouping
