XPath and XQuery. Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018
|
|
|
- Valerie Harrington
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 XPath and XQuery Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018
2 2 Announcements (Tue. Oct. 23) Homework #3 due in two weeks Project milestone #1 feedback : we are a bit behind, but will definitely release it by Wed. morning Milestone #2 due in 2½ weeks To help you manage your team, we will require weekly updates from each team member on a private Piazza thread visible only to your team and the course staff Stay tuned for announcement Even though each project will receive a single score, I may adjust the score that a member gets if there is a flagrant case of irresponsibility
3 3 Query languages for XML XPath Path expressions with conditions FBuilding block of other standards (XQuery, XSLT, XLink, XPointer, etc.) XQuery XPath + full-fledged SQL-like query language XSLT: mostly used a stylesheet language XPath + transformation templates We are not going to cover it in this course
4 4 Example DTD and XML <?xml version="1.0"?> <!DOCTYPE bibliography [ <!ELEMENT bibliography (book+)> <!ELEMENT book (title, author*, publisher?, year?, section*)> <!ATTLIST book ISBN ID #REQUIRED> <!ATTLIST book price CDATA #IMPLIED> <!ELEMENT title (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT author (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT publisher (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT year (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT i (#PCDATA)> <!ELEMENT content (#PCDATA i)*> <!ELEMENT section (title, content?, section*)> ]> <bibliography> <book ISBN="ISBN-10" price="80.00"> <title>foundations of Databases</title> <author>abiteboul</author> <author>hull</author> <author>vianu</author> <publisher>addison Wesley</publisher> <year>1995</year> <section> </section> </book> </bibliography>
5 5 XPath XPath specifies path expressions that match XML data by navigating down (and occasionally up and across) the tree Example Query: /bibliography/book/author Like a file system path, except there can be multiple subdirectories with the same name Result: all author elements reachable from root via the path /bibliography/book/author
6 6 Basic XPath constructs / separator between steps in a path name matches any child element with this tag name * matches any child matches the attribute with this matches any attribute // matches any descendent element or the current element itself. matches the current element.. matches the parent element
7 7 Simple XPath examples All book titles /bibliography/book/title All book ISBN numbers All title elements, anywhere in the document //title All section titles, anywhere in the document //section/title Authors of bibliographical entries (suppose there are articles, reports, etc. in addition to books) /bibliography/*/author
8 8 Predicates in path expressions [condition]matches the current element if condition evaluates to true on the current element Books with price lower than $50 XPath will automatically convert the price string to a numeric value for comparison Books with author Abiteboul /bibliography/book[author='abiteboul'] Books with a publisher child element /bibliography/book[publisher] Prices of books authored by Abiteboul /bibliography/book[author='abiteboul']/@price
9 9 More complex predicates Predicates can use and, or, and not Books with price between $40 and $50 Books authored by Abiteboul or those with price no lower than $50 /bibliography/book[author='abiteboul' /bibliography/book[author='abiteboul' or Any difference between these two queries?
10 10 Predicates involving node-sets /bibliography/book[author='abiteboul'] There may be multiple authors, so author in general returns a node-set (in XPath terminology) The predicate evaluates to true as long as it evaluates true for at least one node in the node-set, i.e., at least one author is Abiteboul Tricky query /bibliography/book[author='abiteboul' and author!='abiteboul'] Will it return any books?
11 11 XPath operators and functions Frequently used in conditions: x + y, x y, x * y, x div y, x mod y contains(x, y) true if string x contains string y count(node-set) counts the number nodes in node-set position() returns the context position (roughly, the position of the current node in the nodeset containing it) last() returns the context size (roughly, the size of the node-set containing the current node) name() returns the tag name of the current element
12 12 More XPath examples All elements whose tag names contain section (e.g., subsection ) //*[contains(name(), 'section')] Title of the first section in each book /bibliography/book/section[position()=1]/title A shorthand: /bibliography/book/section[1]/title Title of the last section in each book /bibliography/book/section[position()=last()]/title Books with fewer than 10 sections /bibliography/book[count(section)<10] All elements whose parent s tag name is not book //*[name()!='book']/*
13 13 A tricky example Suppose for a moment that price is a child element of book, and there may be multiple prices per book Books with some price in range [20, 50] Wrong answer: /bibliography/book [price >= 20 and price <= 50] Correct answer: /bibliography/book [price[. >= 20 and. <= 50]]
14 14 De-referencing IDREF s id(identifier) returns the element with identifier Suppose that books can reference other books <section><title>introduction</title> XML is a hot topic these days; see <bookref ISBN="ISBN-10"/> for more details </section> Find all references to books written by Abiteboul in the book with ISBN-10 /bibliography/book[@isbn='isbn-10'] //bookref[id(@isbn)/author='abiteboul'] Or simply: id('isbn-10')//bookref[id(@isbn)/author='abiteboul']
15 15 General XPath location steps Technically, each XPath query consists of a series of location steps separated by / Each location step consists of An axis: one of self, attribute, parent, child, ancestor, ancestor-or-self, descendant, descendant-or-self, following, followingsibling, preceding, preceding-sibling, and namespace A node-test: either a name test (e.g., book, section, *) or a type test (e.g., text(), node(), comment()), separated from the axis by :: Zero of more predicates (or conditions) enclosed in square brackets These reverse axes produce result node-sets in reverse document order; others (forward axes) produce node-sets in document order
16 16 Example of verbose syntax Verbose (axis, node test, predicate): /child::bibliography /child::book[attribute::isbn='isbn-10'] /descendant-or-self::node() /child::title Abbreviated: child is the default axis // stands for /descendant-or-self::node()/
17 Some technical details on evaluation 17 Given a context node, evaluate a location path as follows: 1. Start with node-set! = {context node} 2.For each location step, from left to right: " For each node % in!: Using % as the context node, compute a node-set! & from the axis and the node-test Each predicate in turn filters! &, in order For each node % & in! &, evaluate predicate with the following context: Context node is % & Context size is the number of nodes in! & Context position is the position of % within! & " "! &! " 3.Return!
18 18 One more example Which of the following queries correctly find the third author in the entire input document? //author[position()=3] Same as /descendant-or-self::node()/author[position()=3] Finds all third authors (for each publication) /descendant-or-self::node() [name()='author' and position()=3] Returns the third element or text node in the document if it is an author /descendant-or-self::node() [name()='author'] [position()=3] Correct! After the first condition is passed, the evaluation context changes: Context size: # of nodes that passed the first condition Context position: position of the context node within the list of nodes
19 19 XQuery XPath + full-fledged SQL-like query language XQuery expressions can be XPath expressions FLWOR expressions Quantified expressions Aggregation, sorting, and more An XQuery expression in general can return a new result XML document Compare with an XPath expression, which always returns a sequence of nodes from the input document or atomic values (boolean, number, string, etc.)
