BON Business Object Notation Based on slides by Prof. Paige
|
|
|
- Earl Cain
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BON Business Object Notation Based on slides by Prof. Paige 17-1
2 What is it? Notation for modeling object oriented software» Static: specifies classes, class relationships» Dynamic: behavioural properties Method» Guidelines to be used when producing specifications and descriptions Does not include» Entity-Relation models» Finite state machines 17-2
3 Characteristics of the Notation Simplicity» Concentrate on design aspects of the method Generality» Not restricted to application domains Design by Contract» Assertions for classes and features Two views» Graphical» Textual Eiffel 17-3
4 Characteristics of the Notation 2 Seamlessness» Smooth transition from requirements through design to implementation all in one form of model Reversibility» Direct mapping of design concepts to and from implementation concepts Scalability» Scales up to large designs 17-4
5 Tool Support Bon tools Eiffel diagrams 17-5
6 Compressed Classes Use to draw views with lots of classes bird's eye view early stages of design NAME NAME Shortest form Reused library * NAME Deferred NAME [G, H] Parameterized + NAME Implemented NAME Root Instances may be separate processes NAME Persistent Inherit STORABLE NAME Interfaces with outside world 17-6
7 Inheritance Relations * PEOPLE + YOUNG_PEOPLE + OLD_PEOPLE ++ TODDLERS ++ PRE_TEEN ++ TEEN_AGERS 17-7
8 Client Supplier Association Client A uses the services of supplier B Each client instance may be attached to one or more supplier instances has a has a PERSON ADDRESS CITY 17-8
9 Client Supplier Aggregation Client A uses the services of supplier B Each client instance is attached to one or more supplier instances that represent integral parts of the client instance part of part of VEHICLE MOTOR CYLINDER propulsion combustion_chamber Difference between association and aggregation? Consider expanded vs reference use. Consider what happens when the client gets deleted. 17-9
10 Bidirectional Uses Links CUSTOMER shoppers : set [... ] preferred_mall SHOPPING_CENTER Client feature label is at the supplier side Generic classes can be used in labels Leave parameter unspecified Useful for recursive structures lists, trees, graphs 17-10
11 Cluster Represents a group of classes, and possibly other clusters, according to some point of view Classes may be grouped differently depending on the characteristics of the specification one wants to highlight» Subsystem functionality, user categories, abstraction level, et cetera 17-11
12 Cluster Example SORTING DATA_STRUCTURES LINEAR_SORT QUICKSORT INSERT_SORT GRAPH DIRECTED_GRAPH WEIGHTED_GRAPH GRAPHS ARRAY RECORD 17-12
13 Cluster Properties Clusters can be shrunk to hide their contents» Keep only the cluster name Every class belongs to exactly one cluster Not a language construct; just a mechanism for dealing with abstraction Implement in Eiffel with directory structure» Each cluster is a directory 17-13
14 Inheritance & Clusters SORTING LINEAR_SORT INSERT_SORT DIRECTED_GRAPH WEIGHTED_GRAPH GRAPHS ARRAY All classes in sorting inherit from ARRAY Only DIRECTED_GRAPH inherits from ARRAY 17-14
15 Graphical BON Class (Uncompressed) CITIZEN No need to show all features, just those of interest for the view name, sex, age : VALUE spouse : CITIZEN children, parents : SET [ CITIZEN ] single : BOOLEAN! Result ( spouse = Void ) divorce? not single! single and ( old spouse ).single invariant single or spouse.spouse parents.count = 2 c children ( p c.parents p 17-15
16 Typed Class Interface Early phases concentrate on public features Restricted features produced during detail design Arbitrary number of sections, each with export list Each feature has a signature and optionally a behavioural specification Conventions» Classes all in upper case» features all in lower case» use underscore for longer names NAME Inherits: parent classes Public features A, B, C Restricted features Invariant Class invariant 17-16
17 Class Feature Decorators Feature names have an optional decorator showing status name* deferred name + effective name ++ redefined name : TYPE result type new_name { ^ CLASS_NAME. old_name } rename clause name : { TYPE aggregation result type name : TYPE input argument 17-17
18 Class Feature Signatures Each feature has a signature attributes name : TYPE queries name ( arg : ARG_TYPE;... ) : RESULT_TYPE commands name ( arg : ARG_TYPE;... ) Types may be expanded 17-18
19 Graphical View Rule Graphical view is not used for just one class Always have two or more classes with inheritance and/or uses relations among them 17-19
20 Views Show Part of a Design PAPER Inherits: REVIEW final_score : VALUE award_best_paper : BOOLEAN accept + reject + PRESENTATION code : VALUE title : VALUE authors : SET [ PERSON ] status : STATUS speakers : SET [ PERSON ] accept * reject * PAPER has other features not important for this view 17-20
21 Assertion Language Queries and commands can be documented with a precondition and a postcondition Follow Eiffel language with respect to inheritance and redefinition of assertions Use predicate calculus and set theory Graphical Form? precondition! postcondition the_invariant Textual Form require precondition ensure postcondition invariant the_invariant 17-21
BON Business Object Notation Based on slides by Prof. Paige
 BON Business Object Notation Based on slides by Prof. Paige 17-1 What is it? Notation for modeling object oriented software» Static: specifies classes, class relationships» Dynamic: behavioural properties
BON Business Object Notation Based on slides by Prof. Paige 17-1 What is it? Notation for modeling object oriented software» Static: specifies classes, class relationships» Dynamic: behavioural properties
BON Business Object Notation Based on slides by Prof. Paige
 BON Business Object Notation Based on slides by Prof. Paige 17-1 What is it? Notation for modeling object oriented software» Static: specifies classes, class relationships» Dynamic: behavioural properties
BON Business Object Notation Based on slides by Prof. Paige 17-1 What is it? Notation for modeling object oriented software» Static: specifies classes, class relationships» Dynamic: behavioural properties
BON Business Object Notation Largely based on slides by Prof. Paige
