CS 303 Design and Analysis of Algorithms
|
|
|
- Arleen Thompson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 inal Exam S 0 esign and nalsis of lgorithms Review or inal Exam ong Xu (Based on class note of avid Luebke) am-0am, onda, a 0 lose book Bring our calculator 40% of our final score Office hours during final ong (09 EBW) : :0pm-4pm, rida, a 7 shwin (0 EBN) : am-pm, Thursda, a 6 am-pm, Wednesda, a (an opportunit to verif the grading of final and quiz scores). /9/004 /9/004 inal Exam Tips 7 problems (6 with pts, with 0 pts) Review our quizzes and homework hard problem in dnamic programming overage.,.,..,.,. 4., 4..,.,. 6., 6. Binar search tree Red-black tree Review Topics ugmenting data structure namic programming Greed algorithm /9/004 4 /9/004 Review: Binar Search Trees BST propert: ke[left(x)] ke[x] ke[right(x)] Example: B Review: Inorder Tree Walk n inorder walk prints the set in sorted order: TreeWalk(x) TreeWalk(left[x]); print(x); TreeWalk(right[x]); Eas to show b induction on the BST propert K /9/004 6 /9/004
2 Review: BST Search Review: BST Insert TreeSearch(x, k) if (x = NULL or k = ke[x]) if (k < ke[x]) return TreeSearch(left[x], k); return TreeSearch(right[x], k); dds an element x to the tree so that the binar search tree propert continues to hold The basic algorithm Like the search procedure above Insert x in place of NULL Use a trailing pointer to keep track of where ou came from (like inserting into singl linked list) Like search, takes time O(h), h = tree height 7 /9/004 /9/004 Review: Sorting With BSTs Review: Sorting With BSTs Basic algorithm: Insert elements of unsorted arra from..n o an inorder tree walk to print in sorted order Running time: Best case: Ω(n lg n) (it s a comparison sort) Worst case: O(n ) verage case: O(n lg n) (it s a quick sort!) verage case analsis It s a form of quicksort! for i= to n TreeInsert([i]); InorderTreeWalk(root); /9/004 0 /9/004 Review: ore BST Operations Review: ore BST Operations inimum: ind leftmost node in tree Successor: x has a right subtree: successor is minimum node in right subtree x has no right subtree: successor is first ancestor of x whose left child is also ancestor of x Intuition: s long as ou move to the left up the tree, ou re visiting smaller nodes. redecessor: similar to successor elete: x has no children: Remove x x has one child: Splice out x x has two children: Swap x with successor erform case or to delete it B Example: delete K or or B K /9/004 /9/004
3 Review: Red-Black Trees Red-black trees: Binar search trees augmented with node color Operations designed to guarantee that the height h = O(lg n) Red-Black roperties The red-black properties:. Ever node is either red or black. Ever leaf (NULL pointer) is black Note: this means ever real node has children. If a node is red, both children are black Note: can t have consecutive reds on a path 4. Ever path from node to descendent leaf contains the same number of black nodes. The root is alwas black black-height: # black nodes on path to leaf Lets us prove RB tree has height h lg(n+) /9/004 4 /9/004 Operations On RB Trees Since height is O(lg n), we can show that all BST operations take O(lg n) time roblem: BST Insert() and elete() modif the tree and could destro red-black properties Solution: restructure the tree in O(lg n) time You should understand the basic approach of these operations Ke operation: rotation RB Trees: Rotation Our basic operation for changing tree structure: x rightrotate() leftrotate(x) B B Rotation preserves inorder ke ordering Rotation takes O() time (just swaps pointers) x /9/004 6 /9/004 Review: namic Order Statistics We ve seen algorithms for finding the ith element of an unordered set in O(n) time OS-Trees: a structure to support finding the ith element of a dnamic set in O(lg n) time Support standard dnamic set operations (Insert(), elete(), in(), ax(), Succ(), red()) lso support these order statistic operations: void OS-Select(root, i); int OS-Rank(x); 7 /9/004 Review: Order Statistic Trees OS Trees augment red-black trees: ssociate a size field with each node in the tree x->size records the size of subtree rooted at x, including x itself: /9/004
4 Example: show OS-Select(root, ): Example: show OS-Select(root, ): r = x->left->size + ; if (i < r) r = x->left->size + ; if (i < r) i = 9 /9/004 0 /9/004 Example: show OS-Select(root, ): Example: show OS-Select(root, ): r = x->left->size + ; if (i < r) i = r = i = r = x->left->size + ; if (i < r) i = r = i = i = r = /9/004 /9/004 Example: show OS-Select(root, ): Example: show OS-Select(root, ): r = x->left->size + ; if (i < r) i = r = i = r = i = i = r = r = x->left->size + ; if (i < r) i = r = i = r = i = i = r = Note: use a sentinel NIL element at the leaves with size = 0 to simplif code, avoid testing for NULL /9/004 4 /9/004 4
5 Review: etermining The Rank Of n Element Idea: rank of right child x is one more than its parent s rank, plus the size of x s left subtree r = x->left->size + ; = x; while (!= T->root) if ( == ->p->right) r = r + ->p->left->size + ; = ->p; /9/004 Review: etermining The Rank Of n Element Example : find rank of element with ke r = x->left->size + ; = x; while (!= T->root) if ( == ->p->right) r = r + ->p->left->size + ; = ->p; r = 6 /9/004 Review: etermining The Rank Of n Element Example : find rank of element with ke r = x->left->size + ; = x; while (!= T->root) if ( == ->p->right) r = r + ->p->left->size + ; = ->p; r = ++ = r = 7 /9/004 Review: etermining The Rank Of n Element Example : find rank of element with ke r = x->left->size + ; = x; while (!= T->root) r = ++ = if ( == ->p->right) r = r + ->p->left->size + ; = ->p; r = r = /9/004 Review: etermining The Rank Of n Element Example : find rank of element with ke r = x->left->size + ; = x; while (!= T->root) r = if ( == ->p->right) r = r + ->p->left->size + ; = ->p; r = r = r = 9 /9/004 Review: aintaining Subtree Sizes So b keeping subtree sizes, order statistic operations can be done in O(lg n) time Next: maintain sizes during Insert() and elete() operations Insert(): Increment size fields of nodes traversed during search down the tree elete(): ecrement sizes along a path from the deleted node to the root Both: Update sizes correctl during rotations 0 /9/004
6 Reivew: aintaining Subtree Sizes x rightrotate() 7 leftrotate(x) 6 Note that rotation invalidates onl x and an recalculate their sizes in constant time x Thm.: can compute an propert in O(lg n) time that depends onl on node, left child, and right child Review: namic rogramming Summar of the basic idea: Optimal substructure: optimal solution to problem consists of optimal solutions to subproblems Overlapping subproblems: few subproblems in total, man recurring instances of each Solve bottom-up, building a table of solved subproblems that are used to solve larger ones /9/004 /9/004 oncrete Instance of LS atrix hain-roducts atrix hain-roduct: ompute = 0 * * * n- i is d i d i+ roblem: ow to parenthesize? atrix hain-roduct lg.: Tr all possible was to parenthesize = 0 * * * n- alculate number of ops for each one ick the one that is best /9/004 4 /9/004 Recursive pproach efine subproblems: ind the best parenthesization of i * i+ * * j. Let N i,j denote the number of operations done b this subproblem. The optimal solution for the whole problem is N 0,n-. Subproblem optimalit: The optimal solution can be defined in terms of optimal subproblems ssume the final multipl is at index i: ( 0 * * i )*( i+ * * n- ). Then the optimal solution N 0,n- is the sum of two optimal subproblems, N 0,i and N i+,n- plus the time for the last multipl. /9/004 haracterizing Equation Let us consider all possible places for that final multipl: Recall that i is a d i d i+ dimensional matrix. So, a characterizing equation for N i,j is the following: N i, j = j+ i k< j min Ni, k + Nk +, j + didk+ d Note that subproblems are not independent--the subproblems overlap. 6 /9/004 6