20 20 A simple XQuery based on XPath Find all books with price lower than $50 <result>{ doc("bib.xml")/bibliography/book[@price<50] }</result> Things outside {} s are copied to output verbatim Things inside {} s are evaluated and replaced by the results doc("bib.xml") specifies the document to query Can be omitted if there is a default context document The XPath expression returns a sequence of book elements These elements (including all their descendants) are copied to output
21 21 FLWR expressions Retrieve the titles of books published before 2000, together with their publisher <result>{ for $b in doc("bib.xml")/bibliography/book let $p := $b/publisher where $b/year < 2000 return <book> { $b/title } { $p } </book> }</result> for: loop $b ranges over the result sequence, getting one item at a time let: assignment $p gets the entire result of $b/publisher (possibly many nodes) where: filtering by condition return: result structuring Invoked in the innermost loop, i.e., once for each successful binding of all query variables that satisfies where
22 22 An equivalent formulation Retrieve the titles of books published before 2000, together with their publisher <result>{ for $b in doc("bib.xml")/bibliography/book[year<2000] return <book> { $b/title } { $b/publisher } </book> }</result>
23 23 Another formulation Retrieve the titles of books published before 2000, together with their publisher <result>{ for $b in doc("bib.xml")/bibliography/book, $p in $b/publisher where $b/year < 2000 return <book> { $b/title } { $p } </book> }</result> Nested loop Is this query equivalent to the previous two? Yes, if there is one publisher per book No, in general Two result book elements will be created for a book with two publishers No result book element will be created for a book with no publishers
24 24 Yet another formulation Retrieve the titles of books published before 2000, together with their publisher <result>{ let $b := doc("bib.xml")/bibliography/book where $b/year < 2000 return <book> { $b/title } { $b/publisher } </book> }</result> Is this query correct? No! It will produce only one output book element, with all titles clumped together and all publishers clumped together All books will be processed (as long as one is published before 2000)
25 25 Subqueries in return Extract book titles and their authors; make title an attribute and rename author to writer <bibliography>{ for $b in doc("bib.xml")/bibliography/book return <book title="{normalize-space($b/title)}">{ for $a in $b/author return <writer>{string($a)}</writer> }</book> }</bibliography> normalize-space(string) removes leading and trailing spaces from string, and replaces all internal sequences of white spaces with one white space What happens if we replace it with $a?
26 26 An explicit join Find pairs of books that have common author(s) <result>{ for $b1 in doc("bib.xml")//book for $b2 in doc("bib.xml")//book where $b1/author = $b2/author and $b1/title > $b2/title return <pair> {$b1/title} {$b2/title} </pair> }</result> These are string comparisons, not identity comparisons!
27 27 Existentially quantified expressions (some $var in collection satisfies condition) Can be used in where as a condition Find titles of books in which XML is mentioned in some section <result>{ for $b in doc("bib.xml")//book where (some $section in $b//section satisfies contains(string($section), "XML")) return $b/title }</result>
28 28 Universally quantified expressions (every $var in collection satisfies condition) Can be used in where as a condition Find titles of books in which XML is mentioned in every section <result>{ for $b in doc("bib.xml")//book where (every $section in $b//section satisfies contains(string($section), "XML")) return $b/title }</result>
29 29 Aggregation (poor man s version) List each publisher and the average prices of all its books <result>{ for $pub in distinct-values(doc("bib.xml")//publisher) let $price := avg(doc("bib.xml")//book[publisher=$pub]/@price) return <publisherpricing> <publisher>{$pub}</publisher> <avgprice>{$price}</avgprice> </publisherpricing> }</result> distinct-values(collection) removes duplicates by value If the collection consists of elements (with no explicitly declared types), they are first converted to strings representing their normalized contents avg(collection) computes the average of collection (assuming each item in collection can be converted to a numeric value)
30 30 Conditional expression List each publisher and, only if applicable, the average prices of all its books <result>{ for $pub in distinct-values(doc("bib.xml")//publisher) let $price := return <publisherpricing> <publisher>{$pub}</publisher> { if ($price) then <avgprice>{$price}</avgprice> else () } </publisherpricing> }</result> Use anywhere you d expect a value, e.g.: let $foo := if ( ) then else Empty list nothing return <bar blah="{ if ( ) then else }"/>
31 31 Aggregation (XQuery >1.0) A new group by clause <result>{ for $book in doc("bib.xml")//book let $pub := string($book/publisher) group by $pub return <publisherpricing> <publisher>{$pub}</publisher> <avgprice>{avg($book/@price)}</avgprice> </publisherpricing> }</result> After the group by clause, for each group, any nongrouping variable (e.g., $book) becomes a a sequence of values that this variable takes for all members of that group Not supported by our saxonb-xquery tool (which only supports XQuery 1.0)
32 32 Sorting (a brief history) A path expression in XPath returns a sequence of nodes according to original document order for loop will respect the ordering in the sequence August 2002 ( Introduce an operator sort by (sort-by-expression-list) to output results in a user-specified order Example: list all books with price higher than $100, in order by first author; for books with the same first author, order by title <result>{ doc("bib.xml")//book[@price>100] sort by (author[1], title) }</result>
33 33 Tricky semantics List titles of all books, sorted by their ISBN <result>{ (doc("bib.xml")//book sort by WRONG! }</result> What is wrong? The last step in the path expression will return nodes in document order! Correct versions <result>{ for $b in doc("bib.xml")//book sort by return $b/title }</result> <result>{ doc("bib.xml")//book/title sort by }</result>
34 34 Current version of sorting Since June 2006 sort by has been ditched A new order by clause is added to FLWR Which now becomes FLWOR Example: list all books in order by price from high to low; for books with the same price, sort by first author and then title <result>{ for $b in doc("bib.xml")//book[@price>100] stable order by number($b/price) descending, $b/author[1], $b/title empty least return $b }</result> Preserve input order Order as number, not string Override default (ascending) Empty value considered smallest
35 35 Summary Many, many more features not covered in class XPath is very mature, stable, and widely used Has good implementations in many systems Is used in many other standards XQuery is also fairly popular Has become the SQL for XML Has good implementations in some systems
36 36 XQuery vs. SQL Where did the join go? Is navigational query going to destroy physical data independence? Strong ordering constraint Can be overridden by unordered { for } Why does that matter?
