CSL 860: Modern Parallel
|
|
|
- Lester Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSL 860: Modern Parallel Computation
2 PARALLEL SORTING
3 BitonicMerge and Sort Bitonicsequence: {a 0, a 1,, a n-1 }: A sequence with a monotonically increasing part and a monotonically decreasing part For some i, {a 0 <= <=a i } and {a i+1 >= >= a n-1 } Or, a cyclic-shift of indices makes it bitonic
4 Two BitonicSequences Subsequence 2 Subsequence 1 Say {a 0 <= <=a n/2 >= a n/2+1 >= >= a n-1 } Subsequence 1: {min(a 0, a n/2+1 ), min(a 1, a n/2+2 ), } Subsequence 2: {max(a 0, a n/2+1 ), max(a 1, a n/2+2 ), } Recursively sort each bitonic subsequence Subsequence 1 <= Subsequence 2
5 BitonicSort Sort each pairs alternately in increasing and decreasing orders Every sequence of length four is now bitonic Sort recursively Again alternate increasing and decreasing orders Forming bitonic sequences of length eight now And so on..
6 BitonicNetwork log n stages Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 log n stages log 2 n time n log 2 n work
7 Batcher s Odd-Even Merge Merge the even indices Get c0, c1, c2, c3, Merge the odd indices Get d0, d1, d2, d3, Perform an odd-even merge c0, min(c1, d0), max(c1, d0), min(c2, d1), max(c2, d1), d n-1
8 Example of a Fast Sort Rank sort Given Array A, For each i, find rank A[i] A[rank[i]] = A[i] How fast can you find Rank(A:A)? If you had n 2 processors (Quiz) If you had n 3 processors
9 Optimal Merge Sort Sort recursively similarly to a sequential Merge at each level of recursion using the optimal parallel merge O(log logn) time O(n) work Log n merge-tree levels => O(log n loglogn) time O(n log n) work
10 Sort n/p elements, then Merge Merge 2n/p-elements pairs P 0,P 1, P 2,P 3 p-processors merging P 0,P Merge n/p-elements 1 P 2,P pairs 3 P 0 P 1 P p-1 Sort first n/p elements Sort second n/p elements HOW EFFICIENTLY CAN YOU MERGE?
11 c-cover Merging Consider sequence A and B X: a c-cover of A and B Two consecutive elements of X have at most c elements of A (and at most c elements of B) between them Given Rank(X:A) and Rank(X:B) Find Rank(A:B) and Rank(B:A) In O(1) time, with O(n) work If X is a c-cover of B, and we know Rank(A:X) and Rank(X:B) Compute Rank(A:B) in O(1)
12 Optimal O(log n)-time Merge Sort Works for any proper binary tree Not necessarily balanced The sorted list L[i] at a given node iis divided into stages s th stage generates list L s [i] Initially: L 0 [i] = null for internal nodes L 0 [i] = value at leaf node i
13 Fast Optimal Merge Sort: Definitions Algorithm proceeds up the tree, one stageat a time At stage s, node n is activeif height(node) <= s <= 3*height(n) height(n) = height(tree) path-length from root to n At each stage a node is active, It merges a sample of lists of its children
14 Algorithm parallel for n = active nodes: L s+1 [n] = Merge(Sample s (left), Sample s (right])) SUB i (l 0, l 1, l 3 ) = (l i, l 2i, l 3i ) Sample s (n) = SUB 4 (L s [n]), if s <= 3*height(n) SUB 2 (L s [n]), if s = 3*height(n) + 1 SUB 1 (L s [n]) = L s [n], if s >= 3*height(n) + 2
15 Analysis Number of elements at a node doubles L s+1 [n] <= 2 L s [v] + 4 Sample s (n) is a 4-cover for Sample s+1 (n) i.e., No more than 4 items of L s+1 [n] between two consecutive items of L s [n] For each stage s > height(n), L s [n] is a 4-cover for Sample s (left) and Sample s (right) For s >= 2, Merge. I.e., compute: Rank(Sample s (left), Sample s (right)) Rank(Sample s (right), Sample s (left)) Use Rank(L s :Sample s (left)) (similarly right)computed by: Rank(L s :Sample s-1 (left)) and Rank(Sample s-1 (left):sample s (left))
16 Parallel Quick-Sort Group of p processors sort a sub-sequence Initially all processors sort the entire sequence The sequence is divided into n/p blocks Together processors choose a pivot Processors rearrange elements into two halves Prefix sum The groups is subdivided into two and assigned to each half The size of each subgroup may be proportional to the size of the half If subgroup size = 1, stop subdividing and sort serially
17 Bucket Sort Decide buckets Parallel for element i: Put it in bucket b Keep incoherent cache of each bucket per processor Merge buckets Sort each bucket separately All buckets need not be equal Load imbalance Sample sort: Choose a sample of size s Sort the samples Choose B-1 evenly spaced element from the sorted list These elements (splitters) demarcate B buckets
18 Parallel Splitter Selection Divide n elements into B (equi-sized) blocks (Quick)Sort each block For each sorted block: Choose B-1 evenly spaced splitters Use the B*(B-1) elements as samples Sort the samples Choose B-1 Splitters No bucket contains more than 2*n/B elements
19 Radix Sort Bucket-sort by each key Sort stably For each key, find its rank Count number of keys < in the sequence Count number of keys = before it in the sequence Use parallel prefix sum Notbit=!bit psum= escan(bit) nzeros = psum[n]+ notbit[n] nbefore= idx psum+ nzeros Rank = bit? nbefore: psum
20 Blocked Radix-sort Consider b bits at a time as key Prefix-sum still required per-bit? Satish/Harris/Garland: Divide sequence into blocks, Divide key into nibbles Load each block into shared memory Sort by 4 iterations of single-bit stable sorts (How?) For each block, write its 16-entry digit histogram and the sorted block to global memory. Perform a prefix sum over the 16B histogram tables Copy elements of each block to their correct output position
Parallel Sorting. Sathish Vadhiyar
 Parallel Sorting Sathish Vadhiyar Parallel Sorting Problem The input sequence of size N is distributed across P processors The output is such that elements in each processor P i is sorted elements in P
Parallel Sorting Sathish Vadhiyar Parallel Sorting Problem The input sequence of size N is distributed across P processors The output is such that elements in each processor P i is sorted elements in P
Algorithms and Applications
 Algorithms and Applications 1 Areas done in textbook: Sorting Algorithms Numerical Algorithms Image Processing Searching and Optimization 2 Chapter 10 Sorting Algorithms - rearranging a list of numbers
