Random Testing in 321
|
|
|
- Miranda Barnett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Random Testing in 321 1
2 Test Cases So Far Each test relates a particular input to a particular output. (test (bound-ids (with 'x (id 'y) (id 'x))) '(x)) (test (binding-ids (with 'x (id 'y) (id 'x))) '(x)) 2
3 Property-based Testing But we can only write so many tests by hand. To find additional bugs, we can automate testing. We start with what we hope is a fact about our program. For example, If bound-ids says 'x is bound, then binding-ids says 'x is binding. 3
4 Property Violation If we can find some WAE for which the property doesn t hold... (define a-wae...) (bound-ids a-wae) ; '(x) (binding-ids a-wae) ; '()... we ve found a bug. 4
5 Property Testing We can test this property in the usual style. ; bound=>binding? : WAE -> boolean ; checks if bound ids are also binding (define (bound=>binding? e)...) (test (bound=>binding? (id 'x)) true) (test (bound=>binding? (with 'x (num 0) (id 'x))) true) Expected result is always true, so if we had lots of WAEs, then we d have lots of tests. 5
6 Automated Property Testing Write a program to generate test inputs! 6
7 Random WAEs ; random-wae: -> WAE (define (random-wae) (case (random 5) [(0) (num (random-nat))] [(1) (id (random-symbol))] [(2) (add (random-wae) (random-wae))] [(3) (sub (random-wae) (random-wae))] [(4) (with (random-symbol) (random-wae) (random-wae))])) Watch out that code is buggy... (read on for why) 7
8 Random WAEs ; random-nat: -> nat (define (random-nat) (case (random 2) [(0) 0] [(1) (add1 (random-nat))])) ; random-symbol: -> symbol (define (random-symbol) (random-elem '(x y z a b c))) ; random-elem: (listof X) -> X (define (random-elem xs) (list-ref xs (random (length xs)))) 8
9 Generation Strategy To build a WAE, 1/5 of the time, build a number 1/5 of the time, build a symbol 3/5 of the time, first build two more WAEs 9
10 Expected Progress On average, we reduce the problem from Generate 1 WAE. to Generate 1.2 WAEs. since 1.2 = (2/5)*0 + (3/5)*2 10
11 Height Bound Limit WAE size by bounding tree height. ; random-wae/b: nat -> WAE (define (random-wae/b h) (case (random (if (zero? h) 2 5)) [(0) (num (random-nat))] [(1) (id (random-symbol))] [(2) (add (random-wae/b (sub1 h)) (random-wae/b (sub1 h)))] [(3) (sub (random-wae/b (sub1 h)) (random-wae/b (sub1 h)))] [(4) (with (random-symbol) (random-wae/b (sub1 h)) (random-wae/b (sub1 h)))])) (Alternatively, tweak weights.) 11
12 Property Implementation ; bound=>binding: WAE -> boolean (define (bound=>binding e) (sublist? (bound-ids e) (binding-ids e))) ; sublist?: (listof X) (listof X) -> boolean ; Expects xs and ys to be sorted and have no dups. (define (sublist? xs ys) (cond [(null? xs) #t] [(null? ys) #f] [(equal? (car xs) (car ys)) (sublist? (cdr xs) (cdr ys))] [else (sublist? xs (cdr ys))])) 12
13 Running Tests ; test-bound=>binding: nat nat -> (or 'passed WAE) (define (test-bound=>binding size attempts) (if (zero? attempts) 'passed (let ([test-input (random-wae/b size)]) (if (bound=>binding test-input) (test-bound=>binding size (sub1 attempts)) test-input)))) (test-bound=>binding ) 13
14 HW2 Test Results We ran random tests on a past year s HW2 submissions. Received 99 submissions (includes multiple attempts from the same person) Tested 6 properties Found a bug in 53 out of those 99 submissions 14
15 Interpreter Properties Interpreter does not crash Produces same result as another implementation (e.g., DrRacket) Type checker accurately predicts result (later) Program equivalences hold 15
16 With Enclosing Example For example, we should be able to replace any subexpression with a new variable. {+ 1 2} {with {x 2} {+ 1 x}} 16
17 Another example: {with {x {+ 5 26}} {- x 4}} {with {z {+ 5 26}} {with {x z} {- x 4}}} 17
18 Transformation Strategy Generate a random path for a WAE expression tree Pick a subexpression based on the path to bind to a new id Replace subexpression with a bound occurrence of the id 18
19 Generating Random Paths Automatically pick leaf nodes Flip a coin to determine whether we move further down the tree Because we are "lifting" a subexpression out of its original context, we only pick expressions which will not contain free id s Always pick the named-expr of the first with we encounter 19
20 Path Generation Implementation ; coin-flip: boolean (define (coin-flip) (zero? (random 2))) ; weighted-chance: number -> boolean (define (weighted-chance pct) (<= (random) (/ pct 100))) 20
21 Path Generation Implementation ; random-path: WAE -> (listof symbol) (define (random-path wae) (type-case WAE wae [num (n) empty] [id (x) empty] [with (name named-expr body) '(left)] [else (if (weighted-chance 20) empty (if (coin-flip) (cons 'left (random-path (get-branch 'left wae))) (cons 'right (random-path (get-branch 'right wae)))))] 21
22 Path Generation Implementation ; get-branch: symbol WAE -> WAE (define (get-branch choice wae) (type-case WAE wae [add (lhs rhs) (case choice [(left) lhs] [(right) rhs])] [sub (lhs rhs) (case choice [(left) lhs] [(right) rhs])] [with (name named-expr body) (case choice [(left) named-expr] [(right) body])] [else wae])) 22
23 Extracting the Subexpression Given a path, we find the subexpression: ; pick-subexpr: WAE (listof symbol) -> WAE (define (pick-subexpr wae path) (cond [(empty? path) wae] [else (pick-subexpr (get-branch (car path) wae) (cdr path))])) 23
24 Replacing with the New ID ; swap-subexpr WAE (listof symbol) symbol -> WAE (define (swap-subexpr wae path new-id) (cond [(empty? path) (id new-id)] [else (type-case WAE wae [add (lhs rhs) (swap-in-bop path new-id add lhs rhs)] [sub (lhs rhs) (swap-in-bop path new-id sub lhs rhs)] [with (name named-expr body) (with name (id new-id) body)] [else wae])])) 24
25 Replacing with the New ID (define (swap-in-bop path new-id op lhs rhs) (case (car path) [(left) (op (swap-subexpr lhs (cdr path) new-id) rhs)] [(right) (op lhs (swap-subexpr rhs (cdr path) new-id))])) 25
26 Implementing the Transformation ; rand-sym-not-in: (listof symbol) -> symbol (define (rand-sym-not-in lst) (let ([leftover (remove* lst syms)]) (list-ref leftover (random (length leftover))))) ; wae->with-wae: WAE -> WAE (define (wae->with-wae wae) (let* ([path (random-path wae)] [subexpr (pick-subexpr wae path)] [new-id (rand-sym-not-in (binding-ids wae))] (with new-id subexpr (swap-subexpr wae path new-id)))) 26