XML, DTD, and XPath. Announcements. From HTML to XML (extensible Markup Language) CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems. Midterm has been graded
 XML, DTD, and XPath CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems Announcements 2 Midterm has been graded Graded exams available in my office Grades posted on Blackboard Sample solution and score distribution
XML, DTD, and XPath CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems Announcements 2 Midterm has been graded Graded exams available in my office Grades posted on Blackboard Sample solution and score distribution
XQuery. Announcements (March 21) XQuery. CPS 216 Advanced Database Systems
 XQuery CPS 216 Advanced Database Systems Announcements (March 21) 2 Midterm has been graded Homework #3 will be assigned next Tuesday Reading assignment due next Wednesday XML processing in Lore (VLDB
XQuery CPS 216 Advanced Database Systems Announcements (March 21) 2 Midterm has been graded Homework #3 will be assigned next Tuesday Reading assignment due next Wednesday XML processing in Lore (VLDB
XML-XQuery and Relational Mapping. Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Spring 2017
 XML-XQuery and Relational Mapping Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Spring 2017 2 Announcements (Wed., Apr. 12) Homework #4 due Monday, April 24, 11:55 pm 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, X1 is posted Please start early
XML-XQuery and Relational Mapping Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Spring 2017 2 Announcements (Wed., Apr. 12) Homework #4 due Monday, April 24, 11:55 pm 4.1, 4.2, 4.3, X1 is posted Please start early
TDDD43. Theme 1.2: XML query languages. Fang Wei- Kleiner h?p:// TDDD43
 Theme 1.2: XML query languages Fang Wei- Kleiner h?p://www.ida.liu.se/~ Query languages for XML Xpath o Path expressions with conditions o Building block of other standards (XQuery, XSLT, XLink, XPointer,
Theme 1.2: XML query languages Fang Wei- Kleiner h?p://www.ida.liu.se/~ Query languages for XML Xpath o Path expressions with conditions o Building block of other standards (XQuery, XSLT, XLink, XPointer,
XSLT. Announcements (October 24) XSLT. CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems. Homework #3 due next Tuesday Project milestone #2 due November 9
 XSLT CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems Announcements (October 24) 2 Homework #3 due next Tuesday Project milestone #2 due November 9 XSLT 3 XML-to-XML rule-based transformation language Used most
XSLT CPS 116 Introduction to Database Systems Announcements (October 24) 2 Homework #3 due next Tuesday Project milestone #2 due November 9 XSLT 3 XML-to-XML rule-based transformation language Used most
XML databases. Jan Chomicki. University at Buffalo. Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 1 / 9
 XML databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 1 / 9 Outline 1 XML data model 2 XPath 3 XQuery Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 2
XML databases Jan Chomicki University at Buffalo Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 1 / 9 Outline 1 XML data model 2 XPath 3 XQuery Jan Chomicki (University at Buffalo) XML databases 2
Querying XML. COSC 304 Introduction to Database Systems. XML Querying. Example DTD. Example XML Document. Path Descriptions in XPath
 COSC 304 Introduction to Database Systems XML Querying Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Querying XML We will look at two standard query languages: XPath
COSC 304 Introduction to Database Systems XML Querying Dr. Ramon Lawrence University of British Columbia Okanagan ramon.lawrence@ubc.ca Querying XML We will look at two standard query languages: XPath
XML in Databases. Albrecht Schmidt. al. Albrecht Schmidt, Aalborg University 1
 XML in Databases Albrecht Schmidt al@cs.auc.dk http://www.cs.auc.dk/ al Albrecht Schmidt, Aalborg University 1 What is XML? (1) Where is the Life we have lost in living? Where is the wisdom we have lost
XML in Databases Albrecht Schmidt al@cs.auc.dk http://www.cs.auc.dk/ al Albrecht Schmidt, Aalborg University 1 What is XML? (1) Where is the Life we have lost in living? Where is the wisdom we have lost
XML-Relational Mapping. Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2014
 XML-Relational Mapping Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2014 2 Approaches to XML processing Text files/messages Specialized XML DBMS Tamino(Software AG), BaseX, exist, Sedna, Not as mature as
XML-Relational Mapping Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2014 2 Approaches to XML processing Text files/messages Specialized XML DBMS Tamino(Software AG), BaseX, exist, Sedna, Not as mature as
XSLT program. XSLT elements. XSLT example. An XSLT program is an XML document containing
 XSLT CPS 216 Advanced Database Systems Announcements (March 24) 2 Homework #3 will be assigned next Tuesday Reading assignment due next Wednesday XML processing in Lore (VLDB 1999) and Niagara (VLDB 2003)
XSLT CPS 216 Advanced Database Systems Announcements (March 24) 2 Homework #3 will be assigned next Tuesday Reading assignment due next Wednesday XML processing in Lore (VLDB 1999) and Niagara (VLDB 2003)
One of the main selling points of a database engine is the ability to make declarative queries---like SQL---that specify what should be done while
 1 One of the main selling points of a database engine is the ability to make declarative queries---like SQL---that specify what should be done while leaving the engine to choose the best way of fulfilling
1 One of the main selling points of a database engine is the ability to make declarative queries---like SQL---that specify what should be done while leaving the engine to choose the best way of fulfilling
JSON & MongoDB. Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018
 JSON & MongoDB Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018 2 Announcements (Tue. Oct. 30) Homework #3 due next Tuesday Project milestone #2 due next Thursday See email about new requirement on weekly
JSON & MongoDB Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018 2 Announcements (Tue. Oct. 30) Homework #3 due next Tuesday Project milestone #2 due next Thursday See email about new requirement on weekly
Query Languages for XML
 Query Languages for XML XPath XQuery 1 The XPath/XQuery Data Model Corresponding to the fundamental relation of the relational model is: sequence of items. An item is either: 1. A primitive value, e.g.,
Query Languages for XML XPath XQuery 1 The XPath/XQuery Data Model Corresponding to the fundamental relation of the relational model is: sequence of items. An item is either: 1. A primitive value, e.g.,
Course: The XPath Language
 1 / 27 Course: The XPath Language Pierre Genevès CNRS University of Grenoble, 2012 2013 2 / 27 Why XPath? Search, selection and extraction of information from XML documents are essential for any kind of
1 / 27 Course: The XPath Language Pierre Genevès CNRS University of Grenoble, 2012 2013 2 / 27 Why XPath? Search, selection and extraction of information from XML documents are essential for any kind of
Semi-structured Data. 8 - XPath
 Semi-structured Data 8 - XPath Andreas Pieris and Wolfgang Fischl, Summer Term 2016 Outline XPath Terminology XPath at First Glance Location Paths (Axis, Node Test, Predicate) Abbreviated Syntax What is
Semi-structured Data 8 - XPath Andreas Pieris and Wolfgang Fischl, Summer Term 2016 Outline XPath Terminology XPath at First Glance Location Paths (Axis, Node Test, Predicate) Abbreviated Syntax What is
XPath. Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University
 XPath Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University 1 Overview What is XPath? Queries The XPath Data Model Location Paths Expressions
XPath Asst. Prof. Dr. Kanda Runapongsa Saikaew (krunapon@kku.ac.th) Dept. of Computer Engineering Khon Kaen University 1 Overview What is XPath? Queries The XPath Data Model Location Paths Expressions
H2 Spring B. We can abstract out the interactions and policy points from DoDAF operational views
 1. (4 points) Of the following statements, identify all that hold about architecture. A. DoDAF specifies a number of views to capture different aspects of a system being modeled Solution: A is true: B.
1. (4 points) Of the following statements, identify all that hold about architecture. A. DoDAF specifies a number of views to capture different aspects of a system being modeled Solution: A is true: B.
XML Query Languages. Yanlei Diao UMass Amherst April 22, Slide content courtesy of Ramakrishnan & Gehrke, Donald Kossmann, and Gerome Miklau
 XML Query Languages Yanlei Diao UMass Amherst April 22, 2008 Slide content courtesy of Ramakrishnan & Gehrke, Donald Kossmann, and Gerome Miklau 1 Querying XML How do you query a directed graph? a tree?
XML Query Languages Yanlei Diao UMass Amherst April 22, 2008 Slide content courtesy of Ramakrishnan & Gehrke, Donald Kossmann, and Gerome Miklau 1 Querying XML How do you query a directed graph? a tree?
