Memory Hierarchy. Bojian Zheng CSCD70 Spring 2018
|
|
|
- Brice Palmer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Memory Hierarchy Bojian Zheng CSCD70 Spring
2 Memory Hierarchy From programmer s point of view, memory has infinite capacity (i.e. can store infinite amount of data) has zero access time (latency) But those two requirements contradict with each other. Large memory usually has high access latency. Fast memory cannot go beyond certain capacity limit. Therefore, we want to have multiple levels of storage and ensure most of the data the processor needs is kept in the fastest level. 2
3 Memory Hierarchy What in reality What we see (Ideally) 3
4 Locality Temporal Locality: If an address gets accessed, then it is very likely that the exact same address will be accessed once again in the near future. unsigned a = 10; // a will hopefully be used again soon 4
5 Locality Spatial Locality: If an address gets accessed, then it is very likely that nearby addresses will be accessed in the near future. unsigned A[10]; A[5] = 10; // A[4] or A[6] will hopefully be used soon 5
6 Cache Basics Memory is divided into fixed size blocks. Each block maps to one location in the cache (called cache block or cache line), determined by the index bites. 6
7 Direct-Mapped Cache 7
8 Direct-Mapped Cache: Problem Suppose that two variables A (address 0 b ) and B (address 0 b ) map to the same cache line. Interleaving accesses to them will lead to 0 hit rate (i.e. A->B->A->B-> ). Those are called conflict misses (more later). 8
9 Set-Associative Cache 9
10 Set-Associative Cache: Problem More expansive tag comparison. More complicated design lots of things to consider: Where should we insert the new incoming cache block? What happens when a cache hit occurs? How should we adjust the priorities? What happens when a cache miss occurs, and the cache set has been fully occupied (Replacement Policy)? 10
11 Replacement Policy Which one to evict under the condition that the cache set is full? Least-Recently-Used? Random? Pseudo-Least-Recently-Used? Belady s (a.k.a. Optimal) Replacement Policy Evict block that will be reused furthest in the future. Impossible to implement in hardware why? But is still useful why? 11
12 Cache Misses There are 3 types of cache misses: Cold Misses: happens whenever we reference one variable (memory location) for the first time. Such misses are unavoidable (???). Capacity Misses: happens because our cache is too small. Misses that happen even under fully-associative cache and optimal replacement policy. Cache size is smaller than working set size. Conflict Misses: happens because we do not have enough associativity. 12
13 Handling Writes Write-Back vs. Write-Through Write-Back: Write modified data to memory when the cache block is evicted. (+) Can effectively combine multiple writes to the same block. (-) Needs an extra bit indicating dirty or clean. Write-Through: Write modified data to memory whenever write occurs. (+) Simple and makes it easy when arguing about consistency. (-) Cannot combine writes and is more bandwidth intensive. 13
14 Prefetching Upon one cache miss, try to predict what the next cache miss will be. For instance, miss on A[0] prefetch A[1] into the cache. Good for memory access patterns that are highly predictable, e.g. Instruction Memory Array Accesses (Uniform Stride) Risk: Cache Pollution Goal: Timeliness, Coverage, Accuracy 14
15 Questions? Cache Basics Cache Locality Set-Associativity Replacement Policy Cache Misses Cold Capacity Conflict Handling Writes Write-Back Write-Through Prefetching Risk Goal 15
16 Preview: Cache & Compiler Ok So how this is related to compiler? unsigned A[20][10]; for (unsigned i = 0; i < 10; ++i) for (unsigned j = 0; j < 20; ++j) A[j][i] = j * 10 + i; // Assume A is row-major. This is not very nice because cache has been utilized badly : ( 16
17 Preview: Cache & Compiler for (i 0, 10 ) for (j 0, 20 ) A[j][i] = j * 10 + i; for (j 0, 20 ) for (i 0, 10 ) A[j][i] = j * 10 + i; 17
18 Preview: Cache & Compiler Consider another example: unsigned A[100][100]; for (unsigned i = 0; i < 100; ++i) for (unsigned j = 0; j < 100; ++j) sum += A[i][j] 18
19 Preview: Cache & Compiler Apply prefetching: unsigned A[100][100]; for (unsigned i = 0; i < 100; ++i) for (unsigned j = 0; j < 100; j += $_BLOCK_SIZE) for (unsigned jj = j; jj < j + $_BLOCK_SIZE; ++jj) prefetch(&a[i][j] + $_BLOCK_SIZE) sum += A[i][jj] 19
20 Preview: Design Tradeoff Consider the following code: unsigned A[20][10]; for (unsigned i = 0; i < 10; ++i) for (unsigned j = 0; j < 19; ++j) A[j][i] = A[j+1][i]; 20
21 Preview: Design Tradeoff Loop Parallelization for (i 0, 10 ) for (j 0, 19 ) A[j][i] = A[j+1][i]; Cache Locality for (j 0, 19 ) for (i 0, 10 ) A[j][i] = A[j+1][i]; 21
Introduction to OpenMP. Lecture 10: Caches
 Introduction to OpenMP Lecture 10: Caches Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors speed doubles every 18 months. True for
Introduction to OpenMP Lecture 10: Caches Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors speed doubles every 18 months. True for
Cray XE6 Performance Workshop
 Cray XE6 Performance Workshop Mark Bull David Henty EPCC, University of Edinburgh Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. 2 1 The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors
Cray XE6 Performance Workshop Mark Bull David Henty EPCC, University of Edinburgh Overview Why caches are needed How caches work Cache design and performance. 2 1 The memory speed gap Moore s Law: processors
Why memory hierarchy? Memory hierarchy. Memory hierarchy goals. CS2410: Computer Architecture. L1 cache design. Sangyeun Cho
 Why memory hierarchy? L1 cache design Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy goals Smaller Faster More expensive per byte CPU Regs L1 cache L2 cache SRAM SRAM To provide