27 Putting It All Together We generate 1000 WAE s and compare interpreter output for the original and transformed programs: (for ([i (in-range )]) (let* ([wae (random-wae/b 2 '())] [new-wae (wae->with-wae wae)]) (test (interp wae) (interp new-wae)))) 27
28 What Went Wrong? Our random WAE generator builds arbitrary expressions Probability we generate a WAE with free identifiers is very high 28
29 Eliminating Free ID s from the Random Generator ; rand-sym-from: (listof symbol) -> symbol (define (rand-sym-from ss) (list-ref ss (random (length ss)))) 29
30 Eliminating Free ID s from the Random Generator (define (random-wae/b h bindingids) (case (random (if (zero? h) 2 5)) [(0) (num (random-nat))] [(1) (if (empty? bindingids) (num (random-nat)) (id (rand-sym-from bindingids)))] [(2) (add (random-wae/b (sub1 h) bindingids) (random-wae/b (sub1 h) bindingids))] [(3) (sub (random-wae/b (sub1 h) bindingids) (random-wae/b (sub1 h) bindingids))] [(4) (let ([new-id (random-symbol)]) (with new-id (random-wae/b (sub1 h) bindingids) (random-wae/b (sub1 h) (cons new-id bindingids))))]) 30
Random Testing in 321
 Random Testing in 321 1 Test Cases So Far Each test relates a particular input to a particular output. (test (bound-ids (with 'x (id 'y) (id 'x))) '(x)) (test (binding-ids (with 'x (id 'y) (id 'x))) '(x))
Random Testing in 321 1 Test Cases So Far Each test relates a particular input to a particular output. (test (bound-ids (with 'x (id 'y) (id 'x))) '(x)) (test (binding-ids (with 'x (id 'y) (id 'x))) '(x))
Administrative Stuff
 Administrative Stuff Use the new version of PLAI from planet. It will download the first time you run a program with the 7, like this: #lang planet plai/plai:1:7 This lets you ignore passing test cases
Administrative Stuff Use the new version of PLAI from planet. It will download the first time you run a program with the 7, like this: #lang planet plai/plai:1:7 This lets you ignore passing test cases
Functional Programming - 2. Higher Order Functions
 Functional Programming - 2 Higher Order Functions Map on a list Apply Reductions: foldr, foldl Lexical scoping with let s Functional-11, CS5314, Sp16 BGRyder 1 Higher Order Functions Functions as 1st class
Functional Programming - 2 Higher Order Functions Map on a list Apply Reductions: foldr, foldl Lexical scoping with let s Functional-11, CS5314, Sp16 BGRyder 1 Higher Order Functions Functions as 1st class
Fall 2017 Discussion 7: October 25, 2017 Solutions. 1 Introduction. 2 Primitives
 CS 6A Scheme Fall 207 Discussion 7: October 25, 207 Solutions Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write
CS 6A Scheme Fall 207 Discussion 7: October 25, 207 Solutions Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write
Functional Programming. Pure Functional Programming
 Functional Programming Pure Functional Programming Computation is largely performed by applying functions to values. The value of an expression depends only on the values of its sub-expressions (if any).
Functional Programming Pure Functional Programming Computation is largely performed by applying functions to values. The value of an expression depends only on the values of its sub-expressions (if any).
Spring 2018 Discussion 7: March 21, Introduction. 2 Primitives
 CS 61A Scheme Spring 2018 Discussion 7: March 21, 2018 1 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme
CS 61A Scheme Spring 2018 Discussion 7: March 21, 2018 1 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme
Introduction to Typed Racket. The plan: Racket Crash Course Typed Racket and PL Racket Differences with the text Some PL Racket Examples
 Introduction to Typed Racket The plan: Racket Crash Course Typed Racket and PL Racket Differences with the text Some PL Racket Examples Getting started Find a machine with DrRacket installed (e.g. the
Introduction to Typed Racket The plan: Racket Crash Course Typed Racket and PL Racket Differences with the text Some PL Racket Examples Getting started Find a machine with DrRacket installed (e.g. the
Functional abstraction. What is abstraction? Eating apples. Readings: HtDP, sections Language level: Intermediate Student With Lambda
 Functional abstraction Readings: HtDP, sections 19-24. Language level: Intermediate Student With Lambda different order used in lecture section 24 material introduced much earlier sections 22, 23 not covered
Functional abstraction Readings: HtDP, sections 19-24. Language level: Intermediate Student With Lambda different order used in lecture section 24 material introduced much earlier sections 22, 23 not covered
Functional abstraction
 Functional abstraction Readings: HtDP, sections 19-24. Language level: Intermediate Student With Lambda different order used in lecture section 24 material introduced much earlier sections 22, 23 not covered
Functional abstraction Readings: HtDP, sections 19-24. Language level: Intermediate Student With Lambda different order used in lecture section 24 material introduced much earlier sections 22, 23 not covered
User-defined Functions. Conditional Expressions in Scheme
 User-defined Functions The list (lambda (args (body s to a function with (args as its argument list and (body as the function body. No quotes are needed for (args or (body. (lambda (x (+ x 1 s to the increment
User-defined Functions The list (lambda (args (body s to a function with (args as its argument list and (body as the function body. No quotes are needed for (args or (body. (lambda (x (+ x 1 s to the increment
Summer 2017 Discussion 10: July 25, Introduction. 2 Primitives and Define
 CS 6A Scheme Summer 207 Discussion 0: July 25, 207 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
CS 6A Scheme Summer 207 Discussion 0: July 25, 207 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
Delayed Expressions Fall 2017 Discussion 9: November 8, Iterables and Iterators. For Loops. Other Iterable Uses
 CS 6A Delayed Expressions Fall 07 Discussion 9: November 8, 07 Iterables and Iterators An iterable is any container that can be processed sequentially. Examples include lists, tuples, strings, and dictionaries.