Progress Report on XQuery
 Progress Report on XQuery Don Chamberlin Almaden Research Center May 24, 2002 History Dec. '98: W3C sponsors workshop on XML Query Oct. '99: W3C charters XML Query working group Chair: Paul Cotton About
Progress Report on XQuery Don Chamberlin Almaden Research Center May 24, 2002 History Dec. '98: W3C sponsors workshop on XML Query Oct. '99: W3C charters XML Query working group Chair: Paul Cotton About
XML Data Management. 6. XPath 1.0 Principles. Werner Nutt
 XML Data Management 6. XPath 1.0 Principles Werner Nutt 1 XPath Expressions and the XPath Document Model XPath expressions are evaluated over documents XPath operates on an abstract document structure
XML Data Management 6. XPath 1.0 Principles Werner Nutt 1 XPath Expressions and the XPath Document Model XPath expressions are evaluated over documents XPath operates on an abstract document structure
XML Technologies. Doc. RNDr. Irena Holubova, Ph.D. Web pages:
 XML Technologies Doc. RNDr. Irena Holubova, Ph.D. holubova@ksi.mff.cuni.cz Web pages: http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~holubova/nprg036/ Outline Introduction to XML format, overview of XML technologies DTD
XML Technologies Doc. RNDr. Irena Holubova, Ph.D. holubova@ksi.mff.cuni.cz Web pages: http://www.ksi.mff.cuni.cz/~holubova/nprg036/ Outline Introduction to XML format, overview of XML technologies DTD
Big Data 12. Querying
 Ghislain Fourny Big Data 12. Querying pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo Declarative Languages What vs. How 2 Functional Languages for let order by if + any else = then every while where return exit with Expression
Ghislain Fourny Big Data 12. Querying pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo Declarative Languages What vs. How 2 Functional Languages for let order by if + any else = then every while where return exit with Expression
XML. Rodrigo García Carmona Universidad San Pablo-CEU Escuela Politécnica Superior
 XML Rodrigo García Carmona Universidad San Pablo-CEU Escuela Politécnica Superior XML INTRODUCTION 2 THE XML LANGUAGE XML: Extensible Markup Language Standard for the presentation and transmission of information.
XML Rodrigo García Carmona Universidad San Pablo-CEU Escuela Politécnica Superior XML INTRODUCTION 2 THE XML LANGUAGE XML: Extensible Markup Language Standard for the presentation and transmission of information.
Big Data 10. Querying
 Ghislain Fourny Big Data 10. Querying pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo 1 Declarative Languages What vs. How 2 Functional Languages for let order by if + any else = then every while where return exit with Expression
Ghislain Fourny Big Data 10. Querying pinkyone / 123RF Stock Photo 1 Declarative Languages What vs. How 2 Functional Languages for let order by if + any else = then every while where return exit with Expression
XML: Extensible Markup Language
 XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
XML: Extensible Markup Language CSC 375, Fall 2015 XML is a classic political compromise: it balances the needs of man and machine by being equally unreadable to both. Matthew Might Slides slightly modified
XML. Document Type Definitions. Database Systems and Concepts, CSCI 3030U, UOIT, Course Instructor: Jarek Szlichta
 XML Document Type Definitions 1 XML XML stands for extensible Markup Language. XML was designed to describe data. XML has come into common use for the interchange of data over the Internet. 2 Well-Formed
XML Document Type Definitions 1 XML XML stands for extensible Markup Language. XML was designed to describe data. XML has come into common use for the interchange of data over the Internet. 2 Well-Formed
Course: The XPath Language
 1 / 30 Course: The XPath Language Pierre Genevès CNRS University of Grenoble Alpes, 2017 2018 2 / 30 Why XPath? Search, selection and extraction of information from XML documents are essential for any
1 / 30 Course: The XPath Language Pierre Genevès CNRS University of Grenoble Alpes, 2017 2018 2 / 30 Why XPath? Search, selection and extraction of information from XML documents are essential for any
XPath Expression Syntax
 XPath Expression Syntax SAXON home page Contents Introduction Constants Variable References Parentheses and operator precedence String Expressions Boolean Expressions Numeric Expressions NodeSet expressions
XPath Expression Syntax SAXON home page Contents Introduction Constants Variable References Parentheses and operator precedence String Expressions Boolean Expressions Numeric Expressions NodeSet expressions
XML. Semi-structured data (SSD) SSD Graphs. SSD Examples. Schemas for SSD. More flexible data model than the relational model.
 Semi-structured data (SSD) XML Semistructured data XML, DTD, (XMLSchema) XPath, XQuery More flexible data model than the relational model. Think of an object structure, but with the type of each object
Semi-structured data (SSD) XML Semistructured data XML, DTD, (XMLSchema) XPath, XQuery More flexible data model than the relational model. Think of an object structure, but with the type of each object
Chapter 1: Semistructured Data Management XML
 Chapter 1: Semistructured Data Management XML XML - 1 The Web has generated a new class of data models, which are generally summarized under the notion semi-structured data models. The reasons for that
Chapter 1: Semistructured Data Management XML XML - 1 The Web has generated a new class of data models, which are generally summarized under the notion semi-structured data models. The reasons for that
Informatics 1: Data & Analysis
 T O Y H Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 26 February 2013 Semester 2 Week 6 E H U N I V E R S I
T O Y H Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 26 February 2013 Semester 2 Week 6 E H U N I V E R S I
Querying XML Data. Querying XML has two components. Selecting data. Construct output, or transform data
 Querying XML Data Querying XML has two components Selecting data pattern matching on structural & path properties typical selection conditions Construct output, or transform data construct new elements
Querying XML Data Querying XML has two components Selecting data pattern matching on structural & path properties typical selection conditions Construct output, or transform data construct new elements
Copyright 2007 Ramez Elmasri and Shamkant B. Navathe. Slide 27-1
 Slide 27-1 Chapter 27 XML: Extensible Markup Language Chapter Outline Introduction Structured, Semi structured, and Unstructured Data. XML Hierarchical (Tree) Data Model. XML Documents, DTD, and XML Schema.
Slide 27-1 Chapter 27 XML: Extensible Markup Language Chapter Outline Introduction Structured, Semi structured, and Unstructured Data. XML Hierarchical (Tree) Data Model. XML Documents, DTD, and XML Schema.