Why memory hierarchy? L1 cache design Sangyeun Cho Computer Science Department Memory hierarchy Memory hierarchy goals Smaller Faster More expensive per byte CPU Regs L1 cache L2 cache SRAM SRAM To provide
Computer Architecture Spring 2016
 Computer Architecture Spring 2016 Lecture 08: Caches III Shuai Wang Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Improve Cache Performance Average memory access time (AMAT): AMAT =
Computer Architecture Spring 2016 Lecture 08: Caches III Shuai Wang Department of Computer Science and Technology Nanjing University Improve Cache Performance Average memory access time (AMAT): AMAT =
10/16/2017. Miss Rate: ABC. Classifying Misses: 3C Model (Hill) Reducing Conflict Misses: Victim Buffer. Overlapping Misses: Lockup Free Cache
 Classifying Misses: 3C Model (Hill) Divide cache misses into three categories Compulsory (cold): never seen this address before Would miss even in infinite cache Capacity: miss caused because cache is
Classifying Misses: 3C Model (Hill) Divide cache misses into three categories Compulsory (cold): never seen this address before Would miss even in infinite cache Capacity: miss caused because cache is
Advanced optimizations of cache performance ( 2.2)
 Advanced optimizations of cache performance ( 2.2) 30 1. Small and Simple Caches to reduce hit time Critical timing path: address tag memory, then compare tags, then select set Lower associativity Direct-mapped
Advanced optimizations of cache performance ( 2.2) 30 1. Small and Simple Caches to reduce hit time Critical timing path: address tag memory, then compare tags, then select set Lower associativity Direct-mapped
CSC D70: Compiler Optimization Memory Optimizations
 CSC D70: Compiler Optimization Memory Optimizations Prof. Gennady Pekhimenko University of Toronto Winter 2018 The content of this lecture is adapted from the lectures of Todd Mowry, Greg Steffan, and
CSC D70: Compiler Optimization Memory Optimizations Prof. Gennady Pekhimenko University of Toronto Winter 2018 The content of this lecture is adapted from the lectures of Todd Mowry, Greg Steffan, and
Portland State University ECE 587/687. Caches and Memory-Level Parallelism
 Portland State University ECE 587/687 Caches and Memory-Level Parallelism Revisiting Processor Performance Program Execution Time = (CPU clock cycles + Memory stall cycles) x clock cycle time For each
Portland State University ECE 587/687 Caches and Memory-Level Parallelism Revisiting Processor Performance Program Execution Time = (CPU clock cycles + Memory stall cycles) x clock cycle time For each
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Computer Organization and Structure. Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University
 Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
Computer Organization and Structure Bing-Yu Chen National Taiwan University Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy The Basic of Caches Measuring & Improving Cache Performance Virtual Memory A Common
1/19/2009. Data Locality. Exploiting Locality: Caches
 Spring 2009 Prof. Hyesoon Kim Thanks to Prof. Loh & Prof. Prvulovic Data Locality Temporal: if data item needed now, it is likely to be needed again in near future Spatial: if data item needed now, nearby
Spring 2009 Prof. Hyesoon Kim Thanks to Prof. Loh & Prof. Prvulovic Data Locality Temporal: if data item needed now, it is likely to be needed again in near future Spatial: if data item needed now, nearby
Memory Cache. Memory Locality. Cache Organization -- Overview L1 Data Cache
 Memory Cache Memory Locality cpu cache memory Memory hierarchies take advantage of memory locality. Memory locality is the principle that future memory accesses are near past accesses. Memory hierarchies
Memory Cache Memory Locality cpu cache memory Memory hierarchies take advantage of memory locality. Memory locality is the principle that future memory accesses are near past accesses. Memory hierarchies
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY
 LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
LECTURE 4: LARGE AND FAST: EXPLOITING MEMORY HIERARCHY Abridged version of Patterson & Hennessy (2013):Ch.5 Principle of Locality Programs access a small proportion of their address space at any time Temporal
Agenda. EE 260: Introduction to Digital Design Memory. Naive Register File. Agenda. Memory Arrays: SRAM. Memory Arrays: Register File
 EE 260: Introduction to Digital Design Technology Yao Zheng Department of Electrical Engineering University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa 2 Technology Naive Register File Write Read clk Decoder Read Write 3 4 Arrays:
EE 260: Introduction to Digital Design Technology Yao Zheng Department of Electrical Engineering University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa 2 Technology Naive Register File Write Read clk Decoder Read Write 3 4 Arrays:
Cache Performance (H&P 5.3; 5.5; 5.6)
 Cache Performance (H&P 5.3; 5.5; 5.6) Memory system and processor performance: CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st
Cache Performance (H&P 5.3; 5.5; 5.6) Memory system and processor performance: CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st
L2 cache provides additional on-chip caching space. L2 cache captures misses from L1 cache. Summary
 HY425 Lecture 13: Improving Cache Performance Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos University of Crete and FORTH-ICS November 25, 2011 Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos HY425 Lecture 13: Improving Cache Performance 1 / 40