CS 6A Delayed Expressions Fall 07 Discussion 9: November 8, 07 Iterables and Iterators An iterable is any container that can be processed sequentially. Examples include lists, tuples, strings, and dictionaries.
Intro. Scheme Basics. scm> 5 5. scm>
 Intro Let s take some time to talk about LISP. It stands for LISt Processing a way of coding using only lists! It sounds pretty radical, and it is. There are lots of cool things to know about LISP; if
Intro Let s take some time to talk about LISP. It stands for LISt Processing a way of coding using only lists! It sounds pretty radical, and it is. There are lots of cool things to know about LISP; if
SCHEME 8. 1 Introduction. 2 Primitives COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A. March 23, 2017
 SCHEME 8 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A March 2, 2017 1 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
SCHEME 8 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A March 2, 2017 1 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
Higher-Order Functions
 Higher-Order Functions 1 Why Functions as Values Abstraction is easier with functions as values abstract over add and sub cases filter, map, etc. What are objects? Callbacks? Separate deffun form becomes
Higher-Order Functions 1 Why Functions as Values Abstraction is easier with functions as values abstract over add and sub cases filter, map, etc. What are objects? Callbacks? Separate deffun form becomes
Typed Scheme: Scheme with Static Types
 Typed Scheme: Scheme with Static Types Version 4.1.1 Sam Tobin-Hochstadt October 5, 2008 Typed Scheme is a Scheme-like language, with a type system that supports common Scheme programming idioms. Explicit
Typed Scheme: Scheme with Static Types Version 4.1.1 Sam Tobin-Hochstadt October 5, 2008 Typed Scheme is a Scheme-like language, with a type system that supports common Scheme programming idioms. Explicit
Typed Racket: Racket with Static Types
 Typed Racket: Racket with Static Types Version 5.0.2 Sam Tobin-Hochstadt November 6, 2010 Typed Racket is a family of languages, each of which enforce that programs written in the language obey a type
Typed Racket: Racket with Static Types Version 5.0.2 Sam Tobin-Hochstadt November 6, 2010 Typed Racket is a family of languages, each of which enforce that programs written in the language obey a type
Macros & Streams Spring 2018 Discussion 9: April 11, Macros
 CS 61A Macros & Streams Spring 2018 Discussion 9: April 11, 2018 1 Macros So far, we ve mostly explored similarities between the Python and Scheme languages. For example, the Scheme list data structure
CS 61A Macros & Streams Spring 2018 Discussion 9: April 11, 2018 1 Macros So far, we ve mostly explored similarities between the Python and Scheme languages. For example, the Scheme list data structure
Quick announcement. Midterm date is Wednesday Oct 24, 11-12pm.
 Quick announcement Midterm date is Wednesday Oct 24, 11-12pm. The lambda calculus = ID (λ ID. ) ( ) The lambda calculus (Racket) = ID (lambda (ID) ) ( )
Quick announcement Midterm date is Wednesday Oct 24, 11-12pm. The lambda calculus = ID (λ ID. ) ( ) The lambda calculus (Racket) = ID (lambda (ID) ) ( )
Higher-Order Functions (Part I)
 Higher-Order Functions (Part I) 1 Why Functions as Values Abstraction is easier with functions as values abstract over add and sub cases filter, map, etc. What are objects? Callbacks? Separate deffun form
Higher-Order Functions (Part I) 1 Why Functions as Values Abstraction is easier with functions as values abstract over add and sub cases filter, map, etc. What are objects? Callbacks? Separate deffun form
Fall 2018 Discussion 8: October 24, 2018 Solutions. 1 Introduction. 2 Primitives
 CS 6A Scheme Fall 208 Discussion 8: October 24, 208 Solutions Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write
CS 6A Scheme Fall 208 Discussion 8: October 24, 208 Solutions Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write
CSE 341 Section Handout #6 Cheat Sheet
 Cheat Sheet Types numbers: integers (3, 802), reals (3.4), rationals (3/4), complex (2+3.4i) symbols: x, y, hello, r2d2 booleans: #t, #f strings: "hello", "how are you?" lists: (list 3 4 5) (list 98.5
Cheat Sheet Types numbers: integers (3, 802), reals (3.4), rationals (3/4), complex (2+3.4i) symbols: x, y, hello, r2d2 booleans: #t, #f strings: "hello", "how are you?" lists: (list 3 4 5) (list 98.5
Principles of Programming Languages
 Principles of Programming Languages Lesson 14 Type Checking Collaboration and Management Dana Fisman www.cs.bgu.ac.il/~ppl172 1 Type Checking We return to the issue of type safety we discussed informally,
Principles of Programming Languages Lesson 14 Type Checking Collaboration and Management Dana Fisman www.cs.bgu.ac.il/~ppl172 1 Type Checking We return to the issue of type safety we discussed informally,
Cost of Substitution
 Cost of Substitution (interp {with {x 1} {with {y 2} {+ 100 {+ 99 {+ 98... {+ y x}}}}}} ) (interp {with {y 2} {+ 100 {+ 99 {+ 98... {+ y 1}}}}} ) (interp {+ 100 {+ 99 {+ 98... {+ 2 1}}}} ) With n variables,
Cost of Substitution (interp {with {x 1} {with {y 2} {+ 100 {+ 99 {+ 98... {+ y x}}}}}} ) (interp {with {y 2} {+ 100 {+ 99 {+ 98... {+ y 1}}}}} ) (interp {+ 100 {+ 99 {+ 98... {+ 2 1}}}} ) With n variables,
CS 61A, Fall, 2002, Midterm #2, L. Rowe. 1. (10 points, 1 point each part) Consider the following five box-and-arrow diagrams.