 BON Business Object Notation Largely based on slides by Prof. Paige 17-1 What is it? Notation for modelling object oriented software Two versions» graphical» textual Static notations for specifying classes,
BON Business Object Notation Largely based on slides by Prof. Paige 17-1 What is it? Notation for modelling object oriented software Two versions» graphical» textual Static notations for specifying classes,
Assertions! How to write correct programs and know it! Harlan Mills! Gunnar Gotshalks! 08-1
 Assertions How to write correct programs and know it Harlan Mills Gunnar Gotshalks 08-1 Assertions Boolean expressions or predicates that evaluate to true or false in every state In a program they express
Assertions How to write correct programs and know it Harlan Mills Gunnar Gotshalks 08-1 Assertions Boolean expressions or predicates that evaluate to true or false in every state In a program they express
Integrating BON and Object-Z
 Vol. 3, No. 3, March April 2004 Integrating BON and Object-Z Richard Paige, Department of Computer Science, University of York, U.K. Phillip J. Brooke, School of Computing, Communications, and Electronics,
Vol. 3, No. 3, March April 2004 Integrating BON and Object-Z Richard Paige, Department of Computer Science, University of York, U.K. Phillip J. Brooke, School of Computing, Communications, and Electronics,
ERC An object-oriented refinement calculus for Eiffel
 DOI 10.1007/s00165-003-0024-3 BCS 2004 Formal Aspects of Computing (2004) 16: 51 79 Formal Aspects of Computing ERC An object-oriented refinement calculus for Eiffel Richard F. Paige and Jonathan S. Ostroff
DOI 10.1007/s00165-003-0024-3 BCS 2004 Formal Aspects of Computing (2004) 16: 51 79 Formal Aspects of Computing ERC An object-oriented refinement calculus for Eiffel Richard F. Paige and Jonathan S. Ostroff
Precise and Formal Metamodeling with the Business Object Notation and PVS
 Precise and Formal Metamodeling with the Business Object Notation and PVS Richard F. Paige and Jonathan S. Ostroff Department of Computer Science York University Toronto, Ontario M3J 1P3, CANADA. fpaige,jonathang@cs.yorku.ca
Precise and Formal Metamodeling with the Business Object Notation and PVS Richard F. Paige and Jonathan S. Ostroff Department of Computer Science York University Toronto, Ontario M3J 1P3, CANADA. fpaige,jonathang@cs.yorku.ca
Multiple & Repeated! Inheritance!
 Multiple & Repeated Inheritance 21-1 Multiple Inheritance Example Combining two abstractions into one» COMPARABLE and NUMERIC are both useful abstractions > Some abstractions make use of both while others
Multiple & Repeated Inheritance 21-1 Multiple Inheritance Example Combining two abstractions into one» COMPARABLE and NUMERIC are both useful abstractions > Some abstractions make use of both while others
Multiple & Repeated Inheritance
 Multiple & Repeated Inheritance 21-1 Multiple Inheritance Example Combining two abstractions into one» COMPARABLE and NUMERIC are both useful abstractions > Some abstractions make use of both while others
Multiple & Repeated Inheritance 21-1 Multiple Inheritance Example Combining two abstractions into one» COMPARABLE and NUMERIC are both useful abstractions > Some abstractions make use of both while others
Spell Checker for EiffelStudio
 Spell Checker for EiffelStudio Software Engineering Laboratory: Open-Source EiffelStudio Semester project by Benjamin Fischer Student number: 10-916-971 Supervised by Julian Tschannen ETH Computer Science
Spell Checker for EiffelStudio Software Engineering Laboratory: Open-Source EiffelStudio Semester project by Benjamin Fischer Student number: 10-916-971 Supervised by Julian Tschannen ETH Computer Science
Object Oriented Programming
 Object Oriented Programming Primary object-oriented language concepts dynamic lookup encapsulation inheritance subtyping Program organization Organize concepts into objects and relationships between them
Object Oriented Programming Primary object-oriented language concepts dynamic lookup encapsulation inheritance subtyping Program organization Organize concepts into objects and relationships between them
Mock exam 1. ETH Zurich. Date: 9./10. November 2009
 Mock exam 1 ETH Zurich Date: 9./10. November 2009 Name: Group: 1 Terminology (8 points) Put checkmarks in the checkboxes corresponding to the correct answers. Multiple correct answers are possible; there
Mock exam 1 ETH Zurich Date: 9./10. November 2009 Name: Group: 1 Terminology (8 points) Put checkmarks in the checkboxes corresponding to the correct answers. Multiple correct answers are possible; there
Lecture 13: Introduction to inheritance and genericity
 Chair of Software Engineering Einführung in die Programmierung Introduction to Programming Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Lecture 13: Introduction to inheritance and genericity On the menu for today (& next
Chair of Software Engineering Einführung in die Programmierung Introduction to Programming Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Lecture 13: Introduction to inheritance and genericity On the menu for today (& next
Introduction to Eiffel
 Introduction to Eiffel Martin Nordio, Christian Estler ETH Zurich Distributed Software Engineering Lab 1 Overview Part 1: Language Constructs Ø Basics: definition, if then else, expressions, loops and
Introduction to Eiffel Martin Nordio, Christian Estler ETH Zurich Distributed Software Engineering Lab 1 Overview Part 1: Language Constructs Ø Basics: definition, if then else, expressions, loops and
Einführung in die Programmierung Introduction to Programming
 Chair of Software Engineering Einführung in die Programmierung Introduction to Programming Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Exercise Session 10 News Mock exam in 2 weeks (December 6 th, 7 th ) You have to be present
Chair of Software Engineering Einführung in die Programmierung Introduction to Programming Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Exercise Session 10 News Mock exam in 2 weeks (December 6 th, 7 th ) You have to be present
Example Test Questions for Inheritance
 2009 November 23 Example Test Questions for Inheritance 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Give and explain the type rule with genericity using an example method call. escribe constraint genericity.
2009 November 23 Example Test Questions for Inheritance 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Give and explain the type rule with genericity using an example method call. escribe constraint genericity.