7 Greed lgorithms greed algorithm alwas makes the choice that looks best at the moment Indicators: Optimal substructure Greed choice propert: a locall optimal choice leads to a globall optimal solution namic programming can be overkill; greed algorithms tend to be easier to code ctivit-selection ormall: Given a set S of n activities s i = start time of activit i f i = finish time of activit i ind max-size subset of compatible activities 4 ssume that f f f n 6 7 /9/004 /9/004 ctivit Selection: Greed lgorithm So actual algorithm is simple: Sort the activities b finish time Schedule the first activit Then schedule the next activit in sorted list which starts after previous activit finishes Repeat until no more activities Intuition is even more simple: lwas pick the activit with the nearest finish time available and reject the conflicts Review: The Knapsack roblem The famous knapsack problem: thief breaks into a museum. abulous paintings, sculptures, and jewels are everwhere. The thief has a good ee for the value of these objects, and knows that each will fetch hundreds or thousands of dollars on the clandestine art collector s market. But, the thief has onl brought a single knapsack to the scene of the robber, and can take awa onl what he can carr. What items should the thief take to maximize the haul? 9 /9/ /9/004 Review: The Knapsack roblem ore formall, the 0- knapsack problem: The thief must choose among n items, where the ith item worth v i dollars and weighs w i pounds arring at most W pounds, maximize value Note: assume v i, w i, and W are all integers 0- b/c each item must be taken or left in entiret variation, the fractional knapsack problem: Thief can take fractions of items Think of items in 0- problem as gold ingots, in fractional problem as buckets of gold dust Solving The Knapsack roblem The optimal solution to the fractional knapsack problem can be found with a greed algorithm ow? The optimal solution to the 0- problem cannot be found with the same greed strateg Greed strateg: take in order of dollars/pound Example: items weighing 0, 0, and 0 pounds, knapsack can hold 0 pounds Suppose item is worth $00. ssign values to the other items so that the greed strateg will fail 4 /9/004 4 /9/004 7
8 This is a knapsack ax weight: W = 0 W = 0 0- Knapsack problem: a picture Items Weight w i 4 Benefit value b i 4 0- Knapsack problem: bruteforce approach Since there are n items, there are n possible combinations of items. We go through all combinations and find the one with the most total value and with total weight less or equal to W Running time will be O( n ) an be done with better efficienc /9/ /9/004
Jana Kosecka. Red-Black Trees Graph Algorithms. Many slides here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke slides
 Jana Kosecka Red-Black Trees Graph Algorithms Many slides here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke slides Binary Search Trees (BSTs) are an important data structure for dynamic sets In addition to satellite
Jana Kosecka Red-Black Trees Graph Algorithms Many slides here are based on E. Demaine, D. Luebke slides Binary Search Trees (BSTs) are an important data structure for dynamic sets In addition to satellite
B Tree. Also, every non leaf node must have at least two successors and all leaf nodes must be at the same level.
 B Tree If there is just one item in the node, then the B Tree is organised as a binar search tree: all items in the left sub tree must be less than the item in the node, and all items in the right sub
B Tree If there is just one item in the node, then the B Tree is organised as a binar search tree: all items in the left sub tree must be less than the item in the node, and all items in the right sub
Search Trees. Undirected graph Directed graph Tree Binary search tree
 Search Trees Undirected graph Directed graph Tree Binary search tree 1 Binary Search Tree Binary search key property: Let x be a node in a binary search tree. If y is a node in the left subtree of x, then
Search Trees Undirected graph Directed graph Tree Binary search tree 1 Binary Search Tree Binary search key property: Let x be a node in a binary search tree. If y is a node in the left subtree of x, then
Augmenting Data Structures
 Augmenting Data Structures [Not in G &T Text. In CLRS chapter 14.] An AVL tree by itself is not very useful. To support more useful queries we need more structure. General Definition: An augmented data
Augmenting Data Structures [Not in G &T Text. In CLRS chapter 14.] An AVL tree by itself is not very useful. To support more useful queries we need more structure. General Definition: An augmented data
Sorted Arrays. Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min
 Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Binary Search Trees FRIDAY ALGORITHMS Sorted Arrays Operation Access Search Selection Predecessor Successor Output (print) Insert Delete Extract-Min 6 10 11 17 2 0 6 Running Time O(1) O(lg n) O(1) O(1)
Computational Optimization ISE 407. Lecture 16. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Computational Optimization ISE 407 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 407 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms in
Ensures that no such path is more than twice as long as any other, so that the tree is approximately balanced
 13 Red-Black Trees A red-black tree (RBT) is a BST with one extra bit of storage per node: color, either RED or BLACK Constraining the node colors on any path from the root to a leaf Ensures that no such
13 Red-Black Trees A red-black tree (RBT) is a BST with one extra bit of storage per node: color, either RED or BLACK Constraining the node colors on any path from the root to a leaf Ensures that no such
Analysis of Algorithms - Greedy algorithms -
 Analysis of Algorithms - Greedy algorithms - Andreas Ermedahl MRTC (Mälardalens Real-Time Reseach Center) andreas.ermedahl@mdh.se Autumn 2003 Greedy Algorithms Another paradigm for designing algorithms
Analysis of Algorithms - Greedy algorithms - Andreas Ermedahl MRTC (Mälardalens Real-Time Reseach Center) andreas.ermedahl@mdh.se Autumn 2003 Greedy Algorithms Another paradigm for designing algorithms
Splay Trees. Splay Trees 1
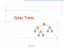 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: items stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored at
Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS )
 Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu October 08, 2014 1 Outline of Today s Class 2 Traversals Querying Insertion and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 3 Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Lecture 6: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu October 08, 2014 1 Outline of Today s Class 2 Traversals Querying Insertion and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 3 Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Splay Trees Goodrich, Tamassia, Dickerson. Splay Trees 1
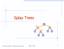 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: entries stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored
Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 Spla Trees 1 Spla Trees are Binar Search Trees BST Rules: entries stored onl at internal nodes kes stored at nodes in the left subtree of v are less than or equal to the ke stored
CSci 231 Final Review
 CSci 231 Final Review Here is a list of topics for the final. Generally you are responsible for anything discussed in class (except topics that appear italicized), and anything appearing on the homeworks.