 CS 61A, Fall, 2002, Midterm #2, L. Rowe 1. (10 points, 1 point each part) Consider the following five box-and-arrow diagrams. a) d) 3 1 2 3 1 2 e) b) 3 c) 1 2 3 1 2 1 2 For each of the following Scheme
CS 61A, Fall, 2002, Midterm #2, L. Rowe 1. (10 points, 1 point each part) Consider the following five box-and-arrow diagrams. a) d) 3 1 2 3 1 2 e) b) 3 c) 1 2 3 1 2 1 2 For each of the following Scheme
CS 320 Homework One Due 2/5 11:59pm
 Name: BU ID (no dashes): CS 320 Homework One Due 2/5 11:59pm Write your answers to the problems in the space indicated. Scan your solution and submit to Gradescope as a PDF file. You will receive an email
Name: BU ID (no dashes): CS 320 Homework One Due 2/5 11:59pm Write your answers to the problems in the space indicated. Scan your solution and submit to Gradescope as a PDF file. You will receive an email
Functional Programming. Pure Functional Languages
 Functional Programming Pure functional PLs S-expressions cons, car, cdr Defining functions read-eval-print loop of Lisp interpreter Examples of recursive functions Shallow, deep Equality testing 1 Pure
Functional Programming Pure functional PLs S-expressions cons, car, cdr Defining functions read-eval-print loop of Lisp interpreter Examples of recursive functions Shallow, deep Equality testing 1 Pure
Module 8: Local and functional abstraction
 Module 8: Local and functional abstraction Readings: HtDP, Intermezzo 3 (Section 18); Sections 19-23. We will cover material on functional abstraction in a somewhat different order than the text. We will
Module 8: Local and functional abstraction Readings: HtDP, Intermezzo 3 (Section 18); Sections 19-23. We will cover material on functional abstraction in a somewhat different order than the text. We will
SCHEME 7. 1 Introduction. 2 Primitives COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A. October 29, 2015
 SCHEME 7 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A October 29, 2015 1 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
SCHEME 7 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A October 29, 2015 1 Introduction In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
CS61A Midterm 2 Review (v1.1)
 Spring 2006 1 CS61A Midterm 2 Review (v1.1) Basic Info Your login: Your section number: Your TA s name: Midterm 2 is going to be held on Tuesday 7-9p, at 1 Pimentel. What will Scheme print? What will the
Spring 2006 1 CS61A Midterm 2 Review (v1.1) Basic Info Your login: Your section number: Your TA s name: Midterm 2 is going to be held on Tuesday 7-9p, at 1 Pimentel. What will Scheme print? What will the
From FP to OOP. Start with data: class Posn { int x; int y; Posn(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; } }
 From FP to OOP Start with data: ; A posn is ; (make-posn num num) (define-struct posn (x y)) class Posn { int x; int y; Posn(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; 1 From FP to OOP Start with data: ;
From FP to OOP Start with data: ; A posn is ; (make-posn num num) (define-struct posn (x y)) class Posn { int x; int y; Posn(int x, int y) { this.x = x; this.y = y; 1 From FP to OOP Start with data: ;
CS61A Notes 02b Fake Plastic Trees. 2. (cons ((1 a) (2 o)) (3 g)) 3. (list ((1 a) (2 o)) (3 g)) 4. (append ((1 a) (2 o)) (3 g))
 CS61A Notes 02b Fake Plastic Trees Box and Pointer Diagrams QUESTIONS: Evaluate the following, and draw a box-and-pointer diagram for each. (Hint: It may be easier to draw the box-and-pointer diagram first.)
CS61A Notes 02b Fake Plastic Trees Box and Pointer Diagrams QUESTIONS: Evaluate the following, and draw a box-and-pointer diagram for each. (Hint: It may be easier to draw the box-and-pointer diagram first.)
An Introduction to Functions
 Chapter 4 An Introduction to Functions Through the agency of with, we have added identifiers and the ability to name expressions to the language. Much of the time, though, simply being able to name an
Chapter 4 An Introduction to Functions Through the agency of with, we have added identifiers and the ability to name expressions to the language. Much of the time, though, simply being able to name an
Local definitions and lexical scope
 Local definitions and lexical scope Readings: HtDP, Intermezzo 3 (Section 18). Language level: Intermediate Student CS 135 Winter 2018 09: Local definitions and lexical scope 1 Local definitions The functions
Local definitions and lexical scope Readings: HtDP, Intermezzo 3 (Section 18). Language level: Intermediate Student CS 135 Winter 2018 09: Local definitions and lexical scope 1 Local definitions The functions
Local definitions and lexical scope. Local definitions. Motivating local definitions. s(s a)(s b)(s c), where s = (a + b + c)/2.
 Local definitions and lexical scope Readings: HtDP, Intermezzo 3 (Section 18). Language level: Intermediate Student CS 135 Winter 2018 09: Local definitions and lexical scope 1 Local definitions The functions
Local definitions and lexical scope Readings: HtDP, Intermezzo 3 (Section 18). Language level: Intermediate Student CS 135 Winter 2018 09: Local definitions and lexical scope 1 Local definitions The functions
Bindings & Substitution
 Bindings & Substitution Even in our simple language, we encounter repeated expressions. 1 {* {+ 4 2} {+ 4 2}} There are several reasons to eliminate duplicated code. It introduces a redundant computation.
Bindings & Substitution Even in our simple language, we encounter repeated expressions. 1 {* {+ 4 2} {+ 4 2}} There are several reasons to eliminate duplicated code. It introduces a redundant computation.
(add1 3) 4 (check-expect (add1 3) 4)
 (add1 3) 4 (check-expect (add1 3) 4) (define T 7) (define (q z) (sqr z)) (cond [(> T 3) (q 4)] [else 9]) (cond [(> T 3) (q 4)] [else 9]) -->[const] ^ (cond [(> 7 3) (q 4)] [else 9]) -->[arith] ^^^^^^^
(add1 3) 4 (check-expect (add1 3) 4) (define T 7) (define (q z) (sqr z)) (cond [(> T 3) (q 4)] [else 9]) (cond [(> T 3) (q 4)] [else 9]) -->[const] ^ (cond [(> 7 3) (q 4)] [else 9]) -->[arith] ^^^^^^^
YOUR NAME PLEASE: *** SOLUTIONS ***
 YOUR NAME PLEASE: *** SOLUTIONS *** Computer Science 201b SAMPLE Exam 1 SOLUTIONS February 15, 2015 Closed book and closed notes. No electronic devices. Show ALL work you want graded on the test itself.
YOUR NAME PLEASE: *** SOLUTIONS *** Computer Science 201b SAMPLE Exam 1 SOLUTIONS February 15, 2015 Closed book and closed notes. No electronic devices. Show ALL work you want graded on the test itself.
Scheme Quick Reference
 Scheme Quick Reference COSC 18 Winter 2003 February 10, 2003 1 Introduction This document is a quick reference guide to common features of the Scheme language. It is by no means intended to be a complete
Scheme Quick Reference COSC 18 Winter 2003 February 10, 2003 1 Introduction This document is a quick reference guide to common features of the Scheme language. It is by no means intended to be a complete
SCHEME The Scheme Interpreter. 2 Primitives COMPUTER SCIENCE 61A. October 29th, 2012
 SCHEME COMPUTER SCIENCE 6A October 29th, 202 In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs, we will eventually
SCHEME COMPUTER SCIENCE 6A October 29th, 202 In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs, we will eventually
MORE SCHEME. 1 What Would Scheme Print? COMPUTER SCIENCE MENTORS 61A. October 30 to November 3, Solution: Solutions begin on the following page.