Software Architecture 4. July 2005
 Chair of Software Engineering Bertrand Meyer Software Architecture 4. July 2005 Name, First name:... I confirm with my signature, that I was able to take this exam under regular conditions and that I have
Chair of Software Engineering Bertrand Meyer Software Architecture 4. July 2005 Name, First name:... I confirm with my signature, that I was able to take this exam under regular conditions and that I have
Assignment 7: Inheritance
 Assignment 7: Inheritance ETH Zurich Hand-out: 11 December 2006 Due: 19 December 2006 Calvin and Hobbes c Bill Watterson 1 Dynamic exercise Goal Understand the effects of dynamic binding. Summary Have
Assignment 7: Inheritance ETH Zurich Hand-out: 11 December 2006 Due: 19 December 2006 Calvin and Hobbes c Bill Watterson 1 Dynamic exercise Goal Understand the effects of dynamic binding. Summary Have
Universe Type System for Eiffel. Annetta Schaad
 Universe Type System for Eiffel Annetta Schaad Semester Project Report Software Component Technology Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich http://sct.inf.ethz.ch/ SS 2006 Supervised by: Dipl.-Ing.
Universe Type System for Eiffel Annetta Schaad Semester Project Report Software Component Technology Group Department of Computer Science ETH Zurich http://sct.inf.ethz.ch/ SS 2006 Supervised by: Dipl.-Ing.
Basic Structural Modeling. Copyright Joey Paquet,
 Basic Structural Modeling Copyright Joey Paquet, 2000 1 Part I Classes Copyright Joey Paquet, 2000 2 Classes Description of a set of objects sharing the same attributes, operations and semantics Abstraction
Basic Structural Modeling Copyright Joey Paquet, 2000 1 Part I Classes Copyright Joey Paquet, 2000 2 Classes Description of a set of objects sharing the same attributes, operations and semantics Abstraction
Patterns Example Exam Questions
 2014 November 27 Patterns Example Exam Questions 1.. Using on, give a generic static diagram of the pattern and include relevant interface s. 2. 3.. Give a scenario and object communication diagram
2014 November 27 Patterns Example Exam Questions 1.. Using on, give a generic static diagram of the pattern and include relevant interface s. 2. 3.. Give a scenario and object communication diagram
Introduction to Software Engineering. 5. Modeling Objects and Classes
 Introduction to Software Engineering 5. Modeling Objects and Classes Roadmap > UML Overview > Classes, attributes and operations > UML Lines and Arrows > Parameterized Classes, Interfaces and Utilities
Introduction to Software Engineering 5. Modeling Objects and Classes Roadmap > UML Overview > Classes, attributes and operations > UML Lines and Arrows > Parameterized Classes, Interfaces and Utilities
UC Santa Barbara. CS189A - Capstone. Christopher Kruegel Department of Computer Science UC Santa Barbara
 CS189A - Capstone Christopher Kruegel Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.ucsb.edu/~chris/ Design by Contract Design by Contract and the language that implements the Design by Contract principles
CS189A - Capstone Christopher Kruegel Department of Computer Science http://www.cs.ucsb.edu/~chris/ Design by Contract Design by Contract and the language that implements the Design by Contract principles
Design by Contract in Eiffel
 Design by Contract in Eiffel 2002/04/15 ctchen@canthink.com.com.tw.tw Reference & Resource Bertrand Meyer, Object-Oriented Oriented Software Construction 2nd,, 1997, PH. Bertrand Meyer, Eiffel: The Language,,
Design by Contract in Eiffel 2002/04/15 ctchen@canthink.com.com.tw.tw Reference & Resource Bertrand Meyer, Object-Oriented Oriented Software Construction 2nd,, 1997, PH. Bertrand Meyer, Eiffel: The Language,,
Motivation State Machines
 Motivation State Machines Generating test cases for complex behaviour Textbook Reading: Chapter 7 We are interested in testing the behaviour of object-oriented software systems Behaviour: Interactions
Motivation State Machines Generating test cases for complex behaviour Textbook Reading: Chapter 7 We are interested in testing the behaviour of object-oriented software systems Behaviour: Interactions
Software Development. Modular Design and Algorithm Analysis
 Software Development Modular Design and Algorithm Analysis Precondition and Postcondition To create a good algorithm, a programmer must be able to analyse a precondition (starting state) and a postcondition
Software Development Modular Design and Algorithm Analysis Precondition and Postcondition To create a good algorithm, a programmer must be able to analyse a precondition (starting state) and a postcondition
JOURNAL OF OBJECT TECHNOLOGY
 JOURNAL OF OBJECT TECHNOLOGY Online at www.jot.fm. Published by ETH Zurich, Chair of Software Engineering JOT, 2002 Vol. 1, no. 4, September-October 2002 Eiffel Assertions and the External Structure of
JOURNAL OF OBJECT TECHNOLOGY Online at www.jot.fm. Published by ETH Zurich, Chair of Software Engineering JOT, 2002 Vol. 1, no. 4, September-October 2002 Eiffel Assertions and the External Structure of
Chapter 3 (part 3) Describing Syntax and Semantics
 Chapter 3 (part 3) Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings
Chapter 3 (part 3) Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings
TDD + ESpec. Test-Driven Development. A test specifies a class interface. Test First Square Root of 10
 Test-Driven Development TDD + ESpec TDD Test Driven Design» Change in software development paradigm» Write tests before code!!! > Step One: write a little test > Step Two: make it pass > Step Three: refactor»
Test-Driven Development TDD + ESpec TDD Test Driven Design» Change in software development paradigm» Write tests before code!!! > Step One: write a little test > Step Two: make it pass > Step Three: refactor»
Chapter 4 Defining Classes I
 Chapter 4 Defining Classes I This chapter introduces the idea that students can create their own classes and therefore their own objects. Introduced is the idea of methods and instance variables as the
Chapter 4 Defining Classes I This chapter introduces the idea that students can create their own classes and therefore their own objects. Introduced is the idea of methods and instance variables as the
Object-Oriented Design
 Object-Oriented Design Lecturer: Raman Ramsin Lecture 15: Object-Oriented Principles 1 Open Closed Principle (OCP) Classes should be open for extension but closed for modification. OCP states that we should
Object-Oriented Design Lecturer: Raman Ramsin Lecture 15: Object-Oriented Principles 1 Open Closed Principle (OCP) Classes should be open for extension but closed for modification. OCP states that we should
The architecture of Eiffel software 3.1 OVERVIEW classes clusters systems
 3 Draft 5.02.00-0, 15 August 2005 (Santa Barbara). Extracted from ongoing work on future third edition of Eiffel: The Language. Copyright Bertrand Meyer 1986-2005. Access restricted to purchasers of the