Algorithms and Applications 1 Areas done in textbook: Sorting Algorithms Numerical Algorithms Image Processing Searching and Optimization 2 Chapter 10 Sorting Algorithms - rearranging a list of numbers
Sorting (Chapter 9) Alexandre David B2-206
 Sorting (Chapter 9) Alexandre David B2-206 Sorting Problem Arrange an unordered collection of elements into monotonically increasing (or decreasing) order. Let S = . Sort S into S =
Sorting (Chapter 9) Alexandre David B2-206 Sorting Problem Arrange an unordered collection of elements into monotonically increasing (or decreasing) order. Let S = . Sort S into S =
Sorting (Chapter 9) Alexandre David B2-206
 Sorting (Chapter 9) Alexandre David B2-206 1 Sorting Problem Arrange an unordered collection of elements into monotonically increasing (or decreasing) order. Let S = . Sort S into S =
Sorting (Chapter 9) Alexandre David B2-206 1 Sorting Problem Arrange an unordered collection of elements into monotonically increasing (or decreasing) order. Let S = . Sort S into S =
Lecture 8 Parallel Algorithms II
 Lecture 8 Parallel Algorithms II Dr. Wilson Rivera ICOM 6025: High Performance Computing Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of Puerto Rico Original slides from Introduction to Parallel
Lecture 8 Parallel Algorithms II Dr. Wilson Rivera ICOM 6025: High Performance Computing Electrical and Computer Engineering Department University of Puerto Rico Original slides from Introduction to Parallel
Sorting Algorithms. Ananth Grama, Anshul Gupta, George Karypis, and Vipin Kumar
 Sorting Algorithms Ananth Grama, Anshul Gupta, George Karypis, and Vipin Kumar To accompany the text ``Introduction to Parallel Computing'', Addison Wesley, 2003. Topic Overview Issues in Sorting on Parallel
Sorting Algorithms Ananth Grama, Anshul Gupta, George Karypis, and Vipin Kumar To accompany the text ``Introduction to Parallel Computing'', Addison Wesley, 2003. Topic Overview Issues in Sorting on Parallel
CSL 860: Modern Parallel
 CSL 860: Modern Parallel Computation PARALLEL ALGORITHM TECHNIQUES: BALANCED BINARY TREE Reduction n operands => log n steps Total work = O(n) How do you map? Balance Binary tree technique Reduction n
CSL 860: Modern Parallel Computation PARALLEL ALGORITHM TECHNIQUES: BALANCED BINARY TREE Reduction n operands => log n steps Total work = O(n) How do you map? Balance Binary tree technique Reduction n
Lecture 3: Sorting 1
 Lecture 3: Sorting 1 Sorting Arranging an unordered collection of elements into monotonically increasing (or decreasing) order. S = a sequence of n elements in arbitrary order After sorting:
Lecture 3: Sorting 1 Sorting Arranging an unordered collection of elements into monotonically increasing (or decreasing) order. S = a sequence of n elements in arbitrary order After sorting:
Parallel Sorting Algorithms
 CSC 391/691: GPU Programming Fall 015 Parallel Sorting Algorithms Copyright 015 Samuel S. Cho Sorting Algorithms Review Bubble Sort: O(n ) Insertion Sort: O(n ) Quick Sort: O(n log n) Heap Sort: O(n log
CSC 391/691: GPU Programming Fall 015 Parallel Sorting Algorithms Copyright 015 Samuel S. Cho Sorting Algorithms Review Bubble Sort: O(n ) Insertion Sort: O(n ) Quick Sort: O(n log n) Heap Sort: O(n log
Parallel Systems Course: Chapter VIII. Sorting Algorithms. Kumar Chapter 9. Jan Lemeire ETRO Dept. Fall Parallel Sorting
 Parallel Systems Course: Chapter VIII Sorting Algorithms Kumar Chapter 9 Jan Lemeire ETRO Dept. Fall 2017 Overview 1. Parallel sort distributed memory 2. Parallel sort shared memory 3. Sorting Networks
Parallel Systems Course: Chapter VIII Sorting Algorithms Kumar Chapter 9 Jan Lemeire ETRO Dept. Fall 2017 Overview 1. Parallel sort distributed memory 2. Parallel sort shared memory 3. Sorting Networks
CSC 447: Parallel Programming for Multi- Core and Cluster Systems
 CSC 447: Parallel Programming for Multi- Core and Cluster Systems Parallel Sorting Algorithms Instructor: Haidar M. Harmanani Spring 2016 Topic Overview Issues in Sorting on Parallel Computers Sorting
CSC 447: Parallel Programming for Multi- Core and Cluster Systems Parallel Sorting Algorithms Instructor: Haidar M. Harmanani Spring 2016 Topic Overview Issues in Sorting on Parallel Computers Sorting
CSC630/CSC730 Parallel & Distributed Computing
 CSC630/CSC730 Parallel & Distributed Computing Parallel Sorting Chapter 9 1 Contents General issues Sorting network Bitonic sort Bubble sort and its variants Odd-even transposition Quicksort Other Sorting
CSC630/CSC730 Parallel & Distributed Computing Parallel Sorting Chapter 9 1 Contents General issues Sorting network Bitonic sort Bubble sort and its variants Odd-even transposition Quicksort Other Sorting
Parallel Sorting Algorithms
 Parallel Sorting Algorithms Ricardo Rocha and Fernando Silva Computer Science Department Faculty of Sciences University of Porto Parallel Computing 2016/2017 (Slides based on the book Parallel Programming:
Parallel Sorting Algorithms Ricardo Rocha and Fernando Silva Computer Science Department Faculty of Sciences University of Porto Parallel Computing 2016/2017 (Slides based on the book Parallel Programming:
Parallel Systems Course: Chapter VIII. Sorting Algorithms. Kumar Chapter 9. Jan Lemeire ETRO Dept. November Parallel Sorting
 Parallel Systems Course: Chapter VIII Sorting Algorithms Kumar Chapter 9 Jan Lemeire ETRO Dept. November 2014 Overview 1. Parallel sort distributed memory 2. Parallel sort shared memory 3. Sorting Networks
Parallel Systems Course: Chapter VIII Sorting Algorithms Kumar Chapter 9 Jan Lemeire ETRO Dept. November 2014 Overview 1. Parallel sort distributed memory 2. Parallel sort shared memory 3. Sorting Networks
CSL 730: Parallel Programming
 CSL 73: Parallel Programming General Algorithmic Techniques Balance binary tree Partitioning Divid and conquer Fractional cascading Recursive doubling Symmetry breaking Pipelining 2 PARALLEL ALGORITHM
CSL 73: Parallel Programming General Algorithmic Techniques Balance binary tree Partitioning Divid and conquer Fractional cascading Recursive doubling Symmetry breaking Pipelining 2 PARALLEL ALGORITHM
Sorting Algorithms. Slides used during lecture of 8/11/2013 (D. Roose) Adapted from slides by
 Sorting Algorithms Slides used during lecture of 8/11/2013 (D. Roose) Adapted from slides by Ananth Grama, Anshul Gupta, George Karypis, and Vipin Kumar To accompany the text ``Introduction to Parallel