 MORE SCHEME COMPUTER SCIENCE MENTORS 61A October 30 to November 3, 2017 1 What Would Scheme Print? Solutions begin on the following page. 1. What will Scheme output? Draw box-and-pointer diagrams to help
MORE SCHEME COMPUTER SCIENCE MENTORS 61A October 30 to November 3, 2017 1 What Would Scheme Print? Solutions begin on the following page. 1. What will Scheme output? Draw box-and-pointer diagrams to help
Working with recursion. From definition to template. Readings: HtDP, sections 11, 12, 13 (Intermezzo 2).
 Working with recursion Readings: HtDP, sections 11, 12, 13 (Intermezzo 2). We can extend the idea of a self-referential definition to defining the natural numbers, which leads to the use of recursion in
Working with recursion Readings: HtDP, sections 11, 12, 13 (Intermezzo 2). We can extend the idea of a self-referential definition to defining the natural numbers, which leads to the use of recursion in
Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs
 CS 6A Spring 203 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs Final Solutions INSTRUCTIONS You have 3 hours to complete the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes, closed computer, closed calculator,
CS 6A Spring 203 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs Final Solutions INSTRUCTIONS You have 3 hours to complete the exam. The exam is closed book, closed notes, closed computer, closed calculator,
Working with recursion
 Working with recursion Readings: HtDP, sections 11, 12, 13 (Intermezzo 2). We can extend the idea of a self-referential definition to defining the natural numbers, which leads to the use of recursion in
Working with recursion Readings: HtDP, sections 11, 12, 13 (Intermezzo 2). We can extend the idea of a self-referential definition to defining the natural numbers, which leads to the use of recursion in
CS2500 Exam 2 Fall 2011
 CS2500 Exam 2 Fall 2011 Name: Student Id (last 4 digits): Section (morning, honors or afternoon): Write down the answers in the space provided. You may use the usual primitives and expression forms, including
CS2500 Exam 2 Fall 2011 Name: Student Id (last 4 digits): Section (morning, honors or afternoon): Write down the answers in the space provided. You may use the usual primitives and expression forms, including
Functional Programming. Pure Functional Languages
 Functional Programming Pure functional PLs S-expressions cons, car, cdr Defining functions read-eval-print loop of Lisp interpreter Examples of recursive functions Shallow, deep Equality testing 1 Pure
Functional Programming Pure functional PLs S-expressions cons, car, cdr Defining functions read-eval-print loop of Lisp interpreter Examples of recursive functions Shallow, deep Equality testing 1 Pure
Name EID. (calc (parse '{+ {with {x {+ 5 5}} {with {y {- x 3}} {+ y y} } } z } ) )
 CS 345 Spring 2010 Midterm Exam Name EID 1. [4 Points] Circle the binding instances in the following expression: (calc (parse '+ with x + 5 5 with y - x 3 + y y z ) ) 2. [7 Points] Using the following
CS 345 Spring 2010 Midterm Exam Name EID 1. [4 Points] Circle the binding instances in the following expression: (calc (parse '+ with x + 5 5 with y - x 3 + y y z ) ) 2. [7 Points] Using the following
Documentation for LISP in BASIC
 Documentation for LISP in BASIC The software and the documentation are both Copyright 2008 Arthur Nunes-Harwitt LISP in BASIC is a LISP interpreter for a Scheme-like dialect of LISP, which happens to have
Documentation for LISP in BASIC The software and the documentation are both Copyright 2008 Arthur Nunes-Harwitt LISP in BASIC is a LISP interpreter for a Scheme-like dialect of LISP, which happens to have
SCHEME AND CALCULATOR 5b
 SCHEME AND CALCULATOR 5b COMPUTER SCIENCE 6A July 25, 203 In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
SCHEME AND CALCULATOR 5b COMPUTER SCIENCE 6A July 25, 203 In the next part of the course, we will be working with the Scheme programming language. In addition to learning how to write Scheme programs,
Comp 411 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 7 Meta-interpreters. Corky Cartwright January 26, 2018
 Comp 411 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 7 Meta-interpreters Corky Cartwright January 26, 2018 Denotational Semantics The primary alternative to syntactic semantics is denotational semantics.
Comp 411 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 7 Meta-interpreters Corky Cartwright January 26, 2018 Denotational Semantics The primary alternative to syntactic semantics is denotational semantics.
CS 61A Interpreters, Tail Calls, Macros, Streams, Iterators. Spring 2019 Guerrilla Section 5: April 20, Interpreters.