Chapter 1: Semistructured Data Management XML
 Chapter 1: Semistructured Data Management XML 2006/7, Karl Aberer, EPFL-IC, Laboratoire de systèmes d'informations répartis XML - 1 The Web has generated a new class of data models, which are generally
Chapter 1: Semistructured Data Management XML 2006/7, Karl Aberer, EPFL-IC, Laboratoire de systèmes d'informations répartis XML - 1 The Web has generated a new class of data models, which are generally
XML & Databases. Tutorial. 3. XPath Queries. Universität Konstanz. Database & Information Systems Group Prof. Marc H. Scholl
 XML & Databases Tutorial Christian Grün, Database & Information Systems Group University of, Winter 2007/08 XPath Introduction navigational access to XML documents sub-language in XQuery, XSLT, or XPointer
XML & Databases Tutorial Christian Grün, Database & Information Systems Group University of, Winter 2007/08 XPath Introduction navigational access to XML documents sub-language in XQuery, XSLT, or XPointer
Semi-structured Data: Programming. Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018
 Semi-structured Data: Programming Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018 2 Announcements (Thu., Nov. 1) Homework #3 due next Tuesday Project milestone #2 due next Thursday But remember your brief
Semi-structured Data: Programming Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2018 2 Announcements (Thu., Nov. 1) Homework #3 due next Tuesday Project milestone #2 due next Thursday But remember your brief
XPath an XML query language
 XPath an XML query language Some XML query languages: XML-QL XPath XQuery Many others 1 XML-QL http://www.w3.org/tr/note-xml-ql (8/98) Features: regular path expressions patterns, templates Skolem Functions
XPath an XML query language Some XML query languages: XML-QL XPath XQuery Many others 1 XML-QL http://www.w3.org/tr/note-xml-ql (8/98) Features: regular path expressions patterns, templates Skolem Functions
XPath. Lecture 36. Robb T. Koether. Wed, Apr 16, Hampden-Sydney College. Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, / 28
 XPath Lecture 36 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 16, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, 2014 1 / 28 1 XPath 2 Executing XPath Expressions 3 XPath Expressions
XPath Lecture 36 Robb T. Koether Hampden-Sydney College Wed, Apr 16, 2014 Robb T. Koether (Hampden-Sydney College) XPath Wed, Apr 16, 2014 1 / 28 1 XPath 2 Executing XPath Expressions 3 XPath Expressions
EXtensible Markup Language (XML) a W3C standard to complement HTML A markup language much like HTML
 XML and XPath EXtensible Markup Language (XML) a W3C standard to complement HTML A markup language much like HTML origins: structured text SGML motivation: HTML describes presentation XML describes content
XML and XPath EXtensible Markup Language (XML) a W3C standard to complement HTML A markup language much like HTML origins: structured text SGML motivation: HTML describes presentation XML describes content
XML and Databases. Lecture 10 XPath Evaluation using RDBMS. Sebastian Maneth NICTA and UNSW
 XML and Databases Lecture 10 XPath Evaluation using RDBMS Sebastian Maneth NICTA and UNSW CSE@UNSW -- Semester 1, 2009 Outline 1. Recall pre / post encoding 2. XPath with //, ancestor, @, and text() 3.
XML and Databases Lecture 10 XPath Evaluation using RDBMS Sebastian Maneth NICTA and UNSW CSE@UNSW -- Semester 1, 2009 Outline 1. Recall pre / post encoding 2. XPath with //, ancestor, @, and text() 3.
Querying XML Documents. Organization of Presentation
 Querying XML Documents Paul Cotton, Microsoft Canada University of Waterloo Feb 1, 2002 1 Organization of Presentation XML query history XML Query WG history, goals and status XML Query working drafts
Querying XML Documents Paul Cotton, Microsoft Canada University of Waterloo Feb 1, 2002 1 Organization of Presentation XML query history XML Query WG history, goals and status XML Query working drafts
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES
 EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML (Part 3): XQuery Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model for XML documents. 5.
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML (Part 3): XQuery Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model for XML documents. 5.
Lecture 20 (Additional/Optional Slides) NoSQL/MongoDB
 CompSci 516 Database Systems Lecture 20 (Additional/Optional Slides) NoSQL/MongoDB Instructor: Sudeepa Roy Duke CS, Fall 2018 CompSci 516: Database Systems 1 Additional and Optional Slides on MongoDB (May
CompSci 516 Database Systems Lecture 20 (Additional/Optional Slides) NoSQL/MongoDB Instructor: Sudeepa Roy Duke CS, Fall 2018 CompSci 516: Database Systems 1 Additional and Optional Slides on MongoDB (May
Burrows & Langford Appendix D page 1 Learning Programming Using VISUAL BASIC.NET
 Burrows & Langford Appendix D page 1 APPENDIX D XSLT XSLT is a programming language defined by the World Wide Web Consortium, W3C (http://www.w3.org/tr/xslt), that provides the mechanism to transform a
Burrows & Langford Appendix D page 1 APPENDIX D XSLT XSLT is a programming language defined by the World Wide Web Consortium, W3C (http://www.w3.org/tr/xslt), that provides the mechanism to transform a
SAX & DOM. Announcements (Thu. Oct. 31) SAX & DOM. CompSci 316 Introduction to Database Systems
 SAX & DOM CompSci 316 Introduction to Database Systems Announcements (Thu. Oct. 31) 2 Homework #3 non-gradiance deadline extended to next Thursday Gradiance deadline remains next Tuesday Project milestone
SAX & DOM CompSci 316 Introduction to Database Systems Announcements (Thu. Oct. 31) 2 Homework #3 non-gradiance deadline extended to next Thursday Gradiance deadline remains next Tuesday Project milestone
Seleniet XPATH Locator QuickRef
 Seleniet XPATH Locator QuickRef Author(s) Thomas Eitzenberger Version 0.2 Status Ready for review Page 1 of 11 Content Selecting Nodes...3 Predicates...3 Selecting Unknown Nodes...4 Selecting Several Paths...5
Seleniet XPATH Locator QuickRef Author(s) Thomas Eitzenberger Version 0.2 Status Ready for review Page 1 of 11 Content Selecting Nodes...3 Predicates...3 Selecting Unknown Nodes...4 Selecting Several Paths...5
2006 Martin v. Löwis. Data-centric XML. XPath
 Data-centric XML XPath XPath Overview Non-XML language for identifying particular parts of XML documents First person element of a document Seventh child element of third person element ID attribute of
Data-centric XML XPath XPath Overview Non-XML language for identifying particular parts of XML documents First person element of a document Seventh child element of third person element ID attribute of
Overview. Structured Data. The Structure of Data. Semi-Structured Data Introduction to XML Querying XML Documents. CMPUT 391: XML and Querying XML
 Database Management Systems Winter 2004 CMPUT 391: XML and Querying XML Lecture 12 Overview Semi-Structured Data Introduction to XML Querying XML Documents Dr. Osmar R. Zaïane University of Alberta Chapter
Database Management Systems Winter 2004 CMPUT 391: XML and Querying XML Lecture 12 Overview Semi-Structured Data Introduction to XML Querying XML Documents Dr. Osmar R. Zaïane University of Alberta Chapter
Navigating Input Documents Using Paths4
 Chapter 4 CHAPTER 4 Navigating Input Documents Using Paths4 Path expressions are used to navigate input documents to select elements and attributes of interest. This chapter explains how to use path expressions
Chapter 4 CHAPTER 4 Navigating Input Documents Using Paths4 Path expressions are used to navigate input documents to select elements and attributes of interest. This chapter explains how to use path expressions
Informatics 1: Data & Analysis
 Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 23 February 2016 Semester 2 Week 6 http://blog.inf.ed.ac.uk/da16
Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 23 February 2016 Semester 2 Week 6 http://blog.inf.ed.ac.uk/da16
XML and Databases. Outline. Outline - Lectures. Outline - Assignments. from Lecture 3 : XPath. Sebastian Maneth NICTA and UNSW
 Outline XML and Databases Lecture 10 XPath Evaluation using RDBMS 1. Recall / encoding 2. XPath with //,, @, and text() 3. XPath with / and -sibling: use / size / level encoding Sebastian Maneth NICTA
Outline XML and Databases Lecture 10 XPath Evaluation using RDBMS 1. Recall / encoding 2. XPath with //,, @, and text() 3. XPath with / and -sibling: use / size / level encoding Sebastian Maneth NICTA
Why do we need an XML query language? XQuery: An XML Query Language CS433. Acknowledgment: Many of the slides borrowed from Don Chamberlin.