CSci 231 Final Review Here is a list of topics for the final. Generally you are responsible for anything discussed in class (except topics that appear italicized), and anything appearing on the homeworks.
Greedy Algorithms CHAPTER 16
 CHAPTER 16 Greedy Algorithms In dynamic programming, the optimal solution is described in a recursive manner, and then is computed ``bottom up''. Dynamic programming is a powerful technique, but it often
CHAPTER 16 Greedy Algorithms In dynamic programming, the optimal solution is described in a recursive manner, and then is computed ``bottom up''. Dynamic programming is a powerful technique, but it often
Red-Black Trees. Based on materials by Dennis Frey, Yun Peng, Jian Chen, and Daniel Hood
 Red-Black Trees Based on materials by Dennis Frey, Yun Peng, Jian Chen, and Daniel Hood Quick Review of Binary Search Trees n Given a node n... q All elements of n s left subtree are less than n.data q
Red-Black Trees Based on materials by Dennis Frey, Yun Peng, Jian Chen, and Daniel Hood Quick Review of Binary Search Trees n Given a node n... q All elements of n s left subtree are less than n.data q
Algorithms in Systems Engineering ISE 172. Lecture 16. Dr. Ted Ralphs
 Algorithms in Systems Engineering ISE 172 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 172 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms
Algorithms in Systems Engineering ISE 172 Lecture 16 Dr. Ted Ralphs ISE 172 Lecture 16 1 References for Today s Lecture Required reading Sections 6.5-6.7 References CLRS Chapter 22 R. Sedgewick, Algorithms
CSC 263 Lecture 4. September 13, 2006
 S 263 Lecture 4 September 13, 2006 7 ugmenting Red-lack Trees 7.1 Introduction Suppose that ou are asked to implement an DT that is the same as a dictionar but has one additional operation: operation:
S 263 Lecture 4 September 13, 2006 7 ugmenting Red-lack Trees 7.1 Introduction Suppose that ou are asked to implement an DT that is the same as a dictionar but has one additional operation: operation:
CS473-Algorithms I. Lecture 11. Greedy Algorithms. Cevdet Aykanat - Bilkent University Computer Engineering Department
 CS473-Algorithms I Lecture 11 Greedy Algorithms 1 Activity Selection Problem Input: a set S {1, 2,, n} of n activities s i =Start time of activity i, f i = Finish time of activity i Activity i takes place
CS473-Algorithms I Lecture 11 Greedy Algorithms 1 Activity Selection Problem Input: a set S {1, 2,, n} of n activities s i =Start time of activity i, f i = Finish time of activity i Activity i takes place
Algorithms. Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees
 Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
Algorithms Deleting from Red-Black Trees B-Trees Recall the rules for BST deletion 1. If vertex to be deleted is a leaf, just delete it. 2. If vertex to be deleted has just one child, replace it with that
We ve done. Now. Next
 We ve done Fast Fourier Transform Polynomial Multiplication Now Introduction to the greedy method Activity selection problem How to prove that a greedy algorithm works Huffman coding Matroid theory Next
We ve done Fast Fourier Transform Polynomial Multiplication Now Introduction to the greedy method Activity selection problem How to prove that a greedy algorithm works Huffman coding Matroid theory Next
Introduction to Algorithms Massachusetts Institute of Technology Professors Erik D. Demaine and Charles E. Leiserson.
 Introduction to Algorithms Massachusetts Institute of Technolog Professors Erik D. Demaine and Charles E. Leiserson October 24, 2005 6.046J/18.410J Handout 16 Problem Set 5 MIT students: This problem set
Introduction to Algorithms Massachusetts Institute of Technolog Professors Erik D. Demaine and Charles E. Leiserson October 24, 2005 6.046J/18.410J Handout 16 Problem Set 5 MIT students: This problem set
Binary Tree. Preview. Binary Tree. Binary Tree. Binary Search Tree 10/2/2017. Binary Tree
 0/2/ Preview Binary Tree Tree Binary Tree Property functions In-order walk Pre-order walk Post-order walk Search Tree Insert an element to the Tree Delete an element form the Tree A binary tree is a tree
0/2/ Preview Binary Tree Tree Binary Tree Property functions In-order walk Pre-order walk Post-order walk Search Tree Insert an element to the Tree Delete an element form the Tree A binary tree is a tree
Design and Analysis of Algorithms 演算法設計與分析. Lecture 7 April 15, 2015 洪國寶
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 演算法設計與分析 Lecture 7 April 15, 2015 洪國寶 1 Course information (5/5) Grading (Tentative) Homework 25% (You may collaborate when solving the homework, however when writing
Design and Analysis of Algorithms 演算法設計與分析 Lecture 7 April 15, 2015 洪國寶 1 Course information (5/5) Grading (Tentative) Homework 25% (You may collaborate when solving the homework, however when writing
Splay Trees 3/20/14. Splay Trees. Splay Trees are Binary Search Trees. note that two keys of equal value may be wellseparated (7,T) (1,Q) (1,C) (5,H)
 Spla Trees 3/20/14 Presentation for use with the tetbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, b M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wile, 2014 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 2013
Spla Trees 3/20/14 Presentation for use with the tetbook Data Structures and Algorithms in Java, 6 th edition, b M. T. Goodrich, R. Tamassia, and M. H. Goldwasser, Wile, 2014 Spla Trees v 6 3 8 4 2013
Search Trees. Chapter 11
 Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
Search Trees Chapter 6 4 8 9 Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Outline Binar Search Trees AVL Trees Spla Trees Binar Search Trees A binar search tree is a proper binar tree storing ke-value
1 Non greedy algorithms (which we should have covered