3 Draft 5.02.00-0, 15 August 2005 (Santa Barbara). Extracted from ongoing work on future third edition of Eiffel: The Language. Copyright Bertrand Meyer 1986-2005. Access restricted to purchasers of the
Assignment 4: Object creation
 Assignment 4: Object creation ETH Zurich Hand-out: 15 November 2005 Due: 22 November 2005 Copyright FarWorks, Inc. Gary Larson 1 Summary Today you are going to write your rst stand-alone program. Please
Assignment 4: Object creation ETH Zurich Hand-out: 15 November 2005 Due: 22 November 2005 Copyright FarWorks, Inc. Gary Larson 1 Summary Today you are going to write your rst stand-alone program. Please
Chapter 1: Principles of Programming and Software Engineering
 Chapter 1: Principles of Programming and Software Engineering Data Abstraction & Problem Solving with C++ Fifth Edition by Frank M. Carrano Software Engineering and Object-Oriented Design Coding without
Chapter 1: Principles of Programming and Software Engineering Data Abstraction & Problem Solving with C++ Fifth Edition by Frank M. Carrano Software Engineering and Object-Oriented Design Coding without
Assertions & Design-by-Contract using JML Erik Poll University of Nijmegen
 Assertions & Design-by-Contract using JML Erik Poll University of Nijmegen Erik Poll - JML p.1/39 Overview Assertions Design-by-Contract for Java using JML Contracts and Inheritance Tools for JML Demo
Assertions & Design-by-Contract using JML Erik Poll University of Nijmegen Erik Poll - JML p.1/39 Overview Assertions Design-by-Contract for Java using JML Contracts and Inheritance Tools for JML Demo
Index. Index. More information. block statements 66 y 107 Boolean 107 break 55, 68 built-in types 107
 A abbreviations 17 abstract class 105 abstract data types 105 abstract method 105 abstract types 105 abstraction 92, 105 access level 37 package 114 private 115 protected 115 public 115 accessors 24, 105
A abbreviations 17 abstract class 105 abstract data types 105 abstract method 105 abstract types 105 abstraction 92, 105 access level 37 package 114 private 115 protected 115 public 115 accessors 24, 105
Assignment 2 - Specifications and Modeling
 Assignment 2 - Specifications and Modeling Exercise 1 A way to document the code is to use contracts. For this exercise, you will have to consider: preconditions: the conditions the caller of a method
Assignment 2 - Specifications and Modeling Exercise 1 A way to document the code is to use contracts. For this exercise, you will have to consider: preconditions: the conditions the caller of a method
Classes The Static Structure
 Classes The Static Structure Abstract data types equipped with a possibly partial implementation 04-1 Style Rules Read page 180 Pick a style and stick to it Recommend that you use Eiffel style or close
Classes The Static Structure Abstract data types equipped with a possibly partial implementation 04-1 Style Rules Read page 180 Pick a style and stick to it Recommend that you use Eiffel style or close
Object-Oriented Software Construction
 1 Object-Oriented Software Construction Bertrand Meyer 2 Lecture 21: Typing issues, covariance The America Conjecture 3 (Pierre America at TOOLS Europe 1990) One can have at most two of the three properties
1 Object-Oriented Software Construction Bertrand Meyer 2 Lecture 21: Typing issues, covariance The America Conjecture 3 (Pierre America at TOOLS Europe 1990) One can have at most two of the three properties
1. Quality issues (5 points)
 ETH Zurich Computer Science Course: Advanced Topics in Object Technology, by Bertrand Meyer Summer semester 2003 Exam (prepared by Karine Arnout) 2 July 2003 10:00 to 12:00 Name:.. Id-Nr:.. No notes, computers,
ETH Zurich Computer Science Course: Advanced Topics in Object Technology, by Bertrand Meyer Summer semester 2003 Exam (prepared by Karine Arnout) 2 July 2003 10:00 to 12:00 Name:.. Id-Nr:.. No notes, computers,
Multi-Methods in Racket
 Multi-Methods in Racket António Menezes Leitão April, 18, 2013 1 Introduction Multi-methods are an advanced concept that extends the single dispatch approach that is used in the majority of object-oriented
Multi-Methods in Racket António Menezes Leitão April, 18, 2013 1 Introduction Multi-methods are an advanced concept that extends the single dispatch approach that is used in the majority of object-oriented
A Eiffel: The Essentials
 A Eiffel: The Essentials This appix addresses people who are familiar with the object-oriented approach but not know Eiffel very well. It introduces all the concepts needed to understand the core of this
A Eiffel: The Essentials This appix addresses people who are familiar with the object-oriented approach but not know Eiffel very well. It introduces all the concepts needed to understand the core of this
Control flow in Eiffel
 Announcements Assignment will be posted this week.» We ll make sure you have enough time to it! A little more Eiffel, Genericity and ADTs Week 3, Lecture 4 January 16 Section N Review What is the definition
Announcements Assignment will be posted this week.» We ll make sure you have enough time to it! A little more Eiffel, Genericity and ADTs Week 3, Lecture 4 January 16 Section N Review What is the definition
Einführung in die Programmierung Introduction to Programming
 Chair of Software Engineering Einführung in die Programmierung Introduction to Programming Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Lecture 4: The Interface of a Class Client, supplier Definitions A client of a software
Chair of Software Engineering Einführung in die Programmierung Introduction to Programming Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer Lecture 4: The Interface of a Class Client, supplier Definitions A client of a software
Lecture 14: More Inheritance & Genericity
 Chair of Software Engineering Einführung in die Programmierung Introduction to Programming Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer October 2006 February 2007 MP1 Lecture 14: More Inheritance & Genericity 2 Genericity:
Chair of Software Engineering Einführung in die Programmierung Introduction to Programming Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer October 2006 February 2007 MP1 Lecture 14: More Inheritance & Genericity 2 Genericity:
BON-CASE: An Extensible CASE Tool for Formal Specification and Reasoning
 BON-CASE: An Extensible CASE Tool for Formal Specification and Reasoning Richard Paige Department of Computer Science, University of York, York, U.K. Liliya Kaminskaya AMDocs Inc., Toronto, Ontario, Canada
BON-CASE: An Extensible CASE Tool for Formal Specification and Reasoning Richard Paige Department of Computer Science, University of York, York, U.K. Liliya Kaminskaya AMDocs Inc., Toronto, Ontario, Canada