HY425 Lecture 13: Improving Cache Performance Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos University of Crete and FORTH-ICS November 25, 2011 Dimitrios S. Nikolopoulos HY425 Lecture 13: Improving Cache Performance 1 / 40
Page 1. Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash )
 Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Page 1 Multilevel Memories (Improving performance using a little cash ) 1 Page 2 CPU-Memory Bottleneck CPU Memory Performance of high-speed computers is usually limited by memory bandwidth & latency Latency
Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science. TDT4255 Memory hierarchies
 TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
TDT4255 Lecture 10: Memory hierarchies Donn Morrison Department of Computer Science 2 Outline Chapter 5 - Memory hierarchies (5.1-5.5) Temporal and spacial locality Hits and misses Direct-mapped, set associative,
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 10
 ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 10 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/ vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 2 October 2014 Performance Concerns Caches Almost all programming can be
ECE 571 Advanced Microprocessor-Based Design Lecture 10 Vince Weaver http://www.eece.maine.edu/ vweaver vincent.weaver@maine.edu 2 October 2014 Performance Concerns Caches Almost all programming can be
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Announcements. ECE4750/CS4420 Computer Architecture L6: Advanced Memory Hierarchy. Edward Suh Computer Systems Laboratory
 ECE4750/CS4420 Computer Architecture L6: Advanced Memory Hierarchy Edward Suh Computer Systems Laboratory suh@csl.cornell.edu Announcements Lab 1 due today Reading: Chapter 5.1 5.3 2 1 Overview How to
ECE4750/CS4420 Computer Architecture L6: Advanced Memory Hierarchy Edward Suh Computer Systems Laboratory suh@csl.cornell.edu Announcements Lab 1 due today Reading: Chapter 5.1 5.3 2 1 Overview How to
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchy Design (III)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchy Design (III) Fall 2006 Reducing cache miss penalty Five techniques Multilevel caches Critical word first and early restart Giving priority to read misses
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchy Design (III) Fall 2006 Reducing cache miss penalty Five techniques Multilevel caches Critical word first and early restart Giving priority to read misses
Memory Management! How the hardware and OS give application pgms:" The illusion of a large contiguous address space" Protection against each other"
 Memory Management! Goals of this Lecture! Help you learn about:" The memory hierarchy" Spatial and temporal locality of reference" Caching, at multiple levels" Virtual memory" and thereby " How the hardware
Memory Management! Goals of this Lecture! Help you learn about:" The memory hierarchy" Spatial and temporal locality of reference" Caching, at multiple levels" Virtual memory" and thereby " How the hardware
Key Point. What are Cache lines
 Caching 1 Key Point What are Cache lines Tags Index offset How do we find data in the cache? How do we tell if it s the right data? What decisions do we need to make in designing a cache? What are possible
Caching 1 Key Point What are Cache lines Tags Index offset How do we find data in the cache? How do we tell if it s the right data? What decisions do we need to make in designing a cache? What are possible
Memory Hierarchies &
 Memory Hierarchies & Cache Memory CSE 410, Spring 2009 Computer Systems http://www.cs.washington.edu/410 4/26/2009 cse410-13-cache 2006-09 Perkins, DW Johnson and University of Washington 1 Reading and
Memory Hierarchies & Cache Memory CSE 410, Spring 2009 Computer Systems http://www.cs.washington.edu/410 4/26/2009 cse410-13-cache 2006-09 Perkins, DW Johnson and University of Washington 1 Reading and
Lecture: Cache Hierarchies. Topics: cache innovations (Sections B.1-B.3, 2.1)
 Lecture: Cache Hierarchies Topics: cache innovations (Sections B.1-B.3, 2.1) 1 Types of Cache Misses Compulsory misses: happens the first time a memory word is accessed the misses for an infinite cache
Lecture: Cache Hierarchies Topics: cache innovations (Sections B.1-B.3, 2.1) 1 Types of Cache Misses Compulsory misses: happens the first time a memory word is accessed the misses for an infinite cache
Computer Architecture Spring 2016
 omputer Architecture Spring 2016 Lecture 09: Prefetching Shuai Wang Department of omputer Science and Technology Nanjing University Prefetching(1/3) Fetch block ahead of demand Target compulsory, capacity,
omputer Architecture Spring 2016 Lecture 09: Prefetching Shuai Wang Department of omputer Science and Technology Nanjing University Prefetching(1/3) Fetch block ahead of demand Target compulsory, capacity,
Advanced Caching Techniques (2) Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University
 Lecture 4: Advanced Caching Techniques (2) Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee282 Lecture 4-1 Announcements HW1 is out (handout and online) Due on 10/15
Lecture 4: Advanced Caching Techniques (2) Department of Electrical Engineering Stanford University http://eeclass.stanford.edu/ee282 Lecture 4-1 Announcements HW1 is out (handout and online) Due on 10/15
CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems. Cache $$$$$
 CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems Cache $$$$$ Memory Systems! How can we supply the CPU with enough data to keep it busy?! We will focus on memory issues,! which are frequently bottlenecks
CS161 Design and Architecture of Computer Systems Cache $$$$$ Memory Systems! How can we supply the CPU with enough data to keep it busy?! We will focus on memory issues,! which are frequently bottlenecks
Memories. CPE480/CS480/EE480, Spring Hank Dietz.