 1 Non greedy algorithms (which we should have covered earlier) 1.1 Floyd Warshall algorithm This algorithm solves the all-pairs shortest paths problem, which is a problem where we want to find the shortest
1 Non greedy algorithms (which we should have covered earlier) 1.1 Floyd Warshall algorithm This algorithm solves the all-pairs shortest paths problem, which is a problem where we want to find the shortest
SFU CMPT Lecture: Week 9
 SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 1 Lecture: Week 9 SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 Lecture: Week 9 Ján Maňuch E-mail: jmanuch@sfu.ca Lecture on July 8, 2008, 5.30pm-8.20pm SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 2 Lecture: Week 9 Binary search trees
SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 1 Lecture: Week 9 SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 Lecture: Week 9 Ján Maňuch E-mail: jmanuch@sfu.ca Lecture on July 8, 2008, 5.30pm-8.20pm SFU CMPT-307 2008-2 2 Lecture: Week 9 Binary search trees
CSE 332 Autumn 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators)
 Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Autumn 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Autumn 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Exercises Optimal binary search trees root
 5.5 Optimal binary search trees 403 e w 5 5 j 4.75 i j 4.00 i 3.75.00 3 3 0.70 0.80 3.5.0. 4 0.55 0.50 0.60 4 0.90 0.70 0.60 0.90 5 0.45 0.35 0. 0.50 5 0 0.45 0.40 0.5 0. 0.50 6 0 0. 0.5 0.5 0.0 0.35 6
5.5 Optimal binary search trees 403 e w 5 5 j 4.75 i j 4.00 i 3.75.00 3 3 0.70 0.80 3.5.0. 4 0.55 0.50 0.60 4 0.90 0.70 0.60 0.90 5 0.45 0.35 0. 0.50 5 0 0.45 0.40 0.5 0. 0.50 6 0 0. 0.5 0.5 0.0 0.35 6
AVL Trees. Reading: 9.2
 AVL Trees Reading: 9.2 Balance Factor of a Node The difference in height of its two subtrees (h R -h L ) Balanced Node if -1 BF 1 Unbalanced Node if BF 1 h L h R Balance Factor of a Binar Tree Corresponds
AVL Trees Reading: 9.2 Balance Factor of a Node The difference in height of its two subtrees (h R -h L ) Balanced Node if -1 BF 1 Unbalanced Node if BF 1 h L h R Balance Factor of a Binar Tree Corresponds
T(n) = expected time of algorithm over all inputs of size n. half the elements in A[1.. j 1] are less than A[ j ], and half the elements are greater.
![T(n) = expected time of algorithm over all inputs of size n. half the elements in A[1.. j 1] are less than A[ j ], and half the elements are greater. T(n) = expected time of algorithm over all inputs of size n. half the elements in A[1.. j 1] are less than A[ j ], and half the elements are greater.](/thumbs/92/108601906.jpg) Algorithms Design and Analysis Definitions: An algorithm: It is any well-defined computational procedure that takes some value, or set of values, as input and produces some value, or set of values, as
Algorithms Design and Analysis Definitions: An algorithm: It is any well-defined computational procedure that takes some value, or set of values, as input and produces some value, or set of values, as
Cpt S 223 Fall Cpt S 223. School of EECS, WSU
 Course Review Cpt S 223 Fall 2012 1 Final Exam When: Monday (December 10) 8 10 AM Where: in class (Sloan 150) Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & class notes
Course Review Cpt S 223 Fall 2012 1 Final Exam When: Monday (December 10) 8 10 AM Where: in class (Sloan 150) Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & class notes
Lecture: Analysis of Algorithms (CS )
 Lecture: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu Fall 2017 1 Binary Search Trees Traversals, Querying, Insertion, and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 2 Example: Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Lecture: Analysis of Algorithms (CS583-002) Amarda Shehu Fall 2017 1 Binary Search Trees Traversals, Querying, Insertion, and Deletion Sorting with BSTs 2 Example: Red-black Trees Height of a Red-black
Module 4: Index Structures Lecture 13: Index structure. The Lecture Contains: Index structure. Binary search tree (BST) B-tree. B+-tree.
 The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
The Lecture Contains: Index structure Binary search tree (BST) B-tree B+-tree Order file:///c /Documents%20and%20Settings/iitkrana1/My%20Documents/Google%20Talk%20Received%20Files/ist_data/lecture13/13_1.htm[6/14/2012
Course Review. Cpt S 223 Fall 2010
 Course Review Cpt S 223 Fall 2010 1 Final Exam When: Thursday (12/16) 8-10am Where: in class Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & class notes Homeworks & program
Course Review Cpt S 223 Fall 2010 1 Final Exam When: Thursday (12/16) 8-10am Where: in class Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & class notes Homeworks & program
Treaps. 1 Binary Search Trees (BSTs) CSE341T/CSE549T 11/05/2014. Lecture 19
 CSE34T/CSE549T /05/04 Lecture 9 Treaps Binary Search Trees (BSTs) Search trees are tree-based data structures that can be used to store and search for items that satisfy a total order. There are many types
CSE34T/CSE549T /05/04 Lecture 9 Treaps Binary Search Trees (BSTs) Search trees are tree-based data structures that can be used to store and search for items that satisfy a total order. There are many types
Uses for Trees About Trees Binary Trees. Trees. Seth Long. January 31, 2010
 Uses for About Binary January 31, 2010 Uses for About Binary Uses for Uses for About Basic Idea Implementing Binary Example: Expression Binary Search Uses for Uses for About Binary Uses for Storage Binary
Uses for About Binary January 31, 2010 Uses for About Binary Uses for Uses for About Basic Idea Implementing Binary Example: Expression Binary Search Uses for Uses for About Binary Uses for Storage Binary
CSE 502 Class 16. Jeremy Buhler Steve Cole. March A while back, we introduced the idea of collections to put hash tables in context.