Sorting Algorithms Slides used during lecture of 8/11/2013 (D. Roose) Adapted from slides by Ananth Grama, Anshul Gupta, George Karypis, and Vipin Kumar To accompany the text ``Introduction to Parallel
John Mellor-Crummey Department of Computer Science Rice University
 Parallel Sorting John Mellor-Crummey Department of Computer Science Rice University johnmc@rice.edu COMP 422/534 Lecture 23 6 April 2017 Topics for Today Introduction Sorting networks and Batcher s bitonic
Parallel Sorting John Mellor-Crummey Department of Computer Science Rice University johnmc@rice.edu COMP 422/534 Lecture 23 6 April 2017 Topics for Today Introduction Sorting networks and Batcher s bitonic
Information Coding / Computer Graphics, ISY, LiTH
 Sorting on GPUs Revisiting some algorithms from lecture 6: Some not-so-good sorting approaches Bitonic sort QuickSort Concurrent kernels and recursion Adapt to parallel algorithms Many sorting algorithms
Sorting on GPUs Revisiting some algorithms from lecture 6: Some not-so-good sorting approaches Bitonic sort QuickSort Concurrent kernels and recursion Adapt to parallel algorithms Many sorting algorithms
Introduction to Parallel Computing
 Introduction to Parallel Computing George Karypis Sorting Outline Background Sorting Networks Quicksort Bucket-Sort & Sample-Sort Background Input Specification Each processor has n/p elements A ordering
Introduction to Parallel Computing George Karypis Sorting Outline Background Sorting Networks Quicksort Bucket-Sort & Sample-Sort Background Input Specification Each processor has n/p elements A ordering
(Sequen)al) Sor)ng. Bubble Sort, Inser)on Sort. Merge Sort, Heap Sort, QuickSort. Op)mal Parallel Time complexity. O ( n 2 )
 Parallel Sor)ng A jungle (Sequen)al) Sor)ng Bubble Sort, Inser)on Sort O ( n 2 ) Merge Sort, Heap Sort, QuickSort O ( n log n ) QuickSort best on average Op)mal Parallel Time complexity O ( n log n ) /
Parallel Sor)ng A jungle (Sequen)al) Sor)ng Bubble Sort, Inser)on Sort O ( n 2 ) Merge Sort, Heap Sort, QuickSort O ( n log n ) QuickSort best on average Op)mal Parallel Time complexity O ( n log n ) /
Sorting and Selection
 Sorting and Selection Introduction Divide and Conquer Merge-Sort Quick-Sort Radix-Sort Bucket-Sort 10-1 Introduction Assuming we have a sequence S storing a list of keyelement entries. The key of the element
Sorting and Selection Introduction Divide and Conquer Merge-Sort Quick-Sort Radix-Sort Bucket-Sort 10-1 Introduction Assuming we have a sequence S storing a list of keyelement entries. The key of the element
DIVIDE AND CONQUER ALGORITHMS ANALYSIS WITH RECURRENCE EQUATIONS
 CHAPTER 11 SORTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY M. AMATO AND
CHAPTER 11 SORTING ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM NANCY M. AMATO AND
Faster Sorting Methods
 Faster Sorting Methods Chapter 9 Contents Merge Sort Merging Arrays Recursive Merge Sort The Efficiency of Merge Sort Iterative Merge Sort Merge Sort in the Java Class Library Contents Quick Sort The Efficiency
Faster Sorting Methods Chapter 9 Contents Merge Sort Merging Arrays Recursive Merge Sort The Efficiency of Merge Sort Iterative Merge Sort Merge Sort in the Java Class Library Contents Quick Sort The Efficiency
CSC 273 Data Structures
 CSC 273 Data Structures Lecture 6 - Faster Sorting Methods Merge Sort Divides an array into halves Sorts the two halves, Then merges them into one sorted array. The algorithm for merge sort is usually
CSC 273 Data Structures Lecture 6 - Faster Sorting Methods Merge Sort Divides an array into halves Sorts the two halves, Then merges them into one sorted array. The algorithm for merge sort is usually
March 3, George Mason University Sorting Networks. Indranil Banerjee. Parallel Sorting: Hardware Level Parallelism
 Sorting George Mason University ibanerje@gmu.edu March 3, 2016 Sorting GMU March 3, 2016 1 / 19 There are mainly two approaches to sorting in parallel: 1 Non-oblivious: Comparisons are data dependent Example:
Sorting George Mason University ibanerje@gmu.edu March 3, 2016 Sorting GMU March 3, 2016 1 / 19 There are mainly two approaches to sorting in parallel: 1 Non-oblivious: Comparisons are data dependent Example:
Sorting Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved.
 1 19 Sorting 2 19.1 Introduction (Cont.) Sorting data Place data in order Typically ascending or descending Based on one or more sort keys Algorithms Insertion sort Selection sort Merge sort More efficient,
1 19 Sorting 2 19.1 Introduction (Cont.) Sorting data Place data in order Typically ascending or descending Based on one or more sort keys Algorithms Insertion sort Selection sort Merge sort More efficient,
Merge Sort
 Merge Sort 7 2 9 4 2 4 7 9 7 2 2 7 9 4 4 9 7 7 2 2 9 9 4 4 Divide-and-Conuer Divide-and conuer is a general algorithm design paradigm: n Divide: divide the input data S in two disjoint subsets S 1 and
Merge Sort 7 2 9 4 2 4 7 9 7 2 2 7 9 4 4 9 7 7 2 2 9 9 4 4 Divide-and-Conuer Divide-and conuer is a general algorithm design paradigm: n Divide: divide the input data S in two disjoint subsets S 1 and
Complexity and Advanced Algorithms Monsoon Parallel Algorithms Lecture 2
 Complexity and Advanced Algorithms Monsoon 2011 Parallel Algorithms Lecture 2 Trivia ISRO has a new supercomputer rated at 220 Tflops Can be extended to Pflops. Consumes only 150 KW of power. LINPACK is
Complexity and Advanced Algorithms Monsoon 2011 Parallel Algorithms Lecture 2 Trivia ISRO has a new supercomputer rated at 220 Tflops Can be extended to Pflops. Consumes only 150 KW of power. LINPACK is
Sorting Algorithms. - rearranging a list of numbers into increasing (or decreasing) order. Potential Speedup
 Sorting Algorithms - rearranging a list of numbers into increasing (or decreasing) order. Potential Speedup The worst-case time complexity of mergesort and the average time complexity of quicksort are
Sorting Algorithms - rearranging a list of numbers into increasing (or decreasing) order. Potential Speedup The worst-case time complexity of mergesort and the average time complexity of quicksort are
We can use a max-heap to sort data.