 Why do we need an XML query language? XQuery: n XML Query Language S433 cknowledgment: Many of the slides borrowed from Don hamberlin XML emerging as dominant standard for data representation and exchange
Why do we need an XML query language? XQuery: n XML Query Language S433 cknowledgment: Many of the slides borrowed from Don hamberlin XML emerging as dominant standard for data representation and exchange
XML, DTD, and XML Schema. Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2014
 XML, DTD, and XML Schema Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2014 2 Announcements (Tue. Oct. 21) Midterm scores and sample solution posted You may pick up graded exams outside my office Mean: 83.9
XML, DTD, and XML Schema Introduction to Databases CompSci 316 Fall 2014 2 Announcements (Tue. Oct. 21) Midterm scores and sample solution posted You may pick up graded exams outside my office Mean: 83.9
Example using multiple predicates
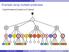 XPath Example using multiple predicates //performance[conductor][date] L C C C C p c s p p s o t d p p c p p Peter Wood (BBK) XML Data Management 162 / 366 XPath Further examples with predicates //performance[composer='frederic
XPath Example using multiple predicates //performance[conductor][date] L C C C C p c s p p s o t d p p c p p Peter Wood (BBK) XML Data Management 162 / 366 XPath Further examples with predicates //performance[composer='frederic
XML and information exchange. XML extensible Markup Language XML
 COS 425: Database and Information Management Systems XML and information exchange 1 XML extensible Markup Language History 1988 SGML: Standard Generalized Markup Language Annotate text with structure 1992
COS 425: Database and Information Management Systems XML and information exchange 1 XML extensible Markup Language History 1988 SGML: Standard Generalized Markup Language Annotate text with structure 1992
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414
 Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 14-15: XML CSE 414 - Spring 2013 1 Announcements Homework 4 solution will be posted tomorrow Midterm: Monday in class Open books, no notes beyond one hand-written
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 14-15: XML CSE 414 - Spring 2013 1 Announcements Homework 4 solution will be posted tomorrow Midterm: Monday in class Open books, no notes beyond one hand-written
~ Ian Hunneybell: DIA Revision Notes ~
 XML is based on open standards, and is text-based, thereby making it accessible to all. It is extensible, thus allowing anyone to customise it for their own needs, to publish for others to use, and to
XML is based on open standards, and is text-based, thereby making it accessible to all. It is extensible, thus allowing anyone to customise it for their own needs, to publish for others to use, and to
Outline of this part (I) Part IV. Querying XML Documents. Querying XML Documents. Outline of this part (II)
 Outline of this part (I) Part IV Querying XML Documents Marc H. Scholl (DBIS, Uni KN) XML and Databases Winter 2007/08 164 8 XPath Navigational access to XML documents Overview Context Location steps Navigation
Outline of this part (I) Part IV Querying XML Documents Marc H. Scholl (DBIS, Uni KN) XML and Databases Winter 2007/08 164 8 XPath Navigational access to XML documents Overview Context Location steps Navigation
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES. XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents
 EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML Documents and Schemas for XML documents Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4. Data Model
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414
 Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 13: XML and XPath 1 Announcements Current assignments: Web quiz 4 due tonight, 11 pm Homework 4 due Wednesday night, 11 pm Midterm: next Monday, May 4,
Introduction to Database Systems CSE 414 Lecture 13: XML and XPath 1 Announcements Current assignments: Web quiz 4 due tonight, 11 pm Homework 4 due Wednesday night, 11 pm Midterm: next Monday, May 4,
Informatics 1: Data & Analysis
 Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 28 February 2017 Semester 2 Week 6 https://blog.inf.ed.ac.uk/da17
Informatics 1: Data & Analysis Lecture 11: Navigating XML using XPath Ian Stark School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Tuesday 28 February 2017 Semester 2 Week 6 https://blog.inf.ed.ac.uk/da17
ADT 2005 Lecture 7 Chapter 10: XML
 ADT 2005 Lecture 7 Chapter 10: XML Stefan Manegold Stefan.Manegold@cwi.nl http://www.cwi.nl/~manegold/ Database System Concepts Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan The Challenge: Comic Strip Finder The Challenge:
ADT 2005 Lecture 7 Chapter 10: XML Stefan Manegold Stefan.Manegold@cwi.nl http://www.cwi.nl/~manegold/ Database System Concepts Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan The Challenge: Comic Strip Finder The Challenge:
XML and XQuery. Susan B. Davidson. CIS 700: Advanced Topics in Databases MW 1:30-3 Towne 309
 XML and XQuery Susan B. Davidson CIS 700: Advanced Topics in Databases MW 1:30-3 Towne 309 http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~susan/cis700/homepage.html 2017 A. Alawini, S. Davidson XML Anatomy
XML and XQuery Susan B. Davidson CIS 700: Advanced Topics in Databases MW 1:30-3 Towne 309 http://www.cis.upenn.edu/~susan/cis700/homepage.html 2017 A. Alawini, S. Davidson XML Anatomy
XML Data Management. 5. Extracting Data from XML: XPath
 XML Data Management 5. Extracting Data from XML: XPath Werner Nutt based on slides by Sara Cohen, Jerusalem 1 Extracting Data from XML Data stored in an XML document must be extracted to use it with various
XML Data Management 5. Extracting Data from XML: XPath Werner Nutt based on slides by Sara Cohen, Jerusalem 1 Extracting Data from XML Data stored in an XML document must be extracted to use it with various
XQuery. Leonidas Fegaras University of Texas at Arlington. Web Databases and XML L7: XQuery 1
 XQuery Leonidas Fegaras University of Texas at Arlington Web Databases and XML L7: XQuery 1 XQuery Influenced by SQL Based on XPath Purely functional language may access elements from documents, may construct
XQuery Leonidas Fegaras University of Texas at Arlington Web Databases and XML L7: XQuery 1 XQuery Influenced by SQL Based on XPath Purely functional language may access elements from documents, may construct
Semistructured data, XML, DTDs
 Semistructured data, XML, DTDs Introduction to Databases Manos Papagelis Thanks to Ryan Johnson, John Mylopoulos, Arnold Rosenbloom and Renee Miller for material in these slides Structured vs. unstructured
Semistructured data, XML, DTDs Introduction to Databases Manos Papagelis Thanks to Ryan Johnson, John Mylopoulos, Arnold Rosenbloom and Renee Miller for material in these slides Structured vs. unstructured
10/24/12. What We Have Learned So Far. XML Outline. Where We are Going Next. XML vs Relational. What is XML? Introduction to Data Management CSE 344
 What We Have Learned So Far Introduction to Data Management CSE 344 Lecture 12: XML and XPath A LOT about the relational model Hand s on experience using a relational DBMS From basic to pretty advanced
What We Have Learned So Far Introduction to Data Management CSE 344 Lecture 12: XML and XPath A LOT about the relational model Hand s on experience using a relational DBMS From basic to pretty advanced
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering. Extensible Markup Language (XML)