 CSE 502 Class 16 Jeremy Buhler Steve Cole March 17 2015 Onwards to trees! 1 Collection Types Revisited A while back, we introduced the idea of collections to put hash tables in context. abstract data types
CSE 502 Class 16 Jeremy Buhler Steve Cole March 17 2015 Onwards to trees! 1 Collection Types Revisited A while back, we introduced the idea of collections to put hash tables in context. abstract data types
CS 380 ALGORITHM DESIGN AND ANALYSIS
 CS 380 ALGORITHM DESIGN AND ANALYSIS Lecture 12: Red-Black Trees Text Reference: Chapters 12, 13 Binary Search Trees (BST): Review Each node in tree T is a object x Contains attributes: Data Pointers to
CS 380 ALGORITHM DESIGN AND ANALYSIS Lecture 12: Red-Black Trees Text Reference: Chapters 12, 13 Binary Search Trees (BST): Review Each node in tree T is a object x Contains attributes: Data Pointers to
Design and Analysis of Algorithms
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms CSE 5311 Lecture 16 Greedy algorithms Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE5311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 1 Overview A greedy
Design and Analysis of Algorithms CSE 5311 Lecture 16 Greedy algorithms Junzhou Huang, Ph.D. Department of Computer Science and Engineering CSE5311 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 1 Overview A greedy
) $ f ( n) " %( g( n)
 CSE 0 Name Test Spring 008 Last Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time to compute the sum of the n elements of an integer array is: # A.
CSE 0 Name Test Spring 008 Last Digits of Mav ID # Multiple Choice. Write your answer to the LEFT of each problem. points each. The time to compute the sum of the n elements of an integer array is: # A.
1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1
![1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1](/thumbs/85/92778785.jpg) Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 2. O(n) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = T(n/2) + n, T(1)
Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 2. O(n) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = T(n/2) + n, T(1)
Trees. (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring / 28
 Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Trees (Trees) Data Structures and Programming Spring 2018 1 / 28 Trees A tree is a collection of nodes, which can be empty (recursive definition) If not empty, a tree consists of a distinguished node r
Course Review. Cpt S 223 Fall 2009
 Course Review Cpt S 223 Fall 2009 1 Final Exam When: Tuesday (12/15) 8-10am Where: in class Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & class notes Homeworks & program
Course Review Cpt S 223 Fall 2009 1 Final Exam When: Tuesday (12/15) 8-10am Where: in class Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & class notes Homeworks & program
Design and Analysis of Algorithms 演算法設計與分析. Lecture 7 April 6, 2016 洪國寶
 Design and Analysis of Algorithms 演算法設計與分析 Lecture 7 April 6, 2016 洪國寶 1 Course information (5/5) Grading (Tentative) Homework 25% (You may collaborate when solving the homework, however when writing up
Design and Analysis of Algorithms 演算法設計與分析 Lecture 7 April 6, 2016 洪國寶 1 Course information (5/5) Grading (Tentative) Homework 25% (You may collaborate when solving the homework, however when writing up
Binary Trees. Recursive definition. Is this a binary tree?
 Binary Search Trees Binary Trees Recursive definition 1. An empty tree is a binary tree 2. A node with two child subtrees is a binary tree 3. Only what you get from 1 by a finite number of applications
Binary Search Trees Binary Trees Recursive definition 1. An empty tree is a binary tree 2. A node with two child subtrees is a binary tree 3. Only what you get from 1 by a finite number of applications
Priority Queues, Binary Heaps, and Heapsort
 Priority Queues, Binary eaps, and eapsort Learning Goals: Provide examples of appropriate applications for priority queues and heaps. Implement and manipulate a heap using an array as the underlying data
Priority Queues, Binary eaps, and eapsort Learning Goals: Provide examples of appropriate applications for priority queues and heaps. Implement and manipulate a heap using an array as the underlying data
Greedy algorithms 2 4/5/12. Knapsack problems: Greedy or not? Compression algorithms. Data compression. David Kauchak cs302 Spring 2012
 Knapsack problems: Greedy or not? Greedy algorithms 2 avid Kauchak cs02 Spring 12 l 0-1 Knapsack thief robbing a store finds n items worth v 1, v 2,.., v n dollars and weight w 1, w 2,, w n pounds, where
Knapsack problems: Greedy or not? Greedy algorithms 2 avid Kauchak cs02 Spring 12 l 0-1 Knapsack thief robbing a store finds n items worth v 1, v 2,.., v n dollars and weight w 1, w 2,, w n pounds, where
CPS 231 Exam 2 SOLUTIONS
 CPS 231 Exam 2 SOLUTIONS Fall 2003 1:00-2:25, Tuesday November 20th Closed book exam NAME: Problem Max Obtained 1 10 2 25 3 (a) 15 3 (b) 15 3 (c) 10 4 (a) 10 4 (b) 15 4 (c) 10 Total 110 1 [10 points ]
CPS 231 Exam 2 SOLUTIONS Fall 2003 1:00-2:25, Tuesday November 20th Closed book exam NAME: Problem Max Obtained 1 10 2 25 3 (a) 15 3 (b) 15 3 (c) 10 4 (a) 10 4 (b) 15 4 (c) 10 Total 110 1 [10 points ]
Binomial Queue deletemin ADTs Seen So Far
 Today s Outline Trees (inary Search Trees) hapter in Weiss S ata Structures Ruth nderson nnouncements Written HW # due next riday, 1/ Project due next Monday, /1 Today s Topics: Priority Queues inomial
Today s Outline Trees (inary Search Trees) hapter in Weiss S ata Structures Ruth nderson nnouncements Written HW # due next riday, 1/ Project due next Monday, /1 Today s Topics: Priority Queues inomial
10/24/ Rotations. 2. // s left subtree s right subtree 3. if // link s parent to elseif == else 11. // put x on s left
 13.2 Rotations MAT-72006 AA+DS, Fall 2013 24-Oct-13 368 LEFT-ROTATE(, ) 1. // set 2. // s left subtree s right subtree 3. if 4. 5. // link s parent to 6. if == 7. 8. elseif == 9. 10. else 11. // put x
13.2 Rotations MAT-72006 AA+DS, Fall 2013 24-Oct-13 368 LEFT-ROTATE(, ) 1. // set 2. // s left subtree s right subtree 3. if 4. 5. // link s parent to 6. if == 7. 8. elseif == 9. 10. else 11. // put x
CS251-SE1. Midterm 2. Tuesday 11/1 8:00pm 9:00pm. There are 16 multiple-choice questions and 6 essay questions.