CITS5501 Software Testing and Quality Assurance Formal methods
 CITS5501 Software Testing and Quality Assurance Formal methods Unit coordinator: Arran Stewart May 1, 2018 1 / 49 Sources Pressman, R., Software Engineering: A Practitioner s Approach, McGraw-Hill, 2005
CITS5501 Software Testing and Quality Assurance Formal methods Unit coordinator: Arran Stewart May 1, 2018 1 / 49 Sources Pressman, R., Software Engineering: A Practitioner s Approach, McGraw-Hill, 2005
Programming Languages Third Edition
 Programming Languages Third Edition Chapter 12 Formal Semantics Objectives Become familiar with a sample small language for the purpose of semantic specification Understand operational semantics Understand
Programming Languages Third Edition Chapter 12 Formal Semantics Objectives Become familiar with a sample small language for the purpose of semantic specification Understand operational semantics Understand
From Z to BON/Eiffel
 From Z to BON/Eiel Richard F. Paige Jonathan S. Ostro Technical Report CS-98-05 July 7, 1998 Department of Computer Science 4700 Keele Street North York, Ontario M3J 1P3 Canada From Z to BON/Eiffel Richard
From Z to BON/Eiel Richard F. Paige Jonathan S. Ostro Technical Report CS-98-05 July 7, 1998 Department of Computer Science 4700 Keele Street North York, Ontario M3J 1P3 Canada From Z to BON/Eiffel Richard
CAT calls (Changed Availability or Type)
 Chair of Software Engineering CAT calls (Changed Availability or Type) these slides contain advanced material and are optional Changed Availability or Type (CAT) Changed Availability (export status) Lifting
Chair of Software Engineering CAT calls (Changed Availability or Type) these slides contain advanced material and are optional Changed Availability or Type (CAT) Changed Availability (export status) Lifting
Programming Languages. Benjamin J. Keller Department of Computer Science, Virginia Tech
 Programming Languages Eiffel Benjamin J. Keller Department of Computer Science, Virginia Tech Programming Languages Eiffel 2 Overview Classes and Objects Builtin types, constants and operations Expressions,
Programming Languages Eiffel Benjamin J. Keller Department of Computer Science, Virginia Tech Programming Languages Eiffel 2 Overview Classes and Objects Builtin types, constants and operations Expressions,
Fondamenti della Programmazione: Metodi Evoluti. Lezione 5: Invariants and Logic
 Fondamenti della Programmazione: Metodi Evoluti Prof. Enrico Nardelli Lezione 5: Invariants and Logic versione originale: http://touch.ethz.ch Reminder: contracts Associated with an individual feature:
Fondamenti della Programmazione: Metodi Evoluti Prof. Enrico Nardelli Lezione 5: Invariants and Logic versione originale: http://touch.ethz.ch Reminder: contracts Associated with an individual feature:
 CS6301 PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES II QUESTION BANK UNIT-I 2-marks ) Give some characteristics of procedure-oriented language. Emphasis is on doing things (algorithms). Larger programs are divided
CS6301 PROGRAMMING AND DATA STRUCTURES II QUESTION BANK UNIT-I 2-marks ) Give some characteristics of procedure-oriented language. Emphasis is on doing things (algorithms). Larger programs are divided
Test-Driven Development (TDD)
 Test-Driven Development (TDD) EECS3311 A: Software Design Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG DbC: Supplier DbC is supported natively in Eiffel for supplier: class ACCOUNT create make feature -- Attributes owner :
Test-Driven Development (TDD) EECS3311 A: Software Design Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG DbC: Supplier DbC is supported natively in Eiffel for supplier: class ACCOUNT create make feature -- Attributes owner :
Inheritance. Inheritance Reserved word protected Reserved word super Overriding methods Class Hierarchies Reading for this lecture: L&L
 Inheritance Inheritance Reserved word protected Reserved word super Overriding methods Class Hierarchies Reading for this lecture: L&L 9.1 9.4 1 Inheritance Inheritance allows a software developer to derive
Inheritance Inheritance Reserved word protected Reserved word super Overriding methods Class Hierarchies Reading for this lecture: L&L 9.1 9.4 1 Inheritance Inheritance allows a software developer to derive
Chapter 1: Programming Principles
 Chapter 1: Programming Principles Object Oriented Analysis and Design Abstraction and information hiding Object oriented programming principles Unified Modeling Language Software life-cycle models Key
Chapter 1: Programming Principles Object Oriented Analysis and Design Abstraction and information hiding Object oriented programming principles Unified Modeling Language Software life-cycle models Key
Automated Fixing of Programs with Contracts
 Automated Fixing of Programs with Contracts Yi Wei, Yu Pei, Carlo A. Furia, Lucas S. Silva, Stefan Buchholz, Bertrand Meyer and Andreas Zeller Chair of Software Engineering, ETH Zürich Software Engineering
Automated Fixing of Programs with Contracts Yi Wei, Yu Pei, Carlo A. Furia, Lucas S. Silva, Stefan Buchholz, Bertrand Meyer and Andreas Zeller Chair of Software Engineering, ETH Zürich Software Engineering
Object-Oriented Software Construction
 1 Object-Oriented Software Construction Bertrand Meyer 2 Lecture 2: EiffelStudio and project presentation Agenda for today 3 EiffelStudio: The ISE Eiffel environment Project presentation Agenda for today
1 Object-Oriented Software Construction Bertrand Meyer 2 Lecture 2: EiffelStudio and project presentation Agenda for today 3 EiffelStudio: The ISE Eiffel environment Project presentation Agenda for today
Singleton Pattern: Motivation. Design Patterns: Singleton and Iterator. What are design patterns? Shared Data through Inheritance
 Singleton Pattern: Motivation Design Patterns: Singleton and Iterator EECS3311: Software Design Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Consider two problems: 1. Bank accounts share a set of data. e.g., interest and exchange
Singleton Pattern: Motivation Design Patterns: Singleton and Iterator EECS3311: Software Design Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Consider two problems: 1. Bank accounts share a set of data. e.g., interest and exchange
Specification-based Testing of Embedded Systems H. Schlingloff, SEFM 2008
 SEFM School 2008 Specification-based Testing of Embedded Systems Prof. Dr. Holger Schlingloff Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Fraunhofer FIRST, Berlin Lecture 5: OCL, ParTeG Course Outline L1: Introduction
SEFM School 2008 Specification-based Testing of Embedded Systems Prof. Dr. Holger Schlingloff Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin and Fraunhofer FIRST, Berlin Lecture 5: OCL, ParTeG Course Outline L1: Introduction
Classes! The Static Structure!