 Sorting 7B N log N Sorts 1 Heap Sort We can use a max-heap to sort data. Convert an array to a max-heap. Remove the root from the heap and store it in its proper position in the same array. Repeat until
Sorting 7B N log N Sorts 1 Heap Sort We can use a max-heap to sort data. Convert an array to a max-heap. Remove the root from the heap and store it in its proper position in the same array. Repeat until
Unit 6 Chapter 15 EXAMPLES OF COMPLEXITY CALCULATION
 DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS Unit 6 Chapter 15 EXAMPLES OF COMPLEXITY CALCULATION http://milanvachhani.blogspot.in EXAMPLES FROM THE SORTING WORLD Sorting provides a good set of examples for analyzing
DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF ALGORITHMS Unit 6 Chapter 15 EXAMPLES OF COMPLEXITY CALCULATION http://milanvachhani.blogspot.in EXAMPLES FROM THE SORTING WORLD Sorting provides a good set of examples for analyzing
Sorting on CUDA. Providence College. Ayushi Sinha Providence College
 Providence College DigitalCommons@Providence Annual Celebration of Student Scholarship and Creativity Spring 2011 Sorting on CUDA Ayushi Sinha Providence College Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.providence.edu/student_scholarship
Providence College DigitalCommons@Providence Annual Celebration of Student Scholarship and Creativity Spring 2011 Sorting on CUDA Ayushi Sinha Providence College Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.providence.edu/student_scholarship
Scan Algorithm Effects on Parallelism and Memory Conflicts
 Scan Algorithm Effects on Parallelism and Memory Conflicts 11 Parallel Prefix Sum (Scan) Definition: The all-prefix-sums operation takes a binary associative operator with identity I, and an array of n
Scan Algorithm Effects on Parallelism and Memory Conflicts 11 Parallel Prefix Sum (Scan) Definition: The all-prefix-sums operation takes a binary associative operator with identity I, and an array of n
MCMD L20 : GPU Sorting GPU. Parallel processor - Many cores - Small memory. memory transfer overhead
 MCMD L20 : GPU Sorting GPU Parallel processor - Many cores - Small memory memory transfer overhead ------------------------- Sorting: Input: Large array A = Output B = -
MCMD L20 : GPU Sorting GPU Parallel processor - Many cores - Small memory memory transfer overhead ------------------------- Sorting: Input: Large array A = Output B = -
Sorting Goodrich, Tamassia Sorting 1
 Sorting Put array A of n numbers in increasing order. A core algorithm with many applications. Simple algorithms are O(n 2 ). Optimal algorithms are O(n log n). We will see O(n) for restricted input in
Sorting Put array A of n numbers in increasing order. A core algorithm with many applications. Simple algorithms are O(n 2 ). Optimal algorithms are O(n log n). We will see O(n) for restricted input in
Sorting and Searching. Tim Purcell NVIDIA
 Sorting and Searching Tim Purcell NVIDIA Topics Sorting Sorting networks Search Binary search Nearest neighbor search Assumptions Data organized into D arrays Rendering pass == screen aligned quad Not
Sorting and Searching Tim Purcell NVIDIA Topics Sorting Sorting networks Search Binary search Nearest neighbor search Assumptions Data organized into D arrays Rendering pass == screen aligned quad Not
CS61BL. Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting
 CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
CS61BL Lecture 5: Graphs Sorting Graphs Graphs Edge Vertex Graphs (Undirected) Graphs (Directed) Graphs (Multigraph) Graphs (Acyclic) Graphs (Cyclic) Graphs (Connected) Graphs (Disconnected) Graphs (Unweighted)
CS61B Fall 2015 Guerrilla Section 3 Worksheet. 8 November 2015
 Fall 2015 8 November 2015 Directions: In groups of 4-5, work on the following exercises. Do not proceed to the next exercise until everyone in your group has the answer and understands why the answer is
Fall 2015 8 November 2015 Directions: In groups of 4-5, work on the following exercises. Do not proceed to the next exercise until everyone in your group has the answer and understands why the answer is
CS475 Parallel Programming
 CS475 Parallel Programming Sorting Wim Bohm, Colorado State University Except as otherwise noted, the content of this presentation is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 license. Sorting
CS475 Parallel Programming Sorting Wim Bohm, Colorado State University Except as otherwise noted, the content of this presentation is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 2.5 license. Sorting
COMP 352 FALL Tutorial 10
 1 COMP 352 FALL 2016 Tutorial 10 SESSION OUTLINE Divide-and-Conquer Method Sort Algorithm Properties Quick Overview on Sorting Algorithms Merge Sort Quick Sort Bucket Sort Radix Sort Problem Solving 2
1 COMP 352 FALL 2016 Tutorial 10 SESSION OUTLINE Divide-and-Conquer Method Sort Algorithm Properties Quick Overview on Sorting Algorithms Merge Sort Quick Sort Bucket Sort Radix Sort Problem Solving 2
1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1
![1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1](/thumbs/85/92778785.jpg) Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 2. O(n) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = T(n/2) + n, T(1)
Asymptotics, Recurrence and Basic Algorithms 1. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = 2T(n-1) + 1, T(1) = 1 2. O(n) 2. [1 pt] What is the solution to the recurrence T(n) = T(n/2) + n, T(1)
Data-Parallel Algorithms on GPUs. Mark Harris NVIDIA Developer Technology
 Data-Parallel Algorithms on GPUs Mark Harris NVIDIA Developer Technology Outline Introduction Algorithmic complexity on GPUs Algorithmic Building Blocks Gather & Scatter Reductions Scan (parallel prefix)
Data-Parallel Algorithms on GPUs Mark Harris NVIDIA Developer Technology Outline Introduction Algorithmic complexity on GPUs Algorithmic Building Blocks Gather & Scatter Reductions Scan (parallel prefix)
Hiroki Yasuga, Elisabeth Kolp, Andreas Lang. 25th September 2014, Scientific Programming
 Hiroki Yasuga, Elisabeth Kolp, Andreas Lang 25th September 2014, Scientific Programming What is sorting and complexity? Big O notation Sorting algorithms: Merge sort Quick sort Comparison: Merge sort &
Hiroki Yasuga, Elisabeth Kolp, Andreas Lang 25th September 2014, Scientific Programming What is sorting and complexity? Big O notation Sorting algorithms: Merge sort Quick sort Comparison: Merge sort &
Array Packing Implementation A Parallel approach. By, Abhishek Cumbakonam Desikan Rajesh Balasubramanian Ramalingam Sankaran Aswin Gokulachandran
 Array Packing Implementation A Parallel approach By, Abhishek Cumbakonam Desikan Rajesh Balasubramanian Ramalingam Sankaran Aswin Gokulachandran The Problem Given an array X, having some labelled items.
Array Packing Implementation A Parallel approach By, Abhishek Cumbakonam Desikan Rajesh Balasubramanian Ramalingam Sankaran Aswin Gokulachandran The Problem Given an array X, having some labelled items.