 Memories CPE480/CS480/EE480, Spring 2018 Hank Dietz http://aggregate.org/ee480 What we want, what we have What we want: Unlimited memory space Fast, constant, access time (UMA: Uniform Memory Access) What
Memories CPE480/CS480/EE480, Spring 2018 Hank Dietz http://aggregate.org/ee480 What we want, what we have What we want: Unlimited memory space Fast, constant, access time (UMA: Uniform Memory Access) What
Memory Management. Goals of this Lecture. Motivation for Memory Hierarchy
 Memory Management Goals of this Lecture Help you learn about: The memory hierarchy Spatial and temporal locality of reference Caching, at multiple levels Virtual memory and thereby How the hardware and
Memory Management Goals of this Lecture Help you learn about: The memory hierarchy Spatial and temporal locality of reference Caching, at multiple levels Virtual memory and thereby How the hardware and
Memory Hierarchy. Maurizio Palesi. Maurizio Palesi 1
 Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Memory Hierarchy Maurizio Palesi Maurizio Palesi 1 References John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Computer Architecture a Quantitative Approach, second edition, Morgan Kaufmann Chapter 5 Maurizio
Advanced Computer Architecture
 ECE 563 Advanced Computer Architecture Fall 2009 Lecture 3: Memory Hierarchy Review: Caches 563 L03.1 Fall 2010 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced DRAM... Four-issue 2GHz superscalar accessing 100ns DRAM could
ECE 563 Advanced Computer Architecture Fall 2009 Lecture 3: Memory Hierarchy Review: Caches 563 L03.1 Fall 2010 Since 1980, CPU has outpaced DRAM... Four-issue 2GHz superscalar accessing 100ns DRAM could
CS222: Cache Performance Improvement
 CS222: Cache Performance Improvement Dr. A. Sahu Dept of Comp. Sc. & Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Outline Eleven Advanced Cache Performance Optimization Prev: Reducing hit time & Increasing
CS222: Cache Performance Improvement Dr. A. Sahu Dept of Comp. Sc. & Engg. Indian Institute of Technology Guwahati Outline Eleven Advanced Cache Performance Optimization Prev: Reducing hit time & Increasing
Memory Hierarchy Basics
 Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Memory Hierarchy Basics Six basic cache optimizations: Larger block size Reduces compulsory misses Increases
Computer Architecture A Quantitative Approach, Fifth Edition Chapter 2 Memory Hierarchy Design 1 Memory Hierarchy Basics Six basic cache optimizations: Larger block size Reduces compulsory misses Increases
Chapter 2 (cont) Instructor: Josep Torrellas CS433. Copyright Josep Torrellas 1999, 2001, 2002,
 Chapter 2 (cont) Instructor: Josep Torrellas CS433 Copyright Josep Torrellas 1999, 2001, 2002, 2013 1 Improving Cache Performance Average mem access time = hit time + miss rate * miss penalty speed up
Chapter 2 (cont) Instructor: Josep Torrellas CS433 Copyright Josep Torrellas 1999, 2001, 2002, 2013 1 Improving Cache Performance Average mem access time = hit time + miss rate * miss penalty speed up
Memory Technology. Caches 1. Static RAM (SRAM) Dynamic RAM (DRAM) Magnetic disk. Ideal memory. 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB
 Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Memory Technology Caches 1 Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per GB Ideal memory Average access time similar
Caches. Hakim Weatherspoon CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University. See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes)
 Caches akim Weatherspoon CS 341, Spring 212 Computer Science Cornell University See P& 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) ctrl ctrl ctrl inst imm B A B D D Big Picture: emory emory: big & slow vs Caches: small &
Caches akim Weatherspoon CS 341, Spring 212 Computer Science Cornell University See P& 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) ctrl ctrl ctrl inst imm B A B D D Big Picture: emory emory: big & slow vs Caches: small &
Chapter 5. Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Processor-Memory Performance Gap 10000 µproc 55%/year (2X/1.5yr) Performance 1000 100 10 1 1980 1983 1986 1989 Moore s Law Processor-Memory Performance
2 Improved Direct-Mapped Cache Performance by the Addition of a Small Fully-Associative Cache and Prefetch Buffers [1]
![2 Improved Direct-Mapped Cache Performance by the Addition of a Small Fully-Associative Cache and Prefetch Buffers [1] 2 Improved Direct-Mapped Cache Performance by the Addition of a Small Fully-Associative Cache and Prefetch Buffers [1]](/thumbs/73/69207197.jpg) EE482: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture #7 Processor Architecture Stanford University Tuesday, June 6, 2000 Memory Systems and Memory Latency Lecture #7: Wednesday, April 19, 2000 Lecturer: Brian
EE482: Advanced Computer Organization Lecture #7 Processor Architecture Stanford University Tuesday, June 6, 2000 Memory Systems and Memory Latency Lecture #7: Wednesday, April 19, 2000 Lecturer: Brian
Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II
 CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II John Wawrzynek Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~johnw
CS 152 Computer Architecture and Engineering Lecture 7 - Memory Hierarchy-II John Wawrzynek Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences University of California at Berkeley http://www.eecs.berkeley.edu/~johnw
Memory Hierarchy. Advanced Optimizations. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Advanced Optimizations Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed. Appendix B and Chapter 2. David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture. MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL.
Memory Hierarchy Advanced Optimizations Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed. Appendix B and Chapter 2. David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture. MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL.