 Classes The Static Structure Abstract data types equipped with a possibly partial implementation 04-1 Style Rules Pick a style and stick to it Recommend that you use Eiffel style or close approximation»
Classes The Static Structure Abstract data types equipped with a possibly partial implementation 04-1 Style Rules Pick a style and stick to it Recommend that you use Eiffel style or close approximation»
1) What is the primary purpose of template functions? 2) Suppose bag is a template class, what is the syntax for declaring a bag b of integers?
 Review for Final (Chapter 6 13, 15) 6. Template functions & classes 1) What is the primary purpose of template functions? A. To allow a single function to be used with varying types of arguments B. To
Review for Final (Chapter 6 13, 15) 6. Template functions & classes 1) What is the primary purpose of template functions? A. To allow a single function to be used with varying types of arguments B. To
CS 315 Software Design Homework 3 Preconditions, Postconditions, Invariants Due: Sept. 29, 11:30 PM
 CS 315 Software Design Homework 3 Preconditions, Postconditions, Invariants Due: Sept. 29, 11:30 PM Objectives Defining a wellformed method to check class invariants Using assert statements to check preconditions,
CS 315 Software Design Homework 3 Preconditions, Postconditions, Invariants Due: Sept. 29, 11:30 PM Objectives Defining a wellformed method to check class invariants Using assert statements to check preconditions,
Java Object Oriented Design. CSC207 Fall 2014
 Java Object Oriented Design CSC207 Fall 2014 Design Problem Design an application where the user can draw different shapes Lines Circles Rectangles Just high level design, don t write any detailed code
Java Object Oriented Design CSC207 Fall 2014 Design Problem Design an application where the user can draw different shapes Lines Circles Rectangles Just high level design, don t write any detailed code
Chapter 3. Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN
 Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN 0-321-49362-1 Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the
Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN 0-321-49362-1 Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the
Chapter 3. Describing Syntax and Semantics
 Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings of Programs:
Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics Chapter 3 Topics Introduction The General Problem of Describing Syntax Formal Methods of Describing Syntax Attribute Grammars Describing the Meanings of Programs:
Object Oriented Programming in Java. Jaanus Pöial, PhD Tallinn, Estonia
 Object Oriented Programming in Java Jaanus Pöial, PhD Tallinn, Estonia Motivation for Object Oriented Programming Decrease complexity (use layers of abstraction, interfaces, modularity,...) Reuse existing
Object Oriented Programming in Java Jaanus Pöial, PhD Tallinn, Estonia Motivation for Object Oriented Programming Decrease complexity (use layers of abstraction, interfaces, modularity,...) Reuse existing
Exercise 3: Objects, Design by Contract. Master Solution
 Exercise 3: Objects, Design by Contract Hand-out: 23 April 2004 Due: 30 April 2004 Master Solution 1. Summary: Objects, Design by Contract 1.1 Feature categories No result Command Procedure No result Routine
Exercise 3: Objects, Design by Contract Hand-out: 23 April 2004 Due: 30 April 2004 Master Solution 1. Summary: Objects, Design by Contract 1.1 Feature categories No result Command Procedure No result Routine
The Eiffel language. Slides partly based on :
 The Eiffel language Slides partly based on : http://se.inf.ethz.ch/courses/2015b_fall/eprog/english_index.html Eiffel, in brief Procedural, object-oriented programming language created by Bertrand Meyer
The Eiffel language Slides partly based on : http://se.inf.ethz.ch/courses/2015b_fall/eprog/english_index.html Eiffel, in brief Procedural, object-oriented programming language created by Bertrand Meyer
Object-Oriented Design
 Object-Oriented Design Department of Computer Engineering Lecture 12: Object-Oriented Principles Sharif University of Technology 1 Open Closed Principle (OCP) Classes should be open for extension but closed
Object-Oriented Design Department of Computer Engineering Lecture 12: Object-Oriented Principles Sharif University of Technology 1 Open Closed Principle (OCP) Classes should be open for extension but closed
Use of Generic Parameters Iterator and Singleton Patterns
 Use of Generic Parameters Iterator and Singleton Patterns EECS3311 A: Software Design Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Generic Collection Class: Motivation (1) class STRING _STACK feature {NONE} -- Implementation
Use of Generic Parameters Iterator and Singleton Patterns EECS3311 A: Software Design Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG Generic Collection Class: Motivation (1) class STRING _STACK feature {NONE} -- Implementation
Composite Structures
 Composite Structures Marie-Agnès Peraldi-Frati UNSA/I3S/INRIA map@unice.fr UML 2 Composition Model Purpose: improve the black diamond composition Supports connections between parts at the same level of
Composite Structures Marie-Agnès Peraldi-Frati UNSA/I3S/INRIA map@unice.fr UML 2 Composition Model Purpose: improve the black diamond composition Supports connections between parts at the same level of
Final Exam. Final Exam Review. Ch 1: Introduction: Object-oriented analysis, design, implementation. Exam Format
 Final Exam Final Exam Review CS 4354 Fall 2012 Jill Seaman Friday, December 14, 11AM Closed book, closed notes, clean desk Content: Textbook: Chapters 1, 2, 4-10 Java Lectures, GRASP + JUnit 35% of your
Final Exam Final Exam Review CS 4354 Fall 2012 Jill Seaman Friday, December 14, 11AM Closed book, closed notes, clean desk Content: Textbook: Chapters 1, 2, 4-10 Java Lectures, GRASP + JUnit 35% of your
Research Collection. Reusable mathematical models. Master Thesis. ETH Library. Author(s): Widmer, Tobias K. Publication Date: 2004
 Research Collection Master Thesis Reusable mathematical models Author(s): Widmer, Tobias K. Publication Date: 2004 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-005115737 Rights / License: In Copyright
Research Collection Master Thesis Reusable mathematical models Author(s): Widmer, Tobias K. Publication Date: 2004 Permanent Link: https://doi.org/10.3929/ethz-a-005115737 Rights / License: In Copyright