II (Sorting and) Order Statistics
 II (Sorting and) Order Statistics Heapsort Quicksort Sorting in Linear Time Medians and Order Statistics 8 Sorting in Linear Time The sorting algorithms introduced thus far are comparison sorts Any comparison
II (Sorting and) Order Statistics Heapsort Quicksort Sorting in Linear Time Medians and Order Statistics 8 Sorting in Linear Time The sorting algorithms introduced thus far are comparison sorts Any comparison
CS2223: Algorithms Sorting Algorithms, Heap Sort, Linear-time sort, Median and Order Statistics
 CS2223: Algorithms Sorting Algorithms, Heap Sort, Linear-time sort, Median and Order Statistics 1 Sorting 1.1 Problem Statement You are given a sequence of n numbers < a 1, a 2,..., a n >. You need to
CS2223: Algorithms Sorting Algorithms, Heap Sort, Linear-time sort, Median and Order Statistics 1 Sorting 1.1 Problem Statement You are given a sequence of n numbers < a 1, a 2,..., a n >. You need to
SORTING, SETS, AND SELECTION
 CHAPTER 11 SORTING, SETS, AND SELECTION ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM
CHAPTER 11 SORTING, SETS, AND SELECTION ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN C++, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND MOUNT (WILEY 2004) AND SLIDES FROM
Lesson 1 4. Prefix Sum Definitions. Scans. Parallel Scans. A Naive Parallel Scans
 Lesson 1 4 Prefix Sum Definitions Prefix sum given an array...the prefix sum is the sum of all the elements in the array from the beginning to the position, including the value at the position. The sequential
Lesson 1 4 Prefix Sum Definitions Prefix sum given an array...the prefix sum is the sum of all the elements in the array from the beginning to the position, including the value at the position. The sequential
Question 7.11 Show how heapsort processes the input:
 Question 7.11 Show how heapsort processes the input: 142, 543, 123, 65, 453, 879, 572, 434, 111, 242, 811, 102. Solution. Step 1 Build the heap. 1.1 Place all the data into a complete binary tree in the
Question 7.11 Show how heapsort processes the input: 142, 543, 123, 65, 453, 879, 572, 434, 111, 242, 811, 102. Solution. Step 1 Build the heap. 1.1 Place all the data into a complete binary tree in the
SORTING AND SELECTION
 2 < > 1 4 8 6 = 9 CHAPTER 12 SORTING AND SELECTION ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 2016)
2 < > 1 4 8 6 = 9 CHAPTER 12 SORTING AND SELECTION ACKNOWLEDGEMENT: THESE SLIDES ARE ADAPTED FROM SLIDES PROVIDED WITH DATA STRUCTURES AND ALGORITHMS IN JAVA, GOODRICH, TAMASSIA AND GOLDWASSER (WILEY 2016)
Quick-Sort fi fi fi 7 9. Quick-Sort Goodrich, Tamassia
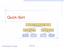 Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 fi 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 fi 2 4 7 9 fi 7 9 2 fi 2 9 fi 9 Quick-Sort 1 Quick-Sort ( 10.2 text book) Quick-sort is a randomized sorting algorithm based on the divide-and-conquer paradigm: x
Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 fi 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 fi 2 4 7 9 fi 7 9 2 fi 2 9 fi 9 Quick-Sort 1 Quick-Sort ( 10.2 text book) Quick-sort is a randomized sorting algorithm based on the divide-and-conquer paradigm: x
/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Sorting lower bound and Linear-time sorting Date: 9/19/17
 601.433/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Sorting lower bound and Linear-time sorting Date: 9/19/17 5.1 Introduction You should all know a few ways of sorting in O(n log n)
601.433/633 Introduction to Algorithms Lecturer: Michael Dinitz Topic: Sorting lower bound and Linear-time sorting Date: 9/19/17 5.1 Introduction You should all know a few ways of sorting in O(n log n)
Sorting. Riley Porter. CSE373: Data Structures & Algorithms 1
 Sorting Riley Porter 1 Introduction to Sorting Why study sorting? Good algorithm practice! Different sorting algorithms have different trade-offs No single best sort for all scenarios Knowing one way to
Sorting Riley Porter 1 Introduction to Sorting Why study sorting? Good algorithm practice! Different sorting algorithms have different trade-offs No single best sort for all scenarios Knowing one way to
CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 9. Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico
 CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 9 Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico 09-21-2010 1 Today Orderings Searching Sorting Priority Queues & Heaps 2 Order Relation We say a binary relation R is an
CS 361 Data Structures & Algs Lecture 9 Prof. Tom Hayes University of New Mexico 09-21-2010 1 Today Orderings Searching Sorting Priority Queues & Heaps 2 Order Relation We say a binary relation R is an
Chapter 10. Sorting and Searching Algorithms. Fall 2017 CISC2200 Yanjun Li 1. Sorting. Given a set (container) of n elements
 Chapter Sorting and Searching Algorithms Fall 2017 CISC2200 Yanjun Li 1 Sorting Given a set (container) of n elements Eg array, set of words, etc Suppose there is an order relation that can be set across
Chapter Sorting and Searching Algorithms Fall 2017 CISC2200 Yanjun Li 1 Sorting Given a set (container) of n elements Eg array, set of words, etc Suppose there is an order relation that can be set across
Lecture 19 Sorting Goodrich, Tamassia
 Lecture 19 Sorting 7 2 9 4 2 4 7 9 7 2 2 7 9 4 4 9 7 7 2 2 9 9 4 4 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia Outline Review 3 simple sorting algorithms: 1. selection Sort (in previous course) 2. insertion Sort (in previous
Lecture 19 Sorting 7 2 9 4 2 4 7 9 7 2 2 7 9 4 4 9 7 7 2 2 9 9 4 4 2004 Goodrich, Tamassia Outline Review 3 simple sorting algorithms: 1. selection Sort (in previous course) 2. insertion Sort (in previous
Multiple-choice (35 pt.)