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Types of cache misses Compulsory Misses: first access to a block cannot be in the cache (cold start misses) Capacity
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II) Edgar Gabriel Spring 2018 Types of cache misses Compulsory Misses: first access to a block cannot be in the cache (cold start misses) Capacity
Cache performance Outline
 Cache performance 1 Outline Metrics Performance characterization Cache optimization techniques 2 Page 1 Cache Performance metrics (1) Miss rate: Neglects cycle time implications Average memory access time
Cache performance 1 Outline Metrics Performance characterization Cache optimization techniques 2 Page 1 Cache Performance metrics (1) Miss rate: Neglects cycle time implications Average memory access time
Caches. Samira Khan March 23, 2017
 Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Agenda Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Agenda Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
Caches 3/23/17. Agenda. The Dataflow Model (of a Computer)
 Agenda Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
Agenda Caches Samira Khan March 23, 2017 Review from last lecture Data flow model Memory hierarchy More Caches The Dataflow Model (of a Computer) Von Neumann model: An instruction is fetched and executed
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2
 EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache performance optimization Bandwidth increase Reduce hit time Reduce miss penalty Reduce miss
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache performance optimization Bandwidth increase Reduce hit time Reduce miss penalty Reduce miss
Cache Performance! ! Memory system and processor performance:! ! Improving memory hierarchy performance:! CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time
 Cache Performance!! Memory system and processor performance:! CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st = Pipeline time +
Cache Performance!! Memory system and processor performance:! CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st = Pipeline time +
Improving Cache Performance. Dr. Yitzhak Birk Electrical Engineering Department, Technion
 Improving Cache Performance Dr. Yitzhak Birk Electrical Engineering Department, Technion 1 Cache Performance CPU time = (CPU execution clock cycles + Memory stall clock cycles) x clock cycle time Memory
Improving Cache Performance Dr. Yitzhak Birk Electrical Engineering Department, Technion 1 Cache Performance CPU time = (CPU execution clock cycles + Memory stall clock cycles) x clock cycle time Memory
Announcements. ! Previous lecture. Caches. Inf3 Computer Architecture
 Announcements! Previous lecture Caches Inf3 Computer Architecture - 2016-2017 1 Recap: Memory Hierarchy Issues! Block size: smallest unit that is managed at each level E.g., 64B for cache lines, 4KB for
Announcements! Previous lecture Caches Inf3 Computer Architecture - 2016-2017 1 Recap: Memory Hierarchy Issues! Block size: smallest unit that is managed at each level E.g., 64B for cache lines, 4KB for
CSE502: Computer Architecture CSE 502: Computer Architecture
 CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
CSE 502: Computer Architecture Memory Hierarchy & Caches Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required
Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging. Cache Performance
 6.823, L11--1 Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 Cache Performance 6.823,
6.823, L11--1 Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 Cache Performance 6.823,
Pick a time window size w. In time span w, are there, Multiple References, to nearby addresses: Spatial Locality
 Pick a time window size w. In time span w, are there, Multiple References, to nearby addresses: Spatial Locality Repeated References, to a set of locations: Temporal Locality Take advantage of behavior
Pick a time window size w. In time span w, are there, Multiple References, to nearby addresses: Spatial Locality Repeated References, to a set of locations: Temporal Locality Take advantage of behavior
Spring 2016 :: CSE 502 Computer Architecture. Caches. Nima Honarmand
 Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
Caches Nima Honarmand Motivation 10000 Performance 1000 100 10 Processor Memory 1 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 Want memory to appear: As fast as CPU As large as required by all of the running applications
Memory Management! Goals of this Lecture!
 Memory Management! Goals of this Lecture! Help you learn about:" The memory hierarchy" Why it works: locality of reference" Caching, at multiple levels" Virtual memory" and thereby " How the hardware and
Memory Management! Goals of this Lecture! Help you learn about:" The memory hierarchy" Why it works: locality of reference" Caching, at multiple levels" Virtual memory" and thereby " How the hardware and
Chapter 09: Caches. Lesson 04: Replacement policy
 Chapter 09: Caches Lesson 04: Replacement policy 1 Objective Understand the replacement Policy Comparisons between write back and write through caches 2 Replacement policy 3 Replacement after eviction
Chapter 09: Caches Lesson 04: Replacement policy 1 Objective Understand the replacement Policy Comparisons between write back and write through caches 2 Replacement policy 3 Replacement after eviction
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1)
 Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Engineering,
Department of Electr rical Eng ineering, Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy (Part 1) 王振傑 (Chen-Chieh Wang) ccwang@mail.ee.ncku.edu.tw ncku edu Depar rtment of Electr rical Engineering,
Memory Hierarchy. Slides contents from:
 Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Memory Hierarchy Slides contents from: Hennessy & Patterson, 5ed Appendix B and Chapter 2 David Wentzlaff, ELE 475 Computer Architecture MJT, High Performance Computing, NPTEL Memory Performance Gap Memory
Lecture 2: Caches. belongs to Milo Martin, Amir Roth, David Wood, James Smith, Mikko Lipasti
 Lecture 2: Caches http://wwwcssfuca/~ashriram/cs885/ belongs to Milo Martin, Amir Roth, David Wood, James Smith, Mikko Lipasti 1 Why focus on caches and memory? CPU can only compute as fast as memory Add
Lecture 2: Caches http://wwwcssfuca/~ashriram/cs885/ belongs to Milo Martin, Amir Roth, David Wood, James Smith, Mikko Lipasti 1 Why focus on caches and memory? CPU can only compute as fast as memory Add
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design Part 2
 Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design Part 2 Introduction (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Caches Review of basics (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Advanced methods (Section 2.3) Main Memory Virtual Memory Fundamental
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design Part 2 Introduction (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Caches Review of basics (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Advanced methods (Section 2.3) Main Memory Virtual Memory Fundamental