 CS 61A Spring 2019 Guerrilla Section 5: April 20, 2019 1 Interpreters 1.1 Determine the number of calls to scheme eval and the number of calls to scheme apply for the following expressions. > (+ 1 2) 3
CS 61A Spring 2019 Guerrilla Section 5: April 20, 2019 1 Interpreters 1.1 Determine the number of calls to scheme eval and the number of calls to scheme apply for the following expressions. > (+ 1 2) 3
Racket: Modules, Contracts, Languages
 Racket: Modules, Contracts, Languages Advanced Functional Programming Jean-Noël Monette November 2013 1 Today Modules are the way to structure larger programs in smaller pieces. Modules can import and
Racket: Modules, Contracts, Languages Advanced Functional Programming Jean-Noël Monette November 2013 1 Today Modules are the way to structure larger programs in smaller pieces. Modules can import and
Scheme Quick Reference
 Scheme Quick Reference COSC 18 Fall 2003 This document is a quick reference guide to common features of the Scheme language. It is not intended to be a complete language reference, but it gives terse summaries
Scheme Quick Reference COSC 18 Fall 2003 This document is a quick reference guide to common features of the Scheme language. It is not intended to be a complete language reference, but it gives terse summaries
Streams, Delayed Evaluation and a Normal Order Interpreter. CS 550 Programming Languages Jeremy Johnson
 Streams, Delayed Evaluation and a Normal Order Interpreter CS 550 Programming Languages Jeremy Johnson 1 Theme This lecture discusses the stream model of computation and an efficient method of implementation
Streams, Delayed Evaluation and a Normal Order Interpreter CS 550 Programming Languages Jeremy Johnson 1 Theme This lecture discusses the stream model of computation and an efficient method of implementation
Interpreters and Tail Calls Fall 2017 Discussion 8: November 1, 2017 Solutions. 1 Calculator. calc> (+ 2 2) 4
 CS 61A Interpreters and Tail Calls Fall 2017 Discussion 8: November 1, 2017 Solutions 1 Calculator We are beginning to dive into the realm of interpreting computer programs that is, writing programs that
CS 61A Interpreters and Tail Calls Fall 2017 Discussion 8: November 1, 2017 Solutions 1 Calculator We are beginning to dive into the realm of interpreting computer programs that is, writing programs that
Types of recursion. Structural vs. general recursion. Pure structural recursion. Readings: none. In this module: learn to use accumulative recursion
 Types of recursion Readings: none. In this module: learn to use accumulative recursion learn to recognize generative recursion CS 135 Fall 2018 07: Types of recursion 1 Structural vs. general recursion
Types of recursion Readings: none. In this module: learn to use accumulative recursion learn to recognize generative recursion CS 135 Fall 2018 07: Types of recursion 1 Structural vs. general recursion
GADTs. Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano. Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences]
![GADTs. Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano. Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences] GADTs. Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano. Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences]](/thumbs/78/76904283.jpg) GADTs Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7 Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano 1 Today s lecture Generalized algebraic data types (GADTs) 2 A datatype data Tree a = Leaf Node (Tree a) a (Tree
GADTs Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7 Wouter Swierstra and Alejandro Serrano 1 Today s lecture Generalized algebraic data types (GADTs) 2 A datatype data Tree a = Leaf Node (Tree a) a (Tree
CSC 533: Programming Languages. Spring 2015
 CSC 533: Programming Languages Spring 2015 Functional programming LISP & Scheme S-expressions: atoms, lists functional expressions, evaluation, define primitive functions: arithmetic, predicate, symbolic,
CSC 533: Programming Languages Spring 2015 Functional programming LISP & Scheme S-expressions: atoms, lists functional expressions, evaluation, define primitive functions: arithmetic, predicate, symbolic,
1. For every evaluation of a variable var, the variable is bound.
 7 Types We ve seen how we can use interpreters to model the run-time behavior of programs. Now we d like to use the same technology to analyze or predict the behavior of programs without running them.
7 Types We ve seen how we can use interpreters to model the run-time behavior of programs. Now we d like to use the same technology to analyze or predict the behavior of programs without running them.
CS 275 Name Final Exam Solutions December 16, 2016
 CS 275 Name Final Exam Solutions December 16, 2016 You may assume that atom? is a primitive procedure; you don t need to define it. Other helper functions that aren t a standard part of Scheme you need
CS 275 Name Final Exam Solutions December 16, 2016 You may assume that atom? is a primitive procedure; you don t need to define it. Other helper functions that aren t a standard part of Scheme you need
GADTs. Alejandro Serrano. AFP Summer School. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences]
![GADTs. Alejandro Serrano. AFP Summer School. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences] GADTs. Alejandro Serrano. AFP Summer School. [Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences]](/thumbs/95/124893351.jpg) GADTs AFP Summer School Alejandro Serrano 1 Today s lecture Generalized algebraic data types (GADTs) 2 A datatype data Tree a = Leaf Node (Tree a) a (Tree a) This definition introduces: 3 A datatype data
GADTs AFP Summer School Alejandro Serrano 1 Today s lecture Generalized algebraic data types (GADTs) 2 A datatype data Tree a = Leaf Node (Tree a) a (Tree a) This definition introduces: 3 A datatype data
An Explicit Continuation Evaluator for Scheme
 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Course Notes 2 6.844, Spring 05: Computability Theory of and with Scheme February 17 Prof. Albert R. Meyer revised March 3, 2005, 1265 minutes An Explicit Continuation
Massachusetts Institute of Technology Course Notes 2 6.844, Spring 05: Computability Theory of and with Scheme February 17 Prof. Albert R. Meyer revised March 3, 2005, 1265 minutes An Explicit Continuation
CS115 - Module 10 - General Trees
 Fall 2017 Reminder: if you have not already, ensure you: Read How to Design Programs, Sections 15 and 16. Arithmetic Expressions Recall with binary trees we could represent an expression containing binary
Fall 2017 Reminder: if you have not already, ensure you: Read How to Design Programs, Sections 15 and 16. Arithmetic Expressions Recall with binary trees we could represent an expression containing binary
Vectors in Scheme. Data Structures in Scheme
 Data Structures in Scheme Vectors in Scheme In Scheme, lists and S-expressions are basic. Arrays can be simulated using lists, but access to elements deep in the list can be slow (since a list is a linked
Data Structures in Scheme Vectors in Scheme In Scheme, lists and S-expressions are basic. Arrays can be simulated using lists, but access to elements deep in the list can be slow (since a list is a linked
The Typed Racket Guide
 The Typed Racket Guide Version 5.3.6 Sam Tobin-Hochstadt and Vincent St-Amour August 9, 2013 Typed Racket is a family of languages, each of which enforce
The Typed Racket Guide Version 5.3.6 Sam Tobin-Hochstadt and Vincent St-Amour August 9, 2013 Typed Racket is a family of languages, each of which enforce
Principles of Programming Languages Topic: Functional Programming Professor L. Thorne McCarty Spring 2003
 Principles of Programming Languages Topic: Functional Programming Professor L. Thorne McCarty Spring 2003 CS 314, LS, LTM: Functional Programming 1 Scheme A program is an expression to be evaluated (in
Principles of Programming Languages Topic: Functional Programming Professor L. Thorne McCarty Spring 2003 CS 314, LS, LTM: Functional Programming 1 Scheme A program is an expression to be evaluated (in
Types of recursion. Readings: none. In this module: a glimpse of non-structural recursion. CS 135 Winter : Types of recursion 1
 Types of recursion Readings: none. In this module: a glimpse of non-structural recursion CS 135 Winter 2018 07: Types of recursion 1 Structural vs. general recursion All of the recursion we have done to
Types of recursion Readings: none. In this module: a glimpse of non-structural recursion CS 135 Winter 2018 07: Types of recursion 1 Structural vs. general recursion All of the recursion we have done to
Racket. CSE341: Programming Languages Lecture 14 Introduction to Racket. Getting started. Racket vs. Scheme. Example.