JAVA BASICS II. Example: FIFO
 JAVA BASICS II Example: FIFO To show how simple data structures are built without pointers, we ll build a doubly-linked list ListItem class has some user data first refers to that ListItem object at the
JAVA BASICS II Example: FIFO To show how simple data structures are built without pointers, we ll build a doubly-linked list ListItem class has some user data first refers to that ListItem object at the
EXAMINATIONS 2009 MID-TERM TEST. COMP 202 / SWEN 202 Formal Methods of Computer Science / Formal Foundations of Software Engineering WITH ANSWERS
 T E W H A R E W Ā N A N G A O T E Ū P O K O O T E I K A A M Ā U I VUW V I C T O R I A UNIVERSITY OF WELLINGTON Time Allowed: 90 minutes EXAMINATIONS 2009 MID-TERM TEST COMP 202 / SWEN 202 Formal Methods
T E W H A R E W Ā N A N G A O T E Ū P O K O O T E I K A A M Ā U I VUW V I C T O R I A UNIVERSITY OF WELLINGTON Time Allowed: 90 minutes EXAMINATIONS 2009 MID-TERM TEST COMP 202 / SWEN 202 Formal Methods
Generic Collection Class: Motivation (2) Use of Generic Parameters Iterator and Singleton Patterns
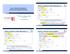 Generic Collection Class: Motivation (2) Use of Generic Parameters Iterator and Singleton Patterns EECS3311 A: Software Design Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG ACCOUNT _STACK {NONE -- Implementation imp: ARRAY[
Generic Collection Class: Motivation (2) Use of Generic Parameters Iterator and Singleton Patterns EECS3311 A: Software Design Fall 2018 CHEN-WEI WANG ACCOUNT _STACK {NONE -- Implementation imp: ARRAY[
An Annotated Language
 Hoare Logic An Annotated Language State and Semantics Expressions are interpreted as functions from states to the corresponding domain of interpretation Operators have the obvious interpretation Free of
Hoare Logic An Annotated Language State and Semantics Expressions are interpreted as functions from states to the corresponding domain of interpretation Operators have the obvious interpretation Free of
CS 215 Software Design Homework 3 Due: February 28, 11:30 PM
 CS 215 Software Design Homework 3 Due: February 28, 11:30 PM Objectives Specifying and checking class invariants Writing an abstract class Writing an immutable class Background Polynomials are a common
CS 215 Software Design Homework 3 Due: February 28, 11:30 PM Objectives Specifying and checking class invariants Writing an abstract class Writing an immutable class Background Polynomials are a common
Chapter 3. Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN
 Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN 0-321-49362-1 Chapter 3 Topics Describing the Meanings of Programs: Dynamic Semantics Copyright 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 2 Semantics There is no
Chapter 3 Describing Syntax and Semantics ISBN 0-321-49362-1 Chapter 3 Topics Describing the Meanings of Programs: Dynamic Semantics Copyright 2015 Pearson. All rights reserved. 2 Semantics There is no
Chapter B: Hierarchical Model
 Chapter B: Hierarchical Model Basic Concepts Tree-Structure Diagrams Data-Retrieval Facility Update Facility Virtual Records Mapping of Hierarchies to Files The IMS Database System B.1 Basic Concepts A
Chapter B: Hierarchical Model Basic Concepts Tree-Structure Diagrams Data-Retrieval Facility Update Facility Virtual Records Mapping of Hierarchies to Files The IMS Database System B.1 Basic Concepts A
An Integrated Development Environment for Business Object Notation
 An Integrated Development Environment for Business Object Notation Ralph Skinner A dissertation submitted in part fulfilment of the degree of MSc. in Advanced Software Engineering Supervisor: Dr. Joseph
An Integrated Development Environment for Business Object Notation Ralph Skinner A dissertation submitted in part fulfilment of the degree of MSc. in Advanced Software Engineering Supervisor: Dr. Joseph
Inheritance and Interfaces
 Inheritance and Interfaces Object Orientated Programming in Java Benjamin Kenwright Outline Review What is Inheritance? Why we need Inheritance? Syntax, Formatting,.. What is an Interface? Today s Practical
Inheritance and Interfaces Object Orientated Programming in Java Benjamin Kenwright Outline Review What is Inheritance? Why we need Inheritance? Syntax, Formatting,.. What is an Interface? Today s Practical
Advanced Database Applications. Object Oriented Database Management Chapter 13 10/29/2016. Object DBMSs
 Object Oriented Database Chapter 13 1 Object DBMSs Underlying concepts: Freely sharing data across processing routines creates unacceptable data dependencies All software should be constructed out of standard,
Object Oriented Database Chapter 13 1 Object DBMSs Underlying concepts: Freely sharing data across processing routines creates unacceptable data dependencies All software should be constructed out of standard,
EINDHOVEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
 EINDHOVEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mathematics & Computer Science Exam Programming Methods, 2IP15, Wednesday 17 April 2013, 09:00 12:00 TU/e THIS IS THE EXAMINER S COPY WITH (POSSIBLY INCOMPLETE)
EINDHOVEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY Department of Mathematics & Computer Science Exam Programming Methods, 2IP15, Wednesday 17 April 2013, 09:00 12:00 TU/e THIS IS THE EXAMINER S COPY WITH (POSSIBLY INCOMPLETE)
CS 4604: Introduction to Database Management Systems. B. Aditya Prakash Lecture #5: Entity/Relational Models---Part 1
 CS 4604: Introduction to Database Management Systems B. Aditya Prakash Lecture #5: Entity/Relational Models---Part 1 E/R: NOT IN BOOK! IMPORTANT: Follow only lecture slides for this topic! Differences
CS 4604: Introduction to Database Management Systems B. Aditya Prakash Lecture #5: Entity/Relational Models---Part 1 E/R: NOT IN BOOK! IMPORTANT: Follow only lecture slides for this topic! Differences
Lecture 16+17: Modeling with UML
 Chair of Software Engineering Software Engineering Spring Semester 2008 Slides: Based on KSE06 With kind permission of Peter Müller Lecture 16+17: Modeling with UML What is modeling? Building an abstraction
Chair of Software Engineering Software Engineering Spring Semester 2008 Slides: Based on KSE06 With kind permission of Peter Müller Lecture 16+17: Modeling with UML What is modeling? Building an abstraction