 CS251-SE1 Midterm 2 Tuesday 11/1 8:00pm 9:00pm There are 16 multiple-choice questions and 6 essay questions. Answer the multiple choice questions on your bubble sheet. Answer the essay questions in the
CS251-SE1 Midterm 2 Tuesday 11/1 8:00pm 9:00pm There are 16 multiple-choice questions and 6 essay questions. Answer the multiple choice questions on your bubble sheet. Answer the essay questions in the
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Binary Search Tree - Best Time All BST operations are O(d), where d is tree depth minimum d is d = ëlog for a binary tree
CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Binary Search Tree - Best Time All BST operations are O(d), where d is tree depth minimum d is d = ëlog for a binary tree
13.4 Deletion in red-black trees
 The operation of Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to the operation of Insertion on the tree. That is, apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees to delete a node z; apply node color changes
The operation of Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to the operation of Insertion on the tree. That is, apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees to delete a node z; apply node color changes
CS60020: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning. Sourangshu Bhattacharya
 CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Balanced search trees Balanced search tree: A search-tree data structure for which a height of O(lg n) is guaranteed when
CS62: Foundations of Algorithm Design and Machine Learning Sourangshu Bhattacharya Balanced search trees Balanced search tree: A search-tree data structure for which a height of O(lg n) is guaranteed when
Advanced Set Representation Methods
 Advanced Set Representation Methods AVL trees. 2-3(-4) Trees. Union-Find Set ADT DSA - lecture 4 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1 Advanced Set Representation. AVL Trees Problem with BSTs: worst case operation
Advanced Set Representation Methods AVL trees. 2-3(-4) Trees. Union-Find Set ADT DSA - lecture 4 - T.U.Cluj-Napoca - M. Joldos 1 Advanced Set Representation. AVL Trees Problem with BSTs: worst case operation
Binary Trees
 Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
Binary Trees 4-7-2005 Opening Discussion What did we talk about last class? Do you have any code to show? Do you have any questions about the assignment? What is a Tree? You are all familiar with what
CS102 Binary Search Trees
 CS102 Binary Search Trees Prof Tejada 1 To speed up insertion, removal and search, modify the idea of a Binary Tree to create a Binary Search Tree (BST) Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees have one
CS102 Binary Search Trees Prof Tejada 1 To speed up insertion, removal and search, modify the idea of a Binary Tree to create a Binary Search Tree (BST) Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees have one
Augmenting Data Structures. General approach Dynamic order statistics Interval trees
 Augmenting Data Structures General approach Dynamic order statistics Interval trees 1 General Approach In some applications custom data structures will be necessary. In others, a well-known data structure
Augmenting Data Structures General approach Dynamic order statistics Interval trees 1 General Approach In some applications custom data structures will be necessary. In others, a well-known data structure
Properties of red-black trees
 Red-Black Trees Introduction We have seen that a binary search tree is a useful tool. I.e., if its height is h, then we can implement any basic operation on it in O(h) units of time. The problem: given
Red-Black Trees Introduction We have seen that a binary search tree is a useful tool. I.e., if its height is h, then we can implement any basic operation on it in O(h) units of time. The problem: given
CISC 235 Topic 3. General Trees, Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 CISC 235 Topic 3 General Trees, Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Outline General Trees Terminology, Representation, Properties Binary Trees Representations, Properties, Traversals Recursive Algorithms
CISC 235 Topic 3 General Trees, Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Outline General Trees Terminology, Representation, Properties Binary Trees Representations, Properties, Traversals Recursive Algorithms
Search Trees - 2. Venkatanatha Sarma Y. Lecture delivered by: Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore. M.S Ramaiah School of Advanced Studies - Bangalore
 Search Trees - 2 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Search Trees - 2 Lecture delivered by: Venkatanatha Sarma Y Assistant Professor MSRSAS-Bangalore 11 Objectives To introduce, discuss and analyse the different ways to realise balanced Binary Search Trees
Course Review for. Cpt S 223 Fall Cpt S 223. School of EECS, WSU
 Course Review for Midterm Exam 1 Cpt S 223 Fall 2011 1 Midterm Exam 1 When: Friday (10/14) 1:10-2pm Where: in class Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & in-class
Course Review for Midterm Exam 1 Cpt S 223 Fall 2011 1 Midterm Exam 1 When: Friday (10/14) 1:10-2pm Where: in class Closed book, closed notes Comprehensive Material for preparation: Lecture slides & in-class
Greedy Algorithms CLRS Laura Toma, csci2200, Bowdoin College
 Greedy Algorithms CLRS 16.1-16.2 Laura Toma, csci2200, Bowdoin College Overview. Sometimes we can solve optimization problems with a technique called greedy. A greedy algorithm picks the option that looks
Greedy Algorithms CLRS 16.1-16.2 Laura Toma, csci2200, Bowdoin College Overview. Sometimes we can solve optimization problems with a technique called greedy. A greedy algorithm picks the option that looks
CSci 231 Homework 7. Red Black Trees. CLRS Chapter 13 and 14
 CSci 31 Homework 7 Red Black Trees CLRS Chapter 13 and 14 1. Problem 13-1 (persistent dynamic sets).. Problem 13-3 (AVL trees) 3. In this problem we consider a data structure for maintaining a multi-set
CSci 31 Homework 7 Red Black Trees CLRS Chapter 13 and 14 1. Problem 13-1 (persistent dynamic sets).. Problem 13-3 (AVL trees) 3. In this problem we consider a data structure for maintaining a multi-set
CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms Lecture 5: Dictionary ADTs; Binary Trees. Linda Shapiro Spring 2016
 CSE373: Data Structures & lgorithms Lecture 5: Dictionary DTs; Binary Trees Linda Shapiro Spring 2016 Today s Outline nnouncements - Homework 1 due TODY at 11:59 pm - Homework 2 out (paper and pencil assignment)
CSE373: Data Structures & lgorithms Lecture 5: Dictionary DTs; Binary Trees Linda Shapiro Spring 2016 Today s Outline nnouncements - Homework 1 due TODY at 11:59 pm - Homework 2 out (paper and pencil assignment)
CSE 326: Data Structures Binary Search Trees
 nnouncements (1/3/0) S 36: ata Structures inary Search Trees Steve Seitz Winter 0 HW # due now HW #3 out today, due at beginning of class next riday. Project due next Wed. night. Read hapter 4 1 Ts Seen
nnouncements (1/3/0) S 36: ata Structures inary Search Trees Steve Seitz Winter 0 HW # due now HW #3 out today, due at beginning of class next riday. Project due next Wed. night. Read hapter 4 1 Ts Seen
TREES. Trees - Introduction
 TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
TREES Chapter 6 Trees - Introduction All previous data organizations we've studied are linear each element can have only one predecessor and successor Accessing all elements in a linear sequence is O(n)
Binary search trees. Binary search trees are data structures based on binary trees that support operations on dynamic sets.