Cache Memory: Instruction Cache, HW/SW Interaction. Admin
 Cache Memory Instruction Cache, HW/SW Interaction Computer Science 104 Admin Project Due Dec 7 Homework #5 Due November 19, in class What s Ahead Finish Caches Virtual Memory Input/Output (1 homework)
Cache Memory Instruction Cache, HW/SW Interaction Computer Science 104 Admin Project Due Dec 7 Homework #5 Due November 19, in class What s Ahead Finish Caches Virtual Memory Input/Output (1 homework)
Fall 2011 Prof. Hyesoon Kim. Thanks to Prof. Loh & Prof. Prvulovic
 Fall 2011 Prof. Hyesoon Kim Thanks to Prof. Loh & Prof. Prvulovic Reading: Data prefetch mechanisms, Steven P. Vanderwiel, David J. Lilja, ACM Computing Surveys, Vol. 32, Issue 2 (June 2000) If memory
Fall 2011 Prof. Hyesoon Kim Thanks to Prof. Loh & Prof. Prvulovic Reading: Data prefetch mechanisms, Steven P. Vanderwiel, David J. Lilja, ACM Computing Surveys, Vol. 32, Issue 2 (June 2000) If memory
Best-Offset Hardware Prefetching
 Best-Offset Hardware Prefetching Pierre Michaud March 2016 2 BOP: yet another data prefetcher Contribution: offset prefetcher with new mechanism for setting the prefetch offset dynamically - Improvement
Best-Offset Hardware Prefetching Pierre Michaud March 2016 2 BOP: yet another data prefetcher Contribution: offset prefetcher with new mechanism for setting the prefetch offset dynamically - Improvement
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design Part 2
 Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design Part 2 Introduction (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Caches Review of basics (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Advanced methods (Section 2.3) Main Memory Virtual Memory Fundamental
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design Part 2 Introduction (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Caches Review of basics (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Advanced methods (Section 2.3) Main Memory Virtual Memory Fundamental
Caches Concepts Review
 Caches Concepts Review What is a block address? Why not bring just what is needed by the processor? What is a set associative cache? Write-through? Write-back? Then we ll see: Block allocation policy on
Caches Concepts Review What is a block address? Why not bring just what is needed by the processor? What is a set associative cache? Write-through? Write-back? Then we ll see: Block allocation policy on
Caching Basics. Memory Hierarchies
 Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
Caching Basics CS448 1 Memory Hierarchies Takes advantage of locality of reference principle Most programs do not access all code and data uniformly, but repeat for certain data choices spatial nearby
LRU. Pseudo LRU A B C D E F G H A B C D E F G H H H C. Copyright 2012, Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 LRU A list to keep track of the order of access to every block in the set. The least recently used block is replaced (if needed). How many bits we need for that? 27 Pseudo LRU A B C D E F G H A B C D E
LRU A list to keep track of the order of access to every block in the set. The least recently used block is replaced (if needed). How many bits we need for that? 27 Pseudo LRU A B C D E F G H A B C D E
CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]
![CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] CSF Cache Introduction. [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005]](/thumbs/73/69213006.jpg) CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
CSF Cache Introduction [Adapted from Computer Organization and Design, Patterson & Hennessy, 2005] Review: The Memory Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much
Lecture notes for CS Chapter 2, part 1 10/23/18
 Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design Part 2 Introduction (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Caches Review of basics (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Advanced methods (Section 2.3) Main Memory Virtual Memory Fundamental
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design Part 2 Introduction (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Caches Review of basics (Section 2.1, Appendix B) Advanced methods (Section 2.3) Main Memory Virtual Memory Fundamental
ECE ECE4680
 ECE468. -4-7 The otivation for s System ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture DRA Hierarchy System otivation Large memories (DRA) are slow Small memories (SRA) are fast ake the average access time
ECE468. -4-7 The otivation for s System ECE468 Computer Organization and Architecture DRA Hierarchy System otivation Large memories (DRA) are slow Small memories (SRA) are fast ake the average access time
VIRTUAL MEMORY READING: CHAPTER 9
 VIRTUAL MEMORY READING: CHAPTER 9 9 MEMORY HIERARCHY Core! Processor! Core! Caching! Main! Memory! (DRAM)!! Caching!! Secondary Storage (SSD)!!!! Secondary Storage (Disk)! L cache exclusive to a single
VIRTUAL MEMORY READING: CHAPTER 9 9 MEMORY HIERARCHY Core! Processor! Core! Caching! Main! Memory! (DRAM)!! Caching!! Secondary Storage (SSD)!!!! Secondary Storage (Disk)! L cache exclusive to a single
Module 5: Performance Issues in Shared Memory and Introduction to Coherence Lecture 9: Performance Issues in Shared Memory. The Lecture Contains:
 The Lecture Contains: Data Access and Communication Data Access Artifactual Comm. Capacity Problem Temporal Locality Spatial Locality 2D to 4D Conversion Transfer Granularity Worse: False Sharing Contention
The Lecture Contains: Data Access and Communication Data Access Artifactual Comm. Capacity Problem Temporal Locality Spatial Locality 2D to 4D Conversion Transfer Granularity Worse: False Sharing Contention
The Memory Hierarchy. Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2)
 The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
The Memory Hierarchy Cache, Main Memory, and Virtual Memory (Part 2) Lecture for CPSC 5155 Edward Bosworth, Ph.D. Computer Science Department Columbus State University Cache Line Replacement The cache
Computer Systems Architecture I. CSE 560M Lecture 17 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James
 Computer Systems Architecture I CSE 560M Lecture 17 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James Plan for Today Announcements and Reminders Project demos in three weeks (Nov. 23 rd ) Questions Today s discussion: Improving
Computer Systems Architecture I CSE 560M Lecture 17 Guest Lecturer: Shakir James Plan for Today Announcements and Reminders Project demos in three weeks (Nov. 23 rd ) Questions Today s discussion: Improving
CS 240 Stage 3 Abstractions for Practical Systems
 CS 240 Stage 3 Abstractions for Practical Systems Caching and the memory hierarchy Operating systems and the process model Virtual memory Dynamic memory allocation Victory lap Memory Hierarchy: Cache Memory
CS 240 Stage 3 Abstractions for Practical Systems Caching and the memory hierarchy Operating systems and the process model Virtual memory Dynamic memory allocation Victory lap Memory Hierarchy: Cache Memory
Mo Money, No Problems: Caches #2...