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Extensible Markup Language (XML) Dr. Basem Suleiman Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Semester 1, 2016, Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2442
Introduction to Data Management CSE 344
 Introduction to Data Management CSE 344 Lecture 11: XML and XPath 1 XML Outline What is XML? Syntax Semistructured data DTDs XPath 2 What is XML? Stands for extensible Markup Language 1. Advanced, self-describing
Introduction to Data Management CSE 344 Lecture 11: XML and XPath 1 XML Outline What is XML? Syntax Semistructured data DTDs XPath 2 What is XML? Stands for extensible Markup Language 1. Advanced, self-describing
Introduction. " Documents have tags giving extra information about sections of the document
 Chapter 10: XML Introduction! XML: Extensible Markup Language! Defined by the WWW Consortium (W3C)! Originally intended as a document markup language not a database language " Documents have tags giving
Chapter 10: XML Introduction! XML: Extensible Markup Language! Defined by the WWW Consortium (W3C)! Originally intended as a document markup language not a database language " Documents have tags giving
Introduction. " Documents have tags giving extra information about sections of the document
 Chapter 10: XML Introduction! XML: Extensible Markup Language! Defined by the WWW Consortium (W3C)! Originally intended as a document markup language not a database language " Documents have tags giving
Chapter 10: XML Introduction! XML: Extensible Markup Language! Defined by the WWW Consortium (W3C)! Originally intended as a document markup language not a database language " Documents have tags giving
XPath. by Klaus Lüthje Lauri Pitkänen
 XPath by Klaus Lüthje Lauri Pitkänen Agenda Introduction History Syntax Additional example and demo Applications Xpath 2.0 Future Introduction Expression language for Addressing portions of an XML document
XPath by Klaus Lüthje Lauri Pitkänen Agenda Introduction History Syntax Additional example and demo Applications Xpath 2.0 Future Introduction Expression language for Addressing portions of an XML document
Pre-Discussion. XQuery: An XML Query Language. Outline. 1. The story, in brief is. Other query languages. XML vs. Relational Data
 Pre-Discussion XQuery: An XML Query Language D. Chamberlin After the presentation, we will evaluate XQuery. During the presentation, think about consequences of the design decisions on the usability of
Pre-Discussion XQuery: An XML Query Language D. Chamberlin After the presentation, we will evaluate XQuery. During the presentation, think about consequences of the design decisions on the usability of
In this lecture. FLWR expressions FOR and LET expressions Collections and sorting
 In this lecture Summary of XQuery Resources FLWR expressions FOR and LET expressions Collections and sorting XQuery: A Query Language for XML Chamberlin, Florescu, et al. W3C recommendation: www.w3.org/tr/xquery/
In this lecture Summary of XQuery Resources FLWR expressions FOR and LET expressions Collections and sorting XQuery: A Query Language for XML Chamberlin, Florescu, et al. W3C recommendation: www.w3.org/tr/xquery/
CSE 344 Midterm. November 9, 2011, 9:30am - 10:20am. Question Points Score Total: 100
 CSE 344 Midterm November 9, 2011, 9:30am - 10:20am Name: Question Points Score 1 40 2 40 3 20 Total: 100 This exam is open book and open notes but NO laptops or other portable devices. You have 50 minutes;
CSE 344 Midterm November 9, 2011, 9:30am - 10:20am Name: Question Points Score 1 40 2 40 3 20 Total: 100 This exam is open book and open notes but NO laptops or other portable devices. You have 50 minutes;
XPath and XSLT. Overview. Context. Context The Basics of XPath. XPath and XSLT. Nodes Axes Expressions. Stylesheet templates Transformations
 XPath and XSLT Michael B. Spring Department of Information Science and Telecommunications University of Pittsburgh spring@imap.pitt.edu http://www.sis.pitt.edu/~spring Context The Basics of XPath Nodes
XPath and XSLT Michael B. Spring Department of Information Science and Telecommunications University of Pittsburgh spring@imap.pitt.edu http://www.sis.pitt.edu/~spring Context The Basics of XPath Nodes
Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML. Overview. How the Web is Today. Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington
 Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington CS330 Lecture April 8, 2003 1 Overview From HTML to XML DTDs Querying XML: XPath Transforming XML: XSLT
Introduction to Semistructured Data and XML Based on slides by Dan Suciu University of Washington CS330 Lecture April 8, 2003 1 Overview From HTML to XML DTDs Querying XML: XPath Transforming XML: XSLT
Semistructured Data and XML
 Semistructured Data and XML Computer Science E-66 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Structured Data The logical models we've covered thus far all use some type of schema to define the structure
Semistructured Data and XML Computer Science E-66 Harvard University David G. Sullivan, Ph.D. Structured Data The logical models we've covered thus far all use some type of schema to define the structure
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering
 COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2015 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2411 1 Extensible
COMP9321 Web Application Engineering Semester 2, 2015 Dr. Amin Beheshti Service Oriented Computing Group, CSE, UNSW Australia Week 4 http://webapps.cse.unsw.edu.au/webcms2/course/index.php?cid=2411 1 Extensible
Advances in Programming Languages
 T O Y H Advances in Programming Languages APL17: XML processing with CDuce David Aspinall (see final slide for the credits and pointers to sources) School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Friday
T O Y H Advances in Programming Languages APL17: XML processing with CDuce David Aspinall (see final slide for the credits and pointers to sources) School of Informatics The University of Edinburgh Friday
Data Services (II): XML Transformation and Query Techniques
 Data Services (II): XML Transformation and Query Techniques Helen Paik School of Computer Science and Engineering University of New South Wales Week 9 H. Paik (CSE, UNSW) XML Week 9 1 / 50 Part I XQuery
Data Services (II): XML Transformation and Query Techniques Helen Paik School of Computer Science and Engineering University of New South Wales Week 9 H. Paik (CSE, UNSW) XML Week 9 1 / 50 Part I XQuery
Big Data Exercises. Fall 2016 Week 9 ETH Zurich
 Big Data Exercises Fall 2016 Week 9 ETH Zurich Introduction This exercise will cover XQuery. You will be using oxygen (https://www.oxygenxml.com/xml_editor/software_archive_editor.html), AN XML/JSON development
Big Data Exercises Fall 2016 Week 9 ETH Zurich Introduction This exercise will cover XQuery. You will be using oxygen (https://www.oxygenxml.com/xml_editor/software_archive_editor.html), AN XML/JSON development
Introduction to XSLT. Version 1.0 July nikos dimitrakas
 Introduction to XSLT Version 1.0 July 2011 nikos dimitrakas Table of contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 XSLT... 3 1.2 PREREQUISITES... 3 1.3 STRUCTURE... 3 2 SAMPLE DATA... 4 3 XSLT... 6 4 EXAMPLES... 7
Introduction to XSLT Version 1.0 July 2011 nikos dimitrakas Table of contents 1 INTRODUCTION... 3 1.1 XSLT... 3 1.2 PREREQUISITES... 3 1.3 STRUCTURE... 3 2 SAMPLE DATA... 4 3 XSLT... 6 4 EXAMPLES... 7
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages. Fall Semester Week 9. Dr Nick Hayward
 Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2018 - Week 9 Dr Nick Hayward DEV Week assessment Course total = 25% project outline and introduction developed using a chosen markup language consider and