 COMP3600/6466 Algorithms 2018 Lecture 12 1 Binary search trees Reading: Cormen et al, Sections 12.1 to 12.3 Binary search trees are data structures based on binary trees that support operations on dynamic
COMP3600/6466 Algorithms 2018 Lecture 12 1 Binary search trees Reading: Cormen et al, Sections 12.1 to 12.3 Binary search trees are data structures based on binary trees that support operations on dynamic
CS 361, Lecture 21. Outline. Things you can do. Things I will do. Evaluation Results
 HW Difficulty CS 361, Lecture 21 Jared Saia University of New Mexico The HW in this class is inherently difficult, this is a difficult class. You need to be able to solve problems as hard as the problems
HW Difficulty CS 361, Lecture 21 Jared Saia University of New Mexico The HW in this class is inherently difficult, this is a difficult class. You need to be able to solve problems as hard as the problems
Lecture Overview. Readings. Recall: Binary Search Trees (BSTs) The importance of being balanced. AVL trees. Balance Insert. Other balanced trees
 alanced inar Search Trees Lecture Overview The importance of being balanced VL trees Definition alance Insert Other balanced trees Data structures in general Readings LRS hapter. and. (but different approach:
alanced inar Search Trees Lecture Overview The importance of being balanced VL trees Definition alance Insert Other balanced trees Data structures in general Readings LRS hapter. and. (but different approach:
CSE2331/5331. Topic 6: Binary Search Tree. Data structure Operations CSE 2331/5331
 CSE2331/5331 Topic 6: Binary Search Tree Data structure Operations Set Operations Maximum Extract-Max Insert Increase-key We can use priority queue (implemented by heap) Search Delete Successor Predecessor
CSE2331/5331 Topic 6: Binary Search Tree Data structure Operations Set Operations Maximum Extract-Max Insert Increase-key We can use priority queue (implemented by heap) Search Delete Successor Predecessor
Review of course COMP-251B winter 2010
 Review of course COMP-251B winter 2010 Lecture 1. Book Section 15.2 : Chained matrix product Matrix product is associative Computing all possible ways of parenthesizing Recursive solution Worst-case running-time
Review of course COMP-251B winter 2010 Lecture 1. Book Section 15.2 : Chained matrix product Matrix product is associative Computing all possible ways of parenthesizing Recursive solution Worst-case running-time
Hash Tables. CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides. Wednesday, April 22, Glenn G. Chappell
 Hash Tables CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Wednesday, April 22, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005
Hash Tables CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Wednesday, April 22, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005
logn D. Θ C. Θ n 2 ( ) ( ) f n B. nlogn Ο n2 n 2 D. Ο & % ( C. Θ # ( D. Θ n ( ) Ω f ( n)
 CSE 0 Test Your name as it appears on your UTA ID Card Fall 0 Multiple Choice:. Write the letter of your answer on the line ) to the LEFT of each problem.. CIRCLED ANSWERS DO NOT COUNT.. points each. The
CSE 0 Test Your name as it appears on your UTA ID Card Fall 0 Multiple Choice:. Write the letter of your answer on the line ) to the LEFT of each problem.. CIRCLED ANSWERS DO NOT COUNT.. points each. The
Priority Queues and Heaps. Heaps of fun, for everyone!
 Priority Queues and Heaps Heaps of fun, for everyone! Learning Goals After this unit, you should be able to... Provide examples of appropriate applications for priority queues and heaps Manipulate data
Priority Queues and Heaps Heaps of fun, for everyone! Learning Goals After this unit, you should be able to... Provide examples of appropriate applications for priority queues and heaps Manipulate data
Data Structures and Algorithms CMPSC 465
 Data Structures and Algorithms CMPSC 465 LECTURE 24 Balanced Search Trees Red-Black Trees Adam Smith 4/18/12 A. Smith; based on slides by C. Leiserson and E. Demaine L1.1 Balanced search trees Balanced
Data Structures and Algorithms CMPSC 465 LECTURE 24 Balanced Search Trees Red-Black Trees Adam Smith 4/18/12 A. Smith; based on slides by C. Leiserson and E. Demaine L1.1 Balanced search trees Balanced
CSci 231 Homework 7. Red Black Trees. CLRS Chapter 13 and 14
 CSci 31 Homework 7 Red Black Trees CLRS Chapter 13 and 14 Choose 4 problems from the list below. 1. (CLRS 13.1-6) What is the largest possible number of internal nodes in a red-black tree with black-height
CSci 31 Homework 7 Red Black Trees CLRS Chapter 13 and 14 Choose 4 problems from the list below. 1. (CLRS 13.1-6) What is the largest possible number of internal nodes in a red-black tree with black-height
/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Balanced Search Trees Date: 9/20/18
 601.433/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Balanced Search Trees Date: 9/20/18 6.1 Introduction For next few lectures we will be looking at several important data structures.
601.433/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Balanced Search Trees Date: 9/20/18 6.1 Introduction For next few lectures we will be looking at several important data structures.
CMSC351 - Fall 2014, Homework #2
 CMSC351 - Fall 2014, Homework #2 Due: October 8th at the start of class Name: Section: Grades depend on neatness and clarity. Write your answers with enough detail about your approach and concepts used,
CMSC351 - Fall 2014, Homework #2 Due: October 8th at the start of class Name: Section: Grades depend on neatness and clarity. Write your answers with enough detail about your approach and concepts used,
CSE 332 Spring 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators)
 Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Spring 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
Name: Email address: Quiz Section: CSE 332 Spring 2013: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will
CSCI Trees. Mark Redekopp David Kempe
 CSCI 104 2-3 Trees Mark Redekopp David Kempe Trees & Maps/Sets C++ STL "maps" and "sets" use binary search trees internally to store their keys (and values) that can grow or contract as needed This allows
CSCI 104 2-3 Trees Mark Redekopp David Kempe Trees & Maps/Sets C++ STL "maps" and "sets" use binary search trees internally to store their keys (and values) that can grow or contract as needed This allows
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Searching Red-Black and Other Dynamically BalancedTrees PLSD210 Searching - Re-visited Binary tree O(log n) if it stays balanced Simple binary tree good for static collections
Data Structures and Algorithms Searching Red-Black and Other Dynamically BalancedTrees PLSD210 Searching - Re-visited Binary tree O(log n) if it stays balanced Simple binary tree good for static collections
Programming II (CS300)
 1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
1 Programming II (CS300) Chapter 11: Binary Search Trees MOUNA KACEM mouna@cs.wisc.edu Fall 2018 General Overview of Data Structures 2 Introduction to trees 3 Tree: Important non-linear data structure
9/24/ Hash functions
 11.3 Hash functions A good hash function satis es (approximately) the assumption of SUH: each key is equally likely to hash to any of the slots, independently of the other keys We typically have no way
11.3 Hash functions A good hash function satis es (approximately) the assumption of SUH: each key is equally likely to hash to any of the slots, independently of the other keys We typically have no way
Algorithms. AVL Tree
 Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
Algorithms AVL Tree Balanced binary tree The disadvantage of a binary search tree is that its height can be as large as N-1 This means that the time needed to perform insertion and deletion and many other
13.4 Deletion in red-black trees
 Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to insertion. Apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees. Apply node color changes and left/right rotations to fix the violations of RBT tree properties.