Lecture 15: Modeling with UML
 Chair of Software Engineering What is modeling? Software Engineering Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer March 2007 June 2007 Slides: Based on KSE06 With kind permission of Peter Müller Lecture 15: Modeling with
Chair of Software Engineering What is modeling? Software Engineering Prof. Dr. Bertrand Meyer March 2007 June 2007 Slides: Based on KSE06 With kind permission of Peter Müller Lecture 15: Modeling with
FreePascal changes: user documentation
 FreePascal changes: user documentation Table of Contents Jochem Berndsen February 2007 1Introduction...1 2Accepted syntax...2 Declarations...2 Statements...3 Class invariants...3 3Semantics...3 Definitions,
FreePascal changes: user documentation Table of Contents Jochem Berndsen February 2007 1Introduction...1 2Accepted syntax...2 Declarations...2 Statements...3 Class invariants...3 3Semantics...3 Definitions,
Introduction to Software Engineering. 5. Modeling Objects and Classes
 Introduction to Software Engineering 5. Modeling Objects and Classes Roadmap > UML Overview > Classes, attributes and operations > UML Lines and Arrows > Parameterized Classes, Interfaces and Utilities
Introduction to Software Engineering 5. Modeling Objects and Classes Roadmap > UML Overview > Classes, attributes and operations > UML Lines and Arrows > Parameterized Classes, Interfaces and Utilities
Object-Oriented Design
 Object-Oriented Design Lecture 14: Design Workflow Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology 1 UP iterations and workflow Workflows Requirements Analysis Phases Inception Elaboration
Object-Oriented Design Lecture 14: Design Workflow Department of Computer Engineering Sharif University of Technology 1 UP iterations and workflow Workflows Requirements Analysis Phases Inception Elaboration
SOFTWARE MODELING AND DESIGN. UML, Use Cases, Patterns, and. Software Architectures. Ki Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS. Hassan Gomaa
 SOFTWARE MODELING AND DESIGN UML, Use Cases, Patterns, and Software Architectures Hassan Gomaa George Mason University, Fairfax, Virginia Ki Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface P"U
SOFTWARE MODELING AND DESIGN UML, Use Cases, Patterns, and Software Architectures Hassan Gomaa George Mason University, Fairfax, Virginia Ki Cambridge UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents Preface P"U
JAVA CONCEPTS Early Objects
 INTERNATIONAL STUDENT VERSION JAVA CONCEPTS Early Objects Seventh Edition CAY HORSTMANN San Jose State University Wiley CONTENTS PREFACE v chapter i INTRODUCTION 1 1.1 Computer Programs 2 1.2 The Anatomy
INTERNATIONAL STUDENT VERSION JAVA CONCEPTS Early Objects Seventh Edition CAY HORSTMANN San Jose State University Wiley CONTENTS PREFACE v chapter i INTRODUCTION 1 1.1 Computer Programs 2 1.2 The Anatomy
Lecture 5 STRUCTURED ANALYSIS. PB007 So(ware Engineering I Faculty of Informa:cs, Masaryk University Fall Bühnová, Sochor, Ráček
 Lecture 5 STRUCTURED ANALYSIS PB007 So(ware Engineering I Faculty of Informa:cs, Masaryk University Fall 2015 1 Outline ² Yourdon Modern Structured Analysis (YMSA) Context diagram (CD) Data flow diagram
Lecture 5 STRUCTURED ANALYSIS PB007 So(ware Engineering I Faculty of Informa:cs, Masaryk University Fall 2015 1 Outline ² Yourdon Modern Structured Analysis (YMSA) Context diagram (CD) Data flow diagram
Hypertext A Case Study of Formal Object-Oriented Software Development
 Hypertext A Case Study of Formal Object-Oriented Software Development Andreas Rüping Forschungszentrum Informatik (FZI) Bereich Programmstrukturen Haid-und-Neu-Straße 10-14 D-76131 Karlsruhe e-mail: rueping@fzi.de
Hypertext A Case Study of Formal Object-Oriented Software Development Andreas Rüping Forschungszentrum Informatik (FZI) Bereich Programmstrukturen Haid-und-Neu-Straße 10-14 D-76131 Karlsruhe e-mail: rueping@fzi.de
Inheritance. OOP: Inheritance 1
 Inheritance Reuse Extension and intension Class specialization and class extension Inheritance The protected keyword revisited Inheritance and methods Method redefinition An widely used inheritance example
Inheritance Reuse Extension and intension Class specialization and class extension Inheritance The protected keyword revisited Inheritance and methods Method redefinition An widely used inheritance example
Topic : Object Oriented Design Principles
 Topic : Object Oriented Design Principles Software Engineering Faculty of Computing Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Objectives Describe the differences between requirements activities and design activities
Topic : Object Oriented Design Principles Software Engineering Faculty of Computing Universiti Teknologi Malaysia Objectives Describe the differences between requirements activities and design activities
Topics in Object-Oriented Design Patterns
 Software design Topics in Object-Oriented Design Patterns Material mainly from the book Design Patterns by Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson and John Vlissides; slides originally by Spiros Mancoridis;
Software design Topics in Object-Oriented Design Patterns Material mainly from the book Design Patterns by Erich Gamma, Richard Helm, Ralph Johnson and John Vlissides; slides originally by Spiros Mancoridis;
Abstract Data Types (ADTs), Classes, and Objects
 Abstract Data Types (ADTs), Classes, and Objects Readings: OOSC2 Chapters 6, 7, 8 EECS3311: Software Design Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Abstract Data Type (ADT) abstract implementation details are not specified!
Abstract Data Types (ADTs), Classes, and Objects Readings: OOSC2 Chapters 6, 7, 8 EECS3311: Software Design Fall 2017 CHEN-WEI WANG Abstract Data Type (ADT) abstract implementation details are not specified!
Motivation. Correct and maintainable software Cost effective software production Implicit assumptions easily broken
 Spec# Andreas Vida Motivation Correct and maintainable software Cost effective software production Implicit assumptions easily broken Need more formal f specification Integration into a popular language
Spec# Andreas Vida Motivation Correct and maintainable software Cost effective software production Implicit assumptions easily broken Need more formal f specification Integration into a popular language