 Racket Next 2+ weeks will use the Racket language (not ML) and the DrRacket programming environment (not emacs) Installation / basic usage instructions on course website CSE34: Programming Languages Lecture
Racket Next 2+ weeks will use the Racket language (not ML) and the DrRacket programming environment (not emacs) Installation / basic usage instructions on course website CSE34: Programming Languages Lecture
Introduction to Scheme
 How do you describe them Introduction to Scheme Gul Agha CS 421 Fall 2006 A language is described by specifying its syntax and semantics Syntax: The rules for writing programs. We will use Context Free
How do you describe them Introduction to Scheme Gul Agha CS 421 Fall 2006 A language is described by specifying its syntax and semantics Syntax: The rules for writing programs. We will use Context Free
GADTs. Wouter Swierstra. Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7. Faculty of Science Information and Computing Sciences
 GADTs Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7 Wouter Swierstra 1 Today s lecture Generalized algebraic data types (GADTs) 2 A datatype data Tree a = Leaf Node (Tree a) a (Tree a) This definition introduces:
GADTs Advanced functional programming - Lecture 7 Wouter Swierstra 1 Today s lecture Generalized algebraic data types (GADTs) 2 A datatype data Tree a = Leaf Node (Tree a) a (Tree a) This definition introduces:
Programming Languages. Datatypes
 Programming Languages Datatypes Review so far Expressions Values Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions Review so far We ve seen some base types and values: Integers, Floats,
Programming Languages Datatypes Review so far Expressions Values Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions Review so far We ve seen some base types and values: Integers, Floats,
CS3L Summer 2011 Final Exam, Part 2 You may leave when finished; or, you must stop promptly at 12:20
 CS3L Summer 2011 Final Exam, Part 2 You may leave when finished; or, you must stop promptly at 12:20 Name: Login: cs3- First names of the people to your left and right, if any: Left: Right: 1. If you have
CS3L Summer 2011 Final Exam, Part 2 You may leave when finished; or, you must stop promptly at 12:20 Name: Login: cs3- First names of the people to your left and right, if any: Left: Right: 1. If you have
Project 2: Scheme Interpreter
 Project 2: Scheme Interpreter CSC 4101, Fall 2017 Due: 12 November 2017 For this project, you will implement a simple Scheme interpreter in C++ or Java. Your interpreter should be able to handle the same
Project 2: Scheme Interpreter CSC 4101, Fall 2017 Due: 12 November 2017 For this project, you will implement a simple Scheme interpreter in C++ or Java. Your interpreter should be able to handle the same
Programming Languages. Next: Building datatypes. Suppose I wanted. Next: Building datatypes 10/4/2017. Review so far. Datatypes.
 Review so far Programming Languages Expressions Values Datatypes Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions Review so far We ve seen some base types and values: Integers, Floats,
Review so far Programming Languages Expressions Values Datatypes Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions Review so far We ve seen some base types and values: Integers, Floats,
HIERARCHICAL DATA What is a Tree? How is it different from a Deep List? When would you use one over the other?
 HIERARCHICAL DATA 5 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61AS Concepts and Definitions 1. What is a Tree? How is it different from a Deep List? When would you use one over the other? A Tree is an Abstract Data Type composed
HIERARCHICAL DATA 5 COMPUTER SCIENCE 61AS Concepts and Definitions 1. What is a Tree? How is it different from a Deep List? When would you use one over the other? A Tree is an Abstract Data Type composed
Programming Languages: Application and Interpretation
 Programming Languages: Application and Interpretation Version 5.0.1 August 3, 2010 This is the documentation for the software accompanying the textbook Programming Languages: Application and Interpretation
Programming Languages: Application and Interpretation Version 5.0.1 August 3, 2010 This is the documentation for the software accompanying the textbook Programming Languages: Application and Interpretation
Lisp Basic Example Test Questions
 2009 November 30 Lisp Basic Example Test Questions 1. Assume the following forms have been typed into the interpreter and evaluated in the given sequence. ( defun a ( y ) ( reverse y ) ) ( setq a (1 2
2009 November 30 Lisp Basic Example Test Questions 1. Assume the following forms have been typed into the interpreter and evaluated in the given sequence. ( defun a ( y ) ( reverse y ) ) ( setq a (1 2
COP4020 Programming Languages. Functional Programming Prof. Robert van Engelen
 COP4020 Programming Languages Functional Programming Prof. Robert van Engelen Overview What is functional programming? Historical origins of functional programming Functional programming today Concepts
COP4020 Programming Languages Functional Programming Prof. Robert van Engelen Overview What is functional programming? Historical origins of functional programming Functional programming today Concepts
2D Syntax. Version October 30, 2017
 2D Syntax Version 6.11 October 30, 2017 #lang 2d package: 2d-test The 2d language installs #2d reader support in the readtables, and then chains to the reader of another language that is specified immediately
2D Syntax Version 6.11 October 30, 2017 #lang 2d package: 2d-test The 2d language installs #2d reader support in the readtables, and then chains to the reader of another language that is specified immediately
Scheme in Scheme: The Metacircular Evaluator Eval and Apply
 Scheme in Scheme: The Metacircular Evaluator Eval and Apply CS21b: Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs Brandeis University Spring Term, 2015 The metacircular evaluator is A rendition of Scheme,
Scheme in Scheme: The Metacircular Evaluator Eval and Apply CS21b: Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs Brandeis University Spring Term, 2015 The metacircular evaluator is A rendition of Scheme,
Fall 2017 December 4, 2017
 CS 61A Final Review Fall 2017 December 4, 2017 Instructions Form a small group. Start on the first problem. Check off with a helper or discuss your solution process with another group once everyone understands
CS 61A Final Review Fall 2017 December 4, 2017 Instructions Form a small group. Start on the first problem. Check off with a helper or discuss your solution process with another group once everyone understands
Wellesley College CS251 Programming Languages Spring, 2000 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PROBLEM SOLUTIONS
 Wellesley College CS251 Programming Languages Spring, 2000 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PROBLEM SOLUTIONS This document contains solutions to the problems on the final exam review problems posted earlier except for
Wellesley College CS251 Programming Languages Spring, 2000 FINAL EXAM REVIEW PROBLEM SOLUTIONS This document contains solutions to the problems on the final exam review problems posted earlier except for
Comp 311: Sample Midterm Examination
 Comp 311: Sample Midterm Examination October 29, 2007 Name: Id #: Instructions 1. The examination is closed book. If you forget the name for a Scheme operation, make up a name for it and write a brief