 CS 161 Practice Midterm I Summer 2018 Released: 7/21/18 Multiple-choice (35 pt.) 1. (2 pt.) Which of the following asymptotic bounds describe the function f(n) = n 3? The bounds do not necessarily need
CS 161 Practice Midterm I Summer 2018 Released: 7/21/18 Multiple-choice (35 pt.) 1. (2 pt.) Which of the following asymptotic bounds describe the function f(n) = n 3? The bounds do not necessarily need
Parallel Algorithms for (PRAM) Computers & Some Parallel Algorithms. Reference : Horowitz, Sahni and Rajasekaran, Computer Algorithms
 Parallel Algorithms for (PRAM) Computers & Some Parallel Algorithms Reference : Horowitz, Sahni and Rajasekaran, Computer Algorithms Part 2 1 3 Maximum Selection Problem : Given n numbers, x 1, x 2,, x
Parallel Algorithms for (PRAM) Computers & Some Parallel Algorithms Reference : Horowitz, Sahni and Rajasekaran, Computer Algorithms Part 2 1 3 Maximum Selection Problem : Given n numbers, x 1, x 2,, x
High Performance Computing Programming Paradigms and Scalability Part 6: Examples of Parallel Algorithms
 High Performance Computing Programming Paradigms and Scalability Part 6: Examples of Parallel Algorithms PD Dr. rer. nat. habil. Ralf-Peter Mundani Computation in Engineering (CiE) Scientific Computing
High Performance Computing Programming Paradigms and Scalability Part 6: Examples of Parallel Algorithms PD Dr. rer. nat. habil. Ralf-Peter Mundani Computation in Engineering (CiE) Scientific Computing
Quick-Sort. Quick-Sort 1
 Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 Quick-Sort 1 Outline and Reading Quick-sort ( 4.3) Algorithm Partition step Quick-sort tree Execution example Analysis of quick-sort (4.3.1) In-place
Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 Quick-Sort 1 Outline and Reading Quick-sort ( 4.3) Algorithm Partition step Quick-sort tree Execution example Analysis of quick-sort (4.3.1) In-place
Chapter 4: Sorting. Spring 2014 Sorting Fun 1
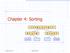 Chapter 4: Sorting 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 Spring 2014 Sorting Fun 1 What We ll Do! Quick Sort! Lower bound on runtimes for comparison based sort! Radix and Bucket sort Spring 2014
Chapter 4: Sorting 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 Spring 2014 Sorting Fun 1 What We ll Do! Quick Sort! Lower bound on runtimes for comparison based sort! Radix and Bucket sort Spring 2014
Exercise 1 : B-Trees [ =17pts]
![Exercise 1 : B-Trees [ =17pts] Exercise 1 : B-Trees [ =17pts]](/thumbs/77/75867713.jpg) CS - Fall 003 Assignment Due : Thu November 7 (written part), Tue Dec 0 (programming part) Exercise : B-Trees [+++3+=7pts] 3 0 3 3 3 0 Figure : B-Tree. Consider the B-Tree of figure.. What are the values
CS - Fall 003 Assignment Due : Thu November 7 (written part), Tue Dec 0 (programming part) Exercise : B-Trees [+++3+=7pts] 3 0 3 3 3 0 Figure : B-Tree. Consider the B-Tree of figure.. What are the values
Selection, Bubble, Insertion, Merge, Heap, Quick Bucket, Radix
 Spring 2010 Review Topics Big O Notation Heaps Sorting Selection, Bubble, Insertion, Merge, Heap, Quick Bucket, Radix Hashtables Tree Balancing: AVL trees and DSW algorithm Graphs: Basic terminology and
Spring 2010 Review Topics Big O Notation Heaps Sorting Selection, Bubble, Insertion, Merge, Heap, Quick Bucket, Radix Hashtables Tree Balancing: AVL trees and DSW algorithm Graphs: Basic terminology and
Algorithm Efficiency & Sorting. Algorithm efficiency Big-O notation Searching algorithms Sorting algorithms
 Algorithm Efficiency & Sorting Algorithm efficiency Big-O notation Searching algorithms Sorting algorithms Overview Writing programs to solve problem consists of a large number of decisions how to represent
Algorithm Efficiency & Sorting Algorithm efficiency Big-O notation Searching algorithms Sorting algorithms Overview Writing programs to solve problem consists of a large number of decisions how to represent
Searching, Sorting. part 1
 Searching, Sorting part 1 Week 3 Objectives Searching: binary search Comparison-based search: running time bound Sorting: bubble, selection, insertion, merge Sorting: Heapsort Comparison-based sorting
Searching, Sorting part 1 Week 3 Objectives Searching: binary search Comparison-based search: running time bound Sorting: bubble, selection, insertion, merge Sorting: Heapsort Comparison-based sorting
DIVIDE & CONQUER. Problem of size n. Solution to sub problem 1
 DIVIDE & CONQUER Definition: Divide & conquer is a general algorithm design strategy with a general plan as follows: 1. DIVIDE: A problem s instance is divided into several smaller instances of the same
DIVIDE & CONQUER Definition: Divide & conquer is a general algorithm design strategy with a general plan as follows: 1. DIVIDE: A problem s instance is divided into several smaller instances of the same
COMP Data Structures
 COMP 2140 - Data Structures Shahin Kamali Topic 5 - Sorting University of Manitoba Based on notes by S. Durocher. COMP 2140 - Data Structures 1 / 55 Overview Review: Insertion Sort Merge Sort Quicksort
COMP 2140 - Data Structures Shahin Kamali Topic 5 - Sorting University of Manitoba Based on notes by S. Durocher. COMP 2140 - Data Structures 1 / 55 Overview Review: Insertion Sort Merge Sort Quicksort
EE382N (20): Computer Architecture - Parallelism and Locality Spring 2015 Lecture 13 Parallelism in Software I
 EE382N (20): Computer Architecture - Parallelism and Locality Spring 2015 Lecture 13 Parallelism in Software I Mattan Erez The University of Texas at Austin N EE382N: Parallelilsm and Locality, Spring
EE382N (20): Computer Architecture - Parallelism and Locality Spring 2015 Lecture 13 Parallelism in Software I Mattan Erez The University of Texas at Austin N EE382N: Parallelilsm and Locality, Spring
Algorithms and Data Structures. Marcin Sydow. Introduction. QuickSort. Sorting 2. Partition. Limit. CountSort. RadixSort. Summary
 Sorting 2 Topics covered by this lecture: Stability of Sorting Quick Sort Is it possible to sort faster than with Θ(n log(n)) complexity? Countsort Stability A sorting algorithm is stable if it preserves
Sorting 2 Topics covered by this lecture: Stability of Sorting Quick Sort Is it possible to sort faster than with Θ(n log(n)) complexity? Countsort Stability A sorting algorithm is stable if it preserves
Example of usage of Prefix Sum Compacting an Array. Example of usage of Prexix Sum Compacting an Array
 Example of usage of Prefix um A 0 0 0 e 1 0 0 0 0 0 B e 1 Example of usage of Prexix um A 0 0 0 e 1 0 0 0 0 0 B e 1 Initialize B with zeroes Any idea on the solution (first in sequential)? If A[i]!= 0
Example of usage of Prefix um A 0 0 0 e 1 0 0 0 0 0 B e 1 Example of usage of Prexix um A 0 0 0 e 1 0 0 0 0 0 B e 1 Initialize B with zeroes Any idea on the solution (first in sequential)? If A[i]!= 0
Copyright 2012 by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 ***This chapter is a bonus Web chapter CHAPTER 17 Sorting Objectives To study and analyze time efficiency of various sorting algorithms ( 17.2 17.7). To design, implement, and analyze bubble sort ( 17.2).
***This chapter is a bonus Web chapter CHAPTER 17 Sorting Objectives To study and analyze time efficiency of various sorting algorithms ( 17.2 17.7). To design, implement, and analyze bubble sort ( 17.2).
Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, Merge Sort & Quick Sort
 Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Merge Sort & Quick Sort 1 Divide-and-Conquer Divide-and conquer is a general algorithm
Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Merge Sort & Quick Sort 1 Divide-and-Conquer Divide-and conquer is a general algorithm
CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II. Binary Search Trees
 CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees Symbol table applications BST definitions and terminologies Search and insert Traversal Ordered operations Delete Symbol
CS 171: Introduction to Computer Science II Binary Search Trees Binary Search Trees Symbol table applications BST definitions and terminologies Search and insert Traversal Ordered operations Delete Symbol
Problem. Input: An array A = (A[1],..., A[n]) with length n. Output: a permutation A of A, that is sorted: A [i] A [j] for all. 1 i j n.
![Problem. Input: An array A = (A[1],..., A[n]) with length n. Output: a permutation A of A, that is sorted: A [i] A [j] for all. 1 i j n. Problem. Input: An array A = (A[1],..., A[n]) with length n. Output: a permutation A of A, that is sorted: A [i] A [j] for all. 1 i j n.](/thumbs/84/89326706.jpg) Problem 5. Sorting Simple Sorting, Quicksort, Mergesort Input: An array A = (A[1],..., A[n]) with length n. Output: a permutation A of A, that is sorted: A [i] A [j] for all 1 i j n. 98 99 Selection Sort
Problem 5. Sorting Simple Sorting, Quicksort, Mergesort Input: An array A = (A[1],..., A[n]) with length n. Output: a permutation A of A, that is sorted: A [i] A [j] for all 1 i j n. 98 99 Selection Sort
Divide and Conquer CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang
 Divide and Conquer CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook by Dr. Y.
Divide and Conquer CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook by Dr. Y.
Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015
 Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 2015 Goodrich and Tamassia
Presentation for use with the textbook, Algorithm Design and Applications, by M. T. Goodrich and R. Tamassia, Wiley, 2015 Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 2 4 7 9 7 9 2 2 9 9 2015 Goodrich and Tamassia
08 A: Sorting III. CS1102S: Data Structures and Algorithms. Martin Henz. March 10, Generated on Tuesday 9 th March, 2010, 09:58
 08 A: Sorting III CS1102S: Data Structures and Algorithms Martin Henz March 10, 2010 Generated on Tuesday 9 th March, 2010, 09:58 CS1102S: Data Structures and Algorithms 08 A: Sorting III 1 1 Recap: Sorting
08 A: Sorting III CS1102S: Data Structures and Algorithms Martin Henz March 10, 2010 Generated on Tuesday 9 th March, 2010, 09:58 CS1102S: Data Structures and Algorithms 08 A: Sorting III 1 1 Recap: Sorting
Divide and Conquer CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Acknowledgement. Outline
 Divide and Conquer CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook by Dr. Y.
Divide and Conquer CISC4080, Computer Algorithms CIS, Fordham Univ. Instructor: X. Zhang Acknowledgement The set of slides have use materials from the following resources Slides for textbook by Dr. Y.
CSL 730: Parallel Programming. Algorithms
 CSL 73: Parallel Programming Algorithms First 1 problem Input: n-bit vector Output: minimum index of a 1-bit First 1 problem Input: n-bit vector Output: minimum index of a 1-bit Algorithm: Divide into
CSL 73: Parallel Programming Algorithms First 1 problem Input: n-bit vector Output: minimum index of a 1-bit First 1 problem Input: n-bit vector Output: minimum index of a 1-bit Algorithm: Divide into
CSE 530A. B+ Trees. Washington University Fall 2013
 CSE 530A B+ Trees Washington University Fall 2013 B Trees A B tree is an ordered (non-binary) tree where the internal nodes can have a varying number of child nodes (within some range) B Trees When a key
CSE 530A B+ Trees Washington University Fall 2013 B Trees A B tree is an ordered (non-binary) tree where the internal nodes can have a varying number of child nodes (within some range) B Trees When a key
Spring 2018 Mentoring 13: April 25, New World Order. return a list of all the words that start with a given prefix.
 CSM 61B Final Review Spring 2018 Mentoring 13: April 25, 2017 1 New World Order 1.1 Draw the trie that results from inserting "hi", "hello", and "hey". h e i l y l o 1.2 Given a list of words (possibly
CSM 61B Final Review Spring 2018 Mentoring 13: April 25, 2017 1 New World Order 1.1 Draw the trie that results from inserting "hi", "hello", and "hey". h e i l y l o 1.2 Given a list of words (possibly
Lower Bound on Comparison-based Sorting
 Lower Bound on Comparison-based Sorting Different sorting algorithms may have different time complexity, how to know whether the running time of an algorithm is best possible? We know of several sorting
Lower Bound on Comparison-based Sorting Different sorting algorithms may have different time complexity, how to know whether the running time of an algorithm is best possible? We know of several sorting
In-place Super Scalar. Tim Kralj. Samplesort
 In-place Super Scalar Tim Kralj Samplesort Outline Quicksort Super Scalar Samplesort In-place Super Scalar Samplesort (IPS 4 o) Analysis Results Further work/questions Quicksort Finds pivots in the array
In-place Super Scalar Tim Kralj Samplesort Outline Quicksort Super Scalar Samplesort In-place Super Scalar Samplesort (IPS 4 o) Analysis Results Further work/questions Quicksort Finds pivots in the array
Outline and Reading. Quick-Sort. Partition. Quick-Sort. Quick-Sort Tree. Execution Example
 Outline and Reading Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 fi 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 fi 2 4 7 9 fi 7 9 2 fi 2 Quick-sort ( 0.3) Algorithm Partition step Quick-sort tree Eecution eample Analysis of quick-sort In-place quick-sort
Outline and Reading Quick-Sort 7 4 9 6 2 fi 2 4 6 7 9 4 2 fi 2 4 7 9 fi 7 9 2 fi 2 Quick-sort ( 0.3) Algorithm Partition step Quick-sort tree Eecution eample Analysis of quick-sort In-place quick-sort
Algorithms for Memory Hierarchies Lecture 2
 Algorithms for emory Hierarchies Lecture Lecturer: odari Sitchianva Scribes: Robin Rehrmann, ichael Kirsten Last Time External memory (E) model Scan(): O( ) I/Os Stacks / queues: O( 1 ) I/Os / elt ergesort:
Algorithms for emory Hierarchies Lecture Lecturer: odari Sitchianva Scribes: Robin Rehrmann, ichael Kirsten Last Time External memory (E) model Scan(): O( ) I/Os Stacks / queues: O( 1 ) I/Os / elt ergesort:
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees
 Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Binary Trees, Binary Search Trees Trees Linear access time of linked lists is prohibitive Does there exist any simple data structure for which the running time of most operations (search, insert, delete)
Data Structures and Algorithms " Sorting!