 Mo Money, No Problems: Caches #2... 1 Reminder: Cache Terms... Cache: A small and fast memory used to increase the performance of accessing a big and slow memory Uses temporal locality: The tendency to
Mo Money, No Problems: Caches #2... 1 Reminder: Cache Terms... Cache: A small and fast memory used to increase the performance of accessing a big and slow memory Uses temporal locality: The tendency to
CACHE OPTIMIZATION. Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi. CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture. Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah
 CACHE OPTIMIZATION Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 3 will be released on Oct. 31 st This
CACHE OPTIMIZATION Mahdi Nazm Bojnordi Assistant Professor School of Computing University of Utah CS/ECE 6810: Computer Architecture Overview Announcement Homework 3 will be released on Oct. 31 st This
Lecture: Large Caches, Virtual Memory. Topics: cache innovations (Sections 2.4, B.4, B.5)
 Lecture: Large Caches, Virtual Memory Topics: cache innovations (Sections 2.4, B.4, B.5) 1 More Cache Basics caches are split as instruction and data; L2 and L3 are unified The /L2 hierarchy can be inclusive,
Lecture: Large Caches, Virtual Memory Topics: cache innovations (Sections 2.4, B.4, B.5) 1 More Cache Basics caches are split as instruction and data; L2 and L3 are unified The /L2 hierarchy can be inclusive,
Caches. Han Wang CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University. See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes)
 Caches Han Wang CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) This week: Announcements PA2 Work-in-progress submission Next six weeks: Two labs and two projects
Caches Han Wang CS 3410, Spring 2012 Computer Science Cornell University See P&H 5.1, 5.2 (except writes) This week: Announcements PA2 Work-in-progress submission Next six weeks: Two labs and two projects
Spring 2018 :: CSE 502. Cache Design Basics. Nima Honarmand
 Cache Design Basics Nima Honarmand Storage Hierarchy Make common case fast: Common: temporal & spatial locality Fast: smaller, more expensive memory Bigger Transfers Registers More Bandwidth Controlled
Cache Design Basics Nima Honarmand Storage Hierarchy Make common case fast: Common: temporal & spatial locality Fast: smaller, more expensive memory Bigger Transfers Registers More Bandwidth Controlled
CACHE MEMORIES ADVANCED COMPUTER ARCHITECTURES. Slides by: Pedro Tomás
 CACHE MEMORIES Slides by: Pedro Tomás Additional reading: Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach, 5th edition, Chapter 2 and Appendix B, John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Morgan Kaufmann,
CACHE MEMORIES Slides by: Pedro Tomás Additional reading: Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach, 5th edition, Chapter 2 and Appendix B, John L. Hennessy and David A. Patterson, Morgan Kaufmann,
Improving Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging. Highly-Associative Caches
 Improving Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging 6.823, L8--1 Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 Highly-Associative
Improving Cache Performance and Memory Management: From Absolute Addresses to Demand Paging 6.823, L8--1 Asanovic Laboratory for Computer Science M.I.T. http://www.csg.lcs.mit.edu/6.823 Highly-Associative
What is Cache Memory? EE 352 Unit 11. Motivation for Cache Memory. Memory Hierarchy. Cache Definitions Cache Address Mapping Cache Performance
 What is EE 352 Unit 11 Definitions Address Mapping Performance memory is a small, fast memory used to hold of data that the processor will likely need to access in the near future sits between the processor
What is EE 352 Unit 11 Definitions Address Mapping Performance memory is a small, fast memory used to hold of data that the processor will likely need to access in the near future sits between the processor
Chapter 5. Memory Technology
 Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
Chapter 5 Large and Fast: Exploiting Memory Hierarchy Memory Technology Static RAM (SRAM) 0.5ns 2.5ns, $2000 $5000 per GB Dynamic RAM (DRAM) 50ns 70ns, $20 $75 per GB Magnetic disk 5ms 20ms, $0.20 $2 per
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory
 EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache optimization Virtual memory Case study AMD Opteron Summary 2 Memory hierarchy 3 Cache
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part 5.1.1: Virtual Memory Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache optimization Virtual memory Case study AMD Opteron Summary 2 Memory hierarchy 3 Cache
Cache Performance! ! Memory system and processor performance:! ! Improving memory hierarchy performance:! CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time
 Cache Performance!! Memory system and processor performance:! CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st = Pipeline time +
Cache Performance!! Memory system and processor performance:! CPU time = IC x CPI x Clock time CPU performance eqn. CPI = CPI ld/st x IC ld/st IC + CPI others x IC others IC CPI ld/st = Pipeline time +
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Caches Part 2
 CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Caches Part 2 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/fa15 Software Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg,
CS 61C: Great Ideas in Computer Architecture Caches Part 2 Instructors: Nicholas Weaver & Vladimir Stojanovic http://insteecsberkeleyedu/~cs61c/fa15 Software Parallel Requests Assigned to computer eg,
Pollard s Attempt to Explain Cache Memory
 Pollard s Attempt to Explain Cache Start with (Very) Basic Block Diagram CPU (Actual work done here) (Starting and ending data stored here, along with program) Organization of : Designer s choice 1 Problem
Pollard s Attempt to Explain Cache Start with (Very) Basic Block Diagram CPU (Actual work done here) (Starting and ending data stored here, along with program) Organization of : Designer s choice 1 Problem
EEC 170 Computer Architecture Fall Cache Introduction Review. Review: The Memory Hierarchy. The Memory Hierarchy: Why Does it Work?
 EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
EEC 17 Computer Architecture Fall 25 Introduction Review Review: The Hierarchy Take advantage of the principle of locality to present the user with as much memory as is available in the cheapest technology
Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory
 Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory Readings: 5.1-5.4, 5.8 Big memories are slow Computer Fast memories are small Processor Memory Devices Control Input Datapath Output Need to get fast, big memories
Memory Hierarchy: Caches, Virtual Memory Readings: 5.1-5.4, 5.8 Big memories are slow Computer Fast memories are small Processor Memory Devices Control Input Datapath Output Need to get fast, big memories
CS7810 Prefetching. Seth Pugsley
 CS7810 Prefetching Seth Pugsley Predicting the Future Where have we seen prediction before? Does it always work? Prefetching is prediction Predict which cache line will be used next, and place it in the
CS7810 Prefetching Seth Pugsley Predicting the Future Where have we seen prediction before? Does it always work? Prefetching is prediction Predict which cache line will be used next, and place it in the
Introduction. Memory Hierarchy
 Introduction Why memory subsystem design is important CPU speeds increase 25%-30% per year DRAM speeds increase 2%-11% per year 1 Memory Hierarchy Levels of memory with different sizes & speeds close to
Introduction Why memory subsystem design is important CPU speeds increase 25%-30% per year DRAM speeds increase 2%-11% per year 1 Memory Hierarchy Levels of memory with different sizes & speeds close to
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture. - Memory Hierarchies (II)
 COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II) Fall 2008 Cache Performance Avg. memory access time = Hit time + Miss rate x Miss penalty with Hit time: time to access a data item which is available
COSC 6385 Computer Architecture - Memory Hierarchies (II) Fall 2008 Cache Performance Avg. memory access time = Hit time + Miss rate x Miss penalty with Hit time: time to access a data item which is available
Improving Cache Performance. Reducing Misses. How To Reduce Misses? 3Cs Absolute Miss Rate. 1. Reduce the miss rate, Classifying Misses: 3 Cs
 Improving Cache Performance 1. Reduce the miss rate, 2. Reduce the miss penalty, or 3. Reduce the time to hit in the. Reducing Misses Classifying Misses: 3 Cs! Compulsory The first access to a block is
Improving Cache Performance 1. Reduce the miss rate, 2. Reduce the miss penalty, or 3. Reduce the time to hit in the. Reducing Misses Classifying Misses: 3 Cs! Compulsory The first access to a block is
Logical Diagram of a Set-associative Cache Accessing a Cache
 Introduction Memory Hierarchy Why memory subsystem design is important CPU speeds increase 25%-30% per year DRAM speeds increase 2%-11% per year Levels of memory with different sizes & speeds close to
Introduction Memory Hierarchy Why memory subsystem design is important CPU speeds increase 25%-30% per year DRAM speeds increase 2%-11% per year Levels of memory with different sizes & speeds close to
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2
 EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache performance optimization Bandwidth increase Reduce hit time Reduce miss penalty Reduce miss
EITF20: Computer Architecture Part4.1.1: Cache - 2 Liang Liu liang.liu@eit.lth.se 1 Outline Reiteration Cache performance optimization Bandwidth increase Reduce hit time Reduce miss penalty Reduce miss
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design, part 1 - Introducation. Advanced Computer Architecture Mehran Rezaei
 Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design, part 1 - Introducation Advanced Computer Architecture Mehran Rezaei Temporal Locality The principle of temporal locality in program references says that if you access
Chapter 2: Memory Hierarchy Design, part 1 - Introducation Advanced Computer Architecture Mehran Rezaei Temporal Locality The principle of temporal locality in program references says that if you access
The levels of a memory hierarchy. Main. Memory. 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms
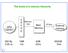 The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
The levels of a memory hierarchy CPU registers C A C H E Memory bus Main Memory I/O bus External memory 500 By 1MB 4GB 500GB 0.25 ns 1ns 20ns 5ms 1 1 Some useful definitions When the CPU finds a requested
CSC 631: High-Performance Computer Architecture
 CSC 631: High-Performance Computer Architecture Spring 2017 Lecture 10: Memory Part II CSC 631: High-Performance Computer Architecture 1 Two predictable properties of memory references: Temporal Locality:
CSC 631: High-Performance Computer Architecture Spring 2017 Lecture 10: Memory Part II CSC 631: High-Performance Computer Architecture 1 Two predictable properties of memory references: Temporal Locality:
Chapter 5. Topics in Memory Hierachy. Computer Architectures. Tien-Fu Chen. National Chung Cheng Univ.
 Computer Architectures Chapter 5 Tien-Fu Chen National Chung Cheng Univ. Chap5-0 Topics in Memory Hierachy! Memory Hierachy Features: temporal & spatial locality Common: Faster -> more expensive -> smaller!
Computer Architectures Chapter 5 Tien-Fu Chen National Chung Cheng Univ. Chap5-0 Topics in Memory Hierachy! Memory Hierachy Features: temporal & spatial locality Common: Faster -> more expensive -> smaller!