Deletion in a red-black tree is similar to insertion. Apply the deletion algorithm for binary search trees. Apply node color changes and left/right rotations to fix the violations of RBT tree properties.
LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS
 Department of Computer Science University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS By Faculty of Science for Women( SCIW), University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@uobabylon.edu.iq
Department of Computer Science University of Babylon LECTURE NOTES OF ALGORITHMS: DESIGN TECHNIQUES AND ANALYSIS By Faculty of Science for Women( SCIW), University of Babylon, Iraq Samaher@uobabylon.edu.iq
2-3 Tree. Outline B-TREE. catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } ADD SLIDES ON DISJOINT SETS
 Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
Outline catch(...){ printf( "Assignment::SolveProblem() AAAA!"); } Balanced Search Trees 2-3 Trees 2-3-4 Trees Slide 4 Why care about advanced implementations? Same entries, different insertion sequence:
CSE 332 Winter 2015: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators)
 _ UWNetID: Lecture Section: A CSE 332 Winter 2015: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will give
_ UWNetID: Lecture Section: A CSE 332 Winter 2015: Midterm Exam (closed book, closed notes, no calculators) Instructions: Read the directions for each question carefully before answering. We will give
Midterm solutions. n f 3 (n) = 3
 Introduction to Computer Science 1, SE361 DGIST April 20, 2016 Professors Min-Soo Kim and Taesup Moon Midterm solutions Midterm solutions The midterm is a 1.5 hour exam (4:30pm 6:00pm). This is a closed
Introduction to Computer Science 1, SE361 DGIST April 20, 2016 Professors Min-Soo Kim and Taesup Moon Midterm solutions Midterm solutions The midterm is a 1.5 hour exam (4:30pm 6:00pm). This is a closed
COMP Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
 COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Binary Search Trees CLRS 12.2, 12.3, 13.2, read problem 13-3 University of Manitoba COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures Shahin Kamali Binary Search Trees CLRS 12.2, 12.3, 13.2, read problem 13-3 University of Manitoba COMP 3170 - Analysis of Algorithms & Data Structures
Input: n jobs (associated start time s j, finish time f j, and value v j ) for j = 1 to n M[j] = empty M[0] = 0. M-Compute-Opt(n)
![Input: n jobs (associated start time s j, finish time f j, and value v j ) for j = 1 to n M[j] = empty M[0] = 0. M-Compute-Opt(n) Input: n jobs (associated start time s j, finish time f j, and value v j ) for j = 1 to n M[j] = empty M[0] = 0. M-Compute-Opt(n)](/thumbs/72/66787339.jpg) Objec&ves Dnamic Programming Ø Wrapping up: weighted interval schedule Ø Ø Subset Sums Summar: Proper&es of Problems for DP Polnomial number of subproblems Solu&on to original problem can be easil computed
Objec&ves Dnamic Programming Ø Wrapping up: weighted interval schedule Ø Ø Subset Sums Summar: Proper&es of Problems for DP Polnomial number of subproblems Solu&on to original problem can be easil computed
Dictionaries. Priority Queues
 Red-Black-Trees.1 Dictionaries Sets and Multisets; Opers: (Ins., Del., Mem.) Sequential sorted or unsorted lists. Linked sorted or unsorted lists. Tries and Hash Tables. Binary Search Trees. Priority Queues
Red-Black-Trees.1 Dictionaries Sets and Multisets; Opers: (Ins., Del., Mem.) Sequential sorted or unsorted lists. Linked sorted or unsorted lists. Tries and Hash Tables. Binary Search Trees. Priority Queues
Questions from the material presented in this lecture
 Advanced Data Structures Questions from the material presented in this lecture January 8, 2015 This material illustrates the kind of exercises and questions you may get at the final colloqium. L1. Introduction.
Advanced Data Structures Questions from the material presented in this lecture January 8, 2015 This material illustrates the kind of exercises and questions you may get at the final colloqium. L1. Introduction.
Data Structures. Dynamic Sets
 Data Structures Binary Search Tree Dynamic Sets Elements have a key and satellite data Dynamic sets support queries such as: Search(S, k) Minimum(S) Maximum(S) Successor(S, x) Predecessor(S, x) Insert(S,
Data Structures Binary Search Tree Dynamic Sets Elements have a key and satellite data Dynamic sets support queries such as: Search(S, k) Minimum(S) Maximum(S) Successor(S, x) Predecessor(S, x) Insert(S,
Greedy algorithms part 2, and Huffman code
 Greedy algorithms part 2, and Huffman code Two main properties: 1. Greedy choice property: At each decision point, make the choice that is best at the moment. We typically show that if we make a greedy
Greedy algorithms part 2, and Huffman code Two main properties: 1. Greedy choice property: At each decision point, make the choice that is best at the moment. We typically show that if we make a greedy
A red-black tree is a balanced binary search tree with the following properties:
 Binary search trees work best when they are balanced or the path length from root to any leaf is within some bounds. The red-black tree algorithm is a method for balancing trees. The name derives from
Binary search trees work best when they are balanced or the path length from root to any leaf is within some bounds. The red-black tree algorithm is a method for balancing trees. The name derives from
Trees. Chapter 6. strings. 3 Both position and Enumerator are similar in concept to C++ iterators, although the details are quite different.
 Chapter 6 Trees In a hash table, the items are not stored in any particular order in the table. This is fine for implementing Sets and Maps, since for those abstract data types, the only thing that matters
Chapter 6 Trees In a hash table, the items are not stored in any particular order in the table. This is fine for implementing Sets and Maps, since for those abstract data types, the only thing that matters
Note that this is a rep invariant! The type system doesn t enforce this but you need it to be true. Should use repok to check in debug version.
 Announcements: Prelim tonight! 7:30-9:00 in Thurston 203/205 o Handed back in section tomorrow o If you have a conflict you can take the exam at 5:45 but can t leave early. Please email me so we have a
Announcements: Prelim tonight! 7:30-9:00 in Thurston 203/205 o Handed back in section tomorrow o If you have a conflict you can take the exam at 5:45 but can t leave early. Please email me so we have a