 Data Structures and Algorithms " Sorting! Outline" Merge Sort! Quick Sort! Sorting Lower Bound! Bucket-Sort! Radix Sort! Phạm Bảo Sơn DSA 2 Merge Sort" 7 2 9 4 2 4 7 9 7 2 2 7 9 4 4 9 7 7 2 2 9 9 4 4 Divide-and-Conquer
Data Structures and Algorithms " Sorting! Outline" Merge Sort! Quick Sort! Sorting Lower Bound! Bucket-Sort! Radix Sort! Phạm Bảo Sơn DSA 2 Merge Sort" 7 2 9 4 2 4 7 9 7 2 2 7 9 4 4 9 7 7 2 2 9 9 4 4 Divide-and-Conquer
Algorithms, Spring 2014, CSE, OSU Lecture 2: Sorting
 6331 - Algorithms, Spring 2014, CSE, OSU Lecture 2: Sorting Instructor: Anastasios Sidiropoulos January 10, 2014 Sorting Given an array of integers A[1... n], rearrange its elements so that A[1] A[2]...
6331 - Algorithms, Spring 2014, CSE, OSU Lecture 2: Sorting Instructor: Anastasios Sidiropoulos January 10, 2014 Sorting Given an array of integers A[1... n], rearrange its elements so that A[1] A[2]...
Lecture Notes for Advanced Algorithms
 Lecture Notes for Advanced Algorithms Prof. Bernard Moret September 29, 2011 Notes prepared by Blanc, Eberle, and Jonnalagedda. 1 Average Case Analysis 1.1 Reminders on quicksort and tree sort We start
Lecture Notes for Advanced Algorithms Prof. Bernard Moret September 29, 2011 Notes prepared by Blanc, Eberle, and Jonnalagedda. 1 Average Case Analysis 1.1 Reminders on quicksort and tree sort We start
More PRAM Algorithms. Techniques Covered
 More PRAM Algorithms Arvind Krishnamurthy Fall 24 Analysis technique: Brent s scheduling lemma Techniques Covered Parallel algorithm is simply characterized by W(n) and S(n) Parallel techniques: Scans
More PRAM Algorithms Arvind Krishnamurthy Fall 24 Analysis technique: Brent s scheduling lemma Techniques Covered Parallel algorithm is simply characterized by W(n) and S(n) Parallel techniques: Scans
Data Structures and Algorithms
 Data Structures and Algorithms Session 24. Earth Day, 2009 Instructor: Bert Huang http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~bert/courses/3137 Announcements Homework 6 due before last class: May 4th Final Review May
Data Structures and Algorithms Session 24. Earth Day, 2009 Instructor: Bert Huang http://www.cs.columbia.edu/~bert/courses/3137 Announcements Homework 6 due before last class: May 4th Final Review May
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 8 TH COMPARISON SORTS
 CSE 373 NOVEMBER 8 TH COMPARISON SORTS ASSORTED MINUTIAE Bug in Project 3 files--reuploaded at midnight on Monday Project 2 scores Canvas groups is garbage updated tonight Extra credit P1 done and feedback
CSE 373 NOVEMBER 8 TH COMPARISON SORTS ASSORTED MINUTIAE Bug in Project 3 files--reuploaded at midnight on Monday Project 2 scores Canvas groups is garbage updated tonight Extra credit P1 done and feedback
Sorting Algorithms Spring 2019 Mentoring 10: 18 April, Asymptotics Potpourri
 CSM 61B Sorting Algorithms Spring 2019 Mentoring 10: 18 April, 2018 1 Asymptotics Potpourri Stability is a property of some sorting algorithms. Stability essentially means that if we have two elements
CSM 61B Sorting Algorithms Spring 2019 Mentoring 10: 18 April, 2018 1 Asymptotics Potpourri Stability is a property of some sorting algorithms. Stability essentially means that if we have two elements
Total Points: 60. Duration: 1hr
 CS800 : Algorithms Fall 201 Nov 22, 201 Quiz 2 Practice Total Points: 0. Duration: 1hr 1. (,10) points Binary Heap. (a) The following is a sequence of elements presented to you (in order from left to right):
CS800 : Algorithms Fall 201 Nov 22, 201 Quiz 2 Practice Total Points: 0. Duration: 1hr 1. (,10) points Binary Heap. (a) The following is a sequence of elements presented to you (in order from left to right):
Real-world sorting (not on exam)
 Real-world sorting (not on exam) Sorting algorithms so far Insertion sort Worst case Average case Best case O(n 2 ) O(n 2 ) O(n) Quicksort O(n 2 ) O(n log n) O(n log n) Mergesort O(n log n) O(n log n)
Real-world sorting (not on exam) Sorting algorithms so far Insertion sort Worst case Average case Best case O(n 2 ) O(n 2 ) O(n) Quicksort O(n 2 ) O(n log n) O(n log n) Mergesort O(n log n) O(n log n)
With regards to bitonic sorts, everything boils down to doing bitonic sorts efficiently.
 Lesson 2 5 Distributed Memory Sorting Bitonic Sort The pseudo code for generating a bitonic sequence: 1. create two bitonic subsequences 2. Make one an increasing sequence 3. Make one into a decreasing
Lesson 2 5 Distributed Memory Sorting Bitonic Sort The pseudo code for generating a bitonic sequence: 1. create two bitonic subsequences 2. Make one an increasing sequence 3. Make one into a decreasing
Binary Search Trees. EECS 214, Fall 2018
 Binary Search Trees EECS 214, Fall 2018 2 A data structure for dictionaries There are several data structures that we can use to represent dictionaries: A list of keys-value pairs A hash table An array
Binary Search Trees EECS 214, Fall 2018 2 A data structure for dictionaries There are several data structures that we can use to represent dictionaries: A list of keys-value pairs A hash table An array
Sorting Algorithms. + Analysis of the Sorting Algorithms
 Sorting Algorithms + Analysis of the Sorting Algorithms Insertion Sort What if first k elements of array are already sorted? 4, 7, 12, 5, 19, 16 We can shift the tail of the sorted elements list down and
Sorting Algorithms + Analysis of the Sorting Algorithms Insertion Sort What if first k elements of array are already sorted? 4, 7, 12, 5, 19, 16 We can shift the tail of the sorted elements list down and
Key question: how do we pick a good pivot (and what makes a good pivot in the first place)?
 More on sorting Mergesort (v2) Quicksort Mergesort in place in action 53 2 44 85 11 67 7 39 14 53 87 11 50 67 2 14 44 53 80 85 87 14 87 80 50 29 72 95 2 44 80 85 7 29 39 72 95 Boxes with same color are
More on sorting Mergesort (v2) Quicksort Mergesort in place in action 53 2 44 85 11 67 7 39 14 53 87 11 50 67 2 14 44 53 80 85 87 14 87 80 50 29 72 95 2 44 80 85 7 29 39 72 95 Boxes with same color are
Hash Tables. CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides. Wednesday, April 22, Glenn G. Chappell
 Hash Tables CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Wednesday, April 22, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005
Hash Tables CS 311 Data Structures and Algorithms Lecture Slides Wednesday, April 22, 2009 Glenn G. Chappell Department of Computer Science University of Alaska Fairbanks CHAPPELLG@member.ams.org 2005