Comp 336/436 - Markup Languages Fall Semester 2018 - Week 9 Dr Nick Hayward DEV Week assessment Course total = 25% project outline and introduction developed using a chosen markup language consider and
Parte IV: XPATH. Prof. Riccardo Torlone
 BASI DI DATI II 2 modulo Parte IV: XPATH Prof. Riccardo Torlone Università Roma Tre Outline Location steps and paths Typical locations paths Abbreviations General expressions Riccardo Torlone: Basi di
BASI DI DATI II 2 modulo Parte IV: XPATH Prof. Riccardo Torlone Università Roma Tre Outline Location steps and paths Typical locations paths Abbreviations General expressions Riccardo Torlone: Basi di
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards. Representing Web Data: XML
 CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
CSI 3140 WWW Structures, Techniques and Standards Representing Web Data: XML XML Example XML document: An XML document is one that follows certain syntax rules (most of which we followed for XHTML) Guy-Vincent
References. Xquery Tutorial. Availability. Xquery Overview. Example XML Document: bib.xml. Advice: Example XML Document: bib.xml
 References Xquery Tutorial Dan Goldberg & Craig Knoblock University of Southern California XQuery 1.0: An XML Query Language www.w3.org/tr/xquery/ XML Query Use Cases www.w3.org/tr/xmlquery-use-cases What
References Xquery Tutorial Dan Goldberg & Craig Knoblock University of Southern California XQuery 1.0: An XML Query Language www.w3.org/tr/xquery/ XML Query Use Cases www.w3.org/tr/xmlquery-use-cases What
Manipulating XML Trees XPath and XSLT. CS 431 February 18, 2008 Carl Lagoze Cornell University
 Manipulating XML Trees XPath and XSLT CS 431 February 18, 2008 Carl Lagoze Cornell University XPath Language for addressing parts of an XML document XSLT Xpointer XQuery Tree model based on DOM W3C Recommendation
Manipulating XML Trees XPath and XSLT CS 431 February 18, 2008 Carl Lagoze Cornell University XPath Language for addressing parts of an XML document XSLT Xpointer XQuery Tree model based on DOM W3C Recommendation
DBS2: Exkursus XQuery and XML-Databases. Jan Sievers Jens Hündling Lars Trieloff
 DBS2: Exkursus XQuery and XML-Databases Jan Sievers Jens Hündling Lars Trieloff Motivation XML ubiquitous data exchange format Can be used to present Object data, relational data, semi-structured data
DBS2: Exkursus XQuery and XML-Databases Jan Sievers Jens Hündling Lars Trieloff Motivation XML ubiquitous data exchange format Can be used to present Object data, relational data, semi-structured data
Navigating an XML Document
 University of Dublin Trinity College Navigating an XML Document Owen.Conlan@scss.tcd.ie Athanasios.Staikopoulos@scss.tcd.ie What is XPath? Language for addressing parts of an XML document Used in XSLT,
University of Dublin Trinity College Navigating an XML Document Owen.Conlan@scss.tcd.ie Athanasios.Staikopoulos@scss.tcd.ie What is XPath? Language for addressing parts of an XML document Used in XSLT,
BlossomTree: Evaluating XPaths in FLWOR Expressions
 BlossomTree: Evaluating XPaths in FLWOR Expressions Ning Zhang University of Waterloo School of Computer Science nzhang@uwaterloo.ca Shishir K. Agrawal Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Department
BlossomTree: Evaluating XPaths in FLWOR Expressions Ning Zhang University of Waterloo School of Computer Science nzhang@uwaterloo.ca Shishir K. Agrawal Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay Department
XML: extensible Markup Language
 Datamodels XML: extensible Markup Language Slides are based on slides from Database System Concepts Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Many examples are from
Datamodels XML: extensible Markup Language Slides are based on slides from Database System Concepts Silberschatz, Korth and Sudarshan See www.db-book.com for conditions on re-use Many examples are from
Chapter 13 XML: Extensible Markup Language
 Chapter 13 XML: Extensible Markup Language - Internet applications provide Web interfaces to databases (data sources) - Three-tier architecture Client V Application Programs Webserver V Database Server
Chapter 13 XML: Extensible Markup Language - Internet applications provide Web interfaces to databases (data sources) - Three-tier architecture Client V Application Programs Webserver V Database Server
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES
 EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML (Part 2): Data Model for XML documents and XPath Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4.
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES XML (Part 2): Data Model for XML documents and XPath Outline 1. Introduction 2. Structure of XML data 3. XML Document Schema 3.1. Document Type Definition (DTD) 3.2. XMLSchema 4.
COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL. Contents. Part I: Introduction 1. Chapter 1: What Is XML? 3. Chapter 2: Well-Formed XML 23. Acknowledgments
 Acknowledgments Introduction ix xxvii Part I: Introduction 1 Chapter 1: What Is XML? 3 Of Data, Files, and Text 3 Binary Files 4 Text Files 5 A Brief History of Markup 6 So What Is XML? 7 What Does XML
Acknowledgments Introduction ix xxvii Part I: Introduction 1 Chapter 1: What Is XML? 3 Of Data, Files, and Text 3 Binary Files 4 Text Files 5 A Brief History of Markup 6 So What Is XML? 7 What Does XML
Contents. 1 Introduction Basic XML concepts Historical perspectives Query languages Contents... 2
 XML Retrieval 1 2 Contents Contents......................................................................... 2 1 Introduction...................................................................... 5 2 Basic
XML Retrieval 1 2 Contents Contents......................................................................... 2 1 Introduction...................................................................... 5 2 Basic
Introduction to XQuery and XML Databases
 Introduction to XQuery and XML Databases TEI@Oxford July 2009 XQuery While XSLT is good for transforming XML to other formats (XML, HTML, PDF, Text, etc.) sometimes you may wish to query a large database
Introduction to XQuery and XML Databases TEI@Oxford July 2009 XQuery While XSLT is good for transforming XML to other formats (XML, HTML, PDF, Text, etc.) sometimes you may wish to query a large database
XML and Semantic Web Technologies. II. XML / 6. XML Query Language (XQuery)
 XML and Semantic Web Technologies XML and Semantic Web Technologies II. XML / 6. XML Query Language (XQuery) Prof. Dr. Dr. Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Institute
XML and Semantic Web Technologies XML and Semantic Web Technologies II. XML / 6. XML Query Language (XQuery) Prof. Dr. Dr. Lars Schmidt-Thieme Information Systems and Machine Learning Lab (ISMLL) Institute
ST.96 - ANNEX VI TRANSFORMATION RULES AND GUIDELINES. Version 3.0
 page: 3.96.vi.1 ST.96 - ANNEX VI TRANSFORMATION RULES AND GUIDELINES Version 3.0 Revision approved by the XML4IP Task Force of the Committee of WIPO Standards (CWS) on February 26, 2018 Table of Contents
page: 3.96.vi.1 ST.96 - ANNEX VI TRANSFORMATION RULES AND GUIDELINES Version 3.0 Revision approved by the XML4IP Task Force of the Committee of WIPO Standards (CWS) on February 26, 2018 Table of Contents
Computer Science E-259
 Computer Science E-259 XML with Java Lecture 4: XPath 1.0 (and 2.0) and XSLT 1.0 (and 2.0) 21 February 2007 David J. Malan malan@post.harvard.edu 1 Computer Science E-259 Last Time DOM Level 3 JAXP 1.3
Computer Science E-259 XML with Java Lecture 4: XPath 1.0 (and 2.0) and XSLT 1.0 (and 2.0) 21 February 2007 David J. Malan malan@post.harvard.edu 1 Computer Science E-259 Last Time DOM Level 3 JAXP 1.3