Comp 311: Sample Midterm Examination October 29, 2007 Name: Id #: Instructions 1. The examination is closed book. If you forget the name for a Scheme operation, make up a name for it and write a brief
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity
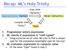 Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set
Recap: ML s Holy Trinity Expressions (Syntax) Exec-time Dynamic Values (Semantics) Compile-time Static Types 1. Programmer enters expression 2. ML checks if expression is well-typed Using a precise set
Fall 2017 December 4, Scheme. Instructions
 CS 61A Final Review Fall 2017 December 4, 2017 Instructions Form a small group. Start on the first problem. Check off with a helper or discuss your solution process with another group once everyone understands
CS 61A Final Review Fall 2017 December 4, 2017 Instructions Form a small group. Start on the first problem. Check off with a helper or discuss your solution process with another group once everyone understands
Lists. CS 5010 Program Design Paradigms Bootcamp Lesson 4.1
 Lists CS 5010 Program Design Paradigms Bootcamp Lesson 4.1 Mitchell Wand, 2012-2017 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. 1 Module 04 Basic
Lists CS 5010 Program Design Paradigms Bootcamp Lesson 4.1 Mitchell Wand, 2012-2017 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. 1 Module 04 Basic
Adding Machine Run 2
 Calculator Run 1 Adding Machine Run 2 Simple Adder (define TOTAL 0) (define total-message (make-message (number->string TOTAL))) (define amount-text (make-text "Amount")) (define add-button (make-button
Calculator Run 1 Adding Machine Run 2 Simple Adder (define TOTAL 0) (define total-message (make-message (number->string TOTAL))) (define amount-text (make-text "Amount")) (define add-button (make-button
Module 10: General trees
 Module 10: General trees Readings: HtDP, Sections 15 and 16 CS 115 Winter 2019 10: General trees 1 General trees Binary trees can be used for a large variety of application areas. One limitation is the
Module 10: General trees Readings: HtDP, Sections 15 and 16 CS 115 Winter 2019 10: General trees 1 General trees Binary trees can be used for a large variety of application areas. One limitation is the
Trees. Binary arithmetic expressions. Visualizing binary arithmetic expressions. ((2 6) + (5 2))/(5 3) can be defined in terms of two smaller
 Trees Readings: HtDP, sections 14, 15, 16. We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Trees Readings: HtDP, sections 14, 15, 16. We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
(Provisional) Lecture 08: List recursion and recursive diagrams 10:00 AM, Sep 22, 2017
 Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Hughes (Provisional) Lecture 08: List recursion and recursive diagrams 10:00 AM, Sep 22, 2017 Contents 1 Announcements 1 2 Evaluation Correction 1 3 Lists 2
Integrated Introduction to Computer Science Hughes (Provisional) Lecture 08: List recursion and recursive diagrams 10:00 AM, Sep 22, 2017 Contents 1 Announcements 1 2 Evaluation Correction 1 3 Lists 2
Trees. Readings: HtDP, sections 14, 15, 16.
 Trees Readings: HtDP, sections 14, 15, 16. We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Trees Readings: HtDP, sections 14, 15, 16. We will cover the ideas in the text using different examples and different terminology. The readings are still important as an additional source of examples.
Principles of Programming Languages
 Principles of Programming Languages Slides by Dana Fisman based on book by Mira Balaban and lecuture notes by Michael Elhadad Lesson 15 Type Inference Collaboration and Management Dana Fisman www.cs.bgu.ac.il/~ppl172
Principles of Programming Languages Slides by Dana Fisman based on book by Mira Balaban and lecuture notes by Michael Elhadad Lesson 15 Type Inference Collaboration and Management Dana Fisman www.cs.bgu.ac.il/~ppl172
Fall Semester, The Metacircular Evaluator. Today we shift perspective from that of a user of computer langugaes to that of a designer of
 1 MASSACHVSETTS INSTITVTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.001 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs Fall Semester, 1996 Lecture Notes { October 31,
1 MASSACHVSETTS INSTITVTE OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science 6.001 Structure and Interpretation of Computer Programs Fall Semester, 1996 Lecture Notes { October 31,
Programming Languages
 What about more complex data? CSE 130 : Fall 2012 Programming Languages Expressions Values Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions
What about more complex data? CSE 130 : Fall 2012 Programming Languages Expressions Values Lecture 3: Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego Types Many kinds of expressions: 1. Simple 2. Variables 3. Functions
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages
 CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 16: Functional Programming Zheng (Eddy Zhang Rutgers University April 2, 2018 Review: Computation Paradigms Functional: Composition of operations on data.
CS 314 Principles of Programming Languages Lecture 16: Functional Programming Zheng (Eddy Zhang Rutgers University April 2, 2018 Review: Computation Paradigms Functional: Composition of operations on data.
Principles of Programming Languages
 Principles of Programming Languages www.cs.bgu.ac.il/~ppl172 Lesson 6 - Defining a Programming Language Bottom Up Collaboration and Management - Elements of Programming Dana Fisman 1 What we accomplished
Principles of Programming Languages www.cs.bgu.ac.il/~ppl172 Lesson 6 - Defining a Programming Language Bottom Up Collaboration and Management - Elements of Programming Dana Fisman 1 What we accomplished
Chapter 15 Functional Programming Languages
 Chapter 15 Functional Programming Languages Fundamentals of Functional Programming Languages Introduction to Scheme A programming paradigm treats computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions.
Chapter 15 Functional Programming Languages Fundamentals of Functional Programming Languages Introduction to Scheme A programming paradigm treats computation as the evaluation of mathematical functions.
Programming Languages
 CSE 130 : Winter 2013 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course, Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 Story So Far... Simple Expressions Branches Let-Bindings... Today: Finish Crash Course Datatypes
CSE 130 : Winter 2013 Programming Languages Lecture 3: Crash Course, Datatypes Ranjit Jhala UC San Diego 1 Story So Far... Simple Expressions Branches Let-Bindings... Today: Finish Crash Course Datatypes
Scheme as implemented by Racket
 Scheme as implemented by Racket (Simple view:) Racket is a version of Scheme. (Full view:) Racket is a platform for implementing and using many languages, and Scheme is one of those that come out of the
Scheme as implemented by Racket (Simple view:) Racket is a version of Scheme. (Full view:) Racket is a platform for implementing and using many languages, and Scheme is one of those that come out of the
How to Design Programs
 How to Design Programs How to (in Racket): represent data variants trees and lists write functions that process the data See also http://www.htdp.org/ 1 Running Example: GUIs Pick a fruit: Apple Banana
How to Design Programs How to (in Racket): represent data variants trees and lists write functions that process the data See also http://www.htdp.org/ 1 Running Example: GUIs Pick a fruit: Apple Banana
